Effects of Catechins on Structural, Functional and in Vitro Digestion Characteristics of Soybean Protein Isolate under Spray Drying
-
摘要: 商用大豆分离蛋白(Soybean Protein Isolate,SPI)经高温喷雾干燥处理后,蛋白会发生一定程度的变性聚集,使溶解性等功能性质降低。本研究通过添加不同含量的儿茶素(Catechin,C),探究儿茶素-大豆蛋白相互作用对喷雾干燥大豆分离蛋白结构和功能特性的影响。结果表明:随着儿茶素添加量的增加,儿茶素的荷载率和装载含量逐渐增加,SPI与儿茶素结合后其表面疏水性和巯基含量逐渐下降;添加儿茶素可有效改善喷雾干燥SPI导致的功能下降问题,在儿茶素添加量为1%时,与对照组SPI相比,溶解性提高了36.4%,乳化性、乳化稳定性分别提高了13.7%和14.3%;在儿茶素添加量为0.25%时,凝胶硬度与对照组相比提高了43.6%,进一步研究发现凝胶网络结构主要依赖于二硫键,其次是氢键、离子键,且此时凝胶流变特性中的储能模量显著高于其他各处理组(P<0.05);通过原子力显微镜发现,添加儿茶素后凝胶的微观结构向规则均匀致密转化,当儿茶素添加量为0.25%时,复合物凝胶的聚集程度较小,但儿茶素的加入降低了喷雾干燥SPI的消化率。综上所述,在喷雾干燥过程中儿茶素能够与SPI中的基团结合,导致巯基含量和表面疏水性降低,进而干预了蛋白质分子间的热聚集,从而改善SPI的功能特性。Abstract: After the commercial soybean protein isolate (SPI) treated by high-temperature spray drying, the proteins were prone to undergo a certain degree of denaturation and aggregation, which reducing the solubility and other functional properties. The present study was aimed to investigate the interaction between different concentrations of catechins and SPI under spray drying treatment and the effects on the structural and functional properties of proteins. The results showed that the loading rate and loading content of catechin increased gradually with the increasing of catechin content, and the surface hydrophobicity and sulfhydryl content decreased gradually after the combination of SPI and catechin. The functional characteristics of spray drying SPI were improved after interacted with catechin. When the addition of catechin was 1%, the solubility of SPI was increased by 36.4%, and the emulsifying property and emulsifying stability were increased by 13.7% and 14.3% respectively. The hardness of gel was increased by 43.6% with the addition of 0.25% catechin. Correlation analysis showed that the network structure of gel mainly depended on disulfide bonds, followed by hydrogen bonds and ionic bonds. Furthermore, the storage modulus of gel rheological properties was significantly higher than that of other treatment groups (P < 0.05). It was found by atomic force microscope that the microstructure of the gel changed to homogeneous and dense in each group of proteins with the complexation of catechin. The addition of catechin at 0.25% could promoted minimal aggregation of gel when compared to the other samples. However, the interaction between catechin and protein led to the decrement of the digestibility of spray dried SPI. These results showed that catechin prevented the heat-induced aggregation and improved the structural and functional properties of SPI after spray drying.
-
Keywords:
- heat treatment /
- spray drying /
- catechin /
- soybean protein /
- structure /
- functional characteristics
-
大豆分离蛋白(Soybean Protein Isolate,SPI)是一种优质的植物蛋白,具有来源广泛、价格低廉且营养价值高等优点,同时具有可降解、热稳定、无污染、绿色环保等优良性能。商用SPI通常高温喷雾干燥生产,这会引起SPI一定程度的变性和聚集,从而使溶解性等功能性质降低,限制了SPI在食品工业中的应用[1]。因此,为了保持或改善喷雾干燥后大豆分离蛋白的功能特性,可以尝试喷雾干燥前在料液中添加外源物降低喷雾干燥引起的热变性或者抑制热聚集[2]。有研究表明,在不使用有机溶剂的情况下,多酚的加入可防止乳铁蛋白的热聚集[3]。Yan等[4]研究了预热处理对多酚-樟子仁分离蛋白结构和功能特性的影响,结果发现加入了多酚后蛋白质的聚集程度降低,并且乳化性增强。Liu等[5]发现酚类化合物中的羟基基团可以与蛋白质中的游离氨基和色氨酸等发生反应,二者之间的相互作用有助于提高蛋白质的变性温度,从而抑制热处理中蛋白质的聚集。
儿茶素是一种黄酮类多酚化合物[6],其羟基含量高并且具有多个适合蛋白质结合的反应位点,大量研究已表明SPI侧链中的氨基和巯基能够与儿茶素的酚羟基结合形成氢键,并且蛋白质上的某些氨基酸基团或残基也会和儿茶素的酚羟基或者苯环结合形成离子键、疏水作用、范德华力等[7],进而改变蛋白质的结构和功能特性,进一步研究也发现通过引入儿茶素可以干预蛋白质热诱导聚集,并提高其某种功能性和生物活性。Wang等[7]将儿茶素与热处理后的α-乳清蛋白复合,结果发现儿茶素的加入提高了α-乳清蛋白的变性温度,并增强了α-乳清蛋白的抗氧化和乳化活性。Zhou等[8]发现将儿茶素与冷冻干燥的大豆分离蛋白复合后,蛋白质的抗氧化性和热稳定性增加,并且提高了蛋白的消化率。
尽管目前关于蛋白质与多酚相互作用的研究较多,但多针对于实验室条件下制备的冷冻干燥的蛋白质,而在实际加工中SPI往往通过喷雾干燥技术制备,而关于喷雾干燥条件下大豆分离蛋白与儿茶素结合的研究较少,多酚与SPI相互作用后是否会受喷雾干燥的影响还尚不明确,通过儿茶素干预SPI喷雾干燥过程中的热聚集行为这一设想也有待验证,基于此本研究系统探究了喷雾干燥条件下儿茶素与SPI复合物的形成机制,以及儿茶素对SPI的结构(表面疏水性、巯基含量)包括结合亲和力的变化规律。通过对儿茶素-大豆分离蛋白复合物结构和功能特性的变化规律的探究,以期为儿茶素与大豆分离蛋白的复合提供理论依据,扩大其应用领域。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
大豆分离蛋白 实验室自制;儿茶素 合肥博美生物公司;色拉油 市售;盐酸、无水乙醇、氢氧化钠、二硫苏糖醇、盐酸胍、氯化钠、胃蛋白酶(酶活1:3000)、胰酶(酶活1:4000)、胰脂肪酶(酶活1:30000)、胆盐(纯度≥60%)、二水氯化钙、磷酸氢二钠、磷酸二氢钠 阿拉丁试剂公司;其他化学试剂 均为分析纯。
LS55荧光分析仪 珀金埃尔默股份有限公司;TMS-Touch 250N质构仪 美国Food Technology Corporation;H-PTD20流变仪 奥地利安东帕有限公司;L535-1型离心机 湖南湘仪实验室仪器开发有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 大豆分离蛋白的提取及复合物的制备
参考Zheng等[9]的制备方法。将400 g豆粕溶于6 L蒸馏水中,充分溶解后将溶液pH调为7.8。搅拌2 h后离心(8000×g,20 min),取离心后的上清液用2 mol/L HCl将溶液pH调至4.5,再次离心(8000×g,10 min),用5倍体积蒸馏水将沉淀溶解,搅拌均匀后离心(8000×g,10 min),取离心后的沉淀加入适量蒸馏水,并将溶液pH调至7.0,此时得到SPI溶液。
根据前期研究结果,将儿茶素按照大豆分离蛋白质量浓度的0.25%、0.5%、0.75%、1%、1.25%、1.5%、1.75%比例添加到SPI溶液中,并将此溶液在25 ℃下搅拌24 h后,于4 ℃在磷酸盐缓冲溶液中透析(截留分子量为8000~14000 kDa)48 h,此时得到儿茶素-大豆分离蛋白复合物溶液。为模拟SPI商业热加工条件,复合后的溶液进行喷雾干燥处理,制备不同结合亲和力的热诱导复合物干燥样品。其中喷雾干燥条件参考Chen等[10]并做适当改动,进风温度根据前期研究结果设置为170 ℃,料液流速3.5 mL/min,所有干燥样品备用待测。
1.2.2 儿茶素/大豆分离蛋白复合物结合亲和力的测定
参考刘雅云[11]多酚荷载率和装载含量的测定方法并做适当修改。大豆分离蛋白包埋儿茶素比率(荷载率)通过公式计算:
荷载率(%)=(1−未结合的儿茶素质量总加入的儿茶素质量)×100 (1) 式中:未结合的儿茶素是指复合物经过离心后(8818×g,20 min)沉淀中儿茶素的含量(mg)。取离心后沉淀部分加入无水乙醇将其溶解,再次离心(8818×g,20 min)后,测定上清液在280 nm处的吸光值,儿茶素的具体含量由标准曲线换算。此外大豆分离蛋白与儿茶素复合物装载儿茶素的含量(装载量)通过下公式计算:
装载量=包埋儿茶素的含量加入大豆分离蛋白的含量 (2) 式中:包埋儿茶素的含量指大豆分离蛋白结合儿茶素的含量(mg),加入大豆分离蛋白的含量根据双缩脲法进行测定,并根据标准曲线换算出具体含量(g)。
1.2.3 表面疏水性(H0)的测定
按照Jiang等 [12]的方法,使用8-苯氨基-奈酚-磺酸(ANS)对SPI和儿茶素-大豆分离蛋白复合物(SPI-C)的表面疏水性进行检测。用10 mmol/L,pH7.0 的磷酸盐缓冲溶液配制不同质量比的SPI-C复合物,将样品溶液置于10000×g下离心30 min,取2 mL浓度为0.1 mg/mL的样品溶液与20 μL浓度为8 mmol/L的ANS混合。激发和发射波长分别为390、468 nm,狭缝宽度设为5 nm,扫描速度设置为10 nm/s,在以上参数下记录荧光强度。H0为荧光强度与蛋白质浓度的比值。
1.2.4 巯基含量的测定
按照Ellman[13]的方法稍作改动。将0.04 mL Ellman试剂、5 mL Tris-甘氨酸缓冲液和1 mL样品溶液混合均匀,40 ℃下保温25 min,在412 nm下测量溶液的吸光值。以含有Ellman的Tris-甘氨酸缓冲液作为空白对照。每克蛋白含有的游离巯基的量(μmol)通过下列公式计算:
巯基含量(µmol/g)=73.53×A412CSPI (3) 式中:73.53=106/1.36×104,1.36×104为摩尔消光系数;CSPI为样品中蛋白质的浓度(mg/mL)。
1.2.5 溶解性的测定
参考Stübler等[14]的方法,将蛋白质浓度为2 mg/mL的SPI和SPI-C溶解于pH6.25的磷酸盐缓冲液中,然后于5000×g、4 °C下离心15 min,蛋白质溶解度的计算方法为:
溶解度(%)=上清液中的蛋白含量原蛋白液中的蛋白含量×100 (4) 1.2.6 乳化性及乳化稳定性的测定
参考祝钢等[15]的方法。将样品蛋白质浓度配制成10 mg/mL,然后取9 mL的样品溶液加入3 mL大豆油(即二者的比例为3:1),高速匀浆器10000 r/min搅打1 min后待测备用。从制备好的乳状液底部取100 μL,再加入浓度为0.1%的SDS溶液10 mL,二者混匀后在500 nm处测吸光值,用SDS溶液做空白。10 min后再次取溶液进行测定。乳化性及乳化稳定性分别按下式计算:
乳化性(m2/g)=2×2.303C×(1−φ)×104×A0×n (5) 乳化稳定性(%)=A10A0×100 (6) 式中:C为样品浓度(g/mL);
φ 为乳状液中油相的比例,0.25;n为稀释倍数;A0为初始乳状液的吸光值;A10为10 min后的吸光值。1.2.7 凝胶性的测定
参考蔡劭恺[16]的方法稍作修改。将各组样品溶液配为蛋白浓度为12%的溶液,20 ℃下磁力搅拌器混匀搅拌30 min,之后于90 ℃水浴加热30 min,冷却后放置于4 ℃冰箱中贮藏12 h。样品在室温下放置30 min后再质构仪测定所需参数。选用P/0.5的探头,以穿刺模式进行测定,测前速度:60 mm/min,测试速度:200 mm/min,测后速度:600 mm/min,记录测试峰的顶点,即为测定凝胶的硬度(N)。
1.2.8 参与形成凝胶作用力的测定
凝胶的分子间作用力测定方法参考Sun等[17]的方法并做适当改动。凝胶溶解度被用来检测稳定蛋白凝胶结构的分子间作用力。按照1.2.5的方法制备不含任何变性剂的蛋白凝胶。根据检测需要,配制以下三种凝胶溶解液:含0.7 mol/L的NaCl;6 mol/L盐酸胍(GuHCl);10 mol/L二硫苏糖醇(DTT)分别溶解在含50 mmol/L PBS中(pH6.25)。分别将1 g凝胶溶解在上述三种凝胶溶解液中,在80 ℃下水浴加热3 h,冷却后离心15 min(4 ℃、10000×g),取上清液测蛋白质含量,计算出凝胶溶解度。
1.2.9 流变特性分析
参考贾娜等[18]方法稍有改动。将SPI以及SPI-C溶液均匀涂抹在测试平台上,除去气泡。将测试频率调整为0.2 Hz,应变力设置为2%,初始和终止温度分别设为30、90 ℃,升温速率设为4 ℃/min。测定指标为流变的弹性模量G'。
1.2.10 原子力显微镜(AFM)分析
参考李颖畅等[19]的方法略做修改,将SPI和SPI-C溶液稀释至浓度为 20 μg/mL,然后吸取 4 μL溶液,涂在载玻片上。放置于载物台进行观察,采用轻敲模式。
1.2.11 体外消化模拟实验
1.2.11.1 模拟消化液的配制
参照Menezes等[20]的方法稍作修改,建立胃-小肠两步连续消化模型。
胃液:2 g/L 氯化钠、7 mL/L 浓盐酸和9600 U/L胃蛋白酶混合,并调节溶液pH为1.2;
肠液:分别取胆盐3.75 g用去离子水定容至50 mL;胰蛋白酶514.29 U/mL、胰酶68.57 U/mL。
电解质溶液:分别取1.101 g 二水氯化钙、6.561 g氯化钠,用去离子水定容至30 mL。
1.2.11.2 体外连续消化
将冷冻干燥的天然SPI、喷雾干燥的天然SPI和各浓度下儿茶素-SPI复合物(儿茶素添加量分别为0.25%、0.5%、0.75%、1%、1.25%、1.5%、1.75%)样品分别与模拟胃液、肠液于37 ℃水浴保温10 min后,取等体积相应的样品溶液与模拟胃液置于离心管内,用1.0 mol/L NaOH将混合物pH调至2.0,置于37 ℃以100 r/min水浴振荡,分别取反应时间为0、30、60、90和120 min的消化产物置于试管中,立即于100 ℃煮沸灭菌,冷却备用。后将离心管溶液pH调至6.8,取胃消化后的溶液30 mL,分别加入1.5 mL电解质溶液、2.5 mL胆盐溶液和3.5 mL酶溶液(胰蛋白酶和胰酶分别为514.29、68.57 U/mL),并用1.0 mol/L NaOH将溶液pH调至7.0,将离心管置于37 ℃水浴摇床中,分别取反应时间为150、180、210和240 min的消化产物于试管中,冷却备用。
体外消化率的计算公式如下:
消化率(%)=C0−C1C0×100 (7) 式中: C0为消化前的总蛋白含量,mg/mL; C1为消化后的蛋白含量,mg/mL。
1.3 数据处理
每组试验设置3个平行样品,结果采用平均数±SD表示。数据分析采用Statistix 8.1分析差异显著性。采用Sigmaplot 12.5软件进行作图。
2. 结果与分析
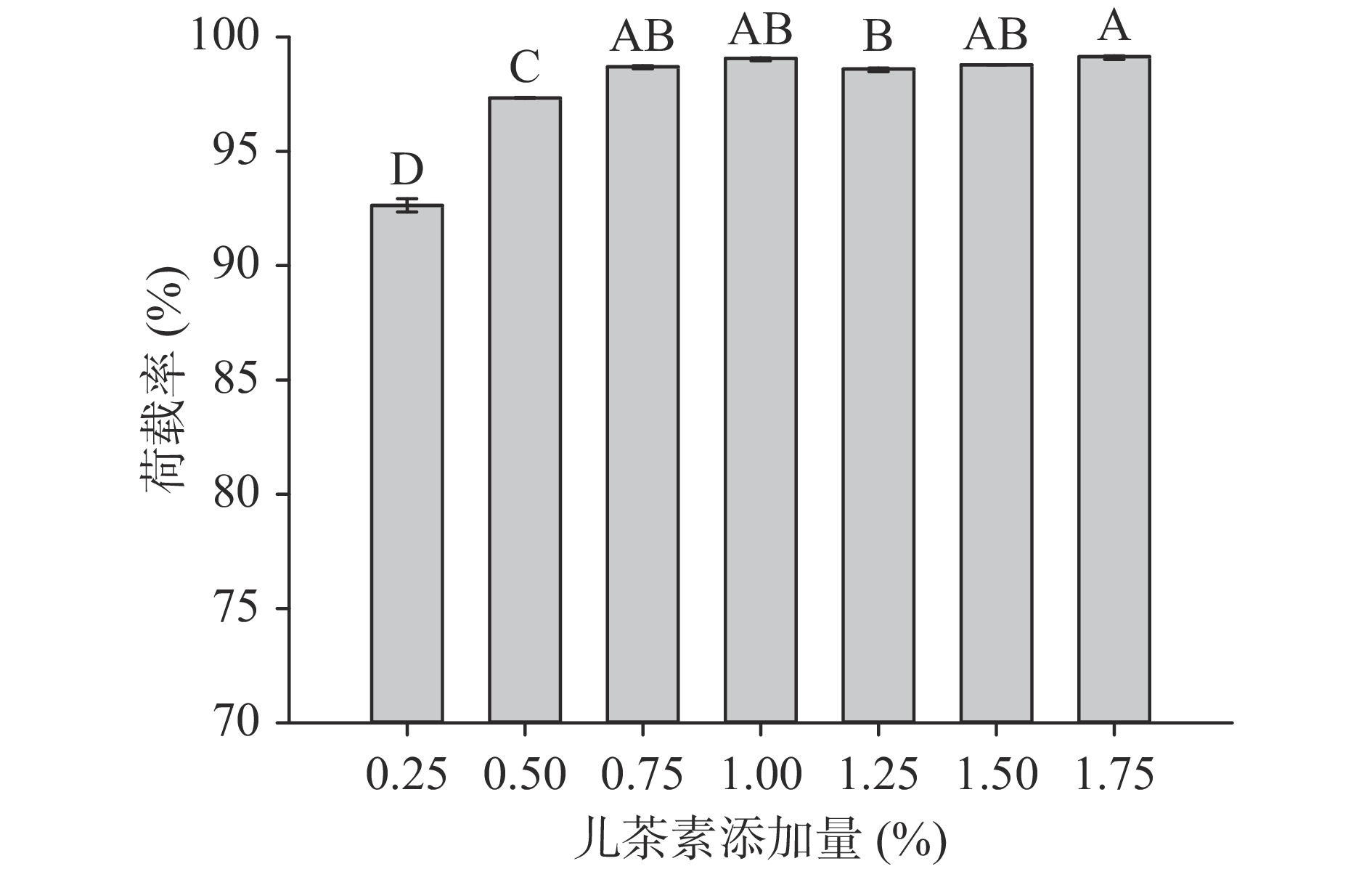
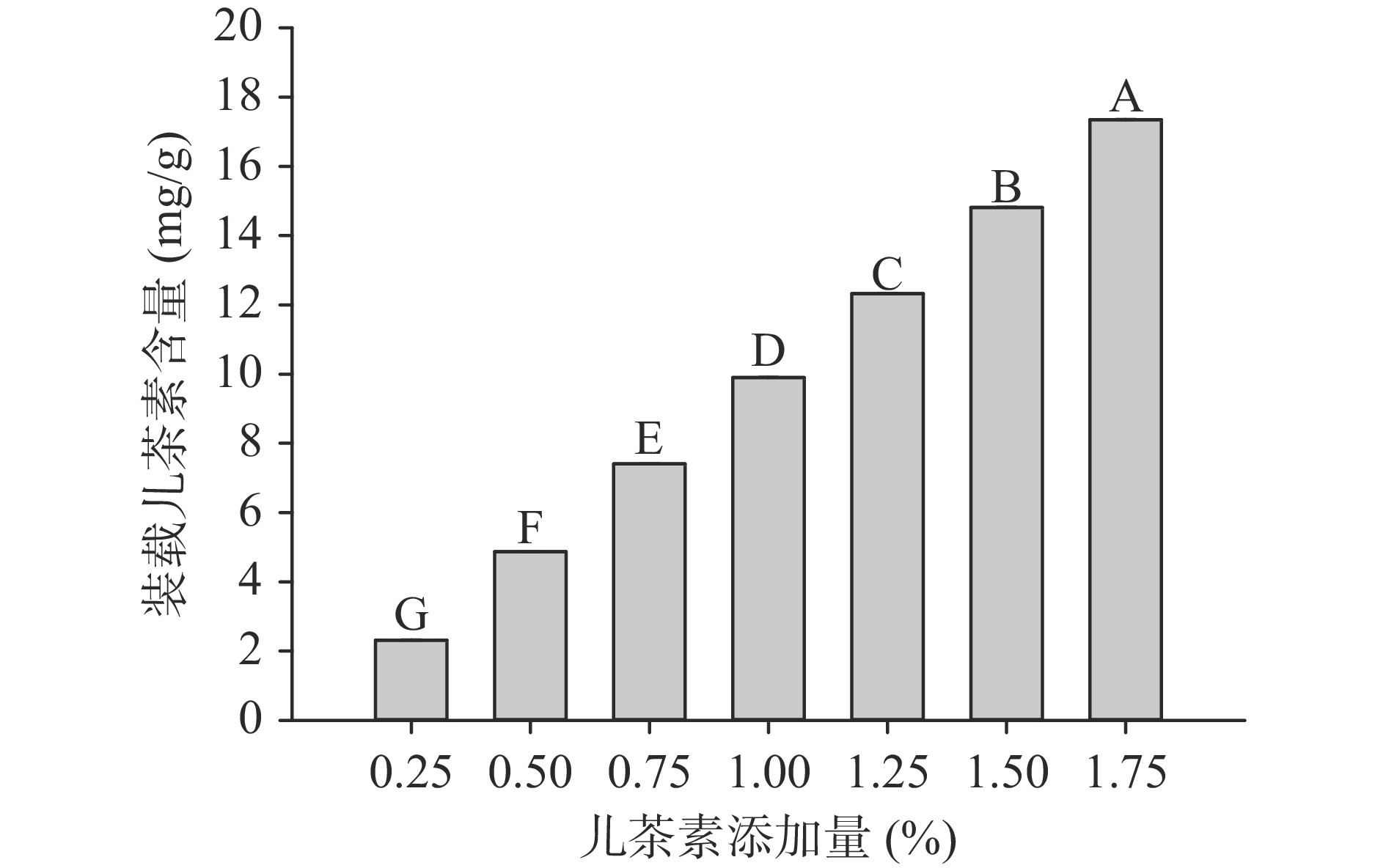
2.1 儿茶素添加量对儿茶素/大豆分离蛋白结合情况的影响
儿茶素荷载率以及装载含量见图1和图2。由图1可知,随着儿茶素添加量的增加,SPI-C对儿茶素的载荷率呈先上升后趋于稳定的趋势,说明随着儿茶素浓度的增加,二者相互作用程度逐步增强,表明SPI-C复合物的结合程度增加。推测的原因可能是SPI的空间结构在喷雾干燥的过程中展开,导致儿茶素与暴露出来的疏水基团结合,从而降低了SPI表面疏水性,提高了二者的结合程度[21]。Chen等[22]的研究也发现了类似的结论。且由图2儿茶素装载含量的变化趋势可知,儿茶素添加量为0.25%~1.75%时,其添加量与儿茶素装载含量呈正相关。
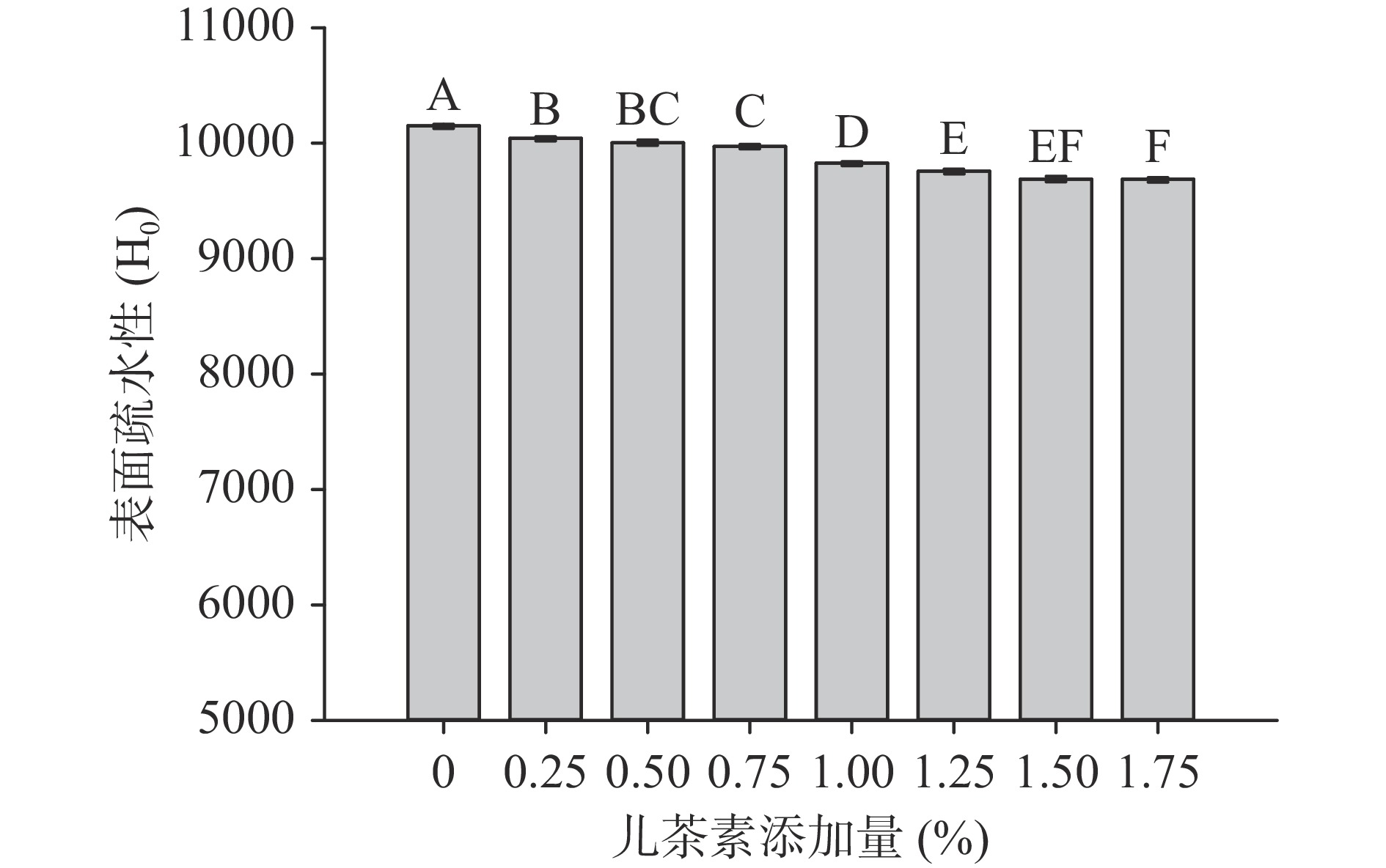
2.2 儿茶素添加量对大豆分离蛋白表面疏水性(H0)的影响
儿茶素对大豆分离蛋白表面疏水性的影响如图3所示。表面疏水性(H0)是蛋白质的重要特性之一,在维持蛋白质稳定性和生物活性方面起着重要作用[23]。H0是衡量SPI分子表面疏水基团数目的重要指标,也是影响分子间相互作用的主要因素之一。由图3可知,随着儿茶素添加量的增加,溶液中表面疏水性的逐渐降低后趋于稳定,这与荷载率的趋势相反。蛋白质的表面疏水性下降原因是儿茶素中所含的羟基属于亲水基团,羟基的存在能够使蛋白质的表面疏水性降低[24]。另一方面,在喷雾干燥过程中儿茶素可与蛋白质暴露的疏水氨基酸残基结合[25],从而减少ANS的结合位点,降低了表面疏水性。Li等[26]发现原花青素的添加会导致乳铁蛋白的疏水性降低,起泡性增强。
蛋白质经过热诱导后,暴露出埋在蛋白质内部的疏水基团[27],促进了酚苯环与蛋白质芳香侧链的疏水结合[24],使得表面疏水性降低。此外,研究也表明热处理会使蛋白质展开或者部分展开、聚集、分子柔韧性和疏水-亲水平衡发生变化,进而影响蛋白质的功能特性[24]。
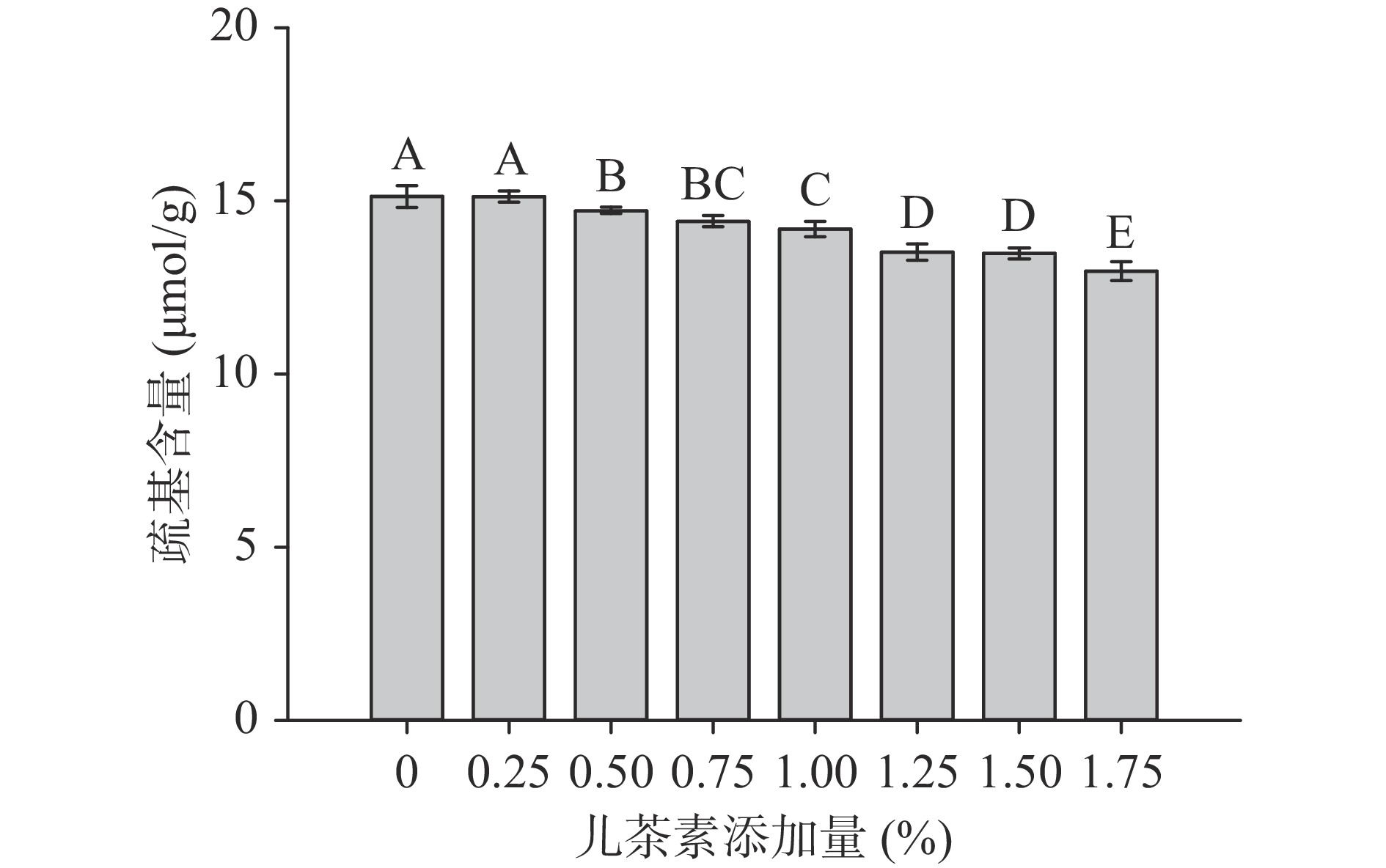
2.3 儿茶素添加量对大豆分离蛋白游离巯基含量的影响
儿茶素添加量对游离巯基含量的影响如图4所示。巯基基团是指蛋白质表面可与Ellman试剂反应的巯基。通常,有关巯基的化学反应涉及多种食品质量指标。由图4可以发现随着儿茶素添加量的增加,SPI-C复合体系中巯基的含量逐渐下降,这是因为儿茶素的羟基能够与SPI中的巯基结合。并且随着儿茶素添加量的进一步增加,可与SPI巯基结合的羟基基团逐渐增多,进而蛋白质的巯基含量逐渐减少[28]。曹艳芸[29]的研究也得到类似结论,乳清蛋白的巯基含量在添加儿茶素后降低。此外,热处理会加强巯基-二硫键之间的交换反应[4],而儿茶素的存在,导致分子内的二硫键含量增多,蛋白质与蛋白质分子间的二硫键减少[21],从而推测儿茶素能够干预蛋白质的热聚集。
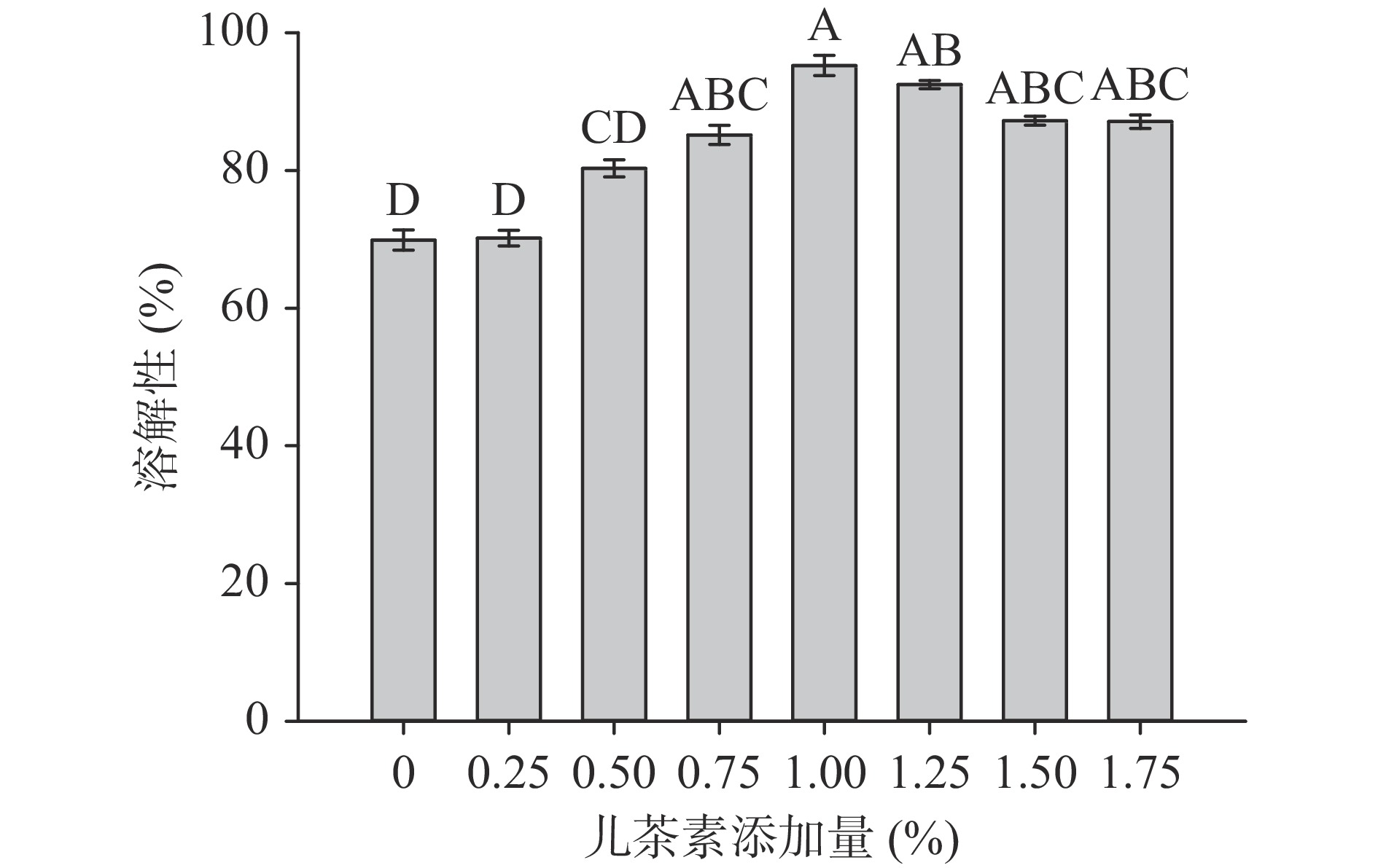
2.4 儿茶素添加量对大豆分离蛋白溶解性的影响
儿茶素添加量对溶解性的影响如图5所示。蛋白质的溶解度决定了其在食品工业中的应用,蛋白质的高蛋白溶解度有利于改善其加工性能并扩大其应用范围[30]。王孟云等[31]研究发现SPI未经喷雾干燥前溶解性约为88.74%,然而如图5儿茶素对大豆分离蛋白溶解性的影响所示,本研究经过喷雾干燥后的SPI溶解性降低至69.90%,说明喷雾干燥处理会大大降低SPI的溶解性。但是通过添加儿茶素可以适当提高SPI的溶解性(图5),在儿茶素添加量为1%时,SPI的溶解性达到最大为95.2%,较未添加儿茶素时提高36.4%。儿茶素的疏水区能够通过疏水相互作用与SPI疏水氨基酸结合,降低SPI的表面疏水性,从而提高SPI的溶解度[32]。另一方面SPI表面附着儿茶素的羟基和羧基,进一步增加了SPI表面的亲水性,使溶解度提高[32]。然而当儿茶素的添加量继续增加时,导致体系中儿茶素浓度过大,儿茶素末端占据蛋白质的多数结合位点,此时儿茶素分子很难找到合适位点与蛋白质结合,引起蛋白质分子之间交联,从而导致溶解度下降[33]。由此可知,适当的儿茶素添加量能够使大豆分离蛋白的溶解性提高。研究发现热处理会导致蛋白质的变性聚集,从而导致溶解性下降[31]。但在加入儿茶素后,喷雾干燥处理的SPI的溶解性增加,结合巯基与表面疏水性的结果推测是因为加入儿茶素能够与SPI暴露的疏水氨基酸残基结合,并干预蛋白质与蛋白质分子间的二硫键的形成,抑制蛋白质的变性聚集,从而使喷雾干燥后SPI的溶解性提高。
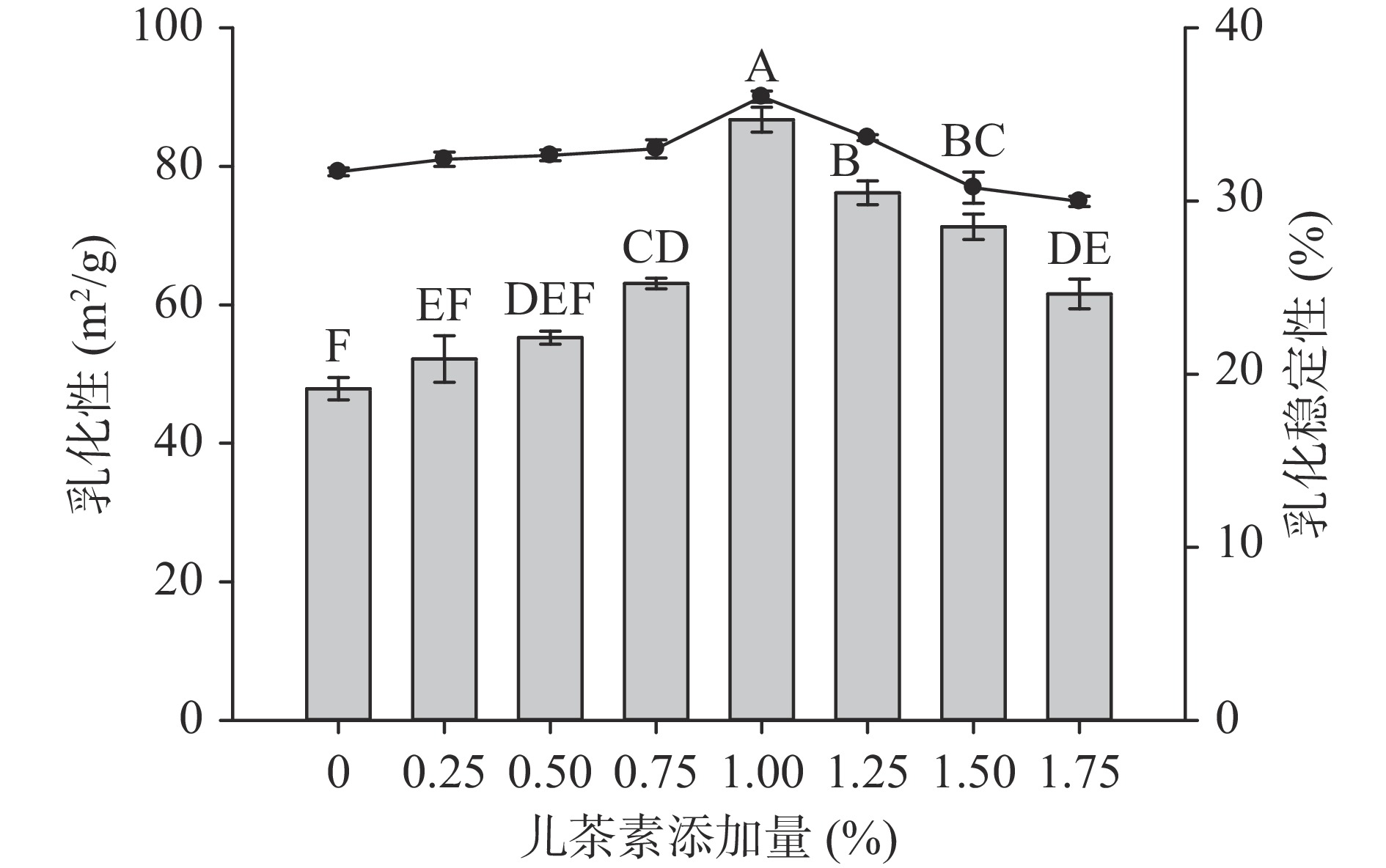
2.5 儿茶素添加量对大豆分离蛋白乳化及乳化稳定性的影响
儿茶素添加量对乳化及乳化稳定性的影响如图6所示。乳化性反映了蛋白质在油水界面形成和稳定乳液的能力,乳化稳定性能够反应乳液抵抗分离和保持分散的强度[34]。从图6乳化性的变化可以看出,随着儿茶素添加量的增加,复合体系的乳化性及乳化稳定性呈现先增加后降低的趋势,在儿茶素添加量为1%时,乳化性达到最大值为90.03 m2/g,比对照组的乳化活性提高了13.7%,乳化稳定性为36.3%,比对照组乳化稳定性提高了14.3%,说明儿茶素的加入干预了SPI的热聚集,提高了其乳化性能。乳化特性取决于蛋白质-蛋白质和蛋白质-脂质相互作用,儿茶素能够改变蛋白质-蛋白质的相互作用,降低自由能,从而降低油水界面的界面张力[35]。加入儿茶素后乳化性能的改善可能是喷雾干燥导致蛋白质分子的构象发生变化,使最初位于蛋白质内部的疏水团簇的暴露[36],增强了与儿茶素的疏水相互作用,从而使改性后蛋白的柔韧性和溶解度的增加,进而增加了蛋白对油水表面的吸附能力[37]。当儿茶素添加量超过1%时,儿茶素与大豆分离蛋白的交联程度增大,但儿茶素活性基团如巯基含量下降,导致不足以形成大的交联网状结构,导致大豆分离蛋白的乳化性能下降。Yan 等[35]研究发现表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯能够提高大豆分离蛋白的乳化性能,与本文的研究结果类似。
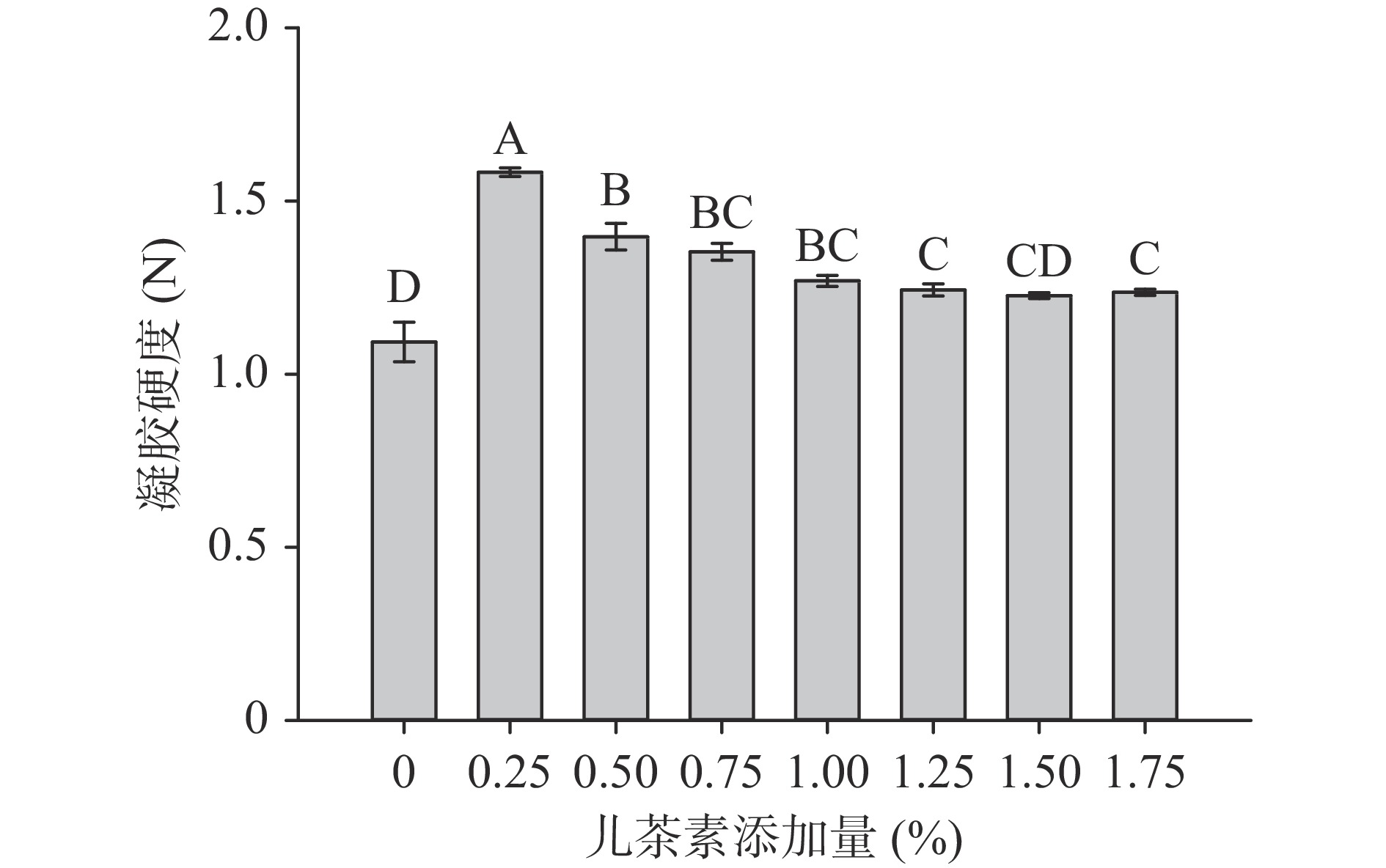
2.6 儿茶素添加量对大豆分离蛋白凝胶性的影响
儿茶素添加量对凝胶性的影响如图7所示。凝胶性反映了SPI可形成立体空间网状结构的能力,是评价SPI功能性质的重要指标之一,对其在食品中的应用起着至关重要的作用。由图7可知,与对照组相比,儿茶素的添加均显著增大了SPI凝胶性,说明儿茶素能够改善SPI喷雾干燥后的凝胶强度。当儿茶素添加量为0.25%时,SPI凝胶性显示最大值,与对照组相比提高了43.6%,而后再继续增大儿茶素添加量,SPI凝胶性反而下降,这可能是由于起初随着儿茶素的加入,为溶液提供了可与蛋白质氨基酸残基结合的活性羟基,促进溶液中蛋白质网络结构的形成[38]。随着儿茶素添加量的增加,过量的儿茶素将SPI中活性基团掩埋,导致凝胶硬度下降[39]。Jongberg等[40]研究表明高浓度的绿茶提取物可与蛋白质的巯基反应生成巯基-醌加合物,从而阻止蛋白质生成稳定的二硫键,导致蛋白质凝胶性降低。其他研究也发现中等或高浓度的酚类物质会损害凝胶性质[41]。此外,Bourvellec等[42]研究发现热处理导致SPI变性和构象发生变化,会暴露更多与多酚的结合位点。因此,添加儿茶素能够促进喷雾干燥后SPI-C间的相互作用,增强凝胶的网络结构,阻止了蛋白质-蛋白质间的相互作用,从而抑制了喷雾干燥过程中SPI的聚集[43]。
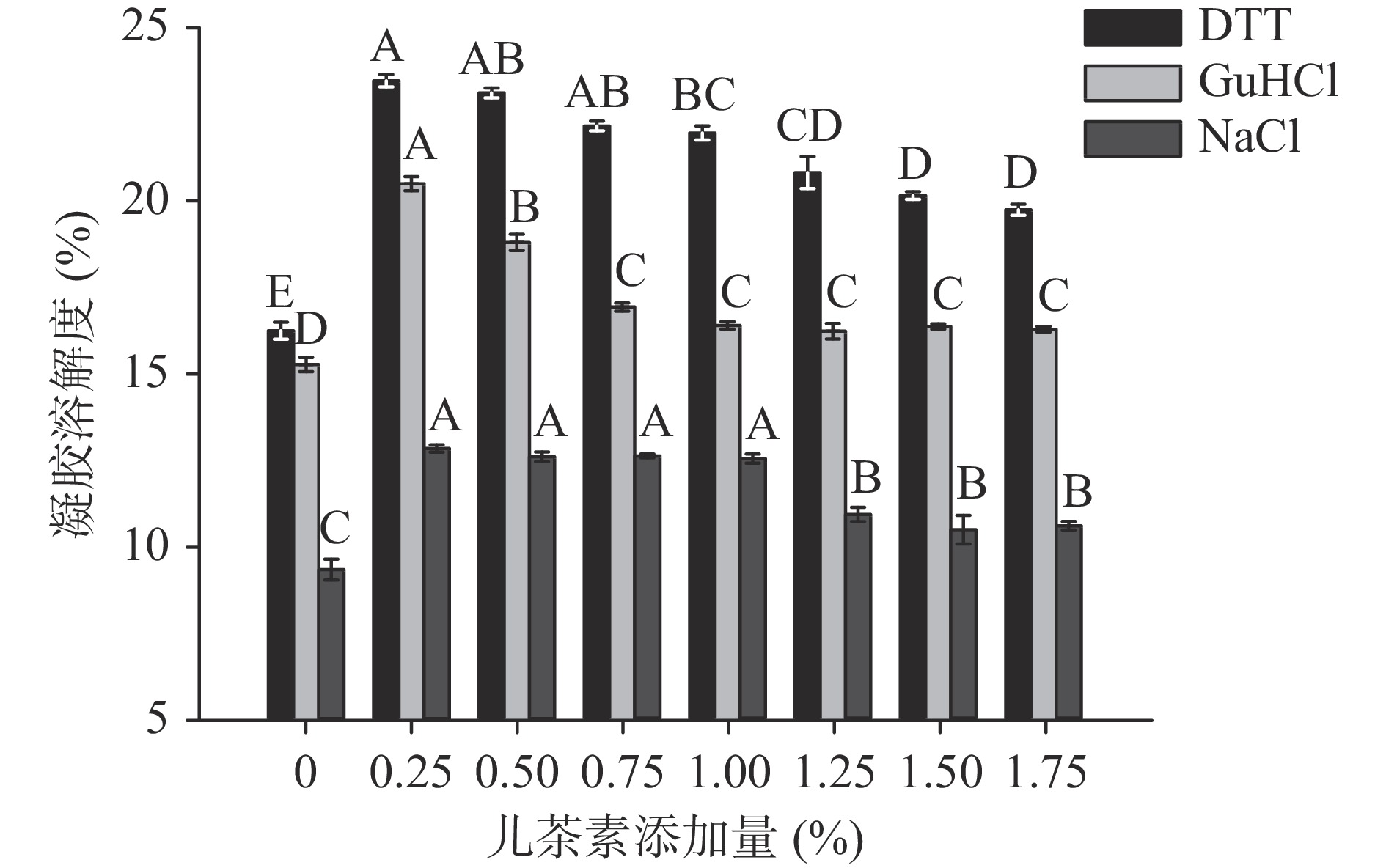
2.7 儿茶素添加量对大豆分离蛋白凝胶化学作用力的影响
凝胶形成过程中,氢键、疏水作用、二硫键以及静电作用是形成蛋白凝胶网络的主要作用力,其构成决定了蛋白凝胶的特性[44]。这些化学键可被特定的化学试剂破坏,通过在不同化学试剂中混合蛋白凝胶溶解度的不同,表征混合蛋白凝胶中化学键的变化。由于DTT能够断裂分子间或者分子内的二硫键,当蛋白凝胶在DTT中溶解的越多,在凝胶成胶起作用的分子间或者分子内的二硫键也就越多;疏水相互作用和氢键能够被GuHCl所破坏打断,因此蛋白凝胶在GuHCl溶解的越多,在凝胶成胶起作用的疏水相互作用和氢键也就越强;NaCl可以用来测定在凝胶网络结构形成的过程中的静电相互作用和其他一些较弱的分子作用力。由图8可知,溶出蛋白质的含量随儿茶素添加量的增加呈现先增加后下降的趋势,并且各个处理组均在0.25%时凝胶的溶解性达到最大值,表明此时参与凝胶形成的作用力最大,这一结果与凝胶硬度的结果一致,在此添加量下凝胶硬度最大。儿茶素的添加增强了凝胶的氢键、二硫键以及疏水相互作用,并且凝胶在DTT中的溶解度最高,说明二硫键是维持SPI-C复合物的凝胶网络结构的主要作用力。
与对照组相比,添加儿茶素后溶液中溶解的二硫键含量显著增加(P<0.05)。二硫键含量的增加可能是由于儿茶素含有的活性基团在热处理下很容易被氧化成醌[38],进而这些活性基团通过氧化蛋白质表面的巯基来促进蛋白质之间通过二硫键之间的连接[45]。凝胶在GuHCl中的溶解度随儿茶素添加量的增加先上升后下降,这是因为低浓度的儿茶素有助于凝胶网络中氢键的形成,过量的儿茶素会改变热诱导过程中SPI的聚集行为[38],阻碍SPI与水的结合,导致氢键和疏水相互作用降低[46]。凝胶在NaCl中的溶解度较低,且随着儿茶素的添加含量变化不大,说明静电相互作用对凝胶形成的影响较小。
2.8 儿茶素添加量对大豆分离蛋白流变特性的影响
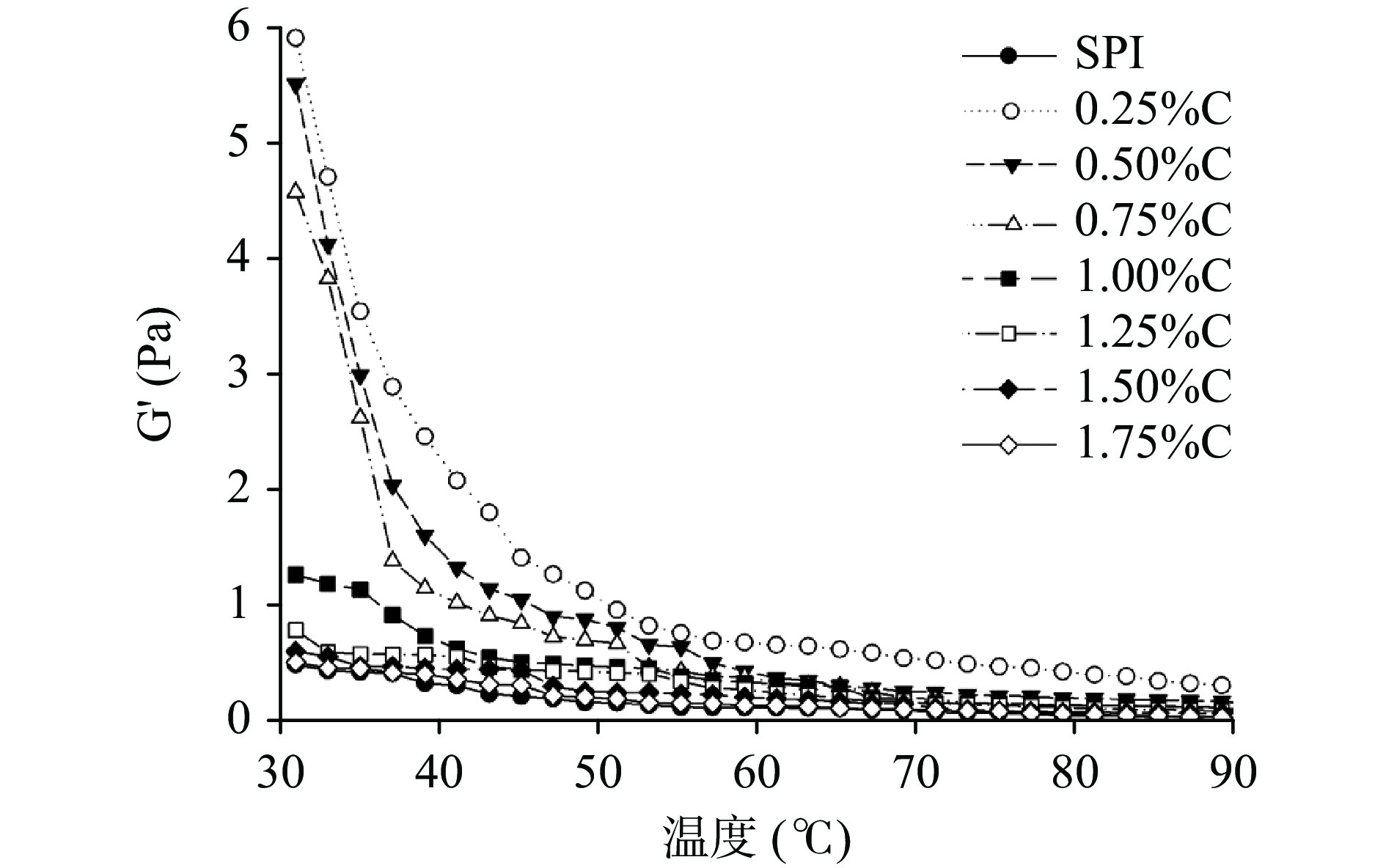
大豆分离蛋白在加热过程中分子的形态和性质的变化,能够用动态流变特性来表征。储能模量(G')代表了测试样品在一定的测试参数如应变、应力下储存能量的能力,G'的大小表征了凝胶网络的致密程度[47]。在加热过程中,儿茶素添加量对大豆分离蛋白储能模量的影响如图9所示。
SPI及SPI-C在30~60 ℃范围内随着温度的升高储能模量下降较快,这是因为温度的升高破坏了蛋白质分子内的氢键,进而导致G′下降[48]。随着温度的继续升高,加剧了蛋白质的亚基解离,以及分子间的运动,增加了分子碰撞机会,从而产生交联形成凝胶[48]。添加C组的G′值高于对照组,说明添加C可以增强SPI的粘弹性,由表面疏水性的测定结果可知,C的添加导致蛋白质间的疏水相互作用降低了,这样能够使静电和疏水相互作用达到平衡,进而增强了C与SPI的交联作用[49],从而能够改善蛋白质的网络结构[50]。Pantelis等[51]研究了茶多酚提取物对胃肠黏蛋白酶作用,发现与本文类似的结果,即多酚的添加能够引起蛋白交联。随着C添加量的增加,G'呈先升高后降低趋势,并当C添加量为0.25%时,储能模量达到最大值。这表明对于大豆分离蛋白凝胶,C添加量存在最适浓度。
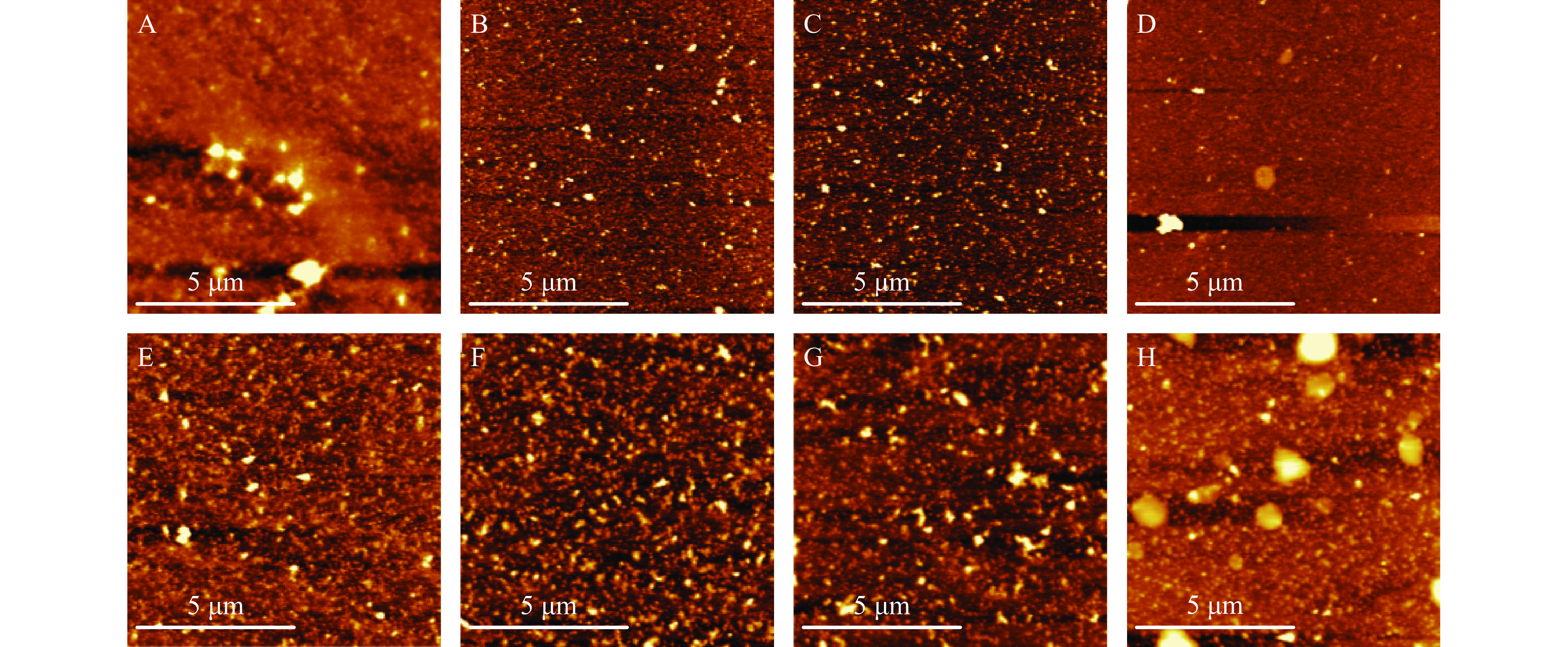
2.9 儿茶素添加量对大豆分离蛋白的凝胶微观结构
AFM可以用来表示蛋白质样品的表观形貌特征[52]。图10显示了SPI及SPI-C复合物凝胶的表面微观形态。由图10A可以看出,未添加儿茶素时,SPI具有无序的聚集且分布不均匀;当添加了儿茶素后,凝胶的微观结构由不规则不均匀向规则均匀致密转化。这是因为儿茶素的加入能够使样品之间交联的程度减弱,儿茶素和SPI间的维持力(包括氢键、二硫键等)被打断,蛋白质分子间作用力破坏,分子解聚,大颗粒蛋白减少,均匀度增加[53]。儿茶素添加量为0.25%和0.5%时,复合物分子逐渐形成较小、较为分散的聚集体(图10B、图10C);随着儿茶素添加量的进一步增大,复合物间的聚集程度有所增加,逐渐产生较大的团状聚集体。
利用Nanoscope analysis软件对SPI及SPI-C聚集过程进行分析,样品号A~H的平均表面粗糙度(Ra)分别为5.153、1.090、1.1345、1.158、2.723、3.392、3.706、4.387 nm,Ra作为统计学的基本参数,能够反应样品表面粗糙程度的大小,即聚集程度的大小,Ra先减少后增加说明SPI随着儿茶素添加量的增加,其微观聚集程度呈先减小后增大的趋势。根据2.7凝胶化学作用力的结果,得出二硫键是参与凝胶形成的主要作用力,由此推测添加儿茶素能够断开参与蛋白质凝胶的二硫键,使蛋白质分子适度解聚,形成均一度较好的小颗粒蛋白,进而提高蛋白质的功能性质。
2.10 儿茶素添加量对蛋白质体外消化率的影响
不同儿茶素添加量对蛋白质体外消化的影响如图11所示。由图11可知,喷雾干燥的SPI及SPI-C复合物的消化率均高于冷冻干燥,这是因为SPI及SPI-C在喷雾干燥中发生了部分变性,进而更容易被人体吸收[54]。然而两种干燥方式蛋白质的胃消化率均低于40%,说明只有少部分蛋白质在胃消化阶段进行消化,肠消化中蛋白质的消化率升高,表明蛋白质的消化主要发生在小肠消化阶段,这与郭阳[55]的研究一致。SPI的消化率显著(P<0.05)高于SPI-C复合物。这可能是由于在SPI与儿茶素在碱性条件下共价反应后,SPI的空间结构发生改变,使其不易于被胃蛋白酶和胰蛋白酶等消化酶水解。
3. 结论
本试验探究了不同儿茶素添加量对喷雾干燥的儿茶素-大豆分离蛋白复合物结构、功能和消化特性的影响。二者结合能力的测定结果表明,载荷率和荷载量随着儿茶素添加量的增加而增加;表面疏水性和巯基含量随着儿茶素添加量的增加逐渐降低。功能特性的测定结果表明,在儿茶素添加量为1%时,溶解性、乳化及乳化稳定性达到最大值;在儿茶素添加量为0.25%时,凝胶硬度最大;并且参与形成凝胶的作用力结果表明SPI-C的凝胶网络形成主要是二硫键的作用;原子力显微镜结果表明儿茶素的加入能够抑制SPI的聚集程度。此外,体外消化结果说明蛋白质的消化主要发生在小肠阶段,且儿茶素的添加会降低喷雾干燥SPI的消化率。以上试验结果为研究喷雾干燥制备的大豆分离蛋白与儿茶素之间的相互作用提供了参考,并为植物蛋白和儿茶素复合物在食品工业中的应用奠定了理论基础。然而目前有关于多酚-蛋白质消化特性的测定大多数是在体外进行测定,机体内部肠道菌群的变化还不清楚,在未来可加强多酚-蛋白质复合物体内方面的研究,以开发新型功能性食品。
-
-
[1] HE Z, LI W, GUO F, et al. Foaming characteristics of commercial soy protein isolate as influenced by heat-induced aggregation[J]. International Journal of Food Properties,2015,18(5-8):1817−1828.
[2] 郑志雄. 大豆分离蛋白喷雾干燥过程中的热变性及其抑制机理研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2011. ZHENG Zhixiong. Study on thermal denaturation and inhibition mechanism of soybean protein isolate during spray drying[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2011.
[3] LIU F, WANG D, MA C, et al. Conjugation of polyphenols prevents lactoferrin from thermal aggregation at neutral pH[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2016,58(7):49−59.
[4] YAN X, ZHAO J, ZENG Z, et al. Effects of preheat treatment and polyphenol grafting on the structural, emulsifying and rheological properties of protein isolate from Cinnamomum camphora seed kernel[J]. Food Chemistry,2022:132044.
[5] LIU F, SUN C, WANG D, et al. Glycosylation improves the functional characteristics of chlorogenic acid–lactoferrin conjugate[J]. Rsc Advances,2015,5(95):78215−78228. doi: 10.1039/C5RA15261E
[6] 代世成, 连子腾, 马林智, 等. 超声预处理对大豆分离蛋白-儿茶素非共价/共价复合物结构及功能的影响[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(1):102−110. [DAI Shicheng, LIAN Ziteng, MA Linzhi, et al. Effect of ultrasonic pretreatment on the structure and function of soybean protein isolate catechin non covalent/covalent complex[J]. Food Science,2022,43(1):102−110. [7] WANG X, JIAO Z, LEI F, et al. Covalent complexation and functional evaluation of ()-epigallocatechin gallate and α-lactalbumin[J]. Food Chemistry,2014,150(5):341−347.
[8] ZHOU S D, LIN Y F, XU X, et al. Effect of non-covalent and covalent complexation of (−)-epigallocatechin gallate with soybean protein isolate on protein structure and in vitro digestion characteristics[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,309:125718. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125718
[9] ZHENG T, LI X, TAHA A, et al. Effect of high intensity ultrasound on the structure and physicochemical properties of soy protein isolates produced by different denaturation methods[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2019,97:105216. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.105216
[10] CHEN F P, LLL A, CHTA B. Spray-drying microencapsulation of curcumin nanocomplexes with soy protein isolate: Encapsulation, water dispersion, bioaccessibility and bioactivities of curcumin[J]. Food Hydrocolloids, 2020, 105: 105821.
[11] 刘雅云. 基于茶多酚-壳聚糖纳米缓释体系的纳米纤维素/淀粉活性包装膜的研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2019. LIU Yayun. Study on nano cellulose/starch active packaging film based on tea polyphenol chitosan nano sustained release system[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2019.
[12] JIANG J, CHEN J, XIONG Y L. Structural and emulsifying properties of soy protein isolate subjected to acid and alkaline pH-shifting processes[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2009,57(16):7576−7583. doi: 10.1021/jf901585n
[13] ELLMAN G L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups[J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics,1959,82(1):70−77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6
[14] STÜBLER A-S, LESMES U, JUADJUR A, et al. Impact of pilot-scale processing (thermal, PEF, HPP) on the stability and bioaccessibility of polyphenols and proteins in mixed protein- and polyphenol-rich juice systems[J]. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies,2020,64:102426.
[15] 祝钢, 鞠梦楠, 崔守琦, 等. 大豆蛋白/表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯纳米复合颗粒制备Pickering乳液及其性质研究[J]. 食品科技,2020,45(9):221−226. [ZHU Gang, JU Mengnan, CUI Shouqi, et al. Soybean protein/epigallocatechin gallate nanocomposite particles to prepare Pickering emulsion and its properties[J]. Food Science and Technology,2020,45(9):221−226. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2020.09.034 [16] 蔡劭恺, 崔雅茹, 邱婷婷, 等. pH-超声复合处理对大豆分离蛋白凝胶性的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(24):209−218. [CAI shaokai, CUI Yaru, QIU Tingting, et al. Effect of pH- ultrasonic treatment on gelation of soy protein isolate[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2021,47(24):209−218. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.028196 [17] SUN X D, ARNTFIELD S D. Molecular forces involved in heat-induced pea protein gelation: Effects of various reagents on the rheological properties of salt-extracted pea protein gels[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2012,28(2):325−332. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2011.12.014
[18] 贾娜, 孙嘉, 刘丹, 等. 槲皮素对氧化条件下猪肉肌原纤维蛋白结构及凝胶特性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(10):45−51. [JIA Na, SUN Jia, LIU Dan, et al. Effects of quercetin on the structure and gel properties of pork myofibrillar protein under oxidative conditions[J]. Food Science,2021,42(10):45−51. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191103-021 [19] 李颖畅, 师丹华, 张馨元, 等. 超声波辅助没食子酸改善海鲈鱼肌原纤维蛋白的凝胶性能[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(11):82−91. [LI Yingchang, SHI Danhua, ZHANG Xinyuan, et al. Ultrasonic assisted gallic acid improving gel properties of myofibrillar protein from sea perch[J]. Food Science,2022,43(11):82−91. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20210409-121 [20] MENEZES E A, OLIVEIRA A F, FRANCA C J, et al. Bioaccessibility of Ca, Cu, Fe, Mg, Zn, and crude protein in beef, pork and chicken after thermal processing[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,240(2):75.
[21] 赵思明, 江连洲, 王冬梅, 等. EGCG对大豆蛋白结构的调控机理[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(12):67−75. [ZHAO Siming, JIANG Lianzhou, WANG Dongmei, et al. The regulation mechanism of EGCG on soybean protein structure[J]. Food Science,2021,42(12):67−75. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200523-273 [22] CHEN Y, XI J. Effects of the non-covalent interactions between polyphenols and proteins on the formations of the heterocyclic amines in dry heated soybean protein isolate[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,373:131557. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131557
[23] CAO Y, MA W, HUANG J, et al. Effects of sodium pyrophosphate coupled with catechin on the oxidative stability and gelling properties of myofibrillar protein[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2020,104:105722. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.105722
[24] CAO Y, XIONG Y L, CAO Y, et al. Interfacial properties of whey protein foams as influenced by preheating and phenolic binding at neutral pH[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,82(9):379−387.
[25] WEI Z, WEI Y, RUI F, et al. Evaluation of structural and functional properties of protein–EGCG complexes and their ability of stabilizing a model β-carotene emulsion[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2015,45(3):337−350.
[26] LI C, DAI T, CHEN J, et al. Protein-polyphenol functional ingredients: The foaming properties of lactoferrin are enhanced by forming complexes with procyanidin[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,339:128145. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128145
[27] WU C, YAN X, WANG T, et al. A self-sorted gel network formed by heating a mixture of soy and cod proteins[J]. Food & Function,2019,10(8):5140−5151.
[28] 文鹏程, 焦瑶瑶, 张卫兵, 等. 茶多酚对牛奶蛋白结构的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(8):40−47. [WEN Pengcheng, JIAO Yaoyao, ZHANG Weibing, et al. Effect of tea polyphenols on the structure of milk protein[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2020,46(8):40−47. [29] 曹艳芸. 乳清蛋白与多酚在中性pH条件下的相互作用对蛋白功能性质的影响研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2017. CAO Yanyun. Effect of interaction between whey protein and polyphenols at neutral pH on protein functional properties [D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2017.
[30] DONG Z Y, LI M Y, TIAN G, et al. Effects of ultrasonic pretreatment on the structure and functionality of chicken bone protein prepared by enzymatic method[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,299(11):125103.1−10.
[31] 王孟云, 陈业明, 孔祥珍, 等. 多元醇对热处理大豆分离蛋白喷雾干燥的影响[J]. 中国油脂,2017,42(10):5. [WANG Mengyun, CHEN Yeming, KONG Xiangzhen, et al. Effect of polyols on spray drying of heat treated soybean protein isolate[J]. China Grease,2017,42(10):5. [32] CHANG K, LIU J, JIANG W, et al. Structural characteristics and foaming properties of ovalbumin-caffeic acid complex[J]. LWT- Food Science and Technology,2021,12:111383.
[33] 刘妍兵, 陶阳, 苗雪, 等. 芸豆加工过程中蛋白-多酚复合物功能性质的变化[J]. 中国粮油学报,2021,36(11):57−64. [LIU Yanbing, TAO Yang, MIAO Xue, et al. Changes in functional properties of protein polyphenol complexes during kidney bean processing[J]. Chinese Journal of Cereals and Oils,2021,36(11):57−64. [34] SUI X, SUN H, QI B, et al. Functional and conformational changes to soy proteins accompanying anthocyanins: Focus on covalent and non-covalent interactions[J]. Food Chemistry,2017,245(4):871−878.
[35] YAN S, XIE F, ZHANG S, et al. Effects of soybean protein isolate polyphenol conjugate formation on the protein structure and emulsifying properties: Protein polyphenol emulsification performance in the presence of chitosan[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2020,609:125641.
[36] CHEN Y, HU J, YI X, et al. Interactions and emulsifying properties of ovalbumin with tannic acid[J]. LWT,2018,95:282−288. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2018.04.088
[37] LI D, ZHAO Y, WANG X, et al. Effects of (+)-catechin on a rice bran protein oil-in-water emulsion: Droplet size, zeta-potential, emulsifying properties, and rheological behavior[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2020,98:105306. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.105306
[38] XUE H, ZHANG G, HAN T, et al. Improvement of gel properties and digestibility of the water-soluble polymer of tea polyphenol-egg white under thermal treatment[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,372(5):131319.
[39] 李立敏, 杨豫菘, 成立新, 等. 茶多酚对羊肉肌原纤维蛋白-多糖复合体系乳化及质构特性的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2021,21(8):67−77. [LI Limin, YANG Yusong, CHENG Lixin, et al. Effects of tea polyphenols on emulsification and texture properties of mutton myofibrillar protein polysaccharide composite system[J]. Chinese Journal of Food,2021,21(8):67−77. [40] JONGBERG S, TERKELSEN L, MIKLOS R, et al. Green tea extract impairs meat emulsion properties by disturbing protein disulfide cross-linking[J]. Meat Science,2015,100(2):2−9.
[41] B C B T A, A W G Z, A Y F Z, et al. Influence of RosA-protein adducts formation on myofibrillar protein gelation properties under oxidative stress[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2017,67(6):197−205.
[42] BOURVELLEC C L, RENARD C. Interactions between polyphenols and macromolecules: Quantification methods and mechanisms[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science & Nutrition,2012,52(3):213−248.
[43] QIAN S, CHEN L, ZHAO Z, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate mediated self-assemble behavior and gelling properties of the ovalbumin with heating treatment[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022:107797.
[44] CHENG Y, WANG J, CHI Y, et al. Effect of dry heating on egg white powder influencing water mobility and intermolecular interactions of its gels[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2021,101(2):433−440. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10652
[45] AI M, ZHOU Q, GUO S, et al. Effects of tea polyphenol and Ca(OH)2 on the intermolecular forces and mechanical, rheological, and microstructural characteristics of duck egg white gel[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2019,94(9):11−19.
[46] 胡曼子, 周雨琪, 罗忆芝, 等. 巴河莲藕粉对白鲢鱼糜制品品质的影响[J]. 食品科技,2021,46(11):136−141. [HU Manzi, ZHOU Yuqi, LUO Yizhi, et al. Effect of lotus root powder on the quality of silver carp surimi[J]. Food Science and Technology,2021,46(11):136−141. [47] 郭艳, 吴进, 李腾宇, 等. 细菌纤维素对鸡肉品质及蛋白性质的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2019,47(3):129−137. [GUO Yan, WU Jin, LI Tengyu, et al. Effects of bacterial cellulose on chicken quality and protein properties[J]. Journal of Northwest University of Agriculture and Forestry Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition),2019,47(3):129−137. [48] 谷雪莲, 孙冰玉, 刘琳琳, 等. 热处理及植酸与脂肪对豆浆中大豆蛋白凝胶体系的影响研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(3):333−340. [GU Xuelian, SUN Bingyu, LIU Linlin, et al. Research progress in the effects of heat treatment and phytic acid and fat on soy protein gel system in soybean milk[J]. Food Science,2022,43(3):333−340. [49] 畅柯飞. 热处理对蛋清蛋白聚集行为及界面性质调控作用机制研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2021. CHANG Kefei. Study on the regulation mechanism of heat treatment on egg white protein aggregation behavior and interface properties[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2021.
[50] 曹媛媛, 周佺, 艾民珉, 等. 仙草提取物对猪肉糜脯感官品质和抗氧化特性的影响[J]. 食品研究与开发,2021,42(11):47−52. [CAO Yuanyuan, ZHOU Quan, AI Minmin, et al. Effects of Xiancao extract on sensory quality and antioxidant properties of pork surimi[J]. Food Research and Development,2021,42(11):47−52. [51] GEORGIADES P, PUDNEY P D, ROGERS S, et al. Tea derived galloylated polyphenols cross-link purified gastrointestinal mucins[J]. PloS One,2014,9(8):e105302. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105302
[52] AWH A, KHBC D, BWHC D. AFM imaging of pore forming proteins [M]. Methods in Enzymology, 2021, 649: 149-188.
[53] 沈玲玲. 超声预处理对植物蛋白生物利用度的影响及其机制研究[D]. 镇江: 江苏大学, 2019. SHEN Lingling. Effect of ultrasonic pretreatment on bioavailability of plant protein and its mechanism [D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University, 2019.
[54] 付露莹, 原双进, 陈浩, 等. 喷雾干燥与真空冷冻干燥对核桃粕红枣复合粉品质的影响[J]. 食品与机械,2019,35(1):204−208. [FU Luying, YUAN Shuangjin, CHEN Hao, et al. Effects of spray drying and vacuum freeze drying on the quality of walnut meal jujube composite powder[J]. Food and Machinery,2019,35(1):204−208. [55] 郭阳. 蛋白质多酚络合物促松仁油凝胶形成机理研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2021. GUO Yang. Study on the formation mechanism of protein polyphenol complex promoting pine nut oil gel [D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2021.
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)













 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:
