Effects of Different Thawing Methods on the Quality Characteristics of the Duck Leg Meat
-
摘要: 为选择一种合适的解冻方式(冷藏解冻、室温解冻、流水解冻和微波解冻),以期减少冷冻原料肉解冻过程的损耗并保障产品质量,为企业生产提供理论参考依据。本文以冷冻鸭腿肉为研究对象,探究不同解冻方式对冷冻鸭腿肉的保水性、pH、色泽、硫代巴比妥酸(TBARS)、羰基、Ca2+-ATPase、总巯基、组织学特性等指标的影响,并结合凝胶电泳和拉曼光谱分析蛋白质的降解及蛋白质二级结构的稳定性。结果表明:冷藏解冻的鸭腿肉解冻损失最低,色泽保持红润,肌纤维间隙最小(6.97 μm),组织结构紧密;TBARS值最低(0.16 mg/100 g),脂质氧化程度轻;羰基含量最低(0.16 nmol/mg),总巯基含量(149.10 μmol/g)和Ca2+-ATPase活性(2.69 U/mg)最高,对蛋白氧化影响小,凝胶电泳显示蛋白降解程度轻,α-螺旋含量高(42.33%),蛋白质的二级结构稳定有序。与冷藏解冻相比,流水解冻对鸭腿肉的保水性、色泽、组织学特性、脂质氧化与蛋白质氧化的影响稍重,其次是室温解冻,微波解冻的影响较严重。因此,冷藏解冻对冷冻鸭腿肉的品质影响较小,是最合适的解冻方式。Abstract: In order to reduce product loss and guarantee product quality, this paper used frozen duck leg meat as raw material. The data would be provided to the enterprises as a theoretical reference. Four kinds of thawing methods, refrigerated thawing, room temperature thawing, running water thawing, and microwave thawing were used. The effects of thawing methods on the quality were discussed including water retention, pH, color, thiobarbituric acid value (TBARS), carbonyl groups, Ca2+-ATPase, total sulfhydryl groups, histological properties. Combined with gel electrophoresis and Raman spectroscopy, the degradation and the secondary structure of proteins were analyzed. The results showed that refrigerated thawing had minimum thawing loss, red color, muscle fiber gap (6.97 μm), and tight tissue structure. Lipid oxidation and protein oxidation were mild with minimum thiobarbituric acid value (0.16 mg/100 g), carbonyl content (0.16 nmol/mg), and maximum total sulfhydryl content (149.10 μmol/g), and Ca2+-ATPase activity (2.69 U/mg). Gel electrophoresis showed light protein degradation and Raman spectroscopy showed a stable and ordered secondary structure of the protein with high alpha helix content (42.33%). Compared with refrigerated thawing, the effect of running water thawing on water retention, color, histological properties, lipid oxidation, and protein oxidation of duck leg meat was slightly heavier, followed by room temperature thawing and more serious effect of microwave thawing. Collectively, refrigerated thawing is the optimal thawingmethod with less effect on the quality loss of frozen duck leg meat.
-
Keywords:
- duck leg meat /
- thawing methods /
- quality /
- lipid oxidation /
- protein oxidation
-
鸭肉富含多种维生素和氨基酸,是一种高蛋白、低胆固醇和低脂肪的肉类,深受消费者的喜爱。新鲜鸭肉不易于保存,冷冻贮藏是工业化鸭肉原料常用的保藏方法[1]。但肉的冷冻贮藏和解冻过程中都可能引发肉类的品质变化,包括保水性下降、组织结构疏松、脂肪氧化和蛋白质氧化等[2-3]。如果采用不恰当的解冻方式,会对肌肉的损耗、品质和组织特性产生恶劣的影响,尤其是对解冻损失率、肌肉组织形态的影响,从而对后续加工而成的熟肉的多汁性和质地等产生负面影响[4],间接给肉及肉制品生产加工带来不可估量的经济损失。为此,需要根据肉的种类选择合适的解冻方式,提高解冻后的产品得率,以应用于企业的大规模生产。
目前国内外关于解冻方式的研究主要集中在实验室研究,工业化应用的研究较少,解冻方式主要包括冷藏解冻、盐水解冻、自然空气解冻、静水解冻、低温高湿变温解冻、微波解冻等。而且以鸭肉为解冻对象的研究较少,仅有对鸭胸肉(去皮去脂肪)[5]、鸭翅的研究[6]等,如张帆等[5]的研究主要探讨4 ℃冷藏解冻、空气解冻、静水解冻等对去皮去脂肪鸭胸肉的品质影响,而未研究流水解冻和微波解冻等解冻方式。本研究以冷冻鸭腿肉为研究对象,从企业直接采样,多角度探讨解冻方式(冷藏解冻、室温解冻、流水解冻和微波解冻)对鸭腿肉保水性、外观、肌纤维形态和脂肪氧化的影响,着重研究解冻方式对蛋白氧化(总巯基、羰基、Ca2+-ATPase活性、SDS-PAGE)的影响,并用拉曼光谱观察蛋白质二级结构。以期减少解冻对肉品质的不良影响,保证解冻后的鸭腿肉品质,选择一种合适的解冻方式,为冷冻鸭腿肉在企业实际生产加工中提供数据支撑和理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
冷冻鸭腿肉(−20 ℃真空包装贮藏,厚度2 cm) 深圳市金谷园实业发展有限公司提供;三氯乙酸 分析纯,天津市百世化工有限公司;乙二胺四乙酸二钠 分析纯,天津市大茂化学试剂厂;2, 4-二硝基苯肼、盐酸胍、Ellman试剂、超微量Ca2+-ATPase试剂盒 南京建成生物工程研究所;Tris-HCl 上海碧云天生物技术有限公司;双缩脲试剂盒、2-硫代巴比妥酸 上海源叶生物科技有限公司。
GT16-3离心机 广州市正一科技有限公司;KT-1热电耦温度计 深圳荣顺腾电子工具有限公司; JY600C电泳仪 北京君意东方电泳设备有限公司;XploRA PLUS共聚焦拉曼光谱仪 堀场(中国)贸易有限公司;LC-220JE卡萨帝保鲜冰吧 青岛海尔特种电冰柜有限公司;Pannoramic SCANⅡ病理切片扫描仪 3DHISTECH Kft;M1-L213B微波炉 广东美的厨房电器制造有限公司;JYL-C022E九阳料理机 九阳股份有限公司;FA25均质机 上海弗鲁克科技发展有限公司;NS800分光测色仪 三恩时科技有限公司;756S紫外可见分光光度计 上海棱光技术有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 解冻方式
a. 冷藏解冻。将鸭腿肉(密封包装)置于4 ℃冷藏室(容积152 L)中解冻,用热电耦温度计测定鸭腿肉中心温度,以0 ℃作为解冻终点。
b. 室温解冻。将鸭腿肉置于试验台上进行解冻,室内恒定温度20 ℃,用热电耦温度计测定鸭腿肉中心温度,以0 ℃作为解冻终点。
c. 流水解冻。将鸭腿肉置于流水下进行解冻,流水流速固定,用热电耦温度计测定鸭腿肉中心温度,以0 ℃作为解冻终点。
d. 微波解冻。将鸭腿肉放入微波炉(700 W 20 L)中解冻,调至“按重量解冻”模式,用热电耦温度计测定鸭腿肉中心温度,以0 ℃作为解冻终点。
1.2.2 肌原纤维蛋白的提取
参考文献[9]的方法并稍作修改,从鸭腿肉分离提取肌原纤维蛋白。将磨碎的鸭腿肉与4倍体积(1:4,w/v)的低温缓冲液(0.1 mol/L KCl,20 mmol/L Tris-HCl),用高速匀浆机匀浆3次,每次30 s。匀浆后,经20目筛(孔径0.9 mm)过滤,并在5000 r/min的条件下离心15 min。将上清液倒出,将颗粒收集为粗蛋白。将上述步骤重复4次,以获得高质量的蛋白,并用于后续的试验,所有分离步骤均在0~4 ℃进行。
1.2.3 肉样解冻损失率(Thawing loss,CL)测定
参照阿依木古丽等[10]的方法,分别称量解冻前后肉的质量,按公式(1)计算:
解冻损失率(%)=m1−m2m1×100 (1) 式中:m1为冷冻肉的质量,g;m2为解冻后肉质量,g。
1.2.4 肉样蒸煮损失率测定
参照阿依木古丽等[10]的方法,肉样精确称量后放于蒸煮袋中,100 ℃的沸水中煮制,待肉样中心温度达70 ℃时,将肉样取出冷却后精确称量,用公式(2)计算:
蒸煮损失率(%)=m1−m2m1×100 (2) 式中:m1为蒸煮前肉质量,g;m2为蒸煮后肉质量,g。
1.2.5 pH测定
使用九阳料理机处理鸭腿肉,搅碎后称取4.0 g,加入蒸馏水36 mL,匀浆30 s,使用pH计测试。
1.2.6 色泽测定
使用分光测色仪测定鸭腿肉的色泽。色差仪进行黑白板校正后,将肉样垂直放到探头中心,随机选取3个点,并记录其L*、a*、b*值。L*代表亮度值,a*表示红度值,b*表示黄度值。
1.2.7 硫代巴比妥酸值(Thiobarbituric acid value,TBARS)的测定
参照顾赛麟等[11]的方法。准确称取试样5.0 g,加入50 mL 7.5%三氯乙酸溶液(含0.1%乙二胺四乙酸二钠),搅拌均匀,30 min后滤纸过滤。取5 mL滤液(若是空白对照,则用5 mL去离子水代替),向其中加入5 mL 0.02 mol/L TBARS溶液,沸水浴中保温40 min。冷却至室温后,4500 r/min条件下离心30 min。弃去沉淀,取上层清液,加入5 mL氯仿,振荡摇匀。待其静置分层后,取上层溶液分别在波长为532、600 nm处测吸光度并记录,最后用公式(3)计算TBARS值。
TBARS值(mg/100g)=A532−A600155×15×72.06×100 (3) 式中:A532、A600分别为532、600 nm的吸光度;155为丙二醛的摩尔吸光度;72.06为丙二醛的相对分子质量;5为样品质量,g。
1.2.8 羰基含量测定
参照Levine等[12]方法略加改进,准确称取0.1 g鸭腿肉,加入0.9 mL磷酸盐缓冲溶液(0.1 mol/L pH7.0),匀浆,4 ℃离心(2500 r/min,10 min),取0.45 mL上清液与0.05 mL的缓冲溶液混匀静置离心(11000 r/min,10 min),上清液用于蛋白质羰基测定和考马斯亮蓝法测蛋白浓度。取0.1 mL上清液和0.4 mL 2, 4-二硝基苯肼的盐酸胍溶液于测定管中,37 ℃避光30 min,加入0.5 mL 20%的三氯乙酸,混匀离心(12000 r/min,10 min),用1 mL的无水乙醇-乙酸乙酯溶液(1:1,V/V)洗涤蛋白沉淀4次后加入1.2 mL盐酸胍溶液,37 ℃水浴15 min,旋涡混匀至沉淀溶解,离心15 min。以空白为对照,取测定管上清液于370 nm处测定吸光值。使用摩尔吸光系数22000 L/(mol·cm)计,蛋白质中的羰基含量为:
羰基含量(nmol/mg)=A22000×C×D×106 (4) 式中:A是样品吸光值;C是蛋白浓度,mg/L;D是比色光径,cm。
1.2.9 Ca2+-ATPase活性测定
根据Ca2+-ATPase活性检测试剂盒说明书,准确称取肉样,测定Ca2+-ATPase活性,单位为U/mg。
1.2.10 总巯基含量测定
参考Beveridge等[13]的Ellman试剂分析方法并稍加改动成微量法,吸取10 μL 5 mg/mL肌原纤维蛋白溶液和150 μL Ellman试剂到酶标板孔中,剧烈震荡使其反应完全,以不加DTNB组为对照,在405 nm处测定吸光值(OD值),计算蛋白中的总巯基含量。
总巯基含量(µmol/g)=测定OD值−对照OD值标准OD值−空白OD值×标准品浓度/待测样本蛋白浓度 (5) 1.2.11 肌纤维的肌束形态HE染色(Hematoxylin-Eosin)
将鸭腿肉分别切成1.0 cm×1.0 cm×1.0 cm的小肉块,4 ℃条件下用2.5%戊二醛溶液浸泡24 h,再用0.1 mol/L的磷酸盐缓冲液(pH7.4)漂洗3次,每次15 min。漂洗后,依次用20%、40%、60%、80%、90%、100%的乙醇梯度脱水各10 min,100%乙醇脱水3次,扫描观察纤维结构。
1.2.12 聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳(SDS-PAGE)
将肌原纤维蛋白溶液稀释至质量浓度为40 mg/mL,使用12%的分离凝胶和4%的浓缩凝胶。取20 μL肌原纤维蛋白溶液和20 μL上样缓冲液混匀,100 ℃水浴5 min后离心处理(10000 r/min,3 min),依次编号。配制电泳液,将玻璃板置于充满电极缓冲液的电泳装置中,在电极缓冲液中取出梳状体后加入混合物样品(20 μL)和Marker(6.5~200 kDa),盖上盖子通电80 V,30 min和120 V,60 min。电泳结束后,固定、染色、脱色,并对凝胶进行拍照,得到电泳图。
1.2.13 拉曼光谱的测定
根据蔡路昀等[14]的方法并稍作修改,利用拉曼光谱测量肌原纤维蛋白的二级结构比例。将样品放在载玻片上,激光波长为532 nm,激光功率为120 mW,扫描范围400~2000 cm−1,曝光时间为8 s,并将样品调整到3个不同位置进行扫描测量。
1.3 数据处理
试验各平行3次,采用Microsoft Excel 2019(微软公司)制表,Origin2018软件(OriginLab公司)制图,IBM SPSS Statistics 22软件(IBM公司)做显著性分析,差异显著性分析由单因素方差分析法(One-way ANOVA)完成,P<0.05表示差异显著;HE染色数据采用CaseViewer软件(JAVS, Inc公司)分析;拉曼光谱数据采用Peakfit 4.12软件(Systat Software公司)作拟合分析。
2. 结果与分析
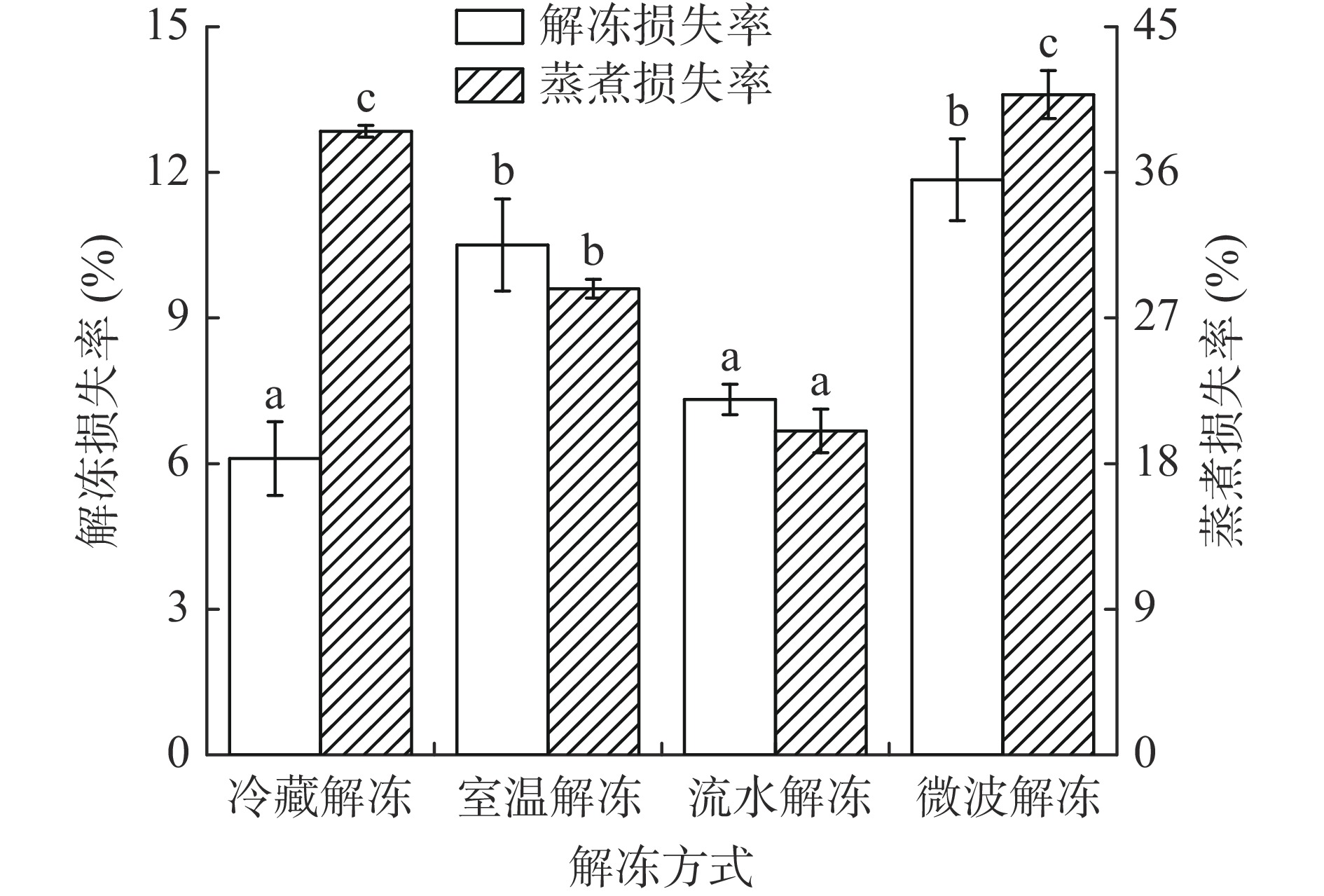
2.1 不同解冻方式对鸭腿肉的解冻损失、蒸煮损失的影响
解冻损失和蒸煮损失是衡量肉及肉制品系水力的指标,能表现食品保水性能的高低。保水性关系到肉品的色泽、嫩度等品质特性,甚至会影响肉品的出品率[8]。如图1所示,四种解冻方式中,冷藏解冻和流水解冻的解冻损失率较小,室温解冻、微波解冻的解冻损失率较高,这与室温解冻环境温度(20 ℃)和微波解冻快速加热有关[15]。在冷藏解冻的方式下,鸭腿肉的保水性最强,张帆等[5]研究也表明冷藏解冻的解冻损失率最低,显著低于空气解冻和静水解冻(P<0.05)。流水解冻的蒸煮损失率最低,与前人研究结果一致[16-17],用水解冻法对冻结肉样品进行解冻,解冻后的肉样保水性较好,蒸煮损失率低。
2.2 不同解冻方式对鸭腿肉pH、色泽的影响
pH的高低与肉的颜色、货架期等重要指标相关[18-19]。如表1所示,流水解冻和冷藏解冻pH最低,两者差异不显著(P>0.05),一般认为肉的pH在6.0左右有助于维持系水力。微波解冻测得的pH最高,牛改改等[20]研究表明解冻过程中,蛋白质被快速分解,产生碱性物质包括氨、胺,pH升高,推测微波解冻对肉的颜色和蛋白质氧化变性有较大的影响。
表 1 不同解冻方式对鸭腿肉的pH、色泽的影响Table 1. Effects of different thawing methods on pH and color of duck leg meat解冻方式 pH 色泽 L*值 a*值 b*值 冷藏解冻 6.30±0.01a 37.93±1.62a 6.13±0.59b 8.41±0.57b 室温解冻 6.44±0.01b 44.27±1.86b 4.66±0.38a 7.08±0.75a 流水解冻 6.28±0.02a 43.77±0.02b 5.92±0.01b 7.69±0.18ab 微波解冻 6.54±0.05c 42.67±0.02b 4.11±0.01a 13.38±0.01c 注:同列不同小写字母表示不同解冻方式间差异显著(P<0.05)。 色泽在正常范围的颜色变化不影响食品的营养价值,但会影响消费者的感官体验,因而色泽是评定食品品质的重要指标。由表1可知,冷藏解冻的L*值偏低,与其他三种解冻方式的L*值有显著差异(P<0.05),说明该方法解冻的肉表面水分不高,保水力较高。a*值与肉中的肌红蛋白和血红蛋白的含量相关,冷藏解冻和流水解冻的a*值高,可能是因为其蛋白氧化程度较低[21],微波解冻的a*值最低,这是因为温度的升高会使肉中其他蛋白质变性量增加,肌红蛋白的溶解度降低[22]。综上,冷藏解冻和流水解冻对肉的色泽影响低。
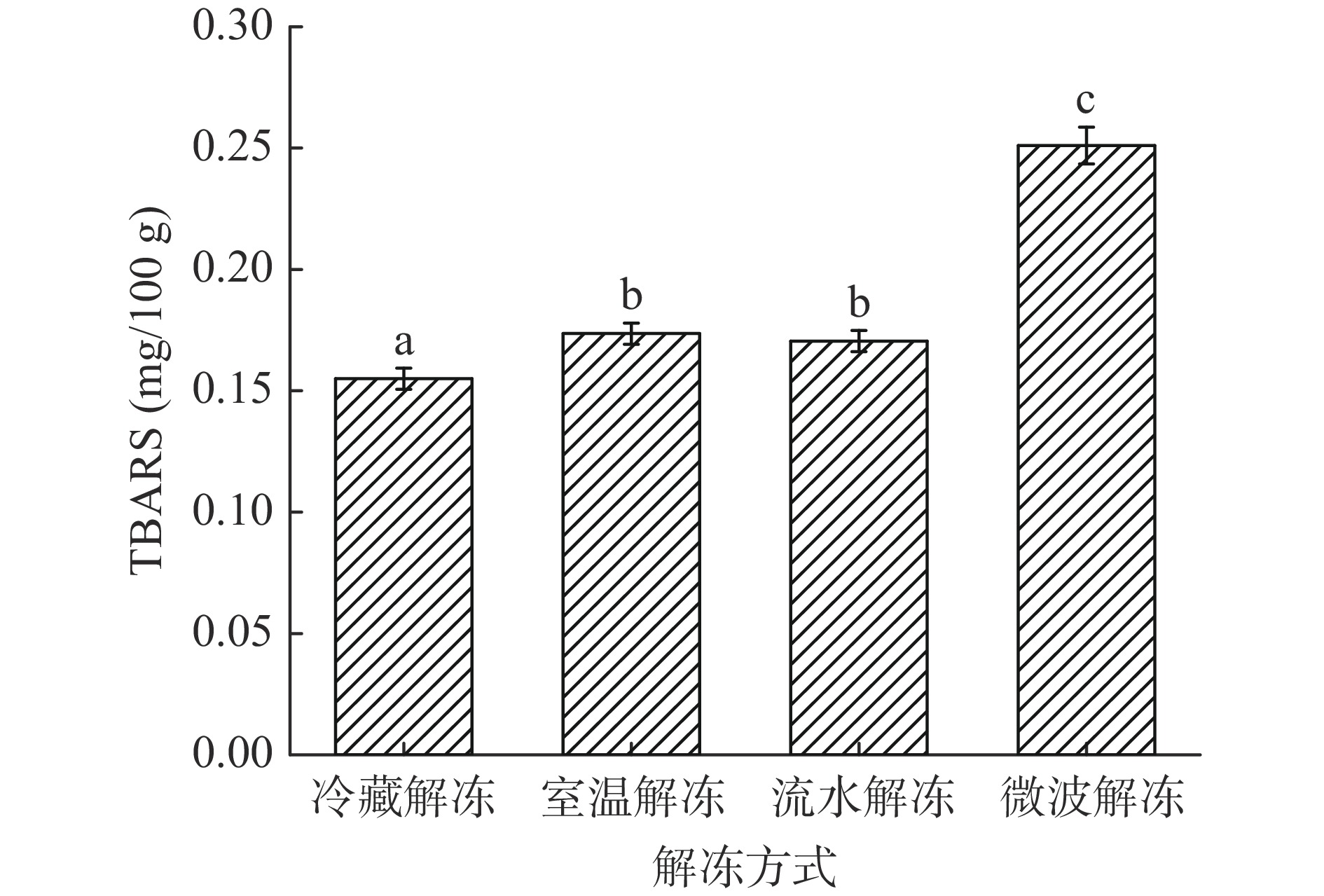
2.3 不同解冻方式对鸭腿肉硫代巴比妥酸(TBARS)值的影响
TBARS表示脂质氧化的程度,主要表征丙二醛的含量,TBARS值越大则表明肉类产品的氧化程度越深[23-24]。由图2可知,不同的解冻方式对TBARS值的影响显著,特别是冷藏解冻和微波解冻。冷藏解冻的TBARS值(0.16 mg/100 g)显著低于其他解冻方式(P<0.05),表明其在低温解冻环境下肉的脂肪氧化程度最低,进而维护肉的色泽稳定性,该结果与色泽和新鲜度相对应。微波解冻的TBARS值(0.25 mg/100 g)显著高于其他解冻方式(P<0.05),王琳琳等[15]研究表明微波解冻过程中传递热量高和速度快,会促进脂肪氧化的发生,从而导致丙二醛含量高。因此,冷藏解冻对鸭腿肉的脂质氧化影响低,微波解冻加速了脂质氧化反应。
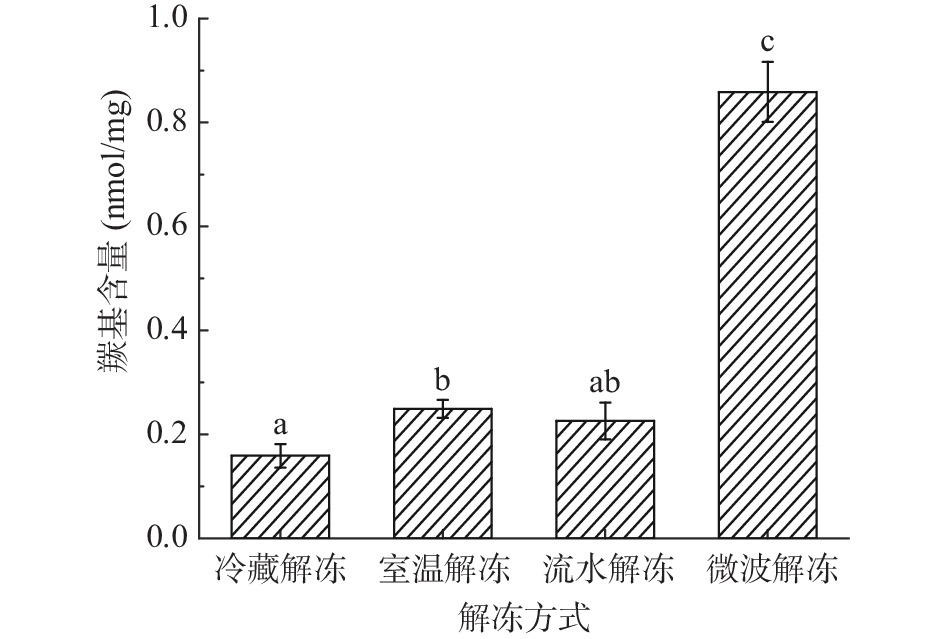
2.4 不同解冻方式对鸭腿肉羰基含量的影响
羰基是蛋白质主要的氧化产物,是判断肌纤维蛋白氧化程度的重要指标之一[25]。研究表明,羰基衍生物增多可能是自由基引起的,或是脂质过氧化引起的[26]。由图3可知,微波解冻的鸭腿肉肌原纤维蛋白的羰基含量最高,为0.86 nmol/mg,这与解冻方式对TBARS值的影响一致,微波解冻的丙二醛含量高,脂质氧化程度深,从而产生较多的羰基衍生物[27]。冷藏解冻的羰基含量最低,为0.16 nmol/mg,低温解冻过程对蛋白质氧化影响程度低,能更好保留肌原纤维蛋白的特性,这与前人对牦牛肉和虾肉的研究一致[15, 28],冷藏解冻后的羰基含量最低,对蛋白的氧化特性影响小。
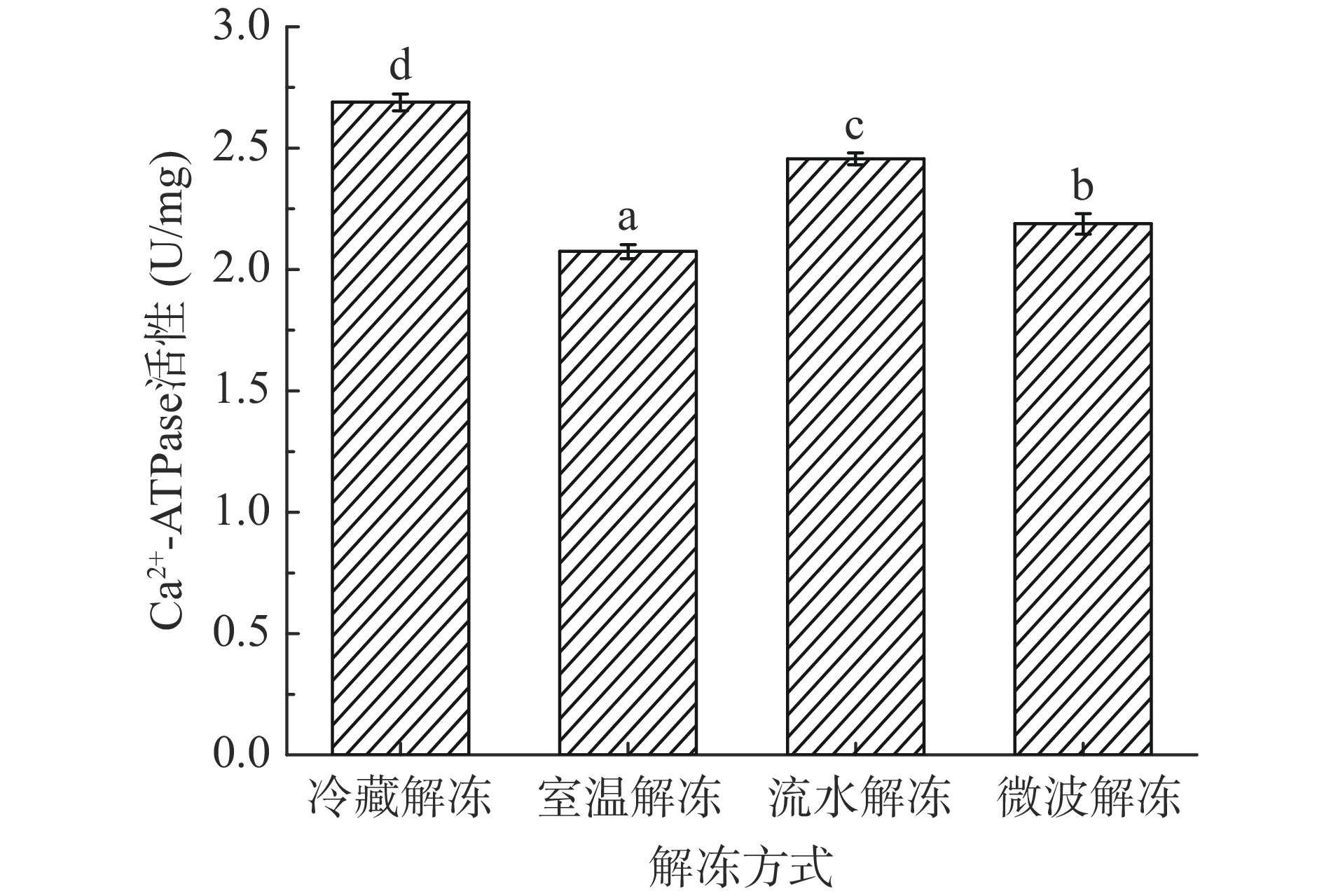
2.5 不同解冻方式对鸭腿肉Ca2+-ATPase活性的影响
肌原纤维蛋白主要包括原肌球蛋白、肌球蛋白、肌动球蛋白,Ca2+-ATPase是表示肌球蛋白完整性的指标[4],Ca2+-ATPase活性越高,蛋白完整性越好,Ca2+-ATPase活性越低,蛋白氧化变性程度越严重。如图 4所示,微波解冻和室温解冻的 Ca2+-ATPase 活性较低,分别为2.19和2.07 U/mg,Ca2+-ATPase活性在较高的解冻温度下易降低,蛋白质水解,其氧化程度严重[4]。冷藏解冻的Ca2+-ATPase活性最高,为2.69 U/mg,流水解冻次之,为2.45 U/mg,这表明鸭腿肉经冷藏解冻后的肌球蛋白完整性最好,不同解冻方式对鸭腿肉的Ca2+-ATPase活性影响与羰基结果相似,这表明冷藏解冻不易引发蛋白质氧化。
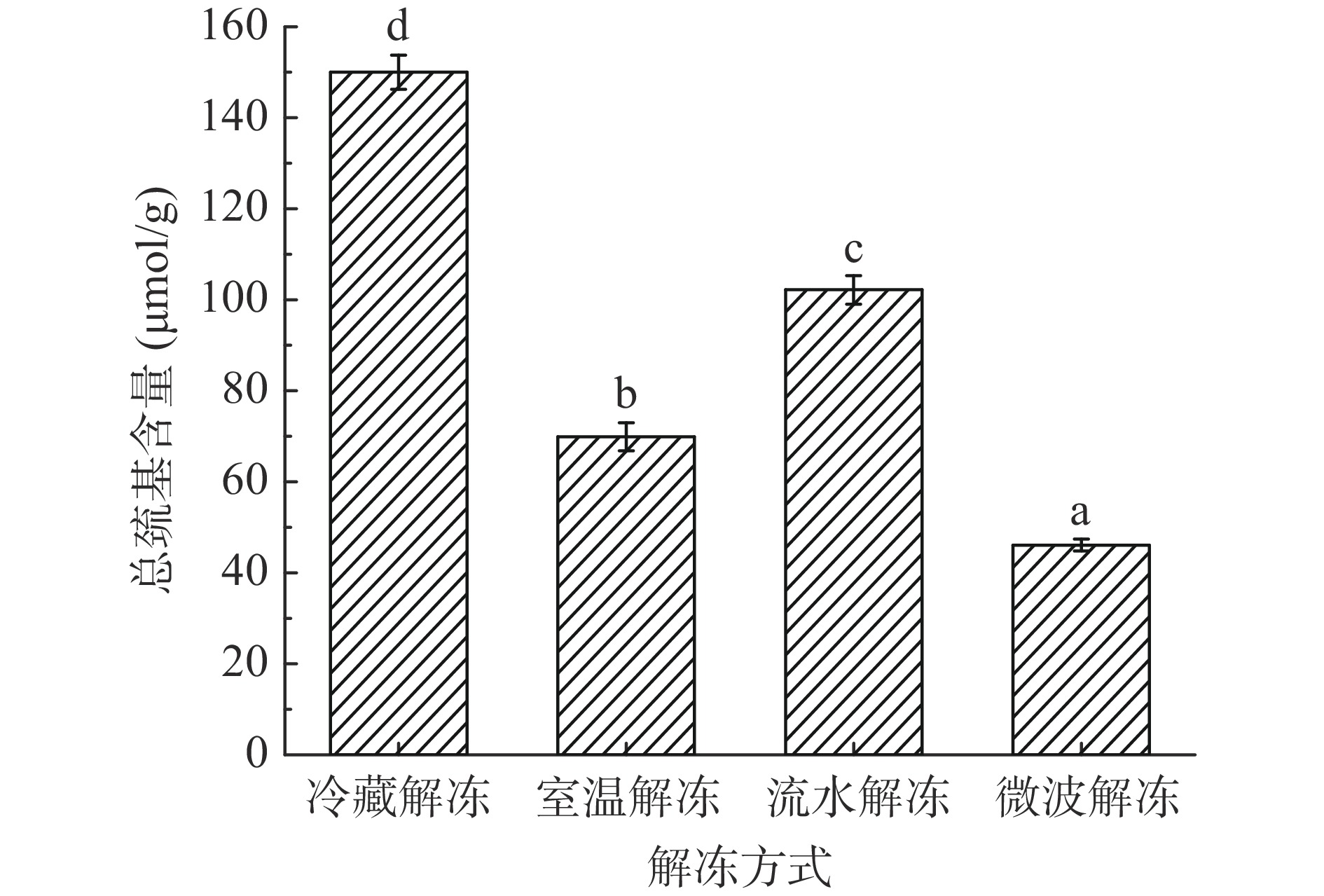
2.6 不同解冻方式对鸭腿肉总巯基含量的影响
总巯基是指暴露在表面和埋藏在内部区域的蛋白质基团,高抗氧化性的巯基容易被氧化成二硫键[29],从而导致总巯基含量减少,总巯基含量与蛋白质氧化程度呈负相关关系[30-31]。如图5所示,解冻方式对鸭腿肉中肌纤维蛋白的总巯基含量具有显著性影响(P<0.05),其中,微波解冻的总巯基含量最低,为46.10 μmol/g,表明该组的肌肉蛋白质氧化程度更严重,总巯基更多的被氧化,可能形成了-SS-、-SOH等氧化产物[15]。Li等[32]指出微波解冻过程中微波场中内部偶极子振动引起的不均匀加热使蛋白质被暴露,蛋白质氧化加深。冷藏解冻的总巯基含量最高,为149.10 μmol/g,巯基基团活跃,说明该组肌肉蛋白质氧化程度最低,这也在羰基含量和Ca2+-ATPase活性指标中得到证实。
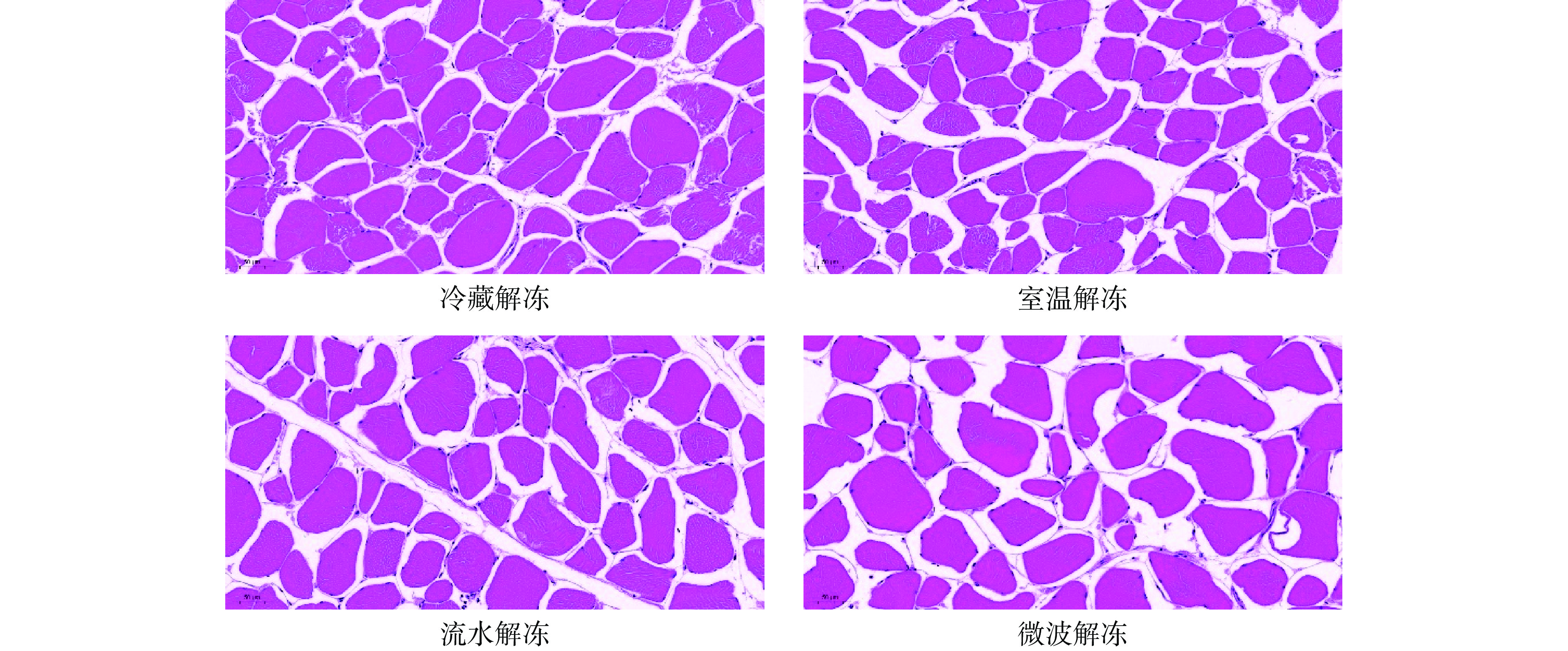
2.7 不同解冻方式对鸭腿肉组织学特性的影响
解冻方式对肌肉组织学特性的影响主要表现在肌纤维的变化,肌纤维的完整性与肌肉的嫩度、保水性、色差等品质指标相关联,肌纤维间结构致密,肌纤维间隙小,肌肉的嫩度和保水性越好。如表2和图6所示,冷藏解冻的肌纤维间隙最小,为6.97±0.91 μm,肌肉组织学特性较紧密。流水解冻的肌纤维间隙仅次于冷藏解冻,无显著性差异(P>0.05),这是由于冷藏解冻的解冻速率慢,冰晶体会随着解冻时间的延长逐渐破坏肌纤维的完整性[33]。鸭腿肉经室温解冻和微波解冻后肌纤维间隙较大,其中微波解冻后肌纤维间隙最大,为15.54±0.81 μm,这与王雪松等[34]的研究一致,肉样在微波解冻过程受热不均,肌纤维间隙增大,保水性降低。综上,经微波解冻和室温解冻后的鸭腿肉的肌纤维间隙较大,冷藏解冻和流水解冻后肌纤维间隙小,对鸭腿肉的品质影响较小。
表 2 不同解冻方式对鸭腿肉肌纤维间隙的影响Table 2. Effect of different thawing methods on the muscle fiber gap of duck leg meat解冻方式 冷藏解冻 室温解冻 流水解冻 微波解冻 肌纤维间隙(μm) 6.97±0.91a 11.72±0.94b 8.06±0.59a 15.54±0.81c 注:同行不同小写字母表示不同解冻方式间差异显著(P<0.05)。 2.8 不同解冻方式鸭腿肉肌原纤维蛋白SDS-PAGE的影响
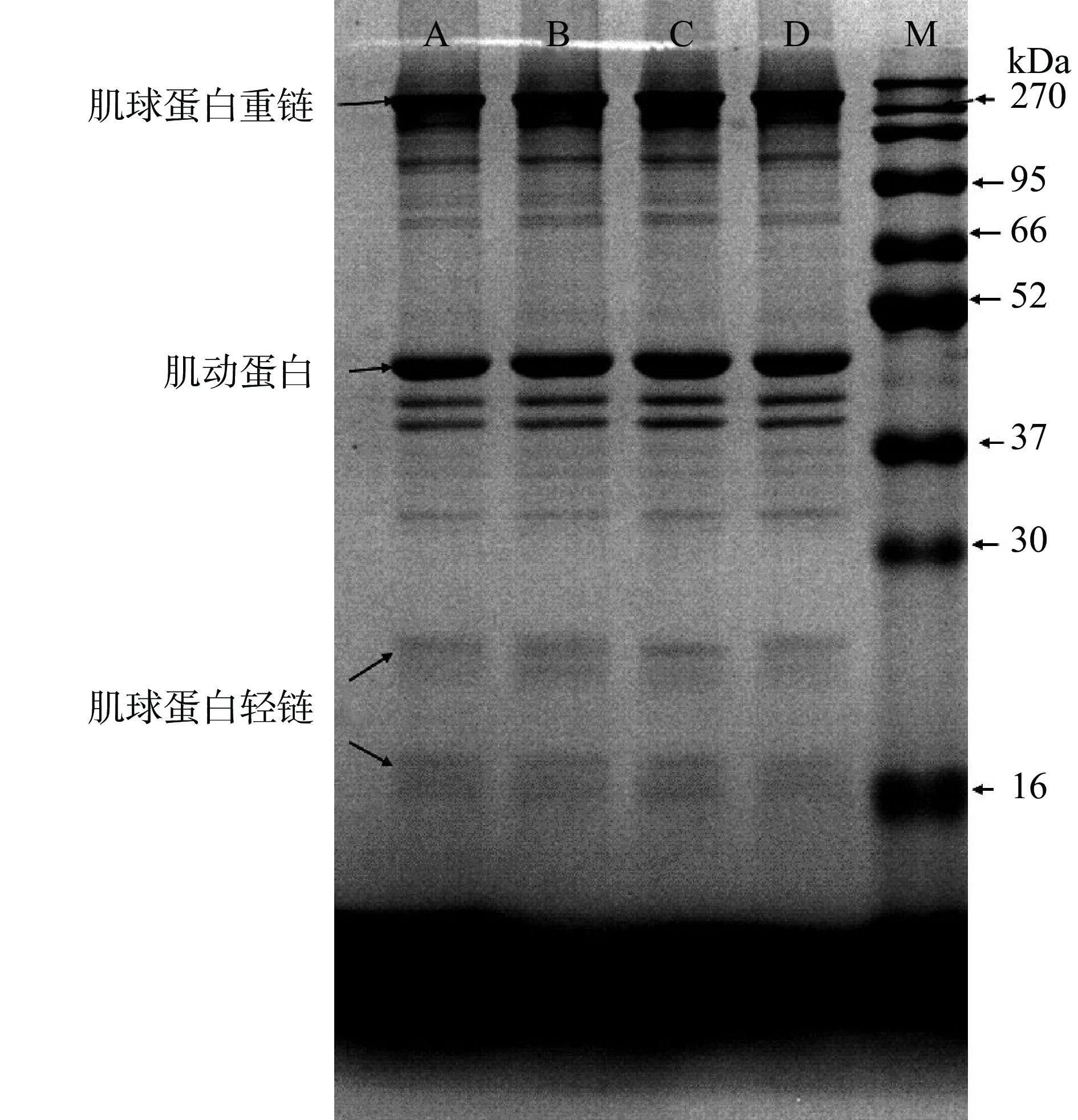
肌球蛋白和肌动蛋白是肌原纤维蛋白最为重要的部分[35],肌球蛋白则是肌肉中含量最丰富的蛋白质,对肉制品的保水性、嫩度和乳化作用起着重要作用,因此肌球蛋白重链是分析鸭腿肉理化性质的重要蛋白质[36-37]。SDS-PAGE图谱显示解冻方式对蛋白质降解的影响,由图7可知,解冻方式对鸭腿肉的肌原纤维蛋白氧化有一定的影响,经冷藏解冻后的肌球蛋白重链和肌动蛋白等相对大分子量蛋白条带最宽,相对较小分子量蛋白条带如肌球蛋白轻链条带相对较窄,蛋白质之间的氧化降解现象不明显。其他解冻方式均在不同程度上促进了蛋白质的氧化降解,加剧了二硫键和羰基衍生物的形成和蛋白质氧化还原作用[38],促使肌球蛋白重链转化为肌球蛋白轻链,从而降低鸭腿肉的保水性等。SDS-PAGE图谱与其他表征蛋白氧化程度改变的指标(总巯基含量、羰基含量、Ca2+-ATPase活性)显示一致,冷藏解冻对蛋白质的氧化程度的影响最小。
2.9 不同解冻方式对鸭腿肉的蛋白质二级结构的影响
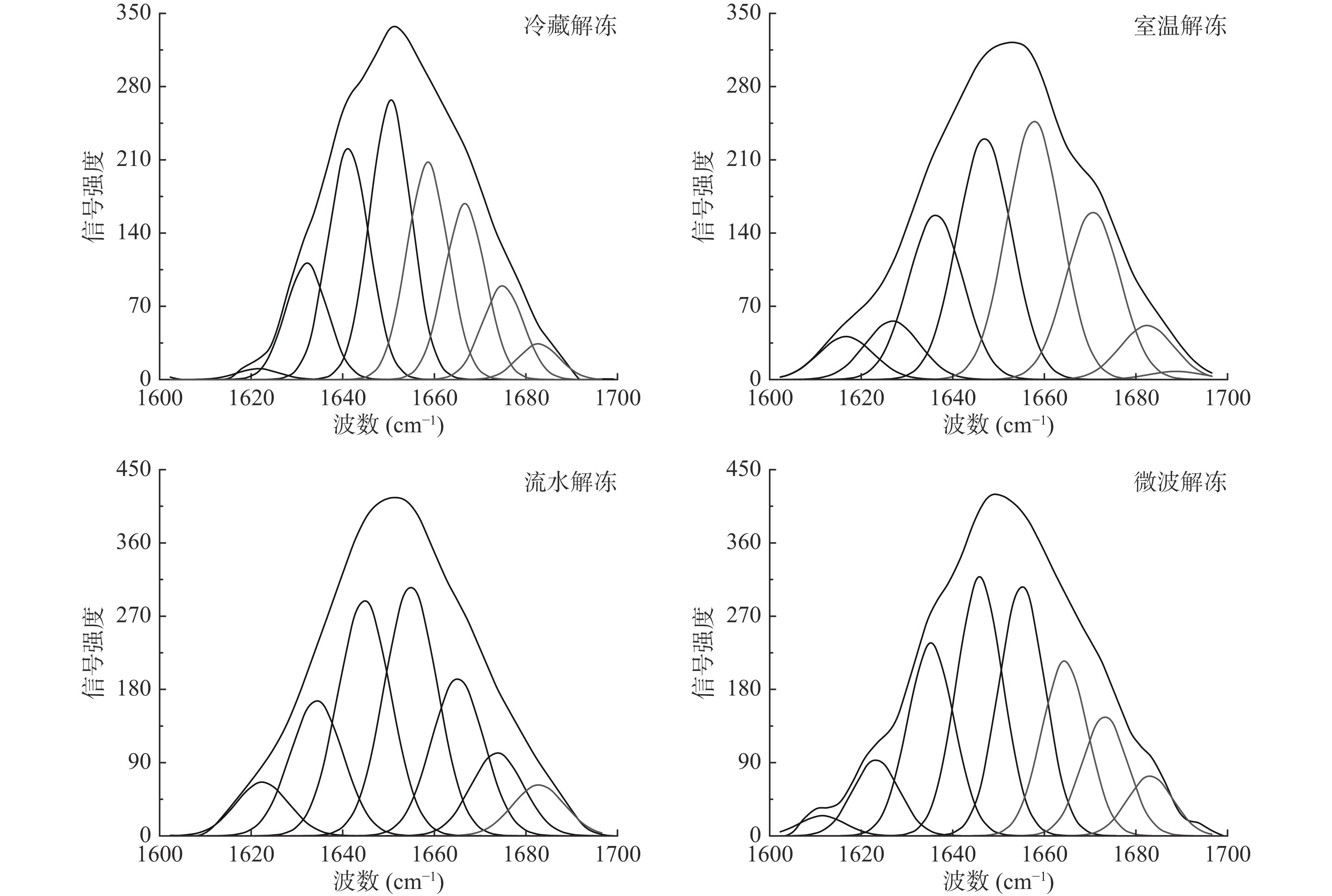
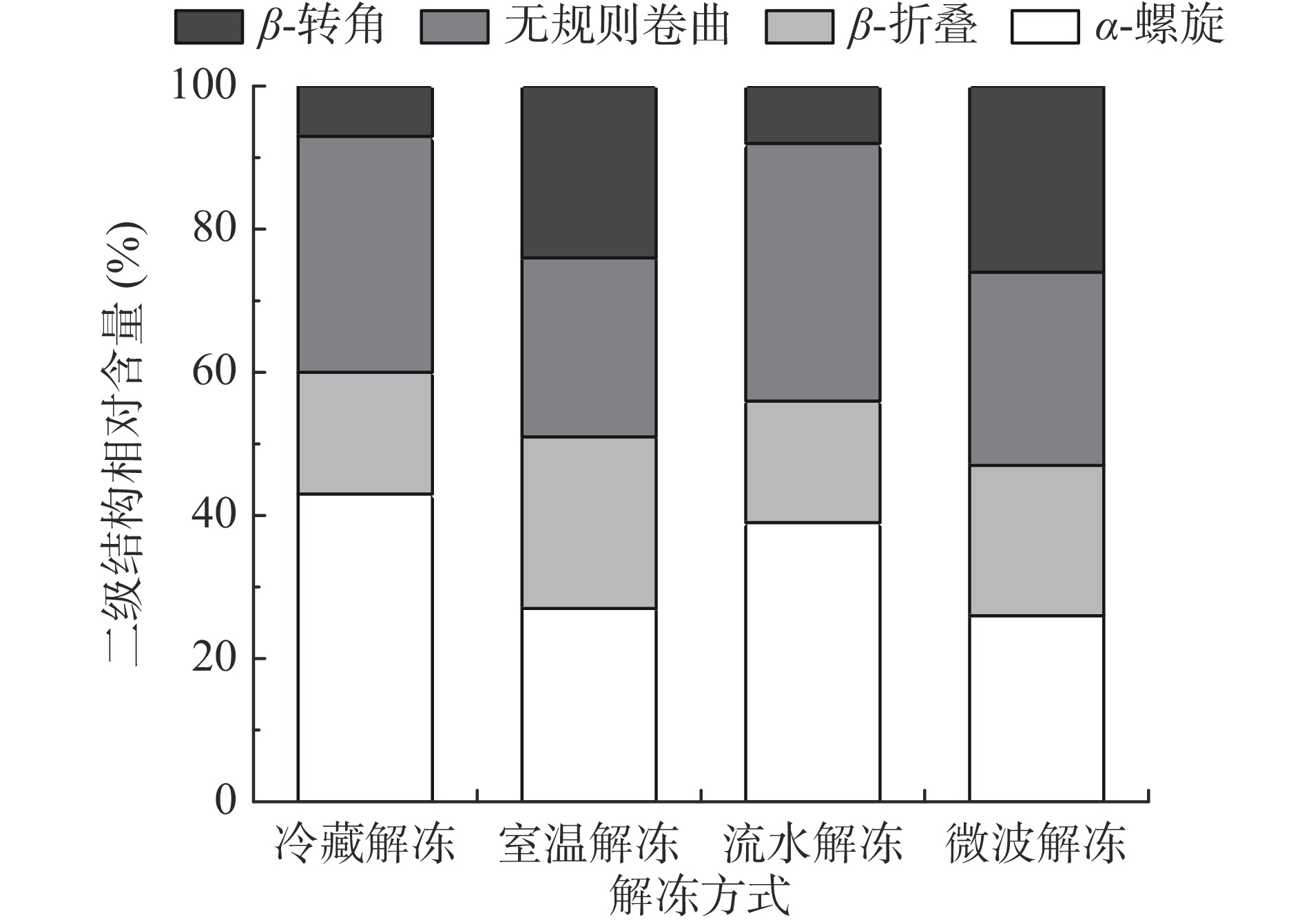
拉曼光谱是基于分子在基态电子态的离散振动跃迁,拉曼光谱条带的波数和强度变化可以反映蛋白质的二级结构和局部环境的改变,其中酰胺Ⅰ带(1600~1700 cm−1)的伸缩振动以C=O为主,与蛋白质二级结构的含量变化密切相关[39-41]。文献指出[42],酰胺Ⅰ带中含有α-螺旋(1650~1660 cm−1)、β-折叠(1620~1632 cm−1,1670~1680 cm−1)、β-转角(1635~1639 cm−1,1680~1690 cm−1)和无规则卷曲(1640~1645 cm−1,1666~1670 cm−1)。通过去卷积和曲线拟合相结合对拉曼光谱峰进行分峰处理,得到拉曼光谱拟合曲线图(图8)和肌原纤维蛋白二级结构相对含量图(图9)。
如图8所示,鸭腿肉肌原纤维蛋白二级结构受解冻方式的影响,研究表明,蛋白质的二级结构和酰胺I带最大峰的拉曼位移有关[43],冷藏解冻组和流水解冻组显示酰胺Ⅰ带最大峰位置出现在1653 cm−1附近,室温解冻组中最大峰位置出现在1660 cm−1附近,而微波解冻组中最大峰位置偏移至1645 cm−1附近。
酰胺Ⅰ带中,α-螺旋表示有序的蛋白质结构,主要由多肽链上羰基和氨基之间的分子内氢键稳定,β-折叠是蛋白质分子间的有序排列,由分子间氢键维持[44]。从α-螺旋和β-折叠的百分比含量总和看,冷藏解冻组的最高,其次到流水解冻、室温解冻和微波解冻。α-螺旋百分比含量最高的是冷藏解冻组,占比达42.33%,流水解冻次之,达38.75%,显著高于其它解冻组(P<0.05),表明蛋白质结构良好,稳定性高;β-折叠百分比含量最高的是室温解冻和微波解冻组,这表示室温解冻和微波解冻可能会破坏α-螺旋稳定结构,使其转化为β-折叠结构[40]。室温解冻和微波解冻中,无规则卷曲和β-转角含量高,表明其蛋白结构较紊乱。综上,冷藏解冻和流水解冻对蛋白质二级结构影响较小,这与其他指标结果相似,该结果也在鹅腿肉和猪肉中得到证实[4, 40]。
2.10 相关性分析
解冻处理鸭腿肉各指标相关性分析如表3所示。由表3可知,解冻损失率与pH、TBARS值、羰基含量、肌纤维间隙呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),与a*值、Ca2+-ATPase活性、总巯基含量呈极显著负相关(P<0.01);蒸煮损失率仅与b*值呈显著正相关(P<0.05)。这表明鸭腿肉的保水性受脂质氧化和蛋白质氧化的影响,氧化程度越深,肌纤维间隙越大,解冻损失率越高。pH与TBARS值、羰基含量、肌纤维间隙呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),与a*值、Ca2+-ATPase活性、总巯基含量呈极显著负相关(P<0.01);L*值与a*值、Ca2+-ATPase活性、总巯基含量呈显著负相关(P<0.05);a*值与TBARS值、羰基含量、肌纤维间隙呈极显著负相关(P<0.01),与Ca2+-ATPase活性、总巯基含量呈极显著正相关(P<0.01);b*值与TBARS值、羰基含量、肌纤维间隙呈极显著正相关(P<0.01)。这表明鸭腿肉的pH、色泽与脂肪和蛋白氧化有关,氧化程度越严重,L*值和a*值越小,b*值越大,这是因为蛋白氧化会影响肌红蛋白,而肌红蛋白是肉色的决定因素[45]。TBARS值与羰基含量、肌纤维间隙呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),与Ca2+-ATPase活性、总巯基含量呈极显著负相关(P<0.01);羰基含量与总巯基含量呈极显著负相关(P<0.01),与肌纤维间隙呈极显著正相关(P<0.01);Ca2+-ATPase活性与总巯基含量呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),与肌纤维间隙呈极显著负相关(P<0.01);总巯基含量与肌纤维间隙呈极显著负相关(P<0.01)。上述相关性描述表明鸭腿肉的保水性、色泽与脂肪氧化和蛋白氧化相关,且脂质氧化和蛋白氧化之间并非独立发生的,两者之间相互影响,有研究显示脂肪氧化程度的加深可能会在蛋白质中产生更多疏水区域,从而促进肌原纤维蛋白质的氧化和变性[46],最终导致肉的品质变化。
表 3 解冻处理鸭腿肉各指标相关性分析Table 3. Correlation analysis of various indicators of thawed duck leg meat指标 解冻损失率 蒸煮损失率 pH L*值 a*值 b*值 TBARS值 羰基
含量Ca2+-ATPase活性 总巯基含量 肌纤维间隙 解冻损失率 1 0.264 0.840** 0.457 −0.857** 0.552 0.759** 0.755** −0.889** −0.920** 0.927** 蒸煮损失率 1 0.505 −0.515 −0.341 0.665* 0.443 0.520 0.051 −0.063 0.418 pH 1 0.291 −0.861** 0.680* 0.843** 0.799** −0.733** −0.820** 0.936** L*值 1 −0.580* −0.097 0.256 0.195 −0.693* −0.675* 0.414 a*值 1 −0.510 −0.724** −0.727** 0.801** 0.848** −0.889** b*值 1 0.909** 0.924** −0.207 −0.529 0.738** TBARS值 1 0.974** −0.799** −0.803** 0.907** 羰基含量 1 −0.542 −0.748** 0.884** Ca2+-ATPase
活性1 0.906** −0.799** 总巯基含量 1 −0.931** 肌纤维间隙 1 注:*表示显著相关(P<0.05),**表示极显著相关(P<0.01)。 3. 结论
本研究表明,不同的解冻方式对鸭腿肉的解冻损失、蒸煮损失、pH、色泽、脂质氧化、组织学特性和蛋白氧化的影响差异显著。4种解冻方式中,从保水性、色泽、pH、组织学特性综合比较,冷藏解冻和流水解冻最优,微波解冻的影响最严重,室温解冻次之。微波解冻的脂肪氧化和蛋白氧化的程度严重,室温解冻次之。冷藏解冻的脂质氧化程度和蛋白氧化程度轻(羰基含量最低(0.16 nmol/mg),总巯基含量(149.10 μmol/g)和Ca2+-ATPase活性(2.69 U/mg)最高,SDS-PAGE显示其蛋白质氧化降解程度小,蛋白质的二级结构稳定有序,α-螺旋含量(42.33%)最高;流水解冻对鸭腿肉的肌纤维、脂质氧化、蛋白质氧化的影响比冷藏解冻稍重。综上所述,微波解冻和室温解冻会加剧脂肪和蛋白氧化,冷藏解冻的解冻损失率低,对色泽和组织的影响小,能在一定程度上降低解冻对冷冻鸭腿肉的脂肪和蛋白氧化影响,从而保证鸭腿肉的品质质量,其次是流水解冻。冷藏解冻是鸭腿肉解冻的最优方法,但冷藏解冻的解冻耗费时间较长,规模化解冻需要提前准备,可以在冷藏解冻的基础上改变环境湿度,研究低温高湿解冻方法,进一步提高解冻效率,保证产品品质。
-
表 1 不同解冻方式对鸭腿肉的pH、色泽的影响
Table 1 Effects of different thawing methods on pH and color of duck leg meat
解冻方式 pH 色泽 L*值 a*值 b*值 冷藏解冻 6.30±0.01a 37.93±1.62a 6.13±0.59b 8.41±0.57b 室温解冻 6.44±0.01b 44.27±1.86b 4.66±0.38a 7.08±0.75a 流水解冻 6.28±0.02a 43.77±0.02b 5.92±0.01b 7.69±0.18ab 微波解冻 6.54±0.05c 42.67±0.02b 4.11±0.01a 13.38±0.01c 注:同列不同小写字母表示不同解冻方式间差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 2 不同解冻方式对鸭腿肉肌纤维间隙的影响
Table 2 Effect of different thawing methods on the muscle fiber gap of duck leg meat
解冻方式 冷藏解冻 室温解冻 流水解冻 微波解冻 肌纤维间隙(μm) 6.97±0.91a 11.72±0.94b 8.06±0.59a 15.54±0.81c 注:同行不同小写字母表示不同解冻方式间差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 3 解冻处理鸭腿肉各指标相关性分析
Table 3 Correlation analysis of various indicators of thawed duck leg meat
指标 解冻损失率 蒸煮损失率 pH L*值 a*值 b*值 TBARS值 羰基
含量Ca2+-ATPase活性 总巯基含量 肌纤维间隙 解冻损失率 1 0.264 0.840** 0.457 −0.857** 0.552 0.759** 0.755** −0.889** −0.920** 0.927** 蒸煮损失率 1 0.505 −0.515 −0.341 0.665* 0.443 0.520 0.051 −0.063 0.418 pH 1 0.291 −0.861** 0.680* 0.843** 0.799** −0.733** −0.820** 0.936** L*值 1 −0.580* −0.097 0.256 0.195 −0.693* −0.675* 0.414 a*值 1 −0.510 −0.724** −0.727** 0.801** 0.848** −0.889** b*值 1 0.909** 0.924** −0.207 −0.529 0.738** TBARS值 1 0.974** −0.799** −0.803** 0.907** 羰基含量 1 −0.542 −0.748** 0.884** Ca2+-ATPase
活性1 0.906** −0.799** 总巯基含量 1 −0.931** 肌纤维间隙 1 注:*表示显著相关(P<0.05),**表示极显著相关(P<0.01)。 -
[1] LEYGONIE C, BRITZ T J, HOFFMAN L C. Protein and lipid oxidative stability of fresh ostrich M. iliofibularis packaged under different modified atmospheric packaging conditions[J]. Food Chemistry,2011,127(4):1659−1667. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.02.033
[2] ALVARENGA T, HOPKINS D L, RAMOS E M, et al. Ageing-freezing/thaw process affects blooming time and myoglobin forms of lamb meat during retail display[J]. Meat Science,2019,153:19−25. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2019.02.016
[3] B G J A, C K S, B J M, et al. Effect of high voltage electrostatic field treatment on thawing characteristics and post-thawing quality of lightly salted, frozen pork tenderloin[J]. LWT,2019,99:268−275. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2018.09.064
[4] XIA X, KONG B, LIU J, et al. Influence of different thawing methods on physicochemical changes and protein oxidation of porcine longissimus muscle[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2012,46(1):280−286. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2011.09.018
[5] 张帆, 范远景, 刘培志, 等. 不同解冻方法对鸭肉品质的影响[J]. 肉类研究,2016,30(5):35−39. [ZHANG F, FAN Y J, LIU P Z, et al. Effects of different thawing methods on quality of duck meat[J]. Meat Research,2016,30(5):35−39. doi: 10.15922/j.cnki.rlyj.2016.05.006 [6] 郭德斌, 刘薇, 苏婷, 等. 不同解冻方式对冷冻鸭翅品质的影响[J]. 浙江农业科学,2020,61(10):2099−2103. [GUO D B, LIU W, SU T, et al. Effects of different thawing methods on the quality of frozen duck wings[J]. Zhejiang Agricultural Science,2020,61(10):2099−2103. doi: 10.16178/j.issn.0528-9017.20201044 [7] 余力, 贺稚非, 王兆明, 等. 不同解冻方式对伊拉兔肉挥发性风味物质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2015,36(22):95−101. [YU L, HE Z F, WANG Z M, et al. Effects of different thawing methods on volatile flavor compounds of Ila rabbit meat[J]. Food Science,2015,36(22):95−101. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201522017 [8] 李锦锦, 莫然, 唐善虎, 等. 不同解冻方式对猪肝理化特性及氧化稳定性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(14):302−309. [LI J J, MO R, TANG S H, et al. Effects of different thawing methods on physicochemical properties and oxidation stability of pig liver[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(14):302−309. [9] 李学鹏, 刘慈坤, 周明言, 等. 羟自由基氧化对草鱼肌原纤维蛋白结构和凝胶性质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(21):30−37. [LI X P, LIU C K, ZHOU M Y, et al. Effects of hydroxyl radical oxidation on the structure and gel properties of myofibrin in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus)[J]. Food Science,2017,38(21):30−37. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201721005 [10] 阿依木古丽, 蔡勇, 陈士恩, 等. 反复冷冻-解冻对牛肉品质及组织结构的影响[J]. 食品科学,2011(7):109−112. [A Y M G L, CAI Y, CHEN S E, et al. Effects of repeated freeze-thawing on beef quality and tissue structure[J]. Food Science,2011(7):109−112. [11] 顾赛麒, 周洪鑫, 郑皓铭, 等. 干制方式对腌腊草鱼脂肪氧化和挥发性风味成分的影响[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(21):1−10. [GU S Q, ZHOU H X, ZHEGN H M, et al. Effects of drying methods on lipid oxidation and volatile flavor components of preserved grass carp[J]. Food Science,2018,39(21):1−10. [12] LEVINE R L, GARLAND D, OLIVER C N, et al. Determination of carbonyl content in oxidatively modified proteins[J]. Methods in Enzymology,1990,186:464−478.
[13] BEVERIDGE T, TOMA S J, NAKAI S. Determination of SH- and SS-groups in some food proteins using Ellman's reagent[J]. Journal of Food Science,1974,39(1):49−51. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.1974.tb00984.x
[14] 蔡路昀, 许晴, 曹爱玲. 不同超声辅助解冻方式对海鲈鱼肌原纤维蛋白的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(20):1−8. [CAI L Y, XU Q, CAO A L. Effects of different ultrasound-assisted thawing methods on myofibrin of sea bass[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(20):1−8. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.024414 [15] 王琳琳, 陈炼红, 李璐倩, 等. 解冻方式对牦牛肉蛋白氧化、功能特性及新鲜度的影响[J]. 农业机械学报,2021,52(5):342−349. [WANG L L, CHEN L H, LI L Q, et al. Effects of thawing methods on oxidation, functional characteristics and freshness of yak protein[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2021,52(5):342−349. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2021.05.038 [16] 刘欢, 陈雪, 宋立玲, 等. 不同解冻方式对鲐鱼鲜度及品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2016,37(10):259−265. [LIU H, CHEN X, SONG L L, et al. Effects of different thawing methods on freshness and quality of mackerel[J]. Food Science,2016,37(10):259−265. [17] 常海军, 唐翠, 唐春红. 不同解冻方式对猪肉品质特性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2014,35(10):1−5. [CHANG H J, TANG C, TANG C H. Effects of different thawing methods on pork quality and characteristics[J]. Food Science,2014,35(10):1−5. [18] HUGHES J, CLARKE F, PURSLOW P, et al. High pH in beef longissimus thoracis reduces muscle fibre transverse shrinkage and light scattering which contributes to the dark colour[J]. Food Research International,2017,101:228−238. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2017.09.003
[19] ZHANG Y M, HOPKINS D L, ZHAO X X, et al. Characterisation of pH decline and meat color development of beef carcasses during the early postmortem period in a Chinese beef cattle abattoir[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture,2018,17(7):1691−1695. doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(17)61890-2
[20] 牛改改, 秦成丰, 游刚, 等. 解冻方式对近江牡蛎肉感官特征和理化指标的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(16):271−278. [NIU G G, QIN C F, YOU G, et al. Effects of thawing methods on sensuality characteristics and physicochemical indexes of Crassostrea crassostrea[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(16):271−278. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020.16.043 [21] ZAKRYS P I, HOGAN S A, O'SULLIVAN M G, et al. Effects of oxygen concentration on the sensory evaluation and quality indicators of beef muscle packed under modified atmosphere[J]. Meat Science,2008,79(4):648−655. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2007.10.030
[22] 朱宏星, 孙冲, 王道营, 等. 肌红蛋白理化性质及肉色劣变影响因素研究进展[J]. 肉类研究,2019,33(6):55−63. [ZHU H X, SUN C, WANG D Y, et al. Research progress on physicochemical properties of myoglobin and influencing factors of meat deterioration[J]. Meat Research,2019,33(6):55−63. [23] 李慧芝, 谢含仪, 赵燕芳, 等. 反复冻融过程对肉类氧化关键指标的影响[J]. 食品科技,2020,45(11):102−109. [LI H Z, XIE H Y, ZHAO Y F, et al. Effects of repeated freezing and thawing on key parameters of meat oxidation[J]. Food Science and Technology,2020,45(11):102−109. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2020.11.017 [24] XIANG W, SONG X, QIU Z, et al. Mapping of TBARS distribution in frozen-thawed pork using NIR hyperspectral imaging[J]. Meat Science,2016,113(MAR.):92−96.
[25] BHATTACHARYA D, KANDEEPAN G, VISHNURAJ M R. Protein oxidation in meat and meat products-A review[J]. Food and Health,2016,2(4):171−183.
[26] AKAGAWA M. Protein carbonylation: Molecular mechanisms, biological implications, and analytical approaches[J]. Free Radical Research,2021,55(4):307−320. doi: 10.1080/10715762.2020.1851027
[27] 赵冰, 张顺亮, 李素, 等. 脂肪氧化对肌原纤维蛋白氧化及其结构和功能性质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(5):40−46. [ZHAO B, ZHANG S L, LI S, et al. Effects of lipid oxidation on myofibrin oxidation and its structure and functional properties[J]. Food Science,2018,39(5):40−46. [28] 侯晓荣, 米红波, 茅林春. 解冻方式对中国对虾物理性质和化学性质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2014,35(4):243−247. [HOU X R, MI H B, MAO L C. Effects of thawing methods on physical and chemical properties of Penaeus chinensis[J]. Food Science,2014,35(4):243−247. [29] 杜清普, 赵英, 王瑞红, 等. 不同解冻方法对冰蛋黄功能特性、理化特性及蛋白质结构的影响[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(11):8−16. [DU Q P, ZHAO Y, WANG R H, et al. Effects of different thawing methods on functional properties, physicochemical properties and protein structure of ice yolk[J]. Food Science,2021,42(11):8−16. [30] LI X, MA Y, SUN P, et al. Effect of ultrasonic thawing on protein properties and muscle quality of bonito[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation,2020,45(1):e14930.
[31] ZALP ZEN B, SOYER A. Effect of plant extracts on lipid and protein oxidation of mackerel (Scomber scombrus) mince during frozen storage[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2018,55(22):120−127.
[32] LI F, WANG B, LIU Q, et al. Changes in myofibrillar protein gel quality of porcine longissimus muscle induced by its structural modification under different thawing methods[J]. Meat Science,2019,147:108−115. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2018.09.003
[33] 李升升. 基于蛋白质组学的牦牛平滑肌嫩度形成机制研究[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2019. LI S S. Study on the formation mechanism of yak smooth muscle tenderness based on proteomics[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2019.
[34] 王雪松, 谢晶. 不同解冻方式对冷冻竹荚鱼品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(23):137−143. [WANG X S, XIE J. Effects of different thawing methods on quality of frozen horse mackerel[J]. Food Science,2020,41(23):137−143. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191105-050 [35] 程述震, 王晓拓, 张洁, 等. 电子束剂量率对牛肉蛋白结构和理化性质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2017,39(3):150−156. [CHENG S Z, WANG X T, ZHAGN J, et al. Effects of electron beam dose rate on protein structure and physicochemical properties of beef[J]. Food Science,2017,39(3):150−156. [36] XIA M, CHEN Y, GUO J, et al. Effects of oxidative modification on textural properties and gel structure of pork myofibrillar proteins[J]. Food Research International,2019,121(JUL.):678−683.
[37] HELLWIG M. The chemistry of protein oxidation in food[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition,2019,58(47):16742−16763. doi: 10.1002/anie.201814144
[38] DLA B, LZ B, RL A, et al. Effect of plant protein mixtures on the microstructure and rheological properties of myofibrillar protein gel derived from red sea bream (Pagrosomus major)[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2019,96:537−545. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.05.043
[39] HERRERO A M. Raman spectroscopy for monitoring protein structure in muscle food systems[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2008,48(6):512−523. doi: 10.1080/10408390701537385
[40] 刘磊, 夏强, 曹锦轩, 等. 不同解冻方法对鹅腿肉理化特性和品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(15):256−261. [LIU L, XIA Q, CAO J X, et al. Effects of different thawing methods on physicochemical properties and quality of goose leg meat[J]. Food Science,2020,41(15):256−261. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191018-196 [41] 吴永祥, 王玉, 袁德现, 等. 超高压处理对臭鳜鱼细菌群落结构和品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2021:1−14. [WU Y X, WANG Y, YUAN D X, et al. Effects of ultra-high pressure treatment on bacterial community structure and quality of smelly Mandarin fish[J]. Food Science,2021:1−14. [42] 张玉林. 宰后活性氧簇(ROS)的形成对鹅肉品质影响机制的研究[D]. 宁波: 宁波大学, 2014. ZHANG Y L. Study on the mechanism of postmortem reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation on goose meat quality[D]. Ningbo: Ningbo University, 2014.
[43] ALIX A, PEDANOU G, BERJOT M. Fast determination of the quantitative secondary structure of proteins by using some parameters of the Raman amide I band[J]. Journal of Molecular Structure,1988,174(none):159−164.
[44] 杨玉玲, 游远, 彭晓蓓, 等. 加热对鸡胸肉肌原纤维蛋白结构与凝胶特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科学,2014,47(10):2013−2020. [YANG Y L, YOU Y, PENG X P, et al. Effects of heating on the structure and gel properties of chicken breast myofibrillar proteins[J]. China Agricultural Science,2014,47(10):2013−2020. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2014.10.015 [45] BAO Y, ERTBJERG P. Effects of protein oxidation on the texture and water-holding of meat: A review[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2019,59(22):3564−3578. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1498444
[46] BAO Y, ERTBJERG P, ESTÉVEZ M, et al. Freezing of meat and aquatic food: Underlying mechanisms and implications on protein oxidation[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety,2021,20(6):5548−5569. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12841
-
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 姜坤,李玉国,张道志,徐恒伟,冯丹萍,孟小茜,郑春英. 微生物发酵对刺五加叶黄酮类成分生物合成的影响. 中国农学通报. 2024(03): 145-151 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陆少君,蔡肇栩,郭瑞雪,谢群巧,罗力,唐春萍,陈文健,江涛. 基于TLR-4/NF-κB信号通路探究金花茶提取物对非酒精性脂肪肝的作用. 食品工业科技. 2024(20): 349-360 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 周月,王一珈,臧健,高英旭,潘丰,郭志富,李胤之. 刺五加活性成分及药用价值研究进展. 辽宁林业科技. 2024(06): 48-50+71 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 何嘉伟,江汉美,黄振阳,曾格格,戴全武,刘天琪,韩蔓. HS-SPME-GC-MS结合化学计量法分析刺五加不同部位的挥发性成分. 南京中医药大学学报. 2023(02): 146-156 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李强,袁勇,李玉,于建海. 刺五加多糖对奶牛生产性能、抗氧化指标及免疫功能的影响. 中国饲料. 2023(12): 28-31 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 丁思宇,张道涵,韩丽琴. 星点-响应面法优化刺五加根黄酮闪式提取工艺研究. 吉林医药学院学报. 2023(04): 269-271 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 孙琳,井长欣,邹睿,辛宇,张晓旭,邱智东,王伟楠. 刺五加-灵芝双向固体发酵工艺优化及抗氧化活性评价. 科学技术与工程. 2023(21): 9004-9014 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 李强,张若冰,杨玉赫,田冰,李文兰,李陈雪. 刺五加叶化学成分及药理作用研究进展. 药学研究. 2023(07): 495-501 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 石玉璞,牛思思,韩璐瑶,李莞颖,余君伟,武冰辉,徐波,张艳萍,曹艳,乔长晟. 枸杞刺梨复合饮料的工艺优化及其降血糖性能. 食品研究与开发. 2023(18): 149-157 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 茆鑫,郑剑斌,李广耀,曲敏,郑心琪. 响应曲面法优化刺五加-五味子混菌发酵工艺的研究. 食品科技. 2023(09): 57-64 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 戴丛书,柴晶美,林长青. 金银花黄酮提取物的降血糖作用. 食品工业科技. 2022(24): 386-393 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(5)










 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



