The Antibacterial Mechanism of Ozone Water Combined with Lactobacillus paracasei Z21 on E.coli O157:H7 in Mung Bean Sprouts
-
摘要: 为研究臭氧水联合副干酪乳杆菌Z21发酵上清液对绿豆芽中大肠杆菌O157:H7的杀菌效果、细胞结构影响和生物膜清除作用,本实验对人工污染大肠杆菌O157:H7的绿豆芽进行联合处理,选出最优的杀菌条件,采用流式细胞仪、扫描电镜、傅里叶红外光谱(Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy,FT-IR)、拉曼光谱分析臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液的杀菌机制;通过菌落计数及胞外聚合物分析,研究了臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液对大肠杆菌O157:H7生物膜的清除效果。结果表明,1.5 mg/L臭氧水联合10%(v/v)Z21发酵上清液处理对大肠杆菌O157:H7杀菌效果最佳,菌落总数减少了2.81 lg CFU/g;与对照组相比,联合处理破坏了大肠杆菌O157:H7细胞壁和细胞膜中的多糖,脂质和蛋白质结构,增加了细胞膜的通透性,改变了菌体形态。联合处理对生物膜有良好的清除效果,显著降低了生物膜的胞外聚合物含量(P<0.05)。本研究为大肠杆菌生物膜的清除及农产品防腐保鲜提供了理论依据。
-
关键词:
- 绿豆芽 /
- 臭氧水 /
- 大肠杆菌O157:H7 /
- 副干酪乳杆菌 /
- 抑菌机制
Abstract: To explore the bactericidal effect, cell structure and biofilm removal mechanism of ozone water combined with Lactobacillus paracasei Z21 fermented supernatant on E. coli O157:H7 in mung bean sprouts, this experiment combined treatment of artificially contaminated E. coli O157:H7 to select the optimal bactericidal conditions. The bactericidal mechanism of ozone water combined with Z21 supernatant was studied by flow cytometry, scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and raman spectroscopy. The effect of ozone water combined with Z21 fermented supernatant on E. coli O157:H7 biofilm was studied by colony counting and extracellular polymer analysis. The results showed that 1.5 mg/L ozone water combined with 10% (V/V) Z21 fermented supernatant had the best bactericidal effect on E. coli O157:H7, and the total number of bacteria decreased by 2.81 lg CFU/g. Compared with the control group, the combined treatment destroyed polysaccharides, lipid and protein structures in the cell walls and membranes of E. coli O157:H7, increased the permeability of cell membrane, and changed the morphology. The combined treatment presented a strong removal effect on biofilm, and the extracellular polymer content of the biofilm was significantly reduced (P<0.05). This study could provide a theoretical basis for the removal of Escherichia coli biofilm and preservation of agricultural products. -
绿豆芽因其具有丰富的营养价值和良好的抗氧化活性而广受消费者的关注[1]。然而在其生产过程中,温暖和潮湿环境为致病菌的生长提供了理想条件。其中,大肠杆菌O157:H7是常见的致病菌之一,大肠杆菌O157:H7容易在绿豆芽表面附着、生长繁殖形成生物膜,它不仅为细菌提供必需的营养物质,还保护细菌免受环境损害[2-3]。形成的生物膜具有较强的黏附力,难以清除,增加了杀菌难度[4-5]。因此,食用绿豆芽而导致的食源性疾病时有发生[6]。数据显示,在2011年德国发生了肠出血性大肠杆菌污染绿豆芽的事件,导致约4000人患病,47人死亡[7]。
臭氧是一种强氧化剂,对食源性病原体具有显著的抑制作用。臭氧能破坏微生物的细胞结构,使菌体蛋白质变性,破坏菌体酶系统,还能够改变细胞膜通透性,使微生物失去生长繁殖能力[8]。臭氧已被普遍应用于芽苗菜的杀菌处理。Singla等[9]研究发现,臭氧水与苹果酸单独使用对萝卜苗和菜豆苗中志贺氏菌的杀菌效果不明显,两者联合处理杀菌效果显著增加。Tachikawa等[10]研究表明,臭氧水和氧化氢联合处理可显著提高荧光假单胞菌生物膜清除率。
乳酸菌是革兰氏阳性球菌或杆状菌,广泛用于发酵食品的商业生产。它们除了能改变食物的风味、气味、质地和营养成分外,还对致病菌有抑制作用。大量研究表明,乳酸菌的上清液可以抑制鸡胸肉、牛肉、面包中的有害细菌[11-12]。乳酸菌代谢产生多种抗菌化合物,包括有机酸、脂肪酸、细菌素、过氧化氢等代谢产物[13]。因此,在食品中使用乳酸菌上清液能更有效地抑制细菌生长。副干酪乳杆菌是乳酸菌的一种,有研究发现,副干酪乳杆菌上清液对酸土脂环芽孢杆菌和黄曲霉有明显的抑制作用[14]。
臭氧水与其它方法联合,可以提高杀菌效果。Baumann等[15]研究发现,臭氧-超声联用与单一处理相比,其对单增李斯特菌的杀菌效果提升约30%;Yuka等[16]发现臭氧有机酸联合处理比单独处理更能有效地降低金针菇上大肠杆菌O157:H7和单增李斯特菌的菌落总数。本实验室前期从东北酸菜中筛选分离出具有较强抑菌作用的副干酪乳杆菌Z21,经实验发现该菌株发酵上清液具有良好的抑菌效果。因此,本实验采用臭氧水联合Z21上清液方法对大肠杆菌O157:H7的杀菌效果及其杀菌机制进行研究,为臭氧水联合Z21上清液处理应用于清除大肠杆菌生物膜和农产品杀菌保鲜提供理论参考。
1. 材料和方法
1.1 材料与仪器
绿豆芽 长春市沃尔玛超市;副干酪乳杆菌Z21 从东北酸菜中分离得到;大肠杆菌O157:H7 CICC 21530 由吉林农业大学食品安全实验室保存;胰蛋白胨大豆肉汤(tryptic soy broth,TSB)、山梨醇麦康凯琼脂基础(sorbitol macconkay agar base,SMAC)、缓冲蛋白胨水(buffer peptone water,BPW)、营养琼脂培养基(nutrient agar,NA) 青岛海博生物技术有限公司;碘化丙啶(propidium iodide,PI) 上海生工生物工程股份有限公司;2.5%戊二醛水溶液 上海远慕生物科技有限公司;Bradford蛋白浓度测定试剂盒 长春鼎国生物科技有限公司;细菌基因组DNA提取试剂盒 天根生物科技有限公司;臭氧水 采用臭氧发生器制备;其余试剂均为国产分析纯。
UV-1800型紫外分光光度计 日本岛津公司;HX-4GM型拍打式均质器 上海沪析实业有限公司;SU8010型场发射电子显微镜 日本日立公司;ZCA-10臭氧发生器 广东中辰臭氧设备有限公司;DXR3显微共聚焦激光拉曼光谱仪 赛默飞科技有限公司;BD LSRFortessa TM Cell流式细胞仪 BD Biosciences公司;VERTEX 70型傅里叶变换红外光谱仪 德国Bruker公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 实验流程
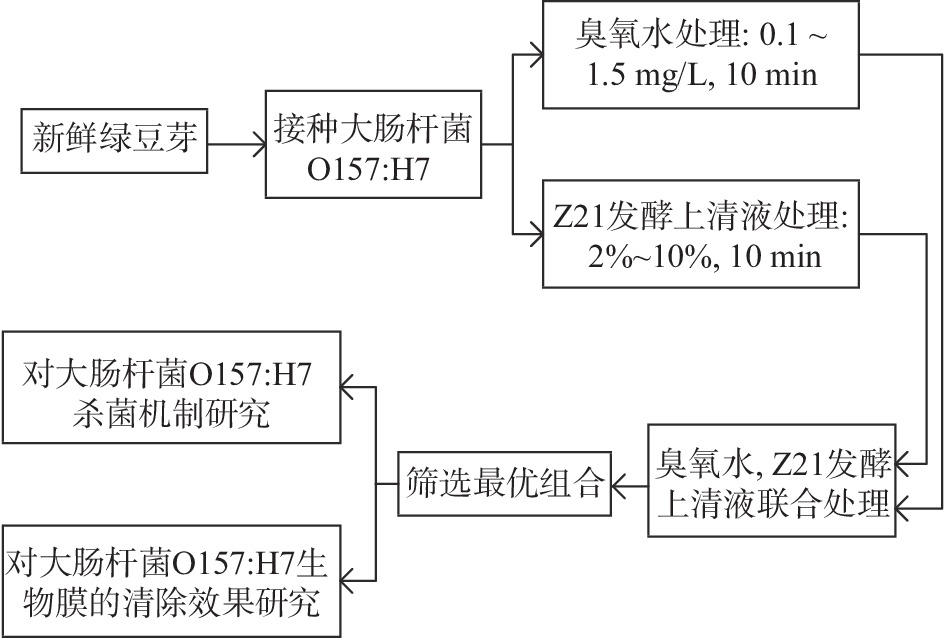
图1所示为臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液对绿豆芽中大肠杆菌O157:H7抑菌机制的实验流程图。
1.2.2 大肠杆菌O157:H7菌悬液及副干酪乳杆菌Z21发酵上清液的制备
大肠杆菌O157:H7接种于TSB培养基中,37 ℃培养24 h,4 ℃、8000 r/min离心10 min。将离心后的菌体用无菌去离子水清洗两次,调整菌悬液浓度至108 CFU/mL。将活化后的副干酪乳杆菌Z21菌体浓度约为108 CFU/mL以1%接种量接种于MRS培养基中,37 ℃培养48 h,4 ℃条件下,8000 r/min离心20 min。上清液经0.22 μm无菌滤膜过滤,用无菌蒸馏水稀释后置于4 ℃冰箱中保存备用。
1.2.3 臭氧水的制备
采用ZCA-10型臭氧发生器制备臭氧水,用碘量法[17]测定水中臭氧的浓度。制备浓度为0.1、0.5、1.0、1.5 mg/L的臭氧水。为避免臭氧挥发,现用现配。
1.2.4 样品处理
选择新鲜的绿豆芽作为实验材料。使用前在4 ℃冰箱储存。用200 mg/L次氯酸钠浸泡2 min,无菌蒸馏水清洗后晾干。将10 g经灭菌的样品浸入装有200 mL菌悬液的烧杯中,浸泡10 min,为了使大肠杆菌O157:H7粘附在样品表面,置于无菌条件下干燥30 min,绿豆芽中大肠杆菌O157:H7接种量为6~7 lg CFU/g。
1.2.5 臭氧水、Z21发酵上清液联合杀菌处理
不同浓度臭氧水处理:将接种后的样品分别浸泡在浓度为0.1、0.5、1.0、1.5 mg/L的臭氧水中处理10 min。不同体积分数的Z21发酵上清液处理:将接种后的样品分别浸泡在体积分数分别为2%、4%、6%、8%、10%的Z21发酵上清液中处理10 min。在前期预实验中发现,臭氧水浓度>1.5 mg/L、Z21发酵上清液体积分数>10%处理时绿豆芽会发生软化,因此,为了保持绿豆芽的品质,选择浓度范围在0.1~1.5 mg/L的臭氧水,体积分数为2%~10%的Z21发酵上清液进行后续联合处理实验。参考Koivunen等[18]的方法用于联合处理,比较了不同浓度臭氧水0.1、0.5、1.0、1.5 mg/L和副干酪乳杆菌Z21发酵上清液2%、4%、6%、8%、10%等 20种组合处理的协同杀菌效果。协同效应值计算公式[19]如下:
式中:A为臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液处理后菌落总数的减少量;B为臭氧水单独处理后菌落总数的减少量;C为Z21上清液单独处理后菌落总数的减少量。正值代表协同作用、负值代表拮抗作用。
1.2.6 大肠杆菌O157:H7菌落总数的测定
在无菌操作条件下,将处理后的10 g绿豆芽放入含有90 mL 0.1%无菌BPW均质袋中,置于均质器中均质3 min。将1 mL均质样品连续稀释在9 mL BPW中进行10倍梯度稀释,取1 mL样液接种于SMAC琼脂培养皿中,37 ℃培养箱中培养24 h后进行菌落计数。每个梯度重复3次[20]。
1.2.7 臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液对大肠杆菌O157:H7杀菌机制研究
1.2.7.1 大肠杆菌O157:H7细胞膜通透性的测定
将培养至对数生长期的大肠杆菌O157:H7用PBS清洗,重悬,调整菌悬液浓度为108 CFU/mL,首先用臭氧水处理5 min后加入终止液(0.85%氯化钠溶液与0.5%硫代硫酸钠),离心后用Z21发酵上清液处理5 min;以生理盐水作对照处理10 min。处理结束后,离心去上清收集菌体,清洗,重悬。参考Saravanan等[21]的方法,加入PI使其最终浓度均为50 μg/mL,37 ℃条件下避光染色30 min后,用流式细胞仪进行分析。
1.2.7.2 大肠杆菌O157:H7细胞结构的测定
参考王永刚等[22]的方法,按照1.2.7.1节中的方法进行处理,将处理后的菌体用PBS清洗,用体积分数为2.5%的戊二醛溶液固定,在4 ℃下过夜。依次用体积分数50%、70%、80%、90%、100%的乙醇进行脱水两次,每次10 min。用乙酸异戊酯将乙醇置换两次,室温干燥。取少量菌体与200 mg KBr混合,压片,使用傅里叶红外光谱检测仪进行检测分析,检测波数范围4000~500 cm−1,分辨率4 cm−1,扫描次数32次。红外光谱采用OMNIC软件进行分析。
1.2.7.3 拉曼光谱分析大肠杆菌O157:H7细胞结构
拉曼光谱采集激光波长为532 nm,激光强度为10 mW,每次测量的曝光时间为5 s。光谱范围为200~2000 cm−1。在批量检测中,激发光直接聚焦在细菌样品溶液上。每个样品测量三次。4 μL细菌样品溶液用于拉曼光谱检测。
1.2.7.4 大肠杆菌O157:H7微观形态的观察
参考Zhang等[23]的方法,按照1.2.7.2节中的方法对大肠杆菌O157:H7进行处理,冷冻干燥后通过扫描电子显微镜观察。
1.2.8 臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液对大肠杆菌O157:H7生物膜的清除效果研究
1.2.8.1 对生物膜中大肠杆菌O157:H7活菌数的测定
参考刘兰芝等[24]的方法,将盖玻片(2 cm×2 cm)用无水乙醇浸泡,超声清洗4 h,用蒸馏水清洗干净,121 ℃灭菌15 min。将无菌盖玻片加入无菌TSB培养基中并接入大肠杆菌O157:H7(108 CFU/mL),每天更换灭菌的TSB培养基,37 ℃连续培养5 d。样品处理分为A:对照组、B:蒸馏水处理组、C:臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液处理组,将3组盖玻片在含有10 mL PBS 的离心管中,低功率超声10 min分离生物膜。将得到的菌悬液进行10倍梯度稀释,涂布于NA琼脂培养基测定残存活菌数。每个测定重复三次取平均值。
1.2.8.2 对大肠杆菌O157:H7生物膜EPS的测定
参考张承慧[25]的方法,将3组盖玻片用PBS洗涤后将其置于含适量PBS的离心管中,低功率超声10 min分离生物膜,将得到的菌悬液4 ℃、12000 r/min 离心20 min。用0.22 μm滤膜过滤,滤液即为EPS样本。用苯酚-硫酸法测定胞外多糖含量[26],利用考马斯亮蓝法测定胞外蛋白含量[27]、使用细菌基因组DNA提取试剂盒提取EPS样本里的DNA,随后测定260 nm处的光密度值[28]。
1.3 数据处理
所有实验重复3次,结果以平均值±标准差标示。采用SPSS 23.0软件进行差异显著分析(P<0.05表示差异显著),制图采用Origin 2018软件。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 臭氧水、Z21发酵上清液对绿豆芽中大肠杆菌O157:H7的杀菌效果
如表1所示,不同浓度的臭氧水0.1、0.5、1、1.5 mg/L和不同体积分数的Z21发酵上清液2%、4%、6%、8%、10%对绿豆芽中大肠杆菌O157:H7具有杀菌作用。臭氧水和Z21发酵上清液单独处理10 min时,绿豆芽中大肠杆菌O157:H7的菌落总数减少量分别为0.22~0.97 lg CFU/g、0.19~0.86 lg CFU/g。结果表明,随着臭氧水浓度和Z21发酵上清液浓度体积分数的增加对大肠杆菌O157:H7杀菌效果显著提高(P<0.05);1.5 mg/L臭氧水和10% Z21发酵上清液联合处理时,绿豆芽中大肠杆菌O157:H7的数量减少了2.81 lg CFU/g,结果表明,臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液处理比单独处理显著降低了绿豆芽中的大肠杆菌O157:H7菌落总数(P<0.05)。
表 1 臭氧水、Z21发酵上清液及其联合处理后绿豆芽中大肠杆菌O157:H7的平均减少量Table 1. Reduction effect of ozone water, Z21 fermented supernatant and their combination on E. coli O157:H7 in mung bean sprouts臭氧水浓度(mg/L) 大肠杆菌平均减少量(lg CFU/g) Z21发酵上清液体积分数(%) 0 2 4 6 8 10 0 − 0.19±0.01d,E 0.24±0.03d,E 0.47±0.06c,E 0.65±0.03b,E 0.86±0.03a,E 0.1 0.22±0.03e,C 0.42±0.03d,D 0.49±0.03d,D 0.72±0.05c,D 0.89±0.04b,D 1.02±0.04a,D 0.5 0.27±0.05f,C 0.52±0.03e,C 0.72±0.03d,C 0.95±0.05c,C 1.15±0.05b,C 1.48±0.03a,C 1.0 0.77±0.01f,B 0.92±0.04e,B 1.38±0.04d,B 1.64±0.03c,B 1.86±0.03b,B 2.32±0.03a,B 1.5 0.97±0.02f,A 1.23±0.04e,A 1.78±0.03d,A 2.23±0.04c,A 2.45±0.03b,A 2.81±0.04a,A 注:同行不同小写字母表示差异显著;同列不同大写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);表2同。 联合处理中的协同效应值均为正数,臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液对绿豆芽中大肠杆菌有着协同杀菌作用,这可能是因为臭氧水在制得后0~10 min内,其浓度衰减速度较快[29],后期Z21发酵上清液杀菌效果强于臭氧水的杀菌效果。如表2所示,在所有的联合处理中,协同作用值最大为0.98 lg CFU/ g。1.5 mg/L臭氧水与10% Z21发酵上清液联合处理是降低绿豆芽中大肠杆菌O157:H7菌落总数的最优组合。所以选择1.5 mg/L臭氧水与10% Z21发酵上清液联合处理进行接下来杀菌机制的研究。
表 2 臭氧水、Z21发酵上清液及其联合处理后绿豆芽中大肠杆菌O157:H7协同效应Table 2. Synergistic effect of E. coli O157:H7 on mung bean sprouts treated with ozone water, Z21 fermented supernatant and their combined action臭氧水
浓度
(mg/L)协同和拮抗作用值(lg CFU/g) Z21发酵上清液体积分数(%) 2 4 6 8 10 0.1 0.01±0.03a,A 0.03±0.03a,D 0.03±0.05a,D 0.02±0.04a,D 0.07±0.04a,D 0.5 0.06±0.04c,A 0.21±0.05b,C 0.21±0.08b,C 0.23±0.05b,C 0.35±0.05a,C 1 0.02±0.03d,A 0.43±0.03c,B 0.46±0.03bc,B 0.50±0.01b,B 0.75±0.01a,B 1.5 0.07±0.03d,A 0.56±0.01c,A 0.79±0.06b,A 0.83±0.03b,A 0.98±0.04a,A 2.2 流式细胞仪分析臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液对大肠杆菌O157:H7细胞膜通透性的影响
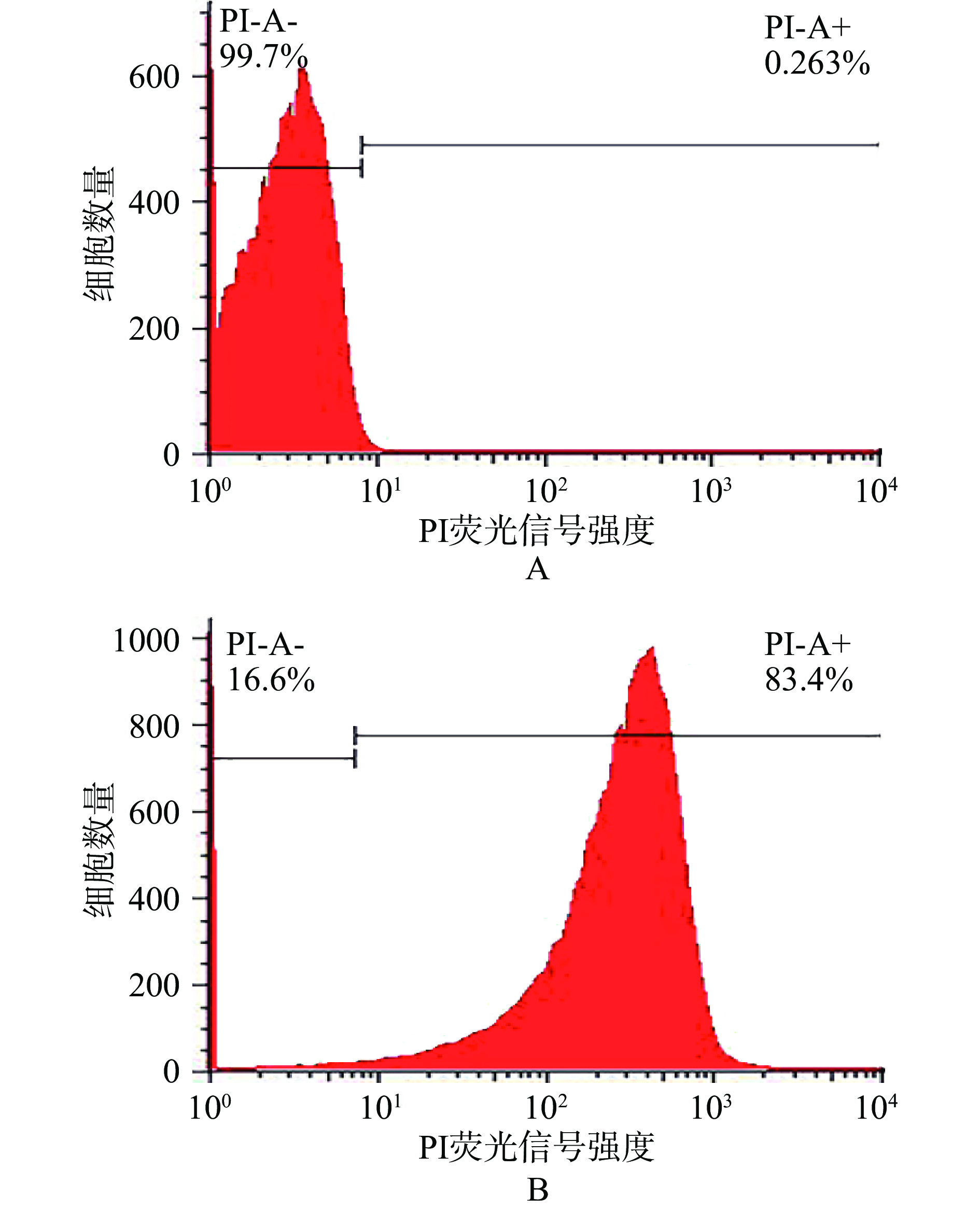
PI能穿透受损细胞的细胞膜与DNA非特异性结合发出红色荧光,利用PI荧光强度来评价细胞膜的通透性[30]。通过流式细胞计数法计算被PI所染的大肠杆菌O157:H7。如图2所示,在对照组中,被PI染色的阳性细胞为0.263%,说明对照组中大肠杆菌O157:H7细胞膜完整;经过臭氧水联合Z21上发酵清液处理后,被PI染色的细胞为83.4%,是对照组的320倍。结果表明,臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液处理破坏了大肠杆菌O157:H7细胞膜通透性。
![]() 图 2 臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液处理对大肠杆菌O157:H7细胞膜通透性的影响注:(A)对照组;(B)臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液处理;图5同。Figure 2. Effect of ozone water combined with Z21 fermented supernatant treatment on the cell membrane of E. coli O157:H7
图 2 臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液处理对大肠杆菌O157:H7细胞膜通透性的影响注:(A)对照组;(B)臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液处理;图5同。Figure 2. Effect of ozone water combined with Z21 fermented supernatant treatment on the cell membrane of E. coli O157:H72.3 FT-IR分析臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液对大肠杆菌O157:H7细胞结构的影响
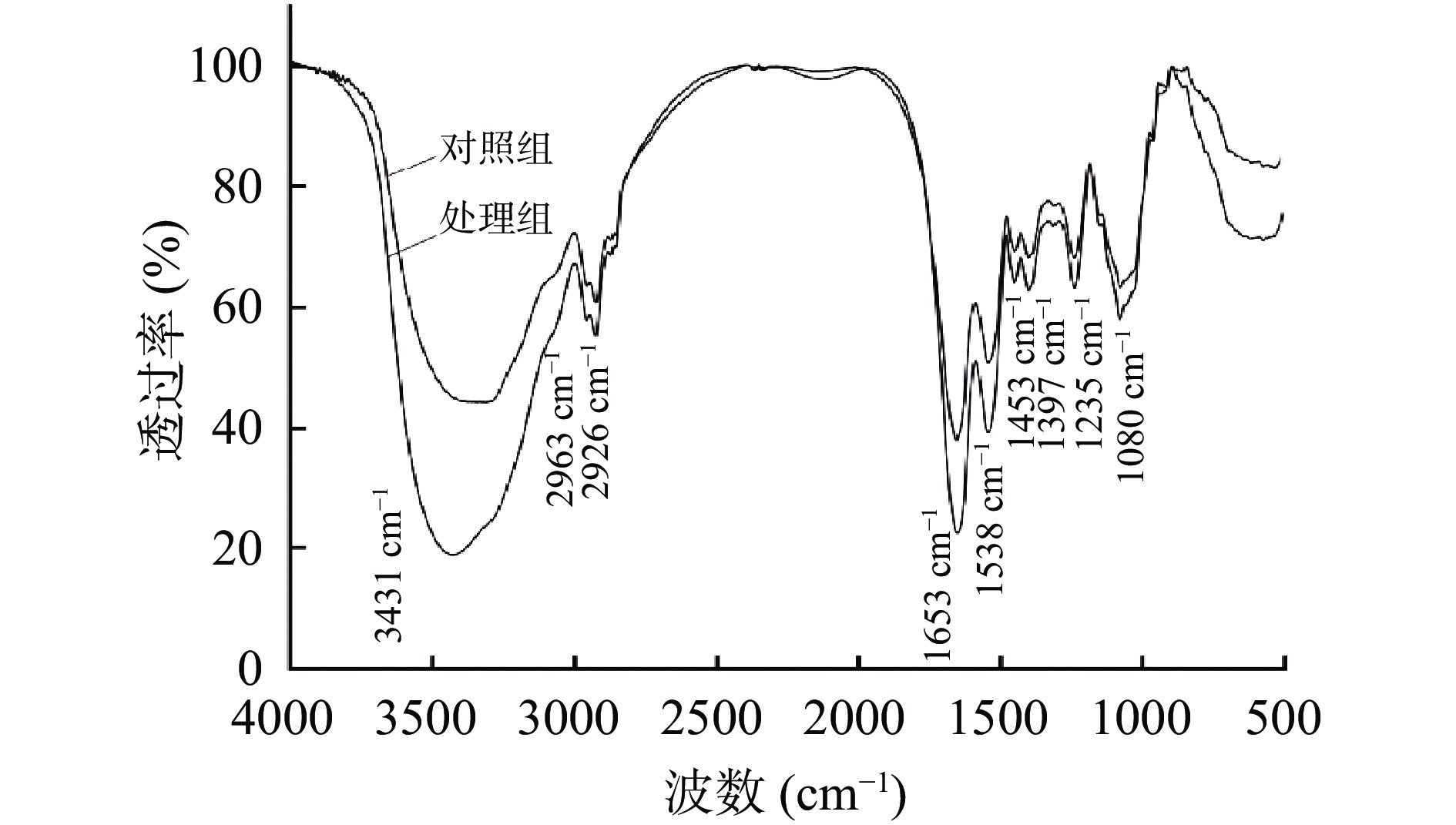
图3为大肠杆菌O157:H7 FT-IR光谱图,经过臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液处理后的大肠杆菌O157:H7细胞壁和细胞膜上大分子蛋白质和脂质的红外振动峰有明显的差异。光谱图中3431 cm−1处的吸收峰为-OH的伸缩振动引起。在3000~2800 cm−1之间的波数代表脂肪酸区域[31],2926、2963 cm−1为CH2和CH3的反对称伸缩振动吸收峰。在1653、1538、1453、1397 cm−1处与蛋白质、多肽、脂质类特征相对应[32],1653 cm−1处属于酰胺I带α螺旋,1538 cm−1处属于酰胺II带N-H键的弯曲峰。1453 cm−1附近的吸收带是由脂质、蛋白质分子中CH2的弯曲振动引起,1397 cm−1附近吸收带为氨基酸侧链或游离脂肪酸COO-中C=O对称伸缩振动所引起[32]。1235、1080 cm−1的吸收峰发生了明显的变化,这两处峰值变化与磷脂、核酸物质>PO-2中P=O双键的不对称拉伸振动有关[33-34]。这些结果进一步说明经过臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液处理后的大肠杆菌O157:H7细胞膜和细胞壁中的脂质与蛋白质结构,细胞核酸物质被破坏。
2.4 臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液处理前后大肠杆菌O157:H7拉曼光谱图
图4为臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液处理前后大肠杆菌O157:H7的拉曼光谱图,在560、802、1095、1520 cm−1处有明显的变化;560 cm−1处拉曼位移代表的多糖中C-O-C特征峰显著降低,同样的1095 cm−1处拉曼位移代表的多糖中C-C、C-O-C键伸缩振动特征峰也出现显著降低;560、1095 cm−1特征峰揭示了细胞壁和细胞膜中多糖结构的变化[35]。802 cm−1、1520 cm−1处拉曼位移分别代表的氨基酸中C-N键伸缩振动、酰胺Ⅱ中C-N键伸缩振动峰均出现显著降低,说明臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液处理破坏了菌体细胞壁和细胞膜中的蛋白质结构。
2.5 臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液对大肠杆菌O157:H7菌体形态的影响
通过扫描电镜观察臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液对大肠杆菌O157:H7菌体形态的影响,如图5所示,对照组大肠杆菌O157:H7细胞形态完好,细胞未被破坏(图5A)。与对照组相比,如图5B所示,经臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液处理后细胞形态结构发生变化,部分菌体表面出现褶皱、发生凹陷等变形现象,有些菌体细胞膜受到严重破坏,导致菌体破裂。结果表明臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液对大肠杆菌O157:H7细胞结构有破坏作用。
2.6 臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液对大肠杆菌O157:H7生物膜的清除效果研究
2.6.1 臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液对大肠杆菌O157:H7生物膜活菌数的影响
如图6所示,与对照组相比处理后的生物膜中的菌落数发生显著变化,对照组中大肠杆菌O157:H7活菌数为5.58 lg CFU/cm2,蒸馏水处理组大肠杆菌O157:H7活菌数量减少了0.47 lg CFU/cm2;臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液处理组大肠杆菌O157:H7活菌数量减少了2.19 lg CFU/cm2。林琳等[36]研究结果表明,生物膜中活菌数的变化与生物膜的清除效果有关,所以上述结果表明臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液处理组对大肠杆菌O157:H7生物膜具有良好的清除效果。
![]() 图 6 臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液对大肠杆菌O157:H7生物膜活菌数的影响注:图中小写字母不同表示差异显著(P<0.05);图7同。Figure 6. Effect of ozone water combined with Z21 fermented supernatant on E. coli O157:H7 biofilm elimination
图 6 臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液对大肠杆菌O157:H7生物膜活菌数的影响注:图中小写字母不同表示差异显著(P<0.05);图7同。Figure 6. Effect of ozone water combined with Z21 fermented supernatant on E. coli O157:H7 biofilm elimination2.6.2 臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液对大肠杆菌O157:H7生物膜EPS的影响
图7A为臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清对大肠杆菌O157:H7生物膜胞外蛋白和多糖含量的影响,对照组中大肠杆菌O157:H7生物膜胞外蛋白含量为38.75 μg/mL,胞外多糖含量为23.93 μg/mL。经处理后,大肠杆菌O157:H7的胞外多糖和蛋白含量显著降低(P<0.05)。臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液处理后的胞外多糖和胞外蛋白含量显著低于蒸馏水处理组(P<0.05)。图7B为臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清对大肠杆菌O157:H7生物膜胞外DNA的影响,经臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液处理后的胞外DNA显著低于蒸馏水处理组(P<0.05)。在生物膜形成过程中,细菌会产生EPS,可以保护细菌免受不利环境的影响,因此生物膜EPS的破坏不利于生物膜内细菌的生存。臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液处理降低了胞外多糖、蛋白、DNA的含量,破坏了大肠杆菌O157:H7生物膜的结构。
3. 结论
实验结果表明,1.5 mg/mL浓度的臭氧水联合10% Z21发酵上清液处理10 min可以有效降低绿豆芽中大肠杆菌O157:H7的菌落总数。通过流式分析技术发现臭氧水联合Z21上清液处理后PI染色细胞增加,说明臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液处理增加了大肠杆菌O157:H7细胞膜的通透性;结合傅里叶红外光谱和拉曼光谱分析充分证明臭氧水联合Z21上清液处理破坏了细胞壁和细胞膜结构,从而达到杀菌作用。臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液对大肠杆菌O157:H7生物膜具有良好清除效果,胞外聚合物中多糖、蛋白、DNA含量均显著减少(P<0.05)。因此,臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液处理对大肠杆菌生物膜的清除及农产品防腐保鲜提供了理论依据。
-
图 2 臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液处理对大肠杆菌O157:H7细胞膜通透性的影响
注:(A)对照组;(B)臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液处理;图5同。
Figure 2. Effect of ozone water combined with Z21 fermented supernatant treatment on the cell membrane of E. coli O157:H7
图 6 臭氧水联合Z21发酵上清液对大肠杆菌O157:H7生物膜活菌数的影响
注:图中小写字母不同表示差异显著(P<0.05);图7同。
Figure 6. Effect of ozone water combined with Z21 fermented supernatant on E. coli O157:H7 biofilm elimination
表 1 臭氧水、Z21发酵上清液及其联合处理后绿豆芽中大肠杆菌O157:H7的平均减少量
Table 1 Reduction effect of ozone water, Z21 fermented supernatant and their combination on E. coli O157:H7 in mung bean sprouts
臭氧水浓度(mg/L) 大肠杆菌平均减少量(lg CFU/g) Z21发酵上清液体积分数(%) 0 2 4 6 8 10 0 − 0.19±0.01d,E 0.24±0.03d,E 0.47±0.06c,E 0.65±0.03b,E 0.86±0.03a,E 0.1 0.22±0.03e,C 0.42±0.03d,D 0.49±0.03d,D 0.72±0.05c,D 0.89±0.04b,D 1.02±0.04a,D 0.5 0.27±0.05f,C 0.52±0.03e,C 0.72±0.03d,C 0.95±0.05c,C 1.15±0.05b,C 1.48±0.03a,C 1.0 0.77±0.01f,B 0.92±0.04e,B 1.38±0.04d,B 1.64±0.03c,B 1.86±0.03b,B 2.32±0.03a,B 1.5 0.97±0.02f,A 1.23±0.04e,A 1.78±0.03d,A 2.23±0.04c,A 2.45±0.03b,A 2.81±0.04a,A 注:同行不同小写字母表示差异显著;同列不同大写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);表2同。 表 2 臭氧水、Z21发酵上清液及其联合处理后绿豆芽中大肠杆菌O157:H7协同效应
Table 2 Synergistic effect of E. coli O157:H7 on mung bean sprouts treated with ozone water, Z21 fermented supernatant and their combined action
臭氧水
浓度
(mg/L)协同和拮抗作用值(lg CFU/g) Z21发酵上清液体积分数(%) 2 4 6 8 10 0.1 0.01±0.03a,A 0.03±0.03a,D 0.03±0.05a,D 0.02±0.04a,D 0.07±0.04a,D 0.5 0.06±0.04c,A 0.21±0.05b,C 0.21±0.08b,C 0.23±0.05b,C 0.35±0.05a,C 1 0.02±0.03d,A 0.43±0.03c,B 0.46±0.03bc,B 0.50±0.01b,B 0.75±0.01a,B 1.5 0.07±0.03d,A 0.56±0.01c,A 0.79±0.06b,A 0.83±0.03b,A 0.98±0.04a,A -
[1] BAENAS N, SUÁREZ-MARTÍNEZ C, GARCÍA-VIGUERA C, et al. Bioavailability and new biomarkers of cruciferous sprouts consumption[J]. Food Research International,2017,100(1):497−503.
[2] PHILIPPE V, TREMBLY YANNICK D N, GRÉGORY J, et al. Biofilm-forming abilities of shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli isolates associated with human infections[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2015,82(5):1448−1458.
[3] SREY S, KABIR J I, HA S D. Biofilm formation in food industries: A food safety concern[J]. Food Control,2013,31(2):572−585. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2012.12.001
[4] NAHAR S, HA A J, BYUN K H, et al. Efficacy of flavourzyme against Salmonella typhimurium, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2021,336:108897. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2020.108897
[5] UHLICH G A, COOKE P H, SOLOMON E B. Analyses of the red-dry-rough phenotype of an Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain and its role in biofilm formation and resistance to antibacterial agents[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2006,72(4):2564−2572. doi: 10.1128/AEM.72.4.2564-2572.2006
[6] KESHRI J, KROUPTISKI Y, ABUFANI L, et al. Dynamics of bacterial communities in alfalfa and mung bean sprout during refrigerated conditions[J]. Food Microbiology,2019,84:1.
[7] SHEN Z Y, MUSTAPHA A, LIN M, et al. Biocontrol of the internalization of Salmonella enterica and enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli in mung bean sprouts with an endophytic Bacillus subtilis[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2017,250:37−44. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2017.03.016
[8] 李翠莲, 黄中培, 方北曙. 臭氧杀菌消毒技术在食品工业中的应用[J]. 湖南农业科学,2008(4):119−121. [LI Cuilinan, HUANG Zhongpei, FANG Beishu. Application of ozone sterilization technology in food industry[J]. Hunan Agricultural Sciences,2008(4):119−121. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-060X.2008.04.046 [9] SINGLA R, GANGULI A, GHOSH M. An effective combined treatment using malic acid and ozone inhibits Shigella spp. on sprouts[J]. Food Control,2011,22(7):1032−1039. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2010.12.012
[10] TACHIKAWA M, YAMANAKA K. Synergistic disinfection and removal of biofilms by a sequential two-step treatment with ozone followed by hydrogen peroxide[J]. Water Research,2014,64:94−101. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.06.047
[11] MOHAMMAD Z, KALBASI-ASHTARI A, RISKOWSKI G, et al. Reduction of salmonella and shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli on alfalfa seeds and sprouts using an ozone generating system[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2018,289:57−63.
[12] DA COSTA W K A, DE SOUZA G T, BRANDÃO L R, et al. Exploiting antagonistic activity of fruit-derived Lactobacillus to control pathogenic bacteria in fresh cheese and chicken meat[J]. Food Research International,2018,108:172−182. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.03.045
[13] SOUZA E C, PAMELA OLIVEIRA DE SOUZA DE A, DOMÍNGUEZ J M, et al. Influence of temperature and pH on the production of biosurfactant, bacteriocin and lactic acid by Lactococcus lactis CECT-4434[J]. CyTA-Journal of Food,2017,15(4):525−530. doi: 10.1080/19476337.2017.1306806
[14] JU H, CHEN H, XIANG A, et al. Identification and characterization of Lactobacillus paracasei strain MRS-4 antibacterial activity against Alicyclobacillusa cidoterrestris[J]. LWT,2021,150:111991. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111991
[15] BAUMANN A R, MARTIN S E, FENG H, et al. Removal of Listeria monocytogenes biofilms from stainless steel by use of ultrasound and ozone[J]. Journal of Food Protection,2009,72, 6:1306−1309.
[16] YUKA H G, YOOC M Y, YOON J W, et al. Effect of combined ozone and organic acid treatment for control of Escherichia coli O157: H7 and Listeria monocytogenes on enoki mushroom[J]. Food Control,2007,18:548−553. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2006.01.004
[17] 刘慈坤. 臭氧介导的肌原纤维蛋白质氧化对草鱼鱼糜凝胶持水性的影响机制研究[D]. 锦州: 渤海大学, 2019 LIU Cikun. Effects of ozone induced myofibrillar protein oxidation on the water-holding capacity in grass carp surimi gel[J]. Jinzhou: Bohai University, 2019.
[18] KOIVUNEN J, HEINONEN-TANSKI H. Inactivation of enteric microorganisms with chemical disinfectants, UV irradiatio and combined chemical/UV treatments[J]. Water Research,2005,39(8):1519−1526. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2005.01.021
[19] PARK S Y, MIZAN M D F R, HA S D. Inactivation of Cronobacter sakazakii in head lettuce by using a combination of ultrasound and sodium hypochlorite[J]. Food Control,2016,60:582−587. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.08.041
[20] GULLIAN-KLANIAN M, SÁNCHEZ-SOLIS M J. Growth kinetics of Escherichia coli O157: H7 on the epicarp of fresh vegetables and fruits[J]. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology,2018,49(1):104−111. doi: 10.1016/j.bjm.2017.08.001
[21] SARAVANAN R, MOHANRAM H, JOSHI M, et al. Structure, activity and interactions of the cysteine deleted analog of tachyplesin-1 with lipopolysaccharide micelle: Mechanistic insights into outer-membrane permeabilization and endotoxin neutralization[J]. BBA-Biomembranes,2012,1818(7):1613−1624. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2012.03.015
[22] 王永刚, 杨光瑞, 陈凯, 等. 内生真菌链格孢菌醋酸乙酯提取物对金黄色葡萄球菌抑菌机制的研究[J]. 中草药,2018,49(3):619−625. [WANG Yonggang, YANG Guangrui, CHEN Kai, et al. Antibacterial mechanisms of ethyl acetate extract from endophytic fungi Alternaria alternata on Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Chinese Herbal Medicine,2018,49(3):619−625. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2018.03.017 [23] ZHANG Y B, LIU X Y, WANG Y F, et al. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of cinnamon essential oil against Escherihia coli and Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Food Control,2016,59:282−289. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.05.032
[24] 刘芝兰, 李宇, 刘颋, 等. 细菌生物膜培养及评估方法[J]. 中国消毒学杂志,2011,28(3):309−311. [LIU Zhilan, LI Yu, LIU Ting, et al. Rresearch the bacteria biofilm cultivation and evaluation methods[J]. Chinese Journal of Disinfection,2011,28(3):309−311. [25] 张承慧. 丁香精油对单核细胞增生李斯特菌及其生物膜的抑制研究[D]. 镇江: 江苏大学, 2020 ZHANG Chenghui. Inhibition of clove essential oil on Listeria monocytogeness and its biofilm[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University, 2020.
[26] 刘美慧. 没食子酸对金黄色葡萄球菌和福氏志贺菌生物膜形成的抑制作用及机理初探[D]. 西安: 陕西师范大学, 2017 LIU Meihui. Inhibition of gallic acid on biofilm formation of Staphylococcus aureus and Shigella flexneri and its mechanism[D]. Xi'an: Shaanxi Normal University, 2017.
[27] LOTT J A, STEPHAN V A, PRITCHARD K A. Evaluation of the coomassie brilliant blue G-250 method for urinary protein[J]. Clinical Chemistry,2019,29(11):1946−1950.
[28] 姜交龙, 张涛, 江波, 等. 杜仲内生真菌代谢产物对大肠杆菌的作用机理研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2012,33(23):110−113. [JIANG Jiaolong, ZHANG Tao, JIANG Bo, et al. Effects of the metabolites of an endophytic fungi from Eucommia ulmoides Oliv on E. coli[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2012,33(23):110−113. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2012.23.081 [29] 鲁建云, 李苗苗, 高丽华, 等. 臭氧水浓度衰减及其杀菌作用[J]. 中南大学学报(医学版),2018,43(2):143−146. [LU Jianyun, LI Miaomiao, GAO Lihua, et al. Attenuation rules and germicidal efficacy of ozoneted water[J]. Journal of Central South University (Medical Science),2018,43(2):143−146. [30] IMURA Y, NISHIDA M, OGAWA Y, et al. Action mechanism of tachyplesin I and effects of pegylation[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Biomembr,2007,1768(5):1160−1169. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.01.005
[31] 王永刚, 杨光瑞, 马雪青, 等. 内生真菌链格孢菌醋酸乙酯提取物对大肠杆菌抑菌机制的研究[J]. 中草药,2018,49(2):374−381. [WANG Yonggang, YANG Guangrui, MA Xueqing, et al. Antibacterial mechanisms of ethyl acetate extract from endophytic fungi Alternaria alternata on Escherichia coil[J]. Chinese herbal medicine,2018,49(2):374−381. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2018.02.017 [32] LU X N, LIU Q, WU D, et al. Using of infrared spectroscopy to study the survival and injury of Escherichia coli O157: H7, Campylobacter jejuni and Pseudomonas aeruginosa under cold stress in low nutrient media[J]. Food Microbiology,2010,28(3):537−546.
[33] NAUMANN D. FT-Infrared and FT-Raman spectroscopy in biomedical research[J]. Applied Spectroscopy Reviews,2001,36(2−3):239−298. doi: 10.1081/ASR-100106157
[34] AL-QADRIR H M, AL-ALAMI N I, Al-HOLY M A, et al. Using fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) absorbance spectroscopy and multivariate analysis to study the effect of chlorine-induced bacterial injury in water[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2008,56(19):8992−8997. doi: 10.1021/jf801604p
[35] BASHIR S, NAWAZ H, MAJEED M I, et al. Rapid and sensitive discrimination among carbapenem resistant and susceptible E. coli strains using surface enhanced raman spectroscopy combined with chemometric tools[J]. Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy,2021,34:102280. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2021.102280
[36] 林琳, 陈文庆, 方厚智, 等. 大气压冷等离子体处理对果蔬表面E. coli O157: H7生物膜的清除作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(21):293−298. [LIN Lin, CHEN Wengqing, FANG Houzhi, et al. Antibacterial activity of atmospheric cold plasma treatment against E. coli O157:H7 biofilms on fruits and vegetables[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(21):293−298. -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 史文锦,刘仁慧. 山药在糖尿病及其并发症治疗中的作用机制研究进展. 山东医药. 2025(01): 144-149 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:



