Quality Analysis and Evaluation of Nine Varieties of Dried Peppers
-
摘要: 为分析朝天椒、线椒和角椒3种类型干椒品质差异,对9个特色品种干辣椒(内黄新一代、花溪党武椒和丘北椒三份朝天椒,大方皱椒、沙湾线椒、陕西秦椒和甘谷线椒四份线椒,托县红辣椒和益都红辣椒两份角椒)结构特征值(籽和肉含量)和9项品质指标(粗纤维、糖、脂肪、蛋白质、水分、灰分、类胡萝卜素、辣椒碱类物质和挥发性物质)进行了检测,并通过主成分分析和聚类分析进行干辣椒综合品质评价。结果表明:籽、肉干基占比分别为21%~47%和52%~79%,主要成分为粗纤维、糖、脂肪和蛋白质,含量分别为35%~46%、11%~28%、13%~19%和14%~18%。还原糖占总糖77%~99%;含19~27种脂肪酸,不饱和脂肪酸占总脂肪酸80%以上,其中亚油酸为61%~73%;类胡萝卜素含量为73~458 mg/100 g,以辣椒红素为主(37~221 mg/100 g);辣椒碱类物质含量18~206 mg/100 g;共检出11类挥发性物质,总含量1.12~7.65 mg/100 g。主成分分析将9项品质指标简化为3个主成分,累计方差贡献率为85.29%,反映了干辣椒品质绝大部分信息。9个品种干辣椒可聚为2类,3个品种的朝天椒为一类、4个品种线椒和2个品种角椒为一类。综合结构特征值及其与品质指标相关性分析发现:籽含量高的朝天椒脂肪、粗纤维和挥发性物质含量高,粗纤维、脂肪含量与籽含量显著正相关(P<0.05);角椒和线椒果肉含量高,总糖含量高,且总糖与果肉含量显著正相关(P<0.05)。朝天椒是制粉和火锅底料等的优质原料,角椒适宜作制酱原料,线椒类胡萝卜素含量高,可作增色调味和色素提取等的原料,本研究结果可为9个品种干辣椒品质评价及加工辣椒品种选择提供理论参考。Abstract: To analyze the quality discrepancies of pod pepper, line pepper and horn pepper , the integrated structural characteristic values ( the seeds content and sarcocarp content), crude fiber, sugar, fat, protein, moisture, ash, carotenoids, capsaicins, and volatile compounds in nine dried pepper varieties were detected in this study, which test samples of pepper varieties included three pod peppers (Neihuang-xinyidai, Huaxi-dangwu pepper and Qiubei pepper), four line peppers (Dafang wrinkly pepper, Shawan line pepper, Shaanxi qin pepper and Gangu line pepper) and two horn peppers (Tuoxian red pepper and Yidu red pepper), respectively. Principal component analysis and cluster analysis were carried out to evaluate the comprehensive quality of dried peppers. The results indicated that the seeds and sarcocarp in whole dried pepper constituted 21%~47% and 52%~79%, respectively. The crude fiber, sugar, fat and protein were 35%~46%, 11%~28%, 13%~19% and 14%~18%, respectively. The reducing sugar was made up 77%~99%. Unsaturated fatty acids represented over 80% among total fatty acids, linoleic acid accounted for 61%~73%. Capsanthin (37~221 mg/100 g) was the dominant in total carotenoids (73~458 mg/100 g), and the contents of capsaicins vary 18~206 mg/100 g. Eleven types of volatile compounds were detected in test samples, and total volatile constituents content was 1.12~7.65 mg/100 g. For principal component analysis, three principal components were extracted, and their cumulative variance contribution rate was up to 85.29%, which reflected mostly the quality characteristics of dried peppers. Nine dried pepper varieties samples were divided into two classes by cluster analysis, the first class includes three pod pepper varieties, the second class inludes six samples of line peppers and horn peppers. The analysis of the integrated structural characteristic values and their correlations with quality indicators revealed that seeds in pod pepper samples were higher, which contained higher fat, crude fiber, and more abundant volatile compounds, the sarcocarp in the samples of line peppers or horn peppers were higher, which contained higher sugar and carotenoids. Meanwhile, the contents of crude fiber and fat were significant positively correlated with seeds content (P<0.05), and the significant positive correlation existed between total sugar content and sarcocarp content (P<0.05). Pod peppers were superior quality raw material for powder or hotpot seasoning etc, and horn peppers were suitable for making sauce. The carotenoid content of line peppers were abundant in carotenoids, which could be used for fried peppers sauce or capsorubin extraction etc. The aim of this research would provide a basic for quality evaluation of dried peppers.
-
辣椒(Capsicum annuum L.)原产于南美洲,属茄科,结构上主要包括果肉、胎座和种子[1]。果实中含蛋白质、脂肪、糖类、膳食纤维、维生素C、矿物质等多种营养素,也是类胡萝卜素等生物活性化合物和潜在药用化合物辣椒碱的来源[2-4]。因其生存适应性强,在我国广泛种植。目前,我国辣椒年播种量约占全国蔬菜总播种面积的10%,产量超6000万t,产值超700亿,播种面积、产量和产值均居世界首位[5]。
国内生产的辣椒主要通过干制、发酵等方式加工成干辣椒、发酵辣椒和剁椒等产品[6]。干辣椒耐贮藏、有香辣特性,是消费者喜食的调味品,部分品种因含丰富的色素和辣椒碱类物质,是提取辣椒红和辣椒碱,开发食品添加剂、药品等的原料。加工原料品种的选取影响产品品质,而我国辣椒种植区域广,栽培品种多[5],现有品种虽多可制成干辣椒,但辣椒品种差别导致的干辣椒品质差异给不同加工用干辣椒的选取增加了难度。如何辅助选取适宜加工目标的干椒原料是当前面临的重要问题。但要高效筛选优质原料首先需要对干辣椒的品质差异进行系统分析,目前关于干辣椒品质分析评价的研究报道较少。张祥等[7]研究了6个品种干辣椒营养品质差异,筛选了优良品种;高佳等[8]对16个品种朝天椒干制加工适宜性进行了评价;蓬桂华等[9]测定分析25个品种干辣椒的色泽、香气与滋味,初步建立了辣椒粉感官电子评价体系,对辣椒粉品质进行了评价分级;巩雪峰等[10]对四川省109份辣椒果实品质进行检测分析,并利用隶属函数值分析法对品质指标的平均隶属值进行排序,为辣椒品质综合排序提供了依据;Samia等[11]、马燕等[12]对辣椒籽品质指标进行了分析评价。这些研究多是单以干辣椒或辣椒籽的营养成分或风味分析为研究内容,而干辣椒的品质受籽肉含量、营养成分、类胡萝卜素、辣度和挥发性物质等影响,当前关于干辣椒籽肉含量,糖、脂肪酸、类胡萝卜素和辣椒碱类组成成分综合评价的报道较少。因此,对干辣椒品质进行更全面、系统的评价,这将为不同产地干辣椒品质评定及合理加工提供参考。
本研究对我国辣椒主产地常见的9个品种干辣椒(内黄新一代、花溪党武椒和丘北椒3三个品种朝天椒,大方皱椒、沙湾线椒、陕西秦椒和甘谷线椒4个品种线椒,托县红辣椒和益都红2个品种角椒)籽和肉含量、粗纤维、糖、脂肪、蛋白质、水分、灰分、类胡萝卜素、辣椒碱类物质和挥发性物质进行对比分析,并采用主成分分析和聚类分析对干辣椒综合品质进行评价,为干辣椒的品质评价提供理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
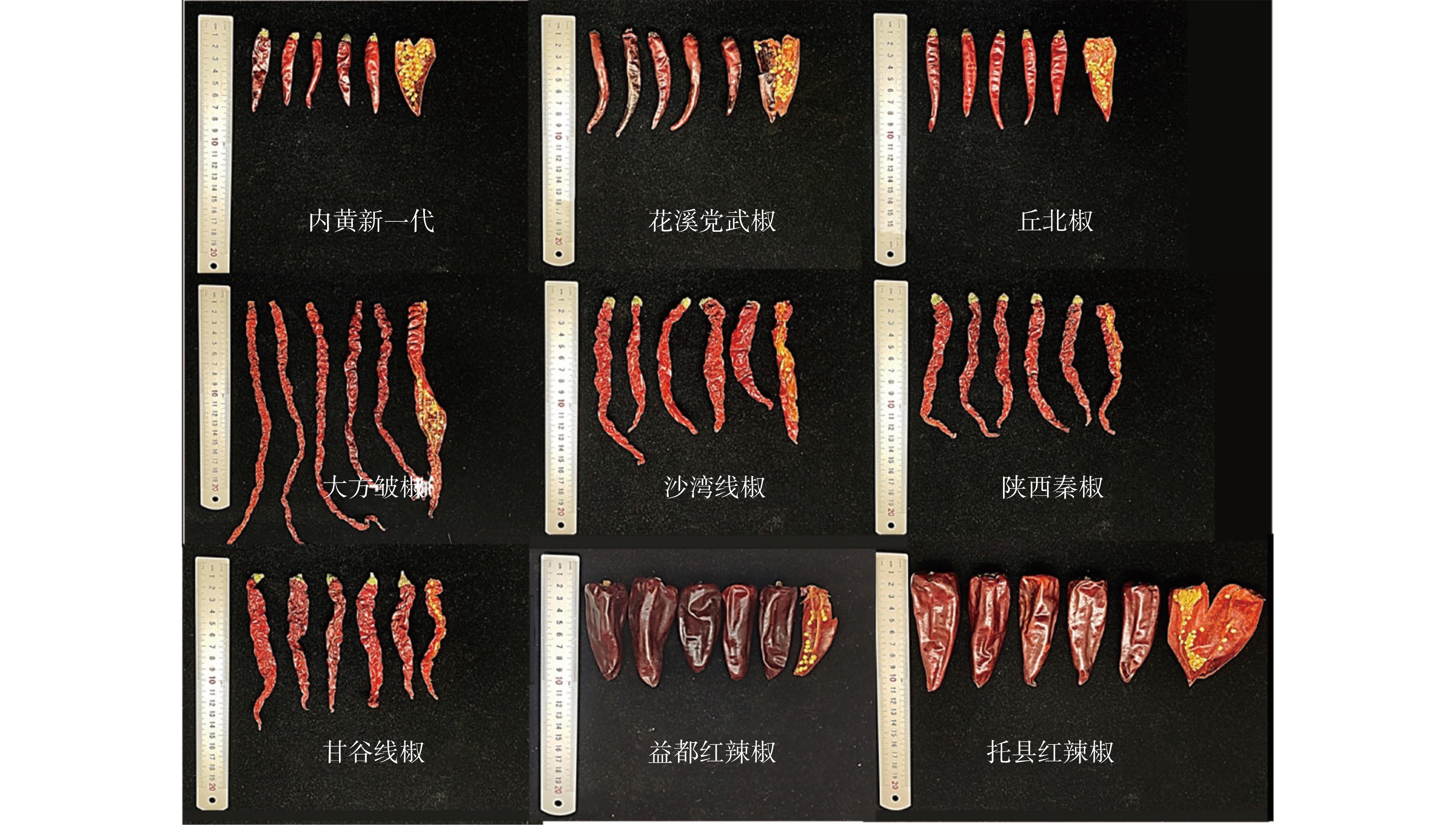
9个品种干辣椒(表1和图1) 购于全国8个省或自治区干辣椒生产基地。干辣椒生产于2020年,购回后去除梗蒂置于恒温干燥箱中45±1℃烘至恒重后粉碎,过40目筛后装入200 mL PE瓶中,贮存于4±1 ℃冷库内备用两个月;甲醇、丙酮、四氢呋喃、乙腈 色谱级,美国赛默飞世尔科技公司;正庚烷 色谱级,麦克林生化科技有限公司;果糖、葡萄糖、蔗糖、麦芽糖、辣椒碱、二氢辣椒碱、降二氢辣椒碱、玉米黄质、叶黄素、β-隐黄质、β-胡萝卜素、37种脂肪酸甲酯混合标准品 源叶生物科技有限公司;辣椒红素、2-甲基-3-庚酮 色谱级,Sigma-Aldrich贸易公司;其余试剂 均为国产分析纯试剂。
表 1 9个品种干辣椒样品基本信息Table 1. Basic information of nine varieties of dried peppers样品名称 果实
类型产地 果实特征 感官特点 内黄新一代
朝天椒河南内黄 短指形、个小红亮 籽多、香辣 花溪党武椒 贵州贵阳 长指形、暗红 肉质肥厚、油多、辣而不烈 丘北椒 云南文山 长指形、光滑油亮 香辣、味道醇正 大方皱椒
线 椒贵州毕节 皱细暗红 辣度适中、香味浓厚 沙湾线椒 新疆沙湾 粗长红亮 肉厚籽少、味香微辣 陕西秦椒 陕西宝鸡 细长红亮 肉厚、辣度较强烈、香醇适口 甘谷线椒 甘肃甘谷 粗长暗红 肉厚、香味浓郁 托县红辣椒 角椒 内蒙托县 短粗牛角形、暗红 肉厚、香而不辣 益都红辣椒 山东益都 短粗牛角形、暗红 肉厚、不辣 7890A/5975C SPME-GC-MS 美国安捷伦科技有限公司;GC-2010Plus气相色谱仪 日本岛津有限公司;e2695高效液相色谱仪 美国Waters公司;CR21GIII台式高速离心机 株式会社日立高新技术;BUCHI R100旋转蒸发仪 瑞士步琦有限公司;KN-6200自动凯氏定氮仪 阿尔瓦仪器有限公司;DHG-9053A电热恒温鼓风干燥箱 上海精宏试验设备有限公司;KQ-500DE数控超声清洗仪 昆山市超声仪器有限公司;XL-600B多功能粉碎机 永康市小宝电器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 干辣椒结构特征值测定
将30根去除梗蒂干辣椒籽肉分离(胎座计入果肉)后于105 ℃烘至恒重,分别称量籽和肉质量并计算籽和肉含量,重复三次。结果以恒重籽、肉分别占二者恒重总和百分比表示。
1.2.2 主要成分测定
含水率测定:参考GB 5009.3-2016《食品中水分的测定》的方法[13];灰分含量测定:参考GB 5009.4-2016《食品中灰分的测定》的方法[14];蛋白质含量测定:参考GB 5009.5-2016《食品中蛋白质的测定》的方法(第一法)[15];脂肪含量测定:参考GB 5009.6-2016《食品中脂肪的测定》的方法(第二法)[16];粗纤维含量测定:参考GB/T 5009.10-2003《食品中粗纤维的测定》的方法[17]。
总糖含量测定:参考GB/T 5009.8-2016《食品中果糖、葡萄糖、蔗糖、麦芽糖、乳糖的测定》的方法[18]并略作修改。称取辣椒粉10.0 g于离心管,加入50 mL石油醚混匀,放气,振摇2 min,1800 r/min离心15 min弃醚层,重复这一步骤除去大部分脂肪。蒸干残留石油醚,用玻璃棒捣碎样品并转移至100 mL容量瓶,冲洗离心管,洗液并入容量瓶中,加1 mol/L乙酸锌和0.3 mol/L亚铁氰化钾溶液各5 mL,加水定容至刻度,常温超声40 min后离心取上清液过滤膜进行色谱分析。流动相:80%乙腈+0.1%氨水等度洗脱,进样量20 µL,流速0.5 mL/min,氨基柱,柱温40 ℃,RI检测器,检测波长254 nm。分别绘制果糖、葡萄糖、蔗糖和麦芽糖标准曲线:y=116219x−55640,R2=0.9930;y=106025x−60154,R2=0.9945;y=131062x−31954,R2=0.9985;y=199010x−108450,R2=0.9912。总糖以还原糖和蔗糖总含量计。
1.2.3 类胡萝卜素含量测定
称取辣椒粉0.3 g于离心管中,加入丙酮和乙醚各20 mL,40 ℃超声处理20 min,频率50 kHz,将离心管中试剂转入玻璃瓶。重复至试剂不变色。随后向玻璃瓶中加入20% KOH-甲醇溶液50 mL摇匀,室温避光皂化2 h。皂化液转入分液漏斗,加超纯水洗涤至中性,收集萃取液并于35 ℃旋转蒸发至干。移取5 mL色谱丙酮溶解色素后过0.22 µm滤膜进行色谱分析。色谱柱:C18柱(4.6 mm×250 mm,5 µm),流动相:A丙酮,B超纯水,梯度洗脱,洗脱条件:0~5 min,A相保持75%;5~10 min,A相由75%上升到95%;10~17 min,A相保持95%;17~22 min,A相从95%上升到100%;22~27 min,A相从100%下降到75%,进样量10 µL,流速1.0 mL/min,柱温30 ℃,PDA检测器,检测波长450 nm。分别绘制辣椒红素、玉米黄质、叶黄素、β-隐黄质、β-胡萝卜素标准曲线:y=71229x−41906,R2=0.9990;y=71781x−104780,R2=0.9987;y=103420x−98921,R2=0.9991;y=87888x−12838,R2=0.9990;y=54663x−69760,R2=0.9914。
1.2.4 辣椒碱类物质含量测定
参考GB/T 21266-2007《辣椒及辣椒制品中辣椒碱类物质测定及辣度表示方法》的方法[19]。称取辣椒粉3.0 g于离心管中,加入25 mL四氢呋喃-甲醇溶液(1:1,V:V),60 ℃超声30 min后5000 r/min离心5 min,收集上清夜,重复上述步骤至试剂不变色。旋转浓缩并用四氢呋喃-甲醇溶液定容至50 mL容量瓶,过0.45 µm滤膜进行色谱分析,色谱柱:C18柱(4.6 mm×250 mm,5 µm),流动相A甲醇:B超纯水(65:35,V:V)等度洗脱,进样量10 µL,流速1 mL/min,柱温30 ℃,PDA检测器,检测波长280 nm,分别绘制辣椒碱、二氢辣椒碱和降二氢辣椒碱标准曲线:y=14808x−14219,R2=0.9963;y=8305.6x−4567.7,R2=0.9903;y=7575.1x−22843,R2=0.9991。斯科维尔指数(SHU)根据(1)式计算,辣度与SHU换算关系为150 SHU = 1度。
(1) 式中:W表示辣椒碱类物质总量得折算系数;16.1×103表示辣椒碱或二氢辣椒碱转换为SHU的系数,每1 g/kg相当于16.1×103 SHU;0.1表示其余辣椒碱类物质含量的折算系数;9.3×103表示其余辣椒碱类物质转化为SHU的系数,其余辣椒素类物质1 g/kg相当于9.3×103 SHU。
1.2.5 脂肪酸相对含量测定
参考马燕等[12]的方法并略作修改。称取1.0 g辣椒粉试样采用酸水解法进行脂肪提取,在脂肪提取物中加入8 mL 2%氢氧化钠-甲醇溶液,在90 ℃水浴上回流10 min至油滴消失;加入15%三氟化硼-甲醇溶液7 mL,在90 ℃水浴中冷凝回流10 min,用少量蒸馏水冲洗回流冷凝器;加入正庚烷15 mL,振摇2 min后加饱和氯化钠溶液静置分层,吸取上层正庚烷提取溶液3 mL,再加入约2 g无水硫酸钠,振摇1 min后静置5 min。将上层溶液移至上机瓶中。测定响应值,根据标准溶液谱图对应的响应值进行换算得到辣椒中脂肪酸含量。
气相色谱条件:SH-Stabilwax-DA毛细管柱(30 m×0.32 mm,0.50 μm);检测器:氢火焰离子检测器;进样量1.0 µL;载气:N2,纯度大于99.999%;载气流量3.0 mL/min;升温程序:100 ℃保持13 min,10 ℃/min升温至180 ℃,保持8 min,再以1 ℃/min升至200 ℃,保持20 min,后以3 ℃/min升至230 ℃,保持11.5 min。进样口温度260 ℃;进样方式为分流进样,分流比10:1。
1.2.6 挥发性物质测定
参考Jia等[20]的方法并作修改。称取1.0 g样品置于15 mL萃取瓶中,加入7 mL饱和NaCl溶液,加入40 µL稀释105倍的2-甲基-3庚酮内标物后旋紧瓶盖;置于磁力搅拌器上恒温水浴60 ℃、300 r/min预平衡30 min;取出放入样品盘中由自动进样器将萃取瓶载入平衡槽,60 ℃平衡20 min后震荡萃取40 min,入GC解吸5 min。
GC-MS条件:色谱柱为DB-5MS毛细管柱(30 m×0.25 mm,0.25 μm);载气:He,纯度大于99.999%;载气流速为1 mL/min;进样口温度250 ℃,不分流进样;采用全扫描模式采集信号,扫描范围(m/z)50 ~ 550,电离方式EI,电子轰击能量为70 eV,离子源温度为230 ℃,四级杆温度为150 ℃。升温程序:色谱柱初温40 ℃,保持5 min后以4 ℃/min的速度升温至150 ℃,保持3 min,再以3 ℃/min的速度升温至180 ℃,保持2 min,最后以8 ℃/min的速度升温至250 ℃,保持3 min。测定结果通过NIST2011普库检索,并用内标法计算各化学成分相对含量。
1.3 数据处理
采用Excel建立数据库。采用SPSS 25.0软件对数据进行单因素方差分析、聚类分析、主成分因子分析。采用Origin 2021Pro b软件进行图表绘制。方差分析采用Duncan’s新复极差法进行差异显著性检验(P<0.05)。
2. 结果分析
2.1 结构特征值分析
如表2所示,辣椒籽占整椒21%~47%,其中7个品种干辣椒的籽含量低于Zang等[21]报道的45%~50%。不同椒型样品的籽含量间存在差异,朝天椒籽含量显著高于线椒和角椒(P<0.05),内黄新一代籽含量最高,超过47%,陕西秦椒只有21.51%。果肉占整椒干基含量的52%~79%,高于Gu等[22]等报道的45%~50%。不同椒型及样品果肉占比存在不同程度差异。线椒和角椒果肉含量显著高于朝天椒(P<0.05),其中甘谷线椒果肉超过78%。由于辣椒籽中含有丰富的油脂,高温加工可为产品带来浓郁香味[21],高籽含量品种可作为制粉、辣椒油和火锅底料原料。而果肉厚的品种常具有很好的复水性,可作为辣椒酱、发酵酱、辣椒丝的原料。
表 2 9个品种干辣椒样品结构特征值Table 2. Integrated structural characteristic values of nine varieties of dried peppers品种 样品名称 结构特征值(DW%) 籽含量 肉含量 朝天椒 内黄新一代 47.02±1.22a 52.98±1.22f 花溪党武椒 46.29±1.33a 53.71±1.33f 丘北椒 36.65±1.09b 63.35±1.09e 线 椒 大方皱椒 32.94±1.46c 67.06±1.46d 沙湾线椒 28.18±1.56d 71.82±1.56c 陕西秦椒 21.52±1.02f 74.87±1.02b 甘谷线椒 25.13±1.20e 78.49±1.20a 角 椒 托县红辣椒 27.09±0.86de 72.91±0.86bc 益都红辣椒 29.68±2.98d 70.32±2.98c 注:同列不同字母代表不同样品间差异显著(P<0.05);表3~表6同。 2.2 品质指标分析
含水率是评价干制食品的重要指标,如表3所示,经前处理过的干辣椒含水率为7%~10%,均小于14%,符合NY/T 3610-2020《干红辣椒质量分级标准》规定,这利于干辣椒贮藏过程品质保持,减少霉变等的发生率。干辣椒中粗纤维干基占比最高,达到35%~46%。朝天椒粗纤维含量高,3份样品均超过40%;线椒和角椒粗纤维含量较低,托县红辣椒含量最低。干辣椒样品粗脂肪含量为12%~19%,与付文婷等[23]测定的10个品种的12%~20%相近。脂肪主要存在于辣椒籽[2],籽含量高的样品其脂肪含量也较高。三个品种中朝天椒脂肪含量最高,样品间脂肪含量存在差异(表3),其中花溪党武椒脂肪含量最高、甘谷线椒脂肪含量最低。干辣椒中蛋白质含量为14%~18%,甘谷线椒含量最高、内黄新一代含量最低,其余7个品种蛋白质含量基本相同。干辣椒中脂肪和蛋白质较为丰富,可为高脂肪、高蛋白质辣椒加工原料的筛选指标。辣椒中灰分主要是矿物质等微量元素[12],干辣椒中灰分干基含量6%~7%之间,不同样品干辣椒灰分含量间存在差异,除益都红外,北方样品灰分含量显著高于南方样品(P<0.05)。
表 3 9个品种干辣椒中的营养物质含量Table 3. Main components of nine varieties of dried peppers样品名称 含水率(%) 粗蛋白(%DW) 总糖(%DW) 粗脂肪(%DW) 粗纤维(%DW) 灰分(%DW) 内黄新一代 8.26±0.05b 14.75±0.05d 11.19±0.09f 17.81±0.16b 45.83±0.10a 6.75±0.05c 花溪党武椒 7.50±0.04d 15.92±0.04bc 18.80±0.10d 19.14±0.32a 43.38±0.10b 5.73±0.08d 丘北椒 8.16±0.00bc 16.23±0.00b 14.74±0.05e 16.42±0.23c 45.39±0.02a 5.17±0.22e 大方皱椒 8.15±0.05bc 16.39±0.05b 27.58±0.00a 14.55±0.58d 37.13±0.19f 5.80±0.08d 沙湾线椒 7.95±0.08c 15.38±0.09cd 24.26±0.72b 14.66±0.15d 41.73±0.53c 7.45±0.07a 陕西秦椒 8.15±0.03bc 16.39±0.03b 21.36±0.02c 14.98±0.14d 38.73±1.10e 7.41±0.01ab 甘谷线椒 9.47±0.03a 17.77±0.03a 24.11±0.06b 12.08±0.19e 40.62±0.02d 6.99±0.04abc 托县红辣椒 7.18±0.03e 16.38±0.03b 24.91±0.04b 14.23±0.40d 35.64±0.56g 6.96±0.05bc 益都红辣椒 9.88±0.02a 15.42±0.89cd 25.13±0.21b 13.36±0.07e 40.21±1.18d 5.96±0.12d 注:除含水率外,检测值以干基含量表示。 干辣椒中糖组成及含量如表4。干辣椒总糖为11%~28%,线椒和角椒总糖显著高于朝天椒,除大方皱椒和陕西秦椒外,线椒和角椒样品间总糖含量无显著差异(P>0.05),三个朝天椒品种总糖含量最低,均低于高佳等[8]报导的16种干辣椒(20%~37%)。干辣椒中糖以果糖为主、葡萄糖次之并含少量麦芽糖,还原糖含量占70%以上,其中陕西秦椒还原糖最高,达到99%。辣椒中丰富的还原糖既有利于改善辣椒产品的口感风味,也有利于微生物发酵[24],这为干辣椒发酵酱用原料的筛选提供了理论依据。因此,线椒和角椒是发酵酱用优质干椒原料。干辣椒中检出的非还原糖为蔗糖,干基含量均在5%以内,但样品间含量差异显著(P<0.05)。南方品种花溪党武椒、丘北椒和大方皱椒蔗糖含量均高于六个北方品种。推测蔗糖含量差异受到南北气候差异影响。
表 4 9个品种干辣椒糖组成及含量(%DW)Table 4. Sugar compositions and contents of nine varieties of dried peppers (%DW)样品名称 还原糖 还原糖
相对含量非还原糖 非还原糖
相对含量果糖 葡萄糖 麦芽糖 蔗糖 内黄新一代 6.67±0.36g 2.47±0.09e 0.64±0.04bc 87.44±1.46f 1.41±0.13e 12.56±1.16c 花溪党武椒 12.27±1.05e 3.62±0.21d 0.66±0.02b 88.04±1.55e 2.25±0.03c 11.96±0.25d 丘北椒 8.20±0.47f 1.71±0.15f 0.61±0.08bcd 71.34±1.55h 4.22±0.23a 28.66±1.55a 大方皱椒 12.84±0.94d 10.04±0.99a 0.93±0.01a 86.33±0.79g 3.78±0.36b 13.67±1.30b 沙湾线椒 17.02±0.26a 5.11±0.21c 0.46±0.02d 93.11±0.60c 1.67±0.10d 6.89±0.40f 陕西秦椒 14.38±0.23c 5.32±0.15c 0.68±0.07b 99.54±0.66a 0.98±0.09f 0.46±0.04i 甘谷线椒 16.25±0.39b 6.40±0.28b 0.50±0.03cd 95.97±0.64b 0.97±0.03f 4.03±0.14g 托县红辣椒 16.16±1.28b 6.40±0.05b 0.55±0.04bcd 92.78±0.78d 1.80±0.10d 7.22±0.39e 益都红辣椒 18.05±0.79a 5.98±0.31bc 0.52±0.05d 97.69±0.82b 0.58±0.06g 2.31±0.07h 注:相对含量表示占总糖%比例。 2.3 类胡萝卜素含量分析
类胡萝卜素是红辣椒的主要呈色物质, 其组分与含量变化受基因型、生长环境等因素影响[25]。如表5所示,干辣椒中主要类胡萝卜素总含量为73~458 mg/100 g,其中辣椒红素含量37~221 mg/100 g,样品间总类胡萝卜素含量差异显著(P<0.05)。沙湾线椒、内黄新一代、甘谷线椒、大方皱椒四个品种的类胡萝卜素总量达到300 mg/100 g,辣椒红素超过150 mg/100 g。此外这四个品种叶黄素含量显著高于其它样品(P<0.05),含量46~62 mg/100 g之间,类胡萝卜素不仅有利于改善辣椒的色泽和抗氧化能力,而且辣椒红素是筛选色素用辣椒的关键指标,叶黄素也是优良的食品着色剂。因此,沙湾线椒、内黄新一代、甘谷线椒、大方皱椒可用作色素椒。干辣椒中玉米黄质含量10~135 mg/100 g,内黄新一代、沙湾线椒玉米黄质含量显著高于其它样品(P<0.05)。玉米黄质占人体血清类胡萝卜素总量的3%,与叶黄素同被证实具有保护人的眼睛、胰腺、肝脏等器官的功效[26],因此干辣椒可作为膳食补充血清类胡萝卜素的经济资源。内黄新一代、大方皱椒和陕西秦椒中β-类胡萝卜素和β-隐黄质含量显著高于其它品种(P<0.05),两个角椒样品含量次之。β-类胡萝卜素是维生素A合成前体,β-类胡萝卜素含量高的内黄新一代、大方皱椒和陕西秦椒是补充人体维生素A的推荐干辣椒样品。
表 5 9个品种干辣椒类胡萝卜素含量(mg/100 g DW)Table 5. Carotenoids content of nine varieties of dried peppers (mg/100 g DW)品种编号 辣椒红素 玉米黄质 叶黄素 β-隐黄质 β-类胡萝卜素 总含量 内黄新一代 159.05±3.59c 135.16±0.51a 45.62±1.00c 30.12±1.90a 63.54±2.56a 433.49±9.56b 花溪党武椒 37.95±1.56g 9.54±0.18g 15.19±0.27f 4.71±0.13f 5.94±0.28f 73.32±2.42h 丘北椒 63.89±1.69f 26.46±1.42f 29.07±0.46d 13.85±0.83d 18.00±0.26d 151.27±4.65g 大方皱椒 201.44±5.98b 28.44±0.65f 61.79±1.92a 10.96±0.68e 14.80±1.47d 317.42±10.69d 沙湾线椒 198.54±8.15b 127.05±4.10b 55.42±2.30b 23.82±1.08b 53.35±2.57b 458.19±18.20a 陕西秦椒 79.43±4.53e 41.65±1.16e 25.07±0.30de 13.52±0.34d 12.92±0.42e 172.61±6.76f 甘谷线椒 220.57±7.51a 63.46±2.71c 59.56±1.83ab 27.88±1.02a 54.91±2.54b 426.38±15.61c 托县红辣椒 72.05±4.72def 21.13±0.08f 20.80±6.25ef 4.17±0.05f 8.28±0.53e 126.44±11.62i 益都红辣椒 128.43±11.98d 50.66±3.40d 25.36±2.03de 16.53±1.70d 40.04±0.79c 261.01±13.06e 2.4 辣椒碱类物质分析
干辣椒特殊的辛辣感是由辣椒碱类物质赋予的。由表6可知,干辣椒辣椒碱类物质含量18~206 mg/100 g,丘北椒辣椒碱含量显著高于其它品种(P<0.05),辣度达特辣级别,丘北椒可作为提取辣椒碱的原料。辣椒碱作为生物活性物质,可广泛用于食品工业、生物医药等领域[4]。中等辣度样品分别包括朝天椒、线椒和角椒中的花溪党武椒、沙湾线椒和益都红,托县红辣椒辣度低,其余4份样品均为高辣度样品。辣椒碱含量主要取决于品种,还受产地环境影响,除花溪党武椒外,产于潮湿地域的云南丘北椒和贵州大方皱椒显著高于降雨量较少的北方所产干辣椒(P<0.05),而四个高辣度品种均产于较炎热地区,它们的辣椒碱类物质含量显著高于干燥且日温差大地区生产的新疆沙湾线椒、内蒙托县红辣椒和辽宁益都红辣椒。此外,不同生长季节和气候也会对辣椒碱类物质的合成产生影响[27]。
表 6 9个品种干辣椒辣椒碱类物质含量(mg/100 g DW)Table 6. Capsicins contents of nine varieties of dried peppers (mg/100 g DW)品种编号 辣椒碱
(mg/100 g)二氢辣椒碱
(mg/100 g)降二氢辣椒碱
(mg/100 g)辣椒碱类物质
(mg/100 g)斯科维尔指数
SHU辣度 辣度
级别内黄新一代 22.31±1.25c 12.55±1.82bc 4.03±0.36cd 38.89±1.09c 5997.23±498.35bc 39.98±3.32bc 高辣 花溪党武椒 20.58±0.47c 9.32±0.32c 2.47±0.03de 32.37±0.45c 4992.09±107.59d 33.28±0.72d 中辣 丘北椒 158.19±1.47a 38.38±0.25a 9.46±0.34a 206.03±2.25a 31769.50±403.17a 211.80±2.69a 特辣 大方皱椒 25.54±1.56b 12.31±0.53bc 6.45±0.15a 44.31±1.56b 6832.60±226.95b 45.55±1.52b 高辣 沙湾线椒 15.28±0.73d 9.59±0.47c 2.88±0.84de 27.75±2.18d 4279.41±119.49d 28.53±1.55d 中辣 陕西秦椒 22.35±0.48c 10.92±0.78c 5.01±0.83bc 38.28±0.48c 5903.10±131.82bc 39.35±0.88bc 高辣 甘谷线椒 23.04±1.33bc 14.92±2.29b 6.08±0.73a 44.06±1.33bc 6793.94±231.89b 45.29±2.87b 高辣 托县红辣椒 10.51±0.56e 5.24±0.19d 2.31±0.12e 18.06±0.56f 2785.15±119.49e 18.57±0.80e 低辣 益都红辣椒 12.85±0.31d 6.51±0.12d 2.54±0.05de 21.90±0.47e 3377.62±72.47e 22.52±0.48e 中辣 注:“辣度级别”采用联合国经济委员会标准《UNECE FFV-61-2013》的方法划分。 2.5 脂肪酸组成及相对含量
如表7所示,干辣椒中脂肪酸组成丰富,共检测到19~27种脂肪酸,主要含9种饱和脂肪酸和5种不饱和脂肪酸。不同品种辣椒的主要脂肪酸组成基本相同,饱和脂肪酸主要有棕榈酸(5.77%~14.87%)、珠光脂酸(0.26%~4.64%)、硬脂酸(0~2.68%)和肉豆蔻酸(0.17%~1.76%),益都红棕榈酸相对含量显著高于其它样品(P<0.05
),花溪党武椒和沙湾线椒硬脂酸相对含量显著高于其它品种(P<0.05),内黄新一代含较高木焦油酸(4.32%),大方线椒中未检测出硬脂酸,其余饱和脂肪酸相对含量均较低;不饱和脂肪酸具有预防炎症、调节血压与血脂、调节心脑血管疾病等多种生理功能[28]。测试品种不饱和脂肪酸含量均超过80%,单不饱和脂肪酸主要是油酸(7.65%~16.41%)、花生油酸(1.97%~5.18%)和棕榈油酸(0.10%~0.80%),多不饱和脂肪酸主要是亚油酸(61.26%~72.54%)和亚麻酸(0.40%~0.96%)。品种间油酸含量差别大,丘北椒和托县红辣椒油酸相对含量显著高于其它试样(P<0.05),大方皱椒和益都红辣椒相对含量次之。样品中亚油酸相对含量除甘谷线椒超70%外,其余8个品种亚油酸相对含量差别不大,表明干辣椒脂肪酸组成相对均匀。其它不饱和脂肪酸如棕榈油酸、亚麻酸等虽相对含量均低于1%,但它们对人体也有重要作用。因此,干辣椒籽可作为开发高含不饱和脂肪酸食用油资源。 表 7 9个品种干辣椒脂肪酸组成及相对含量(%)Table 7. Fatty acid composition of nine varieties of dried peppers (%)脂肪酸组成 内 黄
新一代花 溪
党武椒丘北椒 大方
皱椒沙湾
线椒陕西
秦椒甘谷
线椒托 县
红辣椒益 都
红辣椒脂肪酸数量 27 23 27 23 25 24 19 25 24 饱和脂肪酸 14.65 14.88 11.14 14.80 15.86 16.02 12.27 13.72 17.49 总相对含量 酪酸 0.17±0.01b 0.15±0.01b 0.14±0.00b 0.15±0.00b 0.19±0.00b 0.25±0.01a 0.27±0.00a 0.18±0.01b 0.08±0.00c 月桂酸 0.28±0.00c 0.09±0.00d 0.26±0.02c 0.39±0.01ab 0.38±0.00b 0.46±0.00ab 0.47±0.00a 0.14±0.04d 0.14±0.00d 十三碳酸 0.23±0.00cd 0.28±0.00b 0.28±0.02b 0.35±0.01a 0.21±0.00d 0.26±0.00bc 0.33±0.00a 0.21±0.00d 0.22±0.00d 肉豆蔻酸 0.97±0.00e 0.45±0.01j 0.17±0.01h 1.12±0.04d 1.29±0.00c 1.76±0.00a 1.49±0.01b 0.61±0.03f 0.56±0.01f 棕榈酸 7.14±0.01b 6.73±0.08b 7.39±0.00b 7.30±0.19b 6.89±0.01b 7.19±0.01b 5.77±0.07c 6.72±0.32b 14.87±0.27a 珠光酯酸 1.80±0.05d 4.64±0.02a 0.26±0.02g 2.55±0.16c 4.27±0.19b 1.42±0.14e 1.14±0.03f 1.96±0.07d 0.32±0.01g 硬脂酸 0.10±0.00e 0.82±0.54d 1.03±0.02c / 1.03±0.00c 1.73±0.01b 2.68±0.00a 1.07±0.04c 0.02±0.00f 花生酸 0.40±0.00d 1.61±0.03a 1.18±0.76c 1.34±0.06b 0.16±0.00e / / 1.10±0.10c 0.16±0.06e 木焦油酸 4.32±0.02a / / 1.44±0.05c 0.93±0.05d 2.63±0.05b / 0.82±0.05d 0.56±0.03e 其它 0.36±0.08c 0.11±0.01f 0.43±0.03c 0.16±0.00e 0.51±0.01b 0.32±0.01d 0.12±0.00f 0.91±0.08a 0.16±0.00e 不饱和脂肪酸 85.35 85.12 88.86 85.20 84.14 83.98 87.73 86.28 82.51 总相对含量 棕榈油酸 0.43±0.01cd 0.30±0.00e 0.29±0.01e 0.40±0.02d 0.60±0.00b 0.65±0.00b 0.47±0.00c 0.80±0.05a 0.10±0.00f 油酸 8.85±0.11e 11.46±0.60d 15.23+0.16b 12.61±0.37c 8.97±0.01e 8.53±0.02ef 7.65±0.02f 16.41±0.73a 13.61±0.22c 亚油酸 67.22±0.07b 69.86±0.62a 68.50±0.63b 66.08±1.28b 68.45±0.10b 66.78±0.0b 72.54±0.00a 61.26±1.06c 64.50±1.09d 亚麻酸 0.87±0.01ab 0.96±0.15a 0.49±0.04c 0.82±0.05ab 0.79±0.02ab 0.49±0.02c 0.63±0.06bc 0.70±0.07b 0.40±0.01d 花生油酸 3.77±0.19c 1.97±0.02f 2.97±0.65d 4.47±0.08b 5.18±0.00a 4.29±0.01b 2.66±0.00e 4.90±0.04a 2.47±0.04e 其它 4.21±0.21a 0.57±0.03e 1.24±0.03d 0.82±0.06e 1.26±0.02d 1.34±0.03d 3.05±0.24b 2.63±0.09c 1.43±0.07d 注:“/”表示未检测出。同行不同字母代表不同样品间差异显著(P<0.05)。 2.6 挥发性物质组成及含量
对9个品种干辣椒中挥发性物质的种类和相对含量进行检测和对比分析,结果如表8所示。干辣椒中检测出烷烃、酮、烯烃、醛、醇、酯、酸、呋喃、吡嗪、酚及其它等11类挥发性物质。鉴定出的各品种挥发性成分种类(种)及含量(mg/100 g)分别为115(3.71)、108(6.81)、86(7.65)、77(2.29)、61(2.50)、57(1.73)、51(3.05)、94(1.96)、100(1.12)。品种间挥发性物质种类及含量均存在差别:丘北椒、内黄新一代和益都红烯烃类相对含量超过30%,为其优势挥发性化合物,烯烃多具有辛香味,也具有木香、果香等香气[29]。烯烃类化合物呈味阈值较低,气味强烈[30],其共同作用赋予干辣椒特有香气。甘谷线椒醛类物质相对含量较高,为21.47%,醛类物质阈值较低,多具有果香、油脂和青草味。Neugebauer等[31]报道大多数醛类物质是油酸和亚油酸通过脂氧合酶途径的自氧化反应产物,与甘谷线椒中油酸和亚油酸含量高相一致;其余醛类物质可能来源于Maillard反应或Strecker降解[32],具有坚果香和类烘烤香气。沙湾线椒烷烃相对含量较高,为27.47%,由于烷烃阈值普遍较高,香气常较弱,对干辣椒风味贡献度较低。秦椒酮类相对含量23.09%,为该品种优势挥发性化合物。酮类通常由Maillard反应或醛类进一步氧化生成[29],多数酮类物质具有优异持久的清香、奶油香味或果香等香气[33]。托县红辣椒吡嗪相对含量较高,为18.11%,吡嗪类化合物是Maillard反应和Strecker降解等非酶反应的中间产物,其阈值低,呈现烘焙香气和类似坚果等风味特征[20]。大方皱椒相对含量最高挥发物质为酯类化合物,酯类阈值较低,多具有果香、花香和酒香香气,是重要的呈香物质,通常是由脂质代谢或酸类及醇类物质的酯化反应生成。花溪党武椒中酚类物质总含量超50%,酚类是赋予食物烟熏等风味的主要成分[32]。分析花溪党武椒独特的农家烟熏烘干方式是导致其酚类物质含量高的原因。
表 8 9个品种干辣椒中挥发性组分及相对含量Table 8. Types and relative percentages of flavor components of nine varieties of dried peppers类别 项目 内黄
新一代花溪
党武椒丘北椒 大方
皱椒沙湾
线椒陕西秦椒 甘谷
线椒托 县
红辣椒益都红
辣 椒烷烃类 数量(种) 18 14 9 11 7 6 5 17 15 相对含量(%) 18.90 10.48 14.65 2.38 29.84 8.23 6.89 12.44 18.23 酮类 数量(种) 8 12 7 4 7 9 8 8 3 相对含量(%) 4.48 3.83 9.69 5.02 9.42 25.14 12.73 11.44 1.85 烯烃类 数量(种) 21 8 22 8 6 5 4 7 18 相对含量(%) 35.37 2.99 34.11 13.17 9.14 3.95 9.96 11.73 30.02 醛类 数量(种) 9 4 6 7 7 5 7 9 10 相对含量/% 6.64 1.29 3.39 8.23 7.52 6.83 23.72 10.71 12.49 醇类 数量(种) 12 10 14 10 7 7 5 10 8 相对含量(%) 17.16 12.14 16.04 9.97 11.05 12.83 12.35 8.87 11.73 酯类 数量(种) 14 7 10 17 10 13 7 14 11 相对含量(%) 9.74 4.03 10.55 33.34 15.70 22.62 11.42 13.08 11.97 酸类 数量(种) 6 4 5 5 2 3 4 2 4 相对含量(%) 6.77 6.12 14.19 10.70 1.30 2.82 9.60 2.45 3.08 呋喃类 数量(种) 2 4 2 1 1 1 1 2 3 相对含量(%) 0.50 2.97 0.66 0.65 0.66 0.52 0.40 1.21 0.24 吡嗪类 数量(种) 3 1 3 2 2 1 2 5 3 相对含量(%) 1.57 2.74 1.49 1.77 2.91 8.17 4.37 19.51 3.87 酚类 数量(种) 5 27 4 7 2 1 4 10 11 相对含量 1.16 55.34 0.96 11.12 3.20 6.61 10.13 9.00 6.34 其它类 数量(种) 17 17 2 5 10 6 4 10 11 相对含量(%) 6.70 6.19 3.14 12.51 17.90 5.59 8.89 7.32 11.14 总含量 (mg/100 g) 3.71 6.81 7.65 2.29 2.50 1.73 3.05 1.96 1.12 总计 数量(种) 115 108 86 77 61 57 51 94 100 醇类虽感知阈值多较高,但可与一些酸形成酯类物质[20],呈花草等植物基香气和清新油脂等香气。丘北椒酸相对含量较高,Kalua等[34]报道三碳以上羧酸的形成与脂肪氧化酸败有关,酸类主要呈现苦味和辛辣风味。9个品种均检测出数量及相对含量均较少的呋喃类,其中花溪党武椒相对含量较多。呋喃类和其他类化合物都属于杂环类化合物,常为Maillard反应的产物,无加热条件下大多数以较低的浓度存在,多具有水果香味、焦糖味和坚果等香气[35]。总体来看,不同品种干辣椒挥发性物质总数、总含量及相对含量均存在差别,且籽含量较高的内黄新一代、花溪党武椒和丘北椒挥发性物质较其它品种高,这些品种脂肪含量较其它品种高,可为大量以酯类为基底风味物质的形成提供基本原料。
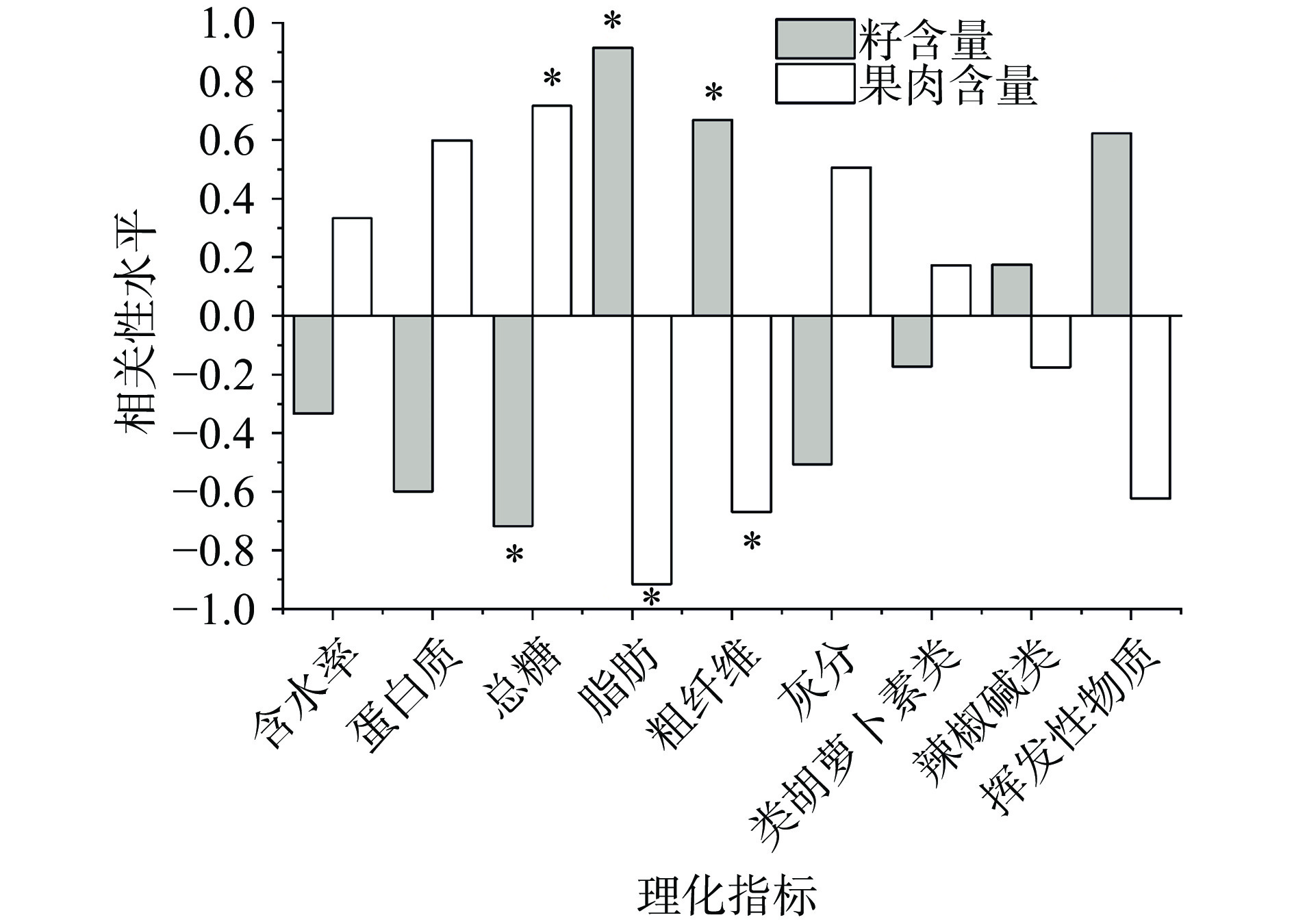
2.7 干辣椒结构特征值与品质指标含量间的简单相关性分析
干辣椒结构特征值与各品质指标含量间的简单相关性分析结果如图2所示,脂肪和粗纤维含量与籽含量呈显著正相关,即干辣椒中籽含量越高,脂肪和粗纤维含量也越高。总糖含量与果肉含量呈显著正相关,即果肉含量越高总糖含量也越高,反之亦然。此外,挥发性物质含量也与籽含量呈较高的相关性。其余品质指标与果肉含量相关性不显著(P>0.05):水分含量作为衡量干辣椒品质指标之一,产生差异的原因是由干辣椒干制和加工过程中保留程度决定的;辣椒碱含量影响因素同2.4。类胡萝卜素和灰分含量受品种、产地、气候和环境等多因素影响;结合样品含量与结构特征值同品质指标相关性分析结果得出9个品种干辣椒间蛋白含量差异不大,这说明干辣椒结构特征值差异并未对样品蛋白质含量差异造成主要影响。
2.8 主成分分析与评价
2.8.1 主成分分析
主成分分析是通过滤去采集信息中重叠共存的部分,降低数据维度,将多指标转化为少数几个不相关的综合指标的一种多元统计分析方法。利用主成分分析可以解析复杂信息中的主要影响因素,简化评价过程[36]。本文选取含水率、蛋白质、总糖、脂肪、粗纤维、灰分、类胡萝卜素、辣椒碱类和挥发性物质含量9个品质指标进行主成分分析,结果表明(表9),第1主成分的方差贡献率为44.39%,该主成分与总糖正相关性高,与脂肪、粗纤维和挥发性物质成很大负相关。第2主成分的方差贡献率为21.63%,与含水率和类胡萝卜素相关性高。第3主成分的方差贡献率为19.27%,与蛋白质成很大负相关,而与类胡萝卜素含量相关性较其它指标高。累积方差贡献率为85.29%。科学研究中,通常以累积方差贡献率大于85%作为判断指标[37]。说明这3个主成分反映了原始变量的绝大部分信息。
表 9 品质指标的综合主成分分析Table 9. Comprehensive principal component analysis of quality indexes检测指标 第一主成分 第二主成分 第三主成分 含水率 0.190 −0.948 −0.080 蛋白质 0.354 −0.378 −0.753 总糖 0.834 0.216 −0.343 脂肪 −0.829 0.307 0.274 粗纤维 −0.818 −0.419 0.340 灰分 0.631 −0.117 0.489 类胡萝卜素 0.353 −0.661 0.561 辣椒碱 −0.668 −0.346 −0.469 挥发性物质 −0.901 −0.133 −0.281 特征值 3.995 1.946 1.734 贡献率(%) 44.393 21.627 19.271 累计方差贡献率(%) 44.393 66.020 85.291 2.8.2 干辣椒品质综合评价
本文以主成分分析得到的3个主成分因子中每个指标所对应的特征向量为权重构建3个主成分的表达函数式:
Z1=0.047X1+0.088X2+0.209X3−0.208X4−0.205X5+0.158X6+0.088X7+0.167X8−0.226X9
Z2=−0.487X1−0.195X2+0.111X3+0.157X4−0.215X5−0.060X6−0.339X7−0.178X8−0.069 X9
Z3=−0.046X1−0.434X2−0.198X3+0.158X4+0.197X5+0.282X6+0.324X7−0.270X8−0.162X9
3个表达式中,X1~X11分别为含水率、蛋白质、总糖、脂肪、粗纤维、灰分、类胡萝卜素、辣椒碱类、挥发性物质含量检测值经标准化处理后的值。
由方差贡献率和主成分函数表达式计算综合得分F:
F=0.44Z1+0.22Z2+0.19Z3
根据主成分得分模型,计算出9份样品各主成分得分值、综合得分值并排序(表10)。角椒排序位于前两位,综合得分高,线椒得分居中,排序位于3~6位。且结合图2可知,果肉含量排序前6位的样品均为角椒和线椒,而果肉含量低的内黄新一代、花溪党武椒和丘北椒综合得分排第7、8和9位。总体上果肉含量较高的样品综合得分也较高。此外,三个朝天椒品种得负分,但它们的籽、脂肪和挥发性物质均较其它品种高,这与干辣椒结构特征值与品质指标含量间的简单相关性分析结果相一致。
表 10 9个品种干辣椒主成分因子得分Table 10. Principal component factor scores of nine varieties of dried peppers品种编号 主成分因子得分及排序 综合得分 综合排序 F1 排序 F2 排序 F3 排序 内黄新一代 −0.87 7 −0.55 7 1.96 3 −0.13 7 花溪党武椒 −1.20 8 1.01 2 −0.67 8 −0.36 8 丘北椒 −1.78 9 −0.66 8 −1.24 2 −1.17 9 大方皱椒 0.60 3 0.17 5 −0.22 5 0.18 5 沙湾线椒 0.51 6 0.19 6 1.18 4 0.41 3 陕西秦椒 0.52 4 0.23 4 −0.02 6 0.28 4 甘谷线椒 0.86 1 −1.03 9 −0.61 1 0.04 6 托县灯笼椒
益都红辣椒0.76
0.522
51.38
0.561
3−0.48
1.849
70.54
0.712
12.9 不同干辣椒品种的聚类分析
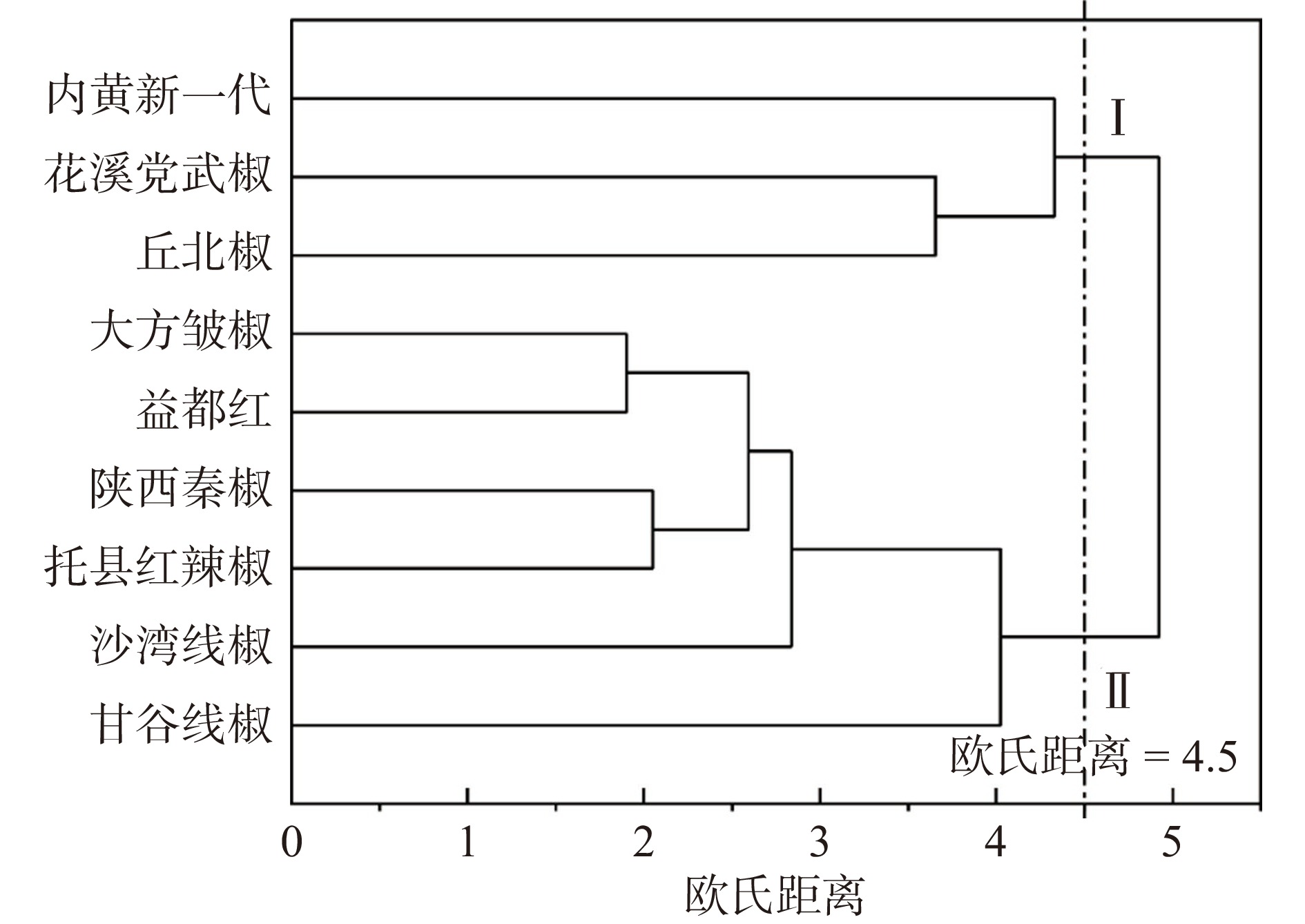
根据干辣椒主成分分析所选取的9项品质指标对9个品种进行聚类分析,结果如图3,依照聚类结果和各品质指标检测值,当欧式距离为4.5时,可将9个品种干辣椒分为2类,其中朝天椒聚为一类,其样品结构特点是籽含量高,品质特征是脂肪、粗纤维和挥发性物质含量高,内黄新一代类胡萝卜素含量高,花溪党武椒和丘北椒类胡萝卜素含量中等,表明增色作用较好,而总糖含量低;线椒和角椒聚为一类,其样品结构特点为果肉含量高,品质特征为总糖含量高。除内蒙红辣椒外其余品种类胡萝卜素含量均高于170 mg/100 g,可用于辣椒色素提取和制增色调味料。这与简单相关性分析(图2)和主成分分析(表10)结果相符。
3. 结论
本文研究朝天椒、线椒和角椒3种类型干辣椒的9个品种间品质差异性。9个品种干辣椒的2项结构特征值表明朝天椒籽含量高,而线椒和角椒果肉含量高,结构特征值与品质指标含量间的简单相关性分析结果显示了结构特征值与品质指标间的相关程度。经聚类分析可将3个品种朝天椒样品聚为一类、4个品种线椒和2个品种角椒聚为一类;进一步采用主成分分析法将影响干辣椒品质的9项指标简化为3个综合指标。综合以上分析结果说明籽肉含量是影响干辣椒品质的重要指标。通过评分反映出角椒得分高,线椒得分居中,它们的果肉和总糖含量高,可作制辣椒酱、发酵酱、辣椒丝和油辣椒原料,线椒类胡萝卜素含量较高,可作色素提取用椒;朝天椒综合得分较低,但其籽、脂肪、粗纤维和挥发性物质含量高,适宜作制粉、辣椒油和火锅底料类调味料的原料。本研究可为不同产地名优辣椒的品质评定及合理加工提供参考和依据。
-
表 1 9个品种干辣椒样品基本信息
Table 1 Basic information of nine varieties of dried peppers
样品名称 果实
类型产地 果实特征 感官特点 内黄新一代
朝天椒河南内黄 短指形、个小红亮 籽多、香辣 花溪党武椒 贵州贵阳 长指形、暗红 肉质肥厚、油多、辣而不烈 丘北椒 云南文山 长指形、光滑油亮 香辣、味道醇正 大方皱椒
线 椒贵州毕节 皱细暗红 辣度适中、香味浓厚 沙湾线椒 新疆沙湾 粗长红亮 肉厚籽少、味香微辣 陕西秦椒 陕西宝鸡 细长红亮 肉厚、辣度较强烈、香醇适口 甘谷线椒 甘肃甘谷 粗长暗红 肉厚、香味浓郁 托县红辣椒 角椒 内蒙托县 短粗牛角形、暗红 肉厚、香而不辣 益都红辣椒 山东益都 短粗牛角形、暗红 肉厚、不辣 表 2 9个品种干辣椒样品结构特征值
Table 2 Integrated structural characteristic values of nine varieties of dried peppers
品种 样品名称 结构特征值(DW%) 籽含量 肉含量 朝天椒 内黄新一代 47.02±1.22a 52.98±1.22f 花溪党武椒 46.29±1.33a 53.71±1.33f 丘北椒 36.65±1.09b 63.35±1.09e 线 椒 大方皱椒 32.94±1.46c 67.06±1.46d 沙湾线椒 28.18±1.56d 71.82±1.56c 陕西秦椒 21.52±1.02f 74.87±1.02b 甘谷线椒 25.13±1.20e 78.49±1.20a 角 椒 托县红辣椒 27.09±0.86de 72.91±0.86bc 益都红辣椒 29.68±2.98d 70.32±2.98c 注:同列不同字母代表不同样品间差异显著(P<0.05);表3~表6同。 表 3 9个品种干辣椒中的营养物质含量
Table 3 Main components of nine varieties of dried peppers
样品名称 含水率(%) 粗蛋白(%DW) 总糖(%DW) 粗脂肪(%DW) 粗纤维(%DW) 灰分(%DW) 内黄新一代 8.26±0.05b 14.75±0.05d 11.19±0.09f 17.81±0.16b 45.83±0.10a 6.75±0.05c 花溪党武椒 7.50±0.04d 15.92±0.04bc 18.80±0.10d 19.14±0.32a 43.38±0.10b 5.73±0.08d 丘北椒 8.16±0.00bc 16.23±0.00b 14.74±0.05e 16.42±0.23c 45.39±0.02a 5.17±0.22e 大方皱椒 8.15±0.05bc 16.39±0.05b 27.58±0.00a 14.55±0.58d 37.13±0.19f 5.80±0.08d 沙湾线椒 7.95±0.08c 15.38±0.09cd 24.26±0.72b 14.66±0.15d 41.73±0.53c 7.45±0.07a 陕西秦椒 8.15±0.03bc 16.39±0.03b 21.36±0.02c 14.98±0.14d 38.73±1.10e 7.41±0.01ab 甘谷线椒 9.47±0.03a 17.77±0.03a 24.11±0.06b 12.08±0.19e 40.62±0.02d 6.99±0.04abc 托县红辣椒 7.18±0.03e 16.38±0.03b 24.91±0.04b 14.23±0.40d 35.64±0.56g 6.96±0.05bc 益都红辣椒 9.88±0.02a 15.42±0.89cd 25.13±0.21b 13.36±0.07e 40.21±1.18d 5.96±0.12d 注:除含水率外,检测值以干基含量表示。 表 4 9个品种干辣椒糖组成及含量(%DW)
Table 4 Sugar compositions and contents of nine varieties of dried peppers (%DW)
样品名称 还原糖 还原糖
相对含量非还原糖 非还原糖
相对含量果糖 葡萄糖 麦芽糖 蔗糖 内黄新一代 6.67±0.36g 2.47±0.09e 0.64±0.04bc 87.44±1.46f 1.41±0.13e 12.56±1.16c 花溪党武椒 12.27±1.05e 3.62±0.21d 0.66±0.02b 88.04±1.55e 2.25±0.03c 11.96±0.25d 丘北椒 8.20±0.47f 1.71±0.15f 0.61±0.08bcd 71.34±1.55h 4.22±0.23a 28.66±1.55a 大方皱椒 12.84±0.94d 10.04±0.99a 0.93±0.01a 86.33±0.79g 3.78±0.36b 13.67±1.30b 沙湾线椒 17.02±0.26a 5.11±0.21c 0.46±0.02d 93.11±0.60c 1.67±0.10d 6.89±0.40f 陕西秦椒 14.38±0.23c 5.32±0.15c 0.68±0.07b 99.54±0.66a 0.98±0.09f 0.46±0.04i 甘谷线椒 16.25±0.39b 6.40±0.28b 0.50±0.03cd 95.97±0.64b 0.97±0.03f 4.03±0.14g 托县红辣椒 16.16±1.28b 6.40±0.05b 0.55±0.04bcd 92.78±0.78d 1.80±0.10d 7.22±0.39e 益都红辣椒 18.05±0.79a 5.98±0.31bc 0.52±0.05d 97.69±0.82b 0.58±0.06g 2.31±0.07h 注:相对含量表示占总糖%比例。 表 5 9个品种干辣椒类胡萝卜素含量(mg/100 g DW)
Table 5 Carotenoids content of nine varieties of dried peppers (mg/100 g DW)
品种编号 辣椒红素 玉米黄质 叶黄素 β-隐黄质 β-类胡萝卜素 总含量 内黄新一代 159.05±3.59c 135.16±0.51a 45.62±1.00c 30.12±1.90a 63.54±2.56a 433.49±9.56b 花溪党武椒 37.95±1.56g 9.54±0.18g 15.19±0.27f 4.71±0.13f 5.94±0.28f 73.32±2.42h 丘北椒 63.89±1.69f 26.46±1.42f 29.07±0.46d 13.85±0.83d 18.00±0.26d 151.27±4.65g 大方皱椒 201.44±5.98b 28.44±0.65f 61.79±1.92a 10.96±0.68e 14.80±1.47d 317.42±10.69d 沙湾线椒 198.54±8.15b 127.05±4.10b 55.42±2.30b 23.82±1.08b 53.35±2.57b 458.19±18.20a 陕西秦椒 79.43±4.53e 41.65±1.16e 25.07±0.30de 13.52±0.34d 12.92±0.42e 172.61±6.76f 甘谷线椒 220.57±7.51a 63.46±2.71c 59.56±1.83ab 27.88±1.02a 54.91±2.54b 426.38±15.61c 托县红辣椒 72.05±4.72def 21.13±0.08f 20.80±6.25ef 4.17±0.05f 8.28±0.53e 126.44±11.62i 益都红辣椒 128.43±11.98d 50.66±3.40d 25.36±2.03de 16.53±1.70d 40.04±0.79c 261.01±13.06e 表 6 9个品种干辣椒辣椒碱类物质含量(mg/100 g DW)
Table 6 Capsicins contents of nine varieties of dried peppers (mg/100 g DW)
品种编号 辣椒碱
(mg/100 g)二氢辣椒碱
(mg/100 g)降二氢辣椒碱
(mg/100 g)辣椒碱类物质
(mg/100 g)斯科维尔指数
SHU辣度 辣度
级别内黄新一代 22.31±1.25c 12.55±1.82bc 4.03±0.36cd 38.89±1.09c 5997.23±498.35bc 39.98±3.32bc 高辣 花溪党武椒 20.58±0.47c 9.32±0.32c 2.47±0.03de 32.37±0.45c 4992.09±107.59d 33.28±0.72d 中辣 丘北椒 158.19±1.47a 38.38±0.25a 9.46±0.34a 206.03±2.25a 31769.50±403.17a 211.80±2.69a 特辣 大方皱椒 25.54±1.56b 12.31±0.53bc 6.45±0.15a 44.31±1.56b 6832.60±226.95b 45.55±1.52b 高辣 沙湾线椒 15.28±0.73d 9.59±0.47c 2.88±0.84de 27.75±2.18d 4279.41±119.49d 28.53±1.55d 中辣 陕西秦椒 22.35±0.48c 10.92±0.78c 5.01±0.83bc 38.28±0.48c 5903.10±131.82bc 39.35±0.88bc 高辣 甘谷线椒 23.04±1.33bc 14.92±2.29b 6.08±0.73a 44.06±1.33bc 6793.94±231.89b 45.29±2.87b 高辣 托县红辣椒 10.51±0.56e 5.24±0.19d 2.31±0.12e 18.06±0.56f 2785.15±119.49e 18.57±0.80e 低辣 益都红辣椒 12.85±0.31d 6.51±0.12d 2.54±0.05de 21.90±0.47e 3377.62±72.47e 22.52±0.48e 中辣 注:“辣度级别”采用联合国经济委员会标准《UNECE FFV-61-2013》的方法划分。 表 7 9个品种干辣椒脂肪酸组成及相对含量(%)
Table 7 Fatty acid composition of nine varieties of dried peppers (%)
脂肪酸组成 内 黄
新一代花 溪
党武椒丘北椒 大方
皱椒沙湾
线椒陕西
秦椒甘谷
线椒托 县
红辣椒益 都
红辣椒脂肪酸数量 27 23 27 23 25 24 19 25 24 饱和脂肪酸 14.65 14.88 11.14 14.80 15.86 16.02 12.27 13.72 17.49 总相对含量 酪酸 0.17±0.01b 0.15±0.01b 0.14±0.00b 0.15±0.00b 0.19±0.00b 0.25±0.01a 0.27±0.00a 0.18±0.01b 0.08±0.00c 月桂酸 0.28±0.00c 0.09±0.00d 0.26±0.02c 0.39±0.01ab 0.38±0.00b 0.46±0.00ab 0.47±0.00a 0.14±0.04d 0.14±0.00d 十三碳酸 0.23±0.00cd 0.28±0.00b 0.28±0.02b 0.35±0.01a 0.21±0.00d 0.26±0.00bc 0.33±0.00a 0.21±0.00d 0.22±0.00d 肉豆蔻酸 0.97±0.00e 0.45±0.01j 0.17±0.01h 1.12±0.04d 1.29±0.00c 1.76±0.00a 1.49±0.01b 0.61±0.03f 0.56±0.01f 棕榈酸 7.14±0.01b 6.73±0.08b 7.39±0.00b 7.30±0.19b 6.89±0.01b 7.19±0.01b 5.77±0.07c 6.72±0.32b 14.87±0.27a 珠光酯酸 1.80±0.05d 4.64±0.02a 0.26±0.02g 2.55±0.16c 4.27±0.19b 1.42±0.14e 1.14±0.03f 1.96±0.07d 0.32±0.01g 硬脂酸 0.10±0.00e 0.82±0.54d 1.03±0.02c / 1.03±0.00c 1.73±0.01b 2.68±0.00a 1.07±0.04c 0.02±0.00f 花生酸 0.40±0.00d 1.61±0.03a 1.18±0.76c 1.34±0.06b 0.16±0.00e / / 1.10±0.10c 0.16±0.06e 木焦油酸 4.32±0.02a / / 1.44±0.05c 0.93±0.05d 2.63±0.05b / 0.82±0.05d 0.56±0.03e 其它 0.36±0.08c 0.11±0.01f 0.43±0.03c 0.16±0.00e 0.51±0.01b 0.32±0.01d 0.12±0.00f 0.91±0.08a 0.16±0.00e 不饱和脂肪酸 85.35 85.12 88.86 85.20 84.14 83.98 87.73 86.28 82.51 总相对含量 棕榈油酸 0.43±0.01cd 0.30±0.00e 0.29±0.01e 0.40±0.02d 0.60±0.00b 0.65±0.00b 0.47±0.00c 0.80±0.05a 0.10±0.00f 油酸 8.85±0.11e 11.46±0.60d 15.23+0.16b 12.61±0.37c 8.97±0.01e 8.53±0.02ef 7.65±0.02f 16.41±0.73a 13.61±0.22c 亚油酸 67.22±0.07b 69.86±0.62a 68.50±0.63b 66.08±1.28b 68.45±0.10b 66.78±0.0b 72.54±0.00a 61.26±1.06c 64.50±1.09d 亚麻酸 0.87±0.01ab 0.96±0.15a 0.49±0.04c 0.82±0.05ab 0.79±0.02ab 0.49±0.02c 0.63±0.06bc 0.70±0.07b 0.40±0.01d 花生油酸 3.77±0.19c 1.97±0.02f 2.97±0.65d 4.47±0.08b 5.18±0.00a 4.29±0.01b 2.66±0.00e 4.90±0.04a 2.47±0.04e 其它 4.21±0.21a 0.57±0.03e 1.24±0.03d 0.82±0.06e 1.26±0.02d 1.34±0.03d 3.05±0.24b 2.63±0.09c 1.43±0.07d 注:“/”表示未检测出。同行不同字母代表不同样品间差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 8 9个品种干辣椒中挥发性组分及相对含量
Table 8 Types and relative percentages of flavor components of nine varieties of dried peppers
类别 项目 内黄
新一代花溪
党武椒丘北椒 大方
皱椒沙湾
线椒陕西秦椒 甘谷
线椒托 县
红辣椒益都红
辣 椒烷烃类 数量(种) 18 14 9 11 7 6 5 17 15 相对含量(%) 18.90 10.48 14.65 2.38 29.84 8.23 6.89 12.44 18.23 酮类 数量(种) 8 12 7 4 7 9 8 8 3 相对含量(%) 4.48 3.83 9.69 5.02 9.42 25.14 12.73 11.44 1.85 烯烃类 数量(种) 21 8 22 8 6 5 4 7 18 相对含量(%) 35.37 2.99 34.11 13.17 9.14 3.95 9.96 11.73 30.02 醛类 数量(种) 9 4 6 7 7 5 7 9 10 相对含量/% 6.64 1.29 3.39 8.23 7.52 6.83 23.72 10.71 12.49 醇类 数量(种) 12 10 14 10 7 7 5 10 8 相对含量(%) 17.16 12.14 16.04 9.97 11.05 12.83 12.35 8.87 11.73 酯类 数量(种) 14 7 10 17 10 13 7 14 11 相对含量(%) 9.74 4.03 10.55 33.34 15.70 22.62 11.42 13.08 11.97 酸类 数量(种) 6 4 5 5 2 3 4 2 4 相对含量(%) 6.77 6.12 14.19 10.70 1.30 2.82 9.60 2.45 3.08 呋喃类 数量(种) 2 4 2 1 1 1 1 2 3 相对含量(%) 0.50 2.97 0.66 0.65 0.66 0.52 0.40 1.21 0.24 吡嗪类 数量(种) 3 1 3 2 2 1 2 5 3 相对含量(%) 1.57 2.74 1.49 1.77 2.91 8.17 4.37 19.51 3.87 酚类 数量(种) 5 27 4 7 2 1 4 10 11 相对含量 1.16 55.34 0.96 11.12 3.20 6.61 10.13 9.00 6.34 其它类 数量(种) 17 17 2 5 10 6 4 10 11 相对含量(%) 6.70 6.19 3.14 12.51 17.90 5.59 8.89 7.32 11.14 总含量 (mg/100 g) 3.71 6.81 7.65 2.29 2.50 1.73 3.05 1.96 1.12 总计 数量(种) 115 108 86 77 61 57 51 94 100 表 9 品质指标的综合主成分分析
Table 9 Comprehensive principal component analysis of quality indexes
检测指标 第一主成分 第二主成分 第三主成分 含水率 0.190 −0.948 −0.080 蛋白质 0.354 −0.378 −0.753 总糖 0.834 0.216 −0.343 脂肪 −0.829 0.307 0.274 粗纤维 −0.818 −0.419 0.340 灰分 0.631 −0.117 0.489 类胡萝卜素 0.353 −0.661 0.561 辣椒碱 −0.668 −0.346 −0.469 挥发性物质 −0.901 −0.133 −0.281 特征值 3.995 1.946 1.734 贡献率(%) 44.393 21.627 19.271 累计方差贡献率(%) 44.393 66.020 85.291 表 10 9个品种干辣椒主成分因子得分
Table 10 Principal component factor scores of nine varieties of dried peppers
品种编号 主成分因子得分及排序 综合得分 综合排序 F1 排序 F2 排序 F3 排序 内黄新一代 −0.87 7 −0.55 7 1.96 3 −0.13 7 花溪党武椒 −1.20 8 1.01 2 −0.67 8 −0.36 8 丘北椒 −1.78 9 −0.66 8 −1.24 2 −1.17 9 大方皱椒 0.60 3 0.17 5 −0.22 5 0.18 5 沙湾线椒 0.51 6 0.19 6 1.18 4 0.41 3 陕西秦椒 0.52 4 0.23 4 −0.02 6 0.28 4 甘谷线椒 0.86 1 −1.03 9 −0.61 1 0.04 6 托县灯笼椒
益都红辣椒0.76
0.522
51.38
0.561
3−0.48
1.849
70.54
0.712
1 -
[1] BAENAS N, BELOVIC M, ILIC N, et al. Industrial use of pepper (Capsicum annum L.) derived products: Technological benefits and biological advantages[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,27(4):872−885.
[2] CERVANTES-HERNÁNDEZ F, PAUL A G, OCTAVIO M, et al. Placenta, pericarp, and seeds of tabasco chili pepper fruits show a contrasting diversity of bioactive metabolites.[J]. Metabolites,2019,9(10):209. doi: 10.3390/metabo9100209
[3] CLAUDIA-JAQUELINE S C, VALDEZ-MORALES M, OOMAH B D, et al. Bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity inscalded Jalapeño pepper industrial byproduct (Capsicum annuum L.)[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2017,54(7):1999−2010. doi: 10.1007/s13197-017-2636-2
[4] MIRIAM F F-M, CUEVAS-BERNARDINO J-C, AYORA-TALAVERA T, et al. Trends in capsaicinoids extraction from habanero chili pepper (Capsicum chinense Jacq
.): Recent advanced techniques[J]. Food Reviews International,2020,36(2):105−134. doi: 10.1080/87559129.2019.1630635 [5] 王立浩, 张宝玺, 张正海, 等. “十三五”我国辣椒育种研究进展、产业现状及展望[J]. 中国蔬菜,2021(2):21−29. [WANG L H, ZHANG B X, ZHANG Z H, et at. Status in breeding and production of Capsicum spp. in China during 'the thirteenth five-year plan' period and future prospect[J]. China Vegetables,2021(2):21−29. doi: 10.19928/j.cnki.1000-6346.2021.0004 WANG L H, ZHANG B X, ZHANG Z H, et at. Status in breeding and production of Capsicum spp. in China during 'the thirteenth five-year plan' period and future prospect [J]. China Vegetables, 2021(2): 21-29. doi: 10.19928/j.cnki.1000-6346.2021.0004
[6] 陆宽, 王雪雅, 孙小静, 等. 电子鼻结合顶空SPME-GC-MS联用技术分析贵州不同品种辣椒发酵后挥发性成分[J]. 食品科学, 2018, 39(4): 199−205. LU K, WANG X Y, SUN X J, et al. Analysis of the volatile components of fermented hot pepper from different varieties grown in guizhou by electronic nose combined with SPME-GC-MS[J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(4): 199−205.
[7] 张祥, 刘雨婷, 李平平, 等. 6个地方名优辣椒品种干椒品质测定及分析[J]. 长江蔬菜,2020(22):60−64. [ZHANG X, LIU Y T, LI P P, et al. Quality determination and analysis of dried pepper of 6 local famous pepper cultivars[J]. Journal of Changjiang Vegetables,2020(22):60−64. ZHANG X, LIU Y T, LI P P, et al. Quality determination and analysis of dried pepper of 6 local famous pepper cultivars. [J]. Journal of Changjiang Vegetables, 2020(22): 60-64.
[8] 高佳, 田玉肖, 罗芳耀, 等. 16个优良朝天椒组合干制品质分析与评价[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2021,12(4):1386−1392. [GAO J, TIAN Y X, LUO F Y, et al. Analysis and evaluation of drying quality of 16 excellent pod pepper materials[J]. Food Safety and Quality Detection Technology,2021,12(4):1386−1392. GAO J, TIAN Y X, LUO F Y, et al. Analysis and evaluation of drying quality of 16 excellent pod pepper materials. [J]. Food Safety and Quality Detection Technology, 2021, 12(4): 1386-1392.
[9] 蓬桂华, 王永平, 李文馨, 等. 25个干辣椒品种色、香、味品质差异评价[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(8):242−248. [PENG G H, WANG Y P, LI W X, et al. Differences and comprehensive of color, aroma and taste quality of 25 dry pepper varieties[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(8):242−248. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020060290 PENG G H, WANG Y P, LI W X, et al. Differences and comprehensive of color, aroma and taste quality of 25 dry pepper varieties. [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(08): 242-248. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020060290
[10] 巩雪峰, 陈鑫, 赵黎明, 等. 109份辣椒种质资源果实品质的分析与评估[J]. 长江蔬菜,2019(18):54−58. [GONG X F, CHEN X, ZHAO L M, et al. Analysis and evaluation of fruit quality of 109 sichuan pepper germplasm resources[J]. Journal of Changjiang Vegetables,2019(18):54−58. GONG X F, CHEN X, ZHAO L M, et al. Analysis and evaluation of fruit quality of 109 sichuan pepper germplasm resources. [J]. Journal of Changjiang Vegetables, 2019(18): 54-58.
[11] SAMIA A, BEN T F, JRIDI M, et al. Discarded seeds from red pepper (Capsicum annum L.) processing industry as a sustainable source of high added-value compounds and edible oil[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2017,24(28):22196−22203. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-9857-9
[12] 马燕, 徐贞贞, 邹辉, 等. 8个品种辣椒籽成分分析与比较[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(22):178−183. [MA Y, XU Z Z, ZOU H, et al. Analysis and comparison of constituents in hot pepper seeds of eight verities[J]. Food Science,2017,38(22):178−183. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630- 201722027. [MAY, XU Z Z, ZOU H, et al. Analysis and comparison of constituents in hot pepper seeds of eight verities[J]. Food Science, 2017, 38(22): 178-183. ] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-
[13] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. GB 5009.3-2016 食品中水分的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. National Health Commission of the people’s Republic of China. GB 5009.3-2016 Determination of moisture in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[14] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. GB 5009.4-2016食品中灰分的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. National Health Commission of the people's Republic of China. GB 5009.4-2016 Determination of ash in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[15] 中华人民共和国卫生健康委员会. GB 5009.5-2016 食品中蛋白质的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. National Health Commission of the people’s Republic of China. GB 5009.5-2016 Determination of protein in food [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[16] 中华人民共和国卫生健康委员会. GB 5009.6-2016食品中脂肪的测定 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. National Health Commission of the people’s Republic of China. GB 5009.6-2016 Determination of fat in food [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[17] 中华人民共和国卫生健康委员会. GB 5009.10-2003食品中粗纤维的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2003. National Health Commission of the people’s Republic of China. GB 5009.10-2003 Determination of crude fiber in food [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2003.
[18] 国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 5009.8-2016食品中果糖、葡萄糖、蔗糖、麦芽糖、乳糖的测定 高效液相色谱法 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. Standardization Administration. GB/T 5009.8-2016 Determination of fructose, glucose, sucrose, maltose and lactose in food by high performance liquid chromatography [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[19] 国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 21266-2007辣椒及辣椒制品中辣椒素类物质测定及辣度表示方法[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2007. Standardization Administration. GB/T 21266-2007 Determination of capsaicin in pepper and pepper products and expression method of spicy degree [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2007.
[20] JIA X, DENG Q C, YANG Y N, et al. Unraveling of the aroma-active compounds in virgin camellia oil (Camellia oleifera Abel) using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry-olfactometry, aroma recombination, and omission studies[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2021,69(32):9043−9055. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c07321
[21] ZANG R Y, LIU H M, MA Y X, et al. Effects of roasting on composition of chili seed and storage stability of chili seed oil[J]. Food Science and Biotechnology,2019,28(5):1475−1486. doi: 10.1007/s10068-019-00578-9
[22] GU L B, PANG H L, LU K K, et al. Process optimization and characterization of fragrant oil from red pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) seed extracted by subcritical butane extraction[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2017,97(6):1894−1903. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.7992
[23] 付文婷, 詹永发, 何建文, 等. 10个贵州地方辣椒品种品质评价[J]. 中国瓜菜,2018,31(12):37−40. [FU W T Z, HAN Y F, HE J W, et al. Quality evaluation of 10 pepper landraces in Guizhou[J]. Zhongguo Gua-cai,2018,31(12):37−40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2871.2018.12.009 Fu W T Z, HAN Y F, HE J W, et al. Quality evaluation of 10 pepper landraces in Guizhou[J]. Zhong Guo Gua-cai, 2018, 31(12): 37-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2871.2018.12.009
[24] 程晓齐. 干辣椒制作发酵型辣椒酱的研究[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2021: 37−40. CHENG X Q. Study on making fermented chili sauce with dry pepper[D]. Xianyang: Northwest A&F University, 2021: 37−40.
[25] AYHAN T, OZDEMIR F. Assessment of carotenoids, capsaicinoids and ascorbic acid composition of some selected pepper cultivars (Capsicum annuum L.) grown in Turkey[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2007,20(7):596−602. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2007.03.007
[26] ZHANG Y T, LIU Z, SUN J N, et al. Biotechnological production of zeaxanthin by microorganisms[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2018:71225−234.
[27] GURUNG T, TECHAWONGSTIEN S, SURIHARN B, et al. Growth, yield and capsaicinoid contents of 14 cultivars of hot pepper (Capsicum spp.) at two elevations of Thailand[J]. SABRAO Journal of Breeding and Genetics,2011,43(2):130−143.
[28] 吴洪号, 张慧, 贾佳, 等. 功能性多不饱和脂肪酸的生理功能及应用研究进展[J]. 中国食品添加剂, 2021, 32(8): 134−140 WU H H, ZHANG H, JIA J, et al. Research progress of physiologic function and application of functional polyunsaturated fatty acids[J]. China Food Additives, 2021, 32(8): 134−140.
[29] SAMIA B B, AMANPOUR A, CHTOUROU F, et al. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry-olfactometry to control the aroma fingerprint of extra virgin olive oil from three tunisian cultivars at three harvest times[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2018,66(11):2851−2861. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b06090
[30] ZHENG Y, SUN B G, ZHAO M M, et al. Characterization of the key odorants in Chinese zhima aroma-type baijiu by gas chromatography-olfactometry, quantitative measurements, aroma recombination, and omission studies[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2016,64(26):5367−5374. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b01390
[31] NEUGEBAUER A J, GRANVOGL M, SCHIEBERLE P. Characterization of the key odorants in high-quality extra virgin olive oils and certified off-flavor oils to elucidate aroma compounds causing a rancid off-flavor[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2020,68(21):5927−5937. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c01674
[32] YU Z, LIU Y P, YANG W X, et al. Characterization of potent aroma compounds in preserved egg yolk by gas chromatography- olfactometry, quantitative measurements, and odor activity value[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2018,66(24):6132−6141. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b01378
[33] SONGUL K, KELEBEK H, SELLI S. Characterization of the key aroma compounds in turkish olive oils from different geographic origins by application of aroma extract dilution analysis (AEDA)[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2014,62(2):391−401. doi: 10.1021/jf4045167
[34] KALUA C-M, ALLEN M-S, BEDGOOD D-R, et al. Olive oil volatile compounds, flavour development and quality: A critical review[J]. Food Chemistry, 2005, 100(1): 273−286.
[35] CHO I H, LEE S, JUN H-R, et al. Comparison of volatile maillard reaction products from tagatose and other reducing sugars with amino acids[J]. Food Science and Biotechnology,2010,19(2):431−438. doi: 10.1007/s10068-010-0061-7
[36] GAO B Y, LU Y J, YI S, et al. Differentiating organic and conventional sage by chromatographic and mass spectrometry flow injection fingerprints combined with principal component analysis[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2013,61(12):2957−2963. doi: 10.1021/jf304994z
[37] LI L M, ZHAO J, WANG C R, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of robotic global performance based on modified principal component analysis[J]. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems,2020,17(4):220−226.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 张敏杰,杨武德,代叶,李玮,魏晴,梁珊珊. 黔产不同商品规格金钗石斛质量评价研究. 亚太传统医药. 2024(04): 39-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 林鑫静,张明,李鑫,周春阳,蒲跃,袁斌,范艺缤,范润勇,夏天琴,尤俊,杨晓曦,胥正敏. 调脏舒秘合剂小鼠急性毒性实验研究. 现代中医药. 2023(02): 91-95 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 杨吉容,石京山. 金钗石斛破壁粉对自发性高血压大鼠血压及心功能的影响. 遵义医科大学学报. 2022(06): 699-705 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
