Dynamic Characteristics of Inorganic Elements in Astragalus membranaceus at Different Growth Stages
-
摘要: 目的:探究不同生长期黄芪中Mg、Ca、V、Mn、Fe、Co、Ni、Cu、Zn、Ba这10种无机元素的含量差异与动态积累特征,从无机元素层面对黄芪适宜采收期的确定提供帮助。方法:收集不同生长期黄芪样品,采用电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定其元素含量,并结合单因素方差分析、主成分分析(PCA)、正偏最小二乘判别分析(OPLS-DA)和相关性分析方法分析黄芪药用部位生长过程中无机元素的变化及积累规律。结果:不同生长期黄芪10种元素含量差异较大,Mg、Ca、V、Mn、Fe、Ni、Cu、Co元素均在10月份时含量达到最大值,Ba在6月份时含量达到最大值,8月为上述元素含量最小值时的生长期,Zn元素在9月的含量显著高于其他生长期,7月时含量显著低于其他生长期(P<0.05),10种元素含量均为先降后升的动态变化趋势。相关性分析结果表明:V与Ca、Fe;Ni与Ba元素之间均存在极显著性相关关系(P<0.01),主成分分析综合得分结果表明10月份黄芪样品得分排名第一,正偏最小二乘判别分析表明Zn、Ni、Cu、V四种元素为鉴别不同生长期黄芪的主要特征元素。结论:黄芪中无机元素含量与其生长期密切相关,无机元素可以作为黄芪采收期确定的指标之一。综合分析,10月中下旬为黄芪药材的最佳采收期。Abstract: Objective: To explore the dynamic accumulation characteristics of 10 inorganic elements including Mg, Ca, V, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn and Ba in Astragalus membranaceus at different growth stages, and determine the optimal harvesting period. Methods: Collected Astragalus membranaceus form different growth stages and determined its element contents by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry(ICP-MS), then analyzed its changes and accumulation rule by one-way ANOVA, principal component analysis(PCA), orthogonal projections to latent structures discriminant analysis(OPLS-DA) and correlation analysis. Results: The contents of 10 elements of Astragalus membranaceus at different growth stages were significantly different. The contents of Mg, Ca, V, Mn, Fe, Ni, Cu and Co reached the peak in October, and Ba reached the peak in June. The contents of above element were the lowest in August. The content of Zn in September was significantly higher and in July was significantly lower than that in other growing seasons (P<0.05). The contents of 10 elements all showed a dynamic trend of decreasing first and then increasing. Correlation analysis showed that there was a very significant correlations between V and Ca, Fe, Ni and Ba (P<0.01). The results of principal component analysis showed that the score of Astragalus in October ranked first. The orthogonal projections to latent structures discriminant analysis showed that Zn, Ni, Cu and V were the main characteristic elements for identifying Astragalus membranaceus in different growth stages. Conclusion: The content of inorganic elements in Astragalus membranaceus was closely related to its growing stage and inorganic elements could be used as one of the indexes to determine the harvest period of Astragalus membranaceus. Comprehensive analysis showed that middle October was the best harvest time for Astragalus membranaceus.
-
Keywords:
- Astragalus membranaceus /
- growth stage /
- inorganic elements /
- dynamic accumulation
-
黄芪为豆科植物蒙古黄芪(Astragalus membranaceus(Fisch.) Bge. var. mongholicus(Bge.)Hsiao)或膜荚黄芪(Astragalus membranaceus(Fisch.)Bge)的干燥根[1],始载于《神农本草经》,含有皂苷、多糖、黄酮等多种化学成分[2],现代药理学表明,黄芪具有抗炎[3]、抗肿瘤[4-5]、抗病毒[6]、保护肾脏[7]等作用,临床上主要用于治疗糖尿病及其并发症[8-9]、心血管疾病[10-11]等症。近年来,随着人们生活水平的提高,养生保健成为人们关注的焦点,黄芪作为中医传统的补虚药,其化学成分多样,药理作用显著,药性温和,受到保健行业一致的青睐。2020年1月,国家卫生健康委员会、国家市场监督总局公布,对黄芪开展按照传统既是食品又是中药材的物质进行生产经营试点工作,2020年12月,欧盟委员会发布法规,批准黄芪提取物作为新型食品投放市场,此类条例的发布进一步推进了黄芪在保健方面的开发与利用。截止2022年3月17日,“特殊食品信息查询平台”检索数据显示,以黄芪为原料的胶囊、口服液等保健商品多达376种。黄芪在临床与日常保健方面的广泛应用,使其质量问题受到更多人的关注。
一直以来,黄芪真伪优劣鉴定方法主要为黄芪甲苷、毛蕊异黄酮等主要化学成分的分析与测定[12-15],而无机元素作为黄芪的重要成分之一,对其产地归属,有效成分含量均具有一定的影响[16-17]。同时,相关研究表明,无机元素对作物生长发育的影响至关重要[18-19],不同生长阶段,作物对无机营养元素的需求有所不同。因此,通过对不同生长期黄芪中的无机元素进行测定,不仅可以进一步完善其质量评价体系,还可以对其生长过程中的无机肥料供给以及最佳采收期的确定提供参考。但目前有关于黄芪在相关方面的研究报道还较为少见。
甘肃陇西莲峰镇是甘肃省黄芪主产区之一,全镇中药材种植约达4.5万亩左右,其中在元明村,杨家咀村和幸福村3村建成千亩黄芪标准化核心示范基地[20]。故本实验选择甘肃省定西市陇西县莲峰镇的栽培黄芪,采用电感耦合等离子体质谱法(Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry,ICP-MS)测定不同生长期黄芪中10种无机元素含量,通过建立无机元素图谱,运用相关性、主成分等计量方法分析其规律,探究黄芪生长过程中无机元素的累积与变化,为黄芪采收期的确定以及质量评价提供一定的参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
黄芪药材 采自甘肃省定西市渭源县莲峰镇杨家咀村(北纬35.06°,东经104.33°)的试验田,经甘肃中医药大学杨扶德教授鉴定均为豆科植物蒙古黄芪Astragalus membranaceus(Fisch.) Bge. var. mongholicus(Bge.)Hsiao的干燥根;65%硝酸 分析纯,德国Meker公司;镁(Mg)、钙(Ca)、钒(V)、锰(Mn)、铁(Fe)、钴(Co)、镍(Ni)、铜(Cu)、锌(Zn)、钡(Ba)混合元素标准溶液 10 μg·mL−1,美国Agilent公司。
7900型ICP-MS质谱仪 美国Agilent公司;Ultra-CLAVELV型大微波消解仪 德国Milestone公司;BSA224S-CW型电子天平 德国Sartorius公司;IQ7000纯水净化系统 美国Millipore;G200型切割式混合研磨仪 德国Retsch公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品的采收
2020年3月进行黄芪的移栽后分别于2020年6月27日、7月28日、8月27日、9月26日、10月26日进行黄芪样品的采收。
1.2.2 样品前处理
采收后的黄芪样品用清水冲洗干净后,分别用去离子水冲洗、阴干、粉碎、过筛(100目),恒重后置于干燥器中备用。
1.2.3 ICP-MS检测条件
载气为氩气,等离子体射频功率为1550 W,等离子体流速为15.0 L·min-1,雾化室温度为2 ℃,采样深度为8.0 mm,重复次数为3次。微波消解条件程序如表1所示。
表 1 微波消解条件Table 1. Microwave digestion procedure消解程序 爬升时间
(min)保持时间
(min)温度
(℃)压强
(Pa)功率
(W)1 10 0 130 6×106 700 2 12 2 200 7×106 850 3 10 2 220 9×106 1000 4 10 10 240 9×106 1100 1.2.4 溶液制备
1.2.4.1 标准溶液
将10种混合元素标准液加2%硝酸逐级稀释成不同质量系列浓度标准溶液,具体浓度见表2。
表 2 10种无机元素标准系列浓度Table 2. Standard series concentrations of ten inorganic elements元素 标准系列(μg·L−1) Mg 0、100、500、2000、5000 Ca 0、100、500、2000、5000 V 0、1、5、10、20、50 Mn 0、5、10、50、100、200 Fe 0、100、500、2000、5000 CO 0、0.1、0.5、1、2、5 Ni 0、1、5、10、20、50 Cu 0、1、5、10、20、50 Zn 0、1、5、10、20、50 Ba 0、5、10、50、100、200 1.2.4.2 供试品溶液
精密称取不同月份采收的黄芪样品0.3000 g置于消解罐中,每个样品平行称取3份,加入3 mL硝酸溶液静置30 min后,按照表1所示微波消解条件进行消解,消解完成后将消解液转移至50 mL容量瓶中,用少量超纯水冲洗消解罐,定容,同时做试剂空白。
1.3 数据处理
本论文中的数据均为3次重复处理结果的平均值,利用Microsoft Excel 2010、SPSS 26.0与SIMCA 14.1软件对数据进行统计分析。热图采用Hiplot(https://hiplot.com.cn)网络平台绘制,数据表现形式为“平均值±标准差”,统计差异水平利用单因素方差分析(One-way ANOVA)中的Duncan多重比较检验,相关性分析采用皮尔逊(Pearson)相关分析法进行。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 方法学考察结果
2.1.1 标准曲线绘制
精密吸取标准溶液,取相对原子质量相近的元素为内标溶液,在1.2.3所示条件下进样进行含量测定,结果如表3所示,各元素R2值均大于0.999,表明其线性关系良好。
表 3 10种无机元素线性关系考察结果Table 3. Results of linear relationship investigation of ten inorganic elements元素 回归方程 R2 Mg y=0.9953x+4.8723 0.9995 Ca y=0.9954x+10.817 0.9993 V y=0.9621x+0.2357 0.9994 Mn y=0.9879x+0.2786 0.9995 Fe y=0.9949x+6.2525 0.9997 CO y=0.9802x+0.0146 0.9996 Ni y=1.1084x+0.1308 0.9995 Cu y=1.03x+0.2723 0.9996 Zn y=0.9837x+0.156 0.9993 Ba y=0.9763x+0.7489 0.9995 2.1.2 精密度
取同一黄芪样品消解液在1.2.2所示条件下连续进样6次,根据测量值计算各元素质量浓度响应值RSD值。各元素RSD<2%,表明仪器精密度良好。
2.1.3 重复性
精密称取同一黄芪样品6份,每份各0.3000 g,分别按照表1和1.2.2所示条件进行消解和测定,根据测量值计算各元素质量浓度响应RSD值。各元素RSD<4%,表明实验的重复性良好。
2.1.4 稳定性
取同一黄芪样品消解液在1.2.2所示条件下分别于0、2、4、8、10、12、24 h时进样测定,根据测量值计算各元素质量浓度响应值的RSD值。结果表明各元素RSD<4%,表明仪器的稳定性良好。
2.1.5 加样回收率
精密称取已知各元素含量的黄芪样品0.3000 g,每份样品平行3份,加入各元素标准液适量,分别按照1.2.2所示条件进行消解和测定。结果显示,各元素加样回收率在90.10%~108.33%之间,回收率良好,且RSD<4%,表明该方法稳定可行。
2.2 不同生长期黄芪无机元素含量测定结果
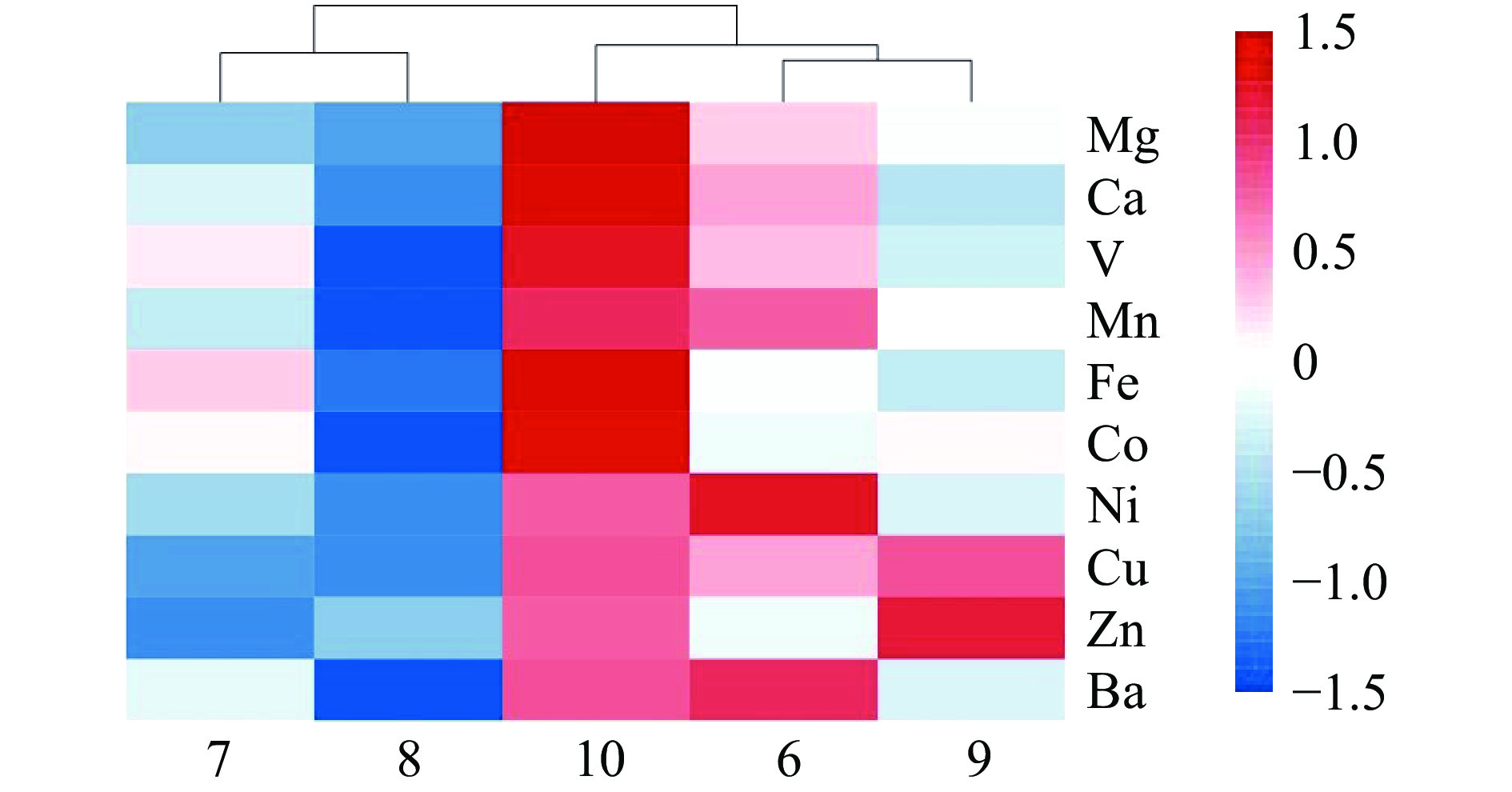
10种元素含量测定结果如表4所示。不同生长期黄芪样品中测得的10种元素含量差异较大,其中Mg、Ca、V、Mn、Fe、Ni和Cu元素含量均在10月份时显著高于其他生长时期(P<0.05),8月时其含量均显著低于其他时期(P<0.05);Co元素含量在10月份时达到最大值,但与7月与9月时的样品无显著性差异,Zn元素在9月时其含量显著高于其他采收期(P<0.05),7月时含量显著低于其他生长期(P<0.05),Ba元素在6月时含量显著高于其他生长期(P<0.05),8月为其含量最小的生长期。Mg、Ca、V、Mn、Fe、Co、Ni、Cu、Zn、Ba10种元素10月份含量相较于6月份分别增加了26.18%、34.15%、40.97%、8.33%、92.36%、77.45%、−19.27%、10.95%、32.49%、−6.66%,结果表明,除Ni元素与Ba元素外,黄芪对其他元素均有富集作用,对Fe元素的富集效果最为明显。为了更直观的表示不同生长期黄芪中无机元素含量的差异,对10种元素含量数据进行标准化处理后绘制热图,结果如图1所示,同种元素在不同生长期内含量具有较大的差异,基于欧式距离对其进行聚类后发现,7、8月样品可以聚为一类,6、9月样品可以聚为一类,10月份样品单独为一类,聚为同一类的样品所在生长期在元素含量上具有一定的相似性。
表 4 不同生长期黄芪样品中10种无机元素含量(mg·kg−1)Table 4. Contents of ten inorganic elements in Astragalus membranaceus samples at different growth stages (mg·kg−1)测定元素 6月 7月 8月 9月 10月 Mg 1232.05±72.08b 990.82±46.26d 905.69±17.94e 1146.38±61.10c 1554.62±79.75a Ca 260.37±18.65b 196.27±17.93c 122.68±17.47e 179.98±9.16d 346.66±16.82a V 0.59±0.01b 0.55±0.04b 0.13±0.07d 0.42±0.07c 0.83±0.06a Mn 10.94±2.64b 7.31±0.53d 4.22±0.78e 8.74±0.62c 11.37±2.21a Fe 201.42±13.77c 243.71±14.29b 154.73±9.55e 165.52±13.38d 387.11±8.79a Co 0.093±0.002b 0.097±0.01ab 0.040±0.007c 0.098±0.01ab 0.104±0.01a Ni 0.859±0.07b 0.313±0.07d 0.136±0.04e 0.453±0.02c 1.062±0.40a Cu 4.323±0.11b 2.537±0.44c 2.364±0.55d 4.857±0.34a 4.863±0.26a Zn 8.348±0.98c 5.426±0.89e 6.688±0.81d 12.422±1.43a 11.065±1.69b Ba 6.585±0.96a 4.260±0.91c 2.278±0.54d 4.161±0.77c 5.898±0.61b 注:同行不同小写字母表示差异显著,P<0.05。 2.3 元素特征图谱的绘制
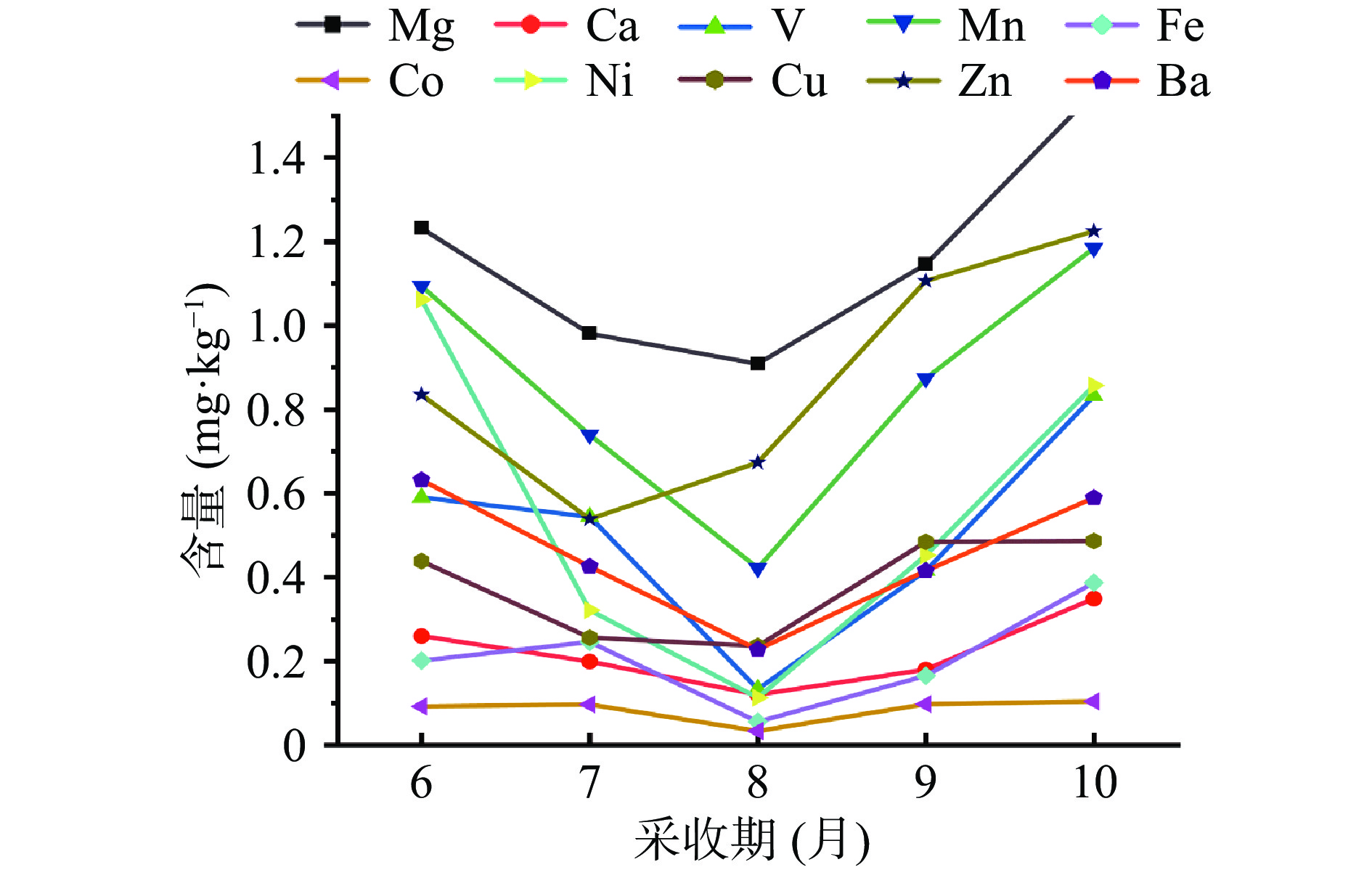
为了进一步观察10种元素累积过程,将Mg、Ca、Fe含量缩小1000倍,Mn、Cu、Zn、Ba含量缩小10倍,其他元素保持不变后制作特征图谱图,结果如图2所示,10种元素含量的累积均为先降后升的动态变化趋势,6月份元素含量均处于较高的水平,然后开始下降,除Cu元素在7月份有最低含量外,其他元素均在8月份时元素含量最低,9月份开始回升,10月份又达到一个高峰。结果表明,黄芪根部在不同生长时期对无机元素的富集效果不同,9~10月为黄芪根部无机元素大量累积的生长期。
2.4 10种无机元素间的相关性分析
植物的生长发育是多种营养元素相互作用的结果,各类无机营养元素也会在植物体内相互协助与制约帮助植物健康的生长,如植物金属锌铁转运蛋白在调节植物体内镉元素的累积过程中起关键作用,避免植物遭受镉元素毒害[21]。本实验对10种元素进行相关系分析,结果如表5所示,Mg与Ca、Mn;Ca与Mn、Fe、Ba;V与Mn、Ba;Ni与Ba元素之间均存在显著性相关关系,V与Ca、Fe;Ni与Ba元素均存在极显著性相关关系,无机元素的相关性强表明一种元素含量因某种因素发生变化时与其相关的元素含量也会发生相应的变化。因此,在调节有益元素含量增长的同时也要注意一些重金属元素对身体造成的危害。
表 5 不同生长期黄芪样品10种无机元素相关性分析结果Table 5. Correlation analysis results of ten inorganic elements in Astragalus membranaceus samples at different growth stagesMg Ca V Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ba Mg 1 0.944* 0.86 0.902* 0.834 0.635 0.785 0.82 0.367 0.874 Ca 1 0.961** 0.921* 0.925* 0.707 0.828 0.668 0.172 0.949* V 1 0.913* 0.969** 0.852 0.767 0.622 0.126 0.949* Mn 1 0.806 0.83 0.925 0.848 0.501 0.983** Fe 1 0.791 0.601 0.522 -0.041 0.847 Co 1 0.621 0.673 0.352 0.815 Ni 1 0.741 0.527 0.928* Cu 1 0.815 0.737 Zn 1 0.357 Ba 1 注:*表示显著性相关,P<0.05;**表示极显著性相关,P<0.01。 2.5 不同生长期黄芪的综合评价
为了对不同生长期黄芪中所含无机元素进行综合性评价,对不同生长期样品中10种无机元素进行主成分分析,结果如表6所示,前两个成分特征值均大于1,且其累积方差贡献率达到了92.132%,表明这两个成分具有较强的代表性。由各生长期样品得分与成分累积方差贡献率和计算其综合得分F,结果如表6所示,10月份样品综合得分排名为第一。结果表明,从无机元素层面来说,10月份黄芪药材质量较优。
表 6 不同生长时期黄芪主成分分析综合排名Table 6. Comprehensive ranking of principal component analysis of Astragalus membranaceus at different growth stages采收期 F1 F2 F 排名 6月 0.59 0.69 0.61 2 7月 −0.34 −1.22 −0.49 4 8月 −1.44 −0.01 −1.21 5 9月 −0.01 1.24 0.20 3 10月 1.20 −0.69 0.90 1 2.6 不同生长期黄芪样品差异性元素筛选
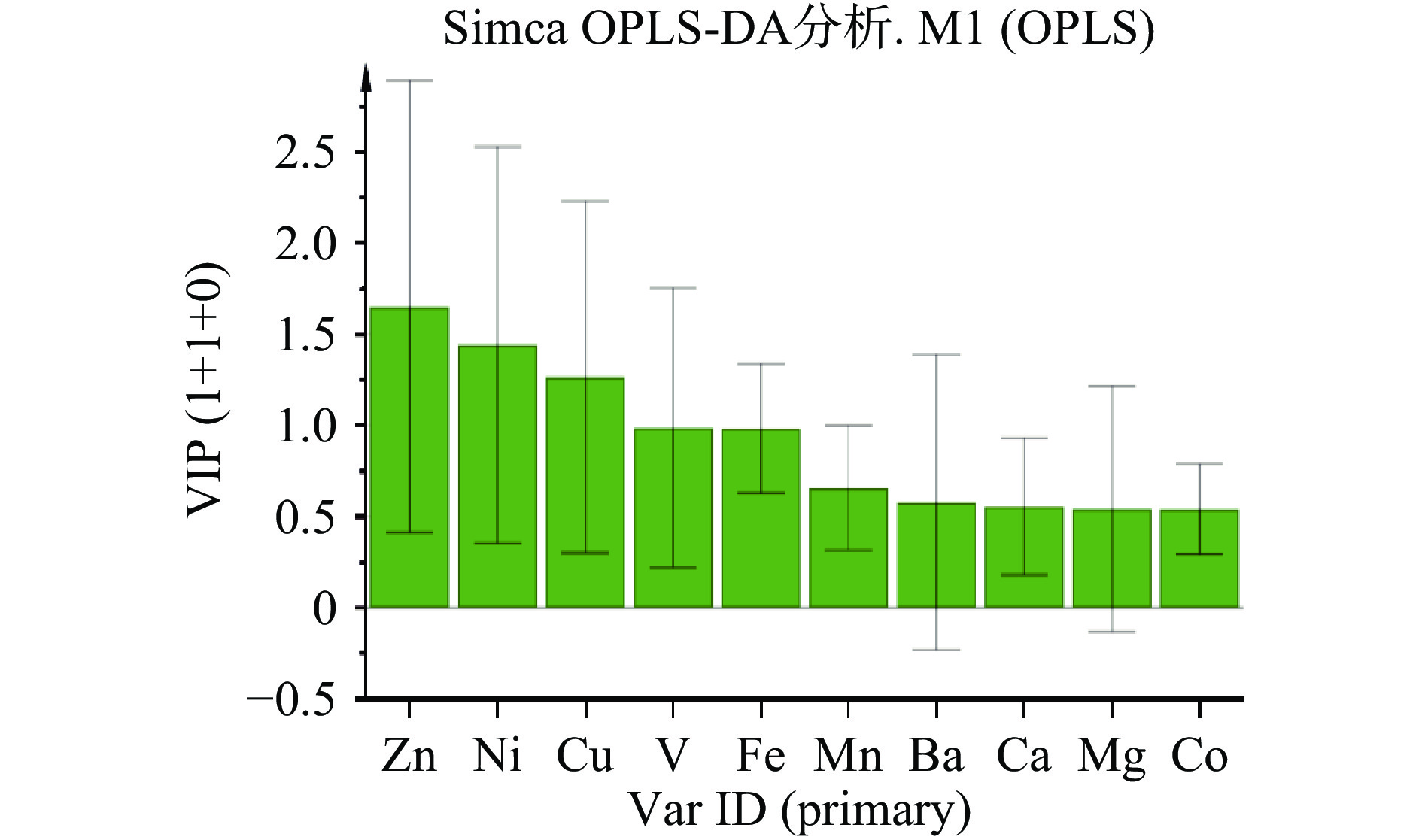
为分析不同生长期黄芪样品的主要影响元素,在主成分分析的基础上,对其进行正偏最小二乘判别分析(OPLS-DA),根据变量重要性投影(VIP),筛选不同生长期黄芪差异性元素,其中VIP值越大表明其对分类的贡献率越大,当VIP>1时,说明该变量为分类的关键因素,分析结果如图3所示。10种元素中Zn、Ni、Cu、V四种元素VIP>1,表明此4种元素可作为特征元素对黄芪的生长进行鉴别。
3. 结论与讨论
不同时期各无机营养元素的积累与黄芪生长发育密切相关,由相关研究可知[22],从移栽期到6月,为黄芪的移栽出苗期,此阶段黄芪根部会吸收土壤中大量养分以满足其快速生长发育,故在6月份时,各无机营养元素会达到一个高峰;6~8月为花果期,植株的快速生长,根部吸收的各类营养成分需要供应地上部分开花、结果,无机营养元素也随之下降,8月份时,各营养元素含量最低;随着花期的结束,8月中旬至10月中旬,为黄芪的根茎增粗期,主要营养元素又向根部积累,无机营养元素也又一次达到了一个高峰,本研究中无机元素含量在其生长期中的变化符合黄芪的生长的供应需求,主成分综合排名表明,10月下旬时,黄芪根部各类营养元素含量累积到了最大值,且根据相关报道可知,黄芪产量、皂苷等有效成分也在相同时期达到其最大积累量[23-25],综合考虑各方面因素,10月中旬,可以作为栽培黄芪的最佳采收期。正偏最小二乘判别分析(OPLS-DA)发现,Zn、Ni、Cu、V四种元素与黄芪的生长密切相关,Zn、Ni、Cu元素均为植物生长发育必需的矿质元素,Zn作为植物多种酶和重要蛋白结构的辅助因子和活化剂,缺锌会导致其生长素含量下降,进而造成植株矮小、生长缓慢等一系列生理问题[26],施用Zn肥不仅可以促进作物生长,还可以通过Zn-Cd拮抗作用缓解Cd毒害[27]。Ni是脲酶所必需的元素,脲酶的缺乏将导致植物叶片坏死损伤,营养生长期镍主要分布于叶和芽中,生殖生长期绝大部分镍会从叶和芽转移到生殖器官[28];Cu是植物叶绿体中质体蓝素的组成成分,参与光合电子传递过程,不同物种地上部和地下部的Cu含量及转移能力存在较大差异[29];V元素作为为人体必需元素之一,尽管目前还没有确定是植物生长所必需的营养元素,但相关研究表明,适量的V元素可以促进作物生长,促进植物的固氮、固氯作用[30],针对此4种元素与黄芪生长发育的密切关系与其在植物体内的重要作用,可以为黄芪无机肥料的配比与供给提供参考。
-
表 1 微波消解条件
Table 1 Microwave digestion procedure
消解程序 爬升时间
(min)保持时间
(min)温度
(℃)压强
(Pa)功率
(W)1 10 0 130 6×106 700 2 12 2 200 7×106 850 3 10 2 220 9×106 1000 4 10 10 240 9×106 1100 表 2 10种无机元素标准系列浓度
Table 2 Standard series concentrations of ten inorganic elements
元素 标准系列(μg·L−1) Mg 0、100、500、2000、5000 Ca 0、100、500、2000、5000 V 0、1、5、10、20、50 Mn 0、5、10、50、100、200 Fe 0、100、500、2000、5000 CO 0、0.1、0.5、1、2、5 Ni 0、1、5、10、20、50 Cu 0、1、5、10、20、50 Zn 0、1、5、10、20、50 Ba 0、5、10、50、100、200 表 3 10种无机元素线性关系考察结果
Table 3 Results of linear relationship investigation of ten inorganic elements
元素 回归方程 R2 Mg y=0.9953x+4.8723 0.9995 Ca y=0.9954x+10.817 0.9993 V y=0.9621x+0.2357 0.9994 Mn y=0.9879x+0.2786 0.9995 Fe y=0.9949x+6.2525 0.9997 CO y=0.9802x+0.0146 0.9996 Ni y=1.1084x+0.1308 0.9995 Cu y=1.03x+0.2723 0.9996 Zn y=0.9837x+0.156 0.9993 Ba y=0.9763x+0.7489 0.9995 表 4 不同生长期黄芪样品中10种无机元素含量(mg·kg−1)
Table 4 Contents of ten inorganic elements in Astragalus membranaceus samples at different growth stages (mg·kg−1)
测定元素 6月 7月 8月 9月 10月 Mg 1232.05±72.08b 990.82±46.26d 905.69±17.94e 1146.38±61.10c 1554.62±79.75a Ca 260.37±18.65b 196.27±17.93c 122.68±17.47e 179.98±9.16d 346.66±16.82a V 0.59±0.01b 0.55±0.04b 0.13±0.07d 0.42±0.07c 0.83±0.06a Mn 10.94±2.64b 7.31±0.53d 4.22±0.78e 8.74±0.62c 11.37±2.21a Fe 201.42±13.77c 243.71±14.29b 154.73±9.55e 165.52±13.38d 387.11±8.79a Co 0.093±0.002b 0.097±0.01ab 0.040±0.007c 0.098±0.01ab 0.104±0.01a Ni 0.859±0.07b 0.313±0.07d 0.136±0.04e 0.453±0.02c 1.062±0.40a Cu 4.323±0.11b 2.537±0.44c 2.364±0.55d 4.857±0.34a 4.863±0.26a Zn 8.348±0.98c 5.426±0.89e 6.688±0.81d 12.422±1.43a 11.065±1.69b Ba 6.585±0.96a 4.260±0.91c 2.278±0.54d 4.161±0.77c 5.898±0.61b 注:同行不同小写字母表示差异显著,P<0.05。 表 5 不同生长期黄芪样品10种无机元素相关性分析结果
Table 5 Correlation analysis results of ten inorganic elements in Astragalus membranaceus samples at different growth stages
Mg Ca V Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ba Mg 1 0.944* 0.86 0.902* 0.834 0.635 0.785 0.82 0.367 0.874 Ca 1 0.961** 0.921* 0.925* 0.707 0.828 0.668 0.172 0.949* V 1 0.913* 0.969** 0.852 0.767 0.622 0.126 0.949* Mn 1 0.806 0.83 0.925 0.848 0.501 0.983** Fe 1 0.791 0.601 0.522 -0.041 0.847 Co 1 0.621 0.673 0.352 0.815 Ni 1 0.741 0.527 0.928* Cu 1 0.815 0.737 Zn 1 0.357 Ba 1 注:*表示显著性相关,P<0.05;**表示极显著性相关,P<0.01。 表 6 不同生长时期黄芪主成分分析综合排名
Table 6 Comprehensive ranking of principal component analysis of Astragalus membranaceus at different growth stages
采收期 F1 F2 F 排名 6月 0.59 0.69 0.61 2 7月 −0.34 −1.22 −0.49 4 8月 −1.44 −0.01 −1.21 5 9月 −0.01 1.24 0.20 3 10月 1.20 −0.69 0.90 1 -
[1] 国家药典委员会. 中国药典(一部)[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020: 315 National Pharmacopoeia Commission. Chinese Pharmacopoeia (part 1)[M]. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2020: 315.
[2] 林红强, 杨娜, 王涵, 等. 黄芪的化学成分、药理活性及临床应用研究进展[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘,2018,18(38):45−47,49. [LIN Hongqiang, YANG Na, WANG Han, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents, pharmacological activity and clinical application of Astragali Radix[J]. World Latest Medicine Information,2018,18(38):45−47,49. LIN Hongqiang, YANG Na, WANG Han, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents, pharmacological activity and clinical application of Astragali Radix[J]. World Latest Medicine Information, 2018, 18(38): 45-47, 49.
[3] 范信晖, 李科, 杨一丹, 等. 基于分子量分布的黄芪多糖抗炎活性组分筛选及代谢组学调控机制研究[J/OL]. 药学学报: 1−25[2022-02-20].https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2163.R.20211026.2234.005.html FAN Xinhui, LI Ke, YANG Yidan, et al. Screening for anti-inflammatory components of Astragalus polysaccharide and metabolomics research based on molecular weight distribution[J/OL]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica: 1−25[2022-02-20].https://kns-cnki-net.webvpn.gszy.edu.cn/kcms/detail/11.2163.R.20211026.2234.005.html.
[4] 张颖, 王淳, 于丹, 等. 基于PI3K/Akt信号通路探讨黄芪多糖对肺腺癌A549/DDP细胞移植瘤EMT进程的影响[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2021,27(23):51−58. [ZHANG Ying, WANG Chun, YU Dan, et al. Effect of Astragalus polysaccharide on EMT of A549/DDP Lung adenocarcinoma xenograft: An exploration based on PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2021,27(23):51−58. ZHANG Ying, WANG Chun, YU Dan, et al. Effect of Astragalus polysaccharide on EMT of A549/DDP Lung adenocarcinoma xenograft: An exploration based on PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2021, 27(23): 51-58.
[5] 段海婧, 龙晓宙, 杜丽东, 等. 黄芪抗恶性肿瘤研究文献计量学分析及作用机制概述[J/OL]. 中药药理与临床: 1−14[2022-02-20]. DOI: 10.13412/j. cnki. zyyl. 20210924.001. DUAN Haijing, LONG Xiaozhou, Du Lidong, et al. Anti-tumor effect and mechanism of astragail radix based on bibiometric analysis[J/OL]. Pharmacology and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica: 1−14[2022-02-20]. DOI: 10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.20210924.001.
[6] ADHIKARI B, MARASINI B P, RAYAMAJHEE B, et al. Potential roles of medicinal plants for the treatment of viral diseases focusing on COVID-19: A review[J]. Phytother Res,2021,35(3):1298−1312. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6893
[7] 刘瑶, 李伟. 基于miRNA测序技术探讨黄芪-丹参药对干预自发性高血压大鼠肾损害的机制研究[J]. 中草药,2021,52(18):5599−5607. [LIU Yao, LI Wei. Mechanism of Astragali Radix and Salviae miltiorrhizae Radix et Rhizoma herbal pair on renal damage of spontaneously hypertensive rats based on miRNA sequencing technology[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2021,52(18):5599−5607. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2021.18.014 LIU Yao, LI Wei. Mechanism of Astragali Radix and Salviae Miltiorrhizae Radix et Rhizoma herbal pair on renal damage of spontaneously hypertensive rats based on miRNA sequencing technology[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2021, 52(18): 5599-5607. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2021.18.014
[8] DENG Shifang, YANG Lei, MA Ke, et al. Astragalus polysaccharide improve the proliferation and insulin secretion of mouse pancreatic β cells induced by high glucose and palmitic acid partially through promoting miR-136-5p and miR-149-5p expression[J]. Bioengineered,2021,12(2):9872−9884. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1996314
[9] LI Xuling, ZHAO Tingting, GU Junling, et al. Intake of flavonoids from Astragalus membranaceus ameliorated brain impairment in diabetic mice via modulating brain-gut axis[J]. Chinese Medicine,2022,17(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s13020-022-00578-8
[10] 魏斓, 王陵军, 何嘉琪, 等. 基于AKT/GSK3-β/SNAIL通路探讨黄芪甲苷对心力衰竭心肌纤维化小鼠的保护作用[J]. 中药新药与临床药理,2021,32(9):1231−1237. [WEI Lan, WANG Lingjun, HE Jiaqi, et al. Effect of Astragaloside IV preventing and treating myocardial fibrosis in mice with heart failure based on AKT/GSK3-β/SNAIL signaling pathway[J]. Traditional Chinese Drug Research and Clinical Pharmacology,2021,32(9):1231−1237. WEI Lan, WANG Lingjun, HE Jiaqi, et al. Effect of Astragaloside IV preventing and treating myocardial fibrosis in mice with heart failure based on AKT/GSK3-β/SNAIL signaling pathway[J]. Traditional Chinese Drug Research and Clinical Pharmacology, 2021, 32(9): 1231-1237.
[11] 秦合伟, 张勤生, 李彦杰, 等. 黄芪甲苷调控miR-17-5p与PCSK9/VLDLR信号通路抗动脉粥样硬化的分子机制研究[J]. 中国中药杂志,2022,47(2):492−498. [QIN Hewei, ZHANG Qinsheng, LI Yanjie, et, al. Molecular mechanism of astragaloside Ⅳ against atherosclerosis by regulating miR-17-5p and PCSK9/VLDLR signal pathway[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2022,47(2):492−498. QIN Hewei, ZHANG Qinsheng, LI Yanjie, et, al. Molecular mechanism of astragaloside Ⅳ against atherosclerosis by regulating miR-17-5p and PCSK9/VLDLR signal pathway[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2022, 47(02): 492-498.
[12] SHENG Zhili, JIANG Yueming, LIU Junmei, et al. UHPLC–MS/MS analysis on flavonoids composition in astragalus membranaceus and their antioxidant activity[J]. Antioxidants,2021,10(11):1853. doi: 10.3390/antiox10111853
[13] 张丽, 钱大玮, 卜凡淑, 等. 基于UPLC-MS的黄芪药材质量评价研究[J]. 药物分析杂志,2020,40(4):722−732. [ZHANG Li, QIAN Dawei, PU Fanshu, et al. Study on quality evaluation of Astragali Radix based on UPLC-MS[J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis,2020,40(4):722−732. ZHANG Li, QIAN Dawei, PU Fanshu, et al. Study on quality evaluation of Astragali Radix based on UPLC-MS[J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 2020, 40(4): 722-732.
[14] 黄华靖, 毕晓黎, 江洁怡, 等. 基于超高效液相色谱指纹图谱和多成分含量测定的黄芪益肾颗粒质量评价[J]. 中国医院药学杂志,2022,42(3):248−253. [HUANG Huajin, BI Xiaoni, JIANG Jieyi, et al. Quality evaluation of astragalus membranaceus kidney particles based on UPLC fingerprint and multi-componey content determination[J]. Chinese Journal of Hospital Pharmacy,2022,42(3):248−253. doi: 10.13286/j.1001-5213.2022.03.05 HUANG Huajin, BI Xiaoni, JIANG Jieyi, et al. Quality evaluation of astragalus membranaceus kidney particles based on UPLC fingerprint and multi-componey content determination[J]. Chinese Journal of Hospital Pharmacy, 2022, 42(3): 248-253. doi: 10.13286/j.1001-5213.2022.03.05
[15] 曹宇欣, 李科, 秦雪梅, 等. 基于糖特征图谱及免疫细胞活性研究的不同产地黄芪的质量评价[J]. 药学学报, 2019, 54(7): 1277−1287 CAO Yuxin, LI Ke, QIN Xuemei, et al. Quality evaluation of different areas of Astragali Radix based on carbohydrate specific chromatograms and immune cell activities[J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica, 2019, 54(7): 1277−1287.
[16] 王玲玲, 王博, 熊丰, 等. 不同产地蒙古黄芪矿物元素比较研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2022(5):1407−1412. [WANG Lingling, WANG Bo, Xiong Feng, et al. A comparative study of iornganic elements in Cultivativing Astragalus membranaceus from different habitats[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2022(5):1407−1412. WANG Lingling, WANG Bo, Xiong Feng, et al. A comparative study of iornganic elements in Cultivativing Astragalus Membranaceus from different habitats [J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2022(5): 1407-1412.
[17] 邹瀚霖, 汪弟, 饶必轩, 等. 基于有效成分和金属元素探讨不同产地黄芪的差异[J]. 中药材,2021(4):905−911. [ZOU Hanlin, WANG Di, RAO Bixuan, et al. Study on the differences of Astragalus membranaceus from different producing areas based on effective components and metal elements[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials,2021(4):905−911. ZOU Hanlin, WANG Di, RAO Bixuan, et al. Study on the differences of Astragalus membranaceus from different producing areas based on effective components and metal elements[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2021(4): 905-911.
[18] 陈植青, 贺超, 闫滨滨, 等. 营养元素对菘蓝生长特性的影响[J]. 中国现代中药, 2021(4): 1−15. CHEN Zhiqing, HE Chao, Yan Binbin, et al. Effects of nutrients on the growth characteristics of Isatis indigotica Fort. [J]. Modern Chinese Medicine, 2021(4): 1−15.
[19] 廉家敏, 陈实, 王立, 等. 微量元素缺乏对党参幼苗表观特征和生长的影响及部分生理特性测定[J]. 种子,2022,41(5):36−41. [LIAN Jiaming, CHEN Shi, WANG Li, et al. Effect of trace element deficiency on the growth, apparent characteristics and partial physiological characteristics determination of Codonopsis pilosula seedlings[J]. Seed,2022,41(5):36−41. LIAN Jiaming, CHEN Shi, WANG Li, et al. Effect of trace element deficiency on the growth, apparent characteristics and partial physiological characteristics determination of Codonopsis pilosula seedlings[J]. Seed, 2022, 41(5): 36-41.
[20] 刘靖, 洪浩, 蔡青圆, 等. 中药黄芪的资源分布与生态习性的调查研究[C]// 淄博: 全国第二届中药资源生态学学术研讨会论文集, 2006: 230−234 LIU Jin, HONG Hao, CAI Qingyuan, et al. Investigation on resource distribution and ecological habit of Astragalus membranaceus[C]// Zibo: Proceedings of the second National Conference on Ecology of Traditional Chinese Medicine Resources, 2006: 230−234.
[21] 韩佳慧, 万思涛, 俞娇, 等. 参与植物体内镉元素运转的植物锌铁运转蛋白ZIP研究进展[J]. 植物生理学报,2019,55(10):1449−1457. [HAN Hiahui, WAN Sitao, YU Jiao, et al. Progress on zinc and iron transporter(ZIP) involved in Cd transport in plants[J]. Plant Physiology Journal,2019,55(10):1449−1457. HAN Hiahui, WAN Sitao, YU Jiao, et al. Progress on zinc and iron transporter(ZIP) involved in Cd transport in plants[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2019, 55(10): 1449-1457.
[22] 姬丽君, 席旭东, 晋小军. 蒙古黄芪物候期研究[J]. 草业学报,2013,22(1):60−67. [JI Lijun, XI Xudong, JIN Xiaojun. A study on phonological phases of Astragalus membranaceus[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica,2013,22(1):60−67. doi: 10.11686/cyxb20130108 JI Lijun, XI Xudong, JIN Xiaojun, et al. A study on phonological phases of Astragalus membranaceus[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2013, 22(1): 60-67. doi: 10.11686/cyxb20130108
[23] 张丽婷, 王志强, 马兴立, 等. 植物中锌转运蛋白的研究进展[J]. 贵州农业科学,2014,42(8):55−60. [ZHANG Liting, WANG Zhiqiang, MA Xingli, et al. Research progress of zinc transporter in plant[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences,2014,42(8):55−60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2014.08.016 ZHANG Liting, WANG Zhiqiang, MA Xingli, et al. Research progress of zinc transporter in plant[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 42(8): 55-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2014.08.016
[24] 董如茵, 徐应明, 王林, 等. 土施和喷施锌肥对镉低积累油菜吸收镉的影响[J]. 环境科学学报,2015,35(8):2589−2596. [DONG Ruyin, XU Yinming, WANG Ling, et al. Effects of soil application and foliar spray of zinc fertilizer on cadmium uptake in a pakchoi cultivar with lowcadmium accumulation[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2015,35(8):2589−2596. DONG Ruyin, XU Yinming, WANG Ling, et al. Effects of soil application and foliar spray of zinc fertilizer on cadmium uptake in a pakchoi cultivar with lowcadmium accumulation[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2015, 35(8): 2589-2596
[25] 张玉秀, 张凯, 李金梅, 等. 镍在植物体中的吸收转运机制[J]. 中国生态农业学报,2008(3):778−782. [ZHANG Yuxiu, ZHANG Kai, LI Jingmei, et al. Absorption and transportation mechanism of nickel in plants[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture,2008(3):778−782. ZHANG Yuxiu, ZHANG Kai, LI Jingmei, et al. Absorption and transportation mechanism of nickel in plants[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2008(3): 778-782.
[26] 王子诚, 陈梦霞, 杨毓贤, 等. 铜胁迫对植物生长发育影响与植物耐铜机制的研究进展[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报,2021,27(10):1849−1863. [WANG Zichen, CHEN Mengxia, YANG Yuxian, et al. Effects of copper stress on plant growth and advances in the mechanisms of plant tolerance research[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer,2021,27(10):1849−1863. doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2021164 WANG Zichen, CHEN MMengxia, YANG Yuxian, et al. Effects of copper stress on plant growth and advances in the mechanisms of plant tolerance research[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2021, 27(10): 1849-1863. doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2021164
[27] 曾英, 倪师军, 张成江. 钒的生物效应及其环境地球化学行为[J]. 地球科学进展,2004(S1):472−476. [ZENG Ying, NI Shijun, ZHANG Chenjiang. Biological effects and environmental geochemical behavior of vanadium[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2004(S1):472−476. ZENG Ying, NI Shijun, ZHANG Chenjiang, et al. Biological effects and environmental geochemical behavior of vanadium[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2004(S1): 472-476.
[28] 黄毅. 黄芪营养特性及其养分状况对总黄酮和多糖的影响研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2006 HUANG Yi. Effects of nutritional properties and nutrient status of Astragalus membranaceus on total flavonoids and polysaccharides[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2006.
[29] 马世震, 陈志国, 李毅, 等. 陇西栽培黄芪不同生长期甲甙含量变化研究[J]. 干旱地区农业研究,2005(3):174−176. [MA Shizhen, CHEN Zhiguo, LI Yi, et al. Study on the changes of Astragalus membranaceus astragaloside IV in different growing stage in Longxi county[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas,2005(3):174−176. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7601.2005.03.037 MA Shizhen, CHEN Zhiguo, Li Yi, et al. Study on the changes of Astragalus Membranaceus astragaloside IV in different growing stage in Longxi county[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2005(3): 174-176. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7601.2005.03.037
[30] 余彦海, 黄婉锋. 不同生长期蒙古黄芪药材中皂苷类成分指纹图谱研究[J]. 西北药学杂志,2008(1):23−24. [YU Yanhai, HUANG Wanfeng. Fingerprint analysis of saponins in Astragalus mongholicus at different growth stages[J]. Northwest Pharmaceutical Journal,2008(1):23−24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2407.2008.01.013 YU Yanhai, HUANG Wanfeng. Fingerprint analysis of saponins in Astragalus mongholicus at different growth stages[J]. Northwest Pharmaceutical Journal, 2008(1): 23-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2407.2008.01.013
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 张苗苗,张雨晨,杨怡中,范盈盈,何伟忠,王成,黄伟,刘峰娟. 拮抗菌防治葡萄采后病害研究进展. 食品工业科技. 2024(09): 410-418 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 汤永玉,吴国星,朱国渊,李冉,施春兰,王思洁,杨燕通,高熹. 附子白绢病菌拮抗菌的鉴定、发酵条件优化及抑菌效果. 微生物学通报. 2023(07): 2892-2906 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 付清泉,王方方,李甜,史学伟,王斌. 鲜食葡萄采后霉菌的分离与鉴定. 食品安全导刊. 2023(33): 73-76 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



