Study on Quick Test Model for the Quality of Frying Oil from Western-style Fast Food Restaurants by Near Infrared Spectroscopy
-
摘要: 为对西式快餐用煎炸油质量进行快速监测,选用近红外光谱法(NIRS)联合偏最小二乘法(PLS),分别建立酸价和极性组分两个煎炸油质量指标的定量模型。结果表明,酸价和极性组分的定标模型校正决定系数(R2)均为0.9974,校正标准差均方根(RMSEC)分别为0.111和0.359,预测标准差均方根(RMSEP)分别为0.171和0.562。盲样验证、精密度及准确度分析结果显示,酸价和极性组分的NIR预测值同真实值的相关方程的相关系数分别为0.9944、0.9761,应用所建模型预测同一煎炸油样品的酸价和极性组分的相对标准偏差(RSD)分别为0.934%和1.278%,表明所建模型对煎炸油样品的酸价和极性组分预测能力较好,且有较好的重现性。因此,基于近红外光谱定量模型,可以对西式快餐用煎炸油质量进行快速、准确地监测。Abstract: In order to quickly detect the quality of frying oil from western-style fast food restaurants, calibration models of acid value and total polar compounds were established using near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) combined with partial least squares (PLS) to evaluate the frying oil quality. The findings presented that the correction coefficient of calibration model of acid value and total polar compounds were both 0.9974. The root mean square error of cross-validation (RMSEC) were 0.111 and 0.359, respectively. The root mean square error of prediction (RMSEP) were 0.171 and 0.562, respectively. The results of blind samples verification showed that the correlation coefficients between prediction value and true value for acid value and total polar compounds of frying oil were 0.9944 and 0.9761, respectively; the precision test showed that the relative standard deviations (RSD) of acid value and total polar components using the calibration models for the same frying oil sample were 0.934% and 1.278%, respectively, which indicated that the models of quantitative analysis of acid value and total polar compounds of frying oils were good with excellent prediction abilities and reproducibility. Therefore, the rapid detection model based on near infrared spectroscopy could rapidly and accurately detect the quality of frying oil from western-style fast food restaurants.
-
Keywords:
- frying oil /
- near infrared spectroscopy /
- acid value /
- total polar compounds
-
煎炸是世界上最为流行的食品烹饪方法之一,煎炸食品因其口感酥脆、色泽金黄和风味特殊而深受人们欢迎[1],尤其是西式快餐(如肯德基、麦当劳、德克士等)随着生活节奏的加快得到空前的发展。然而,在煎炸过程中,作为传热介质的煎炸油因长时间反复使用,发生氧化、水解、聚合等化学反应[2-4],进而产生有害物质,包括非挥发性的游离脂肪酸、非皂化产物、环状化合物、三酰甘油氧化聚合物等以及挥发性的烃类、醛、酮、呋喃、羧酸等[5-7],同时还伴有颜色加深、起泡、黏度增加等感观变化,使食用油的营养价值大大降低,并且影响了煎炸食品的品质和安全性,不利于消费者的健康[8-10]。酸价和极性组分是我国国标GB2716-2018《植物油》中判断煎炸过程中油脂是否劣变的指标[11],但这两个指标的测定相对均需消耗大量化学试剂,对人体与环境的污染较大,且过程繁琐、耗时费力、易造成较大人为误差,因此不便用于大批量样本的快速测定[12]。所以,探索开发快速检测煎炸过程中煎炸油质量的方法,对煎炸油的使用安全具有重要意义。
近红外光谱(NIRS)技术作为将测量技术与化学计量学等学科结合发展起来的一种高新分析技术,因其操作简单、快捷、无损、无污染、可远程分析等优点[13-15],近年来发展迅速,被普遍应用于各种领域,如食品、石油化工、农业、生物工程、医药等[16-18]。同时,在食用油产地鉴别、食用油品质鉴定、掺假等方面都有应用。SINELLI等[19]探讨了NIRS结合化学计量学对意大利特级初榨橄榄油进行品种分类,通过建立软独立建模分类法(SIMCA)与线性判别分析(LDA)两种分类模型,并将其作为特征选择技术,成功鉴别了橄榄油的品质;BASRI等[20]应用NIR技术检测棕榈油中是否存在猪油掺假,采用了SIMCA算法,并将纯棕榈油样本、掺杂(多种掺假)样本进行详细分类,经检测实验发现分类模型的精准度高达95%以上。张青青等[21]也利用NIRS快速分析建立了实验室条件下3种煎炸油的3个质量指标的定量模型,实现了对马铃薯煎炸油品质的快速鉴定。然而,基于近红外光谱建立西式快餐实际煎炸条件下煎炸油的国家标准中现有两个质量指标(酸价和极性组分)的定量模型研究仍鲜有报道。
本研究以模拟西式快餐实际煎炸条件下的煎炸油为研究对象,对使用不同程度的煎炸油样品进行NIR光谱采集,基于NIRS技术结合偏最小二乘法(PLS),分别建立国标中规定的酸价和极性组分两个煎炸油质量指标的定量模型,以实现煎炸油质量的快速检测,为西式快餐行业的质量监控与管理提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
大豆油、菜籽油、棕榈油、稻米油、葵花籽油、玉米油、花生油、高油酸菜籽油、高油酸葵花籽油、高油酸调和油、餐饮调和油A、餐饮调和油B 均采购于当地商场;冷冻薯条 内蒙古蓝威斯顿薯业有限公司;氢氧化钾、乙醚、异丙醇、无水乙醇、石油醚、无水硫酸钠、丙酮、三氯甲烷、冰乙酸、磷钼酸 均为分析纯,上海国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
OFE-28A型电热炸炉 上海一喜食品机械有限公司;Antaris II傅里叶变换近红外光谱仪 美国Thermo Nicolet公司;W201恒温水浴锅 上海申胜生物技术有限公司;恒温干燥箱 安捷伦科技(中国)有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 油样采集
在前期调研的基础上,模拟实际西式快餐煎炸条件[22],即将13 L煎炸油倒入煎炸锅中,加热并保持油温在(170±5)℃,称取市售冷冻薯条200 g,放入热油中炸3 min(中途1.5 min左右提起炸篮翻动一次)后捞起,每小时炸5批,每天炸12 h,连续煎炸8 d。每煎炸6 h后过滤一次,过滤时,停止加热,并清洁油炸锅内壁,向滤油槽加入60 g滤油粉(滤油2次后更换),搅拌5 min,抽回至油缸中,滤油后添加新鲜油至起始刻度线(13 L)处。每天煎炸完成后,待油冷却,用棕色瓶收集油样。试验采集了煎炸不同时间(0~96 h)后的不同煎炸油样品,共101个。煎炸用油的种类及样品个数分别为大豆油(9个)、菜籽油(8个)、棕榈油(12个)、稻米油(8个)、葵花籽油(8个)、玉米油(8个)、花生油(8个)、高油酸菜籽油(8个)、高油酸葵花籽油(8个)、高油酸调和油(8个)、餐饮调和油A(8个)、餐饮调和油B(8个)。采集的样品放置于−4 ℃冰箱中待检测。
1.2.2 光谱采集
参考文献方法[12],光谱采集选用傅里叶变换近红外光谱仪并以透射方式进行NIR光谱扫描。将仪器预热后,取2 mL油样于6 mm样品管中,并于55 ℃下预热2 min,再扫描各煎炸油样的光谱,每个样品平行采集三次,取其平均光谱图进行建模。
NIR光谱扫描范围10000~4000 cm−1,分辨率为8 cm−1,扫描次数32次,以内置背景为参照。
1.2.3 化学指标测定
酸价的测定参照GB/T 5009.229-2016《食品中酸价的测定》中的冷溶剂指示剂滴定法;极性组分的测定参照GB 5009.202-2016《食用油中极性组分(PC)的测定》中的柱层析法。
1.2.4 模型的构建与优化
为消除采集的NIRS原始光谱中噪音信号影响,对原始光谱作必要的预处理,如一阶导数,二阶导数,平滑等。
采用近红外光谱仪自身配置TQ Analyst 9.0软件中的PLS,分别建立煎炸油酸价、极性组分的定量分析模型。以校正决定系数(R2),校正误差均方根(RMSEC),预测误差均方根(RMSEP)作为模型主要的评价指标,即R2越接近1,RMSEC和RMSEP越接近0,表明模型的准确性和可靠性越好,进而挑选出最佳模型。
1.3 数据处理
除特别说明外,所有试验均重复三次,数据均以平均值表示。利用Excel 2017对数据进行处理作图,采用IBM SPSS Statistics 20.0对样品的预测值和真实值进行配对T测验分析,根据分析结果来判断模型的可靠性。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 煎炸油样品近红外光谱
图1为模拟西式快餐条件下所得煎炸油样品的近红外光谱。从图1中可以看出,不同煎炸油在煎炸不同时间后得到101个样品的近红外光谱图间非常相似,几乎重叠在一起,差异性很小,很难通过直观的分析区分煎炸油的煎炸时间长短及质量差异。由图1可见,光谱在4500~4770、5685、5800、7087、7197、8271 cm−1等处有较强的吸收峰,因此,建立模型的波谱范围选择在4400~8600 cm−1。通常来说,4500~4770 cm−1附近可能与C-H和C=O伸缩振动的合频有关;5685、5800 cm−1处的吸收峰是油脂中-CH2、-CH3、-HC=CH-中的C-H伸缩振动的一级倍频;7087和7197 cm−1是OH的倍频吸收;8271 cm−1处吸收峰与脂肪烃中C-H的伸缩振动的二级倍频有关[23-24]。
2.2 理化指标检测结果
本试验收集了101个煎炸油样品,根据煎炸不同时间所得煎炸油样品的酸价和极性组分含量分布,选择校正集和验证集用于定性定量模型的建立,校正集样品信息应该包含验证集样品信息[25],从样品中选取88个作为校正集样品,13个作为验证集样品,其结果分布如表1所示。从表1中可以看出,建模所收集的校正集和验证集煎炸油样品的酸价范围分别为0.11~8.96、0.23~5.22 mg KOH/g,极性组分范围分别为3.83%~28.00%、7.33%~27.67%,这与文献[26]报道的测量范围相符。此外,校正集和验证集样品的酸价和极性组分数值分布均接近且范围较宽,均覆盖了GB2716-2018《植物油》国家标准中规定范围(酸价≤5 mg KOH/g;极性组分≤27%)内可能出现的指标值。因此,建模收集的样品具有较强的代表性,适合建立煎炸油的定量分析模型。
表 1 煎炸油定量分析模型校正集和验证集酸价和极性组分的分布Table 1. Acid value and total polar compounds content of calibration set and validation set of quantitative analysis model for frying oil样品类别 项目 校正集(88个) 验证集(13个) 酸价(mg KOH/g) 范围 0.11~8.96 0.23~5.22 均值 1.56 1.81 极性组分(%) 范围 3.83~28.00 7.33~27.67 均值 13.48 13.66 2.3 筛选波长范围
傅里叶变换近红外光谱仪所采集的光谱除样品的自身信息外,还包含了其它无关的干扰信息。这些无关信息的存在会影响用化学计量学方法对光谱数据建立模型的准确性。通过对NIR光谱图进行一阶导数处理,可以进一步确定建模的波长范围。图2为煎炸油样品的一阶导数光谱图,由图可见,相比于原始近红外图谱具有更高分辨率以及清晰度的图谱变化特征,煎炸油样品主要在4400~8600 cm−1处有吸收峰,故选择4400~8600 cm−1作为校正集与验证集模型的波段范围。
2.4 样品奇异值剔除
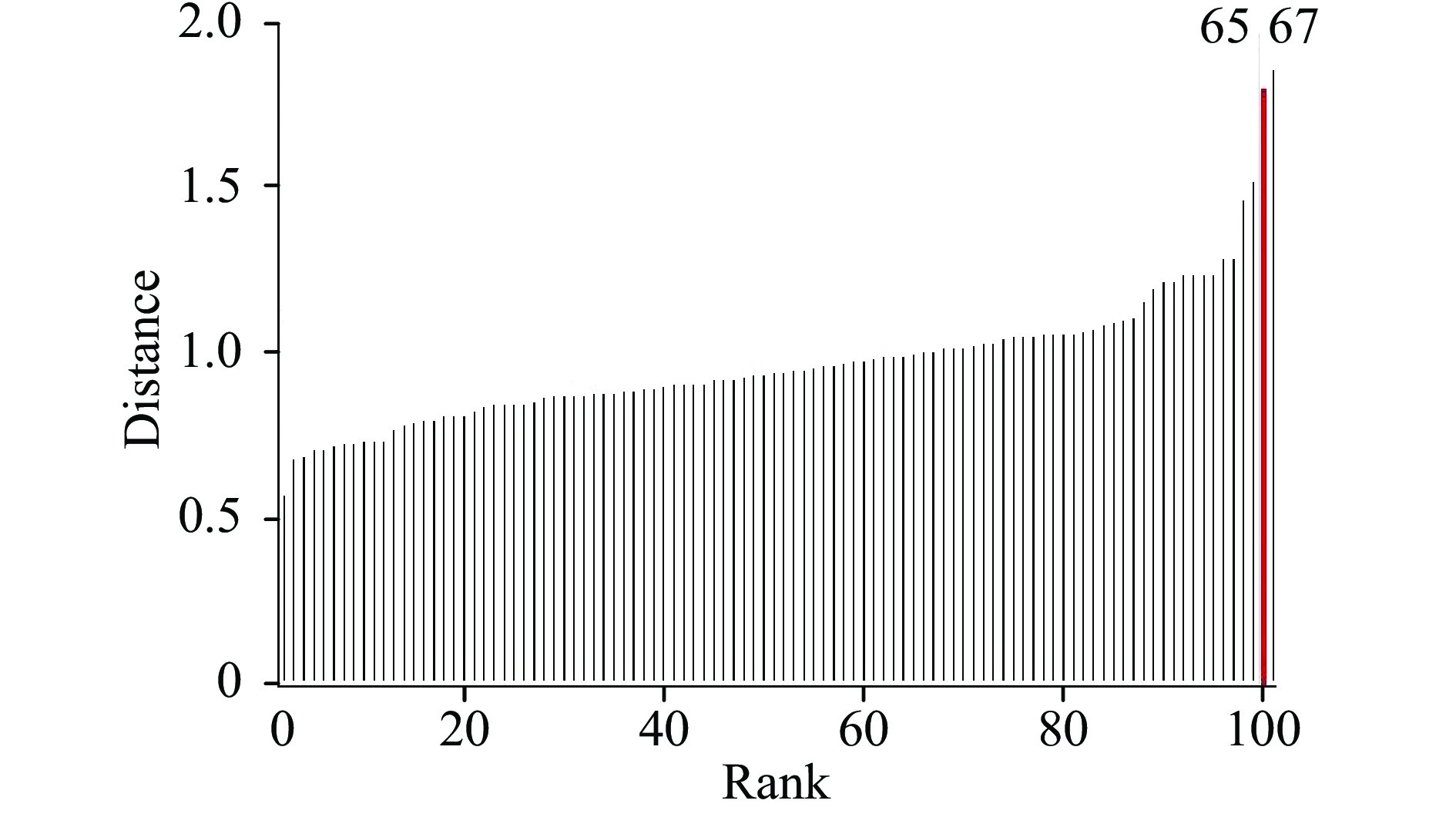
通常,奇异样品是指化学值或光谱的测量值同真实值存在较大误差的样品。样品奇异值(outlier)产生的主要原因包括样品来源或测定方法的变化、仪器或方法的可靠性以及人为操作失误等;此外,光谱也会因光谱仪本身误差、测量环境或方法的变化、样品来源的变化等因素发生异常[27-28]。在近红外光谱建模时,时常会出现奇异样品,奇异样品的存在会对模型的准确度产生一定程度甚至严重的影响[29],因此,需将异常样品剔除。奇异样品可由光谱的分布差异计算马氏距离来鉴别。图3为煎炸油样品的马氏距离分布图,从图中可见,第65号和67号样品马氏距离过大,作为奇异光谱样本给予剔除。
2.5 光谱数据的预处理
在NIR光谱的采集中,高频噪音、散射光、样品背景等因素都会影响建模的准确性,因此,在建模过程中,常先应用化学计量学软件对样品原始光谱进行预处理[30]。通常,导数处理及平滑处理是光谱预处理的常见方法,其中,导数处理包括一阶及二阶导数,主要是为了消除来自背景干扰及光谱基线漂移的影响;平滑处理包括Norris derivative filter(Norris平滑)和Savitzky-Golay filter(S-G平滑)等,主要的目的是消除来自随机噪声的影响[30-31]。本试验通过以R2、RMSEC及RMSEP作为模型综合评价指标,分析了不同光谱预处理方法对煎炸油样品酸价、极性组分定量分析模型的影响,其结果如表2、表3所示。从表中可以看出,相比其他预处理方法,酸价模型的二阶导数结合Norris平滑方法的效果更好,处理后煎炸油PLS酸价定量模型的校正决定系数R2为0.9974,校正标准差均方根RMSEC为0.111,预测标准差均方根RMSEP为0.171;极性组分模型的一阶导数结合Norris平滑方法的效果更优,处理后煎炸油PLS极性组分定量模型的R2为0.9974,RMSEC为0.359,RMSEP为0.562。
表 2 不同光谱预处理对煎炸油酸价定量分析模型的影响Table 2. Effect of various pretreatment methods on the performance of quantitative analysis model of acid value for frying oil预处理方法 R2 RMSEC RMSEP 无处理 0.9966 0.125 0.142 一阶导数 0.9956 0.146 0.343 一阶导数+S-G平滑 0.9940 0.167 0.254 一阶导数+Norris平滑 0.9961 0.134 0.131 二阶导数 0.2197 1.490 1.320 二阶导数+S-G平滑 0.9834 0.277 0.577 二阶导数+Norris平滑 0.9974 0.111 0.171 表 3 不同光谱预处理对煎炸油极性组分定量分析模型的影响Table 3. Effect of various pretreatment methods on the performance of quantitative analysis model of total polar compounds for frying oil预处理方法 R2 RMSEC RMSEP 无处理 0.9956 0.468 0.706 一阶导数 0.9959 0.453 1.130 一阶导数+S-G平滑 0.9956 0.464 1.010 一阶导数+Norris平滑 0.9974 0.359 0.562 二阶导数 0.9445 1.630 3.090 二阶导数+S-G平滑 0.9933 0.576 1.280 二阶导数+Norris平滑 0.9967 0.402 0.652 2.6 主因子数的确定
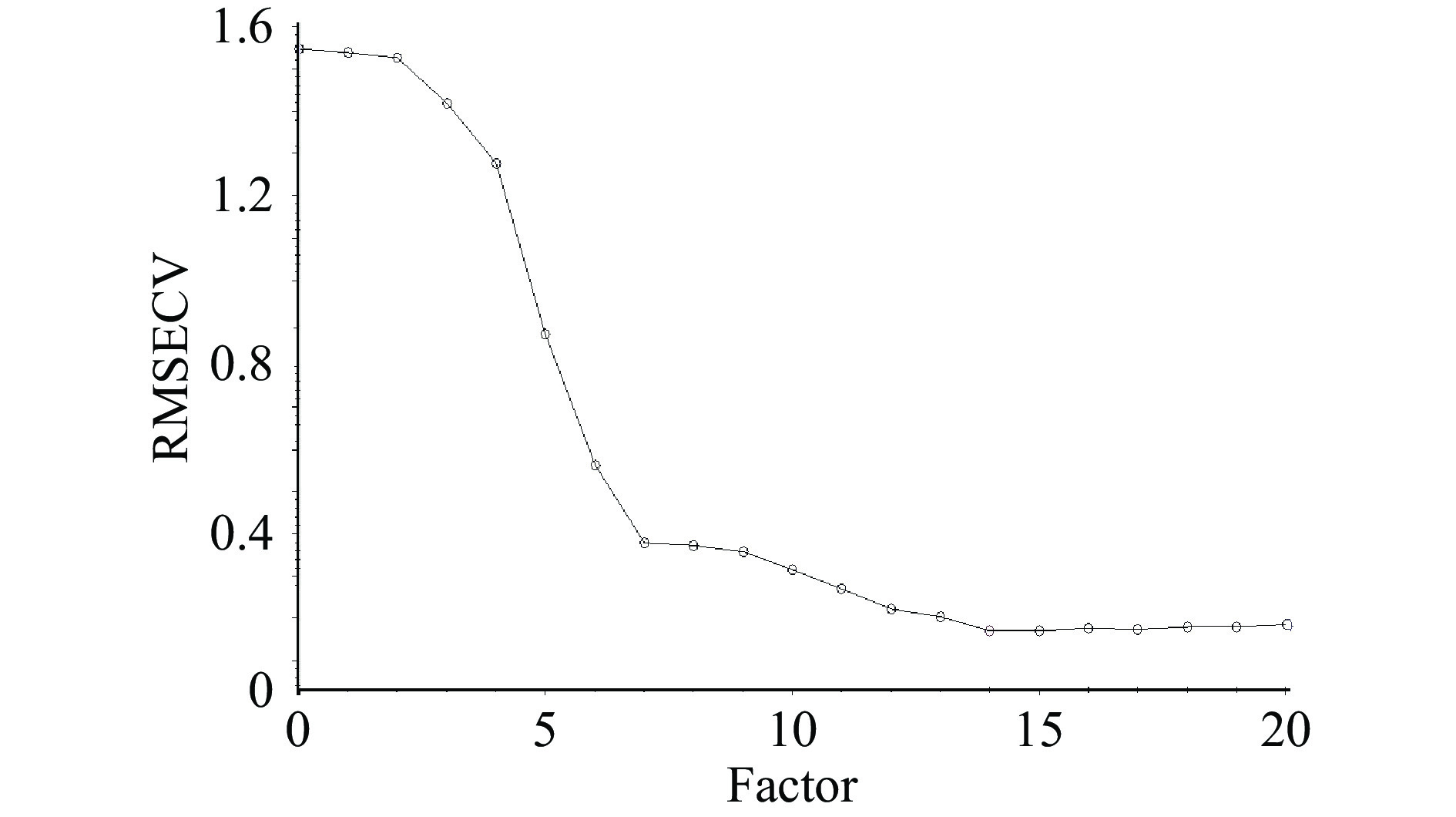
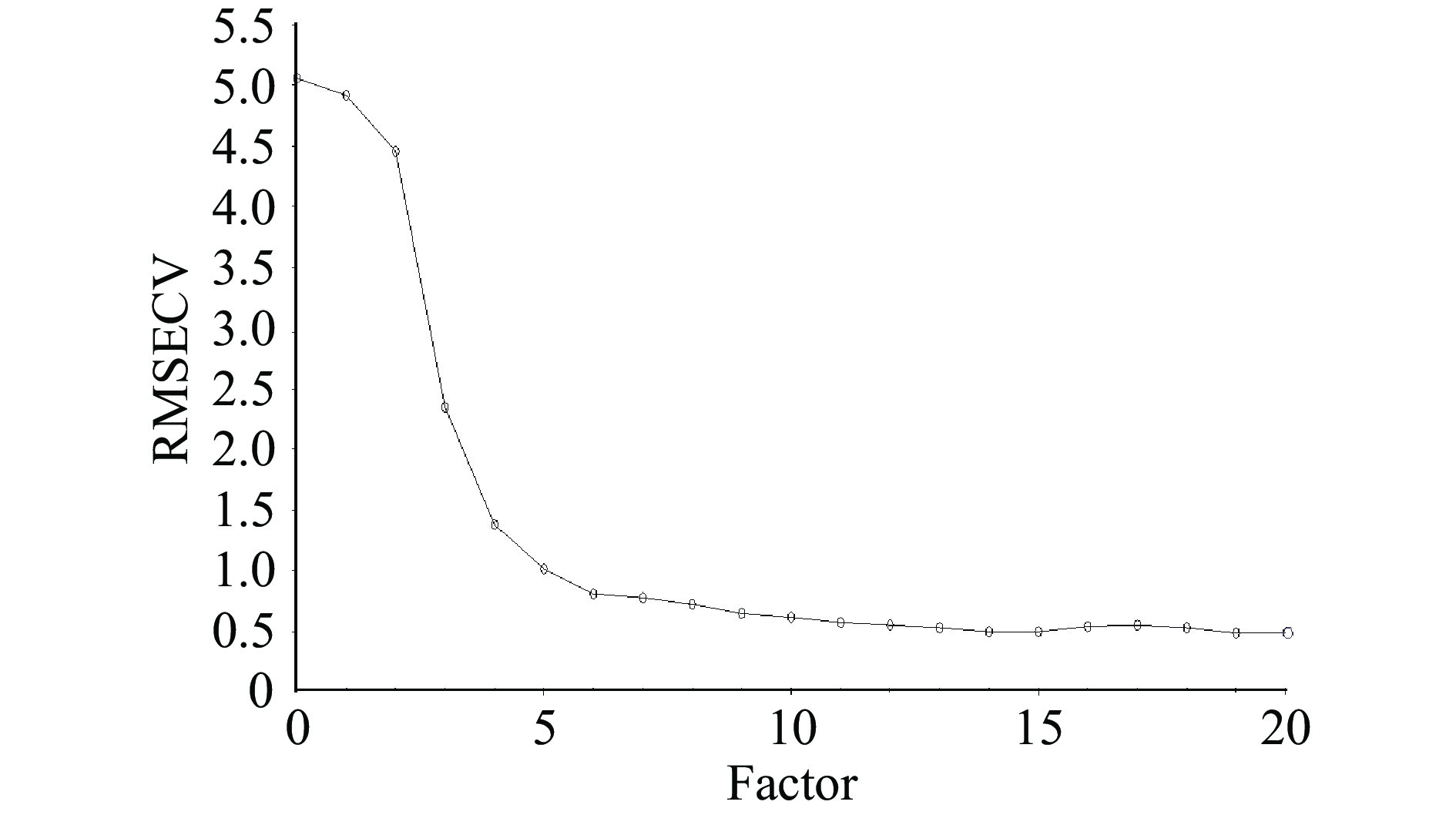
在进行定量回归时,定量模型的稳定性和预测性与PLS模型因子数相关。因子数过小会导致模型产生较大的误差,反之,因子数过多可能会导致模型过度拟合,不适于新样品的预测[32]。定量分析模型以校正集样本的交叉验证均方根误差(RMSECV)为评价指标,当RMSECV的第一个极小值出现时,所建模型的可行性通常为最好,即为最优的主因子数。图4、图5分别为酸价与极性组分定量模型的RMSECV随主因子数的变化图,由图可知,酸价、极性组分定量模型的最佳主因子数均选择14。
2.7 模型建立
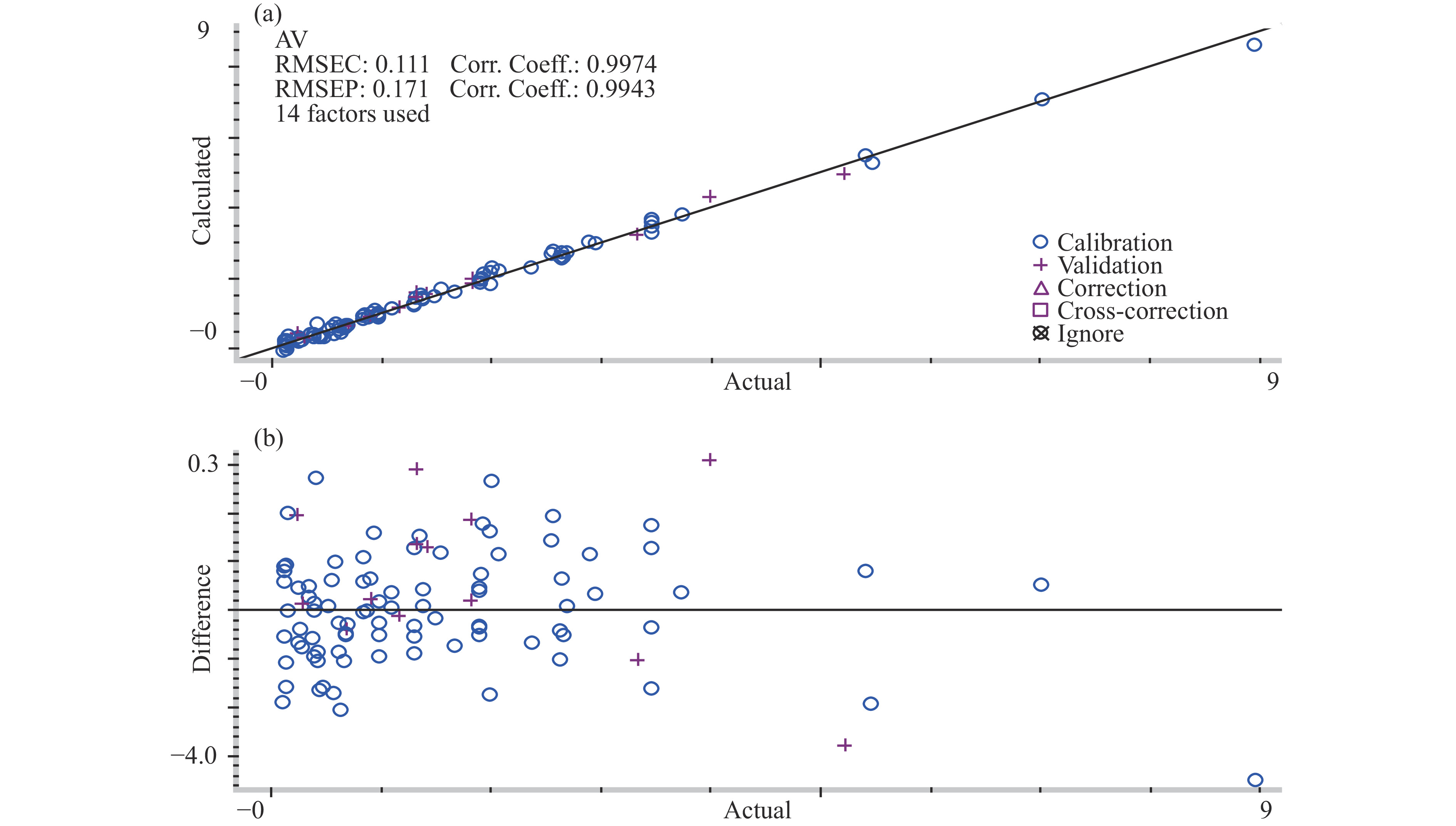
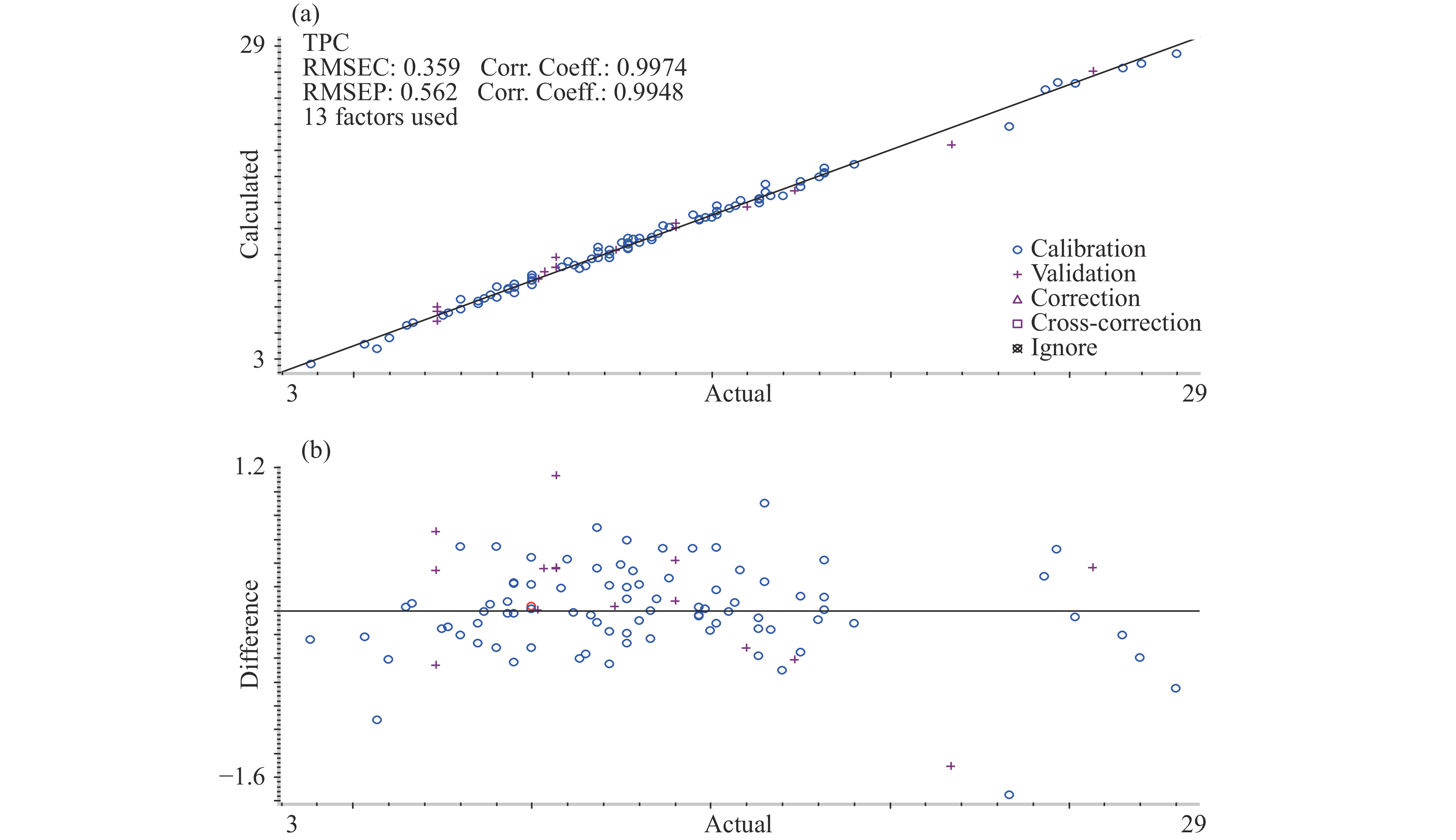
用上述所优化的建模参数建立酸价和极性组分的定量分析模型。酸价模型采用二阶导数结合Norris平滑的光谱预处理方法,主因子数为14,建立模型,煎炸油酸价的近红外光谱PLS建模结果及偏差分布分别如图6a、图6b所示,由图可知,酸价定量模型校正集和验证集的误差均方根分别为0.111、0.117,决定系数分别为0.9974和0.9943,误差分布在−0.38~0.32 mg KOH/g之间,说明模型的预测效果较好;极性组分模型采用一阶导数结合Norris平滑的光谱预处理方法,主因子数为14,建立模型,煎炸油极性组分的近红外光谱PLS建模结果及偏差分布分别如图7a、图7b所示,由图可知,极性组分定量模型校正集和验证集的误差均方根分别为0.359、0.562,决定系数分别为0.9974和0.9948,误差分布在−1.6%~1.2%之间,表明模型的预测能力较好。
2.8 盲样验证
为验证所建模型对未知样品预测的准确性,本试验收集了15个未知煎炸油样品,应用NIR光谱仪扫描获得光谱数据,并将其导入已建好的酸价、极性组分模型得出相应的预测值。另一方面,根据国标方法分别分析未知煎炸油样品的酸价、极性组分,并对NIR预测值同其相应的真实值进行线性回归,分析结果如图8a、图8b所示。由图可见,在煎炸油酸价、极性组分的盲样验证过程中,酸价和极性组分的NIR预测值同真实值的相关方程的相关系数分别为0.9944、0.9761,接近于1,R2都大于0.99且在Y轴上的截距接近于0,这说明盲样验证的效果较理想,进而表明所建酸价、极性组分模型对未知煎炸油样品有较好的预测能力。
此外,通过15个煎炸油盲样的NIR预测值与真实值,可以算出酸价、极性组分两个指标的相对分析误差(RPD)分别为7.25、15.26,均大于3,表明酸价、极性组分模型具有较好的定标效果,可以用于实际检测。
2.9 精密度和准确度分析
应用统计学方法对煎炸油未知盲样的酸价、极性组分预测值的精密度和准确度进行分析,将15个未知盲样的NIR预测值同真实值进行t检验,以判断NIRS法和国标法间差异是否显著。酸价、极性组分的t15,0.05分别为0.968、0.942,均大于0.05,表明NIRS与国标法间不存在显著性差异。
对同一个煎炸油样品的光谱平行扫描8次,应用所建定量分析模型预测该煎炸油样品的酸价和极性组分,其相对标准偏差(RSD)分别为0.934%和1.278%,均小于10%,结果说明该方法有较好的重现性。
3. 结论
本研究以模拟西式快餐实际煎炸条件下得到的101个煎炸油样品为原料,基于近红外光谱结合PLS法分别建立煎炸油质量指标酸价和极性组分的定量分析模型。酸价和极性组分的定标模型校正决定系数(R2)均为0.9974,校正标准差均方根(RMSEC)分别为0.111、0.359,预测标准差均方根(RMSEP)分别为0.171、0.562,说明所建酸价、极性组分定量分析模型均较理想,对煎炸油样品的酸价、极性组分的预测能力较好。
通过盲样验证、精密度及准确度分析,表明NIRS和国标法间相关性较好,无显著性差异,且有较好的重现性,进一步证明所建模型的准确性及稳定性。因此,基于NIRS所建酸价、极性组分定量分析模型可以快速准确地检测煎炸油的酸价和极性组分,为西式快餐煎炸过程中实时监测煎炸油的质量提供了技术参考和理论依据。本研究中煎炸油代表性样品还相对较少,尤其是酸价高于8.96 mg KOH/g或者极性组分含量高于28%的样品,在模型后期的应用中应进一步增加样本种类与数量,继续进行优化,以提高模型的适用性,确保实际应用效果。
-
表 1 煎炸油定量分析模型校正集和验证集酸价和极性组分的分布
Table 1 Acid value and total polar compounds content of calibration set and validation set of quantitative analysis model for frying oil
样品类别 项目 校正集(88个) 验证集(13个) 酸价(mg KOH/g) 范围 0.11~8.96 0.23~5.22 均值 1.56 1.81 极性组分(%) 范围 3.83~28.00 7.33~27.67 均值 13.48 13.66 表 2 不同光谱预处理对煎炸油酸价定量分析模型的影响
Table 2 Effect of various pretreatment methods on the performance of quantitative analysis model of acid value for frying oil
预处理方法 R2 RMSEC RMSEP 无处理 0.9966 0.125 0.142 一阶导数 0.9956 0.146 0.343 一阶导数+S-G平滑 0.9940 0.167 0.254 一阶导数+Norris平滑 0.9961 0.134 0.131 二阶导数 0.2197 1.490 1.320 二阶导数+S-G平滑 0.9834 0.277 0.577 二阶导数+Norris平滑 0.9974 0.111 0.171 表 3 不同光谱预处理对煎炸油极性组分定量分析模型的影响
Table 3 Effect of various pretreatment methods on the performance of quantitative analysis model of total polar compounds for frying oil
预处理方法 R2 RMSEC RMSEP 无处理 0.9956 0.468 0.706 一阶导数 0.9959 0.453 1.130 一阶导数+S-G平滑 0.9956 0.464 1.010 一阶导数+Norris平滑 0.9974 0.359 0.562 二阶导数 0.9445 1.630 3.090 二阶导数+S-G平滑 0.9933 0.576 1.280 二阶导数+Norris平滑 0.9967 0.402 0.652 -
[1] HU M M, ZHU M, XIN L, et al. Change of benzo (a) pyrene during frying and its groove binding to calf thymus DNA[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,350:129276. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129276
[2] LI X, WU X J, LIU R J, et al. Effect of frying conditions on fatty acid profile and total polar materials via viscosity[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,166:349−355.
[3] LI X D, LI J W, WANG Y, et al. Effects of frying oils’ fatty acids profile on the formation of polar lipids components and their retention in French fries over deep-frying process[J]. Food Chemistry,2017,237:98−105. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.05.100
[4] KOH E, SURH J. Food types and frying frequency affect the lipid oxidation of deep frying oil for the preparation of school meals in Korea[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,174:467−472. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.11.087
[5] ZHU Y, LI X, HUANG J H, et al. Correlations between polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and polar components in edible oils during deep frying of peanuts[J]. Food Control,2018,87:109−116. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.12.011
[6] ALADEDUNYE F, PRZYBYLSKI R. Performance of palm olein and modified rapeseed, sunflower, and soybean oils in intermittent deep-frying[J]. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology,2014,116:144−152. doi: 10.1002/ejlt.201300284
[7] HAO X W, LI J, YAO Z L. Changes in PAHs levels in edible oils during deep-frying process[J]. Food Control,2016,66:233−240. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.02.012
[8] WAGHMAREA A, PATILA S, LEBLANC J G, et al. Comparative assessment of algal oil with other vegetable oils for deep frying[J]. Algal Research,2018,31:99−106. doi: 10.1016/j.algal.2018.01.019
[9] SANTOS C S P, MOLINA-GARCIA L, CUNHA S C, et al. Fried potatoes: Impact of prolonged frying in monounsaturated oils[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,243:192−201. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.09.117
[10] RAHIMI J, ADEWALE P, NGADI M, et al. Changes in the textural and thermal properties of batter coated fried potato strips during post frying holding[J]. Food and Bioproducts Processing,2017,102:136−143. doi: 10.1016/j.fbp.2016.12.013
[11] 中华人民共和国卫生部. GB 5009.202-2016. 食品安全国家标准 食用油中极性组分(PC)的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016 Ministry of Health of the People's Republic of China. GB 5009.202-2016. National standards of China-Determination of polar component (PC) in edible oil [S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016.
[12] 万毅, 张玉, 杨华, 等. 基于近红外光谱的橄榄油理化指标快速检测模型研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(21):257−262. [WANG Y, ZHANG Y, YANG H, et al. Study on rapid detection model of physical and chemical indexes of olive oil based on near infrared spectroscopy[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(21):257−262. [13] 汪鑫, 田花丽, 马卓, 等. 近红外光谱技术在油料作物快速检测中的应用研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发,2021,42(22):220−224. [WANG X, TIAN H L, MA Z, et al. Research process in application of near infrared spectroscopy in rapid detection of oil crops[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(22):220−224. [14] 刘爽, 柴春祥. 近红外光谱技术在水产品检测中的应用进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测 学报,2021,12(21):8590−8596. [LIU S, CHAI C X. Application progress of near infrared spectroscopy in aquatic products detection[J]. Food Safety and Quality Detection Technology,2021,12(21):8590−8596. [15] 褚小立, 史云颖, 陈瀑, 等. 近五年我国近红外光谱分析技术研究与应用进展[J]. 分析测试学报,2019,38(5):603−611. [CHU X L, SHI Y Y, CHEN P, et al. Research and application progresses of near infrared spectroscopy analytical technique in China in past five years[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis,2019,38(5):603−611. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2019.05.016 [16] TEIXEIRA DOS SANTOS C A, LOPO M, PÁSCOA R N M J, et al. A review on the applications of portable near-infrared spectrometers in the agro-food industry[J]. Applied Spectroscopy,2013,67(11):1215−1233. doi: 10.1366/13-07228
[17] HELL J, PRÜCKLER M, DANNER L, et al. A comparison between near-infrared (NIR) and mid-infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy for the multivariate determination of compositional properties in wheat bran samples[J]. Food Control,2016,60:365−369. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.08.003
[18] 张勇, 王督, 李雪, 等. 基于近红外光谱技术的农产品产地溯源研究进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2018,9(23):6161−6166. [ZHANG Y, WANG D, LI X, et al. Research progress of near infrared spectroscopy based geographical origin traceability of agricultural products[J]. Food Safety and Quality Detection Technology,2018,9(23):6161−6166. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2018.23.015 [19] SINELLI N, CASALE M, EGIDIO V D, et al. Varietal discrimination of extra virgin olive oils by near and mid infrared spectroscopy[J]. Food Research International,2010,43(8):2126−2131. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2010.07.019
[20] BASRI K N, HUSSAIN M N, BAKAR J, et al. Classification and quantification of palm oil adulteration via portable NIR spectroscopy[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular & Biomolecular Spectroscopy,2017,173:335−342.
[21] 张青青, 沈晓芳, 马晶晶, 等. 近红外光谱法快速分析马铃薯煎炸油的品质[J]. 中国油脂,2019,44(1):132−136. [ZHANG Q Q, SEHN X F, MA J J, et al. Rapid analysis of oil quality in potato frying system by near-infrared spectroscopy[J]. China Oils and Fats,2019,44(1):132−136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7969.2019.01.029 [22] HU M M, PAN K L, NIU Y T, et al. Comparative assessment of thermal resistance of palm stearin and high oleic blended oil when subjected to frying practice in fast food restaurants[J]. Journal of Oil Palm Research,2020,32(1):90−102.
[23] WANG L, LEE F S C, WANG X R, et al. Feasibility study of quantifying and discriminating soybean oil adulteration in camellia oils by attenuated total reflectance MIR and fiber optic diffuse reflectance NIR[J]. Food Chemistry,2006,95(3):529−536. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.04.015
[24] CHRISTY A A, KASEMSUMRAN S, DU Y P, et al. The detection and quantifcation of aduteration in olive oil by near-infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics[J]. Analytical Sciences,2004,20:935−940. doi: 10.2116/analsci.20.935
[25] 胡小莉, 白雁, 雷敬卫, 等. NIRS结合TQ软件对不同产地野菊花定性定量分析[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2016,22(15):37−41. [HU X L, BAI Y, LEI J W, et al. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of Chrysanthemi Indici Flos from different origins by using NIRS and TQ software[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2016,22(15):37−41. [26] 冯国霞. 西式快餐用高油酸型煎炸油的研究与应用[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2015 FENG G X. Research and application of high-oleic frying oil for western-style fast food industry[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2015.
[27] 闵顺耕, 李宁, 张明祥. 近红外光谱分析中异常值的判别与定量模型优化[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2004,24(10):1205−1209. [MIN S G, LING N, ZHANG M X, et al. Outlier diagnosis and calibration model optimization for near infrared spectroscopy analysis[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2004,24(10):1205−1209. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0593.2004.10.014 [28] 赵怡锟, 于燕波, 申兵辉, 等. 近红外光谱分析在玉米单籽粒品种真实性鉴定中的影响因素[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2020,40(7):2229−2234. [ZHAO Y K, YU Y B, SHEN B H, et al. Influence factors in near-infrared spectrum analysis for the authenticity identification of maize single-kernel varieties[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2020,40(7):2229−2234. [29] SHETTY N, DIFFORD G, LASSEN J, et al. Predicting methane emissions of lactating Danish Holstein cows using Fourier transform mid-infrared spectroscopy of milk[J]. Journal of Dairy Science,2017,100(11):9052−9060. doi: 10.3168/jds.2017-13014
[30] RINNAN A, VAN DEN BERG F, ENGELSEN S B. Review of the most common pre-processing techniques for near-infrared spectra[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry,2009,28(10):1201−1222. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2009.07.007
[31] ISAKSSON T, NAES T. The effect of multiplicative scatter correction (MSC) and linearity improvement in NIR spectroscopy[J]. Applied Spectroscopy,1988,42(7):1273−1284. doi: 10.1366/0003702884429869
[32] 冯利辉. 食用植物油掺伪检测与定量分析的近红外光谱研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2010 FENG L H. Detection of adulteration and quantilation analysis of edible vegetable oil by near infrared spectrcosopy[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2010.
-
期刊类型引用(19)
1. 施江南,温乐乐,江丽洁,陈俊宇,施呈林,叶梓,李灿,徐晴,吴建军,崔琦,秦路平,刘巨钊. 基于文献计量学的覆盆子研究热点与趋势分析. 中草药. 2025(02): 598-616 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 贾苗苗,吴明慧,谢和兵,袁志兵,尼玛次仁. 藏药痛风丸HPLC特征图谱及7种成分含量测定研究. 中南药学. 2025(03): 668-673 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李色杰,梁锦,罗清淋,黄龙江,郑广进,黄桔. 鞣花酸对胃癌细胞生长及迁移的作用研究. 广东化工. 2024(07): 69-71 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 吴明慧,江德恩,杨俊峰,王佩,袁志兵,谢和兵. 藏药十味乳香散HPLC特征图谱及5个成分的含量测定. 中国现代中药. 2024(11): 1980-1988 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 殷燕,刘玉宁,王佩,刘艳萍,袁志兵,谢和兵. HPLC法同时测定藏药四味石榴丸中主要指标成分的含量. 中医药导报. 2024(11): 60-63 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 沈树青,贾敏,胡文韬,狄伟. 赤芍治疗银屑病的网络药理学机制. 现代医药卫生. 2023(02): 181-185+191 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 彭雪峰,刘毅,赵飞,王瑞敏,张译心,芦玥,贾跃进. 基于“靶点-成分-中药”网络及临床数据探究贾跃进治疗冠心病合并抑郁症用药规律及核心中药处方. 国际中医中药杂志. 2023(03): 338-346 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 陈两绵,祖里皮亚·塔来提,玉素甫江·艾力,李建梅,霍仕霞,高慧敏,王智民. 维吾尔族药睡莲花中多种活性成分同步测定的质量控制方法建立. 中国实验方剂学杂志. 2023(09): 202-209 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 刘玉杰,季嘉城,张硕,唐丽,陈浪,张敏,王鹏娇,李韬,高秀丽. 刺梨中鞣花酸的分离鉴定及提取工艺的优化. 食品工业科技. 2023(08): 212-220 .  本站查看
本站查看
10. 郗仲玟,田宇柔,冯玉,李军山,牛丽颖. UPLC-MS/MS法同时测定彝族药紫地榆中11个化学成分的含量. 药物分析杂志. 2023(04): 573-581 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 袁奖娟,郝佳波,刘云,冯倩,阚欢,陆斌. 云南3种有色泡核桃仁营养成分及仁衣中多酚类物质分析. 中国油脂. 2023(05): 120-123+128 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 刘月,范高福,姚琪琪,胡婷,郑斌. 石榴提取物鞣花酸乳膏剂的制备工艺初探. 包头医学院学报. 2023(06): 88-91+96 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 罗佳,马若克,乔梦吉,符韵林. 大花序桉边心材酚类成分分布及鉴定. 北京林业大学学报. 2023(06): 127-136 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 夏铭隆,尹业鑫,肖银涛,郑赛珍,谭碧娥,王磊,陈家顺. 鞣花酸的生理功能及其在动物生产中的应用研究进展. 饲料研究. 2023(11): 149-154 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 林潇,张庆霞,王京龙,杨福霞,许莉莉. 鞣花酸纳米微囊的制备及其在乳腺癌MCF-7细胞株中的抗肿瘤效果. 中华实验外科杂志. 2023(08): 1554-1557 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 宋子欣,孙倩茹,方嘉璇,王昌涛,李萌,王冬冬. 石榴皮主要活性成分及其在化妆品中的应用研究进展. 日用化学工业(中英文). 2023(10): 1211-1219 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 张文霞,康亚男. 响应面法优化盐覆盆子有效成分鞣花酸的提取工艺. 中国民族民间医药. 2023(22): 38-41 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 马矜烁,许菲,范传优,崔彤彤,苏慧慧. 余甘子化学成分的提取、生物学功能及其在畜牧生产中的应用. 饲料研究. 2023(24): 165-171 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 贾哲,桑志祥,张梦馨,丁凌霄,徐海军. 鞣花酸对应激小鼠血常规指标的影响. 饲料博览. 2022(05): 38-41 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)






 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



