Study on Carboxymethylation Modification and Antioxidant Activity of Polysaccharides from Zizyphus jujuba
-
摘要: 本研究对红枣多糖进行羧甲基化修饰,探究羧甲基化修饰红枣多糖的结构特征及抗氧化活性变化。以红枣粗多糖为原料,采用Sevage法脱蛋白,大孔树脂AB-8脱色处理,对除杂后的多糖进行羧甲基化修饰。以羧甲基取代度为指标,通过单因素和响应面试验对NaOH浓度、一氯乙酸添加量及温度进行优化,以修饰前后多糖对DPPH、羟基自由基的清除能力及其还原力和对Fe2+的螯合能力为指标,探究羧甲基化修饰对红枣多糖抗氧化特性的影响。结果显示,羧甲基化修饰最佳工艺参数为:反应温度70 ℃,一氯乙酸添加量3.5%,NaOH浓度3 mol/L,此条件下羧甲基化红枣多糖分子修饰取代度高达1.157。浓度5 mg/mL时,羧甲基化修饰的红枣多糖DPPH和羟基自由基清除率达93.83%和44.7%,还原力和对Fe2+的螯合能力分别为0.462和44.05%。红枣多糖抗氧化性的显著提升表明羧甲基化修饰可改善多糖的抗氧化性,可为红枣多糖的深入研究提供一定的理论依据。Abstract: To investigate the changes of structural characteristics and antioxidant activity of carboxymethylated jujube polysaccharides, this study was carried out on the Zizyphus jujuba polysaccharide carboxymethylated modification. The crude polysaccharides of jujube were used as raw materials, deproteinization by Sevage method and decolorization by macroporous resin AB-8, then the polysaccharide was modified by carboxymethylation. With carboxymethyl substitution degree as the index, the concentration of NaOH, the addition amount of monochloroacetic acid and the temperature were optimized by single factor and response surface test. The scavenging ability of DPPH and hydroxyl radical and its reducing power and chelating ability to Fe2+ were taken as indexes before and after modification to explore the effect of antioxidant activity of carboxymethylated jujube polysaccharide. The results showed that the optimal process of carboxymethylation modification was as follows: Reaction temperature was 70 ℃, the addition amount of chloroacetic acid was 3.5%, and the concentration of NaOH was 3 mol/L. Under these conditions, carboxymethylated Zizyphus jujuba polysaccharides had the best molecular modification effect, and the degree of substitution up to 1.157. When the concentration was 5 mg/mL, the scavenging rates of DPPH and hydroxyl radical were 93.83% and 44.7%, and the reducing power and chelating capacity of Fe2+ were 0.462 and 44.05%. The significant improvement of antioxidant activity of Zizyphus jujuba polysaccharides indicated that carboxymethylation modification could improve antioxidant activity of polysaccharides, which could provide theoretical basis for further study of Zizyphus jujuba polysaccharides.
-
红枣(Zizyphus jujuba Mill.)通常被称为红枣或大枣,是枣树的果实,属于鼠李科[1],原产于中国,由于其营养丰富且具有多种药用价值,2002年被国家卫生健康委员会列为药食同源食品[2]。此外,红枣中含有多种重要的生物活性成分,如:维生素C、多酚、黄酮、多糖、环核苷酸[3],在人体保健和疾病防治方面可以发挥重要作用。植物多糖特性独特,在临床上多用于增强机体免疫力与抗氧化能力,调节机体糖代谢等[4]。多糖是红枣的主要生物活性成分,具有抗疲劳[5]、免疫调节、抗氧化、抗肿瘤、保肝、降血糖和胃肠保护等作用[6]。
多糖的分子修饰逐渐成为研究热点之一。羧甲基化修饰是指多糖分子链上引入羧甲基基团的反应,修饰后,多糖的理化性质和组成结构发生了改变,对其活性有较大的影响,主要体现为修饰后的多糖生物活性增强[7],更具有研究意义。再加上其所需设备简单、反应条件温和、投资少、成本低,所以本文采用此方法开展试验。希望通过对红枣多糖的分子修饰,提高原有生物活性或增加新活性[8],扩大多糖利用范围,并应用于功能食品领域,有利于实现红枣产业的高值化应用。
本研究以一氯乙酸为羧甲基化试剂,NaOH为反应溶剂,通过单因素和响应面对羧甲基化条件进行了优化,利用红外光谱和扫描电镜图对其进行了分析。考虑到对红枣多糖进行羧甲基化修饰的目的是提高其抗氧化活性,以DPPH、羟基自由基清除率及还原力和Fe2+螯合能力为指标,探究羧甲基化修饰对多糖抗氧化的影响,以期为红枣多糖分子修饰及其抗氧化特性改善提供一定的理论依据和技术指导。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
红枣多糖(纯度为60%) 西安泽郎生物科技有限公司;透析袋(截留分子量:8000~14000 Da) 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;大孔吸附树脂AB-8 天津市光复精细化工研究所;三氯乙酸 天津市风船化学试剂科技有限公司;正丁醇、硫酸 天津市富宇精细化工有限公司;过氧化氢 成都市科隆化学有限公司;邻苯三酚、硫酸亚铁、氢氧化钠 天津市鑫铂特化工有限公司;菲啰嗪、水杨酸、抗坏血酸、三氯化铁 国药集团化学试剂有限公司;磷酸氢二钠 天津市盛奥化学试剂有限公司;磷酸二氢钠 天津市光复科技发展有限公司;一氯乙酸 上海麦克林生化科技有限公司。
H2500R-2型冷冻离心机 北京澎昆博远科贸发展有限责任公司;RE-52型旋转蒸发仪 上海亚荣生化仪器公司;ENK-PRO型酶标仪 美国Bioteck公司;NJF-120-01型扫描电子显微镜 苏州晋松计量仪器有限公司;Nicolet IS 10型傅里叶变换红外光谱仪 美国Thermo公司;HX-10-50B型真空冷冻干燥机 上海圣科仪器设备有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 红枣多糖前处理
1.2.1.1 蛋白质的脱除
采用Sevage法[9-10]脱除红枣多糖中的游离蛋白质。取0.05 g/mL的粗多糖溶液,按体积3:1比例加入Sevage试剂(氯仿与正丁醇3:1,v/v),放入恒温振荡培养箱中,充分振荡30 min,使蛋白质充分变性。4000 r/min离心10 min,待分层完全后除去水层和试剂层交界处的变性蛋白质,取出上层多糖液。反复操作5~8次直至中间变性蛋白层几乎消失。将脱蛋白后的糖液进行蒸发浓缩、干燥、称重,分析蛋白含量,计算蛋白脱除率和多糖保存率。
蛋白脱除率(%)=脱蛋白前蛋白含量−脱蛋白后蛋白含量脱蛋白前蛋白含量×100 (1) 多糖保存率(%)=脱蛋白后多糖含量脱蛋白前多糖含量×100 (2) 1.2.1.2 脱色
准确称取活化的大孔树脂20 g于250 mL锥形瓶,然后向其中加入100 mL浓度为0.05 g/mL脱蛋白红枣多糖溶液,置于摇床中,225 r/min、室温振荡24 h,抽滤,取滤液测定其脱色后在420 nm处的吸光度值,计算色素脱除率和多糖保存率[11-12]。
脱色率(%)=脱色前吸光度值−脱色后吸光度值脱色前吸光度值×100 (3) 多糖保存率(%)=脱色后多糖含量脱色前多糖含量×100 (4) 1.2.1.3 多糖含量的测定
参考王迎香等[13]的方法,准确量取浓度为0.2 mg/mL葡萄糖标准液0.1、0.2、0.4、0.6、0.8、1.0、1.2 mL于试管,补水至2.0 mL,加1.0 mL质量浓度5%的苯酚,滴加5.0 mL浓硫酸,摇匀,静置30 min,待其温度降低后,于490 nm处测其吸光度,以2.0 mL水按同样显色操作为空白。同一浓度标准溶液重复测定3次,以葡萄糖浓度为横坐标,吸光度值为纵坐标,制作葡萄糖标准曲线[14]。得到线性回归方程:y=0.8589x+0.0068,其中R2=0.991,x为葡萄糖标准品的浓度,y为对应浓度下的吸光度值。
取2.0 mL适宜浓度的红枣多糖,加1.0 mL质量浓度5%的苯酚,滴加5.0 mL浓硫酸,摇匀,静置30 min,待其温度降低后,于490 nm处测其吸光度,并根据标准曲线计算多糖含量。
1.2.1.4 蛋白质含量的测定
参考曹泽虹等[15]和杨静等[16]的方法,量取浓度为0.2 mg/mL蛋白标准品溶液0.1、0.2、0.3、0.4、0.5、0.6 mL分别置试管中,加蒸馏水补至1.0 mL,分别加5.0 mL考马斯亮蓝试剂,混匀,于30 ℃恒温水浴5 min,冷却至室温。另以蒸馏水1.0 mL,同上操作为空白对照,在595 nm处测量吸光度值。同一浓度的标准溶液分别重复测定3次。以蛋白质浓度为横坐标,以吸光度值为纵坐标,绘制标准曲线,得到线性回归方程:y=0.7817x+0.0425,其中R2=0.9956,x是蛋白标准品的浓度,y为不同浓度下测得的吸光度值。
红枣多糖溶液稀释至适当浓度,取1.0 mL于试管中,加入5.0 mL考马斯亮蓝溶液,混匀,于30 ℃恒温水浴5 min,冷却至室温,在595 nm处测量吸光度值,并根据标准曲线计算红枣多糖溶液中蛋白含量。
1.2.2 羧甲基化红枣多糖的制备
参照陈栅[17]和程浩[18]羧甲基化改性的方法,准确称取0.8 g除杂后的红枣多糖于锥形瓶中,加入50 mL一定浓度的NaOH搅拌1 h,使其碱化完全。加入一定量的一氯乙酸,置于一定温度水浴锅中反应5 h,冷却,用冰乙酸调节pH为7.0,透析3 d,冷冻干燥(−50 ℃,72 h),获得羧甲基化红枣多糖。
1.2.2.1 单因素实验
a.NaOH浓度对羧甲基取代度的影响:将50 mL浓度为1.0、1.5、2.0、2.5、3.0、3.5 mol/L的NaOH加入红枣多糖中,搅拌30 min,再加入50 mL质量浓度为3%的一氯乙酸,在80 ℃水浴锅中反应5 h,制备羧甲基化红枣多糖,测定羧甲基取代度,研究NaOH浓度对红枣多糖的羧甲基化修饰的影响。
b.温度对羧甲基取代度的影响:向红枣多糖中加入3 mol/L的NaOH和质量浓度为3%一氯乙酸各50 mL,分别在50、60、70、80、90 ℃下制备羧甲基化红枣多糖,测定羧甲基取代度,研究反应温度对红枣多糖的羧甲基化修饰的影响。
c.一氯乙酸添加量对羧甲基取代度的影响:在红枣多糖中加入50 mL浓度3 moL/L的NaOH和50 mL质量浓度为1%、2%、3%、4%、5%的一氯乙酸,在70 ℃下制备羧甲基化红枣多糖,测定羧基取代度,研究一氯乙酸添加量对红枣多糖的羧甲基化修饰的影响。
1.2.2.2 响应面试验
在单因素实验的基础上,采用三因素三水平Box-Behnken的实验设计方法(表1),以A:一氯乙酸添加量;B:温度;C:NaOH浓度为自变量,取代度为因变量,利用响应面分析软件Design-Expert8建立数字回归模型,确定红枣多糖羧甲基化的最佳条件。
表 1 试验设计因素与水平Table 1. Experimental design factors and levels水平 因素 A一氯乙酸添加量(%) B温度(℃) C NaOH浓度(mol/L) −1 2 60 2.5 0 3 70 3 1 4 80 3.5 1.2.2.3 羧甲基取代度的测定
参照张洋婷和房斐等[19-20]的方法。取10 mg羧甲基化红枣多糖,向其中加入10 mL 0.01 mol/L的NaOH,搅拌30 min使其完全溶解,滴1~3滴酚酞,然后用0.01 mol/L的HCl滴定,以红色消失且30 s不变色为滴定终点,计算公式为:
DS=0.162A1−0.058A (5) A=C1V1−C2V2W (6) 式中:DS为羧甲基取代度;A为羧甲基含量(%);W为羧甲基化红枣多糖质量(g);C1为NaOH浓度(mol/L);V1为NaOH体积(mL);C2是HCl的浓度(mol/L);V2为样品滴定过程中消耗HCl的体积(mL)。
1.2.3 红枣多糖结构表征
1.2.3.1 傅里叶红外光谱(FTIR)
分别称取2 mg羧甲基化修饰前后的红枣多糖,加200 mg KBr粉末研磨均匀,压片处理,分析4000~500 cm−1波数下红外光谱图。
1.2.3.2 扫描电镜(SEM)
取适量羧甲基修饰前后的红枣多糖样品固定于载物盘上,喷金处理后置于仪器内,观察多糖样品微观形态,拍摄不同倍数电镜照片,进行分析。
1.2.4 红枣多糖抗氧化活性测定
1.2.4.1 DPPH自由基清除作用
配制浓度为0.04 mg/mL的DPPH溶液和不同浓度(1、2、3、4、5 mg/mL)修饰前后红枣多糖溶液。试管中依次加入2 mL DPPH溶液,2 mL不同浓度的红枣多糖溶液或者VC,摇匀,室温放置30 min,测定其在517 nm处的吸光度值,VC为阳性对照,蒸馏水为空白对照,计算清除率(S)[21-22]。
S(%)=(1−A1−A2A0)×100 (7) 式中:A1为反应液的吸光度值;A2为不加DPPH时多糖液自身的吸光度值;A0为空白对照DPPH溶液加蒸馏水。
1.2.4.2 羟基自由基清除作用
分别在试管中加入2 mL不同浓度(1、2、3、4、5 mg/mL)的红枣多糖溶液,依次加入2 mL 6 mmol/L FeSO4和2 mL 9 mmol/L水杨酸,再加入2 mL 2.4 mmol/L过氧化氢,摇匀,静置10 min,离心10 min,测其在510 nm处的吸光度值,Vc为阳性对照,蒸馏水为空白,计算清除率(S)[23-24]。
S(%)=(1−A1−A2A0)×100 (8) 式中:A1为样品液的吸光度;A2为不加显色剂H2O2样品本底的颜色;A0为空白对照液的吸光度。
1.2.4.3 Fe2+的螯合能力
分别取2 mL不同浓度的(1、2、3、4、5 mg/mL)红枣多糖液,加入2 mL蒸馏水,2 mmol/L的FeCl2 0.1 mL和5 mmol/L的菲啰嗪溶液0.2 mL,25 ℃水浴10 min,测其在562 nm处的吸光度值,EDTA Na2为阳性对照,蒸馏水为空白,计算Fe2+螯合能力[25-26]。
Fe2+螯合能力(%)=(1−A1−A2A0)×100 (9) 式中:A1为样品溶液反应后的吸光度值;A2为蒸馏水代替FeCl2溶液的吸光度值;A0为蒸馏水代替反应中样品溶液的吸光度值。
1.2.4.4 总还原力测定
分别在试管中加入0.2 mol/L pH6.6的磷酸盐缓冲液2 mL,2 mL不同浓度(1、2、3、4、5 mg/mL)的红枣多糖液,2 mL 1%的铁氰化钾,混合均匀后于50 ℃水浴锅中反应20 min,取出后加入2 mL 10%的三氯乙酸终止反应,然后离心10 min,取2 mL上清液,加2 mL蒸馏水,0.4 mL FeCl3,混匀静置10 min,在700 nm处测定其吸光度值,吸光度值越大表明还原能力越强[23,27]。
1.3 数据处理
本实验数据均重复测定三次,采用Design-Expert8进行响应面试验设计,Excel 2021和SPSS 25统计分析软件对实验数据进行处理,结果表示为平均值±标准偏差。使用Origin 85作图软件对实验数据进行作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 红枣多糖的脱蛋白脱色工艺研究
2.1.1 红枣多糖中蛋白质的脱除
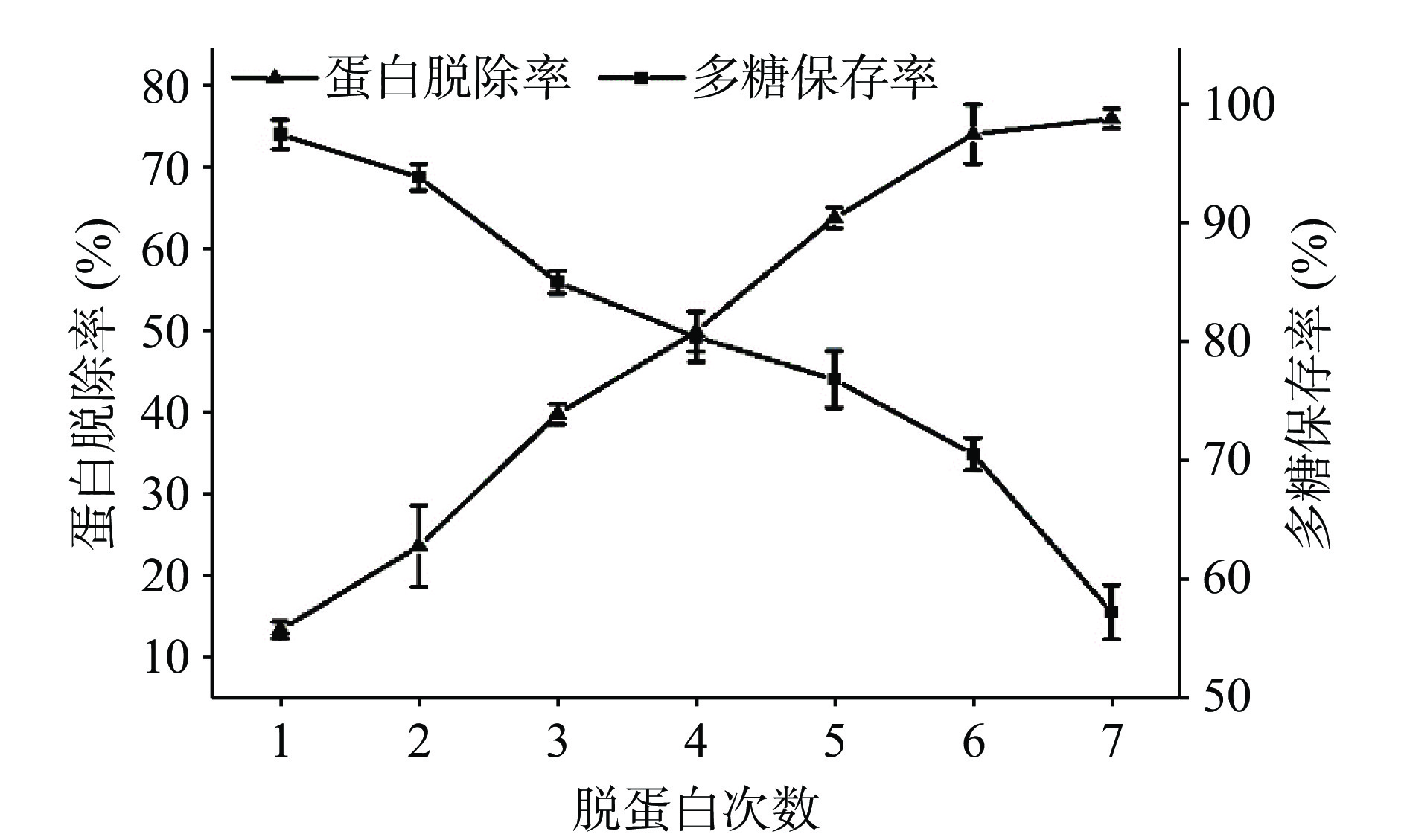
如图1所示,随着脱蛋白次数的增加,红枣多糖中蛋白脱除率逐渐增大,游离蛋白含量不断减少,多糖保存率逐渐减小,多糖含量不断减少,当经过6次蛋白脱除时,蛋白脱除率为74.5%,多糖保存率为70.8%,当进行7次脱蛋白时,蛋白脱除率为76.4%,而多糖保存率急剧下降为57.5%,综合蛋白脱除率和多糖保存率,确定脱蛋白最佳次数为6次,此时游离蛋白多数已经脱除,且多糖保存率较高。
2.1.2 红枣多糖的脱色
利用AB-8大孔树脂脱色后,红枣多糖液脱色率可达87.4%,多糖保存率为72.80%,多糖的损失主要是在脱色过程中,大孔树脂吸附一定量多糖所致。图2是不同浓度脱色前后红枣多糖溶液,可清晰观察到多糖液颜色发生了明显的变化,未脱色多糖溶液的颜色随浓度的增加越来越深,呈黄褐色,但是通过脱色处理后,多糖溶液的颜色明显变浅,而且随着浓度的增大没有明显变化,呈浅黄色,说明多糖中的色素物质基本上被清除干净,不影响后续实验的进行。
2.2 羧甲基化红枣多糖制备单因素实验
2.2.1 NaOH浓度对羧甲基取代度的影响
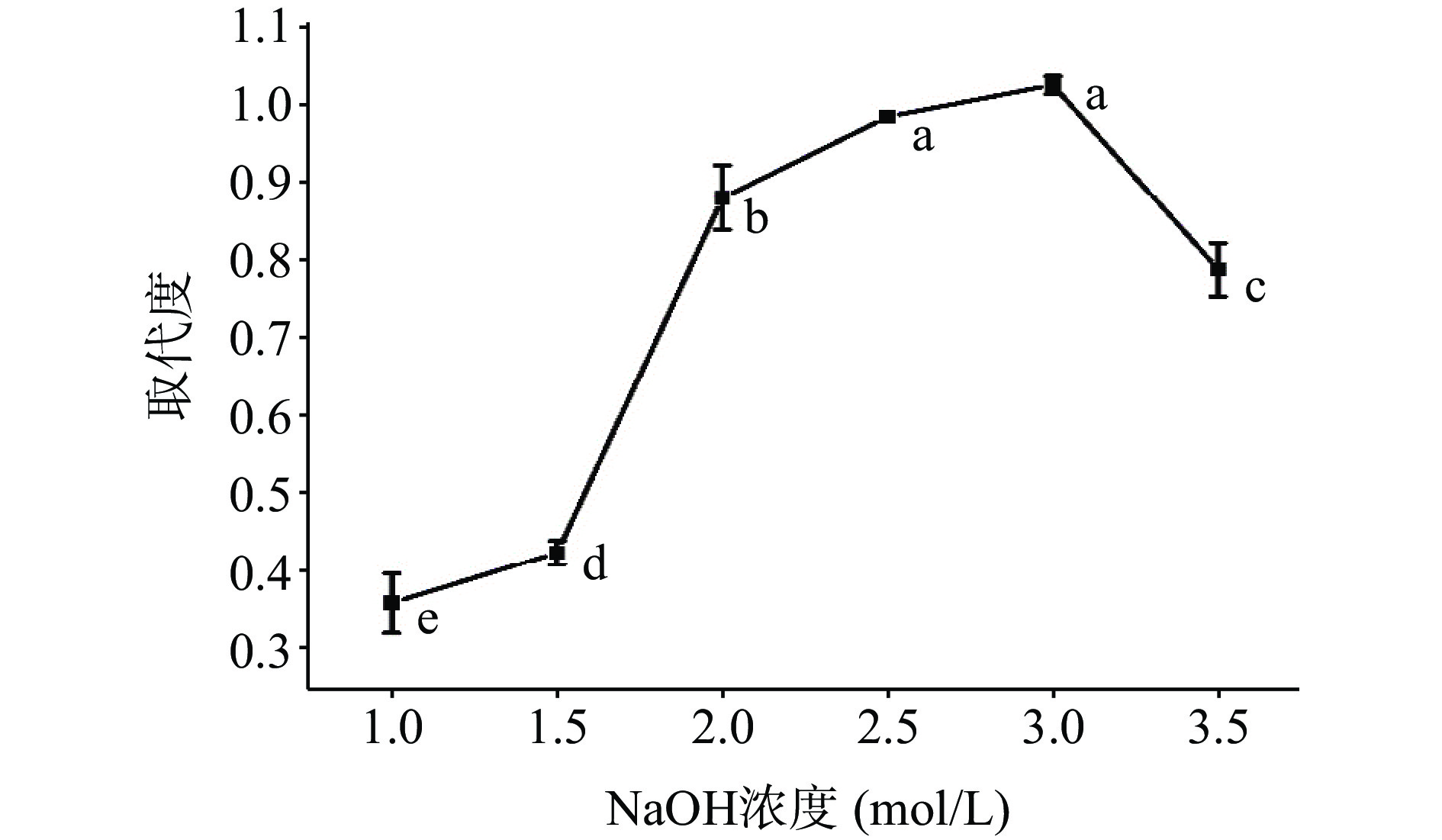
图3是红枣多糖羧甲基修饰过程中,NaOH浓度对羧甲基取代度的影响趋势图。可观察到NaOH浓度从1 mol/L逐渐增加到3 mol/L时,羧甲基取代度显著提高(P<0.05);当NaOH浓度为3 mol/L时,取代度可达1.024。当NaOH浓度大于3 mol/L时,取代度降低,这可能是强碱性条件下,多糖易降解,且当一氯乙酸和NaOH达到一定浓度时会发生副反应,不利于羧甲基修饰,因此确定最佳NaOH浓度为3 mol/L。
2.2.2 温度对羧甲基取代度的影响
图4是羧甲基红枣多糖制备中,反应温度对取代度的影响趋势图。当反应温度从50 ℃增加到70 ℃时,取代度显著增大(P<0.05),70 ℃时,取代度达到最大值1.047。当温度大于70 ℃时,取代度不断下降,这表明在一定的温度范围内,温度升高有利于羧甲基化,温度过高不利于羧甲基修饰,这可能是温度过高,会使氯乙酸和多糖发生降解,阻碍羧甲基化的进程,从而降低了羧甲基化取代度[28],因此确定70 ℃为反应最佳温度。
2.2.3 一氯乙酸添加量对羧甲基取代度的影响
图5是红枣多糖羧甲基修饰过程中,一氯乙酸添加量对取代度的影响趋势图。当一氯乙酸添加量为从1%增加到3%时,羧甲基取代度逐渐增大,当一氯乙酸添加量为3%时,最大取代度可达1.014。大于3%时随添加量的增加取代度急剧降低,这可能是因为过量一氯乙酸的加入,消耗了一定量NaOH,使得反应体系pH降低,不利于反应的进行[29],因此确定一氯乙酸添加量为3%。
2.3 羧甲基化红枣多糖制备响应面试验
2.3.1 响应面优化试验
响应面试验结果如表2所示。对试验数据进行多元回归分析,得出羧甲基化红枣多糖的取代度预测响应Y为:Y=1.05−0.014A−6.500E−003B−0.059C−0.023AB+4.750E−003AC+0.14BC−0.37A2−0.19B2−0.27C2。用F值和P值衡量模型系数的显著性,结果见表3。本试验中,F值为142.52说明模型F值较高,P值(P<0.0001)较低,表明该模型具有高度显著性,就纯误差而言,失拟项(P=0.1390)不显著,这表明模型方程适合羧甲基化红枣多糖的取代度测定[30]。模型决定系数(R2=0.9946),表明建立的模型适用。变异系数(C.V=4.04%)较低,表明试验值的精度和可靠性较高,以P值为依据,检验各系数的显著性,P值越小,对应系数越显著[31-32]。显著性标注如表3所示。BC和A2、B2、C2均为极显著(P<0.01),其他因素间相互作用都不显著(P>0.05),说明BC间相互作用对羧甲基化取代度影响较明显。
表 2 响应面优化试验结果Table 2. Response surface optimization test results序列 A一氯乙酸添加量 B温度 C NaOH浓度 取代度 1 1 1 0 0.548 2 −1 1 0 0.657 3 0 1 −1 0.523 4 0 0 0 1.188 5 0 0 0 1.154 6 −1 −1 0 0.589 7 0 1 1 0.812 8 0 −1 1 0.582 9 −1 0 1 0.508 10 1 0 1 0.523 11 1 0 −1 0.518 12 0 0 0 1.134 13 0 −1 −1 0.847 14 0 0 0 1.136 15 0 0 0 1.147 16 −1 0 −1 0.522 17 1 −1 0 0.574 表 3 回归模型方差分析Table 3. Regression model variance analysis变异来源 平方和 自由度 均方差 F值 P值 显著性 模型 1.22 9 0.14 142.52 <0.0001 ** A-一氯乙酸 1.596E-003 1 1.596E-003 1.68 0.2354 不显著 B-温度 3.380E-004 1 3.380E-004 0.36 0.5691 不显著 C-NaOH浓度 2.813E-005 1 2.813E-005 0.03 0.8681 不显著 AB 2.209E-003 1 2.209E-003 2.33 0.1706 不显著 AC 9.025E-005 1 9.025E-005 0.095 0.7666 不显著 BC 0.077 1 0.077 81.00 <0.0001 ** A2 0.57 1 0.57 597.12 <0.0001 ** B2 0.16 1 0.16 166.04 <0.0001 ** C2 0.30 1 0.30 318.11 <0.0001 ** 残差 6.631E-003 7 9.473E-004 失拟项 4.726E-003 3 1.575E-003 3.31 0.1390 不显著 纯误差 1.905E-003 4 4.762E-004 总和 1.22 16 注:*表示显著(P<0.05);**表示极显著(P<0.01)。 2.3.2 响应面分析与验证试验
图6是红枣多糖羧甲基化修饰响应面图,通过3D图,观察曲面的倾斜度确定两者对响应值的影响程度,倾斜度越高,即坡度越陡,说明两者交互作用越显著。另外,从3D图的颜色可以做一个初步判定,随着变化趋势的剧烈增加,其颜色也呈加深趋势。响应面等高线图可以直观地反映各因素对响应值的影响,以便找出最佳工艺参数以及各参数之间的相互作用,等高线中的最小椭圆的中心点即是响应面的最高点。此外,等高线的形状可反映出交互效应的强弱,椭圆形表示两因素交互作用显著,而圆形则与之相反[33]。结合图6,得出AB和AC之间的相互作用对红枣多糖的羧甲基化修饰具没有显著性影响,BC相互作用对红枣多糖羧甲基化修饰有显著性影响。
根据响应面软件分析得红枣多糖羧甲基化修饰预测最佳工艺为:一氯乙酸添加量3.49%,温度69.52 ℃,NaOH浓度3 mol/L,取代度预测值为1.1519。为了方便操作,最后确定红枣多糖羧甲基化修饰的最佳条件为:一氯乙酸添加量3.5%,NaOH浓度为3 mol/L,温度为70 ℃。在该条件下,进行三次重复试验,其取代度结果分别为1.154、1.183、1.135,平均值为1.157,均优于其他组合,表明最优方法组合合理可用。
2.4 红枣多糖的结构表征
2.4.1 傅里叶红外光谱分析
图7为羧甲基化修饰前后红枣多糖在4000~500 cm−1波长范围内的光谱图。由图可知,3371.38 cm−1和3388.27 cm−1是O-H的拉伸振动引起的,表明红枣多糖存在分子内氢键[34]。2921.99 cm−1和2931.23 cm−1是C-H不对称伸缩振动引起的,1720.41 cm−1是由于酯或羧基中C=O的拉伸振动引起,表明可能存在糖醛酸或乙酰基[35]。1411.81 cm−1对称C-O拉伸振动引起的,1155.29 cm−1和1157.06 cm−1是C-O-H和C-O-C结构产生振动吸收引起的[36]。1024.14 cm−1和1025.93 cm−1为-OH的O-H变角振动,919.99 cm−1和923.72 cm−1为α-吡喃糖的吸收峰[37]。852.49 cm−1和869.72 cm−1为β-吡喃糖的吸收峰,由此推测红枣多糖是α-和β-构型共存的吡喃型甘露糖苷酸性杂多糖[38]。783.05 cm−1和761.73 cm−1是吡喃型特征吸收峰。羧甲基修饰后出现了新的吸收峰1592.89 cm−1和1421.26 cm−1,1592.89 cm−1是羧甲基中COO-的拉伸振动,1421.26 cm−1处的吸收峰为羧甲基化的特征吸收峰[39]。且-OH特征吸收峰明显减弱,说明-OH基团被取代,综上所述,表明红枣多糖成功引入了COO-基团,羧甲基化修饰成功。
2.4.2 SEM分析
由图8扫描电镜观察可得:红枣多糖的微观形态发生明显的变化,主要在于颗粒大小、表面光滑程度、松散程度。未修饰的红枣多糖表面呈蜂窝状,有许多小孔,颗粒较大,呈块状,视觉效果较粗糙。羧甲基修饰过的红枣多糖表面较光滑,颗粒很小,呈片状。扫描电镜图表明羧甲基修饰可以改变多糖的微观形态,这可能是因为多糖结构发生变化造成的。
2.5 红枣多糖抗氧化活性测定
2.5.1 羧甲基修饰红枣多糖对DPPH的清除能力的影响
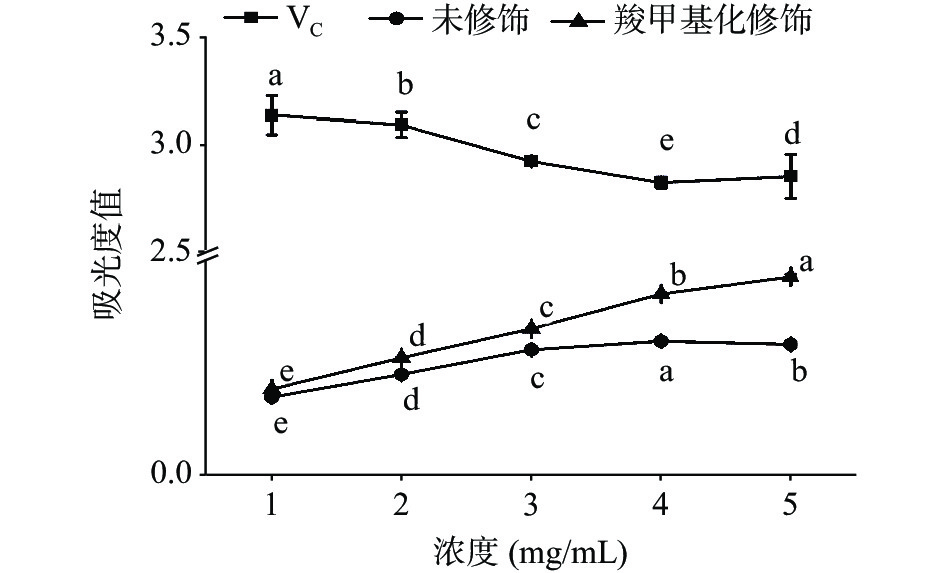
图9为羧甲基化修饰红枣多糖对DPPH自由基的清除能力,Vc为阳性对照组。如图所示,随着浓度的增大,未修饰和羧甲基化修饰的红枣多糖对DPPH自由基都有较强的清除作用,但清除能力均低于Vc,并且清除能力随着多糖浓度的增大逐渐加强,呈现剂量依赖性。此外,羧甲基化修饰后的红枣多糖的清除能力显著高于未修饰多糖(P<0.05)。随多糖浓度的增加,羧甲基化修饰的红枣多糖对DPPH自由基的清除作用显著增大。当浓度为5 mg/mL时几乎和Vc持平,达到了93.83%,而Vc清除率为95.5%,未修饰的红枣多糖清除率为53.85%。此结果表明羧甲基化修饰可以显著提高红枣多糖对DPPH自由基的清除作用。
2.5.2 羧甲基修饰红枣多糖对羟基自由基清除率的影响
如图10所示,红枣多糖对羟基自由基有较强的清除作用,随着多糖浓度的增大,清除作用逐渐增强,呈剂量依赖性增加,羧甲基化修饰的红枣多糖对羟基自由基的清除作用显著提高(P<0.05)。当浓度为5 mg/mL,羧甲基化修饰多糖羟基清除率44.7%,未修饰29.25%,表明羧甲基化修饰可提高红枣多糖对羟基自由基的清除作用。其原因可能是在糖基上引入取代基,可以使一些本来没有活性的化合物具有了活性,而且这些引入多糖取代基的方法都会大大地提高多糖的活性[40]。
2.5.3 羧甲基修饰红枣多糖对Fe2+的清除率的影响
图11为羧甲基化修饰前后红枣多糖对Fe2+的螯合作用。低浓度时,未修饰与羧甲基化修饰的红枣多糖对Fe2+的螯合作用都比较低,其原因可能是低浓度范围,未修饰和羧甲基多糖均表现出较弱的清除活性[41]。随着多糖浓度增大羧甲基化修饰的红枣多糖对Fe2+的螯合作用明显强于未修饰的。同时,螯合能力也逐渐增强,呈现浓度依赖性。表明羧甲基化修饰可以提高红枣多糖对Fe2+的螯合能力。
2.5.4 羧甲基修饰红枣多糖对总还原力的影响
图12体现羧甲基化修饰前后红枣多糖的还原力变化。从图可表明,红枣多糖具有一定的还原力,但其还原力远低于阳性对照Vc。随着浓度的增大,未修饰和羧甲基化修饰的红枣多糖的还原力都有所增加,且呈剂量依赖性。通过羧甲基化修饰的红枣多糖的还原力明显高于未修饰的红枣多糖,表明羧甲基化修饰可以提高红枣多糖的还原力,但由于红枣多糖自身还原能力较弱,修饰前后红枣多糖的还原力较VC而言都较弱。
3. 结论
红枣粗多糖通过除蛋白,脱色得到除杂红枣多糖,经羧甲基化修饰,通过单因素和响应面试验,确定一氯乙酸的添加量为3.5%,温度为70 ℃,NaOH浓度为3 mol/L时,修饰程度最佳,其羧甲基取代度可达1.157。红外光谱分析显示,修饰后-OH吸收峰减弱,且出现了羧甲基化的特征吸收峰1592.89 cm−1和1421.26 cm−1,表明红枣多糖羧甲基化修饰成功。SEM结果显示,羧甲基修饰过的红枣多糖表面比较光滑,颗粒小,呈片状,未修饰的多糖呈蜂窝状,表面较粗糙。DPPH自由基,羟基自由基和还原力的测定结果显示,羧甲基化修饰的红枣多糖对DPPH、羟基自由基的清除率和还原力都有较明显的提高。通过对红枣多糖的羧甲基化修饰,可提高红枣多糖的抗氧化活性,为红枣多糖的进一步发展提供了理论依据,将有利于红枣多糖在食品和医药行业的广泛应用。
-
表 1 试验设计因素与水平
Table 1 Experimental design factors and levels
水平 因素 A一氯乙酸添加量(%) B温度(℃) C NaOH浓度(mol/L) −1 2 60 2.5 0 3 70 3 1 4 80 3.5 表 2 响应面优化试验结果
Table 2 Response surface optimization test results
序列 A一氯乙酸添加量 B温度 C NaOH浓度 取代度 1 1 1 0 0.548 2 −1 1 0 0.657 3 0 1 −1 0.523 4 0 0 0 1.188 5 0 0 0 1.154 6 −1 −1 0 0.589 7 0 1 1 0.812 8 0 −1 1 0.582 9 −1 0 1 0.508 10 1 0 1 0.523 11 1 0 −1 0.518 12 0 0 0 1.134 13 0 −1 −1 0.847 14 0 0 0 1.136 15 0 0 0 1.147 16 −1 0 −1 0.522 17 1 −1 0 0.574 表 3 回归模型方差分析
Table 3 Regression model variance analysis
变异来源 平方和 自由度 均方差 F值 P值 显著性 模型 1.22 9 0.14 142.52 <0.0001 ** A-一氯乙酸 1.596E-003 1 1.596E-003 1.68 0.2354 不显著 B-温度 3.380E-004 1 3.380E-004 0.36 0.5691 不显著 C-NaOH浓度 2.813E-005 1 2.813E-005 0.03 0.8681 不显著 AB 2.209E-003 1 2.209E-003 2.33 0.1706 不显著 AC 9.025E-005 1 9.025E-005 0.095 0.7666 不显著 BC 0.077 1 0.077 81.00 <0.0001 ** A2 0.57 1 0.57 597.12 <0.0001 ** B2 0.16 1 0.16 166.04 <0.0001 ** C2 0.30 1 0.30 318.11 <0.0001 ** 残差 6.631E-003 7 9.473E-004 失拟项 4.726E-003 3 1.575E-003 3.31 0.1390 不显著 纯误差 1.905E-003 4 4.762E-004 总和 1.22 16 注:*表示显著(P<0.05);**表示极显著(P<0.01)。 -
[1] LIU M, WANG J, WANG L, et al. The historical and current research progress on jujube–a superfruit for the future[J]. Horticulture Research,2020,7(1):17. doi: 10.1038/s41438-020-0239-y
[2] CHEN J, TSIM K. A Review of edible jujube, the Ziziphus jujuba fruit: A heath food supplement for anemia prevalence[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology,2020,11:593655. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.593655
[3] 冀晓龙, 尹明松, 侯春彦, 等. 红枣多糖提取、分离纯化及生物活性研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(23):346−353, 358. [JI X L, YIN M S, HOU C Y, et al. Rencent advances in jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) polysaccharides: Extraction, isolation and purification and bioactivities[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(23):346−353, 358. JI X L, YIN M S, HOU C Y, et al. Rencent advances in jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill. ) polysaccharides: extraction, isolation and purification and bioactivities[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(23): 346-353, 358.
[4] ZHENG Y, WANG B, CHEN X, The research on the influence of jujube polysaccharide on anti-fatigue in endurance training [C]// REN P, LI Y, SONG H. International conference on applied engineering and management. Beijing, 2015: 1381−1386.
[5] CHAN P H, CHEN J P, LAM C T W, et al. Fruit of Ziziphus jujuba (Jujube) at two stages of maturity: Distinction by metabolic profiling and biological assessment[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2015,63(2):739−744. doi: 10.1021/jf5041564
[6] LI Z, LIU X, WANG Y, et al. In vitro antioxidative and immunological activities of polysaccharides from Zizyphus jujuba cv. Muzao[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2017,95:1119−1125. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.10.102
[7] 周际松, 汪芷玥, 汤凯, 等. 羧甲基化茯苓多糖的抗氧化性分析[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2020,31(7):120−125. [ZHOU J S, WANG Z Y, TANG K, et al. Antioxidant activity of carboxymethylated poria cocos polysaccharide[J]. China Food Additives,2020,31(7):120−125. ZHOU J S, WANG Z Y, TANG K, et al. Antioxidant activity of carboxymethylated poria cocos polysaccharide [J]. China Food Additives, 2020, 31(07): 120-125.
[8] 陈胜军, 刘先进, 杨贤庆, 等. 鲍鱼内脏多糖分离纯化与抗氧化活性评价[J]. 南方农业学报,2019,50(2):372−377. [CHEN S J, LIU X J, YANG X Q, et al. Isolation, purification and antioxidant activity evaluation of polysaccharides from abalone viscera[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture,2019,50(2):372−377. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2019.02.22 CHEN S J, LIU X J, YANG X Q, et al. Isolation, purification and antioxidant activity evaluation of polysaccharides from abalone viscera [J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2019, 50(2): 372-377. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2019.02.22
[9] 李小蓉, 郭惠, 龙旭, 等. 倒卵叶五加多糖脱蛋白工艺研究[J]. 化学与生物工程,2018,35(8):53−56, 68. [LI X R, GUO H, LONG X, et al. Deproteinization process of polysaccharide from Acanthopanax obovatus Hoo[J]. Chemistry & Bioengineering,2018,35(8):53−56, 68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5425.2018.08.011 LI X R, GUO H, LONG X, et al. Deproteinization process of polysaccharide from Acanthopanax obovatus Hoo[J]. Chemistry & Bioengineering, 2018, 35(8): 53-56, 68 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5425.2018.08.011
[10] 刘佳维, 周君, 高亚杰, 等. 红参多糖脱蛋白的研究[J]. 食品科技,2018,43(7):188−192. [LIU W J, ZHOU J, GAO Y J, et al. Deproteinization of polysaccharide from red ginseng[J]. Food Science and Technology,2018,43(7):188−192. LIU W J, ZHOU J, GAO Y J, et al. Deproteinization of polysaccharide from red ginseng[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2018, 43(7): 188-192.
[11] 韩伟, 陈静雯. 应用大孔树脂提纯蛹虫草多糖的工艺研究[J]. 徐州工程学院学报(自然科学版),2021,36(2):7−14. [HAN W, CHEN J W. Study on purification of cordyceps militaris polysaccharides by macroporous resin[J]. Journal of Xuzhou Institute of Technology (Natural Sciences Edition),2021,36(2):7−14. HAN W, CHEN J W. Study on purification of cordyceps militaris polysaccharides by macroporous resin[J]. Journal of Xuzhou Institute of Technology(Natural Sciences Edition), 2021, 36(2): 7-14.
[12] 艾拉旦·麦麦提艾力, 李洋, 姚军, 等. 管花肉苁蓉多糖水提物的分离及免疫活性研究[J]. 中国药房,2021,32(12):1479−1484. [AILADAN-Maimaitiailli, LI Y, YAO J, et al. Study on separation and immunocompetence of water extract of polysaccharide from Cistanche tubulosa[J]. China Pharmacy,2021,32(12):1479−1484. doi: 10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2021.12.12 AILADAN-Maimaitiailli LI Y, YAO J, et al. Study on separation and immunocompetence of water extract of polysaccharide from Cistanche tubulosa[J]. China Pharmacy, 2021, 32(12): 1479-1484. doi: 10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2021.12.12
[13] 王迎香, 唐子惟, 彭腾, 等. 苯酚-硫酸法测定酒蒸多花黄精多糖含量的优化[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(18):308−316. [WANG Y X, TANG Z W, PENG T, et al. Optimization of phenol sulfuric acid method for the polysaccharide content of wine-steamed Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(18):308−316. WANG Y X, TANG Z W, PENG T, et al. Optimization of phenol sulfuric acid method for the polysaccharide content of wine-steamed Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(18): 308−316.
[14] KONDO M, MULIANDA R, MATAMURA M, et al. Validation of a phenol: Ulfuric acid method in a microplate format for the quantification of soluble sugars in ruminant feeds[J]. Animal Science Journal,2021,92:e13530.
[15] 曹泽虹, 董玉玮, 李超, 等. 骏枣的多糖提取及其蛋白脱除研究[J]. 食品科学技术学报,2020,38(6):121−126. [CAO Z H, DONG Y W, LI C, et al. Study on polysaccharide extraction and protein removal from Ziziphus jujuba Mill. cv Junzao[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2020,38(6):121−126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-6002.2020.06.015 CAO Z H, DONG Y W, LI C, et al. Study on polysaccharide extraction and protein removal from Ziziphus jujuba Mill. cv Junzao[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 2020, 38(6): 121 - 126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-6002.2020.06.015
[16] 杨静, 白冰, 王宁, 等. 考马斯亮蓝法对烟草薄片涂布液中蛋白质含量的测定[J]. 湖北农业科学,2017,56(5):946−947, 950. [YANG J, BAl B, WANG N, et al. Determination of protein content in reconstituted tobacco coating liquid by coomassie brilliant blue method[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences,2017,56(5):946−947, 950. YANG J, BAl B, WANG N, et al. Determination of protein content in reconstituted tobacco coating liquid by coomassie brilliant blue method[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 56(5): 946-947, 950.
[17] 陈栅. 枣和酸枣多糖羧甲基化修饰工艺及活性研究[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2021. CHEN Z. Carboxymethylation modification processes and activity of jujube and wild jujube polysaccharide[D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2021.
[18] 程浩. 大蒜多糖衍生物的制备及抗氧化活性研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆师范大学, 2020. CHENG H. Preparation and antioxidant activity of garlic polysaccharide derivatives[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Normal University, 2020.
[19] 张洋婷, 韩丽琴, 郗艳丽, 等. 红景天多糖羧甲基化修饰及其抗氧化活性[J]. 中国公共卫生,2017,33(10):4. [ZHANG Y T, HAN L Q, XI Y L, et al. Carboxymethylation modification and antioxidant activity of rhodiola polysaccharide[J]. Chinese Journal of Public Health,2017,33(10):4. doi: 10.11847/zgggws2017-33-10-11 ZHANG Y T, HAN L Q, XI Y L, et al. Carboxymethylation modification and antioxidant activity of rhodiola polysaccharide [J]. Chinese Journal of Public Health, 2017, 33(10): 4. doi: 10.11847/zgggws2017-33-10-11
[20] 房斐, 陈雪峰, 刘宁, 等. 羧甲基化苹果渣多糖的制备及其表征[J]. 食品科技,2019,44(9):289−294, 302. [FANG P, CHEN X F, LIU N, et al. Preparation and characterization of carboxymethylated apple pomace polysaccharide[J]. Food Science and Technology,2019,44(9):289−294, 302. FANG P, CHEN X F, LIU N, et al. Preparation and characterization of carboxymethylated apple pomace polysaccharide[J]. Food Science and Technology, [19] 2019, 44(9): 289-294, 302.
[21] 邓威, 孙晓楠, 张润泽, 等. 寒葱精油挥发性成分及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中国调味品,2021,46(10):59−64. [DENG W, SUN X N, ZHANG R Z, et al. Study on the volatile components and antioxidant activity of essential oil from Allium victorialis L[J]. China Condiment,2021,46(10):59−64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2021.10.011 DENG W, SUN X N, ZHANG R Z, et al. Study on the volatile components and antioxidant activity of essential oil from Allium victorialis L[J]. China Condiment, 2021, 46(10): 59-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2021.10.011
[22] KOU X H, CHEN Q, L X H, et al. Quantitative assessment of bioactive compounds and the antioxidant activity of 15 jujube cultivars[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,173:1037−1044. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.10.110
[23] ZHANG Y, SUN X, VIDYARTHI S K, et al. Active components and antioxidant activity of thirty-seven varieties of Chinese jujube fruits (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.)[J]. International Journal of Food Properties,2021,24(1):1479−1494. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2021.1977656
[24] PRASAD K N, CHEW L Y, KHOO H E, et al. Antioxidant capacities of peel, pulp, and seed fractions of Canarium odontophyllum Miq. fruit[J]. Journal of Biomedicine and Biotechnology, 2010, 2010(11).
[25] QIN Y, YUAN Q, ZHANG Y, et al. Enzyme-assisted extraction optimization, characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from sea cucumber Phyllophorus proteus[J]. Molecules,2018,23(3):590. doi: 10.3390/molecules23030590
[26] 和英, 顾婷, 杨永寿, 等. 美洲大蠊提取物抗氧化活性研究[J]. 大理大学学报,2021,6(2):10−14. [HENG Y, GU T, YANG Y S, et al. Study on the antioxidant activity of different Periplaneta Americana extracts[J]. Journal of Dali University,2021,6(2):10−14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-2266.2021.02.002 HENG Y, GU T, YANG Y S, et al. Study on the antioxidant activity of different Periplaneta Americana extracts[J]. Journal of Dali University, 2021, 6(2): 10-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-2266.2021.02.002
[27] 王婧, 陶爱恩, 杨燕, 等. 滇黄精中多糖的分离与抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中草药,2021,52(16):4789−4796. [WANG J, TAO A E, YANG Y, et al. Separation, physicochemical properties and anti-oxidant activities of three polysaccharides from Polygonatum kingianum[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2021,52(16):4789−4796. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2021.16.004 WANG J, TAO A E, YANG Y, et al. Separation, physicochemical properties and anti-oxidant activities of three polysaccharides from Polygonatum kingianum[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2021, 52(16): 4789-4796. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2021.16.004
[28] 李霞, 胡楠, 赵启迪, 等. 肠浒苔多糖的羧甲基化修饰及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 广西植物,2019,39(11):1519−1526. [LI X, HU N, ZHAO Q D, et al. Study on carboxymethylation modification and antioxidant activity of Enteromorpha prolifera polysaccharides[J]. Guangxi Botany,2019,39(11):1519−1526. doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201807003 LI X, HU N, ZHAO Q D, et al. Study on carboxymethylation modification and antioxidant activity of Enteromorpha prolifera polysaccharides [J]. Guangxi botany, 2019, 39(11): 1519-1526. doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201807003
[29] 谢建华. 青钱柳多糖的分子修饰及其生物活性研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2014. XIE J H. Modification of polysaccharides from Cyclocarya paliurus and their biological activities[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2014.
[30] 步营, 吕月月, 朱文慧, 等. 基于模糊数学与响应面分析法开发味噌风味鲅鱼罐头[J]. 中国调味品,2021,46(9):90−94. [BU Y, LÜ Y Y, ZHU W H, et al. Development of canned miso-flavor spanish mackerel based on fuzzy mathematics and response surface analysis[J]. China Condiment,2021,46(9):90−94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2021.09.017 BU Y, LÜ Y Y, ZHU W H, et al. Development of canned miso-flavor spanish mackerel based on fuzzy mathematics and response surface analysis[J]. China Condiment, 2021, 46(9): 90-94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2021.09.017
[31] FENG R F, KOU J J, CHEN S, et al. Preparation optimization, characterization, and antioxidant and prebiotic activities of carboxymethylated polysaccharides from jujube[J/OL]. Journal of Food Quality, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/3268149.
[32] 陈阳, 孙代华, 江丹, 等. 响应面分析法优化艾叶药渣中白坚木皮醇乙醇提取工艺[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2021,32(9):90−96. [CHEN Y, SUN D H, JIANG D, et al. Optimization of quebrachitol ethanol extraction from Folium Artemisiae Argyi extraction dregs by response surface methodology (RSM)[J]. Chinese Food Additives,2021,32(9):90−96. CHEN Y, SUN D H, JIANG D, et al. Optimization of quebrachitol ethanol extraction from Folium Artemisiae Argyi extraction dregs by response surface methodology(RSM) [J]. Chinese food additives, 2021, 32(9): 90-96.
[33] 曹阔, 吴兴雨, 孙凯杨, 等. 响应面分析法优化酶法提取小米谷糠蛋白工艺[J]. 江苏农业科学,2021,49(18):169−173. [CAO K, WU X Y, SUN K Y, et al. Optimization of enzymatic extraction process of millet G protein by response surface methodology[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences,2021,49(18):169−173. CAO K, WU X Y, SUN K Y, et al. Optimization of enzymatic extraction process of millet G protein by response surface methodology[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 49(18): 169-173.
[34] 王银平. 玉木耳多糖的制备、结构表征及其与乳清蛋白相互作用研究[D] 长春: 吉林大学, 2020. WANG Y P. Preparation, structure characterization and interaction with whey protein of polysaccharides from Auricularia auriculata [D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2020.
[35] SUN L, MENG Y, SUN J, et al. Characterization, antioxidant activities and hepatoprotective effects of polysaccharides from pre-pressing separation Fuji apple peel[J]. Cyta Journal of Food,2017,15(2):307−319. doi: 10.1080/19476337.2016.1263241
[36] LIN X, LIU K, YIN S, et al. A novel pectic polysaccharide of jujube pomace: structural analysis and intracellular antioxidant activities[J]. Antioxidants,2020,9(2):127. doi: 10.3390/antiox9020127
[37] JI X, HOU C, YAN Y, et al. Comparison of structural characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) fruit[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,149:1008−1018. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.018
[38] 何培新, 吴双双, 郑凯, 等. 杨树桑黄胞外多糖的分子结构及抗氧化活性[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2018,37(9):939−947. [HE P X, WU S S, ZHENG K, et al. Molecular structure and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Phellinus vaninii Ljup[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology,2018,37(9):939−947. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2018.09.007 HE P X, WU S S, ZHENG K, et al. Molecular structure and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Phellinus vaninii Ljup[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology, 2018, 37(9): 939-947. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2018.09.007
[39] 陈义勇, 张阳. 杏鲍菇多糖羧甲基化修饰工艺及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2016,42(7):119−127. [CHEN Y Y, ZHANG Y. Carboxymethylation modification and antioxidant activity of Pleurotus eryngii polysaccharides[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2016,42(7):119−127. CHEN Y Y, ZHANG Y. Carboxymethylation modification and antioxidant activity of Pleurotus eryngii polysaccharides[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2016, 42(7): 119-127.
[40] 马诣欣. 橡木根皮多糖硫酸酯的制备 、结构表征及抗氧化活性研究[D]. 兰州: 西北师范大学. MA Y X. Preparation, structure characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide sulfate ester from oak root bark[D]. Lanzhou: Northwest Normal University.
[41] 白家峰, 姚延超, 郑毅, 等. 罗汉果多糖的羧甲基化修饰及抗氧化性能影响研究[J]. 湖北农业科学,2021,60(15):107−111. [BAI J F, YAO Y C, ZHENG Y, et al. Study on the effect of carboxymethylation of Siraitia grosvenorii polysaccharide on its antioxidant[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences,2021,60(15):107−111. BAI J F, YAO Y C, ZHENG Y, et al. Study on the effect of carboxymethylation of Siraitia grosvenorii polysaccharide on its antioxidant[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 60(15): 107-111.
-
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 舒丽枝,时苗苗,张牧焓,卞欢,徐为民,王道营. 卟啉类化合物和游离铁对鸡胸肉肌原纤维蛋白理化特性的影响. 江苏农业学报. 2024(10): 1952-1961 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王晓芸,高霞,尤娟,尹涛,刘茹. 超声预处理对鲜湿鱼粉品质的影响及其作用机制. 食品科学. 2024(23): 213-220 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 韩馨蕊,李颖,刘苗苗,范鑫,冯莉,曹云刚. 安石榴苷与焦磷酸钠对肌原纤维蛋白氧化稳定性及凝胶性能的影响. 食品科学. 2022(08): 15-21 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 莫玲,香庆文,李晶晶,叶玉萍,赵超超. 孕哺期摄入氧化乳蛋白对子代小鼠机体氧化还原状态的影响. 食品科学技术学报. 2021(03): 122-128 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 梁恽红,卢涵,张香美. 蛋白二、三级结构对鱼糜凝胶质构和持水力的影响及其测定方法研究进展. 东北农业大学学报. 2021(10): 87-96 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 谢晨,熊泽语,李慧,金素莱曼,陈百科,包海蓉. 金针菇多糖对三文鱼片冻藏期间品质的影响. 食品与发酵工业. 2021(22): 178-183 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 刘芳芳,林婉玲,李来好,吴燕燕,杨少玲,黄卉,杨贤庆,林织. 海鲈鱼糜加工及凝胶形成过程中蛋白质的变化机理. 食品科学. 2020(14): 15-22 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 冯程,Manonose Tariro Upenyu,李志豪,王萍,余雄伟,付琴利,李述刚. 丙烯醛对籽瓜种仁蛋白质结构及凝胶特性影响研究. 食品科技. 2019(09): 66-71 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 刁小琴,关海宁,李杨,刘丽美. 高压均质对肌原纤维蛋白乳化特性及结构的影响. 食品与发酵工业. 2019(18): 107-112 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 郭兆斌,马纪兵,张丽,陈骋,陈立业,刘勇,韩玲,余群力. 传统风干牦牛肉加工过程中肌原纤维蛋白氧化对氨基酸的影响. 食品与发酵工业. 2019(22): 202-207+212 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)









 下载:
下载:














 下载:
下载:
