Research on Improving the Catalytic Activity of Thermoacidophilic Type III Pullulan Hydrolase TK-PUL by Error-prone PCR
-
摘要: 嗜热酸性III型普鲁兰水解酶TK-PUL在液化条件下可完全水解淀粉为淀粉糖,在“液化糖化一步法”的淀粉制糖工艺中具有巨大的应用潜力。本研究拟采用易错聚合酶链式反应(polymerase chain reaction,PCR)技术提高TK-PUL的催化活性。经过两轮易错PCR及高通量筛选,获得了催化活性提高的突变体L538D。与TK-PUL相比,L538D以可溶性淀粉为底物的比酶活力提高了50%,以普鲁兰多糖为底物的比酶活力提高了21%;L538D以可溶性淀粉、普鲁兰多糖为底物的kcat/Km值分别提高了44%、27%。即L538D的α-1,4-糖苷键水解活性和α-1,6-糖苷键水解活性均明显提高,并且其α-1,4-糖苷键水解活性的提高幅度更大。同源模建得到的蛋白质分子结构显示,将TK-PUL中Leu538替换为Asp,可能通过缩短氨基酸残基侧链的长度和减弱氨基酸残基的疏水性,提高了催化活性位点Glu538所在loop结构的柔性,从而提高酶的催化活性。本研究结果表明,TK-PUL中Leu538是影响其催化活性的重要氨基酸残基。
-
关键词:
- III型普鲁兰多糖水解酶 /
- 定向进化 /
- 易错聚合酶链式反应(易错PCR) /
- 高通量筛选技术 /
- 催化活性
Abstract: Thermoacidophilic type III pullulan hydrolase TK-PUL can completely hydrolyze starch to starch sugar under liquefaction condition. It has great application potential in the ''one step liquefaction-saccharification'' starch syrup production process. In this study, error-prone PCR technology was used to improve the catalytic activity of TK-PUL. After two sequential error-prone PCR and high-throughput screening, the mutant L538D with improved catalytic activity was obtained. Compared with TK-PUL, the specific activity of L538D with soluble starch as substrate increased by 50%, the specific activity of L538D toward pullulan increased by 21%. And the kcat/Km value of L538D for soluble starch, pullulan increased by 44% and 27%, respectively. In other words, the hydrolytic activity of L538D toward α-1,4-glycosidic bond and α-1,6-glycosidic bond were significantly improved, and the hydrolytic activity of L538D toward α-1,4-glycosidic bond increased to a greater degree. Homology modeling showed that replacing Leu538 with Asp in TK-PUL may improve the flexibility of the loop structure including the catalytic site Glu538 by shortening the length of the side chain of amino acid residues and reducing the hydrophobicity of amino acid residues, thus improving the catalytic activity of the enzyme. The results demonstrated that Leu538 in TK-PUL is vital for its catalytic activity. -
优化工业淀粉制糖工艺的相关研究对于我国淀粉制糖工业的发展具有重要的技术和经济意义[1-2]。现行工业淀粉制糖工艺包括液化和糖化两个步骤[3-5]。液化步骤和糖化步骤的反应温度、pH均不同,并且淀粉制糖工艺中使用了多种淀粉水解酶(例如α-淀粉酶、β-淀粉酶、普鲁兰酶以及葡萄糖淀粉酶等),这些因素导致淀粉制糖工业的生产成本增加、生产效率降低。因此,如果能够获得一种在高温液化条件下对淀粉原料同时进行液化和糖化作用的酶,则可有效降低生产成本,提高生产效率。
III型普鲁兰多糖水解酶(EC 3.2.1.1/41)属于糖苷水解酶类的第13家族(GH13_20),是一种双功能淀粉水解酶,同时具有α-淀粉酶活性和普鲁兰酶活性[6-9]。嗜热酸性III型普鲁兰多糖水解酶可在淀粉制糖工业的液化条件下完全水解淀粉为淀粉糖,有望实现“液化糖化一步法”淀粉酶法制糖工艺。嗜热酸性III型普鲁兰多糖水解酶TK-PUL来源于极端嗜热古生菌Thermococcus kodakarensis KOD1,具有优良的热稳定性和高温活性,并且其热稳定性和高温活性均不依赖于Ca2+,即TK-PUL的酶学性质完全符合淀粉酶法制糖工业的需求[10-13]。因此TK-PUL在淀粉酶法制糖工业中具有巨大的应用潜力。但是TK-PUL的催化效率尚不能满足淀粉酶法制糖工业的需求,难以在淀粉酶法制糖工业中高效地发挥水解作用,这限制了TK-PUL在淀粉酶法制糖工业中的应用[12]。通过蛋白质工程对TK-PUL进行提高催化活性的分子改造可以为其在淀粉酶法制糖工业中的应用奠定基础,对淀粉制糖工业的升级改造具有重要意义。此外,突变体催化效率强化的分子机制研究也可为其他淀粉水解酶以应用为导向的分子改造提供理论依据和设计思路。
易错聚合酶链式反应(polymerase chain reaction,PCR)就是目前采用最多的一种蛋白质体外定向进化技术,在酶分子的催化特性改善方面发挥重要作用[14-16]。易错PCR技术已经应用于提升淀粉水解酶、脂肪酶、漆酶、β-葡聚糖酶、糖基海藻糖合酶、纤维素酶等酶活力,并对研究影响酶催化性质的关键氨基酸残基起到了重要指导作用[17-22]。本研究拟运用易错PCR技术对TK-PUL进行体外定向进化研究,以期获得酶活力提高的突变体。进一步通过比较突变体与TK-PUL的酶学特性和蛋白质分子结构,揭示突变体酶活力提高的可能分子机制。本研究有助于理解TK-PUL的双功能催化机制,也可为其他淀粉水解酶以应用为导向的分子改造提供理论依据和设计思路。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
TK-PUL表达载体pBE-S-Atkp、大肠杆菌Escherichia coli JM109 均由本实验室保存[13];DNA Marker、蛋白质Marker、质粒DNA小量纯化试剂盒、Bacillus subtilis Secretory Protein Expression System、DNA Ligation Kit Ver.2.1、限制性内切酶 日本TaKaRa公司;StarMut随机突变试剂盒 北京康润诚业生物科技有限公司;Ni-NTA亲和层析柱 德国QIAGEN公司;普鲁兰糖、可溶性淀粉、麦芽糖、麦芽三糖、麦芽四糖、潘糖、异潘糖 上海惠诚生物科技有限公司;Bradford法蛋白质定量检测试剂盒 上海碧云天生物技术有限公司;LB肉汤培养基 生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司;其他试剂 均为国产分析纯。
S1000 PCR仪(Mastercycler gradient) 美国Bio-Rad公司;全自动数码凝胶图像分析系统(Tanon-4100) 上海天能科技有限公司;紫外可见分光光度计(760CRT) 上海仪电分析仪器有限公司;CMax Plus酶标仪 日本Hitachi公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 易错PCR扩增
根据StarMut随机突变试剂盒说明书和TK-PUL的基因序列,设计易错PCR引物。在引物的末端分别引入限制性内切酶Nde I和Xba I的酶切位点(如下划线所示):上游引物F为5'-CGCATATGAGCGGATGTATCTCGGAGAGC-3';下游引物R为5'-TGTCTAGAACCCCGCTCAAGGATGATTATC-3'。易错PCR反应的模板为pBE-S-Atkp。PCR反应体系为50 μL:模板DNA 1 μL、2×StarMut Random system 25 μL、上游引物F 1 μL、下游引物F 1 μL、StarMut Enhancer 0~20 μL、ddH2O补足至50 μL。PCR扩增条件为:94 ℃ 5 min;94 ℃ 30 s,55 ℃ 1 min,72 ℃ 1 min,25个循环;72 ℃ 7 min。通过调整PCR反应体系中StarMut Enhancer的添加量改变碱基突变率。
1.2.2 突变文库的构建
采用DNA胶回收试剂盒对易错PCR产物进行切胶回收。将重组载体pBE-S-Atkp和纯化后的易错PCR产物分别用限制性内切酶Nde I和Xba I双酶切后进行连接,其中酶切反应和连接反应均参照产品说明书进行。将连接产物电击转入大肠杆菌E. coli JM109感受态细胞,转化产物于37 ℃孵育1 h后涂布于含100 μg/mL氨苄青霉素的LB平板,37 ℃培养16 h,提取所有转化子中的重组质粒。采用改进的Spizizen法[23]将所获得的重组质粒转化B. subtilis RIK1285感受态细胞,根据Bacillus subtilis Secretory Protein Expression System说明书,将转化产物涂布于含10 μg/mL卡那霉素的LB平板上,于37 ℃培养24 h,即获得突变文库。
1.2.3 突变文库的高通量培养和高通量筛选
突变文库的高通量培养和高通量筛选参照文献[13]方法进行。突变体文库经高通量培养后,各突变体的发酵液上清用于α-淀粉酶活性的高通量检测。α-淀粉酶活性的高通量检测对应的吸光值的大小反应突变体的酶活大小,筛选出吸光值最大的突变体用做第2轮易错PCR的模板或进行基因测序分析。
1.2.4 重组酶的诱导表达和纯化
重组酶的诱导表达与纯化参照文献[13]进行。采用聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳(Sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, SDS-PAGE)[24]检测重组酶的纯度,并采用Bradford法蛋白质定量检测试剂盒测定重组酶的浓度。
1.2.5 重组酶的酶活力测定
分别以1%(m/V)可溶性淀粉或普鲁兰多糖为底物,参照文献[13]测定重组酶的α-淀粉酶活性和普鲁兰酶活性。酶活力单位(U)[25]定义:在一定反应条件下,每分钟催化产生1 μmol还原糖的酶量为一个酶活力单位(U)。
1.2.6 重组酶的酶学性质测定
分别以1%可溶性淀粉或普鲁兰多糖为底物,测定重组酶的最适反应pH、pH稳定性、最适反应温度及热稳定性。重组酶的酶学性质测定参照文献[26]进行。重组酶的最适反应pH以及pH稳定性的测定范围为pH3.0~9.0;于40~110 ℃下测定重组酶的最适反应温度,并于100 ℃下测定重组酶的热稳定性。测定重组酶的最适反应pH或最适反应温度时,将所测得的最高酶活定义为100%,其余测得酶活与最高酶活的比值定义为相对酶活。测定重组酶的pH稳定性或热稳定性时,将未处理酶液的酶活定义为100%,处理后酶液的酶活与未处理酶液的酶活的比值定义为剩余酶活。
1.2.7 重组酶的动力学常数测定
分别以可溶性淀粉或普鲁兰多糖为底物,测定重组酶的动力学常数。重组酶的动力学常数测定参照文献[26]进行。可溶性淀粉的浓度梯度设定为5.0、10.0、15.0、20.0、30.0、35.0 mg/mL;普鲁兰多糖的浓度梯度设定为1.6、3.2、6.4、12.8、16.0、20.0 mg/mL。
1.2.8 生物信息学分析
将筛选获得的突变体送至生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司进行基因测序,并根据基因的碱基序列生成氨基酸序列,分析碱基及氨基酸的突变情况。以TK-PUL(PDB ID:5OT1)的蛋白质分子结构为模板,采用SWISS-MODEL(http://swissmodel.expasy.org)[27]同源模建突变体的蛋白质分子结构,并采用三维图像软件PyMOL v2.5.2显示TK-PUL及突变体的三级结构。
1.3 数据处理
所有试验均重复3次,试验结果用平均值±标准差表示,运用软件SigmaPlot 14.0对试验数据进行统计分析并作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 易错PCR条件的确立
根据StarMut随机突变试剂盒说明书,调整PCR反应体系中StarMut Enhancer的添加量可以改变碱基突变率。因此我们根据实验要求,在PCR反应体系中加入不同体积的StarMut Enhancer,进行易错PCR反应,构建突变体文库。从每组突变体文库中随机挑取10株菌进行基因测序以计算突变率,如表1所示,其中StarMut Enhancer的添加量为1 μL时的平均突变率为0.26%,接近目前公认的合适突变率0.25%[28],因此本研究易错PCR反应体系中StarMut Enhancer的添加量为1 μL。
表 1 PCR反应体系中StarMut Enhancer添加量对应的PCR突变率Table 1. PCR mutation rates corresponding to the supplemental level of StarMut Enhancer in the PCR reaction system组别 添加量(μL) 突变率(%) 1 0 0.12 2 1 0.26 3 2 0.53 4 4 0.95 5 6 1.23 6 8 1.35 2.2 突变体文库的构建与高通量筛选
以重组质粒pBE-S-Atkp为模板进行第1轮易错PCR,回收PCR产物,将其双酶切处理后连接经同样双酶切处理的载体,将连接产物转化大肠杆菌E. coli JM109感受态细胞,提取所有转化子所含重组质粒。将所获得的重组质粒转化B. subtilis RIK1285感受态细胞,获得容量约为2500株转化子的突变体文库。利用高通量筛选方法筛选突变体文库中酶活力提高的转化子,共获得10株胞外α-淀粉酶活力提高的转化子(数据未显示)。再次采用高通量筛选方法对以上10株转化子(定义为转化子1~转化子10)以及包含重组质粒pBE-S-Atkp的转化子(定义为转化子C)进行胞外α-淀粉酶活力的测定,结果如表2所示,筛选得到2株胞外α-淀粉酶活力提高幅度最大的转化子(转化子2和转化子7)。提取这2株转化子中重组质粒,并以这两种重组质粒为模板进行第2轮易错PCR,按照同样的方法获得容量约为2800株转化子的突变体文库。然而对新的突变体文库进行高通量筛选未能获得酶活力进一步提高的突变体。对经第1轮易错PCR反应获得的2个重组质粒进行测序,测序结果显示这2个重组质粒包含的突变位点一致,其第1612位碱基由C突变为G、第1613位碱基由T突变为A,即基因编码序列CTC突变为GAC,氨基酸序列由Leu538突变为Asp538。即本研究通过易错PCR技术对TK-PUL进行体外定向进化,获得了酶活力提高的突变体L538D。
表 2 转化子的高通量筛选结果Table 2. High throughput screening results of the transformants转化子序号 A540 nm C 0.459±0.018 1 0.501±0.023 2 0.742±0.030 3 0.513±0.019 4 0.563±0.025 5 0.608±0.032 6 0.601±0.029 7 0.750±0.033 8 0.625±0.031 9 0.634±0.037 10 0.654±0.031 2.3 TK-PUL和突变体L538D的表达、纯化及比酶活测定
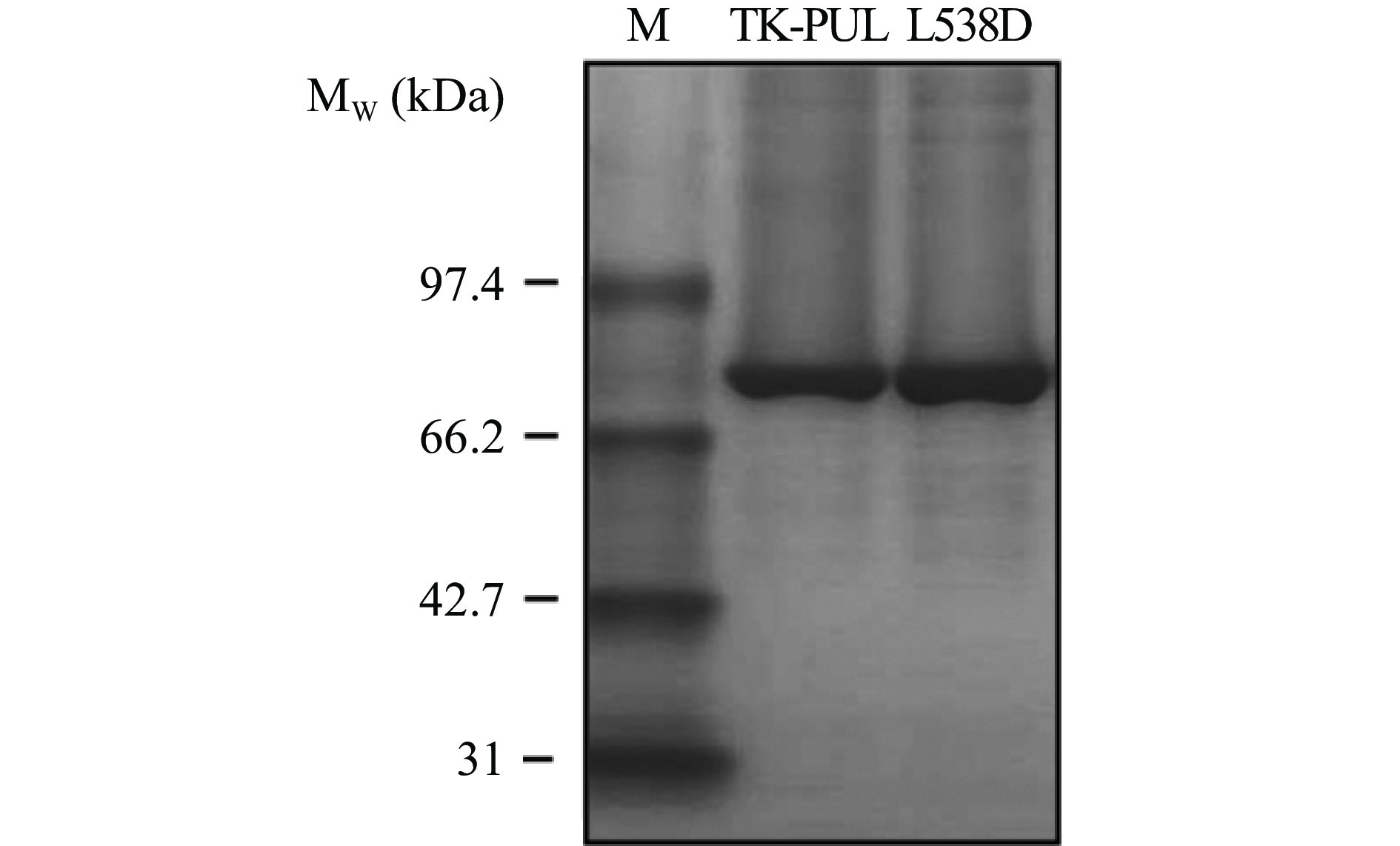
枯草芽孢杆菌作为传统的工业生产菌株,具有分泌能力强、培养条件和基因操作简单、发酵工艺成熟等优点,被认为是理想的外源蛋白质的分泌表达宿主菌。本研究于枯草芽孢杆菌表达系统中表达TK-PUL和突变体L538D,重组酶TK-PUL和突变体L538D均得到成功表达。采用Ni2+亲和层析法对重组酶进行纯化,并采用SDS-PAGE检测各重组酶的纯度。如图1所示,TK-PUL和突变体L538D的表观分子质量分别约为84 kDa,大小均与理论值相符。根据SDS-PAGE检测图中蛋白质条带的灰度分析结果,重组酶TK-PUL和突变体L538D的纯度均达到95%以上。
采用Bradford法测定TK-PUL和突变体L538D的蛋白质浓度,并测定其分别以可溶性淀粉和普鲁兰多糖为底物的比酶活力,结果如表3所示。TK-PUL的α-淀粉酶比酶活力为54.08 U/mg,L538D的α-淀粉酶比酶活力为81.14 U/mg。与TK-PUL相比,L538D的α-淀粉酶比酶活力提高了50%。TK-PUL的普鲁兰酶比酶活力为110.39 U/mg,L538D的普鲁兰酶比酶活力为133.18 U/mg。与TK-PUL相比,L538D的普鲁兰酶比酶活力提高了21%。TK-PUL的α-淀粉酶活性与普鲁兰酶活性的比值为0.49,L538D的α-淀粉酶活性与普鲁兰酶活性的比值为0.61。以上结果表明,与TK-PUL相比,突变体L538D的α-淀粉酶活性和普鲁兰酶活性均明显提高,并且其α-淀粉酶活性的提高幅度更大。
表 3 TK-PUL及突变体L538D于100 ℃的比酶活力Table 3. Specific activities of TK-PUL and the mutant L538D at 100 oC蛋白质浓度
(μg/μL)α-淀粉酶比酶活力
(U/mg)普鲁兰酶比酶活力
(U/mg)α-淀粉酶活性/普鲁兰酶活性 TK-PUL 3.48±0.26 54.08±1.85 110.39±3.46 0.49 L538D 5.06±0.27 81.14±2.33 133.18±3.41 0.61 2.4 TK-PUL和突变体L538D的酶学性质
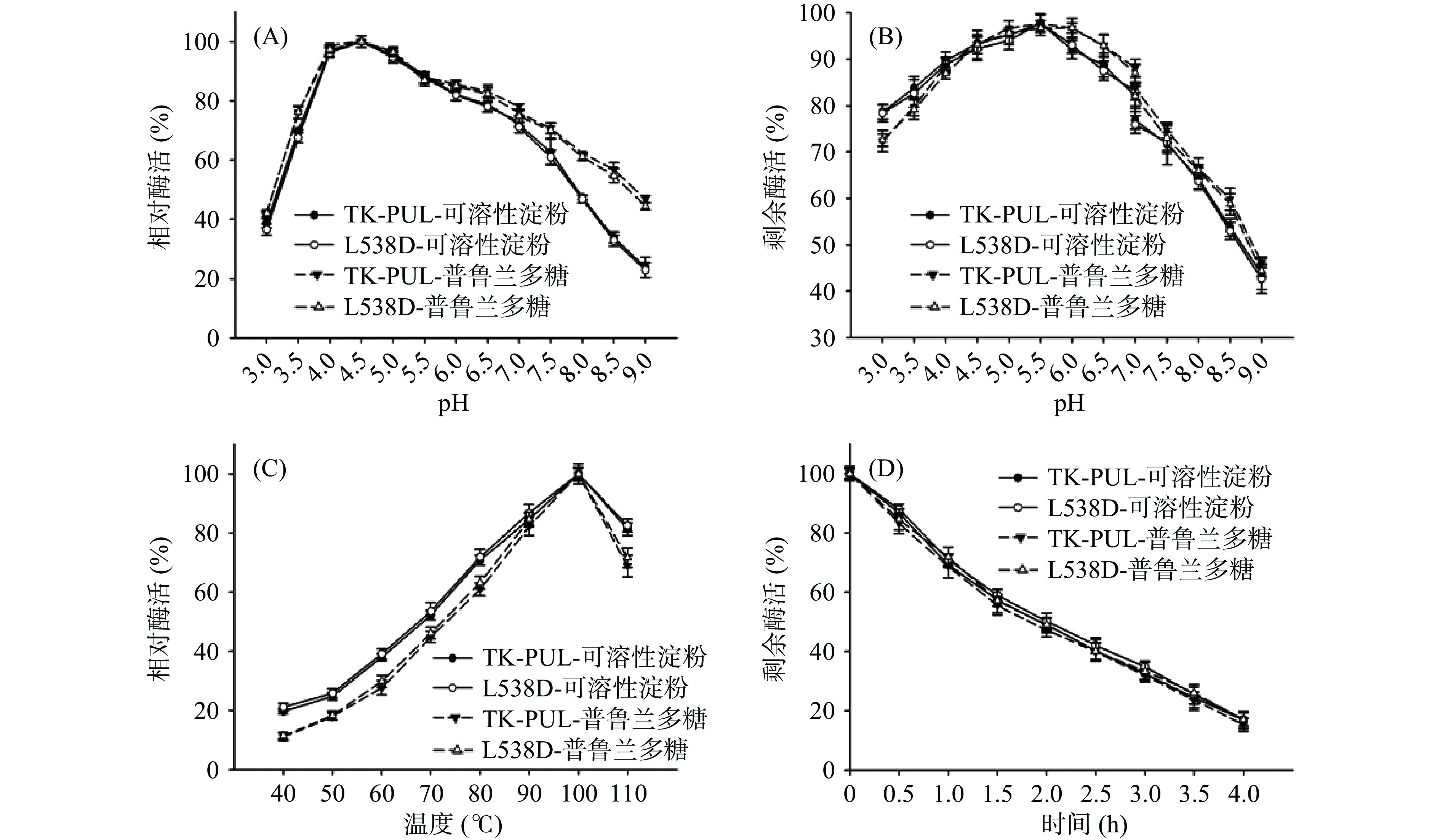
本研究测定了pH和温度对TK-PUL及突变体L538D酶学性质的影响。由图2(A)可知。以1%可溶性淀粉或普鲁兰多糖为底物时,TK-PUL及突变体L538D的最适反应pH均约为4.5,并且两者的相对酶活随pH的变化趋势也基本相同。另外,图2(B)显示,在pH为3.0~9.0的范围内,TK-PUL及突变体L538D的pH稳定性也几乎一致。这表明TK-PUL中L538D位点变化不影响其最适反应pH和pH稳定性。
TK-PUL及突变体L538D的最适反应温度测定结果如图2(C)所示。TK-PUL及突变体L538D的最适反应温度均约为100 ℃,在40~110 ℃的范围内两者的相对酶活随温度的变化趋势也基本相同。同时,由图2(D)可知,TK-PUL及突变体L538D于100 ℃的热稳定性也基本一致,于100 ℃的半衰期均约为2 h。即TK-PUL中L538D位点变化也不影响其最适反应温度和热稳定性。
2.5 TK-PUL及L538D的动力学常数测定
本研究测定并比较了TK-PUL及突变体L538D于100 ℃的动力学常数,依此来确定TK-PUL中L538D位点变化对其底物结合能力和底物降解能力的影响。由表4可知,以可溶性淀粉或普鲁兰多糖为底物时,与TK-PUL相比,突变体L538D的Km值基本不变,kcat值均明显提高。其中以可溶性淀粉为底物时,突变体L538D的kcat/Km值提高了44%;以普鲁兰多糖为底物时,突变体L538D的kcat/Km值提高了27%。以上结果表明,TK-PUL中L538D位点变化不影响TK-PUL对底物的结合能力,并有利于提高其对底物的降解能力,特别有利于提高其对可溶性淀粉的降解能力。
表 4 TK-PUL及突变体L538D的动力学常数Table 4. Kinetic parameters of TK-PUL and the mutant L538D底物 酶 Km(mg/mL) kcat(/s) kcat/Km(mL/(mg·s)) 相对kcat/Km(%) 可溶性淀粉 TK-PUL 1.86±0.18 80.91±3.05 43.49 100.00 L538D 1.90±0.19 118.99±4.12 62.63 144.01 普鲁兰多糖 TK-PUL 2.07±0.19 157.85±5.16 76.23 100.00 L538D 1.96±0.17 189.68±5.48 96.78 126.96 2.6 突变位点分析与分子结构模拟
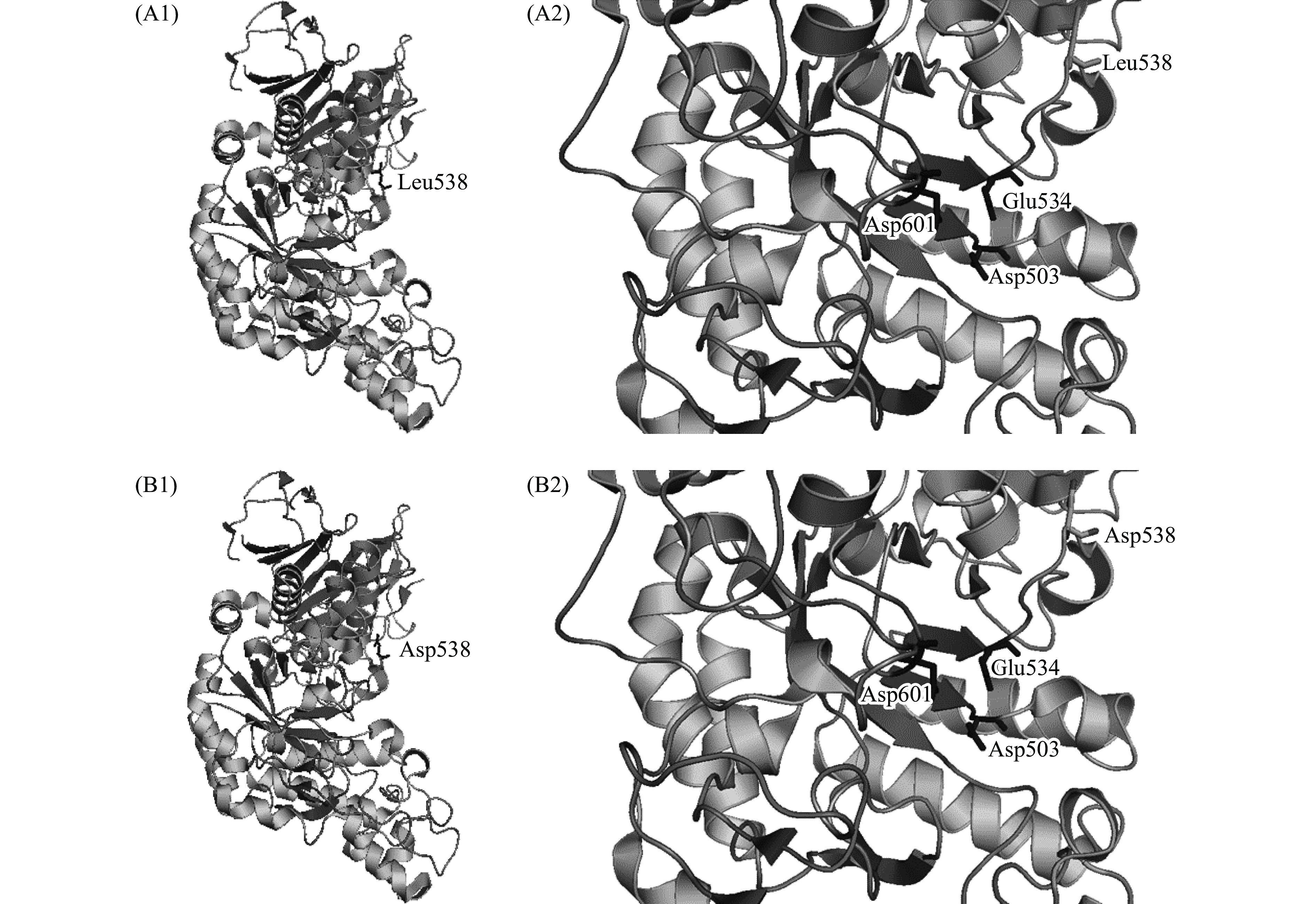
以TK-PUL(PDB ID:5OT1)的蛋白质分子结构[29]为模板,采用Swiss-Model同源模建突变体L538D的蛋白质分子结构。采用三维图像软件PyMOL v2.5.2显示TK-PUL及突变体L538D的三级结构。由图3(A1)可知,TK-PUL具有糖苷水解酶第13家族酶分子结构和催化机制上的共同特征,如三个结构域、四个高度保守的保守基序、保守的催化活性中心(Asp503、Glu534、Asp601)等。蛋白质的分子结构具有较强的稳定性,单个氨基酸残基的突变不会明显改变蛋白质分子的三维结构[30],所以突变体L538D与TK-PUL的三级结构基本一致(如图3所示)。由图3(A2)可知,TK-PUL中Leu538距离其催化活性中心和底物结合中心较远,无直接相互作用。本研究结果也表明,TK-PUL中L538D位点变化不影响其最适反应pH、pH稳定性、最适反应温度及热稳定性。因此蛋白质分子结构对比分析结果与本研究实验结果是相对应的。但是已有研究结果表明,催化活性位点附近的氨基酸残基的侧链大小以及侧链性质影响酶分子水解糖苷键的活性和特异性[30]。Leu538邻近催化活性位点Glue534,两者均位于同一loop结构上。TK-PUL中L538D位点变化可能通过缩短氨基酸残基侧链的长度和减弱氨基酸残基的疏水性,改变催化活性位点Glu534所在loop结构的柔性,进而提高酶的催化活性。
3. 结论
本研究采用易错PCR技术对III型普鲁兰多糖水解酶TK-PUL进行体外定向进化,获得催化活性提高的突变体L538D。TK-PUL中Leu538是影响其催化效率的重要氨基酸残基。将TK-PUL中催化活性位点Glu534邻近的氨基酸残基Leu538替换为侧链长度更短并且极性更强的氨基酸残基Asp538,有利于提高TK-PUL的催化活性。突变体L538D有望应用于“液化糖化一步法”的淀粉制糖工艺,可极大地简化淀粉酶法制糖工艺和提高生产效率。本研究也可为其他淀粉水解酶以应用为导向的分子改造提供理论依据和设计思路。
-
表 1 PCR反应体系中StarMut Enhancer添加量对应的PCR突变率
Table 1 PCR mutation rates corresponding to the supplemental level of StarMut Enhancer in the PCR reaction system
组别 添加量(μL) 突变率(%) 1 0 0.12 2 1 0.26 3 2 0.53 4 4 0.95 5 6 1.23 6 8 1.35 表 2 转化子的高通量筛选结果
Table 2 High throughput screening results of the transformants
转化子序号 A540 nm C 0.459±0.018 1 0.501±0.023 2 0.742±0.030 3 0.513±0.019 4 0.563±0.025 5 0.608±0.032 6 0.601±0.029 7 0.750±0.033 8 0.625±0.031 9 0.634±0.037 10 0.654±0.031 表 3 TK-PUL及突变体L538D于100 ℃的比酶活力
Table 3 Specific activities of TK-PUL and the mutant L538D at 100 oC
蛋白质浓度
(μg/μL)α-淀粉酶比酶活力
(U/mg)普鲁兰酶比酶活力
(U/mg)α-淀粉酶活性/普鲁兰酶活性 TK-PUL 3.48±0.26 54.08±1.85 110.39±3.46 0.49 L538D 5.06±0.27 81.14±2.33 133.18±3.41 0.61 表 4 TK-PUL及突变体L538D的动力学常数
Table 4 Kinetic parameters of TK-PUL and the mutant L538D
底物 酶 Km(mg/mL) kcat(/s) kcat/Km(mL/(mg·s)) 相对kcat/Km(%) 可溶性淀粉 TK-PUL 1.86±0.18 80.91±3.05 43.49 100.00 L538D 1.90±0.19 118.99±4.12 62.63 144.01 普鲁兰多糖 TK-PUL 2.07±0.19 157.85±5.16 76.23 100.00 L538D 1.96±0.17 189.68±5.48 96.78 126.96 -
[1] BELLO-PEREZ L A, FLORES-SILVA P C, AGAMA-ACEVEDO E, et al. Starch digestibility: Past, present, and future[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2020,100(14):5009−5016. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.8955
[2] SCHMIELE M, SAMPAIO U M, CLERICI M T P S. Basic principles: Composition and properties of starch[M]. New York: Academic Press, 2019: 1-22.
[3] OKAFOR D C, OFOEDU C E, NWAKAUDU A, et al. Enzymes as additives in starch processing: A short overview[M]. New York: Academic Press, 2019: 149-168.
[4] MIAO M, JIANG B, JIN Z, et al. Microbial starch-converting enzymes: Recent insights and perspectives[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety,2018,17(5):1238−1260. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12381
[5] ZHANG Q G, HAN Y, XIAO H Z. Microbial α-amylase: A biomolecular overview[J]. Process Biochemistry,2017,53:88−101. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2016.11.012
[6] NISHA M, SATYANARAYANA T. Characteristics, protein engineering and applications of microbial thermostable pullulanases and pullulan hydrolases[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2016,100(13):5661−5679. doi: 10.1007/s00253-016-7572-y
[7] WANG X, NIE Y, XU Y. Industrially produced pullulanases with thermostability: Discovery, engineering, and heterologous expression[J]. Bioresource Technology,2019:360−371.
[8] AKASSOU M, GROLEAU D. Advances and challenges in the production of extracellular thermoduric pullulanases by wild-type and recombinant microorganisms: A review[J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology,2019,39(3):337−350. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2019.1566202
[9] XIA W, ZHANG K, SU L, et al. Microbial starch debranching enzymes: Developments and applications[J]. Biotechnology Advances,2021:107786.
[10] HAN T, ZENG F, LI Z, et al. Biochemical characterization of a recombinant pullulanase from Thermococcus kodakarensis KOD1[J]. Letters in Applied Microbiology,2013,57(4):336−343. doi: 10.1111/lam.12118
[11] AHMAD N, RASHID N, HAIDER M S, et al. Novel maltotriose-hydrolyzing thermoacidophilic type III pullulan hydrolase from Thermococcus kodakarensis[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2014,80(3):1108−1114. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03139-13
[12] TOOR K J, AHMAD N, MUHAMMAD M A, et al. TK-PUL, a pullulan hydrolase type III from Thermococcus kodakarensis, a potential candidate for simultaneous liquefaction and saccharification of starch[J]. Amylase,2020,4(1):45−55. doi: 10.1515/amylase-2020-0004
[13] 曾静, 郭建军, 袁林. 嗜热酸性普鲁兰水解酶Ⅲ的高效分泌表达及其酶学性质[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(3):98−103, 109. [ZENG J, GUO J J, YUAN L. Efficient secretory expression of thermoacidiphilic type III pullulan hydrolase and its enzymatic properties[J]. Science and Technology of Food industry,2020,41(3):98−103, 109. ZENG J, GUO J J, YUAN L. Efficient secretory expression of thermoacidiphilic type III pullulan hydrolase and its enzymatic properties[J]. Science and Technology of Food industry, 2020, 41(3): 98-103, 109.
[14] KATARIA A, SHARMA R, SHARMA S, et al. Recent applications of bio-engineering principles to modulate the functionality of proteins in food systems[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2021,113:54−65.
[15] XU Y, WU Y, LV X, et al. Design and construction of novel biocatalyst for bioprocessing: Recent advances and future outlook[J]. Bioresource Technology,2021:125071.
[16] ZENG W, GUO L, XU S, et al. High-throughput screening technology in industrial biotechnology[J]. Trends in Biotechnology,2020,38(8):888−906. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2020.01.001
[17] WU H, TIAN X, DONG Z, et al. Engineering of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens α-amylase with improved calcium independence and catalytic efficiency by error-prone PCR[J]. Starch-Stärke,2018,70(3−4):1700175.
[18] GAOL M D F L, SATYA A A, PUSPITASARI E, et al. Increasing hydrolytic activity of lipase on palm oil by PCR-based random mutagenesis[J]. International Journal of Oil Palm,2020,3(3):78−87. doi: 10.35876/ijop.v3i3.53
[19] DAI S, YAO Q, YU G, et al. Biochemical characterization of a novel bacterial laccase and improvement of its efficiency by directed evolution on dye degradation[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2021:12.
[20] SUN Z B, XU J L, LU X, et al. Directed mutation of β-glucanases from probiotics to enhance enzymatic activity, thermal and pH stability[J]. Archives of Microbiology,2020,202(7):1749−1756. doi: 10.1007/s00203-020-01886-z
[21] SU L, YAO K, WU J. Improved activity of Sulfolobus acidocaldarius maltooligosyltrehalose synthase through directed evolution[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2020,68(15):4456−4463. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c00948
[22] BASIT A, TAJWAR R, SADAF S, et al. Improvement in activity of cellulase Cel12A of Thermotoga neapolitana by error prone PCR[J]. Journal of Biotechnology,2019,306:118−124. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2019.09.011
[23] ANAGNOSTOPOULOS C, SPIZIZEN J. Requirements for transformation in Bacillus subtilis[J]. Journal of Bacteriol,1961,81(5):741−746. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.5.741-746.1961
[24] GREEN M R, SAMBROOK J. Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual[M]. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 2012: 101-200.
[25] MILLER G L. Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar[J]. Analytical Chemistry,1959,31(3):426−428. doi: 10.1021/ac60147a030
[26] 曾静, 何础阔, 郭建军, 等. N末端结构模块缺失对嗜热酸性III型普鲁兰多糖水解酶TK-PUL酶学性质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(10):201−208. [ZENG J, HE C K, GUO J J, et al. Effect of truncation of N-terminal structural modules on enzymatic properties of thermoacidiphilic type III pullulan hydrolase TK-PUL[J]. Food Science,2021,42(10):201−208. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200408-099 ZENG J, HE C K, GUO J J, et al. Effect of truncation of N-terminal structural modules on enzymatic properties of thermoacidiphilic type III pullulan hydrolase TK-PUL[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(10): 201-208. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200408-099
[27] WATERHOUSE A, BERTONI M, BIENERT S, et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology modelling of protein structures and complexes[J]. Nucleic Acids Research,2018,46(W1):W296−W303. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky427
[28] LIU B, PENG Q, SHENG M, et al. Directed evolution of sulfonylurea esterase and characterization of a variant with improved activity[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2018,67(3):836−843.
[29] GUO J, COKER A, WOOD S, et al. Structure and function of the type III pullulan hydrolase from Thermococcus kodakarensis[J]. Acta Crystallographica Section D,2018,74(4):305−314. doi: 10.1107/S2059798318001754
[30] MØLLER M S, HENRIKSEN A, SVENSSON B. Structure and function of α-glucan debranching enzymes[J]. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences,2016,73(14):2619−2641. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2241-y
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 李越,池慧兵,牛家峰,马斌,周慧敏,朱萍,吕凤霞. 基于定向进化技术提高呕吐毒素解毒酶DepA的催化活性. 南京农业大学学报. 2024(04): 750-759 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



