Optimization of Ultrasound Assisted Extraction Process of Cyperus esculentus L. Starch and Its Physicochemical Properties
-
摘要: 为了得到超声波辅助提取油莎豆淀粉的最佳条件,以及油莎豆淀粉的理化特性,本文通过单因素和响应面试验研究提取油莎豆淀粉的最佳条件,通过扫描电镜分析、傅里叶红外变换分析、X射线衍射分析、DSC分析研究其理化特性。结果表明:最佳工艺条件为温度30 ℃、时间50 min、液料比15:1 mL/g、pH8,此条件下油莎豆淀粉提取率为92.22%±0.99%。将油莎豆淀粉与小麦淀粉等五种淀粉的理化特性对比发现:油莎豆淀粉颗粒较其它淀粉表面光滑,粒径范围与木薯淀粉、红薯淀粉、小麦淀粉相近,明显小于马铃薯淀粉,粒径范围2~15 μm,处于中小水平;油莎豆淀粉C-O和O-H拉伸程度较低,C-H的伸缩振动程度较低;油莎豆淀粉晶型与大多数谷物淀粉相似,属于A型淀粉;油莎豆淀粉在DSC实验中起始温度、峰值温度仅低于红薯淀粉,终止温度低于红薯淀粉和玉米淀粉。综上,油莎豆淀粉粒径相对较小,其属于A型淀粉,与B型淀粉相比不易发生水解,且其支链淀粉结构较多。Abstract: In order to obtain the optimum conditions of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of Cyperus esculentus L. starch and its physicochemical properties, this paper studied the optimum conditions of extraction of Cyperus esculentus L. starch by single factor and response surface experiments, and studied its physicochemical properties by scanning electron microscope analysis, Fourier transform infrared analysis, X-ray diffraction analysis and DSC analysis. The results showed that the optimum technological conditions were determined as temperature 30 ℃, time 50 min, liquid-solid ratio 15:1 mL/g and pH8. Under these conditions, the extraction rate of Cyperus esculentus L. starch was 92.22%±0.99%. By comparing the physicochemical properties of five kinds of starches, such as Cyperus esculentus L. starch and wheat starch, it was found that Cyperus esculentus L. starch granules had a smoother surface than other starches, and the particle size range was similar to tapioca starch, sweet potato starch and wheat starch, which was obviously smaller than potato starch, and the particle size range was 2~15 μm, which was in the middle and small level. The stretching degree of C-O and O-H of Cyperus esculentus L. starch was low, and the stretching vibration degree of C-H was low. The crystal form of Cyperus esculentus L. starch was similar to that of most cereal starches, and belonged to type A starch. In DSC experiment, the starting temperature and peak temperature of Cyperus esculentus L. starch were only lower than that of sweet potato starch, and the ending temperature was lower than that of sweet potato starch and corn starch. The results showed that the particle size of Cyperus esculentus L. starch was relatively small, which belonged to type A starch, and it was not easy to hydrolyze compared with type B starch, and its amylopectin structure was more.
-
油莎豆(Cyperus esculentus L),又称地果、油豆、人参豆,还拥有虎坚果、地下核桃等称号,属多年生单子叶植物[1]。油莎豆营养丰富,经济效益高,其油、蛋白质、淀粉含量分别占比20%~35%、10%~15%、20%~25%,并含有丰富的微量元素,其综合营养成份位于大多数谷物之上[2]。油莎豆淀粉中直链和支链淀粉含量比值大概有1:3,使其具有许多优良的特性,包括透明度、溶解度以及膨胀度等[3]。此外,油莎豆凝胶淀粉耐酸性强,热糊和冷糊稳定性优良,且具有明显优于玉米淀粉的冻融稳定性[4]。
油莎豆有着广泛的应用前景,国内大多是将油莎豆当作油料作物[5],而关于淀粉的研究还不够完善,仍处于初期阶段,产品质量无法保障,标准也缺乏统一[6]。王璐阳等研究了油莎豆压榨饼淀粉,得出了油莎豆淀粉具有优良的凝胶特性[5]。于淑艳等指出油莎豆淀粉的冻融稳定性优于玉米淀粉[2]。在国外,人们大多将油莎豆磨成粉而制作成面制品,也有人做成豆乳汁食用[7],以及做成油莎豆饮料、糖果等[8]。Manek等研究了油莎豆淀粉的提取工艺和理化特性,指出了油莎豆淀粉可作为一些药物的粘合剂的研究方向[9]。Busola等则直接研究了油莎豆淀粉在甲硝唑片剂中的应用[10]。因此油莎豆淀粉在食品、制药方面有很大的应用前景,研究其提取工艺和理化特性具有重要价值。
目前对于油莎豆提取工艺的研究大多单纯的使用碱法将蛋白质去除,然后得到淀粉。王璐阳等研究油莎豆压榨饼的淀粉的提取工艺,通过正交试验优化提取条件,得到油莎豆压榨饼的最大提取率为77.61%[5]。陈星等通过正交试验优化碱法的液料比、温度等因素,所得到的油莎豆淀粉最大提取率为89.9%[11]。Meng等通过石灰水浸泡法,通过正交试验优化浸泡液pH、液料比和浸泡时间,得到油莎豆淀粉的含量为35.4%[12]。超声波辅助提取淀粉研究已被广泛应用,但是用于提取油莎豆淀粉的研究较少。由于这种方法提取淀粉不仅能够提高产率和缩短提取时间,而且所得淀粉的功能性质也更好[13-14],所以本试验将石油醚脱脂-超声波辅助碱法作为去除油莎豆中的蛋白质,得到油莎豆淀粉的方法,并优化超声条件,以提高淀粉提取率。通过单因素实验和响应面试验研究最适宜的超声辅助碱法提取的条件。通过对油莎豆淀粉与小麦淀粉等五种淀粉进行扫描电镜分析、傅里叶红外变换分析、X射线衍射分析、DSC分析,分析油莎豆淀粉与其它淀粉的不同特性,为研究油莎豆淀粉在食品中的应用提供依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
油莎豆 定州老位油莎豆;小麦、木薯、玉米、红薯、马铃薯五种淀粉 新乡良润全谷物食品有限公司;氢氧化钠 分析纯,天津市晶科化工有限公司;盐酸 分析纯,扬州市华富化工有限公司;石油醚 分析纯,天津大茂化学试剂厂;硫酸锌 分析纯,天津登峰化学试剂厂;亚铁氰化钾 分析纯,天津恒兴化学试剂制造有限公司。
101AS-3干燥箱 南通华泰实验仪器有限公司;SGW-537旋光仪 上海仪电分析仪器有限公司;BSA224S电子天平 北京赛多利斯科学仪器有限公司;KQ-300E超声清洗机 昆山超声仪器有限公司;JSM-IT200扫描电子显微镜 日本电子珠式会社;Nicolet iS50傅里叶红外光谱仪 赛默飞世尔科技公司;D2 PHASERX射线衍射仪 德国布鲁克;DSC2500差示扫描量热仪 美国TA公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 原料预处理
将新鲜油莎豆放于干燥箱中烘干,水分控制在15%左右,用粉碎机粉碎后过40目筛,使用石油醚去除油脂后粉碎过60目筛,得到油莎豆豆粕粉。
1.2.2 提取方法及淀粉提取率的测定
采用湿法提取淀粉[15]。称量预处理得到的油莎豆豆粕粉20.00 g放入250 mL烧杯中,加入一定比例的NaOH溶液摇匀,在超声仪器中处理油莎豆豆粕粉一段时间,通过超声波处理,淀粉和蛋白质、非淀粉多糖等物质的结合能力降低,淀粉细胞破碎,从而减少淀粉的提取时间并提高提取率[16]。超声波处理之后,在磁力搅拌锅中室温下搅拌30 min,使碱液进一步作用,蛋白质被充分去除,使油莎豆淀粉纯度提高[17]。使用离心机,4000 r/min离心15 min后,弃去上清液,向沉淀物中加入适量蒸馏水,用200目左右的细纱布过滤,得到的滤下物继续离心过滤,重复三次,离心沉淀物通过鼓风干燥箱进行干燥,温度40 ℃,时间24 h,即得油莎豆淀粉。
称取过40目的油莎豆淀粉2.50 g,采用旋光法测定淀粉含量[18],采用以下公式计算油莎豆淀粉含量和提取率。
淀粉含量(%)=测得旋光度×100淀粉的比旋光度×旋光管长度×样品重量×100 式中:油莎豆淀粉的比旋光度为203°。
淀粉提取率(%)=粗淀粉质量×粗淀粉淀粉含量豆粕粉质量×豆粕粉淀粉含量×100 1.2.3 单因素实验
单因素实验采用控制变量法,确定液料比、浸泡时间、浸泡温度、浸泡液pH四个因素,并用以考察对油莎豆淀粉提取率的影响,为响应面试验确定最佳提取率的因素范围。
1.2.3.1 温度对淀粉提取率的影响
在液料比9:1 mL/g,浸泡时间40 min,浸泡液pH10的条件下,依次以20、30、40、50、60、70 ℃,6个梯度的温度考察温度对淀粉提取率的影响。
1.2.3.2 时间对淀粉提取率的影响
在液料比9:1 mL/g,浸泡温度40 ℃,浸泡液pH10的条件下,依次以10、20、30、40、50、60 min,6个梯度的时间考察时间对淀粉提取率的影响。
1.2.3.3 液料比对淀粉提取率的影响
在浸泡时间40 min,浸泡温度40 ℃,浸泡液pH10的条件下,依次以3:1、6:1、9:1、12:1、15:1、18:1 mL/g,6个梯度的液料比考察液料比对淀粉提取率的影响。
1.2.3.4 pH对淀粉提取率的影响
在液料比9:1 mL/g,浸泡时间40 min,浸泡温度40 ℃的条件下,依次以pH8、9、10、11、12、13,6个梯度的pH,考察pH对淀粉提取率的影响。
1.2.4 响应面试验
响应面试验以单因素实验为基础,借助Design-Expert8.0软件,每个因素在最高提取率周围选择三个条件,进行29组实验。响应面分析因素及水平见表1。
表 1 响应面分析因素及水平Table 1. Factors and levels of response surface analysis水平 A 温度(℃) B 时间(min) C 液料比(mL/g) D pH −1 30 30 9:1 8 0 40 40 12:1 9 1 50 50 15:1 10 1.2.5 扫描电镜测定方法
分别取油莎豆淀粉和小麦、木薯、玉米、红薯、马铃薯五种淀粉,沾到导电胶上,在真空环境中喷金处理,然后上机测试,观察颗粒的形态结构[19]。
1.2.6 红外变换测定方法
分别取油莎豆淀粉和小麦、木薯、玉米、红薯、马铃薯五种淀粉,采用常规压片的方法,范围4000~400 cm−1[20]。
1.2.7 X射线衍射测定方法
分别取油莎豆淀粉和小麦、木薯、玉米、红薯、马铃薯五种淀粉,采用粉末状样品常规衍射法测定,扫描速度为10°/min[21]。
1.2.8 糊化特性测定方法
分别取油莎豆淀粉和小麦、木薯、玉米、红薯、马铃薯五种淀粉,称取2 mg,加入70%(m/m)的蒸馏水,从10 ℃扫描到110 ℃,升温速率10 ℃/min,使用差示扫描量热仪进行测定,观察其加热糊化过程中的相变行为和热焓值的变化[22]。使用TA Universal Analysis Q2000软件分析糊化开始温度、峰值温度和终止温度(分别为To、Tp和Te)等[23]。
1.3 数据处理
单因素实验和响应面试验重复两次,测定六种淀粉性质实验重复一次,使用Origin 2019作图,Design-Expert 8.0处理响应面试验数据,平行实验的之间的差异通过标准差反映,并通过Excel 2010计算提取率与标准差。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 油莎豆淀粉提取单因素实验结果
2.1.1 温度对油莎豆淀粉提取率的影响
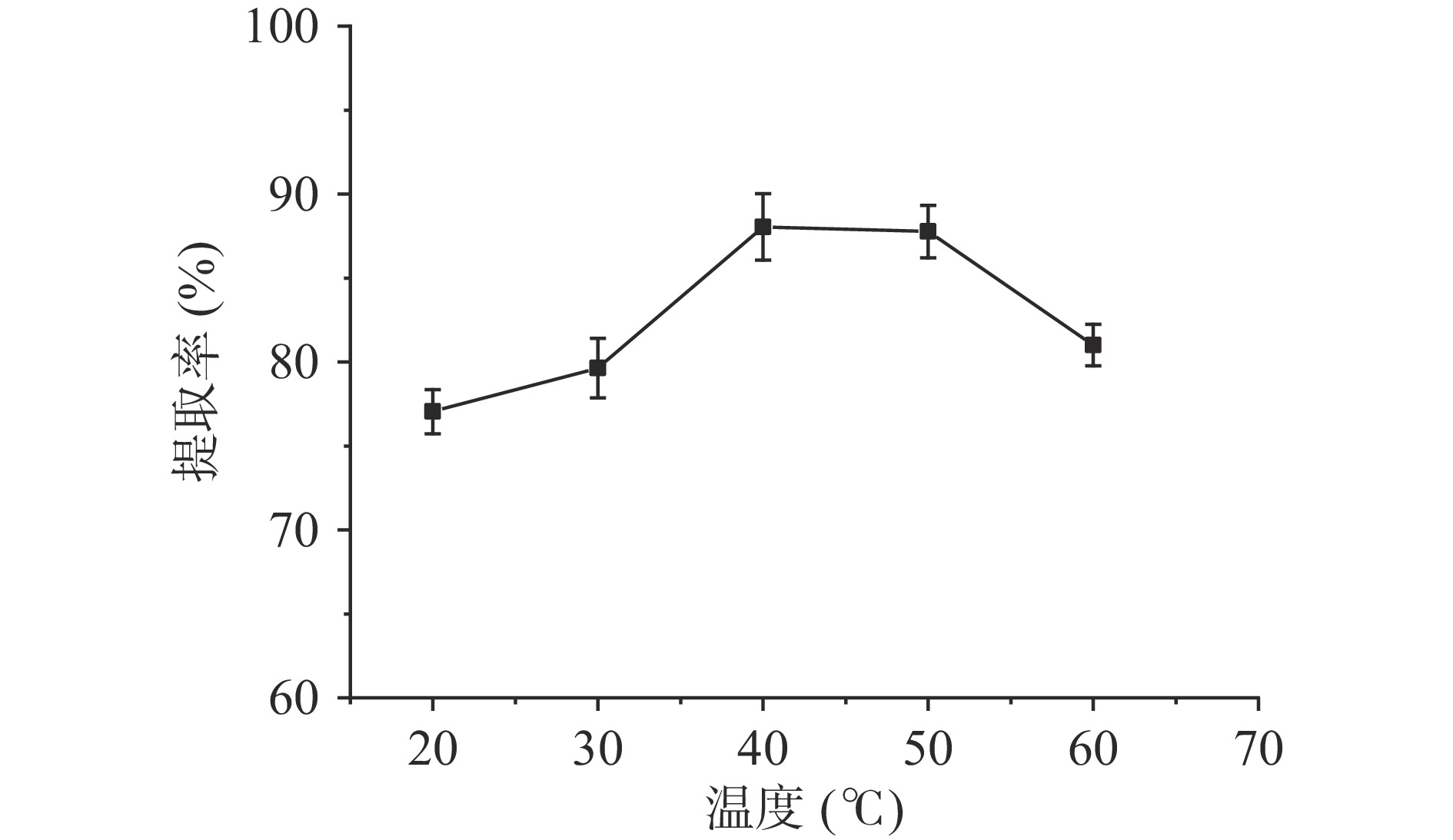
超声波辅助下温度对淀粉提取率的影响如图1所示。
刚开始提取率随着温度的增加而增加。温度40 ℃时,提取率达到最大,为88.04%。随着温度的上升,提取率逐渐下降,这可能是因为随着温度的升高,淀粉的溶解度和膨胀度增加[11]。当温度达到70 ℃时,油莎豆豆粕粉溶液变成黏稠的胶体溶液,无法进行过滤等操作,此时测定其淀粉提取率无实际意义。因此确定超声波辅助提取油莎豆淀粉的最佳提取温度为40 ℃。
2.1.2 时间对油莎豆淀粉提取率的影响
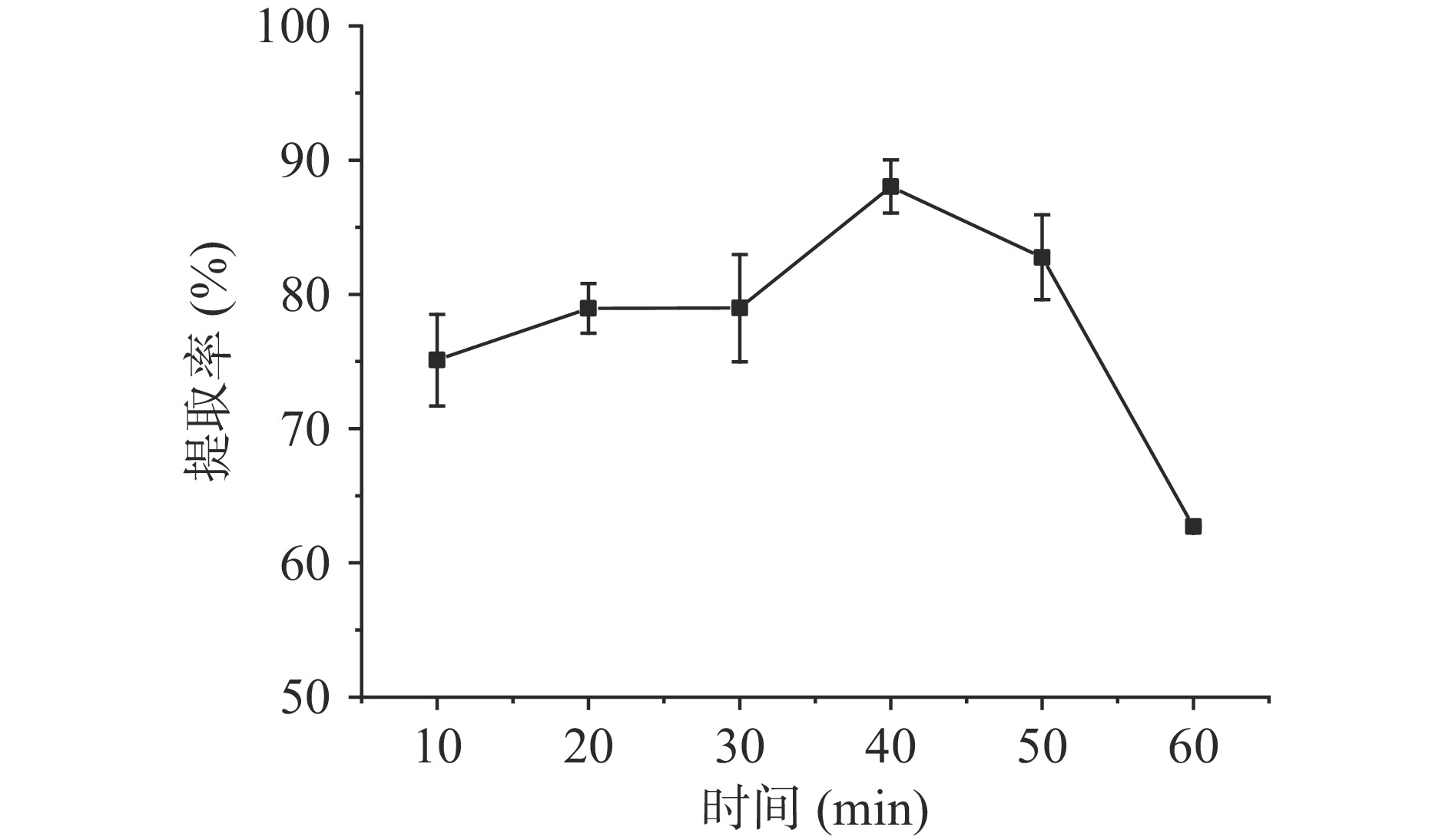
超声波辅助下时间对淀粉提取率的影响如图2所示。
随着超声时间的增加,油莎豆淀粉的提取率也随之增加,在40 min时,提取率达到最大值,为88.04%,但是随着时间继续增加,提取率开始呈现下降趋势。可能是因为随着超声时间的增加,细胞破碎程度提升,淀粉与其它成分结合的强度降低,使得淀粉更容易被提取[13],但是随着时间继续增加,蛋白质和可溶性糖的溶解度达到饱和[5],且淀粉的溶解度和膨胀度增加[11],使得提取率呈现下降趋势。因此确定超声波辅助提取油莎豆淀粉的最佳提取时间为40 min。
2.1.3 液料比对油莎豆淀粉提取率的影响
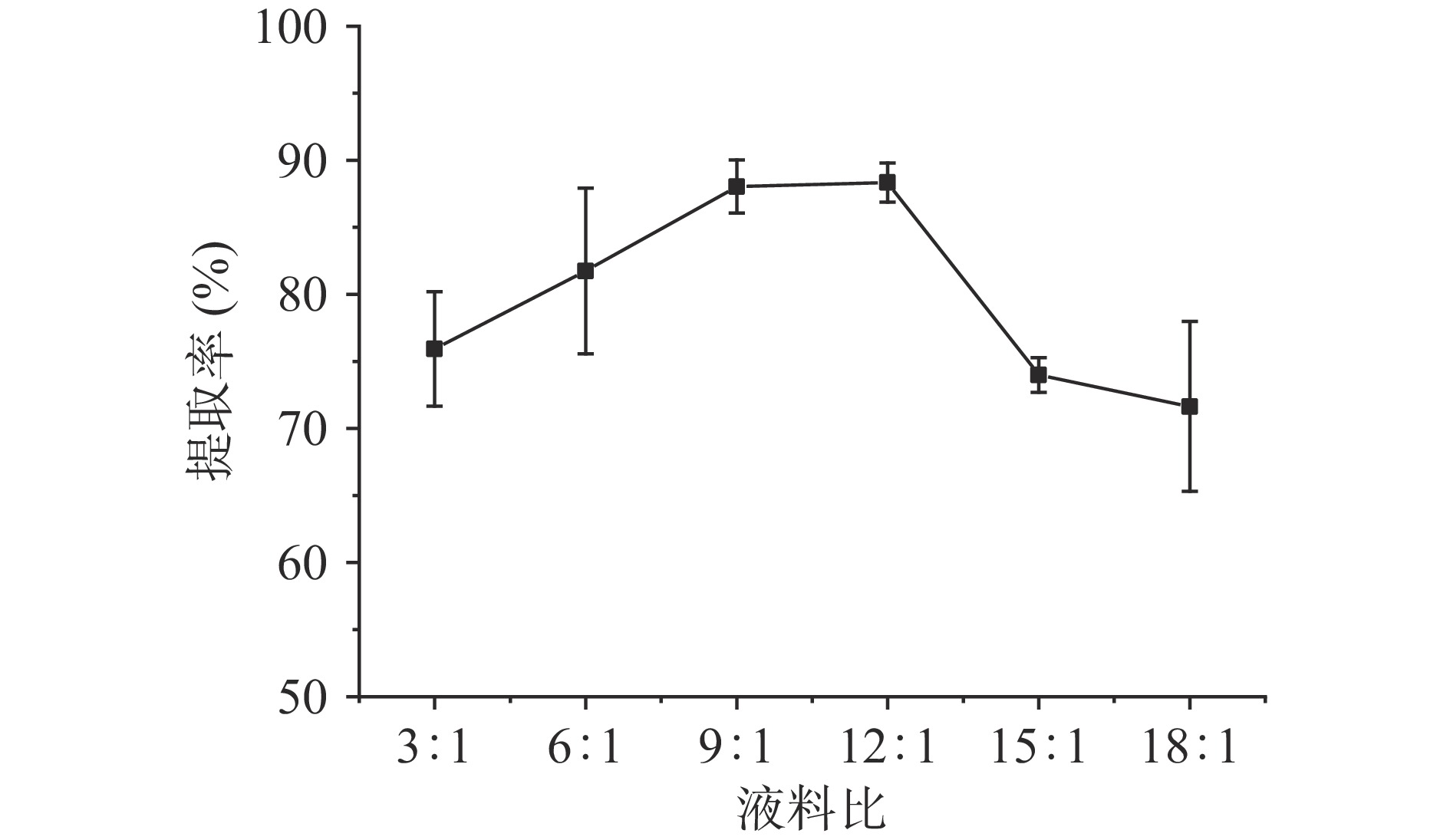
超声波辅助下液料比对淀粉提取率的影响如图3所示。
随着液料比的增加,提取率也逐渐增加,当液料比为12:1 mL/g时,提取率最大,为88.34%,这可能是因为在水的作用下淀粉与蛋白质的结合力降低[11]。但是随着液料比的继续增加,提取率却逐渐下降,因此确定超声波辅助提取油莎豆淀粉的最佳提取液料比为12:1 mL/g。
2.1.4 pH对油莎豆淀粉提取率的影响
超声波辅助下pH对淀粉提取率的影响如图4所示。
当提取液的碱性增加时,提取率逐渐增加,当pH达到9时,提取率最大,为90.62%,随着碱性继续增加时,提取率开始逐渐下降。这可能是因为碱性较弱时,蛋白质未完全溶解,导致粗淀粉纯度较低[5],提取率较低,当溶液呈强碱性,淀粉在碱液的作用下,溶解性和膨胀性增加[11],导致提取的粗淀粉的质量降低,提取率呈下降趋势。因此确定超声波辅助提取油莎豆淀粉的最佳提取pH为9。
2.2 响应面法优化提取油莎豆淀粉工艺条件分析
2.2.1 回归方程的建立及显著性分析
Box-Behnken试验设计及结果见表2。
表 2 Box-Behnken试验设计及结果Table 2. Box-Behnken experimental design and results实验号 A B C D 淀粉提取率(%) 1 0 0 1 1 73.99 2 0 0 −1 −1 80.35 3 −1 0 0 −1 88.08 4 0 −1 1 0 84.19 5 1 0 0 −1 76.55 6 −1 1 0 0 85.71 7 1 −1 0 0 87.61 8 −1 0 −1 0 84.90 9 0 0 −1 1 88.04 10 0 1 0 1 75.48 11 0 −1 0 1 90.43 12 1 1 0 0 81.85 13 0 −1 0 −1 72.90 14 0 −1 −1 0 86.21 15 −1 0 1 0 88.03 16 0 1 1 0 86.53 17 0 0 1 −1 79.90 18 1 0 0 1 79.47 19 0 0 0 0 83.40 20 −1 0 0 1 85.93 21 −1 −1 0 0 86.40 22 0 0 0 0 84.72 23 1 0 −1 0 82.61 24 0 0 0 0 84.82 25 1 0 1 0 79.62 26 0 0 0 0 83.09 27 0 1 0 −1 87.30 28 0 0 0 0 86.89 29 0 1 −1 0 84.21 利用Design-Expert8.0软件进行多元回归拟合,得到油莎豆淀粉提取率对温度(A)、时间(B)、液料比(C)、pH(D)的回归方程为:
Y=84.58−2.61A−0.55B−1.17C+0.69D−1.27AB−1.53AC+1.27AD+1.09BC−7.34BD−3.40CD+0.37A2+0.63B2−0.65C2−3.17D2
通过回归方程中各项系数的正负和绝对值的大小判断各因素对响应值的影响程度和方向[24],各因素对提取率的主次关系为:A>C>D>B,即温度>液料比>pH>时间。
对回归模型进行方差分析,结果见表3。
表 3 回归模型的方差分析Table 3. Analysis of variance of the regression model变异来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 476.58 14 34.04 5.21 0.0019 ** A 81.85 1 81.85 12.54 0.0033 ** B 3.70 1 3.70 0.57 0.4642 C 16.47 1 16.47 2.52 0.1345 D 5.69 1 5.69 0.87 0.3665 AB 6.43 1 6.43 0.98 0.3379 AC 9.36 1 9.36 1.43 0.2509 AD 6.43 1 6.43 0.98 0.3379 BC 4.71 1 4.71 0.72 0.4100 BD 215.36 1 215.36 32.99 <0.0001 ** CD 46.24 1 46.24 7.08 0.0186 * A2 0.91 1 0.91 0.14 0.7147 B2 2.59 1 2.59 0.40 0.5390 C2 2.73 1 2.73 0.42 0.5286 D2 65.11 1 65.11 9.97 0.0070 ** 残差 91.39 14 6.53 失拟项 82.36 10 8.24 3.65 0.1118 纯误差 9.03 4 2.26 总和 567.97 28 注:*表示差异显著,P<0.05;**表示差异极显著,P<0.01。 由表3可知,该模型的P=0.0019<0.01,表示此模型具有显著性[25]。回归模型失拟项不显著(P=0.1118>0.05),决定系数R2=0.8391,说明本试验模型与试验值拟合程度良好,试验误差小,可以对油莎豆淀粉提取率进行良好的预测。模型中一次项A,二次项BD和D2对响应值的影响极显著(P<0.01),二次项CD显著(P<0.05),其余不显著(P>0.05)。
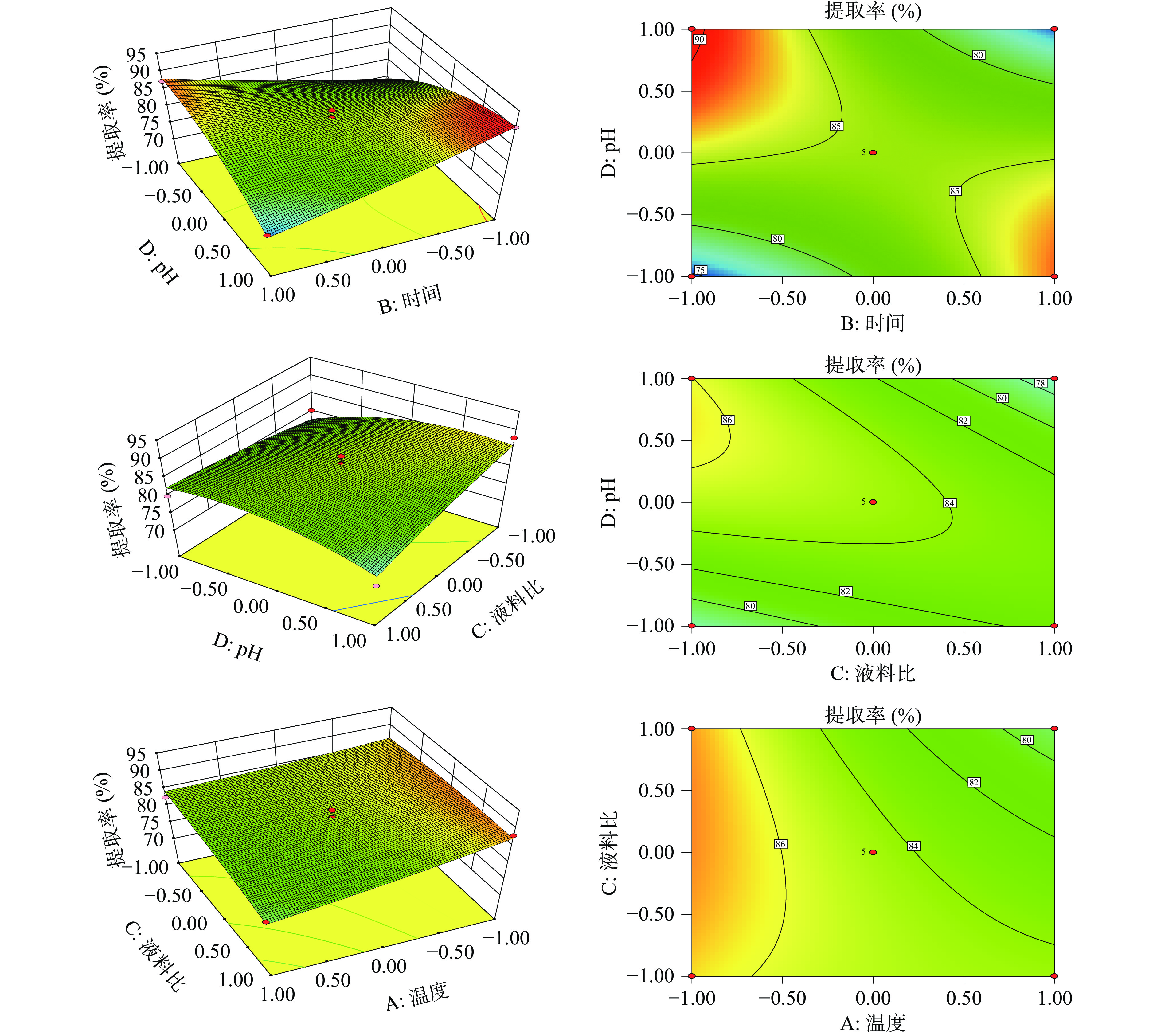
2.2.2 因素交互作用
如图5所示为时间和液料比、液料比和pH、温度和液料比的交互作用的响应面和等高线。响应面坡度越陡则交互作用越显著,反之,越平缓则交互作用越不显著[26]。由图5中pH和时间的响应面图可知,随着pH和时间的增大,淀粉提取率也随之增大,而在pH的方向上,响应面的坡度更陡,因此相对时间而言,pH对淀粉提取率更显著。由图5中pH和液料比的响应面图可知,随着pH和液料比的增大,淀粉提取率也随之增大,而在液料比的方向上,响应面的坡度更陡,因此相对pH而言,液料比对淀粉提取率更显著。由图5中温度和液料比的响应面图可知,随着液料比和温度的增大,淀粉提取率也随之增大,而在温度的方向上,响应面的坡度更陡,因此相对液料比而言,温度对淀粉提取率更显著。分析表明:各因素对提取率的主次关系为:A>C>D>B,即温度>液料比>pH>时间,与方差分析的结果一致,该模型具有良好的预测性。
2.2.3 回归模型的验证
通过Design-Expert 8.0软件分析得出,超声波辅助提取油莎豆淀粉最佳工艺参数为:温度30.00 ℃、时间49.93 min、液料比14.99:1、pH8,此条件下油莎豆淀粉提取率为97.78%,可信度为0.918。考虑实际操作,将上述最佳参数中的温度调至30 ℃,时间为50 min,液料比15:1 mL/g,pH8,其余不变,在此条件下重复3次试验,油莎豆淀粉提取率分别为90.83%、92.79%、93.05%,平均值为92.22%±0.99%,与理论预测值相比,其相对误差约为5.69%,在可接受范围内,此方案可行。
2.3 油莎豆淀粉的理化特性
2.3.1 扫描电镜分析
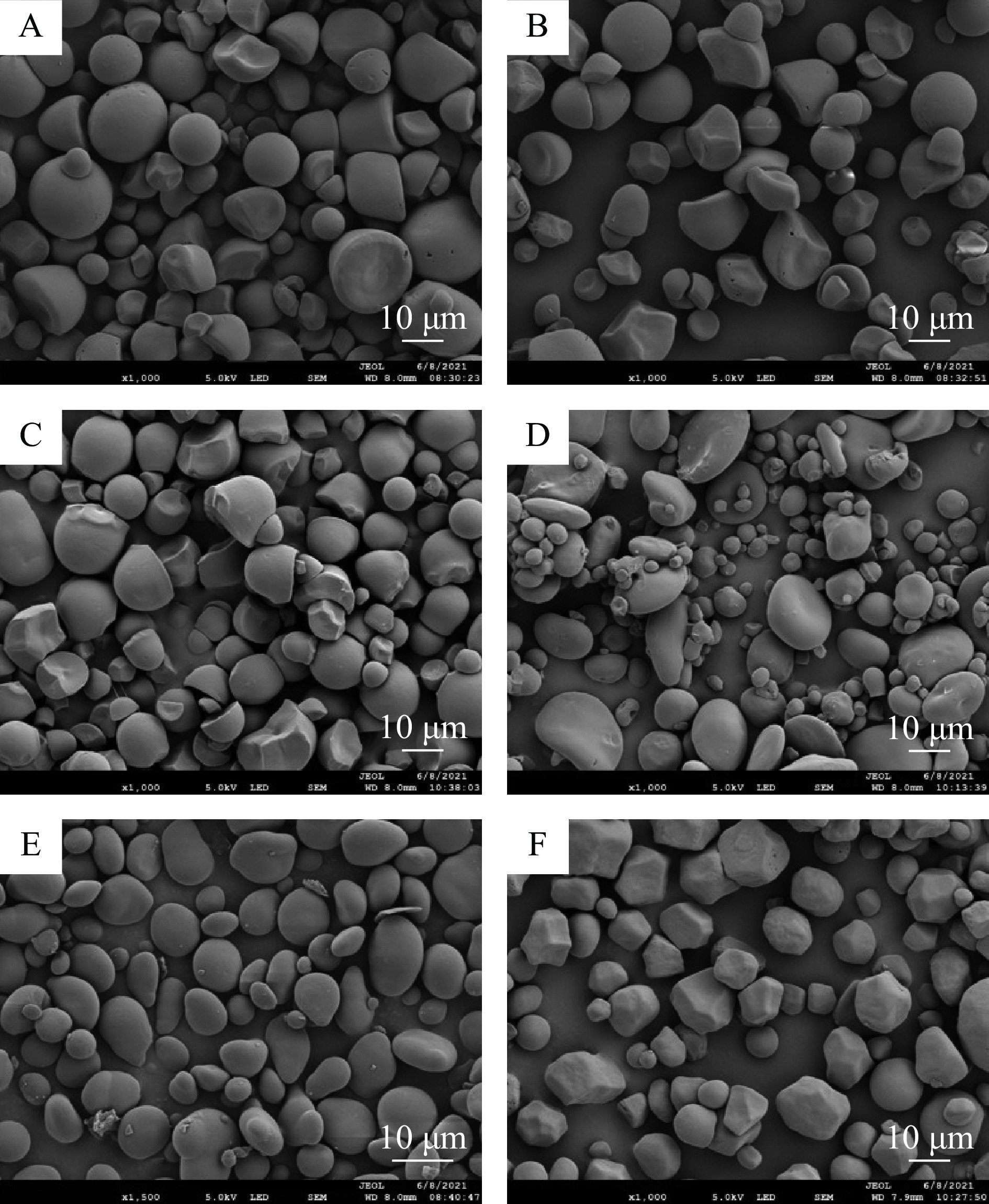
淀粉的颗粒大小决定了它的用途[27]。研究表明,粒径偏小的淀粉可用于制作淀粉基生物膜和淀粉降解材料等[28]。如图6所示,不同种类的淀粉颗粒在形状上有不同特点。从形态上看,呈球形、多面体形、椭圆形、扁平形等,可以根据这些特点确定淀粉的种类[19]。从图6可以看出,红薯淀粉颗粒多为半球形且中心凹陷;马铃薯淀粉颗粒为块茎形;木薯淀粉颗粒与红薯淀粉颗粒形状类似;小麦淀粉颗粒大小不一,且大颗粒呈扁平状;油莎豆淀粉颗粒呈卵球形,表面光滑,粒径范围2~15 μm,与于淑艳等人的观察一致[2];玉米淀粉颗粒呈多面体结构,部分未熟粒为球形。与其它五种淀粉相比,油莎豆淀粉粒径偏小,属于中小粒度的淀粉。
2.3.2 傅里叶红外变换分析
由图7可知,图中1162、1084、1023 cm−1出现的吸收信号,是C-O-H中的C-O拉伸和C-O-C中的C-O拉伸;在2933 cm−1处为C-H伸缩振动;3387 cm−1处对应O-H拉伸[29-30]。如图7所示,玉米淀粉和油莎豆淀粉在1084、1023 cm−1处的红外信号波动降低,说明二者C-O拉伸程度较低。在2933和3387 cm−1处,玉米淀粉和油莎豆淀粉的红外信号波动降低,说明二者C-H和O-H伸缩振动程度较低。
2.3.3 X射线衍射分析
Jane等的研究表明[31],B型淀粉的晶体结构比A型淀粉更容易水解。通过XRD分析确定油莎豆淀粉颗粒的晶型并与小麦淀粉等五种淀粉颗粒的晶型进行对比,如图8所示为油莎豆等六种淀粉的XRD衍射图谱,马铃薯在5.6°、17°、22°、24°有较强的衍射峰出现,属于B型淀粉。油莎豆淀粉与小麦淀粉、木薯淀粉、红薯淀粉、玉米淀粉的淀粉颗粒的晶型相似,在15°、17°、18°、23°有较强的衍射峰,属于A型淀粉。由此也可以得知油莎豆淀粉较马铃薯淀粉不易水解。
2.3.4 糊化特性分析
差示扫描量热仪可以通过物体相变的过程,体现其热力学性质,也可用来区分支链淀粉结晶、直链淀粉结晶。根据表4,油莎豆淀粉的在DSC实验中起始温度、峰值温度和终止温度较高,分别为68.03、72.47、79.59 ℃,表明油莎豆淀粉的支链淀粉丰富[31]。马铃薯淀粉的凝胶化焓值最大,为15.75 J/g,油莎豆淀粉的焓值位于其它五种淀粉之间。
表 4 油莎豆淀粉等六种淀粉的DSC热力学参数Table 4. DSC gelatinization thermodynamic parameters of six kinds of starches including Cyperus esculentus L.样品 To(℃) Tp(℃) Te(℃) ∆H(J/g) 油莎豆淀粉 68.03 72.47 79.59 13.77 小麦淀粉 57.06 61.79 69.31 9.06 木薯淀粉 62.25 67.92 79.09 10.87 玉米淀粉 67.52 71.70 79.97 14.76 红薯淀粉 70.24 75.16 84.54 14.76 马铃薯淀粉 60.81 65.20 73.21 15.75 3. 结论
在单因素和响应面试验下得到超声波辅助提取油莎豆淀粉的最佳条件为:温度30 ℃、时间50 min、液料比15:1 mL/g、pH8,此条件下油莎豆淀粉提取率为92.22%,且响应面试验结果表明4个因素对油莎豆淀粉提取率影响大小依次为:温度>液料比>pH>时间。
在对油莎豆淀粉理化特性的分析中,扫描电镜分析表明,油莎豆淀粉颗粒成卵球形,表面光滑,颗粒度较小;傅里叶红外变换分析表明,油莎豆淀粉C-O和O-H拉伸程度较低,C-H的伸缩振动程度较低。X射线衍射分析表明,油莎豆淀粉与小麦淀粉、木薯淀粉、红薯淀粉、玉米淀粉的晶型相似,属于A型淀粉,而马铃薯属于B型淀粉。DSC分析表明,油莎豆淀粉的起始温度、峰值温度仅低于红薯淀粉,终止温度低于红薯淀粉和玉米淀粉。
综上所述,油莎豆淀粉粒径相对较小,可将其作为淀粉基生物膜和淀粉降解材料。其起始糊化温度略低于红薯淀粉,终止糊化温度低于红薯淀粉和玉米淀粉说明它具有丰富的支链淀粉结构。另外油莎豆淀粉属于A型淀粉,与B型淀粉相比不易水解,但是与其它A型淀粉水解程度的差异,还需进一步研究。
-
表 1 响应面分析因素及水平
Table 1 Factors and levels of response surface analysis
水平 A 温度(℃) B 时间(min) C 液料比(mL/g) D pH −1 30 30 9:1 8 0 40 40 12:1 9 1 50 50 15:1 10 表 2 Box-Behnken试验设计及结果
Table 2 Box-Behnken experimental design and results
实验号 A B C D 淀粉提取率(%) 1 0 0 1 1 73.99 2 0 0 −1 −1 80.35 3 −1 0 0 −1 88.08 4 0 −1 1 0 84.19 5 1 0 0 −1 76.55 6 −1 1 0 0 85.71 7 1 −1 0 0 87.61 8 −1 0 −1 0 84.90 9 0 0 −1 1 88.04 10 0 1 0 1 75.48 11 0 −1 0 1 90.43 12 1 1 0 0 81.85 13 0 −1 0 −1 72.90 14 0 −1 −1 0 86.21 15 −1 0 1 0 88.03 16 0 1 1 0 86.53 17 0 0 1 −1 79.90 18 1 0 0 1 79.47 19 0 0 0 0 83.40 20 −1 0 0 1 85.93 21 −1 −1 0 0 86.40 22 0 0 0 0 84.72 23 1 0 −1 0 82.61 24 0 0 0 0 84.82 25 1 0 1 0 79.62 26 0 0 0 0 83.09 27 0 1 0 −1 87.30 28 0 0 0 0 86.89 29 0 1 −1 0 84.21 表 3 回归模型的方差分析
Table 3 Analysis of variance of the regression model
变异来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 476.58 14 34.04 5.21 0.0019 ** A 81.85 1 81.85 12.54 0.0033 ** B 3.70 1 3.70 0.57 0.4642 C 16.47 1 16.47 2.52 0.1345 D 5.69 1 5.69 0.87 0.3665 AB 6.43 1 6.43 0.98 0.3379 AC 9.36 1 9.36 1.43 0.2509 AD 6.43 1 6.43 0.98 0.3379 BC 4.71 1 4.71 0.72 0.4100 BD 215.36 1 215.36 32.99 <0.0001 ** CD 46.24 1 46.24 7.08 0.0186 * A2 0.91 1 0.91 0.14 0.7147 B2 2.59 1 2.59 0.40 0.5390 C2 2.73 1 2.73 0.42 0.5286 D2 65.11 1 65.11 9.97 0.0070 ** 残差 91.39 14 6.53 失拟项 82.36 10 8.24 3.65 0.1118 纯误差 9.03 4 2.26 总和 567.97 28 注:*表示差异显著,P<0.05;**表示差异极显著,P<0.01。 表 4 油莎豆淀粉等六种淀粉的DSC热力学参数
Table 4 DSC gelatinization thermodynamic parameters of six kinds of starches including Cyperus esculentus L.
样品 To(℃) Tp(℃) Te(℃) ∆H(J/g) 油莎豆淀粉 68.03 72.47 79.59 13.77 小麦淀粉 57.06 61.79 69.31 9.06 木薯淀粉 62.25 67.92 79.09 10.87 玉米淀粉 67.52 71.70 79.97 14.76 红薯淀粉 70.24 75.16 84.54 14.76 马铃薯淀粉 60.81 65.20 73.21 15.75 -
[1] 瞿萍梅, 程治英, 龙春林, 等. 油莎豆资源的综合开发利用[J]. 中国油脂,2007,32(9):61−63. [QU P M, CHENG Z Y, LONG C L, et al. Comprehensive development and utilization of Cyperus esculentus L. resources[J]. China Oils and Fats,2007,32(9):61−63. QU P M, CHENG Z Y, LONG C L, et al. Comprehensive development and utilization of Cyperus esculentus L resources[J]. China Oils and Fats, 2007, 32(9): 61-63.
[2] 于淑艳, 吴琼, 陈星, 等. 油莎豆淀粉理化性质的研究[J]. 食品科技,2011,36(3):245−248. [YU S Y, WU Q, CHEN X, et al. Study on physical and chemical properties of Cyperus esculentus L starch[J]. Food Science and Technology,2011,36(3):245−248. YU S Y, WU Q, CHEN X, et al. Study on physical and chemical properties of Cyperus esculentus L starch[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2011, 36(3): 245-248.
[3] 焦兵阳, 王英, 尹诗慧, 等. 油莎豆生物学特性、功能与遗传研究进展[J]. 现代化农业,2021(1):40−44. [JIAO B Y, WANG Y, YING S H, et al. Research progress on biological characteristics, function and genetics of Cyperus esculentus L[J]. Modernizing Agriculture,2021(1):40−44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0254.2021.01.021 JIAO B Y, WANG Y, YING S H, et al. Research progress on biological characteristics, function and genetics of Cyperus esculentus L[J]. Modernizing Agriculture, 2021(1): 40-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0254.2021.01.021
[4] 郑桂富, 徐振相, 周彬, 等. 油莎豆凝胶淀粉的理化特性研究[J]. 中国粮油学报,2002,17(6):59−62. [ZHENG G F, XU Z X, ZHOU B, et al. Study on physical and chemical properties of Cyperus esculentus L gel starch[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2002,17(6):59−62. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-0174.2002.06.015 ZHENG G F, XU Z X, ZHOU B, et al. Study on physical and chemical properties of Cyperus esculentus L gel starch[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2002, 17(6): 59-62. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-0174.2002.06.015
[5] 王璐阳, 刘玉兰, 田瑜. 油莎豆压榨饼淀粉提取及其理化性质研究[J]. 粮食与油脂,2017,30(12):29−33. [WANG L Y, LIU Y L, TIAN Y. Study on extraction and physicochemical properties of starch from Cyperus esculentus L. press cake[J]. Cereals & Oils,2017,30(12):29−33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2017.12.009 WANG L Y, LIU Y L, TIAN Y. Study on extraction and physicochemical properties of starch from Cyperus esculentus L press cake[J]. Cereals & Oils, 2017, 30(12): 29-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2017.12.009
[6] OLUWAJUYITAN T D, IJAROTIMI O S. Nutritional, antioxidant, glycaemic index and antihyperglycaemic properties of improved traditional plantain-based (Musa AAB) dough meal enriched with tigernut (Cyperus esculentus L.) and defatted soybean (Glycine max) flour for diabetic patients[J]. Heliyon,2019,5(4):e01504. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01504
[7] 阳振乐. 油莎豆的特性及其研究进展[J]. 北方园艺,2017,4(17):192−201. [YANG Z L. Characteristics and research progress of Cyperus esculentus L J]. Northern Horticulture,2017,4(17):192−201.
[8] GUO T, WAN C, HUANG F, et al. Evaluation of quality properties and antioxidant activities of tiger nut (Cyperus esculentus L.) oil produced by mechanical expression or/with critical fluid extraction[J]. LWT,2021,141:110915. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.110915
[9] MANEK R V, BUILDERS P F, KOLLING W M, et al. Physicochemical and binder properties of starch obtained from Cyperus esculentus[J]. AAPS PharmSciTech,2012,12(3):379−388.
[10] BUSOLA S, TOLULOPE O A, OLUWATOYIN A O. The glidant properties of Cyperus esculentus L. (Tigernut) starch in metronidazole tablet formulation[J]. Starch-Stärke, 2018, 70(3−4).
[11] 陈星, 沈新锋, 邹险峰. 油莎豆淀粉提取工艺研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2011(4):266−271. [CHEN X, SHEN X F, ZOU X F. Study on extraction technology of Cyperus esculentus L. starch[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2011(4):266−271. CHEN X, SHEN X F, ZOU X F. Study on extraction technology of Cyperus esculentus L starch[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2011(4): 266-271.
[12] MENG W B, BAO L D, LI C Q, et al. Extraction of starch and proteins from the tubers of large-grain Cyperus esculentus L[J]. Romanian Biotechnological Letters,2015,20(2):10287−10293.
[13] BEMARD C O, CHAVEZ D W H. Ultrasound assisted extraction of yam (Dioscorea bulbífera) starch: Effect on morphology and functional properties[J]. Starch-Stä rke,2018,70(5−6):170−185.
[14] WIDIASTUTI S, KARMILA, ROHMAH NUR F, et al. Process optimization for ultrasound-assisted starch production from Cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) using response surface methodology[J]. Agronomy,2021,11(1):117−117. doi: 10.3390/agronomy11010117
[15] AMBIGAIPALAN P, HOOVER R, DONNER R, et al. Structure of faba bean, black bean and pinto bean at different levels of granule organization and their physicochemical propertie[J]. Food Research International,2011,44(9):2962−2974. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2011.07.006
[16] 张静. 甘薯淀粉生产工艺研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2018 ZHANG J. Study on the production technology of sweet potato starch[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2018.
[17] 唐艳, 颜嘉良, 吴文, 等. 超声波辅助碱法提取小麦麸皮淀粉条件的优化[J]. 农产品加工,2017(1):1−8. [TANG Y, YAN J L, WU W, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted alkaline extraction conditions of wheat bran starch[J]. Farm Products Processing,2017(1):1−8. TANG Y, YAN J L, WU W, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted alkaline extraction conditions of wheat bran starch[J]. Farm Products Processing, 2017(1): 1-8.
[18] 那布其, 奥·乌力吉, 王秀兰, 等. 旋光法测定大米淀粉含量[J]. 北方药学,2020,12(9):6−8. [NA B Q, AO W L J, WANG X L, et al. Determination of rice starch content by polarimetry[J]. Journal of North Pharmacy,2020,12(9):6−8. NA B Q, AO W L J, WANG X L, et al. Determination of rice starch content by polarimetry[J]. Journal of North Pharmacy, 2020, 12(9): 6-8.
[19] 王绍清, 王琳琳, 范文浩, 等. 扫描电镜法分析常见可食用淀粉颗粒的超微形貌[J]. 食品科学,2011,32(15):74−79. [WANG S Q, WANG L L, FAN W H, et al. Scanning electron microscopy was used to analyze the ultrastructure of common edible starch granules[J]. Food Science,2011,32(15):74−79. WANG S Q, WANG L L, FAN W H, et al. Scanning electron microscopy was used to analyze the ultrastructure of common edible starch granules[J]. Food Science, 2011, 32(15): 74-79.
[20] 李茹, 古丽热汗·依明, 黄钰雯, 等. 马铃薯全粉产品结构及性质的测定研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2016(16):89−92. [LI R, GULIREHAN Y M, HUANG Y W, et al. Study on the determination of the structure and properties of potato flour products[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2016(16):89−92. LI R, GULIREHAN Y M, HUANG Y W, et al. Study on the determination of the structure and properties of potato flour products[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2016(16): 89-92.
[21] 张令文, 琚星, 李欣欣, 等. 8个品种甘薯淀粉的理化性质及其相关性分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(4):26−32. [ZHANG L W, JU X, LI X X, et al. Physicochemical properties and correlation analysis of eight varieties of sweet potato starch[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(4):26−32. ZHANG L W, JU X, LI X X, et al. Physicochemical properties and correlation analysis of eight varieties of sweet potato starch[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(4): 26-32.
[22] 谭洪卓, 谭斌, 刘明, 等. 甘薯淀粉性质与其粉丝品质的关系[J]. 农业工程学报,2009,25(4):286−292. [TAN H Z, TAN B, LIU M, et al. Relationship between starch properties of sweet potato and vermicelli quality[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2009,25(4):286−292. TAN H Z, TAN B, LIU M, et al. Relationship between starch properties of sweet potato and vermicelli quality[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2009, 25(4): 286-292.
[23] HAN L H, QIU S. Molecular characteristics and physicochemical properties of very small granule starch isolated from Agriophyllum squarrosum seeds[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2021(273):118−583.
[24] 张润楚, 郑海涛, 兰蓝. 实验设计与分析及参数优化[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2003 ZHANG R C, ZHENG H T, LAN L. Experimental design and analysis and parameter optimization[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2003.
[25] 汪磊, 云月英, 游新勇, 等. 莜麦淀粉的提取及其性质的研究[J]. 中国粮油学报,2015,30(4):23−26. [WANG, YUN Y, YOU X, et al. Study on extraction and properties of naked oat starch[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2015,30(4):23−26. WANG, YUN Y, YOU X, et al. Study on extraction and properties of naked oat starch[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2015, 30(4): 23-26.
[26] 古明朗, 郭影琪, 尹永祺, 等. 响应面法优化西兰花芽苗富集异硫氰酸酯发芽工艺[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(7):1−9. [GU MING L, GUO Y Q, YIN Y Q, et al. Optimization of germination process of isothiocyanate enrichment in broccoli sprouts by response surface methodology[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(7):1−9. GU MING L, GUO Y Q, YIN Y Q, et al. Optimization of germination process of isothiocyanate enrichment in broccoli sprouts by response surface methodology[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(7): 1−9.
[27] ASHOGBON A O, AKINTAYO E T, OLADEBEYE A O, et al. Developments in the isolation, composition, and physicochemical properties of legume starches[J]. Food Science and Nutrition,2020,61(17):2928−2959.
[28] BELAY D. Composition, morphology and physicochemical properties of starches derived from indigenous Ethiopian tuber crops: A review[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021(187):911−921.
[29] 高凡, 纪桂英, 陈凯斐, 等. 沙米淀粉的结构和糊化性质[J]. 海南师范大学学报,2020,33(4):441−445. [GAO F, JI G Y, CHEN K F, et al. Structure and gelatinization properties of rice starch[J]. Journal of Hainan Normal University (Natural Science),2020,33(4):441−445. GAO F, JI G Y, CHEN K F, et al. Structure and gelatinization properties of rice starch[J]. Journal of Hainan Normal University(Natural Science), 2020, 33(4): 441-445.
[30] LEI M, JIANG F C, CAI J, et al. Facile microencapsulation of olive oil in porous starch granules: Fabrication, characterization, and oxidative stability[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,111:755−761. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.01.051
[31] JANE J L, WONG K S, MCPHERSON A E. Branch-structure difference in starches of A- and B-type X-ray patterns revealed by their naegeli dextrins[J]. Carbohydrate Research,1997,300(3):219−227. doi: 10.1016/S0008-6215(97)00056-6
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 薛淑贞,梁婷,赵祥民,张家玮,汝应俊,唐德富. 葡萄籽提取物和有机铁对蛋鸡生产性能和蛋品质的影响. 饲料工业. 2025(04): 59-63 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 常安其,毛帅翔,柳广斌. 葡萄残渣的饲料化利用及其在羊生产中的应用研究进展. 中国畜牧兽医. 2024(11): 4842-4850 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 杨辉,胡雅婕. 活性包装薄膜对冷藏圣女果的保鲜效果研究. 农业科技与装备. 2024(05): 61-64 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王建康,郭诗琼,王静,魏丽娜,冯莉,黄峻榕,Fereidoon SHAHIDI. 浆果籽油的生物活性与应用研究进展. 食品与生物技术学报. 2024(10): 32-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 赵明洪,卢天明,刘莉,王启新,杨通,林娜,邱崇,钟田雨,郭秋岩,王继刚. 甘草减轻雷公藤多苷片所致肝损伤的作用机制. 中国实验方剂学杂志. 2023(05): 24-31 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 尚嘉毅,初柏君,赵文君,翟孟婷,王翔宇,马欲明,孙晴,孟祥永,陈吉江,张宇. 市售牛油果油和葡萄籽油品质研究. 中国油脂. 2023(06): 119-125+152 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 盖永强,蓝天婵,李金生,朴美子,李岩. 葡萄籽果冻的工艺. 食品工业. 2022(06): 107-110 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)







 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:



