Phytochemical Composition and α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity of Campanumoea lancifolia (Roxb.) Merr Fruit
-
摘要: 为了探究红果参果化学成分及其α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性。本实验以红果参果为材料,采用溶剂法制备红果参果乙醇提取物和粗多糖。采用紫外分光光度法测定其总黄酮、总花色苷、总多酚和多糖含量,进一步通过超高效液相色谱-飞行时间-串联质谱技术分析其化学成分。利用α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制模型考察粗多糖、乙醇提取物及其主要代表成分的体外α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制作用。结果表明,5个批次的红果参果粗多糖多糖含量为27.59%~37.59%;乙醇提取物的总黄酮含量为1.22%~1.77%,总花色苷为0.90%~1.14%,总多酚含量为13.11%~18.85%。红果参果乙醇提取物化学成分丰富多样,从中共鉴定出21个化合物,其中包含10个黄酮、3个有机酸、3个花色苷、3个酚酸、1个氨基酸和1个聚炔类成分。红果参果乙醇提取物、粗多糖和代表化合物木犀草素的α-葡萄糖苷酶的IC50分别为7.52、37.43和8.03 μg/mL,明显高于阳性对照阿卡波糖(616.17 μg/mL)。本研究初步明确了红果参果的物质基础,并首次报道了红果参果具有潜在抗糖尿病活性,为红果参果的开发利用提供理论参考。
-
关键词:
- 红果参果 /
- 超高效液相色谱-飞行时间-串联质谱技术 /
- 化学成分 /
- α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性
Abstract: Hong Guo Shen Guo (HGSG) are the fruits of Campanumoea lancifolia (Roxb.) Merr, which are mainly cultivated in Southwest China. This study was to investigate the ingredients from HGSG extracts and their α-glucosidase inhibition in vitro. The contents of polysaccharide, total flavonoids, total anthocyanins and total phenols in extracts from HGSG were measured using UV spectrophotometry. Chemical ingredients were further analyzed applying ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-time of flight-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-QTOF-MS). The results showed that the content of crude polysaccharide in five batches of HGSG was 27.59%~37.59%. The total flavone content of ethanol extract was 1.22%~1.77%, the total anthocyanin content was 0.90%~1.14%, and the total polyphenol content was 13.11%~18.85%. Twenty one compounds were identified from HGSG, including 10 flavonoids, 3 phenolic acids, 3 organic acids, 3 anthocyanins, 1 amino acid and 1 polyacetylene. The ethanol extract, crude polysaccharide and luteolin of HGSG exhibited potent α-glucosidase inhibitory activities with IC50 values of 7.52, 37.43 and 8.03 μg/mL, respectively, which were significantly higher than that of acarbose (616.17 μg/mL). This study preliminarily defined the material basis of HGSG, and reported for the first time that HGSG had potential anti diabetes activity, which would provide a theoretical reference for the development and utilization of HGSG. -
糖尿病(diabetes mellitus,DM)是以多种病因引起的以慢性高血糖为特征的代谢紊乱性疾病,分为1和2型糖尿病。其中2型糖尿病(type two diabetes mellitus,T2DM)是糖尿病的主要类型,占糖尿病发病率的90%~95%[1]。受不健康的饮食结构和生活方式等因素的影响,全球糖尿病的发病率不断攀升,预计2030年达到5.78亿例,2050年达到7亿例[2],已经成为继心血管疾病和癌症之后,威胁人们生命的第三大杀手[3]。
α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂能抑制人类小肠粘膜刷状缘上的α-葡萄糖苷酶对碳水化合物的转化,从而降低餐后血糖,是治疗2型糖尿病的重要靶点之一[4]。目前临床上用于治疗2型糖尿病的α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂主要包括阿卡波糖、伏格列波糖、米格列醇三种[5],但是这些药物也会引起患者诸如腹泻、腹痛、肠胃胀气等不良反应[6]。天然来源的α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂一直是近年来研究的热点,国内外学者已经从天然植物中提取到多种能够抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶活性的化合物,如多酚[7-9]、多糖[10-12]、黄酮[13-15]、生物碱和萜类[16]等。同时研究人员发现黑醋栗、蓝莓、蓝果忍冬、桑椹等小型浆果对α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性显著[17-18],是天然的α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制的良好来源。
红果参为桔梗科金钱豹属植物长叶轮钟草Campnumoea lancifolia (Roxb.) Merr.的根,其性平、味甘、微苦,具补虚益气、祛痰止痛功效,主要用于劳倦气虚乏力,跌打损伤和肠绞痛[19]。长叶轮钟草的果实即红果参果为小型浆果,普遍作为水果使用,具有滋补,保健等功效[20]。少量研究文献报道显示红果参果富含黄酮类、多糖类以及酚酸类等化学成分[21],具有清除羟基自由基、超氧阴离子自由基和DPPH等自由基的作用,有较好的体外抗氧化作用[22-25]。
目前红果参从野生到规范化种植,并在我国西南地区作为经济水果规模种植,带动了当地的扶贫产业和经济发展。但对红果参果化学成分和生物活性研究相对薄弱,制约了其开发和利用,而关于红果参果的α-糖苷酶抑制活性和潜在抗糖尿病作用未见报道。本研究以人工规模栽培的红果参果为研究对象,制备两种提取物,并对其多糖、总黄酮、总花色苷、总多酚等大类成分含量进行测定。通过UPLC-QTOF-MS技术对其化学成分表征和结构鉴定,并对红果参果提取物样品以及其代表性成分的α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性考察。旨在对红果参果资源的开发利用提供更多的科学实验依据和数据支撑,为天然来源的α-糖苷酶抑制剂的发现提供更多选择。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
5批红果参鲜果(批号1-A-7,2-A-9,3-B-11,4-A-12和5-B-5) 采摘时间2021年3月8日,贵州创兴农业发展有限责任公司;矢车菊素-3-O-葡萄糖苷 批号ST04290120MG,纯度≥98.0%,上海诗丹德技术有限公司;对硝基苯-α-D-葡萄糖苷(p-nitrophenyl-α-D-glucopyran oside,pNPG) 批号C12462390,纯度99%,上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;α-葡萄糖苷酶 批号SLBT8587,酶活力18.5 U/mg(G5003-100UN),美国Sigma公司;阿卡波糖水合物 批号G1718046,纯度≥98%,阿拉丁试剂(上海)有限公司;党参炔苷、木犀草素-7-O-葡萄糖苷、芦丁、木犀草素、芹菜素 实验室自制对照品;乙腈 质谱级;其他试剂 均为分析纯。
ZG TP101电子分析天平 松竫精密天平;PHS-3C pH计 上海精密科学仪器有限公司;UV-2600紫外-可见分光光度仪 SHIMADZU;HWS-24电热恒温水浴锅 上海齐欣科学仪器有限公司;BUCHI Lyovapor™ L-200冷冻干燥机 瑞士步琦有限公司;梅特勒MS105DU电子天平 梅特勒·托利多公司;KQ-250DE型数控超声波清洗器 昆山市超声仪器有限公司;Waters ACQUITY UPLC I-Class串联Xevo G2-XS QTOF质谱仪 美国沃特世公司;Sigma 1-14k离心机 美国Sigma公司;EPOCH酶标仪 美国Bio-Teck公司;Minipore纯化水系统 德国Merck公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 红果参果乙醇提取物的制备
参考宛美志等[26]的方法稍作修改。称取5批等质量的红果参鲜果(约100 g)于烧杯中,用料理机匀浆,按照料液比1:10(g/mL)加入含0.1%盐酸的65%乙醇水溶液,保鲜膜封口,水浴温度40 ℃,提取120 min,过滤,滤液转入旋转蒸发仪浓缩除去乙醇,浓缩液冷冻干燥得红果参果乙醇提取物,分别记为批号1-A-7、2-A-9、3-B-12、4-A-12和5-B-5,密封,避光贮存在−80 ℃冰箱中,备用。
1.2.2 红果参果粗多糖的制备
参考陈莉华等[22]的方法稍作修改。称取5批等质量的红果参鲜果(约100 g)于烧杯中,用料理机粉粹匀浆,按照料液比1:20(g/mL)加入去离子水,保鲜膜封口,热水超声(功率250 W,频率40 kHz,80 ℃)提取三次,每次45 min,提取液过滤,合并浓缩至一定体积,加入四倍量无水乙醇,过夜,离心(转速5000 r/min)15 min,冷冻干燥得红果参果粗多糖。
1.2.3 红果参果粗多糖含量测定
以硫酸-苯酚法显色[23],紫外可见分光光度法测定红果参粗多糖多糖含量。
称取干燥至恒重的葡萄糖,配制成100 μg·mL−1标准使用液。分别移取0、0.1、0.2、0.4、0.8、1.0 mL标准使用液置于10 mL刻度管中,补充蒸馏水至1.0 mL。分别加入苯酚试剂1.0 mL,摇匀,于冷水浴中缓缓加入3.0 mL硫酸,立刻摇匀。静置5 min后,置于沸水浴加热15 min,取出后立即以流水冷却至室温。以相应试剂为空白,在λ=488 nm处以紫外可见分光光度计测定吸光度,以吸光度(A)为纵坐标,葡萄糖溶液浓度(μg/mL)为横坐标绘制标准曲线y=47.6125x−0.0818(R2=0.9925)。
取1.2.2项下的红果参果粗多糖约10 mg,精密称定,置10 mL容量瓶中,加水至刻度线,摇匀。精密量取0.1 mL,照标准曲线的制备项下的方法,自“补充蒸馏水至1.0 mL”起,依法测定吸光度,从标准曲线上读出供试品溶液中无水葡萄糖的浓度,计算出红果参果粗多糖中多糖含量。
1.2.4 红果参果乙醇提取物黄酮含量测定
总黄酮的测定采用硝酸铝-亚硝酸钠法[27]测定。
精密称取芦丁对照品10 mg,置10 mL量瓶中,用70%乙醇溶解后并稀释定容,摇匀,即得1 mg/mL的芦丁对照品溶液。精密量取对照品溶液0.2、0.4、0.8、1.0、1.6、2.0 mL,分别置25 mL量瓶中,各加50%乙醇溶液补足至6 mL,再分别加入5%亚硝酸钠溶液1 mL,摇匀,放置6 min;加10%硝酸铝溶液1 mL,摇匀,放置6 min;加4%氢氧化钠溶液10 mL后再加水稀释至刻度,摇匀,放置15 min。以相应的试剂为空白对照,照紫外-可见分光光度法(通则0401),在510 nm的波长处下测定吸光度。以吸光度(A)为纵坐标,芦丁溶液浓度C(mg/mL)为横坐标绘制标准曲线:y=12.0350x−0.0136(R2=0.9996)。
取红果参果乙醇提取物0.2 g,精密称定,置50 mL具塞锥形瓶中,精密加入50%乙醇20 mL,密塞,称定重量,超声处理(功率250 W,频率40 Hz)15 min,放冷,再称定重量,用50%乙醇补足减失的重量,摇匀,滤过。精密量取滤液3 mL,置25 mL容量瓶中,再加入50%乙醇溶液3 mL照标准曲线的制备项下的方法,自“加入5%亚硝酸钠溶液1 mL”起,依法测定吸光度,从标准曲线中读出供试品溶液中芦丁浓度,再换算成提取液中总黄酮的质量,计算红果参果乙醇提取物中总黄酮含量。
1.2.5 红果参果乙醇提取物总花色苷含量测定
采用pH示差法,参考文献[28-31]的方法。取红果参果提取物约50 mg,精密称定,置于10 mL量瓶中,用0.1%盐酸甲醇溶液溶解并定容,作为供试品溶液。
取供试品溶液两份各1 mL,分别用pH1.0的氯化钾缓冲溶液和pH4.5的乙酸钠缓冲溶液稀释至10 mL,混匀后于室温条件下静置反应30 min,分别在波长520和700 nm处,用1 cm比色皿测定吸光度,重复操作3次,取平均值。按照下列公式计算总花色苷的含量:
式中:ΔA为缓冲液稀释后的吸光度;V为花色苷供试品溶液体积,mL;n为稀释倍数;M为矢车菊素-3-葡萄糖苷摩尔质量,449.2 g/mol;ξ为矢车菊-3-葡萄糖苷消光系数,26900 L/(mol·cm);m为称取样品质量,g;b为比色皿厚度,cm。
1.2.6 红果参果乙醇提取物总多酚含量测定
参照谭晓舒等[32]的方法并做适当修改。
标准曲线制作:精密称取没食子酸10 mg,用乙醇溶解后用蒸馏水定容至10 mL,配制成1 mg/mL标准储备液。准确移取没食子酸标准储备液0.1、0.2、0.3、0.4、0.5、0.6、0.7和0.8 mL,用乙醇溶液稀释成质量浓度为10、20、30、40、50、60、70、80 μg/mL的溶液。吸取对照品溶液各0.5 mL于10 mL比色管中,先后加入2.5 mL稀释10倍的福林酚试剂(0.1 mol/L)、2.0 mL 7.5%的碳酸钠溶液,充分混匀,黑暗处反应1 h,用紫外可见分光光度计在765 nm波长处测定吸光度值,吸光值(A)为纵坐标,以没食子酸浓度(mg/mL)为横坐标绘制标准曲线:y=0.0055x−0.1363(R2=0.9996)。同样吸取样品溶液0.5 mL,依法测定,根据标准曲线计算供试品溶液中的总酚含量,结果表示为没食子酸(gallic acid equivalents,GAE)当量浓度即μg(GAE)/mL,进一步计算出样品中的多酚含量。
1.2.7 红果参果乙醇提取物的化学成分鉴定
通过实验室前期的质谱色谱条件优化,采用UPLC-QTOF-MS技术对红果参果乙醇提取物进行化学成分分析。
供试品溶液制备:取红果参果乙醇提取物适量,精密称定,置入25 mL具塞锥形瓶中,精密加入含1%甲酸的甲醇溶液10 mL,密塞,称重,超声处理(功率250 W,频率40 Hz)30 min,放冷,再称定重量,用相应溶剂补足减失的重量,摇匀,滤过。
对照品溶液配制:取党参炔苷、木犀草苷、芦丁、木犀草素和芹菜素的对照品适量,用甲醇配制成混合标准备品溶液,备用。
UPLC条件:Waters ACQUITY I-class超高效液相色谱仪;Waters ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3色谱柱(2.1 mm×100 mm,1.8 μm);流动相系统:0.1%甲酸水(A):乙腈(B);流速:0.30 mL/min;洗脱程序:0~1 min,98% A;1~15 min,98%~80% A;15~20 min,80%~69% A;20~28 min,69%~58% A;28~35 min,58%~20% A;35~38 min,20% A;38~41 min,20%~0 A;柱温:35 ℃;进样量:1.0 μL。
MS条件:Waters Xevo G2-XS QTOF质谱仪,离子源为电喷雾离子源(Electrospray ionization,ESI);正、负离子扫描模式,飞行时间质量分析器;源电压:2.5 kV(−),3.0 kv(+);碰撞气体为氮气,N2流速:800 L/h;毛细管温度400 ℃;锥孔气体流速:100 L/h;气源温度:120 ℃;采用全扫描方式,质量扫描范围50~1500 Da;碰撞诱导解离电压:6 V(低能量)、30~60 V(高能量)
1.2.8 α-葡萄糖苷酶活性测定
α-葡萄糖苷酶活性参考文献[33-34]方法测定略作改动。在96孔板中加入各样品溶液10 μL和0.2 U/mL的α-葡萄糖苷酶溶液60 μL,于37 ℃摇床中孵育10 min,再加入2.0 mmo/L的pNPG溶液80 μL,继续37 ℃摇床中孵育20 min后立即用0.2 mol/L的Na2CO3溶液50 μL终止反应,于405 nm波长处测定吸光度值A,每个样品平行测定3次。以阿卡波糖为阳性对照,按照抑制率(%)=[1−(A样品组−A样品空白组)/(A阴性组−A空白组)]×100,计算抑制率,并用SPSS18.0软件求出相应的IC50值。样品溶液包括红果参果乙醇提取物样品溶液、红果参果粗多糖样品溶液、木犀草素、矢车菊素-3-O-芸香糖苷和党参炔苷溶液。
1.3 数据处理
所有实验均重复操作3次,采用Excel软件对数据进行整理绘图,采用SPSS18.0计算IC50。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 红果参果样品含量测定结果
多糖、黄酮、多酚和花色苷是植物果实的重要大类成分,因此本研究考察了红果参果提取物中各大类成分的含量。5批粗多糖多糖的含量分别为27.59%±1.89%、33.20%±2.62%、34.62%±2.06%、37.59%±2.34%和33.47%±2.51%,含量范围在27.59%~37.59%,其中4-A-12批次多糖含量最高,为37.59%;1-A-7批次多糖含量较低,为27.59%,与其他4批样品存在显著性差异(P<0.05),红果参果乙醇提取物的测定结果见表1。
表 1 红果参果乙醇提取物的总黄酮、总花色苷及总多酚含量(批号 总黄酮(%) 总花色苷(%) 总多酚(gGAE/100 g) 1-A-7 1.32±0.03c 0.95±0.06c 13.51±0.93b 2-A-9 1.32±0.04c 0.91±0.06c 13.11±0.82b 3-B-11 1.64±0.06b 1.04±0.01b 13.82±0.25b 4-A-12 1.77±0.09a 1.14±0.01a 18.85±1.14a 5-B-5 1.22±0.04c 0.90±0.04c 14.45±0.75b 注:同列不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 由表1可见,不同批次红果参提取样品的总黄酮、总花色苷和总多酚含量存在一定的差异。5批红果参果提取物的总黄酮含量为1.22%~1.77%,其中5-B-5批次黄酮含量较低,1.22%,4-A-12批次黄酮含量最高,为1.77%;总花色苷含量为0.90%~1.14%,5-B-5花色苷含量最低为0.90%,4-A-12批次花色苷含量最高,为1.14%;总多酚含量在13.11~18.85 gGAE/100 g之间,其中2-A-9总多酚含量最低为13.11 gGAE/100 g,4-A-12批次总多酚含量最高,为18.85 gGAE/100 g。5批红果参果提取物中4-A-12批次的多糖、总黄酮、总花色苷和总多酚含量均最高,其中多酚比桑葚、蓝莓及黑加仑等浆果更高,黄酮含量相当[35];2-A-9批次提取物与其他批次的提取物相比含量差异相对较小,因此,后续选择来源于2-A-9的粗多糖和乙醇提取物做后续的研究。
2.2 红果参果乙醇提取物的化学成分结构鉴定分析
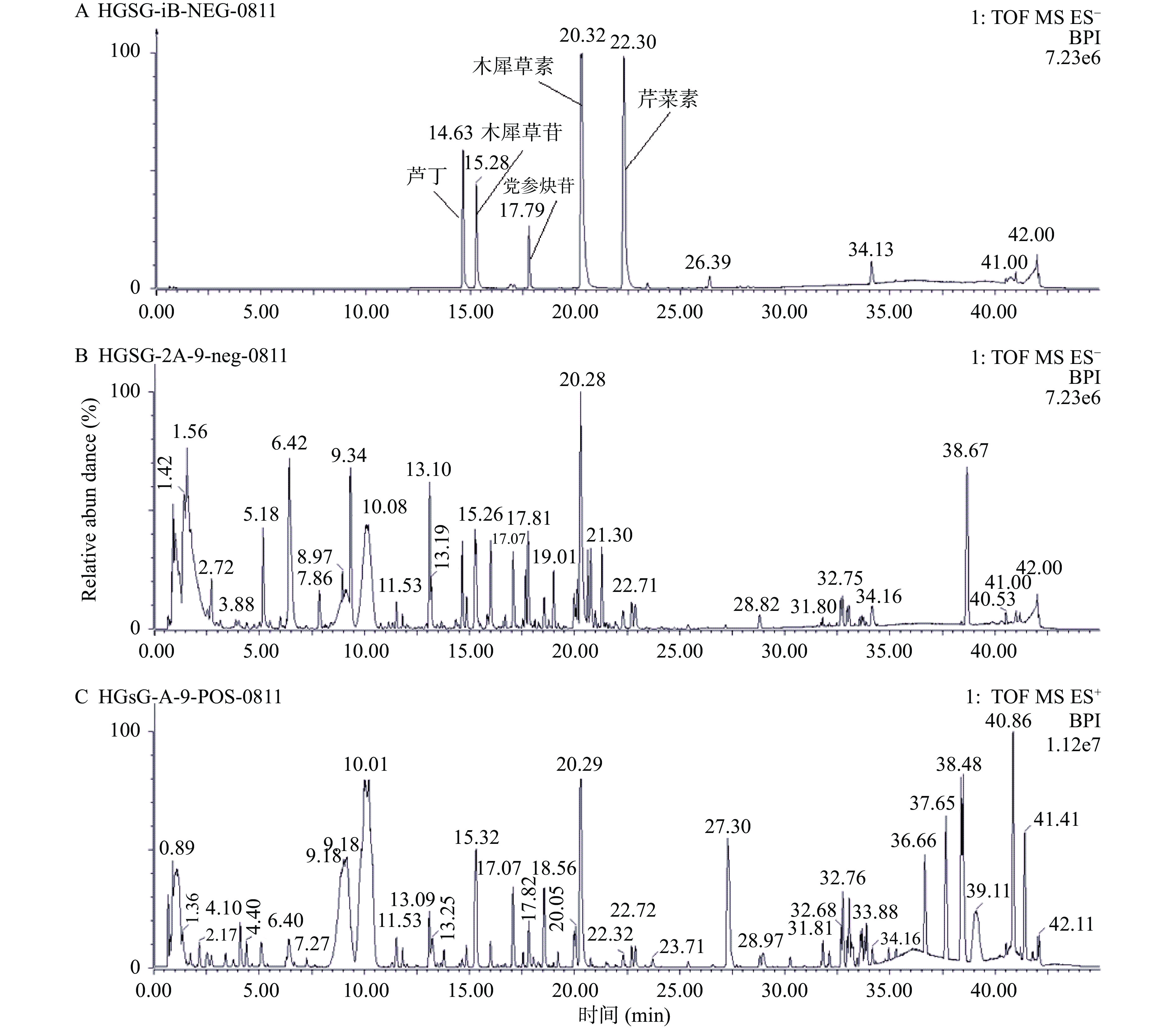
采用Waters ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3色谱柱,以添加0.1%甲酸的水溶液-乙腈为洗脱流动相来增加花色苷的稳定性和分离度[36],建立UPLC-QTOF-MS分析方法。由于红果参乙醇提取物所含化学成分在正、负离子模式下有一定差异,因此本研究在正、负离子模式下,对2-A-9红果参果乙醇提取物进行数据采集,其质谱基峰离子色谱图见图1。
采用Waters Masslynx软件和UNIFI数据处理系统对质谱数据进行处理,通过精确分子量、质谱碎片裂解规律、化合物极性及保留时间分析,并结合参考文献及对照品比对,在红果参果乙醇提取物中共鉴定出21个化合物,包括10个黄酮、3个有机酸、3个花色苷、3个酚酸、1个氨基酸和1个聚炔,见表2。从表2中可见红果参果实化学成分种类丰富,富含多种活性成分。矢车菊素-3-O-葡萄糖苷、矢车菊素-3-O-芸香糖苷和飞燕草素-3-O-芸香糖苷为三种花色苷成分,已被证实具有良好的降糖活性[45-46]。鉴定的非花色苷类酚性成分以黄酮和酚酸类成分为主,其中黄酮类成分最为丰富,10个黄酮类成分中8个为黄酮糖苷,主要是木犀草素的糖苷类成分,糖基以葡萄糖、芸香糖为主,同时还检测到木犀草素和芹菜素游离的苷元。3个酚酸类物质为咖啡酸和绿原酸类成分。这些天然来源的黄酮类物质和酚酸类物质均具有一定的降糖作用[47-49],这为后续的深入研究提供了科学依据。此外,从红果参果中首次鉴定出具有抗炎、抗癌等药理活性的聚炔类党参炔苷成分[50]。
表 2 红果参果乙醇提取物化学成分鉴定结果Table 2. Identification of ethanol extracts from Campanumoea lancifolia (Roxb.) Merr fruits序号 保留时间
(min)实际值
(m/z)理论值
(m/z)加合离子 分子式 碎片离子(m/z) 最大吸收波长(nm) 化合物 结构类型 1 4.10 166.0860 166.0868 [M+H]+ C9H11NO2 166.0860,120.0811 260 苯丙氨酸[37] 氨基酸 2 5.18 279.1089 279.1093 [M-H]− C11H20O8 279.1089,117.0554,71.0136 − 戊酸葡萄糖苷[38] 有机酸 3 6.42 219.0569 219.0505 [M-H]− C8H12O7 219.0569,201.0414,173.0102,157.0515,111.0093 − 柠檬酸乙酯[39] 有机酸 4 7.86 367.1608 367.1604 [M-H]− C15H28O10 413.1662,367.1608 − 戊二酸-1,5-二[3-羟基-2,2-二(羟甲基)丙基]酯[40] 有机酸 5 8.97 353.0877 353.0873 [M-H]− C16H18O9 353.0877,191.0557,175.0061,161.0238 243,325 绿原酸[25] 酚酸 6 9.18 609.1473 609.1456 [M-Cl]− C27H29O16 609.1473,300.0277 232,276 飞燕草素-3-O-芸香糖苷[25] 花色苷 7 9.34 487.1473 487.1452 [M-H]− C21H28O13 487.1473,443.1553,179.0346,135.0446 237,315 咖啡酸-4'-O-芸香糖苷[25] 酚酸 8 10.07 593.1526 593.1506 [M-Cl]− C27H29O15Cl 593.1526,285.0461 232,280 矢车菊素-3-O-芸香糖苷[25] 花色苷 9 14.48 609.1458 609.1456 [M-H]− C27H30O16 609.1619,301.0421,257.0489 251,335 6-羟基木犀草素-7-O-芸香糖苷[41] 黄酮 10 14.65 609.1462 609.1456 [M-H]− C27H30O16 609.1462,301.0408 255,354 芦丁* 黄酮 11 14.85 593.1511 593.1511 [M-H]− C27H30O15 593.1511,285.0559 265,348 木犀草素-7-O-芸香糖苷[25] 黄酮 12 15.28 447.0935 447.0927 [M-H]− C21H20O11 447.0935,285.0461 253,349 木犀草苷* 黄酮 13 15.30 447.0927 447.0927 [M-Cl]− C21H19O11Cl 447.0927,285.0449 292 矢车菊素-3-O-葡萄糖苷[25] 花色苷 14 16.01 381.1191 381.1186 [M-H]− C18H22O9 381.1191,179.0380,161.0273,135.0480 245,325 绿原酸乙酯[42] 酚酸 15 16.50 577.1549 577.1557 [M-H]− C27H29O14 577.1549,269.0449 267,338 芹菜素-7-O-芸香糖苷[25] 黄酮 16 17.07 447.0931 447.0927 [M-H]− C21H20O11 447.0931,285.0461 267,336 木犀草素-4'-O-葡萄糖苷[43] 黄酮 17 17.54 533.0928 533.0931 [M-H]− C24H22O14 533.0928,489.1037,285.0461 251,348 木犀草素-7-O-malonylglucoside[44] 黄酮 18 17.74 441.1770 441.1761 [M+HCOO]− C20H28O8 441.1770,395.1794,215.1091 253,267,283 党参炔苷* 聚炔 19 20.23 285.0447 285.0399 [M-H]− C15H10O6 285.0447 253,348 木犀草素* 黄酮 20 22.30 269.0453 269.0450 [M-H]− C15H10O5 269.0453 267,329 芹菜素* 黄酮 21 22.90 299.0558 299.0556 [M-H]− C16H12O6 299.0558,284.0363 251,267,343 甲氧基木犀草素 黄酮 注:“−”无紫外吸收;*通过对照品确认。 2.3 α-糖苷酶抑制活性
本研究采用pNPG法,以2-A-9红果参果乙醇提取物、2-A-9粗多糖及其主要代表成分为代表考察红果参果的体外α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性。如表3所示,红果参果乙醇提取物和粗多糖在2.00 mg/mL下显示出较强的抑制活性,抑制率在80%以上;在1.00 mg/mL的浓度下,木犀草素对α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制率超过90%,显示出较强抑制活性;在1.00 mg/mL的浓度下矢车菊素-3-O-芸香糖苷的α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性较弱,抑制率为30%;党参炔苷对α-葡萄糖苷酶无抑制作用。
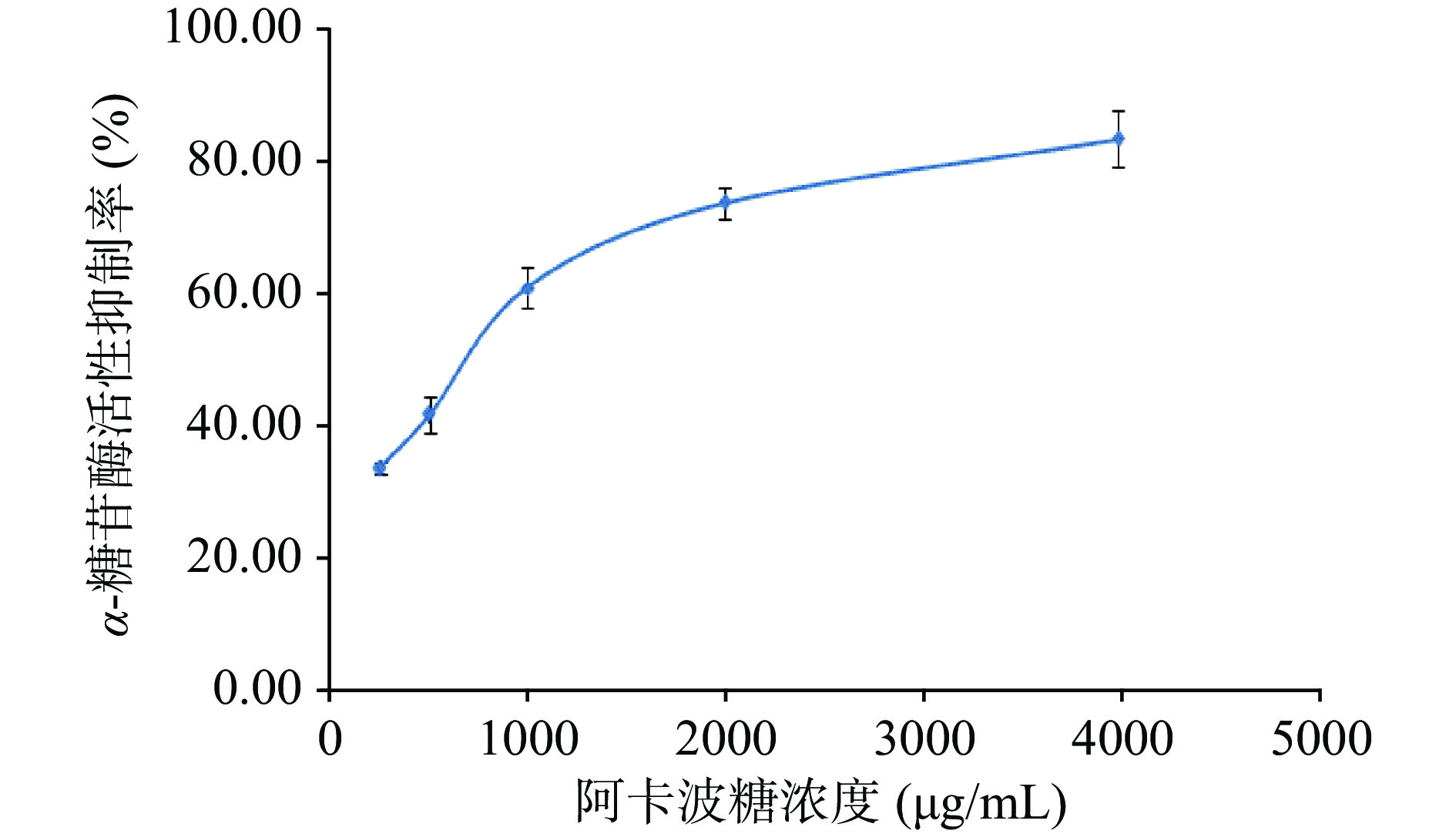
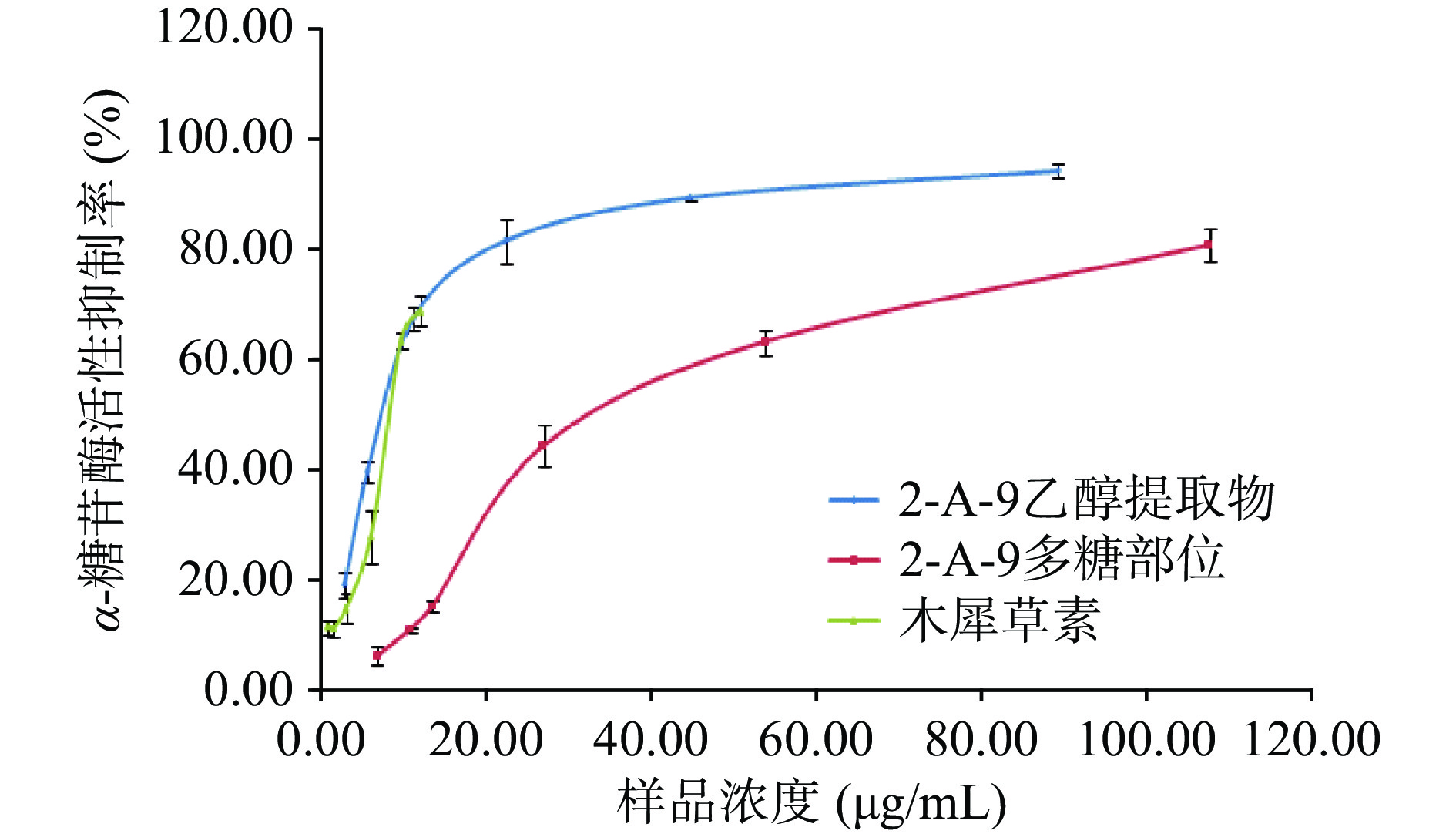
表 3 样品α-糖苷酶抑制活性实验Table 3. α-Glycosidase inhibitory activity test名称 样品浓度(mg/mL) 抑制率(%) 结论 2-A-9乙醇提取物 2.00 >90 强活性 2-A-9粗多糖 2.00 80.75±2.98 强活性 木犀草素 1.00 >90 强活性 矢车菊素-3-O-芸香糖苷 1.00 30.06±2.55 弱活性 党参炔苷 1.00 / 无活性 进一步考察红果参果乙醇提取物、红果参果粗多糖和代表黄酮成分木犀草素在不同浓度下的α-葡萄糖苷酶的活性抑制能力,见图2,阳性对照阿卡波糖的抑制能力见图3。可见各实验样品在一定的质量浓度(红果参粗多糖6.72~107.5 μg/mL、红果参乙醇提取物质量浓度2.79~89.25 μg/mL、木犀草素0.75~12.06 μg/mL)范围内对α-糖苷酶活性的抑制呈现质量浓度依赖,随着各样品质量浓度的增加对α-葡萄糖苷酶活性的抑制作用加强。采用SPSS18.0软件对实验数据进行分析,计算出实验样品的半数抑制浓度IC50,红果参果乙醇提取物、粗多糖、木犀草素和阿卡波糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶半数抑制浓度IC50分别为7.52、37.43、8.03和616.17 μg/mL,4个实验样品对α-葡萄糖苷酶活性的抑制作用强度:红果参果乙醇提取物>木犀草素>粗多糖>阿卡波糖,三个样品的抑制活性均显著高于临床糖尿病常用的药物阿卡波糖(P<0.05),红果参乙醇提取物的IC50与木犀草素相当,约为阿卡波糖的82倍,具有更强的抑制作用。蓝莓乙醇提取物α-糖苷酶抑制活性(IC50=13.0 mg/mL),阿卡波糖(IC50=3.09±0.14 mg/mL)[51];桑葚乙酸乙酯提取物(IC50=72.01±4.18 μg/mL),阿卡波糖(IC50=77.05±6.10 μg/mL)[52];蓝果忍冬多糖HEP-2(IC50=1.56 mg/mL),阿卡波糖(IC50=10.13 mg/mL)[53],与这些浆果提取物相比红果参果提取物对α-葡萄糖苷酶活性的抑制作用更有优势。
3. 结论
本文采用经典的紫外分光光度法测定红果参果乙醇提取物中总黄酮、总花色苷和总多酚等大类成分含量,进一步通过UPLC-QTOF-MS技术对其化学成分进行分析和结构鉴定,结果显示红果参果乙醇提取物富含花色苷、酚酸、木犀草素及其糖苷黄酮类等多种酚类活性成分。本研究首次对红果参果乙醇提取物和粗多糖的体外α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性进行考察,对红果参果降糖作用的药理价值进行评估。实验结果显示红果参果乙醇提取物和粗多糖均对α-葡萄糖苷酶活性有良好的抑制作用,红果参果乙醇提取物在7.52 μg/mL质量浓度下与木犀草素(8.03 μg/mL)抑制作用相当,具有更强的α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制作用。红果参果乙醇提取物α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性优于粗多糖以及木犀草素、党参炔苷和矢车菊素-3-O-葡萄糖苷等三个不同结构类别的代表化合物,可能是多成分协同作用的结果,初步推断黄酮类、酚酸类等酚类成分可能是红果参果抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶活性的重要药效物质基础。酚类物质作为小浆果代谢过程中重要的次生代谢产物,存在于浆果的茎叶、果肉以及种皮中,其含量仅次于纤维素、半纤维素和木质素,具有多种药理活性[54]。黄酮类化合物又是酚类中的重要组成部分,众多研究显示其具有良好的抗糖尿病活性作用,有望成为用于调节2型糖尿病中的餐后高血糖更安全的替代品[55]。
本研究结果丰富了红果参果的化学成分库并首次报道其潜在的天然降糖能力。后续尚需要对红果参果的α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制类型及抑制作用机理进行深入研究,进一步明确其药效物质成分群,为红果参果开发为降糖功能性食品提供更多的实验依据,为新型的天然α-糖苷酶抑制剂的开发提供新的来源。
-
表 1 红果参果乙醇提取物的总黄酮、总花色苷及总多酚含量(
Table 1 Contents of total flavonoids, total anthocyanins and total phenols in ethanol extracts of HGSG (
批号 总黄酮(%) 总花色苷(%) 总多酚(gGAE/100 g) 1-A-7 1.32±0.03c 0.95±0.06c 13.51±0.93b 2-A-9 1.32±0.04c 0.91±0.06c 13.11±0.82b 3-B-11 1.64±0.06b 1.04±0.01b 13.82±0.25b 4-A-12 1.77±0.09a 1.14±0.01a 18.85±1.14a 5-B-5 1.22±0.04c 0.90±0.04c 14.45±0.75b 注:同列不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 2 红果参果乙醇提取物化学成分鉴定结果
Table 2 Identification of ethanol extracts from Campanumoea lancifolia (Roxb.) Merr fruits
序号 保留时间
(min)实际值
(m/z)理论值
(m/z)加合离子 分子式 碎片离子(m/z) 最大吸收波长(nm) 化合物 结构类型 1 4.10 166.0860 166.0868 [M+H]+ C9H11NO2 166.0860,120.0811 260 苯丙氨酸[37] 氨基酸 2 5.18 279.1089 279.1093 [M-H]− C11H20O8 279.1089,117.0554,71.0136 − 戊酸葡萄糖苷[38] 有机酸 3 6.42 219.0569 219.0505 [M-H]− C8H12O7 219.0569,201.0414,173.0102,157.0515,111.0093 − 柠檬酸乙酯[39] 有机酸 4 7.86 367.1608 367.1604 [M-H]− C15H28O10 413.1662,367.1608 − 戊二酸-1,5-二[3-羟基-2,2-二(羟甲基)丙基]酯[40] 有机酸 5 8.97 353.0877 353.0873 [M-H]− C16H18O9 353.0877,191.0557,175.0061,161.0238 243,325 绿原酸[25] 酚酸 6 9.18 609.1473 609.1456 [M-Cl]− C27H29O16 609.1473,300.0277 232,276 飞燕草素-3-O-芸香糖苷[25] 花色苷 7 9.34 487.1473 487.1452 [M-H]− C21H28O13 487.1473,443.1553,179.0346,135.0446 237,315 咖啡酸-4'-O-芸香糖苷[25] 酚酸 8 10.07 593.1526 593.1506 [M-Cl]− C27H29O15Cl 593.1526,285.0461 232,280 矢车菊素-3-O-芸香糖苷[25] 花色苷 9 14.48 609.1458 609.1456 [M-H]− C27H30O16 609.1619,301.0421,257.0489 251,335 6-羟基木犀草素-7-O-芸香糖苷[41] 黄酮 10 14.65 609.1462 609.1456 [M-H]− C27H30O16 609.1462,301.0408 255,354 芦丁* 黄酮 11 14.85 593.1511 593.1511 [M-H]− C27H30O15 593.1511,285.0559 265,348 木犀草素-7-O-芸香糖苷[25] 黄酮 12 15.28 447.0935 447.0927 [M-H]− C21H20O11 447.0935,285.0461 253,349 木犀草苷* 黄酮 13 15.30 447.0927 447.0927 [M-Cl]− C21H19O11Cl 447.0927,285.0449 292 矢车菊素-3-O-葡萄糖苷[25] 花色苷 14 16.01 381.1191 381.1186 [M-H]− C18H22O9 381.1191,179.0380,161.0273,135.0480 245,325 绿原酸乙酯[42] 酚酸 15 16.50 577.1549 577.1557 [M-H]− C27H29O14 577.1549,269.0449 267,338 芹菜素-7-O-芸香糖苷[25] 黄酮 16 17.07 447.0931 447.0927 [M-H]− C21H20O11 447.0931,285.0461 267,336 木犀草素-4'-O-葡萄糖苷[43] 黄酮 17 17.54 533.0928 533.0931 [M-H]− C24H22O14 533.0928,489.1037,285.0461 251,348 木犀草素-7-O-malonylglucoside[44] 黄酮 18 17.74 441.1770 441.1761 [M+HCOO]− C20H28O8 441.1770,395.1794,215.1091 253,267,283 党参炔苷* 聚炔 19 20.23 285.0447 285.0399 [M-H]− C15H10O6 285.0447 253,348 木犀草素* 黄酮 20 22.30 269.0453 269.0450 [M-H]− C15H10O5 269.0453 267,329 芹菜素* 黄酮 21 22.90 299.0558 299.0556 [M-H]− C16H12O6 299.0558,284.0363 251,267,343 甲氧基木犀草素 黄酮 注:“−”无紫外吸收;*通过对照品确认。 表 3 样品α-糖苷酶抑制活性实验
Table 3 α-Glycosidase inhibitory activity test
名称 样品浓度(mg/mL) 抑制率(%) 结论 2-A-9乙醇提取物 2.00 >90 强活性 2-A-9粗多糖 2.00 80.75±2.98 强活性 木犀草素 1.00 >90 强活性 矢车菊素-3-O-芸香糖苷 1.00 30.06±2.55 弱活性 党参炔苷 1.00 / 无活性 -
[1] FAN W. Epidemiology in diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease[J]. Cardiovascular Endocrinology,2017,6(1):8−16. doi: 10.1097/XCE.0000000000000116
[2] SAEEDI P, PETERSOHN I, SALPEA P, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the international diabetes federation diabetes atlas, 9th edition[J]. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice,2019,157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843
[3] WHO. Global Report on Diabetes[EB/OL]. Available online:http://www.who.int/diabetes/global-report/en/(accessed on 15 July 2016).
[4] 于彩云, 高兆兰, 陈天资, 等. 天然产物中α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂的研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2015,36(22):394−399. [YU Caiyun, GAO Zhaolan, CHEN Tianzi, et al. Advancement in research of α-glucosidase inhibitors of natural products[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2015,36(22):394−399. YU Caiyun, GAO Zhaolan, CHEN Tianzi, et al. Advancement in research of α-glucosidase inhibitors of natural products[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2015, 36(22): 394-399.
[5] 阎成炟, 郭崇真, 林建阳, 等. 新型α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂筛选及药理作用研究进展[J]. 药物评价研究,2021,44(2):440−445. [YAN Chengda, GUO Chongzhen, LIN Jianyang, et al. Research progress of screen and pharmacological effect for novel α-glucosidase[J]. Drug Evaluation Research,2021,44(2):440−445. YAN Chengda, GUO Chongzhen, LIN Jianyang, et al. Research progress of screen and pharmacological effect for novel α-glucosidase[J]. Drug Evaluation Research, 2021, 44(2): 440-445.
[6] 季涛, 宿树兰, 郭盛, 等. 基于α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性评价桑叶多组分药效相互作用研究[J]. 中国中药杂志,2016(11):1999−2006. [JI Tao, SU Shulan, GUO Sheng, et al. Evaluate drug interaction of multi-components in Morus alba leaves based on α-glucosidase inhibitory activity[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2016(11):1999−2006. JI Tao, SU Shulan, GUO Sheng, et al. Evaluate drug interaction of multi-components in morus alba leaves based on α-glucosidase inhibitory activity[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2016(11): 1999-2006.
[7] RYU H, LEE B, CURTIS-LONG M, et al. Polyphenols from Broussonetia papyrifera displaying potent α-glucosidase inhibition[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2010,58(1):202−208. doi: 10.1021/jf903068k
[8] 乔锦莉, 张妍, 刘佩, 等. 野生蓝果忍冬多酚鉴定及其抗氧化、降血糖活性[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(11):47−55. [QIAO Jinli, ZHANG Yan, LIU Pei, et al. Polyphenol composition and antioxidant and hypoglycemic activities in wild blue honeysuckle fruit[J]. Food Science,2021,42(11):47−55. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200709-123 QIAO Jinli, ZHANG Yan, LIU Pei, et al. Polyphenol composition and antioxidant and hypoglycemic activities in wild blue honeysuckle fruit[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(11): 47-55. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200709-123
[9] AURIANE D, NAWEL B, TRISTAN R, et al. α-Glucosidase inhibitory activity of tannat grape phenolic extracts in relation to their ripening stages[J]. Biomolecules,2020,10(8):1088. doi: 10.3390/biom10081088
[10] JIANG Z D, YU G, LIANG Y, et al. Inhibitory effects of a sulfated polysaccharide isolated from edible red alga Bangiafusco-purpurea on α-amylase and α-glucosidase[J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry,2019,83(11):2065−2074. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2019.1634515
[11] CAO C L, HUANG Q, ZHANG B, et al. Physicochemical characterization and in vitro hypoglycemic activities of polysaccharides from Sargassum pallidum by microwave-assisted aqueous two-phase extraction[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,109:357−368. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.12.096
[12] CAO X, XIA Y, LIU D, et al. Inhibitory effects of Lentinus edodes mycelia polysaccharide on α- glucosidase, glycation activity and high glucose-induced cell damage[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2020,246:116659. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116659
[13] PROENÇA C, FREITAS M, RIBEIRO D, et al. α-Glucosidase inhibition by flavonoids: An in vitro and in silico structure-activity relationship study[J]. Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry,2017,32(1):1216−1228. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2017.1368503
[14] PENG X, ZHANG G, LIAO Y, et al. Inhibitory kinetics and mechanism of kaempferol on α-glucosidase[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,190:207−215. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.05.088
[15] 郅丽超, 张琳依, 梁馨元, 等. 天然活性成分对α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制作用的研究进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2021,12(6):2276−2282. [ZHI Lichao, ZHANG Linyi, LIANG Xinyuan, et al. Research progress on the inhibitory effect of natural active ingredients on α-glucosidase[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2021,12(6):2276−2282. ZHI Lichao, ZHANG Linyi, LIANG Xinyuan, et al. Research progress on the inhibitory effect of natural active ingredients on α-glucosidase[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality, 2021, 12(6): 2276-2282.
[16] 陈慧, 熊磊, 王文君. 植物次生代谢产物来源的α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂研究进展[J]. 中国中药杂志,2017,42(15):2915−2924. [CHEN Hui, XIONG Lei, WANG Wenjun. Reviews on α-glucosidase inhibitor from plant secondary metabolites[J]. China Journal of Chinesemateria Medica,2017,42(15):2915−2924. CHEN Hui, XIONG Lei, WANG Wenjun. Reviews on α-glucosidase inhibitor from plant secondary metabolites[J]. China Journal of Chinesemateria Medica, 2017, 42(15): 2915-2924.
[17] ZHANG J, SUN L, DONG Y, et al. Chemical compositions and α-glucosidase inhibitory effects of anthocyanidins from blueberry, blackcurrant and blue honeysuckle fruits[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,299:125102. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125102
[18] LI R, WANG Q, ZHAO M, et al. Flavonoid glycosides from seeds of Hippophae rhamnoides subsp. sinensis with alpha-glucosidase inhibition activity[J]. Fitoterapia,2019,137:104248. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2019.104248
[19] 南京中医药大学. 中药大辞典[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2006: 1397-1398 Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine. Chinese materia medica dictionary[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific & Technical Literature Publishers, 2006: 1397-1398.
[20] 陈雅, 李贵, 吴帅玲, 等. 红果参叶中总黄酮的提取工艺初步探讨[J]. 中国野生植物资源,2014,33(2):24−27. [CHEN Ya, LI Gui, WU Shuailing, et al. Preliminary discussion on extration of total flavonids from the leaves of “Hong Guoshen” plant[J]. Chinese Wild Plant Resources,2014,33(2):24−27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9690.2014.02.007 CHEN Ya, LI Gui, WU Shuailing, et al. Preliminary discussion on extration of total flavonids from the leaves of “Hong Guoshen” plant[J]. Chinese Wild Plant Resources, 2014, 33(2): 24-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9690.2014.02.007
[21] 陈莉华, 王晓静, 肖琴, 等. 红果参果胶提取物的抗氧化作用研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2015,36(4):143−146. [CHEN Lihua, WANG Xiaojing, XIAO Qin, et al. Study on antioxidant activities of pectin from Hong Guo ginseng[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2015,36(4):143−146. CHEN Lihua, WANG Xiaojing, XIAO Qin, et al. Study on antioxidant activities of pectin from Hong Guo ginseng[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2015, 36(4): 143-146.
[22] 陈莉华, 龙进国, 谭林艳, 等. 红果参多糖的提取纯化及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2013,25:170−173. [CHEN Lihua, LONG Jinguo, TAN Linyan, et al. Extraction and purification of polysaccharides from Hong Guo ginseng and the comparison of antioxidant activity[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2013,25:170−173. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6880.2013.02.005 CHEN Lihua, LONG Jinguo, TAN Linyan, et al. Extraction and purification of polysaccharides from Hong Guo ginseng and the comparison of antioxidant activity[J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 2013, 25: 170-173. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6880.2013.02.005
[23] 李斌, 李贵, 陈功锡, 等. 红果参果实多糖的提取及其单糖组分研究[J]. 亚热带植物科学,2015,44(1):13−17. [LI Bin, LI Gui, CHEN Gongxi, et al. Extraction and composition of polysaccharide from the fruits of Campnumoea lancifolia[J]. Subtropical Plant Science,2015,44(1):13−17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7791.2015.01.003 LI Bin, LI Gui, CHEN Gongxi, et al. Extraction and composition of polysaccharide from the fruits of Campnumoea lancifolia[J]. Subtropical Plant Science, 2015, 44(1): 13-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7791.2015.01.003
[24] 王晓静, 陈莉华, 莫宇婷. 红果参黄酮与VC的协同抗氧化活性[J]. 食品发酵与工业,2014,40(12):111−115. [WANG Xiaojing, CHEN Lihua, MO Yuting. Cooperative antioxidant effects of flavonoids from Hong Guo ginseng and VC[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2014,40(12):111−115. WANG Xiaojing, CHEN Lihua, MO Yuting. Cooperative antioxidant effects of flavonoids from Hong Guo ginseng and VC[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2014, 40(12): 111-115.
[25] XIANG Z, LIN C, ZHU Y, et al. Phytochemical profiling of antioxidative polyphenols and anthocyanins in the wild plant Campanumoea lancifolia (Roxb. ) Merr[J]. International Journal of Food Propertise,2021,24(1):105−114. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2020.1867570
[26] 宛美志, 孟宪军. 蔓越莓花色苷的组成鉴定及抗氧化能力[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(22):45−50. [WAN Meizhi, MENG Xianjun. Anthocyanin composition and antioxidant activity of cranberry[J]. Food Science,2018,39(22):45−50. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201822008 WAN Meizhi, MENG Xianjun. Anthocyanin composition and antioxidant activity of cranberry[J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(22): 45-50. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201822008
[27] 邓菊庆, 柏春玲, 杨学芳, 等. 紫外可见分光光度法测定不同品种柑橘皮中总黄酮含量[J]. 安徽农业科学,2020,48(9):210−211,252. [DENG Juqing, BAI Chunling, YANG Xuefang, et al. Determination of total flavonoids in different varieties of citrus peels by ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2020,48(9):210−211,252. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2020.09.058 DENG Juqing, BAI Chunling, YANG Xuefang, et al. Determination of total flavonoids in different varieties of citrus peels by ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(9): 210-211, 252. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2020.09.058
[28] 王艺菲, 辛秀兰, 陈亮, 等. pH示差法测定不同种类蓝果忍冬总花色苷含量[J]. 食品研究与开发,2014,35(7):75−77. [WANG Yifei, XIN Xiulan, CHEN Liang, et al. Total anthocyanins content in different species of Lonicera cearulea Linn. by pH-differential spectrophotometry[J]. Food Research and Development,2014,35(7):75−77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2014.07.021 WANG Yifei, XIN Xiulan, CHEN Liang, et al. Total anthocyanins content in different species of Lonicera cearulea Linn. by pH-differential spectrophotometry[J]. Food Research and Development, 2014, 35(7): 75-77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2014.07.021
[29] 王凤娟, 孙飞龙, 叶文文, 等. pH示差法测定红菊苣中花青素条件的优化[J]. 包装与食品机械,2018,36(5):61−64. [WANG Fengjuan, SUN Feilong, YE Wenwen, et al. Optimization of analytical conditions for determining content of anthocyanin in Cichoricum intybus Var. Foliosum Hegi by pH differential method[J]. Packaging and Food Machinery,2018,36(5):61−64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1295.2018.05.012 WANG Fengjuan, SUN Feilong, YE Wenwen, et al. Optimization of analytical conditions for determining content of anthocyanin in Cichoricum intybus Var. Foliosum Hegi by pH differential method[J]. Packaging and Food Machinery, 2018, 36(5): 61-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1295.2018.05.012
[30] VEGA A J D, HECTOR R E, JOSE L G J, et al. Effect of solvents and extraction methods on total anthocyanins, phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity of Renealmia alpinia (Rottb.) Maas peel[J]. Czech Journal of Food Sciences,2017,35(5):456−465. doi: 10.17221/316/2016-CJFS
[31] JIANG T, MAO Y, SUI L, et al. Degradation of anthocyanins and polymeric color formation during heat treatment of purple sweet potato extract at different pH[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,274:460−470. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.07.141
[32] 谭晓舒, 吴建文, 梨贵卿, 等. 火麻仁油总酚含量福林酚测定法的优化[J]. 食品研究与开发,2021,42(2):166−173. [TAN Xiaoshu, WU Jianwen, LI Gui-qing, et al. Optimization of folin-ciocalteu method for the determination of total polyphenols in hemp seed oil[J]. Food Research and Development,2021,42(2):166−173. TAN Xiaoshu, WU Jianwen, LI Gui-qing, et al. Optimization of folin-ciocalteu method for the determination of total polyphenols in hemp seed oil[J]. Food Research and Development, 2021, 42(2): 166-173.
[33] GOKHAN Z H. A study on in vitro enzyme inhibitory properties of asphodelineanatolica: New sources of natural inhibitors for public health problems[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2016,83:39−43. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.12.033
[34] 卫强, 纪小影, 徐飞, 等. 木槿叶化学成分及抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶活性研究[J]. 中药材,2015,38(5):975−979. [WEI Qiang, JI Xiaoying, XU Fei, et al. Chemical constituents from leaves of Hibiscus syriacus and their α-glucosidase inhibitory activities[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials,2015,38(5):975−979. WEI Qiang, JI Xiaoying, XU Fei, et al. Chemical constituents from leaves of Hibiscus syriacus and their α-glucosidase inhibitory activities[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2015, 38(5): 975-979.
[35] 范金波, 蔡茜彤, 冯叙桥, 等. 桑葚、蓝莓、黑加仑中多酚类物质的抗氧化活性[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2015,41(2):157−162. [FAN Jinbo, CAI Xitong, FENG Xuqiao, et al. Phenolic content and antioxidant capacity of blueberry, mulberry and blackcurrant[J]. Food and Fermention Industries,2015,41(2):157−162. FAN Jinbo, CAI Xitong, FENG Xuqiao, et al. Phenolic content and antioxidant capacity of blueberry, mulberry and blackcurrant[J]. Food and Fermention Industries, 2015, 41(2): 157-162.
[36] 张上上, 郑姝宁, 王学涛, 等. 超高效液相色谱-飞行时间-串联质谱法对3种蓝靛果忍冬果实中花青苷的比较分析[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(20):256−262. [ZHANG Shangshang, ZHENG Shuning, WANG Xuetao, et al. Comparative analysis of anthocyanins in the fruits of three varieties of blue honeysuckle (Lonicera caerulea L.) by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-time of flight-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Food Science,2020,41(20):256−262. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190822-223 ZHANG Shangshang, ZHENG Shuning, WANG Xuetao, et al. Comparative analysis of anthocyanins in three Lonicera edulis fruits by ultra high performance liquid chromatography time of flight tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Food Science, 2020, 41(20): 256-262. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190822-223
[37] SARAVANAKUMAR K, PARK S J, MARIADOSS A V A, et al. Chemical composition, antioxidant, and anti-diabetic activities of ethyl acetate fraction of Stachys riederi var. japonica (Miq.) in streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic mice[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2021,155:112374. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2021.112374
[38] CORRALES G, FERNANDEZ-MAYORALAS A, GARCIA-JUNCEDA E, et al. A new strategy for liquid-phase synthesis of disaccharides based on the use of glycosidases[J]. Biocatalysis and Biotransformation,2000,18(4):271−281. doi: 10.3109/10242420009015250
[39] SIOMH S, ZAINAL A. Chemical profiling of Curcuma aeruginosa Roxb. rhizome using different techniques of solvent extraction[J]. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine,2015,5(5):412−417. doi: 10.1016/S2221-1691(15)30378-6
[40] GUORUOLUO Y, ZHOU H, WANG W, et al. Chemical constituents from the immature buds of Cinnamomum cassia (Lauraceae)[J]. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology,2018,78:102−105. doi: 10.1016/j.bse.2018.04.008
[41] OLENNIKOV D N, KASHCHENKO N I. New flavonoids and turkesterone-2-O-cinnamate from leaves of Rhaponticum uniflorum[J]. Chemistry of Natural Compounds,2019,55(2):256−264. doi: 10.1007/s10600-019-02662-2
[42] HU X, CHEN L, SHI S, et al. Antioxidant capacity and phenolic compounds of Lonicera macranthoides by HPLC-DAD-QTOF-MS/MS[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis,2016,124:254−260. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2016.03.008
[43] KOLEY T K, KHAN Z, OULKAR D, et al. Profiling of polyphenols in phalsa (Grewia asiatica L.) fruits based on liquid chromatography high resolution mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2020,57(2):606−616. doi: 10.1007/s13197-019-04092-y
[44] NOUI A, BOUDIAR T, BAKHOUCHE A, et al. Chemical characterization of polyphenols from Daucus muricatus growing in Algeria by RP-UHPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS[J]. Natural Product Research,2018,32(8):982−986. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2017.1371162
[45] SIRICHAI A, SIRINTORN Y, PIYAWAN C, et al. Cyanidin-3-rutinoside alleviates postprandial hyperglycemia and its synergism with acarbose by inhibition of intestinal α-glucosidase[J]. Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition,2011,49:36−41. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.10-116
[46] TSUBASA T, SHO N, MASAKI K, et al. Delphinidin 3-rutinoside-rich blackcurrant extract ameliorates glucose tolerance by increasing the release of glucagon-like peptide-1secretion[J]. Food Science Nutrition,2017,5:929−933. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.478
[47] 朱晓丹, 江冰洁, 刘新元, 等. 天然产物中黄酮多酚及生物碱类化合物治疗2型糖尿病研究进展[J]. 中国现代中药,2019,21(11):1592−1598. [Zhu Xiaodan, JIANG Bingjie, Liu Xinyuan, et al. Mechanism and research progress of flavonoids, polyphenols and alkaloids in natural products for type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Modern Chinese Medicine,2019,21(11):1592−1598. Zhu Xiaodan, JIANG Bingjie, Liu Xinyuan, et al. Mechanism and research progress of flavonoids, polyphenols and alkaloids in natural products for type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Modern Chinese Medicine, 2019, 21(11): 1592-1598.
[48] YAN J, ZHANG G, PAN J, et al. α-Glucosidase inhibition by luteolin: Kinetics, interaction andmolecular docking[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2014,64:213−223. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.12.007
[49] SUN L, MIAO M. Dietary polyphenols modulate starch digestion and glycaemic level: A review[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2020,60(4):541−555. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1544883
[50] YOON I S, CHO S S. Effects of lobetyolin on xanthine oxidase activity in vitro and in vivo: Weak and mixed inhibition[J]. Natural Product Research,2021,35(10):1667−1670. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2019.1622108
[51] WU T, LUO J, XU B. In vitro antidiabetic effects of selected fruits and vegetables against glycosidase and aldose reductase[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2015,3(6):495−505.
[52] WANG Y, XIANG L, WANG C, et al. Antidiabetic and antioxidant effects and phytochemicals of mulberry fruit (Morus alba L.) polyphenol enhanced extract[J]. Plos One,2013,8(7):e71144. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071144
[53] FU X, YANG H, MA C, et al. Characterization and inhibitory activities on α-amylase and α-glucosidase of the polysaccharide from blue honeysuckle berries[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,163:414−422. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.267
[54] 石碧, 狄莹. 植物多酚[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2002: 5-30 SHI Bi, DI Ying. Plant polyphenols[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2002: 5-30.
[55] PROENC C, RIBEIRO D, FREITAS M, et al. Flavonoids as potential agents in the management of type 2 diabetes through the modulation of a-amylase and a-glucosidase activity: A review[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2020:1−71.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 黄素艳,曹荣,刘楠,孙永,周德庆,王珊珊. 提取方式对微拟球藻蛋白理化性质和功能特性的影响. 食品工业科技. 2025(01): 87-96 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 陈亭菊,刘远超,蔡曼君,郭慧阳,陈少丹,吴清平,胡惠萍. 食药用菌蛋白质研究现状及应用. 食用菌学报. 2024(02): 113-126 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)









 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



