Study on Protective Effects of Glycyrrhiza and Pueraria Fermentation Composition on Rats with Chronic Liver Injury
-
摘要: 目的:研究甘草葛根发酵组合物对四氯化碳(CCl4)致慢性肝损伤大鼠的保护作用及潜在作用机制。方法:采用SD大鼠分别灌胃生理盐水、甘利欣甘草酸二铵胶囊(GLX)、甘草葛根发酵组合物,通过四氯化碳处理建立大鼠慢性肝损伤模型。采用酶联免疫吸附法检测小鼠血清中肝功能指标(ALT、AST、TBIL、TP)、肝纤指标(PLD、TGF-β1、HA)、内毒素(LPS)和炎症因子(TNF-α、IL-6)的含量;通过光镜和透射电镜观察小鼠肝组织病理性改变;同时,对不同处理组进行肠道菌群的定量分析。结果:与生理盐水处理组比较,甘草葛根发酵组合物处理组小鼠血清中AST、ALT水平极显著降低(P<0.01);甘草葛根发酵组合物处理组造模前后血清中TBIL、TP水平无明显差异;肝纤维化指标结果显示,甘草葛根发酵组合物保护组TGF-β1(P<0.01)、PLD(P<0.01)、HA(P<0.05)指标显著低于生理盐水处理对照组;与生理盐水处理对照组比较,甘草葛根发酵组合物处理组造模前后血清IL-6、LPS水平差异不显著,甘草葛根发酵组合物处理组极显著降低TNF-α水平(P<0.01);病理观察显示,甘草葛根发酵组合物和GLX处理组肝组织未出现明显的病理性改变;菌群分析显示,甘草葛根发酵组合物保护组EMB、EC、KV、CD数量降低,TPY、MRS增高;结论:甘草葛根发酵组合物和GLX对CCl4所致大鼠慢性肝损伤具有一定的保护作用,其中甘草葛根发酵组合物在抗慢性肝损伤过程中的肝纤维化、降低炎症和内毒素水平以及调节肠道菌群方面具有更显著的作用。Abstract: Objective: To study the protective effect and potential mechanism of glycyrrhiza and pueraria fermentation composition on chronic liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). Methods: SD rats were intragastric with normal saline, Diammonium Glycyrrhizinate Capsules (GLX) and glycyrrhiza and pueraria fermentation composition, respectively, and treated with carbon tetrachloride to establish chronic liver injury model. The contents of liver function indexes (ALT, AST, TBIL, TP), liver fiber indexes (PLD, TGF-β1, HA), endotoxin and inflammatory factors (LPS, TNF-α, IL-6) in serum of mice were detected by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. Pathological changes of liver tissue were observed by light microscope and transmission electron microscope. At the same time, the intestinal flora of different treatment groups was quantitatively analyzed. Results: Compared with normal saline treatment group, treatment group glycyrrhiza and pueraria fermentation composition mice serum AST, ALT level decreased extremely significant (P<0.01). There were no significant differences in serum TBIL and TP levels in glycyrrhiza and pueraria fermentation composition treatment group before and after modeling. The results of liver fibrosis index showed that TGF-β1 (P<0.01), PLD (P<0.01) and HA (P<0.05) in glycyrrhiza and pueraria fermentation composition protected group were significantly lower than those in normal saline control group. Compared with normal saline treatment group, there were no significant differences in serum IL-6 and LPS levels before and after modeling in glycyrrhiza and pueraria fermentation composition treatment group, while TNF-α level extremely significant decreased in glycyrrhiza and pueraria fermentation composition treatment group (P<0.01). Pathological observation showed that there were no obvious pathological changes in liver tissues in glycyrrhiza and pueraria fermentation composition and GLX treatment groups. The number of EMB, EC, KV and CD in glycyrrhiza and pueraria fermentation composition protection group decreased, while TPY and MRS increased. Conclusion: Glycyrrhiza and pueraria fermentation composition and GLX had certain protective effects on chronic liver injury induced by CCl4 in rats, and glycyrrhiza and pueraria fermentation composition had more significant effects on liver fibrosis, reducing inflammation and endotoxin levels, and regulating intestinal flora during chronic liver injury.
-
中医学自古以来就有“药食同源”理论,如许多中药即是食物也是药物,食物和药物一样均可防治疾病。中药里面许多中药都属于药食同源类中药。卫生部于2002年发布的《关于进一步规范保健食品原料管理的通知》(卫法监发[2002]51号),通知明确规定了药食同源中药的名称,甘草和葛根均在此类中药中。保健食品中,许多以甘草、葛根为原料,传统食品中,也多用甘草、葛根煲汤、炖煮,用于保健。其中,甘草活性成分甘草酸苷、异甘草酸、甘草酸二铵在保肝护肝中已广泛应用于临床[1-2],在日常饮食中应用广泛:甘草及其提取物常被添加于零食、饮料、啤酒等食品中。葛根为药食同源两种中药,其化学成分主要有黄酮、三萜、香豆素、皂苷等类化合物[3],其中葛根素对化学性肝损伤、酒精/非酒精性肝损伤等多种肝损伤具有不同程度的治疗作用[4-6]。葛根含有丰富的碳水化合物、蛋白质、维生素、矿物质等营养物质,属于药食同源中药,也是常见的养生补品,始记于《神农本草经》中,在我国食用、药用领域已有3000多年的应用历史。常见的葛根产品有葛根粉粥、葛根羹、葛根汤等。
现代研究发现,肝脏和肠道经胆管、门静脉和体循环进行双向交流。肝脏代谢产物影响着肠道菌群的组成与肠屏障的完整,肠道菌群的代谢产物经门静脉系统影响着肝脏功能及糖脂代谢等,肝脏与肠道之间相互联系与影响,组成了“肠-肝”轴(Gut-Liver Axis)[7-8]。肝脏产物影响肠道菌群组成和屏障完整性,肠道因子调控肝脏的胆汁酸合成和糖脂代谢;肝脏和肠道中的促炎性变化介导肝纤维化、肝硬化和肝细胞癌的发展,这些疾病有共同的发展途径[9-10];益生菌及其发酵产物能够调节肠道菌群,有效地减轻各因素对肝脏的损伤,改善肝脏功能[11-12]。
发酵炮制法是中药炮制的传统方法之一,在我国具有悠久的应用历史。中药发酵炮制过程是应用微生物代谢酶系等作用的生物转化过程,具有反应条件温和、转化效率高、副产物少、毒副作用小等特点[13-14]。对于传统发酵炮制法而言,发酵微生物菌种不明确,发酵过程以自然发酵为主,发酵终点以经验为主。应用菌种明确的一种或多种微生物,采用现代微生物工程技术,提升发酵类中药产品的品质与功效,是发酵炮制中药技术发展创新的重要研究内容,也是中药现代化的重要发展方向之一[15]。本研究基于肠-肝轴的最新研究进展,以益生菌发酵这一新型炮制方式,对甘草、葛根进行复合发酵处理,以促进中药活性成分的释放。发酵获得的乳酸菌发酵产物不仅含有较高的活性成分,同时含有后生元成分,通过中药、益生菌“协同增效”的模式,提升了中药性能,并建立了基于发酵物指纹图谱与标志性活性成分相结合的质量控制体系。本文以益生菌发酵中药技术制备的甘草葛根发酵物GCQ作为供试物,分析其对四氯化碳致慢性肝损伤大鼠的肝保护、降低内毒素、降低炎症、调节肠道菌群的作用,初步阐明益生菌甘草葛根发酵物GCQ对慢性肝损伤大鼠的肝保护及与肠道菌群的相关影响及其作用机理。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
甘草葛根发酵组合物(GCQ) 实验室自制;SPF级SD雌性和雄性大鼠(180±20)g(合格证:NO.1107261911004282) 济南朋悦实验动物繁育有限公司;甘利欣甘草酸二铵胶囊(GLX) 正大天晴;谷丙转氨酶(ALT)、谷草转氨酶(AST)、总胆红素(TBIL)、总蛋白(TP)、内毒素(LPS)、肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)、脯氨酸肽酶(PLD)、转化生长因子β(TGF-β1)、透明质酸(HA)、白细胞介素-6(IL-6)检测试剂盒 上海酶联生物科技有限公司;伊红美蓝培养基、EC肠球菌培养基、TPY琼脂培养基、MRS固体培养基、EG琼脂培养基、TSC琼脂培养基 青岛海博生物技术有限公司;L-半胱氨酸盐酸盐 Solarbio;绵羊血 青岛海博生物;CCl4 分析纯,上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司。
F50酶标仪 Infinite公司;CX21FS1电子生物显微镜 Olympus公司;JEM-1230透射电子显微镜 日本电子株式会社;ML204电子分析天平 Mettler Toledo公司;DHP-9162型电热恒温培养箱 上海一恒科学仪器有限公司,CL5高速离心机 长沙高新技术产业开发区湘仪离心机仪器有限公司;THZ-C型恒温振荡器 苏州培英实验室设备有限公司;BCD-256WDGH型冰箱 青岛海尔股份有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 甘草葛根发酵组合物的制备
甘草发酵物的制备:应用现代发酵工程技术,以甘草为发酵原料,经真菌(茯苓5.28)发酵酶解,获得甘草酶解产物;以甘草酶解产物为发酵原料,经乳酸杆菌(植物乳杆菌)二次发酵处理,添加适当比例的麦芽糊精冻干处理,获得甘草发酵物(甘草酸:4.18%,甘草次酸:1.39 g/kg)。
葛根发酵物的制备:以葛根为发酵原料,经乳酸杆菌(副干酪乳杆菌)发酵处理,添加适当比例的麦芽糊精冻干处理,获得葛根发酵物(葛根素:1.15%。)
甘草葛根发酵组合物:6.2 g发酵组合物:甘草发酵物3.59 g,葛根发酵物2.61 g成分含量:甘草酸150 mg、葛根素30 mg、甘草次酸5 mg。
1.2.2 分组及给药
48只SD大鼠,雌雄分笼饲养,饲养室保持温度23±2 ℃、湿度50%±15%、昼夜12 h交替条件,预饲养1周后,随机分为生理盐水处理对照组(NS组)、甘草酸二铵阳性对照组(GLX组)、甘草葛根发酵组合物处理组(GCQ组)。其中,GLX阳性对照组参照甘利欣(GLX)甘草酸二铵胶囊用量,甘草酸二铵灌胃剂量为15 mg/kg·d;GCQ样品组甘草葛根发酵物灌胃剂量为650 mg/kg·d;以生理盐水配制成适宜浓度给药,每天2次,生理盐水处理对照组灌胃同等剂量生理盐水。NS组、GLX阳性对照组、GCQ样品组采用2% CCl4溶液(以市售橄榄油为溶剂稀释)灌胃造模,造模剂量为0.2 mL/kg/次,每周两次(造模期间间隔4 h继续给药灌胃)。
1.2.3 实验动物状态观察
实验期间观察记录实验动物的生活状态变化,包括运动、神志、进食、皮毛、小便、大便、体重等病态观察,记录慢性肝损伤造模开始后12周内动物的死亡和因病淘汰情况。
1.2.4 血清中ALT、AST、TBIL、TP、LPS、TNF-α、PLD、TGF-β1、HA、IL-6含量检测
实验动物造模给药12周后,末次CCl4造模48 h后,禁食不禁水16 h,采用眼球静脉取血,血浆置于37 ℃温浴30 min,转速3500 r/min离心10 min,移液枪取上层血清分装于EP管中,−20 ℃保存备用。严格按照试剂盒说明书操作步骤进行肝功能指标(ALT、AST、TBIL、TP)、内毒素定量(LPS)、肝纤指标(PLD、TGF-β1、HA)、炎症因子(IL-6、TNF-α)相应指标检测。
1.2.5 肝组织病理学检测
肉眼观察肝脏形态及颜色改变(畸形、肿大、挛缩、缺血等)。取大鼠肝脏左叶用10%福尔马林固定,从肝左叶中部做横切面取材,常规病理制片(H.E.染色)[16];光镜下观察肝组织细胞病理改变。取出肝脏,切成1 mm3的组织块,进行锇酸染色[17],制片后采用透射电镜观察细胞组织变化。
1.2.6 肠道菌群定量分析
实验动物剖杀后,无菌条件下取盲肠粪便,精确称取1 g置于100 mL带玻璃珠无菌生理盐水三角瓶中,密封,置于恒温摇床,转速160 r/min,混匀30 min,进行不同梯度稀释,采用平板计数法,选用适宜不同类型细菌的选择培养基:伊红美蓝琼脂、EC肠球菌、TPY琼脂、MRS琼脂、EG琼脂、TSC琼脂培养基,分别进行选择性培养基配制及高压灭菌,选择合适的稀释度分别接种在各培养基上,培养后以菌落形态、革兰氏染色镜检、生化反应等鉴定计数菌落,分别计算出每克湿便中大肠杆菌、肠球菌、双歧杆菌、乳杆菌、类杆菌和梭杆菌的活菌数。
1.3 数据处理
采用SPSS Statistics 20软件对数据进行统计分析。试验数据均以平均值±标准误差(Mean±SEM)表示,检验方法采用t检验,P<0.05为具有统计学意义,即差异显著,P<0.01即极显著差异。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 甘草葛根发酵组合物对慢性肝损伤模型大鼠的机体状态的影响
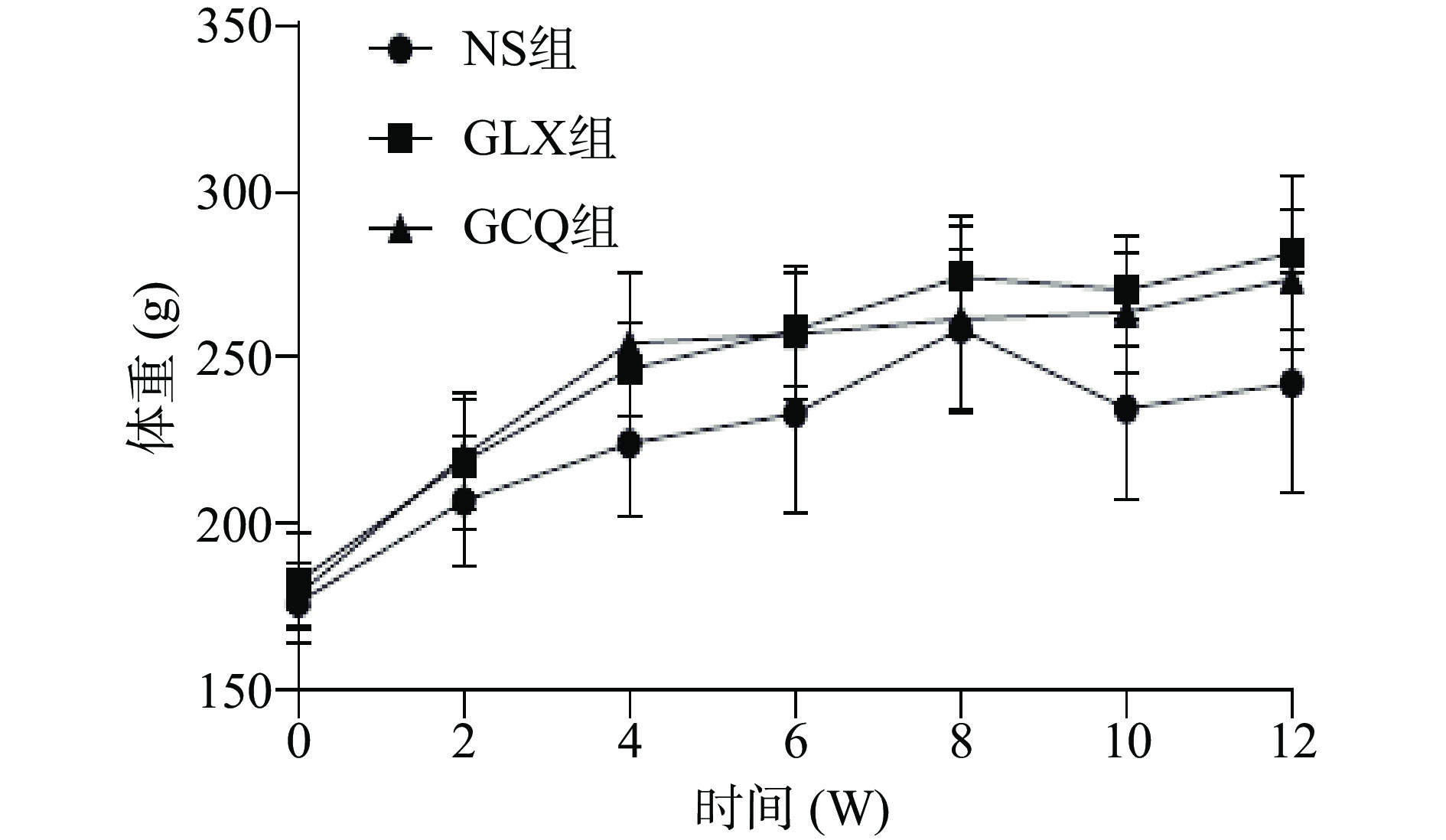
处理及观察12周,生理盐水组和GCQ组未见受试动物死亡;GLX组在CCl4处理过程中发生重度感染,淘汰1只,期间未发生因病淘汰。与未给予GLX和GCQ进行保护性治疗的慢性肝损伤模型动物相比,连续给药6周后,给药与未给药模型动物的生活状态开始发生差异,主要表现为给药动物活力更强,精神、食欲和皮毛亮度、密度更好,体重增加明显(见图1),尿色浅,大便成形;12周时给药与未给药模型动物上述差异更为明显。
2.2 GCQ对慢性肝损伤模型大鼠血清中ALT、AST、TBIL、TP的影响
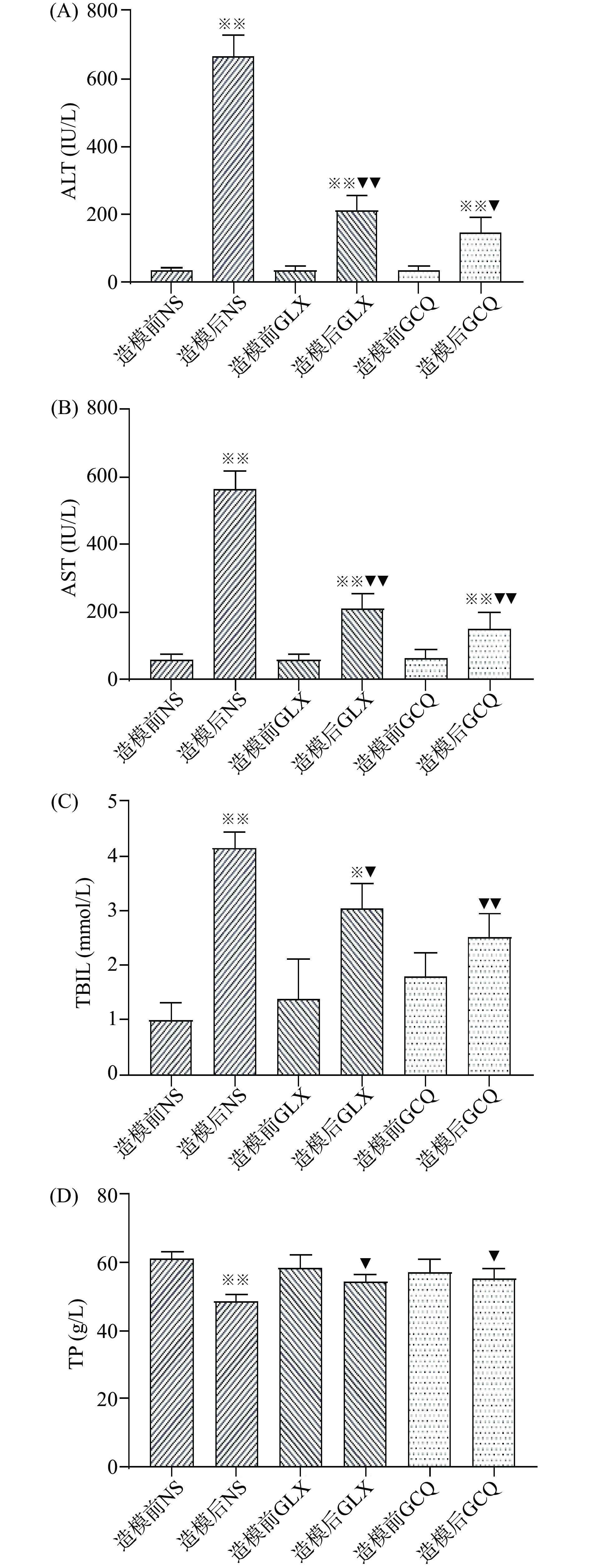
四氯化碳(CCl4)受到肝微粒体酶活化成为三氯甲烷自由基(CCl3·)与蛋白质共价结合导致蛋白合成障碍、脂质分解代谢紊乱,引起肝细胞内甘油三酯(TG)蓄积,CCl3·也能迅速与O2结合转化为过氧化三甲烷自由基(CCl3 O2·)导致脂质过氧化,从而引起细胞膜的变性损伤,产生酶渗漏及各种类型的细胞病变、炎症反应,甚至坏死[9]。由图2可知,GLX和GCQ保护组慢性肝损伤模型动物,肝损伤指标ALT、AST造模后较造模前增高极显著(P<0.01),表明GLX和GCQ的肝脏保护作用不够完全;但与生理盐水处理组造模后相比,ALT和AST水平呈极显著降低(P<0.01);生理盐水处理组造模后TP水平呈极显著降低(P<0.01),GLX和GCQ保护组造模前后无明显差异;生理盐水处理组造模后TBIL水平呈极显著增高(P<0.01),GCQ保护组造模前后无明显差异;表明GLX和GCQ有明显保护作用。
研究显示,NS组造模后ALT、AST水平显著增高,说明肝细胞损伤严重,肝细胞通透性增加,产生酶渗漏;TBIL水平显著升高,说明肝细胞代谢功能水平降低。GCQ可以显著降低四氯化碳(CCl4)致慢性肝损伤大鼠的ALT、AST和TBIL水平,说明GCQ可以对肝细胞膜产生保护作用,增强肝细胞的代谢功能,降低四氯化碳(CCl4)对肝脏的损伤程度,抑制肝损伤产生的代谢紊乱问题。
2.3 甘草葛根发酵组合物对慢性肝损伤模型大鼠肝纤维化指标PLD、TGF-β1、HA的影响
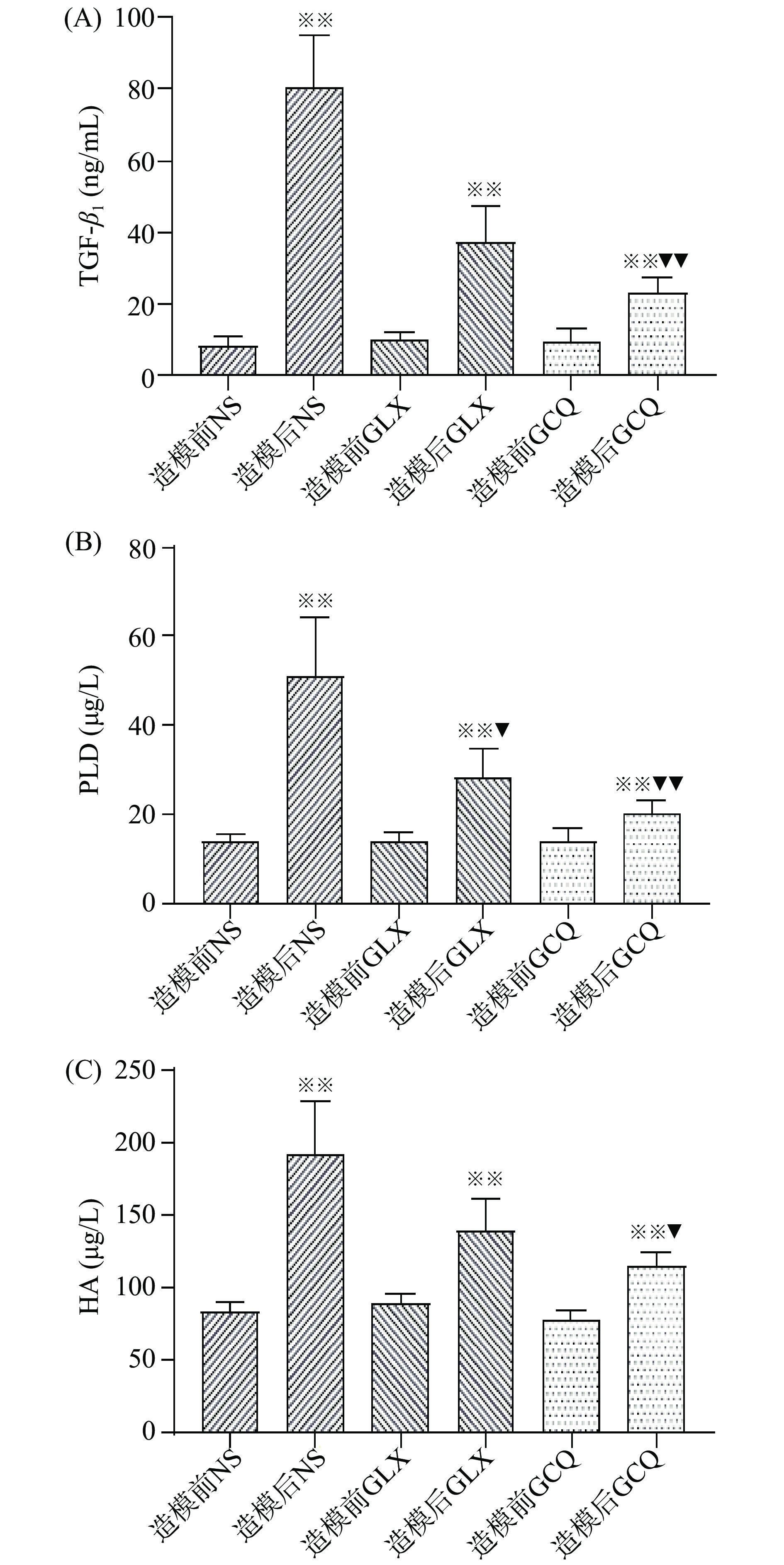
任何肝脏损伤在肝脏修复愈合的过程中都有肝纤维化的过程,是肝脏的一个病理生理过程,如果损伤因素长期不能去除,纤维化的过程长期持续就会发展成肝硬化。肝纤维化指标PLD、TGF-β1、HA检测结果见图3。结果显示,GLX和GCQ保护组造模后PLD、TGF-β1、HA水平高于造模前,但GCQ保护组指标HA显著低于生理盐水处理对照组造模后水平(P<0.05),GLX保护组则与对照组无显著差异;与生理盐水处理对照组造模后水平比较,GCQ保护组PLD和TGF-β1水平极显著降低(P<0.01);提示GCQ具有抗慢性肝损伤过程中发生的肝纤维化作用。
血清中TGF-β1、PLD、HA是反映肝损害严重程度、诊断肝纤维化的重要指标。研究显示,慢性肝病患者PLD升高,可能与肝细胞内PLD活性增强、细胞内胶原降解加速、脯氨酸含量升高,使细胞间胶原合成增加有关。透明质酸是由肝内皮细胞摄取分解,肝功能受损时,血清中HA升高,血清HA水平是判断有无活动性肝纤维化的定量指标[18]。TGF-β1与肝胶原、纤维连结蛋白等细胞外基质蛋白的合成明显相关,是近年来发现的反映肝纤维化的重要指标之一,是重要的促纤维化介质,已成为纤维化疾病的中药医治靶标,通过抑制TGF-β1的产生,阻断其与受体结合和调控其信号传导进程,可以达到抗纤维化的目的[19]。GCQ可通过保护肝细胞、促进细胞代谢功能等作用方式,进一步达到抑制TGF-β1的产生、促进透明质酸的分解、抑制细胞间胶原合成,抑制慢性肝损伤的纤维化作用。
2.4 甘草葛根发酵组合物对慢性肝损伤模型大鼠血清中IL-6、TNF-α、LPS的影响
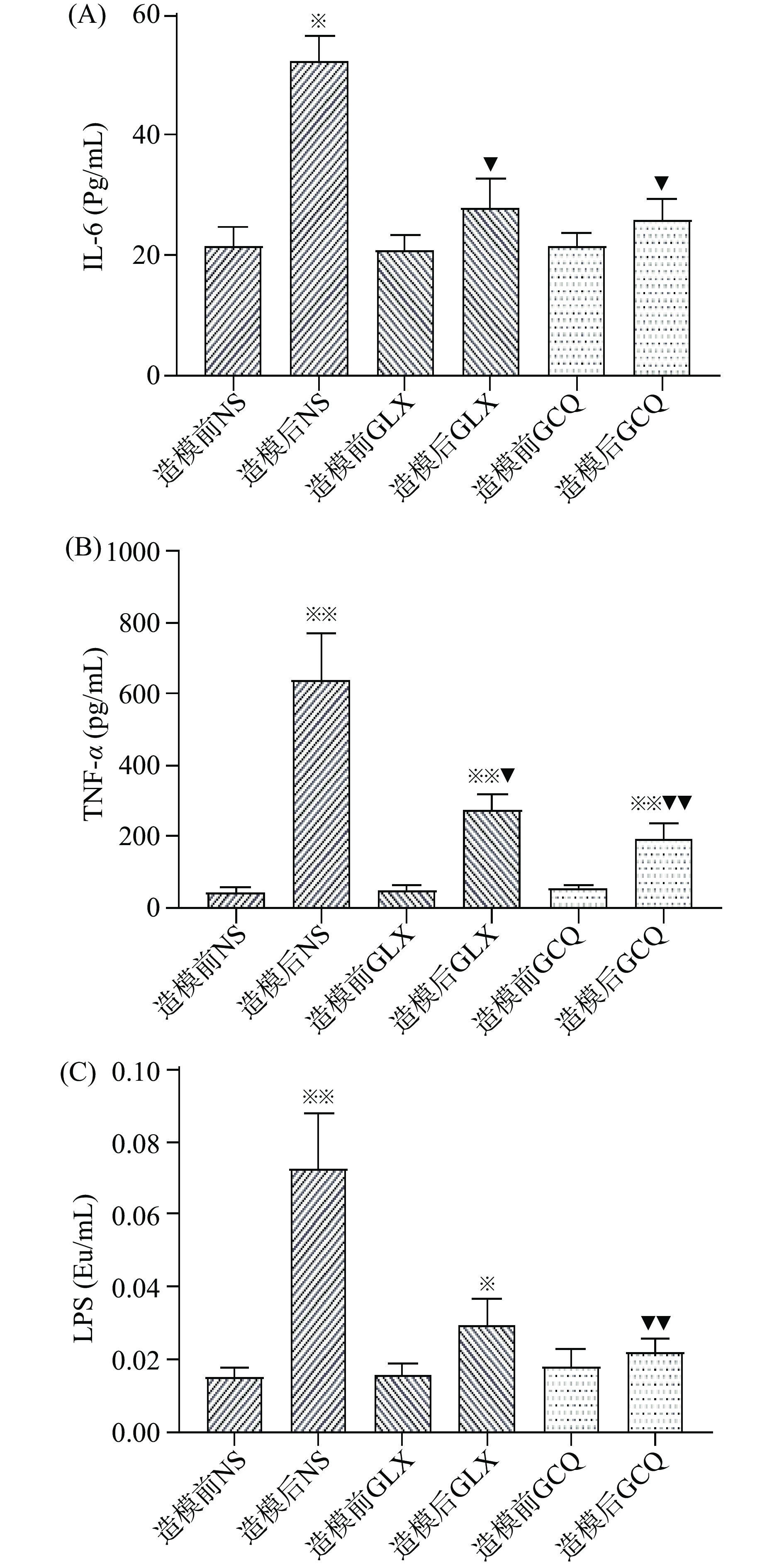
IL-6和TNF-α是参与多种生理与免疫过程的重要细胞因子,与细菌感染性疾病的发病有关,是参与全身炎症反应综合征的重要炎症介质,它们水平的高低反映了感染的严重程度。内毒素是革兰氏阴性细菌细胞壁中的一种脂多糖,脂多糖进入血液引起内毒素血症,肠道菌群会随着肝损伤的发展而发生变化,进而引起内毒素产生菌的增加[20]。由图4结果显示,GLX和GCQ保护组造模前后血清IL-6水平变化不大,但生理盐水处理对照组造模前后血清IL-6水平差异显著(P<0.05);GLX和GCQ保护组造模前后血清TNF-α水平差异极显著(P<0.01),在阻止TNF-α升高方面,GCQ效果较GLX明显,与生理盐水处理对照组比较具有极显著性差异(P<0.01);GCQ保护组造模前后LPS水平无显著性差异,与生理盐水处理对照组造模后比较具有极显著性差异(P<0.01);说明GCQ在降低CCl4慢性肝损伤大鼠内毒素、炎症方面具有一定的保护作用。
IL-6能诱导B细胞分化和产生抗体,诱导T细胞活化增殖、分化,参与机体的免疫应答,是炎性反应的促发剂,IL-6已成为某些细胞因子风暴综合征(CSS)的关键节点。TNF-α是炎症反应过程中出现最早、最重要的炎性介质,能激活中性粒细胞和淋巴细胞,使血管内皮细胞通透性增加,调节其他组织代谢活性并促使其他细胞因子的合成和释放。GCQ可有效降低机体内的炎性因子,降低因炎性因子风暴导致的肝损伤程度。
肠屏障功能障碍会导致危险的肠道菌群及其产物进入肠系膜静脉进而经门静脉进入肝脏,从而导致或加剧肝损伤。发酵组合物GCQ在生物发酵过程中会产生多种次级代谢产物,在肠道中发挥抑制致病菌、清除肠道毒素、促进有益菌增殖等多种益生功效,进一步达到平衡肠道菌群、降低炎症及增强肠道免疫功能的作用,促进肠道构建稳定的肠道屏障,降低内毒素水平及慢性炎症的发生[21]。
2.5 甘草葛根发酵组合物对慢性肝损伤模型大鼠肝组织病理性改变的影响
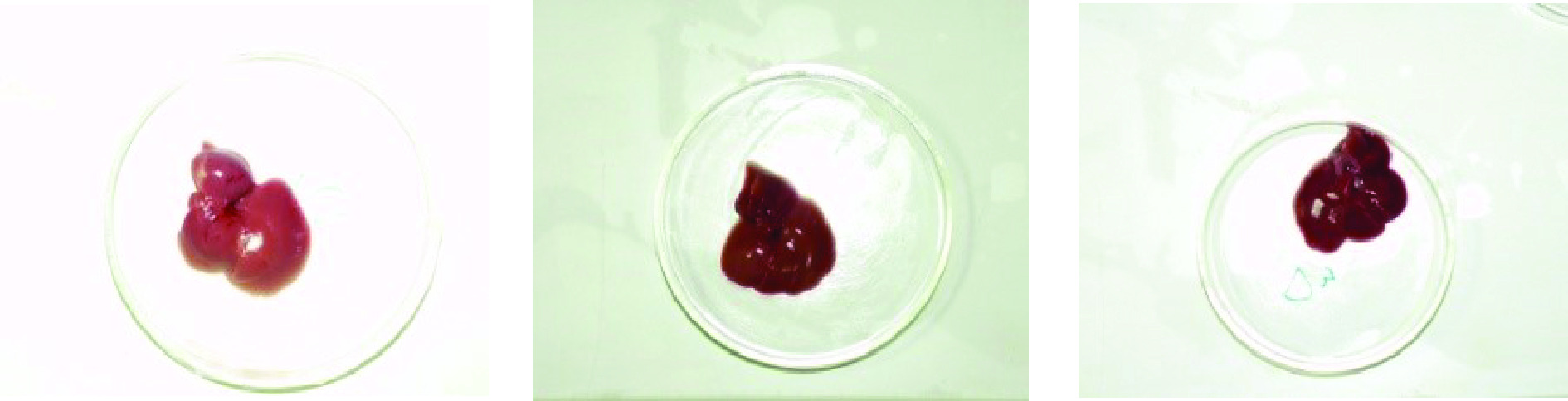
肉眼观察与生理盐水处理未保护的慢性肝损伤大鼠比较,GLX和GCQ保护肝脏的大小、色泽、质地均有差异,但两者间比较差异不大(见图5)。
光镜观察与生理盐水处理未保护的慢性肝损伤大鼠比较,GLX和GCQ保护肝组织肝细胞气球样变数量相对较少,发生肿胀性炎症和局部坏死改变的程度偏轻,但GLX和GCQ对慢性肝损伤的保护作用无显著差异(见图6)。
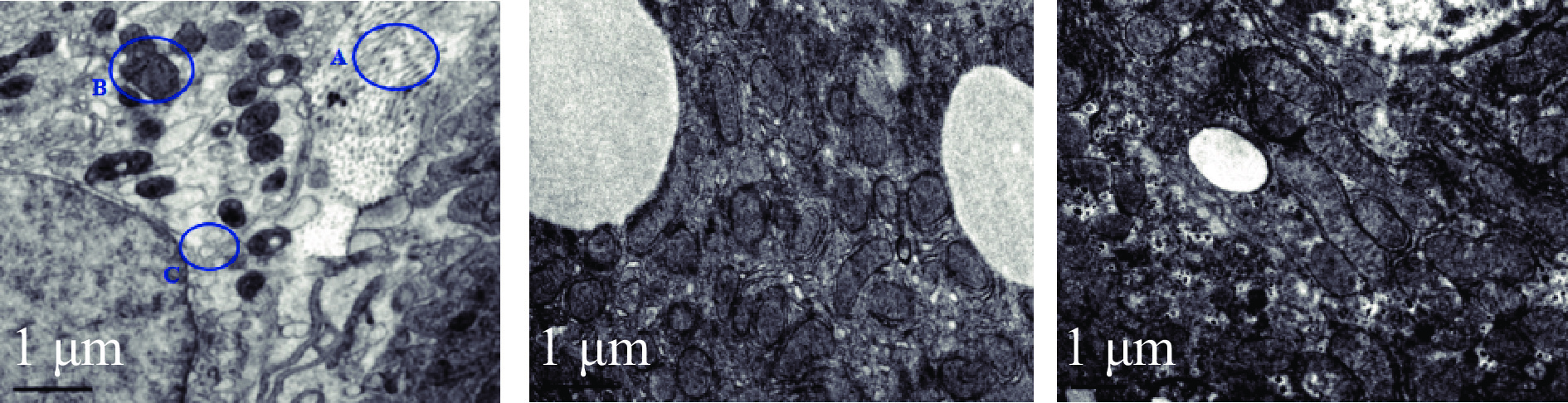
电镜观察与生理盐水处理未保护的慢性肝损伤大鼠比较,GLX和GCQ保护肝细胞及其细胞发生炎症、线粒体变性或破坏的程度偏轻,细胞外基质中胶原原纤维较少,但GLX和GCQ对慢性肝损伤的保护作用无显著差异(见图7)。
2.6 甘草葛根发酵组合物对慢性肝损伤模型大鼠肠道菌群的影响
肠道菌群的变化在与慢性肝病、脂肪肝及肝硬化的发病及病情进展中有重要作用,研究发现粪便、结肠黏膜的菌群相对丰度及功能的改变对慢性肝炎及肝硬化的发病及预后有不同程度的影响[22]。图8结果表明,经CCL4造模处理后,与未处理前相比双歧杆菌合乳杆菌数量减少;经GLX和GCQ保护慢性肝损伤模型动物,EMB、EC、KV、CD数量降低,而TPY、MRS增高,尤以GCQ组明显,说明CCl4肝损伤可以引起肠道菌群的变化,GLX和GCQ在起到保肝护肝作用的同时,起到一定的调节肠道菌群作用。
中草药成分影响菌群的丰度和多样性,菌群组成改变与宿主免疫和代谢活动密切相关。中草药含有许多具有益生元活性的成分,这些成分可增加双歧杆菌、乳杆菌属、拟杆菌门、普氏菌属的丰富度,抑制厚壁菌门,降低肠道中厚壁菌门/拟杆菌门的比例;中草药活性成分作为一种特殊益生元,通过促进肠道内有益菌增殖和抑制致病菌的双向作用方式,达到平衡肠道菌群的目的[23]。中草药成分可以被肠道菌群转化代谢而赋予新的功能活性、生物利用度,研究发现,中药多糖被肠道菌群降解/发酵产生低聚糖等,能促进有益菌生长并调节宿主生理;中药可影响参与氨基酸和脂质代谢的肠道细菌及其代谢物,发挥治疗作用;同时,一些中药小化学分子经菌群转化后会进一步增加其生物活性[24]。
3. 讨论与结论
肝脏是人体重要的代谢器官,肝损伤疾病严重影响人们的身体健康和生活质量。研究指出,引起肝损伤的原因有多种,如化学性肝损伤、病毒性肝损伤、酒精性肝损伤等,其中化学性肝损伤是一类影响因子多且多发的肝损伤类疾病,主要病理改变包括肝纤维化、脂肪变性及肝硬化等。近年来采用中药治疗肝损伤逐渐成为相关治疗领域的研究热点。本研究通过腹腔注射CCl4溶液的方式建立大鼠慢性肝损伤模型,对经微生物发酵这一特殊炮制手段处理的中药-甘草葛根发酵组合物对慢性肝损伤的作用进行评价研究。
综上研究,通过对甘草葛根发酵组合物保护慢性肝损伤大鼠造模给药后的动物表现、死亡及淘汰率、肝功指标、肝脏组织学变化和肠菌群定量分析显示:甘草葛根发酵组合物对CCl4致大鼠慢性肝损伤具有明显的保护作用,该作用与保护肝细胞、抑制肝组织纤维化水平、抑制炎症反应、降低内毒素水平及调节肠道菌群有关。
Liu等[25]研究显示,甘草酸的生物转化主要发生在大鼠结肠内容物中;广谱抗生素抑制了中药主要成分的吸收,并且通过抑制结肠菌群显著抑制了甘草酸向甘草次酸的生物转化。Li等[26]研究甘草酸二铵通过干预改变了非酒精性脂肪肝病小鼠的肠道菌群组成,提高了乳酸杆菌属等益生菌的丰度;降低厚壁菌门/拟杆菌门的比值,减少了内毒素产生菌,增加了短链脂肪酸产生菌,显著减轻肠道低度炎症,进一步改善紧密连接蛋白的表达、杯状细胞数量和黏液分泌,从而增强肠道屏障功能,达到降低小鼠体重、肝脏脂肪变性及肝脏炎症的作用。本研究对象甘草葛根发酵组合物作为微生物发酵后的产物组合物,除含有中药活性成分及衍生成分外,还可能含有大量益生菌次级代谢产物短链脂肪酸、肽类、氨基酸等活性物质,可通过促进双歧杆菌和乳酸杆菌等有益菌增殖,平衡肠道菌群,降低肠道内毒素的水平,起到保肝护肝作用[27]。
通过本研究显示,传统中药可通过体外生物发酵处理:一方面,促进原有中药活性成分的高效溶出与生物转化;另一方面,通过发酵过程富集微生物次级代谢产物,丰富活性成分的种类以及提高活性物质含量,达到增强传统中药功效作用、增强生物利用度的目的。但是,中药活性成分通过微生物发酵转化的机理及不同活性代谢产物与活性成分间的协同作用关系,以及活性物质的具体作用靶点和代谢过程相关机理研究,还需要进一步深入地研究与探讨。
-
-
[1] 李冀, 李想, 曹明明, 等. 甘草药理作用及药对配伍比例研究进展[J]. 上海中医药杂志,2019,53(7):83−87. [LI Ji, LI Xiang, CAO Mingming, et al. Research progress in pharmacological actions of liquorice and proportion of couplet medicines in combination[J]. Shanghai Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2019,53(7):83−87. LI Ji, LI Xiang, CAO Mingming, et al. Research progress in pharmacological actions of liquorice and proportion of couplet medicines in combination[J]. Shanghai Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 53(7): 83-87.
[2] 甘草酸制剂肝病临床应用专家共识[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2016, 32(5): 844−852. Expert consensus on clinical application of glycyrrhizin preparation in the treatment of liver diseases[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2016, 32(5): 844−852.
[3] 史晨旭, 杜佳蓉, 吴威, 等. 葛根化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J]. 中国现代中药,2021,23(12):2177−2195. [SHI Chenxu, DU Jiarong, WU Wei, et al. Advances in the study of chemical constituents and pharmacological action of Puerariae lobatae radix[J]. Modern Chinese Medicine,2021,23(12):2177−2195. SHI Chenxu, DU Jiarong, WU Wei, et al. Advances in the study of chemical constituents and pharmacological action of Puerariae lobatae radix[J]. Modern Chinese Medicine, 2021, 23(12): 2177-2195.
[4] 木盼盼, 安琪, 张彦昭, 等. 一测多评法测定葛根药材中9个异黄酮成分的含量[J]. 中国中药杂志,2019,44(22):4888−4895. [MU Panpan, AN Qi, ZHANG Yanzhao, et al. Determination of 9 isoflavonoids in Puerariae lobatae radix with quantitative analysis of multi-components by single marker[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2019,44(22):4888−4895. MU Panpan, AN Qi, ZHANG Yanzhao, et al. Determination of 9 isoflavonoids in Puerariae lobatae radix with quantitative analysis of multi-components by single marker[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2019, 44(22) : 4888-4895.
[5] 赵月蓉, 侯碧玉, 张莉, 等. 葛根素对实验性肝损伤的治疗作用研究进展[J]. 中国新药杂志,2017,26(9):1005−1010. [ZHAO Yuerong, HOU Biyu, ZHANG Li, et al. Research progress of puerarin in the treatment of experimental liver injury[J]. Chinese Journal of New Drugs,2017,26(9):1005−1010. ZHAO Yuerong, HOU Biyu, ZHANG Li, et al. Research progress of puerarin in the treatment of experimental liver injury[J]. Chinese Journal of New Drugs, 2017, 26(9): 1005-1010.
[6] 朱振元, 罗游, 薛婧, 等. 葛根功能饮料的急性毒性及解酒护肝功效评价[J]. 食品研究与开发,2016,37(21):160−163. [ZHU Zhenyuan, LUO You, XUE Jing, et al. Acute toxicity test and sober and hepatoproctive efficacy evaluation of radix puerariae functional beverage[J]. Food Research and Development,2016,37(21):160−163. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2016.21.037 ZHU Zhenyuan, LUO You, XUE Jing, et al. Acute toxicity test and sober and hepatoproctive efficacy evaluation of radix puerariae functional beverage[J]. Food Research and Development, 2016, 37(21): 160-163. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2016.21.037
[7] KAI M C, STEFANIE A, CHRISTIAN T. Role of bile acids in the gut-liver axis[J]. Journal of Hepatology,2018,68(5):1083−1085. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.11.025
[8] WANG Rui, TANG Ruqi, LI Bo, et al. Gut microbiome, liver immunology, and liver diseases[J]. Cellular & Molecular Immunology,2021(8):4−17.
[9] ANUPRIYA T, JUSTINE D, DAVID A B, et al. The gut-liver axis and the intersection with the microbiome[J]. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology,2018,15:397−411.
[10] SIDDHARTHA S G, WANG J, PAUL J Y, et al. Intestinal barrier function and metabolic/liver diseases[J]. Liver Research,2020(4):81−87.
[11] RYO A. Commensal microbe-derived acetate suppresses NAFLD/NASH development via hepatic FFAR2 signalling in mice[J]. Microbiome,2021,9(1):188. doi: 10.1186/s40168-021-01125-7
[12] SHARPTON S, SCHNABL B, KNIGHT R, et al. Current concepts, opportunities and challenges of gut microbiome-based personalized medicine in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Cell Metabolism,2011,33(1):21−32.
[13] 孟凡涛, 刘冬菊. 研究中药发酵炮制法[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘,2018,18(10):8−9. [MENG Fantao, LIU Dongju. To study the method of fermentation of Chinese medicine[J]. World Latest Medicine Informationn (Electronic Version),2018,18(10):8−9. MENG Fantao, LIU Dongju. To study the method of fermentation of Chinese medicine[J]. World Latest Medicine Informationn (Electronic Version), 2018, 18(10): 8-9.
[14] 李艳凤, 翟梦颖, 李雨昕, 王等. 发酵法在中药研究中的应用[J]. 医学综述,2020,26(4):753−757. [LI Yanfeng, ZHAI Mengying, LI Yuxin, et al. Application of fermentation method in study of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Medical Recapitulate,2020,26(4):753−757. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2020.04.025 LI Yanfeng, ZHAI Mengying, LI Yuxin, et al. Application of fermentation method in study of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Medical Recapitulate, 2020, 26(4): 753-757. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2020.04.025
[15] 张丽霞, 高文远, 王海洋. 微生物技术在中药炮制中的应用[J]. 中国中药杂志,2012,37(24):3695−3699. [ZHANG Lixia, GAO Wenyuan, WANG Haiyang. Application of microbial technology in the processing of traditional[J]. Chinese Medicine China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2012,37(24):3695−3699. ZHANG Lixia, GAO Wenyuan, WANG Haiyang. Application of microbial technology in the processing of traditional[J]. Chinese Medicine China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2012, 37(24): 3695-3699.
[16] 彭静, 陈曦. 滨蒿内酯对四氯化碳致小鼠急性肝损伤的保护作用研究[J]. 中国药房,2021,32(2):231−235. [PENG Jing, CHEN Xi. Study on protective effects of scoparone on acute liver injury induced by CCl4 in mice[J]. China Pharmacy,2021,32(2):231−235. doi: 10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2021.02.18 PENG Jing, CHEN Xi. Study on protective effects of scoparone on acute liver injury induced by CCl4 in mice[J]. China Pharmacy, 2021, 32(2): 231-235. doi: 10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2021.02.18
[17] 王昱. 红腹锦鸡肝脏结构的透射电镜观察[J]. 甘肃农业大学学报,2011,4:43−46. [WANG Yu. Transmission electron microscopical observation on the liver structure of Chroysolophus pictus[J]. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University,2011,4:43−46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4315.2011.03.009 WANG Yu. Transmission electron microscopical observation on the liver structure of Chroysolophus pictus[J]. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2011, 4: 43-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4315.2011.03.009
[18] 刘旭凌, 杨广越, 张玮, 等. 桃红四物汤对CCl4诱导肝纤维化小鼠模型的干预作用及其机制[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志,2021,37(11):2563−2568. [LIU Xuling, YANG Guangyue, ZHANG Wei, et al. Therapeutic effect of Taohong Siwu decoction on a mouse model of carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis and its mechanism[J]. J Clin Hepatol,2021,37(11):2563−2568. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.11.016 LIU Xuling, YANG Guangyue, ZHANG Wei, et al. Therapeutic effect of Taohong Siwu decoction on a mouse model of carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis and its mechanism[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37(11). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.11.016
[19] 张燕, 范晓翔, 章美武, 等. NLRC5 调节转化生长因子-β1诱导的肝星状细胞活化及逆转对肝纤维化的影响[J]. 中国全科医学,2020,23(24):3051−3059. [ZHANG Yan, FAN Xiaoxiang, ZHANG Meiwu, et al. Role of NLRC5 in the activation of hepatic stellate cells induced by TGF-β1 and reversal of hepatic fibrosis[J]. Chinese General Practice,2020,23(24):3051−3059. ZHANG Yan, FAN Xiaoxiang, ZHANG Meiwu, et al. Role of NLRC5 in the activation of hepatic stellate cells induced by TGF-β1 and reversal of hepatic fibrosis[J]. Chinese General Practice, 2020, 23(24): 3051-3059.
[20] 张永超, 毕研贞, 方萧, 等. 益生菌对慢加急性肝衰竭大鼠模型的保护作用及其机制[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志,2019,35(7):1570−1575. [ZHANG Yongchao, BI Yanzhen, FANG Xiao, et al. Protective effect of probiotics in rats with acute-on-chronic liver failure and related mechanism[J]. J Clin Hepatol,2019,35(7):1570−1575. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.07.029 ZHANG Yongchao, BI Yanzhen, FANG Xiao, et al. Protective effect of probiotics in rats with acute-on-chronic liver failure and related mechanism[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(7): 1570-1575. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.07.029
[21] JASMOHAN S B. Alcohol, liver disease and the gut microbiota[J]. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology,2019,16:235−246.
[22] NAGA S B, PATRICK M G, JASMOHAN S B. Gut microbiome and liver disease[J]. Translational Research,2017,179:49−59. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2016.07.005
[23] MING Lyu, WANG Yuefei. Balancing herbal medicine and functional food for prevention and treatment of cardiometabolic diseases through modulating gut microbiota[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2017,8:2146. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02146
[24] LIN Tzulung, LU Chiachen, LAI Weifan, et al. Role of gut microbiota in identification of novel TCM-derived active metabolites[J]. Protein & Cell,2021,12:394−410.
[25] LIU Meng, YUAN Jie, HU Wenjuan, et al. Pretreatment with broad-spectrum antibiotics alters the pharmacokinetics of major constituents of Shaoyao-Gancao decoction in rats after oral administration[J]. Pharmacologica Sinica,2019,40(2):288−296. doi: 10.1038/s41401-018-0011-0
[26] LI Yun, LIU Tianyu, YAN Chen, et al. Diammonium glycyrrhizinate protects against non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice through modulation of gut microbiota and restoring intestinal barrier[J]. Molecular Pharmaceutics,2018,15(9):3860−3870. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00347
[27] ZHANG Feng, HE Fang, LI Li, et al. Bioavailability based on the gut microbiota: A new perspective[J]. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 2020, 84(2):19.
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 李文廷,叶沛,刘玲,陶蓉蓉,张瑞雨,师真,蒋孟圆. 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定发酵乳制品中米酵菌酸和异米酵菌酸. 分析测试学报. 2025(02): 326-333 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 郑圣乐,李卓颖,王家浩,刘峻铭,方桂娇,韩鹿. 益生菌清除食品毒素的研究进展. 农产品加工. 2024(21): 129-134+139 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 宋娓娜,薛笛笛,路飞,李国德,肖志刚,史梦娜,张一凡. 食品中米酵菌酸的相关研究. 现代食品. 2023(11): 23-26 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 宋娓娜,张嘉慧,赵秀红,路飞,肖志刚,张一凡. 植物乳杆菌对食品中常见毒素的抑制作用研究进展. 食品安全导刊. 2023(24): 174-177 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
