Main Nutritional and Functional Ingredients and Antioxidant Evaluation of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge Bud Tea and Leaf Tea
-
摘要: 以张掖高台种植的文冠果芽茶与叶茶为试验材料,对其营养功能成分及抗氧化活性进行比较;使用INQ法对其营养成分进行质量评价,并对功能成分与抗氧化能力进行相关性分析。结果表明,芽茶中K、Zn、Cu含量及K/Na显著高于叶茶(P<0.05),二者均呈现高K低Na特点。芽茶中粗蛋白含量显著高于叶茶(P<0.05)、而粗脂肪含量叶茶显著高于芽茶(P<0.05)。营养质量评价表明,芽茶、叶茶K、Ca、Fe、Mn、Zn、Cu、粗脂肪、粗蛋白INQ均>1;Na、Mg和可溶性总糖INQ芽茶<叶茶<1。芽茶多酚含量显著高于叶茶(P<0.05),黄酮含量差异不明显。芽茶与叶茶对DPPH自由基、ABTS自由基、O2−·清除能力的IC50分别为2.52和2.69、1.65和1.74、1.64和2.10 μg·mL−1,阳性对照芦丁在此浓度范围内无IC50,抗氧化能力强弱为芽茶>叶茶>芦丁。相关性分析表明,芽茶、叶茶多酚、黄酮含量与DPPH自由基、ABTS自由基、O2−·清除率均呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),芽茶相关系数为0.892~0.990,叶茶相关系数为0.879~0.994。以上研究表明,文冠果芽茶的营养功能价值及抗氧化能力优于叶茶,有开发新产品的潜力。Abstract: With the Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge bud tea and leaf tea grown on Gaotai, Zhangye as the test materials, the nutritional functional components and antioxidant activity of them were compared. INQ method was used to evaluate the quality of its nutritional ingredients and the correlation between functional ingredients and antioxidant capacity was analyzed. The results showed that the contents of K, Zn, Cu and K/Na in bud tea were significantly higher than those in leaf tea (P<0.05), and both had the characteristics of high K and low Na. The crude protein content of bud tea was significantly higher than that of leaf tea (P<0.05), while the crude fat content was the opposite. Nutritional quality evaluation revealed that the INQ of bud tea, leaf tea K, Ca, Fe, Mn, Zn, Cu, crude fat, and crude protein were all >1. Na, Mg and total soluble sugar INQ of bud tea<leaf tea<1. The content of polyphenols in bud tea was significantly higher than that in leaf tea (P<0.05), and there was no significant difference in the content of flavonoids. The IC50 of bud tea and leaf tea on DPPH free radical, ABTS free radical and O2−· scavenging capacity were 2.52 and 2.69, 1.65 and 1.74, 1.64 and 2.10 μg·mL−1, respectively, the positive control rutin had no IC50 within the concentration range, and the antioxidant capacity was bud tea>leaf tea>rutin. Correlation analysis showed that the contents of polyphenols and flavonoids in bud tea and leaf tea were positively correlated with DPPH free radical, ABTS free radical and O2−· scavenging rate (P<0.01), the correlation coefficients of bud tea and leaf tea ranged from 0.892 to 0.990 and 0.879 to 0.994. In conclusion, the nutritional value and antioxidant capacity of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge bud tea are better than leaf tea, and it has the potential to develop new products.
-
文冠果(Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge)为无患子科 (Sapindaceae) 文冠果属植物,单属单种,多分布于我国东北、华北、西北等地[1]。文冠果树种耐寒、耐旱、耐盐碱、耐风沙,生长速度快,土壤适应性强[2],其地上部分含有丰富的黄酮、皂苷、氨基酸、脂肪酸等物质,经济价值高[3-4],文冠果茎、枝,味甘、微苦,性凉,具有消肿止痛、祛风湿、抗氧化、抗炎、抗肿瘤等药理活性[5]。基于文冠果的药用保健价值,研究其芽茶、叶茶的营养功能成分及抗氧化能力,对文冠果综合开发利用具有现实意义。
近年来,国内外学者对文冠果营养成分及抗氧化功能进行了诸多研究,孙丙寅等[6]对比分析西北地区不同产地文冠果种仁营养成分,均检测出了蛋白质、脂肪、总糖,不同产地营养成分差异显著。SUN等[7]以文冠果果壳进行动物实验,发现果壳中的三萜皂苷和多酚对动物神经炎症及抗氧化作用显著;ZHANG等[8]通过研究文冠果总皂苷对酪氨酸酶的抑制作用,发现文冠果抗氧化能力较好;王慧芳等[9]优化文冠果叶总黄酮提取工艺及其黄酮的抗氧化活性,发现总黄酮的抗氧化效果高于芦丁。从大量文献报道可以看出,目前的研究普遍针对文冠果的单一器官进行考察,且大都围绕其果实及叶茶的营养成分及活性物质展开研究,对芽茶和叶茶的营养功能成分的研究相对较少。
鉴于此,本研究以张掖高台栽培的文冠果为研究对象,对其芽茶及叶茶进行营养功能成分检测及抗氧化评价,系统对比芽茶与叶茶主要营养功能成分差异,并比较不同芽茶、叶茶的抗氧化能力,以期为河西走廊文冠果的综合开发利用提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
文冠果芽茶和叶茶 由甘肃新怡文冠果开发有限公司提供,文冠果叶茶:平均长2~3 cm;文冠果芽茶:7~10个芽,且长度为0.5~1 cm。供试样品经粉碎、过80目筛后备用;硝酸、氢氧化钠、盐酸、石油醚、葡萄糖、乙醇、硝酸铝、亚硝酸钠、碳酸钠 均为国产分析纯;没食子酸、芦丁标准品(HPLC≥98%)、1.1-二苯基-2-苦肼基(DPPH)(HPLC≥98%)、2,2-连氮基-双-(3-乙基苯并二氢噻唑啉-6-磺酸)二铵盐(ABTS)(纯度≥99.0%) 美国Sigma公司。
HD-200型高速多功能粉碎机 诸暨市海道机械有限公司;CP214电子天平 奥豪斯仪器(上海)有限公司;Sx2-5-12型马弗炉 长沙市华光电炉厂;SP-3520AAPC-8原子吸收分光光度计 上海光谱仪器有限公司;DHG-9140A型电热恒温鼓风干燥箱 上海—恒科技有限公司;KDN-08消化炉 上海新嘉电子有限公司;CR21GII型高速冷冻离心机 日本日立公司;KQ-250B型超声波清洗器 昆山市超声仪器有限公司;722型可见分光光度计 上海光谱仪器有限公司;HH-4数显恒温水浴锅 国华电器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 主要营养成分测定
1.2.1.1 矿物质测定
矿物质测定采用火焰原子吸收分光光度计法,准确称取文冠果芽茶、叶茶粉末各1.00 g采用干法灰化法[10]处理样品,根据仪器要求用2%硝酸定容至50 mL。按以下公式计算矿物质元素含量。
矿物质含量(μg⋅g−1)=C×nm 式中:C—元素浓度,μg·mL−1;n—定容体积,mL;m—文冠果芽茶、叶茶样品质量,g。
1.2.1.2 粗蛋白含量测定
粗蛋白测定采用凯氏定氮法,准确称取文冠果芽茶、叶茶粉末各0.50 g,参考GB 5009.5-2016[11]。按以下公式计算粗蛋白含量。
蛋白质含量(%)=(V−V0)×0.1031×0.014×50m×V1×6.25×100 式中:0.1031—盐酸浓度,mol·L−1;V—样品消耗盐酸体积,mL;V0—空白消耗盐酸体积,mL;50—样品定容体积,mL;m—文冠果芽茶、叶茶样品质量,g;V1—定氮取样体积,mL;6.25—氮换算为蛋白质的系数。
1.2.1.3 粗脂肪测定
采用索氏提取法[12]测定文冠果芽、叶茶的粗脂肪含量。按以下公式计算粗脂肪含量。
粗脂肪含量(%)=m1−m2m×100 式中:m1—抽提前文冠果芽茶、叶茶样品质量,g;m2—抽提后文冠果芽茶、叶茶样品质量,g;m—文冠果芽茶、叶茶质量,g。
1.2.1.4 还原糖和可溶性总糖的测定
供试样液的制备:准确称取文冠果芽茶、叶茶粉末各1.50 g,加入蒸馏水10 mL,50 ℃恒温水浴提取20 min,冷却后在4000 r·min−1离心5 min,取上清液,沉淀在同等条件下提取3次,提取液并入50 mL容量瓶中定容至刻度,用于还原糖测定。
可溶性总糖水解液的制备:精确吸取供试样液5 mL于10 mL具塞试管中,加6 mol·L−1盐酸0.5 mL,70 ℃水浴15 min,冷却后,加1~2滴甲基红指示剂,用6 mol·L−1氢氧化钠中和至红色褪去呈黄色,转移到10 mL的容量瓶中定容至刻度,备用。
参照杨泉女等[13]的介绍的方法测定还原糖和可溶性总糖,稍作修改。标准曲线工作液:精确吸取1 mg·mL−1葡萄糖标准溶液各0、0.2、0.4、0.6、0.8、1.0、1.2、1.6、1.8、2.0 mL,用蒸馏水补至2 mL,分别加入1.5 mL DNS 试剂,置于沸水浴中加热 5 min,冷却后用蒸馏水定容至25 mL的容量瓶中;精确吸取供试样液0.5 mL、水解液0.6 mL,同标准曲线测定,在540 nm波长处测吸光值。以葡萄糖含量(mg)为横坐标,吸光度为纵坐标绘出标准曲线,得到的回归方程为y=0.2632x−0.0299,R2=0.9939。按以下公式计算还原糖和可溶性总糖含量。
还原糖含量(%)=M×Vm×V1×1000×100 式中:M—文冠果芽茶和叶茶测定样品中葡萄糖的含量,mg;V—文冠果芽茶和叶茶供试样液体积,mL;m—文冠果芽茶、叶茶质量,g;V1—测定时样液的体积,mL。
可溶性总糖含量(%)=M×V×V0m×V2×V3×1000×100 式中:M—测定水解液的葡萄糖含量,mg;V—供试液定容体积,mL;m—文冠果芽茶、叶茶质量,g;V0—可溶性总糖水解液体积,mL;V2—供试液分取体积,mL;V3—测定时水解液用量,mL。
1.2.2 营养质量指数计算
参照文献[14]对文冠果芽茶、叶茶的主要营养成分进行营养质量指数评价,其计算公式如下:
INQ=营养密度热量密度=100g食物中某营养素的含量/该营养素推荐摄入量100g食物提供的能量/推荐摄入能量 1.2.3 样品功能成分提取液的制备
准确称取文冠果芽茶、叶茶粉末各0.50 g于试管中,加入体积分数70%乙醇溶液10 mL,超声(250 W,45 ℃)提取20 min,冷却至室温,在3500 r·min−1离心10 min,重复上述操作3次,合并提取液定容至50 mL,摇匀备用,用于功能成分和抗氧化测定。
1.2.4 主要功能成分测定
1.2.4.1 多酚含量测定
采用GB/T 8313-2018测定多酚含量[15]。得到回归方程y=0.0104x+0.0082,R2=0.9993,其中y为吸光度,x为没食子酸含量(μg)。按以下公式计算总多酚含量。
总酚含量(mg⋅g−1)=M×V×nm×V0×1000 式中:M—测定样品中没食子酸含量,μg;V—功能成分提取液的总体积,mL;n—样品测定稀释倍数;m—文冠果芽茶、叶茶质量,g;V0—测定样品体积,mL。
1.2.4.2 黄酮含量测定
参照文献[16-17]的方法,有所改动,芦丁标准溶液:准确称取芦丁标准品20.00 mg,加70%乙醇溶解,定容至100 mL。
芦丁标准曲线的制作:精确吸取0.209 mg·mL−1芦丁溶液各0、0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0、2.5、3.0、3.5 mL,以体积分数70%乙醇补至3.5 mL,分别加入0.3 mL 5%亚硝酸钠,反应6 min后分别加入0.3 mL 10%硝酸铝,反应6 min后分别加入4% NaOH 4 mL,暗反应15 min,用70%乙醇定容至10 mL,以试剂空白为参比,508 nm下测定吸光值,以芦丁含量为横坐标,吸光度为纵坐标得回归方程,y=1.141x+0.0023,R2=0.9991,其中y为吸光度,x为芦丁含量(mg)。
样品中总黄酮含量测定:精密吸取样品提取液0.5 mL,依据标准曲线制作方法测定样品反应液的吸光度,根据回归方程计算提取液中黄酮的含量,样品中黄酮的含量按以下公式计算。
黄酮含量(mg⋅g−1)=M×Vm×V0 式中:M—测定样品中芦丁的含量,mg;V—功能成分提取液的总体积,mL;m—文冠果芽茶、叶茶质量,g;V0—测定样品体积,mL。
1.2.5 文冠果芽茶、叶茶提取液的抗氧化性测定
1.2.5.1 文冠果芽茶、叶茶提取液对DPPH自由基的清除作用
DPPH自由基清除能力测定采用甄兆孟[18]的方法,有所改动。DPPH工作液:称取DPPH标准品15.9 mg,加95%乙醇溶解定容至250 mL,即DPPH工作液浓度为0.16 mmol·L−1,避光保存备用。
DPPH自由基清除率的测定:准确吸取质量浓度为20、40、60、80、100、120 μg·mL−1样品溶液0.2 mL,使其黄酮终浓度为1、2、3、4、5、6 μg·mL−1,分别加入体积分数70%乙醇1.8 mL,DPPH 工作液2 mL,混合均匀,避光反应30 min,在517 nm波长处测定吸光值,以同等体积提取溶剂代替样品溶液作为空白对照组,同法测定吸光度。以不同浓度的芦丁溶液作为阳性对照,测定DPPH自由基的清除率。
DPPH自由基清除率(%)=A0−AA0×100 式中:A0—空白对照吸光值;A—样品吸光值。
1.2.5.2 文冠果芽茶、叶茶提取液对ABTS自由基的清除作用
ABTS测定采用李彩霞等[19]的方法,ABTS工作液:准确称取40.00 mg ABTS,加入1.0 mg·mL−1过硫酸钾溶液8.0 mL,密封后静置反应16 h,然后转移到250 mL容量瓶中,用80%乙醇定容至刻度,避光保存备用,用前用体积分数70%稀释至吸光度为0.70±0.02,得ABTS工作液。
ABTS自由基清除率的测定:准确吸取质量浓度为20、40、60、80、100、120 μg·mL−1样品溶液0.1 mL,使终体积中黄酮具有不同的浓度,分别加入体积分数70%乙醇1.9 mL,ABTS工作液 2 mL,混合均匀,避光反应6 min,在734 nm波长下测定吸光值,空白对照组以同等体积提取溶剂代替样品溶液,以同法测定吸光度。以不同浓度的芦丁溶液作为阳性对照,测定ABTS自由基的清除率。
ABTS自由基清除率(%)=A0−AA0×100 式中:A0—空白对照吸光值;A—样品吸光值。
1.2.5.3 文冠果芽茶、叶茶提取液对超氧阴离子自由基(O2−·)的清除作用
超氧阴离子自由基的抑制率测定采用氮蓝四唑光还原法[20],准确吸取质量浓度为20、40、60、80、100、120 μg·mL−1样品溶液0.2 mL,使终体积中黄酮具有不同的浓度,分别加入pH7.8磷酸缓冲液1.6 mL,依次加入750 mmol·L−1 氮蓝四唑、30 mmol·L−1甲硫氨酸、20 mmol·L−1核黄素、100 mmol·L−1乙二胺四乙酸各0.3 mL,在4000 lx光照下反应20 min,在560 nm波长处测定吸光值,空白对照组以同等体积的提取溶剂代替样品溶液,同法测定吸光度。以不同浓度的芦丁溶液作为阳性对照,测定O2−·的清除率。
超氧阴离子自由基清除率(%)=A0−AA0×100 式中:A0—空白对照吸光值;A—样品吸光值。
1.3 数据处理
采用Excel 2010软件对测试数据进行统计,结果均为3次测试的平均值±标准偏差。用SPSS 17软件进行独立样本t检验,显著性水平为0.05。功能成分与抗氧化之间的相关性通过SPSS 17皮尔逊相关软件分析,采用Origin7.5软件作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 文冠果芽茶与叶茶主要营养成分
2.1.1 文冠果芽茶与叶茶的矿物质比较
文冠果芽茶和叶茶中的矿质元素含量如表1所示,从表1看出,芽茶和叶茶均含有K、Ca、Na、Fe、Zn、Cu、Mn、Mg、Ni 9种矿质元素,其中二者富含K和Ca两种常量元素,且K元素在芽茶中的含量显著高于叶茶(P<0.05),而Ca元素在叶茶中含量显著高于芽茶(P<0.05),约为芽茶的3倍,并且高于文献[21]所报道的绿茶中Ca的含量(1.37~2.66 mg·g−1),说明叶茶是优质的Ca元素的植物性来源。微量元素Zn、Cu在芽茶中的含量显著高于叶茶(P<0.05),而Mn元素在叶茶中含量高于芽茶。芽茶未检出Pb元素,叶茶Pb含量为0.50 μg·g−1,符合国家限量标准[22],Cd元素均未检出。Fe、Zn、Cu、Mn、Mg是人体必需的有益微量元素,可以作为无机成分以配位键的形式与黄酮等有机成分形成各种配合物,能很好地发挥其营养价值[23]。有学者研究表明性质相似的元素,其生物学功能是相互拮抗的,当Zn/Cu>10且Zn/Fe>1时会发生拮抗作用[24],文冠果芽茶和叶茶的Zn/Cu、Zn/Fe分别为1.16、0.18和0.99、0.06,说明文冠果芽茶和叶茶的Zn、Cu、Fe不发生拮抗作用,有利于动物体吸收。文冠果芽茶K元素含量为17.29 mg·g−1,约是文冠果叶茶的2倍,Na元素含量(0.35 mg·g−1)低于叶茶(0.39 mg·g−1),芽茶、叶茶的K/Na分别为49.13和24.74,均具有高钾低钠的特点,这种特点对于心血管和肾脏等疾病有一定益处[25],相较而言,文冠果芽茶K/Na比例高于叶茶。
表 1 文冠果芽茶、叶茶矿物质含量Table 1. The mineral content of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge bud tea and leaf tea成分 文冠果芽茶 文冠果叶茶 K(mg·g−1) 17.29±0.66* 9.53±0.31 Ca(mg·g−1) 1.08±0.07 2.99±0.06* Na(mg·g−1) 0.35±0.01 0.39±0.04 Fe(mg·g−1) 0.28±0.004 0.29±0.004 Zn(μg·g−1) 49.04±6.02* 16.74±3.95 Cu(μg·g−1) 33.55±2.87* 16.98±1.84 Mn(μg·g−1) 29.53±1.81 34.07±0.66 Mg(μg·g−1) 28.14±4.66 38.62±9.31 Ni(μg·g−1) 2.71±0.85 1.49±0.51 Pb(μg·g−1) — 0.50±0.001 Cd(μg·g−1) — — K/Na 49.13±2.41* 24.74±2.03 Zn/Cu 1.16±0.142* 0.18±0.089 Zn/Fe 0.99±0.012* 0.06±0.008 注:“—”表示未检出;*表示显著性差异(P<0.05),表2~表4同。 2.1.2 文冠果芽茶与叶茶基本营养成分
文冠果芽茶、叶茶的基本营养成分结果见表2。蛋白质是生命的物质基础,其含量的高低是衡量茶叶营养价值和品质的重要指标[26],文冠果芽茶蛋白含量(25.06%)显著高于叶茶(11.11%)(P<0.05),芽茶蛋白质含量是叶茶的2.26倍,说明文冠果新稍萌发过程中,氮从老枝输送到幼嫩的叶片中进行代谢,在幼嫩的芽中形成大量的蛋白质,叶的鲜嫩程度降低,粗蛋白含量也在降低。文冠果叶茶和芽茶粗脂肪含量分别为11.47%和12.88%,高于文献[27]所报道的文冠果叶片脂肪含量。可溶性糖类物质是茶汤滋味和香气的来源之一,也是茶汤甜味的主要成分,对茶的苦涩味有一定的掩盖和协调作用,其含量越高,茶叶的滋味越甘醇[28]。从表2可以看出,文冠果芽茶与叶茶还原糖、可溶性总糖含量差异不显著(P>0.05),芽茶可溶性总糖稍高于叶茶。综上分析,文冠果营养丰富,尤其芽茶蛋白质较高。
表 2 文冠果芽茶、叶茶基本营养成分Table 2. The basic nutritional components of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge bud tea and leaf tea项目 文冠果芽茶 文冠果叶茶 粗蛋白(%) 25.06±0.48* 11.11±1.35 粗脂肪(%) 11.47±0.37 12.88±0.23* 还原糖(%) 5.53±0.11 5.37±0.25 可溶性总糖(%) 9.86±0.35 9.77±0.08 2.1.3 文冠果芽茶与叶茶营养质量评价
100 g文冠果芽茶提供能量242.966 kcal,叶茶199.383 kcal(1 g粗蛋白提供能量4 kcal,1 g粗脂肪提供能量9 kcal,1 g碳水化合物提供能量4 kcal)[14]。营养素推荐摄入量及能量推荐摄入量参考《中国居民膳食营养素参考摄入量》[29-30]、GB 28050-2011[31]。
从营养学角度分析,当INQ=1,表示食物中该营养素与热能含量均衡;当INQ>1时,说明该食物中营养素的供给量大于热能的供给量,食物的营养价值较高;INQ<1时,说明食物中该营养素的供给量少于热能的供给量,食物的营养价值较低,长期食用此种食物,可能发生该营养素的不足或热能过剩[14]。由表3可见,芽茶、叶茶Mg、Na元素和可溶性总糖INQ均<1,这些指标的营养价值较低;K、Cu、Ca、Fe、Mn、Zn元素、粗蛋白、粗脂肪INQ均>1,其中Cu的INQ远远大于1,芽茶Cu的INQ高达40.56,说明这8种成分有较高的营养价值。综合各主要营养成分在芽茶与叶茶中的INQ值,文冠果芽茶与叶茶均具有较高的营养价值,但INQ小于1的部分营养需搭配其它食品获取。
表 3 文冠果芽茶、叶茶主要营养成分INQ值Table 3. INQ values of main nutrients in Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge bud tea and leaf tea成分 推荐摄入(mg·d−1) 芽茶INQ 叶茶INQ K 2000 10.99±0.26* 6.15±0.18 Ca 800 1.30±0.13 4.41±0.08* Na 1500 0.23±0.03 0.30±0.03* Fe 16 16.80±0.26 21.19±0.27* Zn 10 4.74±0.58* 1.97±0.47 Cu 0.8 40.56±0.34* 25.02±0.13 Mn 4.5 6.35±0.27 8.92±0.17* Mg 330 0.08±0.01 0.14±0.03 可溶性总糖 120000 0.80±0.03 0.96±0.01* 粗蛋白 60000 4.04±0.08* 2.18±0.27 粗脂肪 60000 1.85±0.06 2.53±0.04* 注:推荐能量按18~50周岁中度体力劳动的男、女均值进行计算。 2.2 文冠果芽茶与叶茶主要功能成分和抗氧化评价
2.2.1 文冠果芽茶与叶茶主要功能成分
多酚类物质是茶叶中水溶性色素的主要部分,是茶汤色泽的主体,也是茶叶滋味的主体物质,由儿茶素、黄酮类、酚酸、花色素类组成[28],影响着茶的色泽和滋味,是茶叶品质的主要成分。由表4可知,文冠果芽茶和叶茶多酚含量分别为83.24、64.42 mg·g−1,均高于梵净山茶中多酚含量(0.64 g·100 g−1~1.53 g·100 g−1)[32]。
表 4 文冠果芽茶、叶茶主要功能成分Table 4. The main functional components of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge bud tea and leaf tea项目 文冠果芽茶 文冠果叶茶 多酚(mg·g−1) 83.24±0.27* 64.42±0.24 黄酮(mg·g−1) 58.02±0.08 52.42±0.02 黄酮类化合物是广泛存在于植物中的一种天然有机物,黄酮类化合物在抗氧化、癌症、糖尿病、血管疾病、神经学等临床领域具有广泛的有益作用[33-34],文冠果叶茶和芽茶黄酮含量分别为52.42、58.02 mg·g−1,高于苗方等[35]测得银杏叶茶中黄酮含量(2.4%)。以上结果说明,文冠果芽茶和叶茶含有丰富的活性物质,多酚和黄酮在芽茶中含量较高。
2.2.2 抗氧化评价
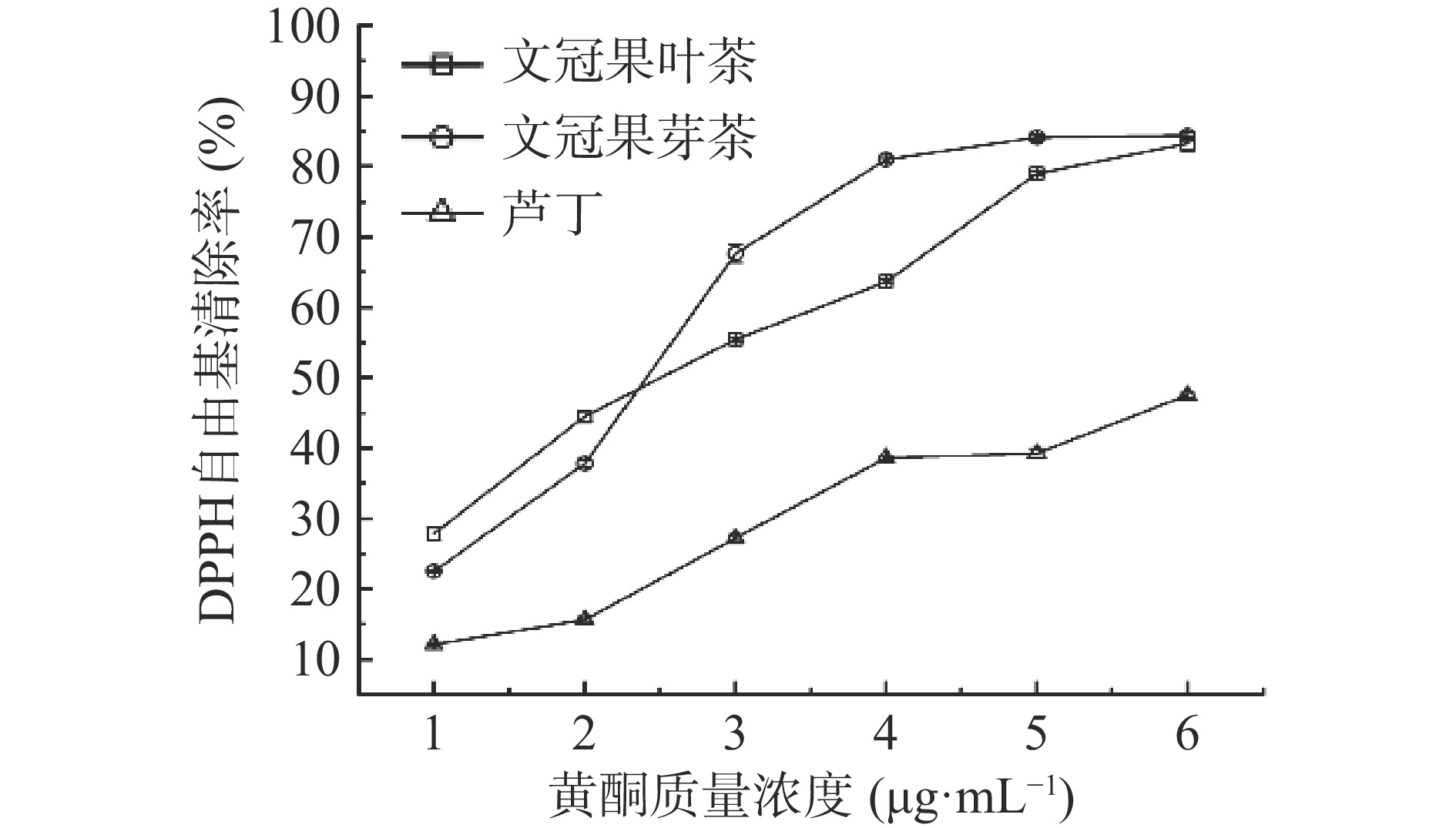
2.2.2.1 文冠果芽茶和叶茶黄酮对DPPH自由基的清除作用
IC50是自由基清除率达到50%时样品和对照品的质量浓度,IC50越小,样品的抗氧化效果越好,反之越差。由图1可知,文冠果芽茶提取物中黄酮在质量浓度3~6 μg·mL−1范围内对DPPH自由基的清除率高于叶茶,清除率由67.64%上升至84.42%,IC50为2.52 μg·mL−1;而叶茶黄酮在6 μg·mL−1下清除率达到83.30%,其IC50为2.69 μg·mL−1,稍弱于芽茶。阳性对照芦丁在1~6 μg·mL−1浓度范围内,清除率由12.08%上升到47.54%,在此范围内未测到IC50。综合分析,对DPPH自由基的清除作用芽茶提取物>叶茶提取物>芦丁。
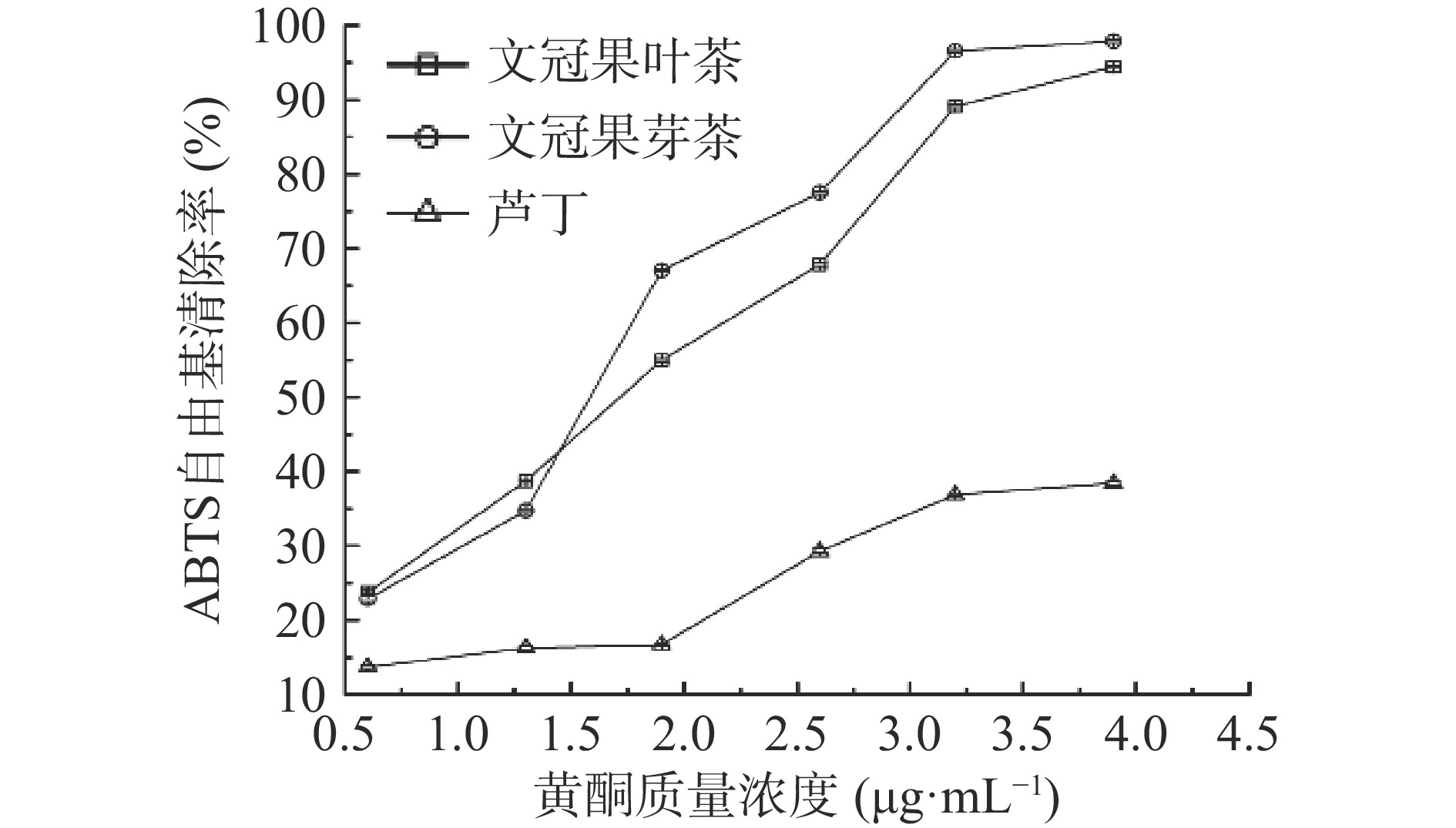
2.2.2.2 文冠果芽茶和叶茶黄酮对ABTS自由基的清除作用
由图2可以看出,随着芽茶、叶茶提取物中黄酮质量浓度的升高,对ABTS自由基的清除率也在升高,在黄酮质量浓度为4 μg·mL−1时,清除率分别为97.88%和94.45%,IC50分别为1.65和1.74 μg·mL−1,芽茶提取液中黄酮的清除率高于叶茶。阳性对照芦丁在0.6~4 μg·mL−1浓度范围内,清除率由13.70%上升到38.45%,清除率明显小于芽茶和叶茶。综上可知,对ABTS自由基的清除作用芽茶提取物>叶茶提取物>芦丁。
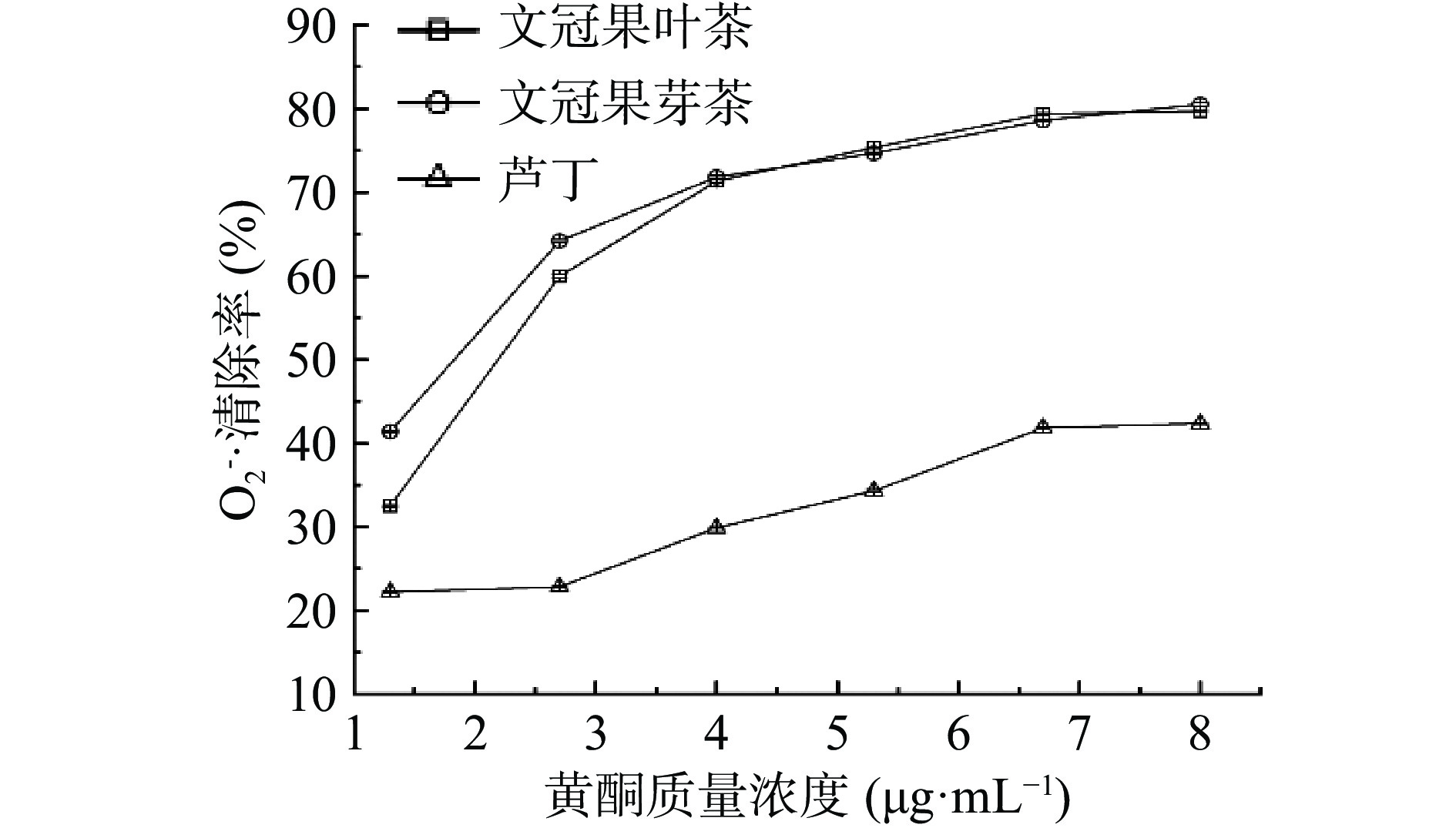
2.2.2.3 文冠果芽茶和叶茶黄酮对O2−·的清除作用
超氧阴离子自由基是机体中寿命最长的自由基,在一定条件下可生成羟基自由基、脂质过氧化物、过氧化氢及单线态氧等其他活性氧,从而造成机体的氧化损伤[36]。由图3可知,芽茶、叶茶提取物中黄酮及芦丁对O2−·清除率随着浓度升高而逐渐升高,芽茶提取物黄酮在质量浓度为4 μg·mL−1时清除率大于叶茶,而后变化不大。在质量浓度为8 μg·mL−1时,芽茶、叶茶提取物中黄酮及芦丁对O2−·清除率为分别为80.53%、79.74%和42.34%,其IC50 分别为1.64、2.10 μg·mL−1,芦丁在检测浓度范围内无IC50。综上分析,对O2−·的清除作用芽茶提取物>叶茶提取物>芦丁。
2.3 文冠果芽茶、叶茶抗氧化活性与功能成分的相关性
由表5可知,文冠果芽茶、叶茶中的黄酮含量与DPPH自由基、ABTS自由基和O2−·清除率的相关系数范围分别为0.892~0.990和0.880~0.994;多酚含量与DPPH自由基、ABTS自由基和O2−·清除率的相关系数范围分别为0.893~0.973和0.879~0.993,表明多酚、黄酮含量与抗氧化活性存在极显著正相关(P<0.01),即多酚、黄酮含量越高,抗氧化能力越好。茶叶中富含多种总多酚类、总黄酮类物质,余启明等[37]的研究表明这些功能性成分也是茶叶具有较好的抗氧化活性的原因。
表 5 黄酮、多酚与DPPH、ABTS、超氧阴离子自由基清除率的相关性分析Table 5. Correlation analysis of flavonoids and polyphenols with DPPH, ABTS and superoxide anion free radical scavenging rateFC-DPPH FC-ABTS FC-O2−· PC-DPPH PC-ABTS PC-O2−· 文冠
果芽茶0.990** 0.973** 0.892** 0.931** 0.973** 0.893** 文冠
果叶茶0.990** 0.994** 0.880** 0.989** 0.993** 0.879** 注:FC-DPPH、FC-ABTS和FC-O2−·分别表示黄酮含量与DPPH自由基清除率、ABTS自由基清除率和超氧阴离子自由基清除率的相关性。PC-DPPH、PC-ABTS和PC-O2−·分别表示多酚含量与DPPH自由基清除率、ABTS自由基清除率和超氧阴离子自由基清除率的相关性。*表示相关性显著(P<0.05),**表示相关性极显著(P<0.01)。 3. 结论
本文对文冠果芽茶和叶茶的营养功能成分及其抗氧化活性进行了研究。研究表明,芽茶矿物质元素K、Zn、Ni、Cu含量高于叶茶,而Ca、Mn、Mg的含量叶茶高于芽茶,其它指标差异不大,且叶茶中Pb含量低于国家限量标准,Cd在两茶中均未检出。芽茶和叶茶的K/Na、Zn/Cu、Zn/Fe分别为49.13、1.16、0.99和24.74、0.18、0.06,芽茶比值大于叶茶,其比例较为合理,利于机体吸收。因此,文冠果芽茶更适宜作为高血压、肾脏疾病高发人群补K的很好来源。Na、Mg、可溶性总糖INQ文冠果芽茶<叶茶<1,因此可根据个人需要,在日常饮食中合理选择和科学搭配。文冠果芽茶、叶茶Ca、Fe、Mn、Zn、粗脂肪INQ均大于1,说明这5种矿质营养素高于推荐供给量,K、Cu、粗蛋白INQ文冠果芽茶>叶茶>1。从该结果可以看出,叶茶的Ca、Fe、Mn、粗脂肪的营养价值高于芽茶,而K、Cu、Zn、粗蛋白营养价值低于芽茶。
芽茶、叶茶对DPPH自由基的IC50分别为2.52、2.69 μg·mL−1;对ABTS自由基的IC50分别为1.65、1.74 μg·mL−1;对O2−·的IC50分别为1.64、2.10 μg·mL−1;芦丁在此浓度范围内没有对DPPH自由基、ABTS自由基、O2−·的IC50。与叶茶相比,芽茶具有更高的抗氧化活性和多酚、黄酮含量,且芽茶与叶茶的抗氧化活性与多酚和黄酮含量呈极显著正相关,说明酚类物质与抗氧化能力有很大的关系。
以上结果表明:文冠果芽茶与叶茶营养功能成分丰富,且芽茶具有高钾、高蛋白、高多酚、高黄酮、低钠的特征,具有很好的药用价值。
-
表 1 文冠果芽茶、叶茶矿物质含量
Table 1 The mineral content of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge bud tea and leaf tea
成分 文冠果芽茶 文冠果叶茶 K(mg·g−1) 17.29±0.66* 9.53±0.31 Ca(mg·g−1) 1.08±0.07 2.99±0.06* Na(mg·g−1) 0.35±0.01 0.39±0.04 Fe(mg·g−1) 0.28±0.004 0.29±0.004 Zn(μg·g−1) 49.04±6.02* 16.74±3.95 Cu(μg·g−1) 33.55±2.87* 16.98±1.84 Mn(μg·g−1) 29.53±1.81 34.07±0.66 Mg(μg·g−1) 28.14±4.66 38.62±9.31 Ni(μg·g−1) 2.71±0.85 1.49±0.51 Pb(μg·g−1) — 0.50±0.001 Cd(μg·g−1) — — K/Na 49.13±2.41* 24.74±2.03 Zn/Cu 1.16±0.142* 0.18±0.089 Zn/Fe 0.99±0.012* 0.06±0.008 注:“—”表示未检出;*表示显著性差异(P<0.05),表2~表4同。 表 2 文冠果芽茶、叶茶基本营养成分
Table 2 The basic nutritional components of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge bud tea and leaf tea
项目 文冠果芽茶 文冠果叶茶 粗蛋白(%) 25.06±0.48* 11.11±1.35 粗脂肪(%) 11.47±0.37 12.88±0.23* 还原糖(%) 5.53±0.11 5.37±0.25 可溶性总糖(%) 9.86±0.35 9.77±0.08 表 3 文冠果芽茶、叶茶主要营养成分INQ值
Table 3 INQ values of main nutrients in Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge bud tea and leaf tea
成分 推荐摄入(mg·d−1) 芽茶INQ 叶茶INQ K 2000 10.99±0.26* 6.15±0.18 Ca 800 1.30±0.13 4.41±0.08* Na 1500 0.23±0.03 0.30±0.03* Fe 16 16.80±0.26 21.19±0.27* Zn 10 4.74±0.58* 1.97±0.47 Cu 0.8 40.56±0.34* 25.02±0.13 Mn 4.5 6.35±0.27 8.92±0.17* Mg 330 0.08±0.01 0.14±0.03 可溶性总糖 120000 0.80±0.03 0.96±0.01* 粗蛋白 60000 4.04±0.08* 2.18±0.27 粗脂肪 60000 1.85±0.06 2.53±0.04* 注:推荐能量按18~50周岁中度体力劳动的男、女均值进行计算。 表 4 文冠果芽茶、叶茶主要功能成分
Table 4 The main functional components of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge bud tea and leaf tea
项目 文冠果芽茶 文冠果叶茶 多酚(mg·g−1) 83.24±0.27* 64.42±0.24 黄酮(mg·g−1) 58.02±0.08 52.42±0.02 表 5 黄酮、多酚与DPPH、ABTS、超氧阴离子自由基清除率的相关性分析
Table 5 Correlation analysis of flavonoids and polyphenols with DPPH, ABTS and superoxide anion free radical scavenging rate
FC-DPPH FC-ABTS FC-O2−· PC-DPPH PC-ABTS PC-O2−· 文冠
果芽茶0.990** 0.973** 0.892** 0.931** 0.973** 0.893** 文冠
果叶茶0.990** 0.994** 0.880** 0.989** 0.993** 0.879** 注:FC-DPPH、FC-ABTS和FC-O2−·分别表示黄酮含量与DPPH自由基清除率、ABTS自由基清除率和超氧阴离子自由基清除率的相关性。PC-DPPH、PC-ABTS和PC-O2−·分别表示多酚含量与DPPH自由基清除率、ABTS自由基清除率和超氧阴离子自由基清除率的相关性。*表示相关性显著(P<0.05),**表示相关性极显著(P<0.01)。 -
[1] 赵彩云, 宿华, 赵英顺. 文冠果的综合开发利用价值[J]. 内蒙古林业调查设计,2008(6):118−119. [ZHAO C Y, SU H, ZHAO Y S. The comprehensive development and utilization value of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge[J]. Inner Mongolia Forestry Investigation and Design,2008(6):118−119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6993.2008.06.049 ZHAO C Y, SU H, ZHAO Y S. The comprehensive development and utilization value of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge [J]. Inner Mongolia Forestry Investigation and Design, 2008(6): 118-119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6993.2008.06.049
[2] 孙萍, 南定, 金廷文, 等. 简述文冠果的生物特征、经济价值及发展前景[J]. 农业科技与信息,2012(23):51−54. [SUN P, NAN D, JIN T W, et al. Biological characteristics, economic value and development prospect of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge[J]. Agricultural Science-Technology and Information,2012(23):51−54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6997.2012.23.030 SUN P, NAN D, JIN T W, et al. Biological characteristics, economic value and development prospect of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge[J]. Agricultural Science-Technology and Information, 2012(23): 51-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6997.2012.23.030
[3] CHIRVA V Y, KINTYA P K, SOSNOVSKII V A. The structure of Xanthoceras saponin[J]. Chem Nat Compd,1971,7(4):418-420. doi: 10.1007/BF00564728
[4] ZHANG Y, MA J N, MA C L, et al. Simultaneous quantification of ten constituents of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge using UHPLC-MS methods and evaluation of their radical scavenging, DNA scission protective, and α-glucosidase inhibitory activities[J]. ChinJ Nat Med,2015,13(11):873-880.
[5] YANG C Y, HA W, LIN Y, et al. Polyphenols isolated from Xanthoceras sorbifolia Husks and their anti-tumor and radical-scavenging activities[J]. Molecules,2016,21(12):1694. doi: 10.3390/molecules21121694
[6] 孙丙寅, 邓振义, 陈彦斌, 等. 西北地区文冠果营养成分比较研究[J]. 西北林学院学报,2011,26(6):135−137. [SUN B Y, DENG Z Y, CHEN Z Y, et al. A staudies of nutrition of Xanthoceras sorbi folia of the seed kernel in different area[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University,2011,26(6):135−137. SUN B Y, DENG Z Y, CHEN Z Y, et al. A staudies of nutrition of Xanthoceras sorbi folia of the seed kernel in different area[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2011, 26(6): 135-137.
[7] SUN Z, LI Q, BI K. Rapid HPLC-ESI-MS/MS analysis of neurotransmitters in the brain tissue of Alzheimer's disease rats before and after oral administration of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge[J]. Molecules,2018,23(12):3111. doi: 10.3390/molecules23123111
[8] ZHANG H M, ZHOU Q C. Tyrosinase inhibitory effects and antioxidative activities of saponins from Xanthoceras sorbifolia nutshell[J]. PLoS One,2017,8(8):4−5.
[9] 王慧芳, 赵飞燕, 刘勇军, 等. 文冠果叶总黄酮微波辅助酶提取工艺的优化及其抗氧化、抑菌活性[J]. 中成药,2020,42(2):290−296. [WANG H F, ZHAO F Y, LIU Y J, et al. Microwave-assisted enzyme extraction process optimization and antioxidant, bacteriostasis activities of total flavonoids from Xanthoceras sorbifolium leaves[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2020,42(2):290−296. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2020.02.004 WANG H F, ZHAO F Y, LIU Y J, et al. Microwave-assisted enzyme extraction process optimization and antioxidant, bacteriostasis activities of total flavonoids from Xanthoceras sorbifolium leaves[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine, 2020, 42(02): 290-296. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2020.02.004
[10] 王永华, 戚穗坚. 食品分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国轻工业出版社, 2019: 218−240 WANG Y H, QI S J. Food analytical[M]. Third edition. Beijing: China Light Industry Press, 2019: 218−240.
[11] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.5-2016 食品安全国家标准食品中蛋白质的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016 National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China, State Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.5-2016 National food safety standard Determination of food safety[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2016.
[12] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.6-2016 食品安全国家标准食品中脂肪的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016 National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China, State Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.6-2016 National food safety standard Determination of food fat[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2016.
[13] 杨泉女, 周权驹, 吴松健, 等. 3, 5-二硝基水杨酸法与酶法测定甜玉米还原糖和蔗糖含量的比较[J]. 中国农业科技导报,2017,19(11):125−131. [YANG Q N, ZHOU Q J, WU S J, et al. Comparison of 3, 5-dinitrosalicylic acid method and enzymatic method in the determination of sugar and sucrose content in sweet corn[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology,2017,19(11):125−131. YANG Q N, ZHOU Q J, WU S J, et al. Comparison of 3, 5-dinitrosalicylic acid method and enzymatic method in the determination of sugar and sucrose content in sweet corn[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017, 19(11): 125-131.
[14] 李凤林, 王英臣. 食品营养与卫生学[M]. 2版. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2014: 81 LI F L, WANG Y C. Food nutrition and hygiene[M]. Second Edition. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2014: 81.
[15] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 8313-2018 茶叶中茶多酚和儿茶素类含量的检测方法[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018. China National Standardization Management Committee. GB/T 8313-2018 Determination of total polyphenols and catechins content in tea[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2018.
[16] 王晓军, 刘佳佳, 李霞, 等. NaNO2-Al(NO3)3显色分光光度法测定萼翅藤叶总黄酮的含量[J]. 广东化工,2008,35(11):134−137. [WANG X J, LIU J J, LI X, et al. NaNO2-Al (NO3)3 spectrophotometric determination of total flavonoids in Calycopteris floribunda leaves[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry,2008,35(11):134−137. WANG X J, LIU J J, LI X, et al. NaNO2-Al (NO3)3 Spectrophotometric determination of total flavonoids in Calycopteris floribunda Leaves[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2008, 35 (11): 134-137.
[17] 班超, 秦亚东, 李林华. 安徽结香花蕾中总黄酮的含量测定[J]. 中国林副特产,2020(6):1−3. [BAN C, QING Y D, LI L H. Determination of total flavonoids in flowers buds of Edegeworthia chrysantha Lindl. buds from Anhui Province[J]. Forest by-Product and Speciality in China,2020(6):1−3. BAN C, QING Y D, LI L H. Determination of total flavonoids in flowers buds of Edegeworthia chrysantha Lindl. buds from Anhui Province[J]. Forest by-Product and Speciality in China, 2020(6): 1-3.
[18] 甄兆孟. 非洲白参的抗氧化活性及化学成分研究[D]. 武汉: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院武汉植物园), 2020 ZHEN Z M. Study on the antioxidant activity and chemical constiuents of Mondia whiteii[D]. Wuhan: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Wuhan Botanical Garden, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2020.
[19] 李彩霞, 高海宁, 焦扬, 等. “黑美人”土豆黄酮提取及抗氧化活性[J]. 食品科学,2013,34(4):88−93. [LI C X, GAO H N, JIAO Y, et al. Extraction and antioxidant activity of flavonoids from “Black Beauty” potatoes[J]. Food Science,2013,34(4):88−93. LI C X, GAO H N, JIAO Y, et al. Extraction and antioxidant activity of flavonoids from “Black Beauty” potatoes[J]. Food Science, 2013, 34(4): 88-93.
[20] 李小方, 张志良. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 5版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2016: 202−203 LI X F, ZHANG Z L. Experimental guidance of plant physiology[M]. Five Edition. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2016: 202−203.
[21] 刘元林, 张棚, 张宇霞, 等. 南方与北方茶叶中矿质元素研究[J]. 茶叶通讯,2020,47(3):456−461. [LIU Y L, ZHANG P, ZHANG Y X, et al. Study on mineral elements in tea from of south and north china[J]. Journal of Tea Communication,2020,47(3):456−461. LIU Y L, ZHANG P, ZHANG Y X, et al. Study on mineral elements in tea from of south and north china[J]. Journal of Tea Communication, 2020, 47(3): 456-461.
[22] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.12-2017 食品安全国家标准食品中铅的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017 National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China, State Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.12-2017 National food safety standard Determination of food lead[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2017.
[23] 上官海燕, 吴巧凤. 紫苏叶与白苏叶的总黄酮和微量元素的比较分析[J]. 广东微量元素科学,2008(4):29−32. [SHANGGUAN H Y, WU Q F. Comparative of total flavones and trace elaments between leaves of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. var. arguta (Benth.) Hand.-Mazz. and leaves of Perilla frutescens (L. ) Britt doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-446X.2008.04.008 J]. Guangdong Trace Elements Science,2008(4):29−32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-446X.2008.04.008
[24] DOMINGO J L, BOCIO A, FALO G, et al. Benefits and risks of fish consumption. Part Ⅰ. A quantitative analysis of the intake of omega-3 fatty acids and chemical contaminants[J]. Toxicology,2007,230(2/3):219−226.
[25] OBELREITHNERA H, CALLIESA C, KUSCHE-VIHORGA K, et al. Potassium softens vascular endothelium and increas-es nitric oxide release[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2009,106(8):2829−2834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0813069106
[26] 王广铭. 信阳茶区不同嫩度茶鲜叶灰分蛋白质含量与品质的关系[J]. 信阳农业高等专科学校学报,2010,20(1):110−112. [WANG G M. Relationship betwee nash and protein content and quality of different tendernee fresh leaves in Xinyang tea area[J]. Journal of Xinyang Agricultural College,2010,20(1):110−112. WANG G M. Relationship betwee nash and protein content and quality of different tendernee fresh leaves in Xinyang tea area[J]. Journal of Xinyang Agricultural College, 2010, 20(1): 110-112.
[27] 戚建莉, 柴春山, 王子婷, 等. 文冠人工种群叶片成分分析[J]. 甘肃林业科技,2014,39(4):33−37. [QI J L, CHAI C S, WANG Z T, et al. A nalysis on leaf contents of a rtificial Xanthoceras sorbifolia population[J]. Journal of Gansu Forestry Science and Technolgy,2014,39(4):33−37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0960.2014.04.009 QI J L, CHAI C S, WANG Z T, et al. A nalysis on leaf contents of a rtificial Xanthoceras sorbifolia population[J]. Journal of Gansu Forestry Science and Technolgy. 2014, 39(4): 33-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0960.2014.04.009
[28] 顾谦, 陆锦时, 叶宝存. 《茶叶化学》[M]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 2002, 30 GU Q, LU J S, YE B C. Tea chemistry[M]. Hefei: China University of Science and Technology Press, 2002, 30.
[29] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. WS/T 578.2-2018中国居民膳食营养素参考摄入量第2部分常量元素[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018 National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China. WS/T 578.2-2018 Chinese dietary reference intakes-Part 2: Macroelement[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2018.
[30] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. WS/T 578.3-2017中国居民膳食营养素参考摄入量第3部分微量元素[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017 National Health Commission of the people's Republic of China. WS/T 578.3-2017 Chinese dietary reference intakes-Part 3: Trace element[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2017.
[31] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 28050-2011 食品安全国家标准预包装食品营养标签通则[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2011 National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China, State Food and Drug Administration. GB 28050-2011 National food safety standard Determination of general principles for nutrition labeling of prepackaged food[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2011.
[32] 陆雨芳, 刘庆庆, 朱成成, 等. 梵净山茶生物活性成分及其抗氧化能力的分析[J]. 食品研究与开发,2021,42(12):46−53. [LU Y F, LIU Q Q, ZHU C C, et al. Analysis of bio-active components and antioxidant capacity of Fanjing Mountain tea[J]. Food Research and Development,2021,42(12):46−53. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2021.12.008 LU Y F, LIU Q Q, ZHU C C, et al. Analysis of bio-active components and antioxidant capacity of Fanjing Mountain tea[J]. Food Research and Development, 2021, 42(12): 46-53. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2021.12.008
[33] WANG L, YANG X, QIN P, et al. Flavonoid composition, antibacterial and antioxidant properties of tartary buckwheat bran extract[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2013,49(8):312−317.
[34] LEE C, SHEN S, LAI Y, et al. Rutin and quercetin, bioactive compounds from tartary buckwheat, prevent liver inflammatory injury[J]. Food and Function,2013,4(5):794−802. doi: 10.1039/c3fo30389f
[35] 苗方, 侯刚健, 安芸, 等. 分光光度法对银杏茶中总黄酮的含量测定[J]. 医学理论与实践,2009,22(3):359−360. [MIAO F, HOU G J, AN Y, et al. Determination of total flavonoids in ginkgo tea by spectrophotometry[J]. The Journal of Medical Theory and Practice,2009,22(3):359−360. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7585.2009.03.091 MIAO F, HOU G J, AN Y, et al. Determination of total flavonoids in ginkgo tea by spectrophotometry[J]. The Journal of Medical Theory and Practice, 2009, 22(3): 359-360. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7585.2009.03.091
[36] TAO H X, ZHOU J G, WU T, et al. High-throughput superoxide anion radical scavenging capacity assay[J]. Journal of Agri- cultural and Food Chemistry,2014,62(38):9266−9272. doi: 10.1021/jf502160d
[37] 余启明, 张金华, 黄泽强, 等. 12种广西地区茶叶的水提物活性成分测定及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2021,42(17):19−24. [YU Q M, ZHANG J H, HUANG Z Q, et al. Active components and antioxidant activities of aqueous extracts of twelve types of tea in Guangxi Region[J]. Food Research and Development,2021,42(17):19−24. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2021.17.004 YU Q M, ZHANG J H, HUANG Z Q, et al. Active components and antioxidant activities of aqueous extracts of twelve types of tea in Guangxi Region[J]. Food Research and Development, 2021, 42(17): 19-24. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2021.17.004
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)
















 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
