Optimization of Conditions for γ-Aminobutyric Acid Yield by Co-fermentation of Enterococcus faecium with Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Mechanism Research
-
摘要: 为提高γ-氨基丁酸(γ-aminobutyric acid,GABA)产量,以产GABA屎肠球菌(Enterococcus faecium)AB157与酿酒酵母(Saccharomyces cerevisiae)SC-125为研究对象,通过单因素实验和响应面法优化共发酵条件;同时分析最优条件下共发酵和单菌发酵体系谷氨酸脱羧酶(glutamate decarboxylase,GAD)的酶活力及通过添加无细胞上清液(cell-free supernatant,CFS)探究高产GABA机制。结果表明:当总接种量2%(V/V),发酵温度为35 ℃、屎肠球菌AB157和酿酒酵母SC-125的接种比例为5:1(V/V)、L-谷氨酸钠浓度为12 g/L、发酵96 h时,共发酵体系GABA产量最高,达6.55 g/L,较单菌发酵体系产量提高到1.78倍;GAD酶活力分析表明,共发酵可显著提高GAD酶活;添加屎肠球菌AB157或酿酒酵母SC-125的CFS可显著提升GABA产量。本研究为屎肠球菌和酿酒酵母共发酵提高GABA产量及高产GABA机制的探讨提供了一定的理论参考。Abstract: In order to improve the yield of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the co-fermentation conditions of Enterococcus faecium AB157 and Saccharomyces cerevisiae SC-125 were optimized by one-factor-at-a-time method and response surface methodology (RSM). Simultaneously, the enzyme activity of glutamate decarboxylase (GAD) was analyzed under optimal conditions in co-fermentation and single strain fermentation systems, and the mechanism of high GABA yield was explored by adding cell-free supernatant (CFS). The optimization results showed that when the overall quantity of inoculum was 2% (V/V), the optimal co-fermentation conditions were as follows: The fermentation temperature was 35 ℃, the inoculum proportions of E. faecium AB157 and S. cerevisiae SC-125 was 5:1 (V/V), and the L-monosodium glutamate concentration was 12 g/L with shaking fermentation for 96 h. In addition, the yield of 6.55 g/L GABA was 1.78 times higher than in single strain fermentation systems. The GAD enzyme activity analysis showed that co-fermentation could significantly improve GAD enzyme activity. Meanwhile, GABA yield could be significantly increased by adding CFS of E. faecium AB157 or S. cerevisiae SC-125. This study served as a theoretical foundation for the discussion of the co-fermentation of E. faecium and S. cerevisiae to increase GABA yield and the mechanism of high GABA yield.
-
γ-氨基丁酸(γ-aminobutyric acid,GABA)是一种四碳氨基酸,广泛存在于生物体内,由L-谷氨酸经谷氨酸脱羧酶(glutamate decarboxylase,GAD)脱羧合成[1],具有降压[2]、抗抑郁[3]、预防糖尿病[4]、缓解疼痛[5]等功能。随着年龄增长,人体内的GABA合成能力不断减弱,会出现失眠、焦躁、疲乏等症状,因此日常进食含GABA的食药品是补充该功能物质的一种有效方式[6]。然而,动植物体内的GABA含量低,难以大量提取分离,寻求高效合成GABA的途径受到越来越多研究者的关注[7]。微生物发酵合成GABA不受时间、空间、能源的限制,且兼有低成本、高产量等显著特点,成为当前生产食药级GABA较为理想的途径[8]。目前微生物产GABA的研究大多使用单一乳酸菌发酵[9-12],而以乳酸菌和酵母菌共发酵产GABA的研究鲜有报道。
对于底物成分复杂的发酵体系,单一纯种发酵具有明显的应用局限,优势互补的多菌株协同发酵为解决该局限性提供了新的思路[13]。特别是乳酸菌酵母菌之间的良性互动,为解决单一纯种发酵某些底物难以代谢的问题营造了良好的代谢环境。有研究表明,共生乳酸菌酵母菌的互作可基于营养物质交换,从而促进菌株的生长代谢以提高目标化合物的产量[14];乳酸菌难以代谢蛋白质,引入蛋白质代谢能力较强的酵母菌产生的各种氨基酸则可以被乳酸菌良好利用,且酵母菌也可产生维生素和肽类等营养因子[15];乳酸菌也可利用酵母菌难以代谢的苹果酸等物质,产生丙酸、丁酸,作为酵母菌合成风味物质的前体[16]。基于以上研究,筛选具有共生作用的乳酸菌和酵母菌并采用共发酵的方式提高GABA产量是可行的。
屎肠球菌为常见的肠道益生乳酸菌,可改善哺乳动物体内的肠道环境,增强免疫能力,对哺乳动物的生长及肠道菌群的稳定具有重要的意义[17]。酿酒酵母为具有潜在益生特性的菌株,广泛应用于食品、医药及饲料等行业[18]。通过合理构建屎肠球菌和酿酒酵母的共发酵条件从而提高GABA产量,以及研究其高产GABA机理具有重要的意义。因此,本研究以前期筛选的产GABA的屎肠球菌AB157和酿酒酵母SC-125为发酵菌株,研究采用共发酵提高GABA产量,通过响应面分析法优化共发酵的发酵条件,且分析GAD酶活及互作模式,旨在为具有共生作用的乳酸菌和酵母菌高产GABA及机理探讨提供一定的理论参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
本实验室筛选鉴定的产GABA的屎肠球菌AB157[19](Enterococcus faecium AB157,NCBI登录号MH578625)和酿酒酵母SC-125(Saccharomyces cerevisiae SC-125,NCBI登录号为MW279237) 西华大学古法发酵(酿造)生物技术研究所保藏;GABA 色谱纯(含量≥98%),上海金穗生物科技有限公司;丹磺酰氯 色谱纯(含量≥98%),成都华夏化学试剂有限公司;L-谷氨酸钠(L-monosodium glutamate,L-MSG) 分析纯(含量≥98.5%),成都科龙化工试剂厂;MRS肉汤、MRS选择性琼脂、YPD液体培养基和PDA选择性琼脂参照文献[20]配制,根据需要添加不同质量浓度的L-MSG。
FA1104电子天平 上海舜宇恒平有限公司;pHS-3C pH计 成都方舟科技公司;Allerga X-15R冷冻离心机 美国赛默飞公司;JY98-IIIDN超声细胞破碎机 宁波新芝生物科技有限公司;GM-0.33AL隔膜真空泵 天津津腾实验设备有限公司;Waters2695高效液相色谱 美国Waters公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 共发酵的单因素实验
选择培养至对数生长期的屎肠球菌AB157(8.79 lg (CFU/mL))和酿酒酵母SC-125(7.81 lg (CFU/mL))作为种子。根据查阅文献及前期试验筛选[21-22],以MRS肉汤为基础培养基。在总接种量为2%(V/V),分别考察在接种比例为1:1(V/V),L-谷氨酸钠添加量为12 g/L,静置发酵96 h时,不同发酵温度(30、32、35、38、40 ℃);在发酵温度为35 ℃,L-谷氨酸钠添加量为12 g/L,静置发酵96 h时,不同屎肠球菌AB157和酿酒酵母SC-125接种比例(1:4、1:2、1:1、2:1、4:1、6:1、1:0、0:1(V/V));在发酵温度为35 ℃,接种比例为4:1(V/V),静置发酵96 h时,不同L-谷氨酸钠质量浓度(0、4、8、12、16、20 g/L);及在发酵温度为35 ℃,接种比例为4:1(V/V)和L-谷氨酸钠添加量为12 g/L时,不同发酵时间(0、12、24、36、48、60、72、84、96、108、120 h)对屎肠球菌AB157和酿酒酵母SC-125共发酵时GABA产量和活菌数的影响。
1.2.2 响应面试验
在单因素实验的基础上,以发酵温度、接种比例和L-谷氨酸钠质量浓度为考察因素,选取相应的响应面设计中心点,以GABA产量为响应值,对试验数据进行优化试验。因素水平见表1。
表 1 因素水平表Table 1. The factors and levels水平 因素 A 发酵温度(℃) B 接种比例(V/V) C L-谷氨酸钠(g/L) −1 33 3:1 10 0 35 4:1 12 1 37 5:1 14 1.2.3 GABA含量测定
GABA参照Zhang等[23]利用丹磺酰氯衍生的方法,采用HPLC分析。HPLC检测条件:色谱柱为ODS-C18柱(4.6 mm×150 mm,5 μm);检测波长254 nm;柱温30 ℃;进样10 μL;水系为四氢呋喃-甲醇-乙酸钠溶液(4.1 g/L,乙酸调pH至6.2)=1:15:84(V/V/V),有机系为甲醇;1 mL/min梯度洗脱,水系比例为:80%保持6 min,14 min降至50%,1 min降至0%,0%保持5 min,1 min升至80%,80%保持3 min,总洗脱时间30 min。
1.2.4 选择性培养基法测定活菌数
待测菌液适当稀释,涂布计数。其中共发酵同时用MRS选择性琼脂和PDA选择性琼脂计数,屎肠球菌单菌发酵用MRS选择性琼脂计数,酿酒酵母单菌发酵用PDA选择性琼脂计数。
1.2.5 GAD酶活力测定
1.2.5.1 GAD粗酶液制备
参照彭春龙等[24]的试验方法,略有修改,收集最优条件下不同发酵时期及不同发酵体系的菌体,10000 r/min,4 ℃离心10 min,PBS洗涤2次,保留菌体;加入等体积含2.47 mg/mL磷酸吡哆醛,0.2 mg/mL溶菌酶的0.02 mol/L磷酸钠缓冲液(pH7.2)悬浮菌体,37 ℃振荡1 h,冰浴细胞破碎,功率400 W,运行时间5 s,间歇时间5 s,循环180次。破碎液4 ℃、10000 r/min离心10 min,去除沉淀,即为GAD粗酶液。
1.2.5.2 GAD酶活力测定
取GAD粗酶液400 μL,与等体积底物溶液(0.02 mol/L磷酸钠缓冲液,pH4.4,含12 g/L L-MSG,2.47 mg/mL磷酸吡哆醛)混合,37 ℃温浴30 min,置于沸水浴中10 min,离心收集上清液,采用HPLC测定生成的GABA,HPLC条件同1.2.3。酶活(U)定义:在试验条件下,1000 μL粗酶液1 min产生1 μmol GABA的酶量。
1.2.6 无细胞上清液对菌株发酵产GABA的影响
收集培养至12 h的屎肠球菌AB157单菌发酵液、酿酒酵母SC-125单菌发酵液及屎肠球菌AB157和酿酒酵母SC-125共发酵液,调pH与MRS肉汤pH相等,将发酵液在8000 r/min转速下离心10 min,取上清液,过0.22 μm有机滤膜,收集上清液即为无细胞上清液(cell-free supernatant,CFS)。
将制备的屎肠球菌AB157 CFS、酿酒酵母SC-125 CFS和共发酵CFS分别按培养基总体积分数20%的量加入到MRS肉汤(L-MSG终浓度为12 g/L)中,等体积的MRS肉汤作对照[14]。分别接入酿酒酵母SC-125(2%,V/V)和屎肠球菌AB157(2%,V/V)进行单一菌株发酵,35 ℃发酵96 h,测定GABA产量。
1.3 数据处理
试验数据采用SPSS 20.0进行显著性分析,柱状图折线图采用Origin 8.5进行绘制,响应面采用Design Expert 8.0.6分析。每组试验三个平行,所有结果用平均值±标准差表示。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 共发酵单因素实验
2.1.1 发酵温度对共发酵产GABA和活菌数的影响
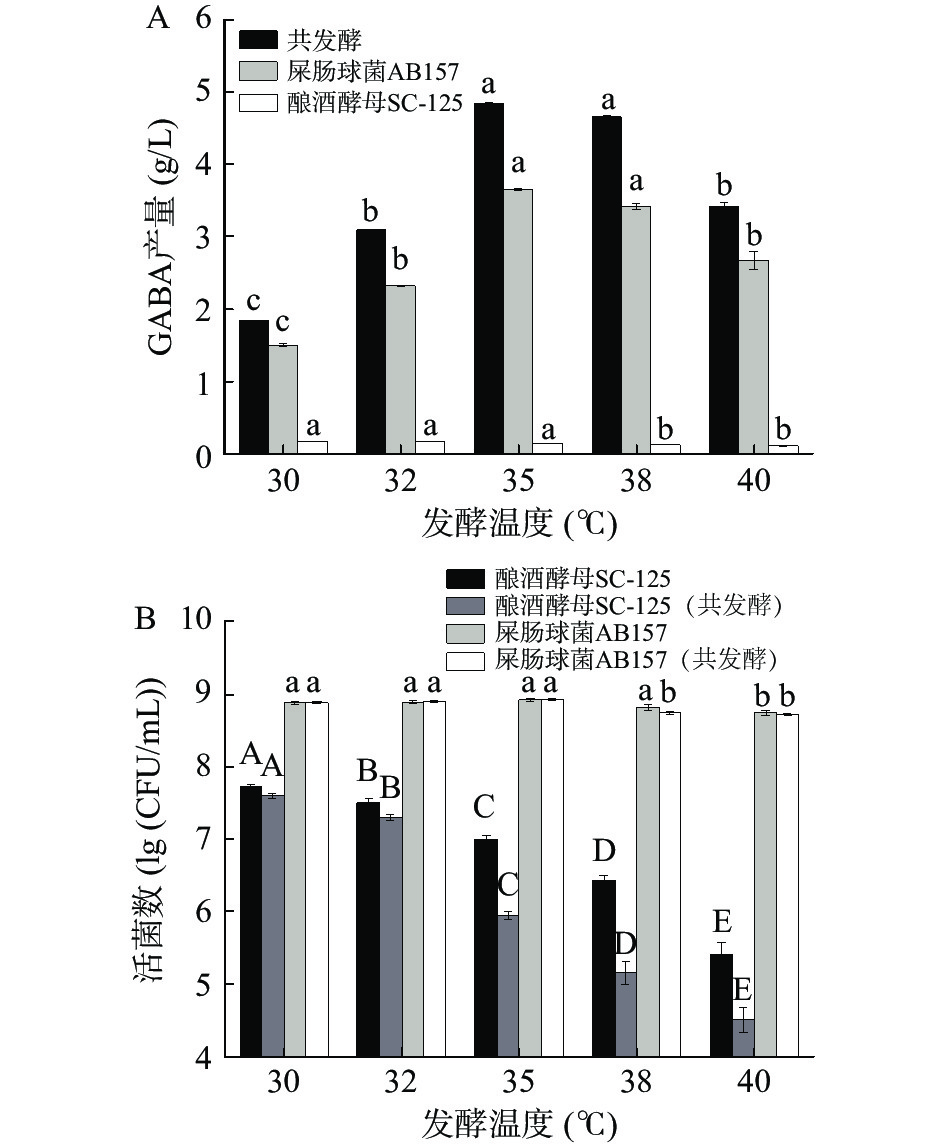
发酵温度对GABA产量(图1A)和活菌数(图1B)影响结果如图1所示。随温度升高,共发酵及屎肠球菌AB157单菌发酵中的GABA浓度表现为先显著增加后逐渐降低,在35 ℃达到GABA产量最大值,GABA最高产量为共发酵4.81 g/L,屎肠球菌AB157单菌发酵为3.66 g/L,酿酒酵母SC-125单菌发酵为0.14 g/L。分析发酵体系的活菌数(图1B)可知,屎肠球菌AB157在共发酵和单菌发酵中,其活菌数随温度的改变变化不大,当发酵温度高于35 ℃时,其活菌数开始下降;酿酒酵母SC-125的活菌数随着发酵温度的升高逐渐降低,温度升高其生长被显著抑制。发酵温度可影响微生物的代谢以及胞内催化L-MSG生成GABA的酶GAD的酶活力,适宜的发酵温度有助于提高GABA的产量[25-26]。因此,确定共发酵的温度为35 ℃。
2.1.2 接种比例对共发酵产GABA和活菌数的影响
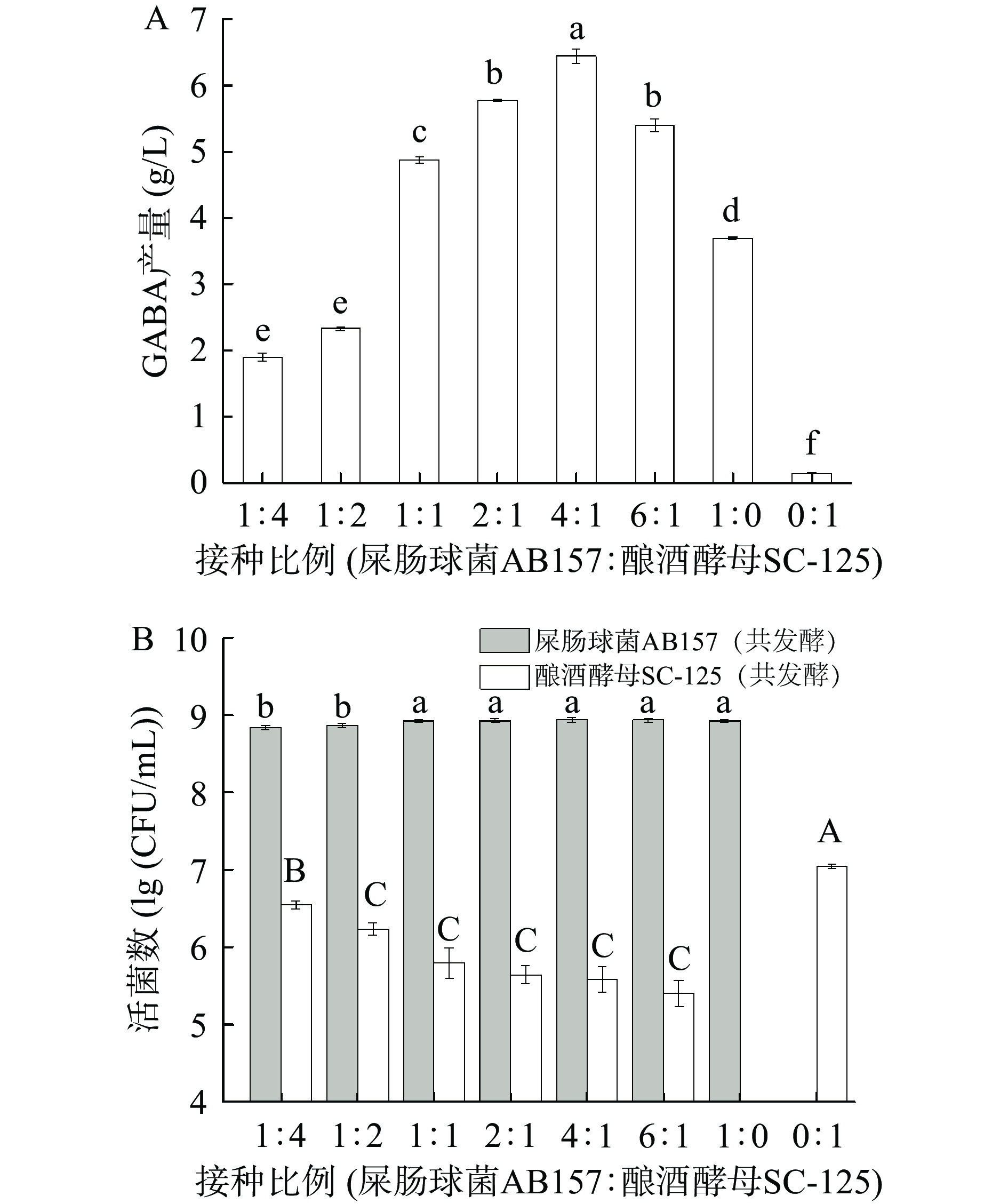
不同接种比例对GABA产量(图2A)和活菌数(图2B)影响结果如图2所示。由图2A可知,当屎肠球菌AB157和酿酒酵母SC-125的接种比例为4:1时,GABA产量最高,达6.44 g/L。由图2B可知,不同接种比例对屎肠球菌AB157的活菌数影响不大;而随着接种比例的增加,酿酒酵母SC-125的活菌数呈下降趋势。有研究表明,酿酒酵母可分泌营养因子促进乳酸菌的代谢,且消耗氧气和产生CO2为乳酸菌提供良好的生长环境[27-29]。适宜的接种比例可为共发酵体系中微生物的生长及GABA的转化合成提供良好的环境。因此,确定最适接种比例为4:1。
2.1.3 底物浓度对共发酵产GABA和活菌数的影响
不同L-谷氨酸钠质量浓度对GABA产量(图3A)和活菌数(图3B)影响结果如图3所示。由图3A可知,各发酵体系中的GABA产量随着L-谷氨酸钠浓度的增加表现为先显著增加后逐渐降低,添加L-谷氨酸钠12 g/L时,共发酵GABA产量达到最大6.56 g/L,此时屎肠球菌和酿酒酵母单菌发酵GABA产量分别为3.67 g/L和0.13 g/L。由图3B可知,不同L-谷氨酸钠浓度对屎肠球菌AB157的活菌数基本无影响,而在共发酵体系中,随着底物浓度增加,酿酒酵母SC-125的活菌数呈现先增加后降低的趋势。Komatsuzaki等[30]研究表明,适量的增加L-谷氨酸钠有利于微生物的生长和产物GABA的生成,但L-谷氨酸钠浓度过高,发酵体系的渗透压增大,微生物的代谢会受到抑制,GABA的产量反而降低。因此,确定最适的L-谷氨酸钠质量浓度为12 g/L。
2.1.4 发酵时间对共发酵产GABA和活菌数的影响
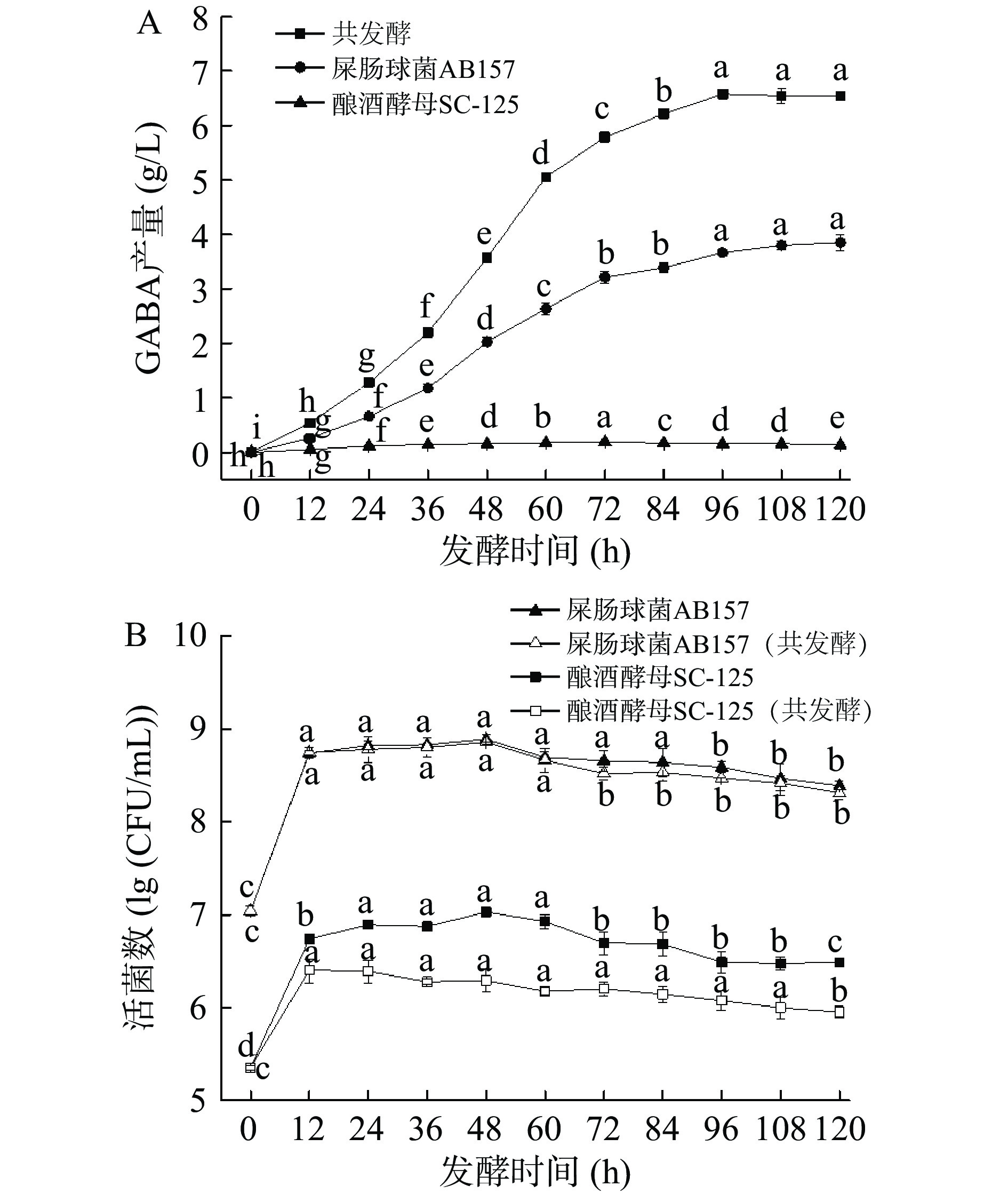
不同发酵时间对GABA产量(图4A)和活菌数(图4B)影响结果如图4所示。由图4A可知,各发酵体系中的GABA产量随着发酵时间的延长而显著增加,在96 h时,共发酵GABA产量达到最大6.57 g/L,且高于单菌发酵,随后趋于稳定。由图4B可知,屎肠球菌AB157和酿酒酵母SC-125的活菌数随着发酵的进行其变化趋势基本一致,且在达到对数生长期后趋于稳定。因此,确定最适宜的发酵时间为96 h。
2.2 响应面试验优化结果
采用Box-Behnken响应面设计结合单因素试验结果,以发酵温度(A)、接种比例(B)和L-谷氨酸钠质量浓度(C)为自变量,GABA产量为响应值。以发酵温度35 ℃、接种比例4:1和底物浓度12 g/L为分析中心点(如表2),进行响应面试验。
表 2 响应面试验设计与结果Table 2. Response surface experimental design and resultsA 发酵温度(℃) B 接种比例(V/V) C L-谷氨酸钠(g/L) GABA产量(g/L) 1 33 3:1 12 5.55 2 35 5:1 14 6.52 3 35 4:1 12 6.55 4 33 5:1 12 5.98 5 35 4:1 12 6.55 6 37 4:1 10 5.33 7 35 4:1 12 6.54 8 35 4:1 12 6.51 9 37 4:1 14 6.21 10 37 3:1 12 5.86 11 37 5:1 12 6.26 12 35 5:1 10 5.85 13 33 4:1 10 5.26 14 33 4:1 14 5.69 15 35 3:1 10 5.45 16 35 4:1 12 6.50 17 35 3:1 14 6.1 对试验数据进行拟合分析,得到以GABA产量(Y)的回归方程:
Y=6.55+0.15A+0.21B+0.33C−0.0078AB+0.11AC+0.0039BC−0.50A2−0.14B2−0.43C2
根据回归模型方差分析(表3)可知,该模型极显著,即P<0.0001,F=178.69,且失拟项P>0.05不显著,表明该模型可用于发酵预测。此外,R2=0.9957,可以解释99.57%的响应值变化,校正后R2Adj=0.9901与R2接近,表明模型拟合度较好。以上结果表明该模型拟合度较好,可用于试验预测。同时,发酵温度(A)、接种比例(B)、L-谷氨酸钠质量浓度(C)和A2、B2及C2的P值小于0.01,表明对GABA的产量影响极显著;交互项中,AC达到极显著水平(P<0.01),表明发酵温度和L-谷氨酸钠质量浓度的交互作用对GABA的生成影响最为显著。由F值可知,影响GABA产量的因素依次为L-谷氨酸钠质量浓度>接种比例>发酵温度。
表 3 回归模型方差分析Table 3. Analysis of variance of regression model方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 3.50 9 0.39 178.69 < 0.0001 ** A 0.17 1 0.17 77.56 < 0.0001 ** B 0.34 1 0.34 157.86 < 0.0001 ** C 0.87 1 0.87 398.46 < 0.0001 ** AB 2.403E-004 1 2.403E-004 0.11 0.7495 AC 0.051 1 0.051 23.19 0.0019 ** BC 6.006E-005 1 6.006E-005 0.028 0.8728 A2 1.04 1 1.04 476.00 < 0.0001 ** B2 0.082 1 0.082 37.74 0.0005 ** C2 0.78 1 0.78 358.01 < 0.0001 ** 残差 0.015 7 2.178E-003 失拟项 0.012 3 3.864E-003 4.23 0.0987 净误差 3.655E-003 4 9.137E-004 总离差 3.52 16 决定系数 R2=0.9957 R2Adj=0.9901 注:**表示差异极显著P<0.01。 对该回归方程分析,得到最优的共发酵条件为发酵温度35.26 ℃、屎肠球菌AB157和酿酒酵母SC-125的接种比例4.92:1(V/V)、底物浓度12.24 g/L,该条件下预测GABA产量为6.67 g/L。
为验证预测的可靠性,结合最优值和实际应用确定共发酵因素值为:发酵温度35 ℃、接种比例为5:1(V/V)、底物浓度12 g/L。重复试验三次,试验结果为,优化条件下GABA产量为6.55±0.09 g/L,与预测接近,且GABA产量与屎肠球菌单菌发酵(3.67 g/L)相比,提高到1.78倍。
2.3 GAD酶活力分析结果
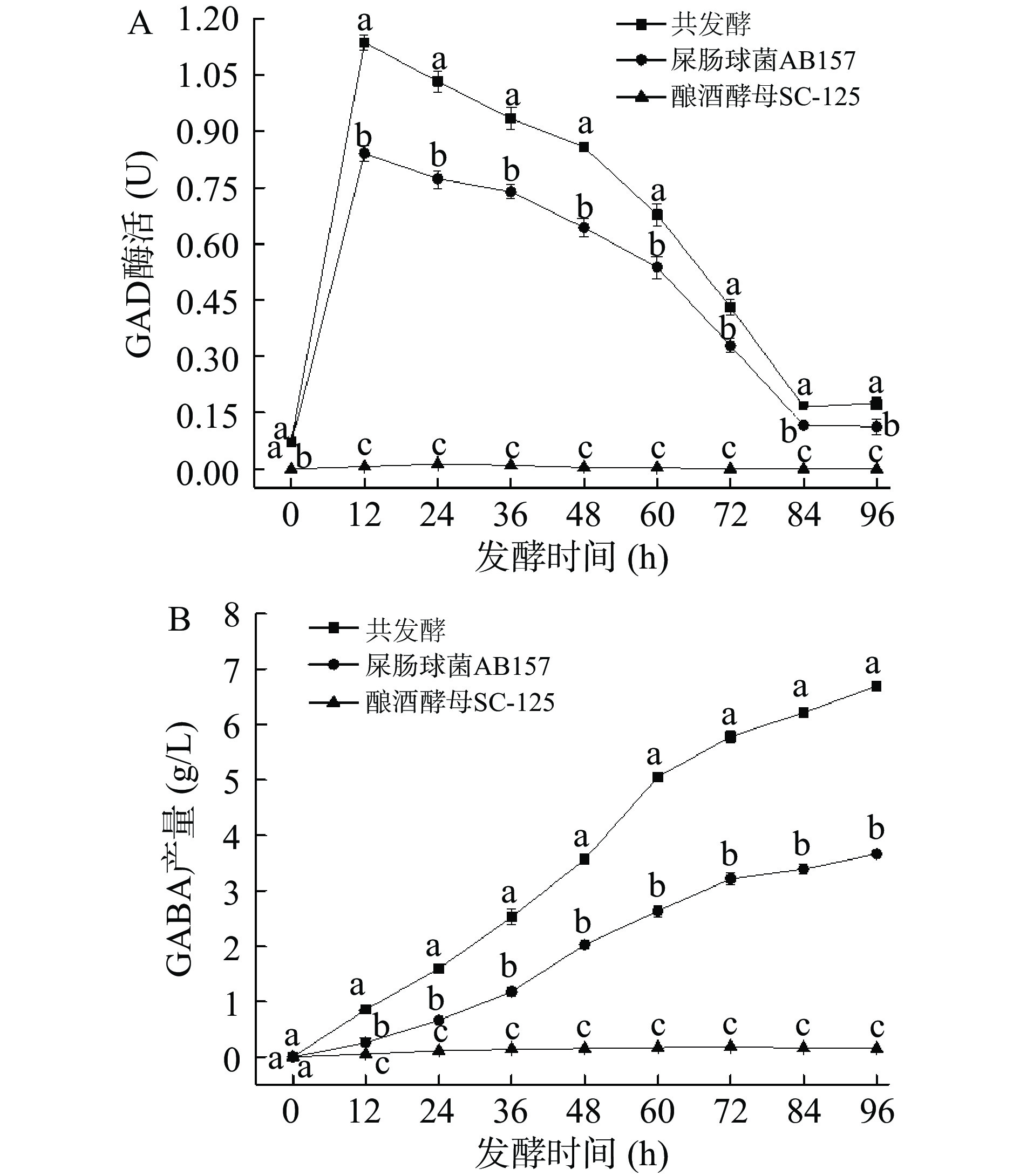
在最优条件下,分析不同时间以及不同发酵体系中微生物GAD酶活力(图5A)与GABA产量(图5B)的关联。GAD为催化L-MSG生成GABA的限速酶[31],因此GAD酶活力的检测对于研究GABA的合成能力尤为重要。由图5A可知,GAD酶活随时间变化表现为先显著增加后逐渐降低的趋势,在12 h时共发酵体系酶活达到最高,为1.14 U,此时屎肠球菌和酿酒酵母单菌发酵分别为0.84 U和0.01 U,且发酵12 h后,共发酵体系GAD酶活显著高于单菌发酵体系。由图5B可知,共发酵中GABA产量显著高于单菌发酵。以上结果表明,共发酵中GABA产量的显著提高与GAD酶活的显著增强紧密相关。
2.4 添加CFS对GABA产量的影响
有研究表明乳酸菌和酵母菌在发酵环境中能够通过生物膜包被、群体感应或营养代谢产物交换等方式进行相互作用,从而影响发酵进程[32-33]。本研究通过分别添加CFS探究是否存在营养代谢产物交换的相互作用影响菌株产GABA,结果见图6。结果表明,添加屎肠球菌AB157 CFS和共发酵CFS后,酿酒酵母SC-125发酵产GABA分别为0.18 g/L和0.17 g/L,高于对照组的0.13 g/L;添加酿酒酵母SC-125的CFS后,屎肠球菌AB157发酵产GABA为4.61 g/L,高于对照组的3.77 g/L,但添加共发酵的CFS后,对其产GABA无显著影响,具体原因有待进一步研究。上述表明,屎肠球菌AB157或酿酒酵母SC-125的CFS对GABA产量提升有帮助,其具体作用机制接下来将进一步深入研究。
3. 结论
本试验研究产GABA屎肠球菌AB157和酿酒酵母SC-125采用共发酵提高GABA产量,及分析相互作用和关键酶GAD。采用单因素和响应面分析法优化共发酵条件,确定在总接种量为2%(V/V)的共发酵条件为发酵温度35 ℃、屎肠球菌AB157和酿酒酵母SC-125的接种比例5:1(V/V)、底物浓度12 g/L,发酵时间96 h,此时,GABA产量为6.55 g/L,与屎肠球菌单菌发酵相比,产量提高到1.78倍;高产GABA机制研究表明,共发酵体系的高GAD酶活及菌株发酵代谢物的营养供给对GABA的产量提高有明显促进作用。接下来,基于屎肠球菌AB157和酿酒酵母SC-125共培养高产GABA的相互作用,对其具体互作机制将进行深入研究。
-
表 1 因素水平表
Table 1 The factors and levels
水平 因素 A 发酵温度(℃) B 接种比例(V/V) C L-谷氨酸钠(g/L) −1 33 3:1 10 0 35 4:1 12 1 37 5:1 14 表 2 响应面试验设计与结果
Table 2 Response surface experimental design and results
A 发酵温度(℃) B 接种比例(V/V) C L-谷氨酸钠(g/L) GABA产量(g/L) 1 33 3:1 12 5.55 2 35 5:1 14 6.52 3 35 4:1 12 6.55 4 33 5:1 12 5.98 5 35 4:1 12 6.55 6 37 4:1 10 5.33 7 35 4:1 12 6.54 8 35 4:1 12 6.51 9 37 4:1 14 6.21 10 37 3:1 12 5.86 11 37 5:1 12 6.26 12 35 5:1 10 5.85 13 33 4:1 10 5.26 14 33 4:1 14 5.69 15 35 3:1 10 5.45 16 35 4:1 12 6.50 17 35 3:1 14 6.1 表 3 回归模型方差分析
Table 3 Analysis of variance of regression model
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 3.50 9 0.39 178.69 < 0.0001 ** A 0.17 1 0.17 77.56 < 0.0001 ** B 0.34 1 0.34 157.86 < 0.0001 ** C 0.87 1 0.87 398.46 < 0.0001 ** AB 2.403E-004 1 2.403E-004 0.11 0.7495 AC 0.051 1 0.051 23.19 0.0019 ** BC 6.006E-005 1 6.006E-005 0.028 0.8728 A2 1.04 1 1.04 476.00 < 0.0001 ** B2 0.082 1 0.082 37.74 0.0005 ** C2 0.78 1 0.78 358.01 < 0.0001 ** 残差 0.015 7 2.178E-003 失拟项 0.012 3 3.864E-003 4.23 0.0987 净误差 3.655E-003 4 9.137E-004 总离差 3.52 16 决定系数 R2=0.9957 R2Adj=0.9901 注:**表示差异极显著P<0.01。 -
[1] LIN J H, XU Z J, PENG J S, et al. OsProT1 and OsProT3 function to mediate proline- and γ-aminobutyric acid-specific transport in yeast and are differentially expressed in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Rice,2019,12(1):1−10. doi: 10.1186/s12284-018-0262-x
[2] SANCHART C, RATTANAPORN O, HALTRICH D, et al. Technological and safety properties of newly isolated GABA-producing Lactobacillus futsaii strains[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology,2016,121(3):734−745. doi: 10.1111/jam.13168
[3] 周春英, 陶荣芬, 顾永健, 等. γ-氨基丁酸对亚综合征性抑郁认知功能的作用[J]. 临床精神医学杂志,2011,21(1):12−14. [ZHOU C Y, TAO R F, GU Y J, et al. Effect of sertraline with γ-aminobutyric acid on cognitive function of the subsyndromal symptomatic depression[J]. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry,2011,21(1):12−14. ZHOU C Y, TAO R F, GU Y J, et al. Effect of sertraline with γ-aminobutyric acid on cognitive function of the subsyndromal symptomatic depression[J]. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 2011, 21(1): 12-14.
[4] HUANG C Y, KUO W W, WANG H F, et al. GABA tea ameliorates cerebral cortex apoptosis and autophagy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2014,6:534−544. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2013.11.020
[5] 国立东, 张文文, 刘艳, 等. 传统发酵东北酸菜中植物乳杆菌HUCM115的分离及益生特性[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(18):140−145. [GUO L D, ZHANG W W, LIU Y, et al. Isolation and probiotic properties of Lactobacillus plantarum HUCM115 from traditional pickled Chinese cabbage[J]. Food Science,2020,41(18):140−145. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190807-084 GUO L D, ZHANG W W, LIU Y, et al. Isolation and probiotic properties of Lactobacillus plantarum HUCM115 from traditional pickled Chinese cabbage[J]. Food Science, 2020, 41(18): 140-145. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190807-084
[6] 刘璐, 吴江丽, 杨金桃, 等. 发酵鱼酱酸产GABA乳酸菌的分离筛选及发酵特性研究[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(18):73−79. [LIU L, WU J L, YANG J T, et al. Isolation and fermentation characteristics of γ-aminobutyric acid-producing lactic acid bacteria from Yujiang, a traditional Miao ethnic fermented condiment[J]. Food Science,2021,42(18):73−79. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200914-182 LIU L, WU J L, YANG J T, et al. Isolation and fermentation characteristics of γ-aminobutyric acid-producing lactic acid bacteria from Yujiangsuan, a traditional Miao ethnic fermented condiment[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(18): 73-79. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200914-182
[7] 司阔林, 徐捐捐, 岳田利, 等. 布氏乳杆菌产γ-氨基丁酸发酵条件的优化[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(2):87−93. [SI K L, XU J J, YUE T L, et al. Optimization of fermentation conditions for γ-aminobutyric acid production by Lactobacillus buchneri[J]. Food Science,2020,41(2):87−93. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181218-210 SI K L, XU J J, YUE T L, et al. Optimization of fermentation conditions for γ-aminobutyric acid production by Lactobacillus buchneri[J]. Food Science, 2020, 41(2): 87-93. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181218-210
[8] 谭霄, 孙擎, 曾林, 等. 1株产γ-氨基丁酸植物乳杆菌谷氨酸脱羧酶基因的克隆与表达[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(18):159−165. [TAN X, SUN Q, ZENG L, et al. Cloning and expressing of glutamate decarboxylase gene from Lactobacillus plantarum producing γ-aminobutyric acid[J]. Food Science,2018,39(18):159−165. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201818025 TAN X, SUN Q, ZENG L, et al. Cloning and expressing of glutamate decarboxylase gene from Lactobacillus plantarum producing γ-aminobutyric acid[J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(18): 159-165. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201818025
[9] 陈烟兰, 杨民和. 产谷氨酸脱羧酶真菌的检测和筛选[J]. 微生物学杂志,2013,33(4):22−29. [CHEN Y L, YANG M H. Detection and screening of fungal strains producing glutamic acid decarboxylase[J]. Journal of Microbiology,2013,33(4):22−29. CHEN Y L, YANG M H. Detection and screening of fungal strains producing glutamic acid decarboxylase[J]. Journal of Microbiology, 2013, 33(4): 22-29.
[10] 赵炜彤. 高产γ-氨基丁酸酵母菌菌株的筛选、诱变及发酵条件优化[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学, 2015 ZHAO W T. The study on screening and mutation breeding of high-yield γ-aminobutyric acid yeast strains and optimization of its fermentation conditions[D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2015.
[11] 曾林, 刘波, 许小艳, 等. 四川泡菜中产γ-氨基丁酸微生物的系统发育与表达能力评估[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(2):87−91. [ZENG L, LIU B, XU X Y, et al. Phylogeny and performance assessment of γ-aminobutyric acid-producing microorganisms from Sichuan pickles[J]. Food Science,2017,38(2):87−91. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201702014 ZENG L, LIU B, XU X Y, et al. Phylogeny and performance assessment of γ-aminobutyric acid-producing microorganisms from Sichuan pickles[J]. Food Science, 2017, 38(2): 87-91. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201702014
[12] 李文, 董明盛. 发酵鹰嘴豆乳产γ-氨基丁酸乳酸菌的复合诱变选育[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(16):147−153. [LI W, DONG M S. Improving γ-aminobutyric acid production of lactic acid bacteria in chickpea milk by compound mutagenesis[J]. Food Science,2018,39(16):147−153. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201816022 LI W, DONG M S. Improving γ-aminobutyric acid production of lactic acid bacteria in chickpea milk by compound mutagenesis[J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(16): 147-153. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201816022
[13] 刘豪栋, 杨昳津, 林高节, 等. 酵母与乳酸菌的相互作用模式及其在发酵食品中的应用研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(9):268−274. [LIU H D, YANG Y J, LIN G J, et al. Research progress on interaction patterns between yeast and lactic acid bacteria and their application in fermented foods[J]. Food Science,2022,43(9):268−274. LIU H D, YANG Y J, LIN G J, et al. Research progress on interaction patterns between yeast and lactic acid bac- teria and their application in fermented foods[J]. Food Science,2022,43(9):268-274.
[14] 赵小燕. 酿酒酵母与植物乳杆菌IMAU10120共生菌株筛选及其益生特性研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2014 ZHAO X Y. Screening strains of S. cerevisiae with the co-symbiosis of L. plantarum IMAU10120 for probiotic properties[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2014.
[15] ROOSTITA R, FLEET G H. The occurrence and growth of yeasts in Camembert and Blue-veined cheeses[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,1996,28(3):393−404. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(95)00018-6
[16] 莫依灿, 钟伟俊, 何湛, 等. 黄酒中乳酸菌的研究进展[J]. 中国酿造,2015,34(9):5−8. [MO Y C, ZHONG W J, HE Z, et al. Research progress of lactic acid bacteria in Chinese rice wine[J]. China Brewing,2015,34(9):5−8. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2015.09.002 MO Y C, ZHONG W J, HE Z, et al. Research progress of lactic acid bacteria in Chinese rice wine[J]. China Brewing, 2015, 34(9): 5-8. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2015.09.002
[17] 白天天, 郭雪峰. 屎肠球菌的特性及其在畜牧生产中的应用研究进展[J]. 中国畜牧杂志,2021,57(2):16−20. [BAI T T, GUO X F. Characteristics of Enterococcus faecium and its application in livestock production[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science,2021,57(2):16−20. BAI T T, GUO X F. Characteristics of Enterococcus faecium and its application in livestock production[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2021, 57(2): 16-20.
[18] 丁耿芝. 酵母菌添加对饲喂不同精粗比饲粮肉牛瘤胃发酵、养分降解和血浆代谢组的影响[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2014 DING G Z. Effect of Saccharomyces cerevisiae on ruminal fermentation characteristics, nutrient degradation and plasma metabonomics of steers fed diets with different concentrate to forage ratios[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2014.
[19] 孙擎, 曾林, 谭霄, 等. 一株产γ-氨基丁酸屎肠球菌的筛选和发酵条件优化及其益生特性分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(14):87−93,100. [SUN Q, ZENG L, TAN X, et al. Screening and optimization of fermentation conditions for γ-aminobutyric acid- producing Enterococcus faecium and analysis of probiotic properties[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(14):87−93,100. SUN Q, ZENG L, TAN X, et al. Screening and optimization of fermentation conditions for γ-aminobutyric acid- producing Enterococcus faecium and analysis of probiotic properties[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(14): 87-93, 100.
[20] 刘君彦. 食品体系中乳杆菌的压力应答机制及其与酵母的群体相互作用[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2019 LIU J Y. Lactobacilli stress response mechanism and polymicrobial interaction with yeast in food system[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2019.
[21] 苗凯. Lactobacillus plantarum产γ-氨基丁酸发酵条件优化及基因组分析[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2020 MIAO K. Optimization of fermentation conditions of γ-aminobutyric acid produced by Lactobacillus plantarum and genome analysis[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020.
[22] 张敏. γ-氨基丁酸乳酸菌诱变选育及其发酵条件优化[D]. 芜湖: 安徽工程大学, 2020 ZHANG M. Mutagenesis breeding of Enterococcus faecalis producing GABA and optimization of fermentation conditions[D]. Wuhu: Anhui Polytechnic University, 2020.
[23] ZHANG Q, SUN Q, TAN X, et al. Characterization of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-producing Saccharomyces cerevisiae and coculture with Lactobacillus plantarum for mulberry beverage brewing[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering,2020,129(4):447−453. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2019.10.001
[24] 彭春龙, 黄俊, 赵伟睿, 等. 酸胁迫下短乳杆菌谷氨酸脱羧酶系统关键基因的表达及酶活性响应[J]. 高校化学工程学报,2015,29(2):359−365. [PENG C L, HUANG J, ZHAO W R, et al. Effects of acid stress on the expression of key genes of glutamate decarboxylase system and enzyme activity in Lactobacillus brevis[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities,2015,29(2):359−365. PENG C L, HUANG J, ZHAO W R, et al. Effects of acid stress on the expression of key genes of glutamate decarboxylase system and enzyme activity in Lactobacillus brevis[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities, 2015, 29(2): 359-365.
[25] VILLEGAS J M, BROWN L, GIORI G D, et al. Optimization of batch culture conditions for GABA production by Lactobacillus brevis CRL 1942, isolated from quinoa sourdough[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2016,67:22−26. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2015.11.027
[26] 黄祖耀, 薛正莲, 陈涛. 粪肠球菌HX-3细胞转化合成γ-氨基丁酸条件的优化[J]. 食品与发酵科技,2012,48(3):6−9. [HUANG Z Y, XUE Z L, CHEN T, et al. Optimization of biotransformation conditions for γ-aminobutyric acid production by Enterococcus faecalis HX-3 cells[J]. Food and Fermentation Sciences & Technology,2012,48(3):6−9. HUANG Z Y, XUE Z L, CHEN T, et al. Optimization of biotransformation conditions for γ-aminobutyric acid production by Enterococcus faecalis HX-3 cells[J]. Food and Fermentation Sciences & Technology 2012, 48(3): 6-9.
[27] SIEUWERTS S, BRON P A, SMID E J. Mutually stimulating interactions between lactic acid bacteria and Saccharomyces cerevisiae in sourdough fermentation[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2018,90:201−206. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2017.12.022
[28] BARTLE L, SUMBY K, SUNDSTROM J, et al. The microbial challenge of winemaking: Yeast-bacteria compatibility[J]. FEMS Yeast Research,2019,19(4):1−47.
[29] JAROSZ D F, BROWN J C S, WALKER G A, et al. Cross-kingdom chemical communication drives a heritable, mutually beneficial prion-based transformation of metabolism[J]. Cell,2014,158(5):1083−1093. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.07.025
[30] KOMATSUZAKI N, SHIMA J, KAWAMOTO S, et al. Production of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) by Lactobacillus paracasei isolated from traditional fermented foods[J]. Food Microbiology,2005,22(6):497−504. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2005.01.002
[31] XIONG Q, XU Z, XU L, et al. Efficient production of γ-GABA using recombinant E. coli expressing glutamate decarboxylase (GAD) derived from eukaryote Saccharomyces cerevisiae[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology,2017,183(4):1390−1400. doi: 10.1007/s12010-017-2506-4
[32] 韩雪, 雷鹏, 樵飞, 等. 发酵乳制品中乳酸菌与酵母菌相互作用研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2014,35(7):388−391. [HAN X, LEI P, QIAO F, et al. Research progress on symbiotic between yeasts and lactic acid bacteria in fermented dairy products[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2014,35(7):388−391. HAN X, LEI P, QIAO F, et al. Research progress on symbiotic between yeasts and lactic acid bacteria in fermented dairy products[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2014, 35(7): 388-391.
[33] XU D, BEHR J, GEIßLER A J, et al. Label-free quantitative proteomic analysis reveals the lifestyle of Lactobacillus hordei in the presence of Sacchromyces cerevisiae[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2019,294:18−26. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2019.01.010
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 薛淑贞,梁婷,赵祥民,张家玮,汝应俊,唐德富. 葡萄籽提取物和有机铁对蛋鸡生产性能和蛋品质的影响. 饲料工业. 2025(04): 59-63 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 常安其,毛帅翔,柳广斌. 葡萄残渣的饲料化利用及其在羊生产中的应用研究进展. 中国畜牧兽医. 2024(11): 4842-4850 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 杨辉,胡雅婕. 活性包装薄膜对冷藏圣女果的保鲜效果研究. 农业科技与装备. 2024(05): 61-64 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王建康,郭诗琼,王静,魏丽娜,冯莉,黄峻榕,Fereidoon SHAHIDI. 浆果籽油的生物活性与应用研究进展. 食品与生物技术学报. 2024(10): 32-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 赵明洪,卢天明,刘莉,王启新,杨通,林娜,邱崇,钟田雨,郭秋岩,王继刚. 甘草减轻雷公藤多苷片所致肝损伤的作用机制. 中国实验方剂学杂志. 2023(05): 24-31 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 尚嘉毅,初柏君,赵文君,翟孟婷,王翔宇,马欲明,孙晴,孟祥永,陈吉江,张宇. 市售牛油果油和葡萄籽油品质研究. 中国油脂. 2023(06): 119-125+152 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 盖永强,蓝天婵,李金生,朴美子,李岩. 葡萄籽果冻的工艺. 食品工业. 2022(06): 107-110 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



