Effect of Polysaccharide from Ilex kudingcha C.J. Tseng on the Immune Regulation and Antioxidation of Spleen Lymphocytes from Mice
-
摘要: 本文通过体外培养小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞研究苦丁茶冬青多糖对正常小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞免疫调节和抗氧化作用的影响。测定了不同浓度的苦丁茶冬青多糖(polysaccharide from Ilex kudingcha C.J. Tseng)对脾脏淋巴细胞体外增殖能力、抗氧化酶(SOD、T-AOC、GSH-Px和CAT)活力、丙二醛(MDA)含量及炎性细胞因子(TNF-α、IFN-γ和IL-1β)分泌水平的影响。结果显示,小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞的增殖与苦丁茶冬青多糖浓度呈正相关,在80和160 μg/mL浓度时,吸光度值分别为0.38和0.41,与空白对照组(0.31)相比具有极显著差异(P<0.01);SOD、T-AOC、GSH-Px和CAT活力随苦丁茶冬青多糖浓度的增加而增强,浓度为160 μg/mL时,抗氧化酶活力分别为4.54 U/mg蛋白、1.06 mmol/mg蛋白、799.01 mU/mg蛋白和806.85 U/mg蛋白,与空白对照组相比具有极显著性差异(P<0.01);此外,与空白对照组相比,苦丁茶冬青多糖显著降低MDA含量、促进NO分泌和促进脾脏淋巴细胞分泌TNF-α、IFN-γ和IL-1β。本研究结果表明苦丁茶冬青多糖可通过促进小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞增殖、增强细胞抗氧化能力及诱导炎性细胞因子分泌等发挥其免疫增强活性,该研究可为苦丁茶冬青的开发和利用提供理论支撑。Abstract: To investigate the immune regulation and antioxidation effects of polysaccharide from Ilex kudingcha C.J. Tseng on mouse spleen lymphocytes in vitro. The proliferation, antioxidant capacity (SOD, T-AOC, GSH-Px and CAT) activity and malonic dialdehyde (MDA) content, as well as the secretion of cytokines (TNF-α, IFN-γ and IL-1β) were detected after treating with polysaccharide from Ilex kudingcha C.J. Tseng. The results showed that polysaccharide from Ilex kudingcha C.J. Tseng could promote the proliferation of spleen lymphocytes dose-dependently. Compared to the OD value of control group (0.31), the OD values at the concentration of 80 and 160 μg/mL were increased significantly (P<0.01) to 0.38 and 0.41, respectively. The activities of SOD, T-AOC, GSH-Px and CAT were increased with increasing concentration of polysaccharide from Ilex kudingcha C.J. Tseng. And there were significant differences (P<0.01) between control group and 160 μg/mL polysaccharide from Ilex kudingcha C.J. Tseng group, the activities of SOD, T-AOC, GSH-Px and CAT were of 4.54 U/mg protein, 1.06 mmol/mg protein, 799.01 mU/mg protein and 806.85 U/mg protein, respectively. Meanwhile, compared to control group, polysaccharide from Ilex kudingcha C.J. Tseng could significantly decrease the contents of MDA, increase NO production and promote the secretion of TNF-α, IFN-γ and IL-1β. In conclusion, the immunomodulatory effect of polysaccharide from Ilex kudingcha C.J. Tseng may be related to the promotion of splenic lymphocyte proliferation, the enhancement of antioxidant activity and the induction of cytokine secretion level. The results are beneficial to provide a theoretical basis for the development and utilization of Ilex kudingcha C.J. Tseng.
-
多糖是一类广泛存在于植物、动物、海洋生物和微生物中的生物活性大分子物质。近年来,多糖的免疫调节功能受到广泛关注。多糖可通过调节淋巴细胞亚群、激活免疫细胞、诱导炎性细胞因子和活化补体等多途径发挥其免疫调节作用[1]。脾脏作为机体免疫应答的重要场所,含有大量的T淋巴细胞和B淋巴细胞,同时刺激或选择性刺激T、B细胞分裂增殖并促进相关细胞因子和抗体的分泌,直接反映机体的免疫调节能力。例如:蛹虫草胞外多糖可提高免疫器官指数、促进T、B细胞增殖和增加免疫球蛋白G、免疫球蛋白A、免疫球蛋白M、肿瘤坏死因子-α、白介素-6、白介素-2和干扰素-γ等的分泌,具有显著的免疫调节效果[2];库尔勒香梨粗多糖能提高小鼠血清白介素-2和干扰素-γ水平、增加实验动物脾脏和胸腺等免疫器官指数,提高巨噬细胞的吞噬能力等[3];苦瓜多糖可通过提升溶血素水平、提高巨噬细胞的吞噬能力和刺激小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞的增殖,提高免疫抑制小鼠的免疫功能[4]。
苦丁茶冬青(Ilex kudingcha C.J. Tseng)是冬青科冬青属(Ilex aquifolium L.)常绿乔木,其茶叶中富含多糖、多酚、多种必需氨基酸、维生素、微量元素等营养物质,具有抑菌、降血压、降血糖、降血脂等药用价值,且安全无毒[5-8]。许实波等[9]开展了苦丁茶水提物的毒理学研究,发现苦丁茶水提物的最大耐受量为168 g/kg,属于无毒性级,服用安全。
苦丁茶冬青多糖是一类含α-吡喃糖环结构的高分子化合物,具有抑制特定异常细胞增殖和分化的功效,极具开发前景[10-11]。韦晓洁等[12]研究了超临界CO2萃取参数对苦丁茶多糖得率的影响,并优化了其工艺条件。于淑池等[13]研究表明海南苦丁茶多糖可降低糖尿病小鼠的血糖,具有降血糖功效。课题组前期研究发现苦丁茶冬青萃取物具有调节血脂和高胆固醇血症的功效[14],苦丁茶冬青多糖具有较强的体外抗氧化活性等生物活性[11]。为进一步探索苦丁茶冬青多糖的免疫调节效果,本研究以苦丁茶冬青多糖为实验材料,以小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞为研究对象,分析苦丁茶冬青多糖对体外培养小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞的增殖作用,并通过测定超氧化物歧化酶(total superoxide dismutase, SOD)、总抗氧化能力(total antioxidant capacity, T-AOC)、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(glutathione peroxidase, GSH-Px)、过氧化氢酶(catalase, CAT)活力等抗氧化酶活性,检测肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor-α, TNF-α)、干扰素-γ(interferon-γ, IFN-γ)和白介素-1β(interleukin-1β, IL-1β)等细胞因子的分泌水平,研究苦丁茶冬青多糖对小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞的免疫调节和抗氧化作用,为海南苦丁茶资源的高值化开发和利用提供理论基础和实验依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
苦丁茶冬青多糖 苦丁茶冬青原料由中国热带农业科学院香料饮料研究所(兴隆热带植物园)提供,多糖制备参照团队建立的方法[11],通过热水浸提和终浓度为20%、40%、60%和80%的四种不同浓度乙醇分级沉淀以制备苦丁茶冬青多糖,其主要由鼠李糖、阿拉伯糖、半乳糖和葡萄糖醛酸等组成,其相对分子质量为440.44 kDa,纯度为87.59%[15]。
BALB/c雄性小鼠 6周,体重20~30 g,北京华阜康生物科技股份有限公司,许可证号:SCXK(京)2019-0008;胎牛血清 杭州四季青生物工程材料有限公司;无水乙醇 西陇科学股份有限公司;台盼蓝染料 美国Sigma公司;RPMI-1640培养基 美国Gibco公司;CCK-8试剂盒、SOD、T-AOC、GSH-Px、CAT和MDA检测试剂盒 上海碧云天生物技术有限公司;NO检测试剂盒 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;TNF-α、IFN-γ和IL-1β细胞因子ELISA检测试剂盒 武汉博士德生物工程有限公司;其他化学试剂均为分析纯。
3110系列二氧化碳培养箱 Thermo Fisher Scientific公司;奥林巴斯CKX41倒置显微镜 Olympus公司;Varioskan Flash全波长多功能酶标仪 Thermo Fisher Scientific公司;SW-CJ-2FD净化工作台 苏州净化设备有限公司;3K15通用型台式高速冷冻离心机 Sigma公司;ZDX-35B压力蒸汽灭菌锅 上海申安医疗器械厂;Milli-Q50超纯水系统 Millipore公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞的制备
小鼠脱椎处理,75%医用酒精浸泡后取其脾脏,参照文献[16]的方法制备脾淋巴细胞悬液,将收集的脾淋巴细胞用RPMI-1640培养基,37 ℃、5% CO2无菌条件培养2 h,收集未贴壁的细胞悬液即为脾脏淋巴细胞。采用台盼蓝细胞活性染料对细胞进行计数,利用活细胞数大于95%的脾脏淋巴细胞悬液开展研究和分析。
1.2.2 小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞增殖的检测
参照文献[16]的方法将收集到的脾脏淋巴细胞悬液调整浓度至5×106个/mL,以190 μL/孔接种至96孔板,再添加10 μL不同浓度的苦丁茶冬青多糖溶液至RPMI-1640培养基,分别调节最终作用浓度为20、40、80和160 μg/mL,设计一组仅加入10 μL RPMI-1640的培养基为空白对照组,每组设6个复孔,试验平行3次,37 ℃、5% CO2条件下预孵育48 h。按照CCK-8试剂盒操作说明,每孔加入20 μL CCK-8溶液继续孵育4 h。在450 nm处通过全波长多功能酶标仪检测吸光度,测定苦丁茶冬青多糖对小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞增殖的影响。
1.2.3 抗氧化活性的测定
按1.2.2节方法培养后离心收集细胞,按照SOD、T-AOC、GSH-Px、CAT和MDA检测试剂盒说明测定,并计算SOD、T-AOC、GSH-Px和CAT等抗氧化酶活力以及MDA含量。
1.2.4 NO含量的测定
按照NO检测试剂盒的操作说明,540 nm处测定吸光度,绘制标准曲线(y=0.0095x+0.0482, R2=0.9963),分析苦丁茶冬青多糖对脾脏淋巴细胞NO含量的影响。
1.2.5 细胞因子分泌水平的测定
参考Li等[17]实验方法,吸取收集细胞培养上清液,参照ELISA试剂盒说明书,绘制标准曲线(TNF-α:y=0.001x+0.0769,R2=0.9973;IFN-γ:y=0.0012x+0.2183,R2=0.9879;IL-1β:y=0.0033x+0.1259,R2=0.9989),分析小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞上清液中TNF-α、IFN-γ和IL-1β细胞因子的分泌水平。
1.3 数据处理
数据统计通过SPSS Statistics 17.0分析软件进行,组间两两比较采用独立样本t检验,多组间比较采用ANOVA方差分析,结果以
2. 结果与分析
2.1 苦丁茶冬青多糖对小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞增殖的影响
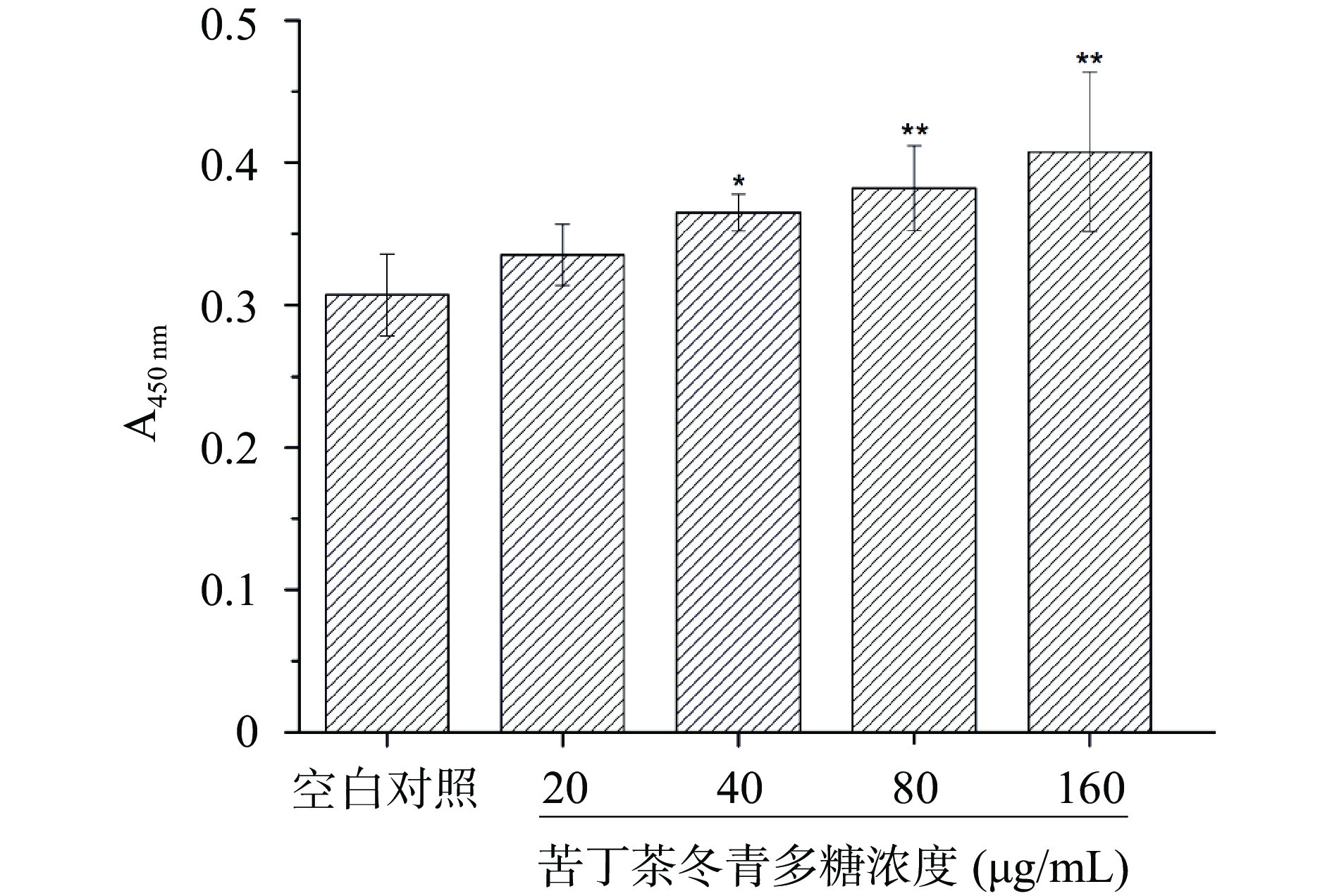
如图1所示,与空白对照组(0.31)相比,20 μg/mL的低浓度苦丁茶冬青多糖处理后小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞溶液的吸光度为0.34,作用效果无显著性差异(P>0.05);当浓度为40 μg/mL时,吸光度值为0.36,与空白对照组相比具有显著性差异(P<0.05);在80和160 μg/mL浓度时,吸光度值分别为0.38和0.41,与对照组相比,脾脏淋巴细胞的增殖作用具有极显著差异(P<0.01)。结果表明,苦丁茶冬青多糖可能直接作用于脾脏淋巴细胞,促进细胞的增殖功能,提高机体的免疫力。
CCK-8法是一种最常用的淋巴细胞增殖检测方法[18]。李芳宇等[19]采用CCK-8法检测细胞的增殖情况,发现人参根提取物能显著增强小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞的增殖能力。庞敏等[20]利用CCK-8法探讨术芩总多糖对免疫抑制小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞增殖的影响,结果显示浓度为0.1 μg/mL的术芩总多糖作用小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞12 h,细胞的增殖能力最强。孙延斌等[21]发现苦丁茶可促进免疫功能低下小鼠抗体生成水平和巨噬细胞的吞噬能力,调节机体免疫功能。本研究表明,苦丁茶冬青多糖能显著提高小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞的体外增殖能力(P<0.05),推断其可能通过增强小鼠淋巴细胞增殖能力以发挥其免疫调节作用。
2.2 苦丁茶冬青多糖对小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞抗氧化能力的影响
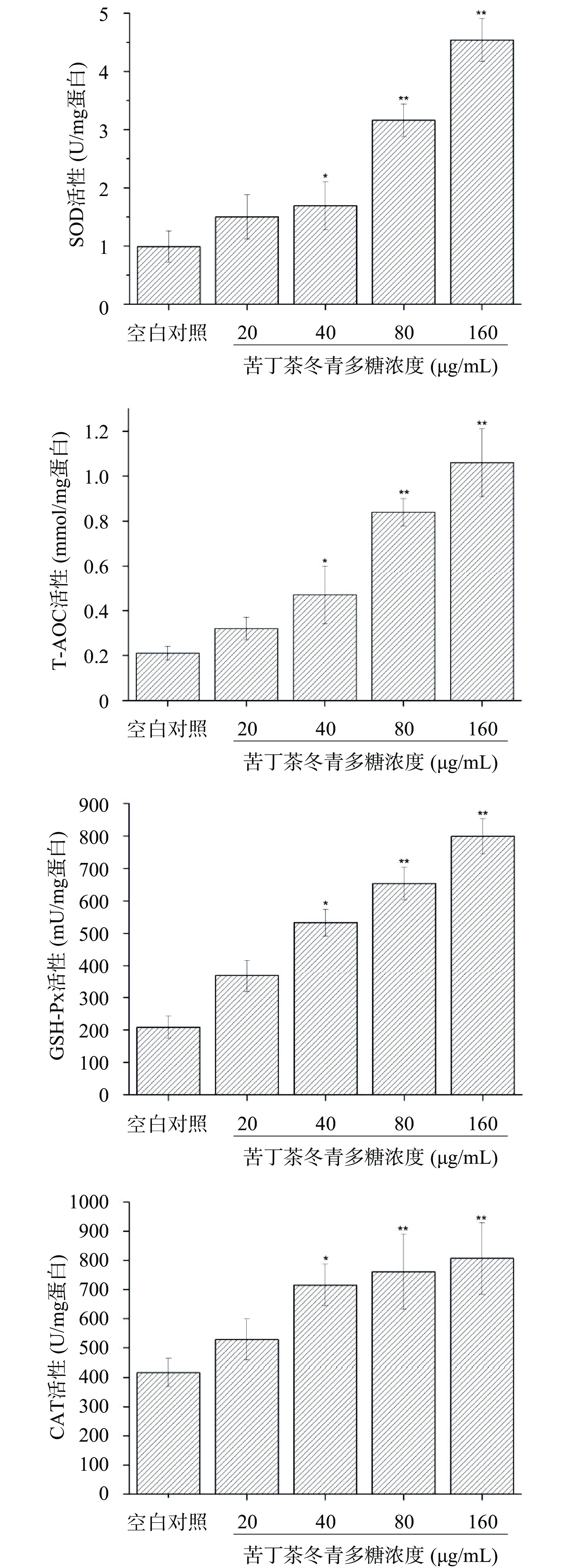
由图2可知,空白对照组SOD、T-AOC、GSH-Px和CAT活性分别为0.99 U/mg蛋白、0.21 mmol/mg蛋白、208.06 mU/mg蛋白和416.83 U/mg蛋白。苦丁茶冬青多糖浓度在20~160 μg/mL范围内,SOD、T-AOC、GSH-Px和CAT活力随浓度的增加而升高,当浓度为80和160 μg/mL时,与对照组相比,抗氧化酶活力极显著增强(P<0.01);其中,当浓度为160 μg/mL时,SOD、T-AOC、GSH-Px和CAT活性分别提高至4.54 U/mg蛋白、1.06 mmol/mg蛋白、799.01 mU/mg蛋白和806.85 U/mg蛋白。
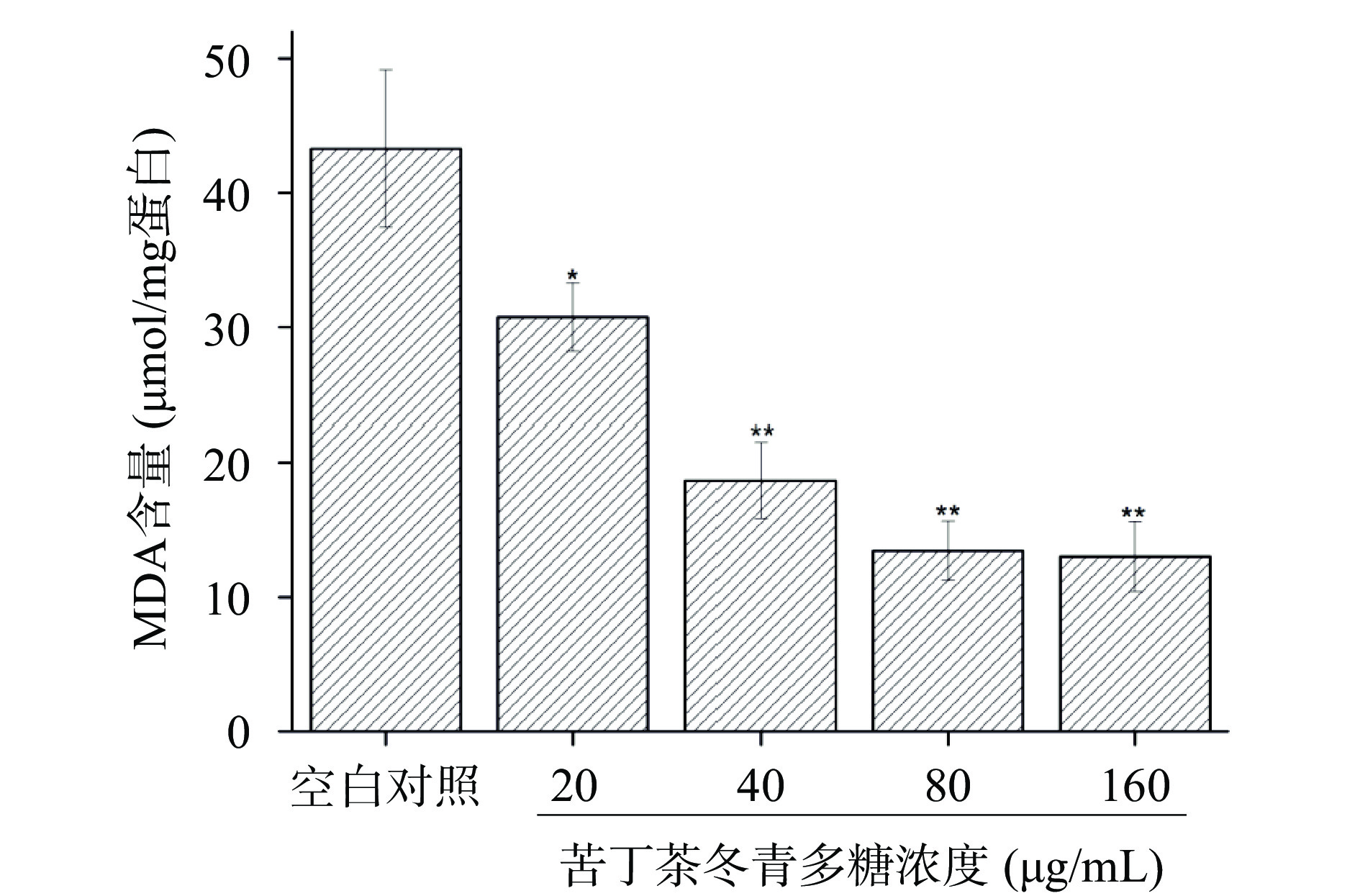
图3结果显示,空白对照组MDA含量为43.29 μmol/mg蛋白,苦丁茶冬青多糖浓度为20 μg/mL时,MDA含量下降至30.76 μmol/mg蛋白,具有显著降低效果(P<0.05);在40、80和160 μg/mL浓度时,MDA含量分别降到18.67、13.44和13.022 μmol/mg蛋白,具有极显著降低效果(P<0.01)。
机体抗氧化系统与免疫系统密不可分,当机体氧化自由基的产生大于自身自由基的清除时,就会造成氧化损伤,诱导机体保护性免疫反应。SOD、GSH-Px和CAT等是机体防御氧化损伤的关键酶,在维持体内的氧化与自由基动态平衡中发挥着重要作用[22]。丙二醛(MDA)是衡量机体自由基代谢程度的重要指标[23]。华岩[24]的研究结果显示,补充黄精多糖的运动组MDA含量明显降低,而SOD、GSH-Px活性相较于运动组明显升高,表明黄精多糖能改善受损细胞膜功能,降低大强度运动导致的脂质过氧化损伤。团队前期研究发现苦丁茶多糖具有较强的DPPH自由基和OH-自由基清除能力,本研究发现,苦丁茶冬青多糖对小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞SOD、T-AOC、GSH-Px和CAT活力具有显著增强作用,并显著降低MDA含量,该结果表明苦丁茶冬青多糖能够提高抗氧化酶活性、抑制细胞的氧化损伤水平,调节细胞的免疫功能。
2.3 苦丁茶冬青多糖对小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞NO分泌水平的影响
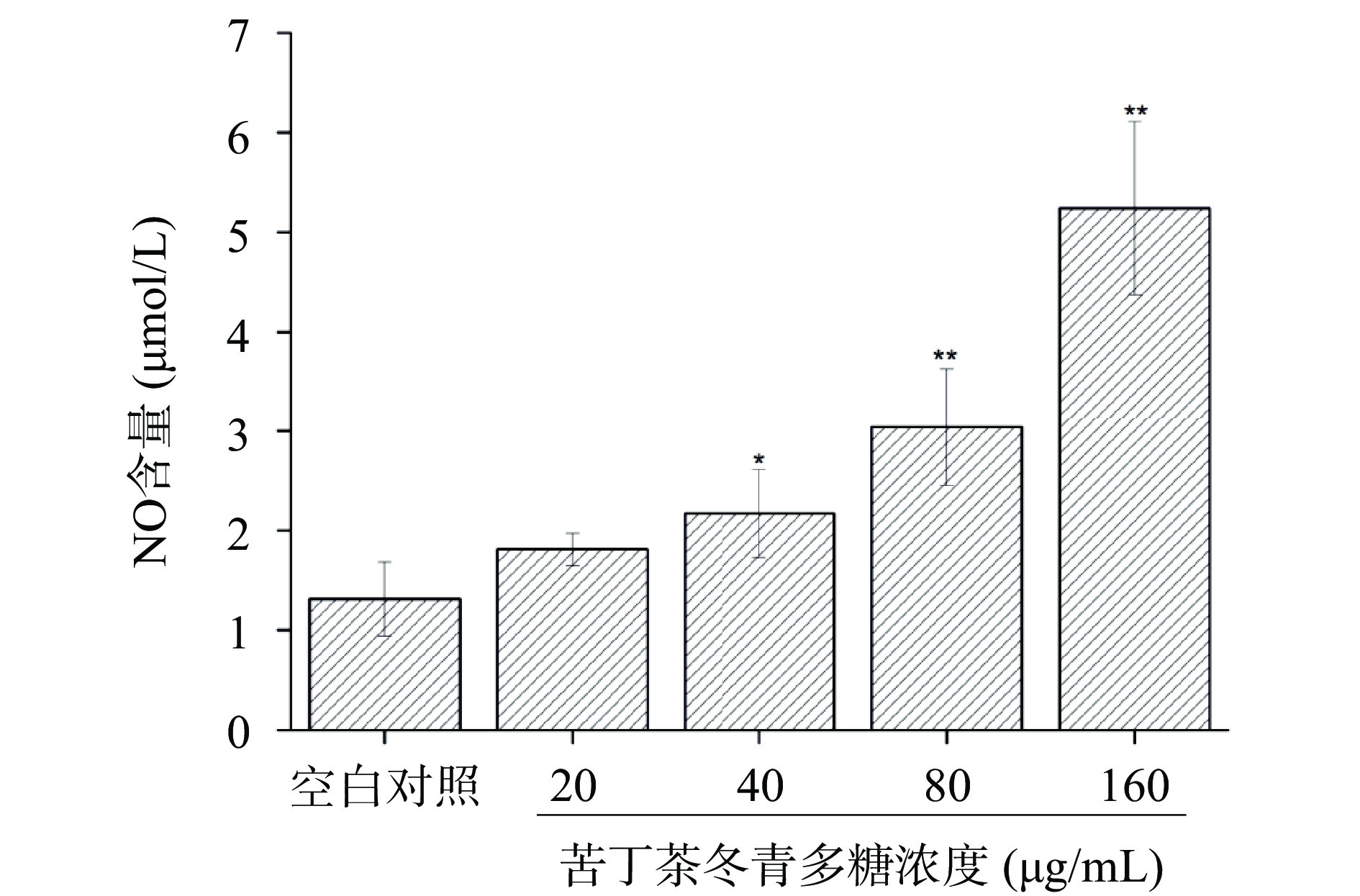
如图4所示,苦丁茶冬青多糖能刺激脾脏淋巴细胞分泌NO,与空白对照组相比,苦丁茶冬青多糖浓度为20、40、80、160 μg/mL时可分别提高小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞NO含量1.38倍、1.62倍、2.31倍和4.04倍。浓度高于40 μg/mL时,NO分泌效果呈显著增强趋势(P<0.05)。
NO被认为是一种细胞神经递质,能发挥非特异性免疫反应,可调节多种免疫功能,包括T淋巴细胞、巨噬细胞和NK细胞以及炎性细胞的生长和凋亡等[25]。研究表明,金线莲多糖[26]、蕨麻多糖[27]和金樱子多糖[28]可促进小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞分泌NO;山豆根多糖能诱导淋巴细胞产生NO,并通过NO信号转导通路发挥免疫调节功能[29]。本研究结果表明苦丁茶冬青多糖对小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞分泌NO具有较强的促进作用,有助于增强其免疫调节能力。
2.4 苦丁茶冬青多糖对小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞分泌细胞因子的影响
如表1所示,空白对照组TNF-α、IFN-γ和IL-1β的含量分别为475.75、41.85和42.31 pg/mL。经苦丁茶冬青多糖处理后,脾脏淋巴细胞TNF-α、IFN-γ和IL-1β等炎性细胞因子分泌水平均呈现增加趋势,且呈浓度依赖性。在浓度为20 μg/mL时,苦丁茶冬青多糖对细胞因子TNF-α、IFN-γ和IL-1β均无显著的促进作用(P>0.05);在浓度为160 μg/mL时,苦丁茶冬青多糖对TNF-α、IFN-γ和IL-1β的分泌水平极显著增加(P<0.01),分别达到610.91、129.33和84.16 pg/mL。推断苦丁茶冬青多糖能够促进脾脏淋巴细胞的增殖与分化,进而通过促进脾脏淋巴细胞分泌TNF-α、IFN-γ和IL-1β以发挥免疫增强作用。
表 1 苦丁茶冬青多糖对体外培养脾脏淋巴细胞分泌细胞因子的影响Table 1. Effect of polysaccharide of Ilex kudingcha C.J. Tseng on cytokine secretion in spleen lymphocytes in vitro组别 TNF-α
(pg/mL)IFN-γ
(pg/mL)IL-1β
(pg/mL)空白对照 475.75±24.87 41.85±5.38 42.31±11.49 苦丁茶冬青多糖
浓度(μg/mL)20 518.79±22.98 76.39±12.73 52.14±5.76 40 549.01±23.28 93.89±21.30* 64.01±8.33* 80 579.35±46.27* 113.97±8.40** 79.26±16.46** 160 610.91±40.44** 129.33±11.99** 84.16±10.49** 脾脏淋巴细胞中含大量的T细胞,T细胞被活化后会分泌TNF-α、IFN-γ和IL-1β等多种细胞因子,而当这些细胞因子分泌量上升时,亦促进T细胞激活[30-31]。T细胞主要分为CD4+和CD8+亚群,其中,CD4+细胞又分为Th1及Th2亚群,Th1细胞主要分泌IFN-γ,Th2细胞主要分泌IL-1β等细胞因子,参与细胞免疫调节[32]。大量研究发现多糖具有调节细胞因子分泌的功能,如太子参参须多糖[33]能够促进免疫功能低下小鼠分泌IL-2和IFN-γ;悬钩子木多糖[34]可以促进淋巴细胞分泌IL-2、IFN-γ和TNF-α;金针菇子实体多糖[35]可以提高IL-1β、IL-6和TNF-α的分泌水平。本研究结果表明,苦丁茶冬青多糖可能通过调节Th1/Th2平衡,促进小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞TNF-α、IFN-γ和IL-1β的分泌,通过诱导细胞因子的分泌发挥其免疫调节作用。
3. 结论
本文通过分析苦丁茶冬青多糖对体外培养小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞增殖、抗氧化和细胞因子分泌的影响,脾脏淋巴细胞的增殖分别为0.34、0.36、0.38和0.41;浓度为160 μg/mL时,SOD、T-AOC、GSH-Px和CAT活性分别提高至4.54 U/mg蛋白、1.06 mmol/mg蛋白、799.01 mU/mg蛋白和806.85 U/mg蛋白,MDA含量降至13.022 μmol/mg蛋白;TNF-α、IFN-γ和IL-1β的含量分别从475.75、41.85和42.31 pg/mL增加到610.91、129.33和84.16 pg/mL。研究表明苦丁茶冬青多糖能够提高小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞免疫活性,其作用机制可能是通过促进淋巴细胞增殖、增强细胞抗氧化能力及诱导炎性细胞因子分泌等途径,发挥其免疫调节作用。研究结果可为苦丁茶冬青及同类资源的营养健康产品开发和应用奠定理论基础,在未来研究中,将从免疫调节通路和分子机制进行深入研究和探讨。
-
表 1 苦丁茶冬青多糖对体外培养脾脏淋巴细胞分泌细胞因子的影响
Table 1 Effect of polysaccharide of Ilex kudingcha C.J. Tseng on cytokine secretion in spleen lymphocytes in vitro
组别 TNF-α
(pg/mL)IFN-γ
(pg/mL)IL-1β
(pg/mL)空白对照 475.75±24.87 41.85±5.38 42.31±11.49 苦丁茶冬青多糖
浓度(μg/mL)20 518.79±22.98 76.39±12.73 52.14±5.76 40 549.01±23.28 93.89±21.30* 64.01±8.33* 80 579.35±46.27* 113.97±8.40** 79.26±16.46** 160 610.91±40.44** 129.33±11.99** 84.16±10.49** -
[1] TZIANABOS A O. Polysaccharide immunomodulators as therapeutic agents: Structural aspects and biologic function[J]. Clinical Microbiology Reviews,2000,13(4):523−533. doi: 10.1128/CMR.13.4.523
[2] 于悦, 陈卓, 王亚非, 等. 蛹虫草胞外多糖的制备、结构分析及其免疫活性[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(23):106−113. [YU Yue, CHEN Zhuo, WANG Yafei, et al. Preparation, structure and immune activity of exopolysaccharide from Cordyceps militaris[J]. Food Science,2021,42(23):106−113. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20201017-156 YU Yue, CHEN Zhuo, WANG Yafei, et al. Preparation, structure and immune activity of exopolysaccharide from Cordyceps militaris[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42 (23): 106-113. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20201017-156
[3] 乌英, 李亚童, 聂昌宏, 等. 库尔勒香梨粗多糖的免疫调节作用研究[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2021,12(4):1405−1411. [WU Ying, LI Yatong, NIE Changhong, et al. Immunoregulation effect of crude polysaccharides from Korla fragrant pear[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2021,12(4):1405−1411. doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2021.04.031 WU Ying, LI Yatong, NIE Changhong, et al. Immunoregulation effect of crude polysaccharides from Korla fragrant pear[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality, 2021, 12(4): 1405-1411. doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2021.04.031
[4] 周惠萍, 周东海, 彭宇轩. 苦瓜多糖对环磷酰胺诱导的免疫抑制小鼠免疫功能的影响[J]. 湖北科技学院学报(医学版),2021,35(1):5−8. [ZHOU Huiping, ZHOU Donghai, PENG Yuxuan. Effects of Momordica Charantia polysaccharide on cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppressive mice[J]. Journal of Hubei University of Science and Technology (Medical Sciences),2021,35(1):5−8. ZHOU Huiping, ZHOU Donghai, PENG Yuxuan. Effects of Momordica Charantia polysaccharide on cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppressive mice[J]. Journal of Hubei University of Science and Technology (Medical Sciences), 2021, 35(1): 5-8.
[5] 易帆, 彭勇, 许利嘉, 等. 大叶苦丁茶的研究进展[J]. 中国现代中药,2013,15(8):710−717. [YI Fan, PENG Yong, XU Lijia, et al. Research progress on large-leaved Kudingcha[J]. Modern Chinese Medicine,2013,15(8):710−717. doi: 10.13313/j.issn.1673-4890.2013.08.009 YI Fan, PENG Yong, XU Lijia, et al. Research progress on large-leaved Kudingcha[J]. Modern Chinese Medicine, 2013, 15(8): 710-717. doi: 10.13313/j.issn.1673-4890.2013.08.009
[6] ZHANG T T, ZHENG C Y, HU T, et al. Polyphenols from Ilex latifolia Thunb. (a Chinese bitter tea) exert anti-atherosclerotic activity through suppressing NF-κB activation and phosphorylation of ERK1/2 in macrophages[J]. Medchemcomm,2018,9(2):254−263. doi: 10.1039/C7MD00477J
[7] CHEN G, XIE M, DAI Z, et al. Kudingcha and fuzhuan brick tea prevent obesity and modulate gut microbiota in high-fat diet fed mice[J]. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research,2018,62(6):1700485.
[8] YI R, ZHANG J, SUN P, et al. Protective effects of kuding tea (Ilex kudingcha C. J. Tseng) polyphenols on UVB-induced skin aging in skh1 hairless mice[J]. Molecules,2019,24(6):1016. doi: 10.3390/molecules24061016
[9] 许实波, 蒋建敏, 许东晖, 等. 苦丁茶水提物的毒理学研究[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版),2001,40(3):92−94, 111. [XU Shibo, JIANG Jianmin, XU Donghui, et al. The toxicological studies of Kudingcha Ilex latifolia thunb water extractive on mice and rats[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni,2001,40(3):92−94, 111. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0529-6579.2001.03.024 XU Shibo, JIANG Jianmin, XU Donghui, et al. The toxicological studies of Kudingcha Ilex latifolia thunb water extractive on mice and rats[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2001, 40(3): 92-94, 111. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0529-6579.2001.03.024
[10] LI J, LIU R, WU T, et al. A comparison of the inhibitory effects of different tea polysaccharides on the differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes[J]. Food Science,2017,21(38):187−194.
[11] 朱科学, 朱红英, 贺书珍, 等. 苦丁茶冬青粗多糖的分离表征及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 热带作物学报,2016,37(10):2014−2019. [ZHU Kexue, ZHU Hongying, HE Shuzhen, et al. Characterization and antioxidant activities of crude polysaccharides isolated from Ilex kudingcha C. J. Tseng[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops,2016,37(10):2014−2019. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2016.10.027 ZHU Kexue, ZHU Hongying, HE Shuzhen, et al. Characterization and antioxidant activities of crude polysaccharides isolated from Ilex kudingcha C. J. Tseng[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2016, 37(10): 2014-2019. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2016.10.027
[12] 韦晓洁, 银慧慧, 孟菲, 等. 超临界CO2流体萃取苦丁茶多糖的工艺优化[J]. 广西植物,2018,38(5):590−595. [WEI Xiaojie, YIN Huihui, MENG Fei, et al. Supercritical CO2 fluid extraction process optimization for polysaccharides from Ilex kudingcha[J]. Guihaia,2018,38(5):590−595. doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201706021 WEI Xiaojie, YIN Huihui, MENG Fei, et al. Supercritical CO2 fluid extraction process optimization for polysaccharides from Ilex kudingcha[J]. Guihaia, 2018, 38( 5) : 590-595 doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201706021
[13] 于淑池, 陈文, 杭瑜瑜, 等. 海南苦丁茶多糖的降血糖功效评价[J]. 食品研究与开发,2017,38(4):161−164. [YU Shuchi, CHEN Wen, HANG Yuyu, et al. An evaluation on the hypoglycemic efficacy of polysaccharide from Hainan Kuding tea[J]. Food Research and Development,2017,38(4):161−164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2017.04.036 YU Shuchi, CHEN Wen, HANG Yuyu, et al. An evaluation on the hypoglycemic efficacy of polysaccharide from Hainan Kuding tea[J]. Food Research and Development, 2017, 38(4): 161-164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2017.04.036
[14] 朱科学, 赵书凡, 朱红英, 等. 苦丁茶冬青不同萃取组分降血脂活性的比较[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(8):330−334. [ZHU Kexue, ZHAO Shufan, ZHU Hongying, et al. A comparative study on the hypolipidemic activities of various solvent extracts derived from Ilex kudingcha C. J. Tseng[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(8):330−334. ZHU Kexue, ZHAO Shufan, ZHU Hongying, et al. A comparative study on the hypolipidemic activities of various solvent extracts derived from Ilex kudingcha C. J. Tseng[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2017, 38 (8): 330-334.
[15] 赵书凡, 朱科学, 朱红英, 等. 苦丁茶冬青多糖乙醇分级纯化及其理化性质研究[J]. 热带农业科学,2017,37(4):80−86. [ZHAO Shufan, ZHU Kexue, ZHU Hongying, et al. Ethanol fractionation and physico-chemical properties of soluble polysaccharides from Ilex kudingcha C. J. Tseng[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Agriculture,2017,37(4):80−86. ZHAO Shufan, ZHU Kexue, ZHU Hongying, et al. Ethanol fractionation and physico-chemical properties of soluble polysaccharides from Ilex kudingcha C. J. Tseng[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Agriculture, 2017, 37(4), 80-86.
[16] 朱科学, 聂少平, 李文娟, 等. 黑灵芝多糖对小鼠脾淋巴细胞增殖及诱生细胞因子的影响[J]. 食品科学,2010,31(19):351−354. [ZHU Kexue, NIE Shaoping, LI Wenjuan, et al. Effect of polysaccharides from Ganoderma atrum on spleen lymphocyte proliferation and induction of cytokine in mice[J]. Food Science,2010,31(19):351−354. ZHU Kexue, NIE Shaoping, LI Wenjuan, et al. Effect of polysaccharides from Ganoderma atrum on spleen lymphocyte proliferation and induction of cytokine in mice[J]. Food Science, 2010, 31(19): 351-354.
[17] LI C, YAN Q, TANG S, et al. Alteration of mevalonate pathway in rat splenic lymphocytes: Possible role in cytokines secretion regulated by L-Theanine[J]. BioMed Research International,2018,2018(10):1−8.
[18] ZHANG Y, ZHAI W, ZHAO M, et al. Effects of iron overload on the bone marrow microenvironment in mice[J]. PloS One,2015,10(3):e120219.
[19] 李芳宇, 齐滨, 边帅, 等. 人参根提取物对小鼠脾淋巴细胞自噬、增殖和细胞因子分泌的影响及机制研究[J]. 中国药房,2020,31(21):2597−2602. [LI Fangyu, QI Bin, BIAN Shuai, et al. Study on the effects of ginseng root extract on autophagy, proliferation and cytokine secretion of mice splenic lymphocytes and its mechanism[J]. China Pharmacy,2020,31(21):2597−2602. doi: 10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2020.21.07 LI Fangyu, QI Bin, BIAN Shuai, et al. Study on the effects of ginseng root extract on autophagy, proliferation and cytokine secretion of mice splenic lymphocytes and its mechanism[J]. China Pharmacy, 2020, 31(21): 2597-2602. doi: 10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2020.21.07
[20] 庞敏, 朱兆荣, 乔芊芊, 等. 术芩总多糖对免疫低下小鼠脾淋巴细胞增殖与自噬的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报,2018,49(12):2762−2770. [PANG Min, ZHU Zhaorong, QIAO Qianqian, et al. Effect of polysaccharides from Zhuqin formula on the proliferation and autophagy of spleen lymphocyte in immunocompromised mice[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica,2018,49(12):2762−2770. doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2018.12.026 PANG Min, ZHU Zhaorong, QIAO Qianqian, et al. Effect of polysaccharides from ZhuQin formula on the proliferation and autophagy of spleen lymphocyte in immunocompromised mice[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2018, 49(12): 2762-2770. doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2018.12.026
[21] 孙延斌, 王淑秋, 于新慧, 等. 苦丁茶对小鼠免疫功能的调节研究[J]. 牡丹江医学院学报,2009,30(2):14−16. [SUN Yanbin, WANG Shuqiu, YU Xinhui, et al. The effect of Ilex latifolia thumb on immune function in mouse[J]. Journal of Mudanjiang Medical College,2009,30(2):14−16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7550.2009.02.006 SUN Yanbin, WANG Shuqiu, YU Xinhui, et al. The effect of Ilex latifolia thumb on immune function in mouse[J]. Journal of Mudanjiang Medical College, 2009, 30(2): 14-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7550.2009.02.006
[22] RUAN J, ZHANG Y, YUAN J, et al. A long-term high-fat, high-sucrose diet in Bama minipigs promotes lipid deposition and amyotrophy by up-regulating the myostatin pathway[J]. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology,2016,425:123−132. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2016.02.001
[23] 王君巧, 聂少平, 余强, 等. 黑灵芝多糖对免疫抑制小鼠的免疫调节和抗氧化作用[J]. 食品科学,2012,33(23):274−277. [WANG Junqiao, NIE Shaoping, YU Qiang, et al. Immune modulation and antioxidation activity of polysaccharides from Ganoderma atrum in immunosuppressed mice[J]. Food Science,2012,33(23):274−277. WANG Junqiao, NIE Shaoping, YU Qiang, et al. Immune modulation and antioxidation activity of polysaccharides from Ganoderma atrum in immunosuppressed mice[J]. Food Science, 2012, 33(23): 274-277.
[24] 华岩. 黄精多糖对大强度运动大鼠肾脏损伤的调理作用[J]. 扬州大学学报(农业与生命科学版),2020,41(1):50−54. [HUA Yan. Regulatory effect of polysaccharides on kidney injury induced by high-intensity exercise rats[J]. Journal of Yangzhou University (Agricultural and Life Science Edition),2020,41(1):50−54. HUA Yan. Regulatory effect of polysaccharides on kidney injury induced by high-intensity exercise rats[J]. Journal of Yangzhou University (Agricultural and Life Science Edition), 2020, 41(1): 50-54.
[25] 于思文, 张妍, 田海玲, 等. 黄精粗多糖对体外培养小鼠脾淋巴细胞及巨噬细胞免疫活性的影响[J]. 延边大学医学学报,2019,42(2):107−110. [YU Siwen, ZHANG Yan, TIAN Hailing, et al. Effects of crude polysaccharide from Polygonatum sibiricum on the immune activity of mouse spleen lymphocytes and macrophages cultured in vitro[J]. Journal of Medical Science Yanbian University,2019,42(2):107−110. YU Siwen, ZHANG Yan, TIAN Hailing, et al. Effects of crude polysaccharide from Polygonatum sibiricum on the immune activity of mouse spleen lymphocytes and macrophages cultured in vitro[J]. Journal of Medical Science Yanbian University, 2019, 42(2): 107-110.
[26] 马玉芳, 郑小香, 衣伟萌, 等. 金线莲多糖对免疫抑制小鼠脾淋巴细胞体外增殖、分泌NO及细胞因子的影响[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2018,30(1):21−26. [MA Yufang, ZHENG Xiaoxiang, YI Weimeng, et al. Effects of Anoectochilus roxburghii polysaccharide on splenic lymphocytes proliferation, NO and cytokine secretion in immunosuppressed mice in vitro[J]. Nat Prod Res Dev,2018,30(1):21−26. MA Yufang, ZHENG Xiaoxiang, YI Weimeng, et al. Effects of Anoectochilus roxburghii polysaccharide on splenic lymphocytes proliferation, NO and cytokine secretion in immunosuppressed mice in vitro[J]. Nat Prod Res Dev, 2018, 30(1): 21-26.
[27] 陈炅然, 胡庭俊, 程富胜, 等. 蕨麻多糖对小鼠淋巴细胞增殖和一氧化氮分泌的影响[J]. 中国兽医科技,2005(9):735−738. [CHEN Jiongran, HU Tingjun, CHENG Fusheng, et al. Effect of Potentilla anserine polysaccharide on proliferation of splenic lymphocytes and production of nitric oxide in mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science and T echnology,2005(9):735−738. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4696.2005.09.015 CHEN Jiongran, HU Tingjun, CHENG Fusheng, et al. Effect of Potentilla anserine polysaccharide on proliferation of splenic lymphocytes and production of nitric oxide in mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science and T echnology, 2005(9): 735-738. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4696.2005.09.015
[28] 皮建辉, 谭娟, 胡朝暾. 金樱子多糖的体外免疫活性研究[J]. 华西药学杂志,2014,29(2):149−151. [PI Jianhui, TAN Juan, HU Zhaotun. Study on in vitro immune activity of Rosa laevigata polysaccharide[J]. West China Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences,2014,29(2):149−151. PI Jianhui, TAN Juan, HU Zhaotun. Study on in vitro immune activity of rosa laevigata polysaccharide[J]. West China Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2014, 29(2): 149-151.
[29] 胡庭俊, 康乐, 帅学宏, 等. 山豆根多糖对小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞体外增殖及分泌一氧化氮的影响[J]. 中药药理与临床,2009,25(5):70−72. [HU Tingjun, KANG Le, SHUAI Xuehong, et al. The effect of Sophora subprosrate polysaccharide on proliferation and nitric oxide release of splenic lymphocytes from mice[J]. Pharmacology and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica,2009,25(5):70−72. HU Tingjun, KANG Le, SHUAI Xuehong, et al. The effect of Sophora subprosrate polysaccharide on proliferation and nitric oxide release of splenic lymphocytes from mice[J]. Pharmacology and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica, 2009, 25(5): 70-72.
[30] FORT M M, CHEUNG J, YEN D, et al. IL-25 induces IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 and Th2-associated pathologies in vivo[J]. Immunity,2001,15(6):985−995. doi: 10.1016/S1074-7613(01)00243-6
[31] 郑乃珍, 郑小香, 潘晓丽, 等. 猴头菇多糖协同ConA对小鼠脾细胞分泌Th1、Th2细胞因子及基因表达的影响[J]. 中国兽医学报,2016,36(5):795−800. [ZHENG Naizhen, ZHENG Xiaoxiang, PAN Xiaoli, et al. The effect of synergistical stimulation of Hericium erinaceus polysaccharide with ConA on secretion and mRNA expression of Th1 and Th2 type cytokine of murine splenic lymphocyte[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science,2016,36(5):795−800. ZHENG Naizhen, ZHENG Xiaoxiang, PAN Xiaoli, et al. The effect of synergistical stimulation of Hericium erinaceus polysaccharide with ConA on secretion and mRNA expression of Th1 and Th2 type cytokine of murine splenic lymphocyte[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2016, 36(5): 795-800.
[32] SONG C, HALBREICH U, HAN C, et al. Imbalance between pro-and anti-inflammatory cytokines, and between Th1 and Th2 cytokines in depressed patients: The effect of electroacupuncture or fluoxetine treatment[J]. Pharmacopsychiatry,2009,42(5):182−188. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1202263
[33] 闵思明, 赵晓瑶, 陈赛红, 等. 太子参参须多糖对免疫抑制小鼠的免疫调节作用研究[J]. 动物医学进展,2020,41(8):23−28. [MIN Siming, ZHAO Xiaoyao, CHEN Saihong, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of Radix Pseudostellariae fibrous root polysaccharides on cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppressed mice[J]. Progress In Veterinary Medicine,2020,41(8):23−28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5038.2020.08.005 MIN Siming, ZHAO Xiaoyao, CHEN Saihong, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of Radix Pseudostellariae fibrous root polysaccharides on cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppressed mice[J]. Progress In Veterinary Medicine, 2020, 41(8): 23-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5038.2020.08.005
[34] 刘贝女, 张屏, 吴迎香, 等. 悬钩子木多糖的分离纯化及免疫调节活性研究[J]. 中草药,2019,50(24):5941−5949. [LIU Beinv, ZHANG Ping, WU Yingxiang, et al. Separation, purification and immunomodulatory activity of polysaccharides from Rubus sachalinensis[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2019,50(24):5941−5949. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2019.24.005 LIU Beinv, ZHANG Ping, WU Yingxiang, et al. Separation, purification and immunomodulatory activity of polysaccharides from Rubus sachalinensis[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2019, 50(24): 5941-5949. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2019.24.005
[35] 刘肖肖, 汪雯翰, 冯婷, 等. 金针菇子实体多糖FVPB1对小鼠T细胞和巨噬细胞的免疫调节作用[J]. 食用菌学报,2019,26(4):123−130. [LIU Xiaoxiao, WANG Wenhan, FENG Ting, et al. Immunomodulatory effect of Homogeneous polysaccharide FVPB1 from fruiting body of Lammulina velutipes on mouse T cells and macrophages[J]. Acta Edulis Fungi,2019,26(4):123−130. LIU Xiaoxiao, WANG Wenhan, FENG Ting, et al. Immunomodulatory effect of Homogeneous polysaccharide FVPB1 from fruiting body of Lammulina velutipes on mouse T cells and macrophages[J]. Acta Edulis Fungi, 2019, 26(4): 123-130.






 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
