Optimization Preparation and Property Analysis of Sulfate Polysaccharide from Eucheuma spinosum by Probiotic Fermentation
-
摘要: 为制备粘度低、溶解性高、生物利用度高的刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖,利用发酵食品中常见的益生菌鼠李糖乳杆菌(Lactobacillus rhamnosus)发酵刺麒麟菜制备发酵刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖(Fermented Eucheuma spinosum sulfate polysaccharide,F-ESP),借助响应面法以粗多糖得率为指标进一步优化制备工艺;以冷冻刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖(Low temperature freeze-thaw Eucheuma spinosum sulfate polysaccharide,L-ESP)为对照,经DEAE-52柱层析纯化后测定总糖、还原糖、硫酸根等物质的含量以及单糖组成,分析F-ESP的化学成分;测定粘度、溶解度、分子量及微观形貌,表征F-ESP的物理性质;利用红外光谱解析F-ESP的官能团结构;通过大鼠嗜碱性粒细胞脱颗粒实验评价F-ESP的抗过敏活性。当料液比为1:70,接菌量为5%,发酵时间为24 h时,F-ESP得率最高(41.70%±2.00%);经纯化的F-ESP-3单糖结构主要由半乳糖构成,总糖含量为97.77%±1.10%、硫酸根含量为28.40%±1.40%,与L-ESP-3相比,F-ESP-3还原糖含量(7.87%±0.09%)极显著提高(P<0.01)、分子量(33.58 kD)极显著降低(P<0.01)、比浓粘度(0.01±0.002 dL/g)极显著降低(P<0.01)、溶解度(89.33%±3.10%)极显著提高(P<0.01)、在扫描电镜下观察发现L-ESP-3为光滑致密的片状,F-ESP-3为粗糙的不规则颗粒状;发酵制备的F-ESP-3糖链结构并未发生改变,是一种含3,6内醚半乳糖残基的α-硫酸吡喃糖,且能够通过抑制β-氨基己糖苷酶释放从而抑制嗜碱性粒细胞的激活。综上所述,益生菌发酵可以作为刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖的制备方式,并通过改变其物理性质显著提高抗过敏活性。这一结果为刺麒麟菜多糖工业化生产和开发利用提供了数据支撑和理论依据。Abstract: To prepare Eucheuma spinosum sulfated polysaccharides with low viscosity, high solubility and high bioavailability, fermented Eucheuma spinosum sulfate polysaccharides (F-ESP) was prepared by fermenting Lactobacillus rhamnoides, a common probiotic bacteria in fermented food, response surface methodology was used to optimize the preparation process with the yield of crude polysaccharide as the index. Low temperature freeze-thaw Eucheuma spinosum sulfate polysaccharide (L-ESP) was used as control. After purification by DEAE-52 column chromatography, the contents of total sugar, reducing sugar, sulfate and other substances and monosaccharide composition were determined, and the chemical composition of F-ESP was analyzed. The physical properties of F-ESP were characterized by viscosity, solubility, molecular weight and microstructure. The functional group structure of F-ESP was analyzed by infrared spectroscopy. The antiallergic activity of F-ESP was evaluated by Rat Basophilic Leukemia-2H3 (RBL-2H3) degranulation assay. When the ratio of material to liquid was 1:70, the inoculation amount was 5%, and the fermentation time was 24 h, the yield of crude polysaccharide was the highest (41.70%±2.00%). The purified F-ESP-3 monosaccharide structure was mainly composed of galactose, and the total sugar content was 97.77%±1.10%. The sulfate content was 28.40%±1.40%. Compared with L-ESP-3, the reducing sugar content of F-ESP-3 (7.87%±0.09%) was significantly higher, the molecular weight (33.58 kD) was significantly decreased (P<0.01), the specific viscosity (0.01±0.002 dL/g) was significantly lower (P<0.01), and the solubility (89.33%±3.10%) was significantly higher (P<0.0l). Under scanning electron microscope, L-ESP-3 was smooth and dense flake, and F-ESP-3 was rough and irregular granule. The sugar chain structure of F-ESP-3 prepared by fermentation did not change. It was a kind of α-pyranose sulfate containing 3-methylether-galactose residue, and inhibit the activation of basophils by inhibit the release of β-hexosaminidase. To sum up, probiotic fermentation could be used as a way to prepare Eucheuma spinosum sulfated polysaccharides, and its anti-allergic activity could be significantly improved by changing its physical properties. This result provides data support and theoretical basis for the industrial production, development and utilization of Eucheuma spinosum polysaccharides.
-
近年来,海洋藻类作为丰富且重要的海洋生物资源,因含有糖类、多酚、蛋白质等丰富的天然活性物质,被广泛报道[1-2]。据《2021中国渔业统计年鉴》统计,2020年我国麒麟菜养殖产量高达3856吨,同比2019年增长818%。刺麒麟菜(Eucheuma spino- sum)属于红藻纲,红翎菜科,是生产卡拉胶的主要原材料,其富含的硫酸多糖在卡拉胶加工过程中一直被当作废弃物处理[3]。但硫酸基团被认为是酸性多糖主要的活性基团,硫酸多糖也被证实具有更高的生物活性[4],因此富含硫酸基团的刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖在食品工业与医药领域具有极大的发展潜力。
刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖的物理制备方式以热水浸提和低温冻融为主,常辅以超声破碎处理以提高得率,低温冻融刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖(Low temperature freeze-thaw Eucheuma spinosum sulfate polysaccha- ride,L-ESP)对比热提多糖粘度降低,溶解性提高,硫酸基团保护较好,但依旧存在着分子量大、生物利用度低等问题,往往给进一步加工利用带来困难。因此,刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖制备方式的开发备受关注。
益生菌不仅可以生产健康的发酵食品[5],益生菌与膳食互作更是被定为2020年益生菌科学研究十大热点之一[6]。有研究报道,采用益生菌发酵得到的多糖,生物活性物质溶出率显著提升,分子量降低,更易被肠道吸收[7-8],其生物活性也优于未发酵多糖[9-11]。鼠李糖乳杆菌(Lactobacillus rhamnosus)是一种益生菌菌株,常作为乳品[12]、饮料[13]、保健食品或饲料的原料或发酵剂被广泛使用。Wu等[14]利用鼠李糖乳杆菌发酵四种海藻,发现得到的海藻低聚糖(SwOS-LAFP)显示出更大的还原能力和亚铁离子螯合能力以及对过氧化氢的清除能力,抗氧化活性显著提高。综上所述,益生菌发酵已经应用于天然多糖的制备,但刺麒麟菜多糖的发酵制备工艺、性质特征、抗过敏活性以及相关的构效关系尚不明确。
因此本文利用鼠李糖乳杆菌发酵刺麒麟菜制备发酵刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖(Fermented Eucheuma spi- nosum、 sulfate polysaccharide,F-ESP),借助Box-Behnken响应面法进一步优化制备条件,并对其化学成分、物理性质和官能团结构进行进一步解析,通过大鼠嗜碱性粒细胞(Rat Basophilic Leukemia-2H3,RBL-2H3)经典脱颗粒模型初步评价其抗过敏活性,旨在为刺麒麟菜多糖工业化生产和功能食品的开发提供理论基础,为刺麒麟菜的高值化利用提供新思路。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
刺麒麟菜 绿新(福建)食品有限公司;鼠李糖乳杆菌(BNCC185356) 北京北纳创联生物技术研究院;RBL-2H3细胞 上海复祥生物技术有限公司;MEM液体培养基 美国HyClone公司;胎牛血清 美国Gemini生物科技公司;台氏缓冲液(PB180338) 武汉普诺赛生命科技有限公司;MRS培养基、DEAE-52纤维素 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;BCA蛋白检测试剂盒 上海碧云天生物技术有限公司;内毒素检测鲎试剂盒 厦门鲎试剂生物科技股份有限公司;MTT、β-氨基己糖苷酶底物、抗二硝基苯单克隆抗体小鼠抗 美国sigma公司;DNP-BSA 基因生物技术国际贸易(上海)有限公司;其他试剂为国产分析纯。
InfiniteM200PRO酶标仪 德国Tecan公司;NP80紫外分光光度计 德国IMPLEN公司;内径0.7~0.8 mm乌氏粘度计 上海宝山启航玻璃仪器厂;Waters 2695型高效液相色谱 美国Waters公司;Forma3111水套式CO2细胞培养箱 美国Thermo公司;SG-403生物安全柜 美国Baker公司;Nunc细胞培养板 美国Thermo公司;PhenomPro台式扫描电镜 美国Phenomworld公司;ALPHA傅里叶红外光谱仪 德国Bruker公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 发酵刺麒麟菜粗多糖的制备
刺麒麟菜淘洗去除泥沙后于50 ℃烘箱烘干,将干燥后的刺麒麟菜剪碎放入破壁机粉碎过100目筛,置于保鲜盒存放于阴凉干燥处待用。参考Zhang等[15]的方法稍作修改,将刺麒麟菜菜粉按照一定料液比与超纯水混合后,加入2.5%(w/w)的果葡糖浆,然后121 ℃高温灭菌20 min,冷却至室温后加入适量已活化的鼠李糖乳杆菌,于37 ℃厌氧发酵,然后100 ℃灭活10 min,于室温下8000 r/min离心10 min,收集上清。加入4倍体积的无水乙醇,4 ℃静置过夜,8000 r/min离心10 min得到沉淀,将沉淀复溶于超纯水,冷冻干燥后,即得到发酵刺麒麟菜粗多糖。参考陈玉芳等[16]的方法,将刺麒麟菜粉和超纯水按照料液比1:90混合,−18 ℃冷冻2 h,解冻温度55 ℃,反复冻融三次,制备冷冻刺麒麟菜多糖作为后续样品对照。
1.2.2 单因素实验设计
取刺麒麟菜10 g,固定接菌量为4%(v/v),发酵时间为24 h,探究料液比(w/v)为1:40、1:50、1:60、1:70,1∶80时对粗多糖得率的影响;固定料液比1:70、发酵时间为24 h,探究接菌量为0.5%、1%、2%、4%、8%时对粗多糖得率的影响;固定料液比1:70、接菌量4%,探究发酵6、12、18、24、30 h时对粗多糖得率的影响。粗多糖得率以冻干粗多糖质量与菜粉质量之比计算。
1.2.3 响应面法优化发酵刺麒麟菜粗多糖制备工艺
根据单因素实验结果,选取料液比、接菌量、发酵时间为自变量,以发酵刺麒麟菜粗多糖得率为响应值,以Box-Benhnken设计原理进行响应面试验设计(见表1),用Design Expert 12软件拟合因素与响应值之间的函数关系,分析回归方程从而预测最优工艺参数。
表 1 响应面试验设计的因素及水平Table 1. Factors and level of response surface test design水平 因素 A料液比(w/v) B接菌量(%) C发酵时间(h) −1 1:60 2 18 0 1:70 5 24 1 1:80 8 30 1.2.4 发酵刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖的分离纯化
按照最佳工艺发酵得到发酵刺麒麟菜粗多糖后,取1 g按10 mg/mL复溶于超纯水,上样于预装20 g的DEAE Cellulose-52的直径2.5 cm的层析柱,恒流泵流速设置为2 mL/min,依次用0、0.5、1、2 mol/L的氯化钠溶液阶段洗脱,每管收集5 mL。蒽酮硫酸比色法测定每管洗脱液在630 nm处的吸光度,并做出洗脱曲线,收集糖含量较高的部分,3 kDa透析膜透析72 h,冷冻干燥机冻干,即得到发酵刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖F-ESP;低温冻融刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖L-ESP纯化方式同上。
1.2.5 发酵刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖的化学组成分析
按照Zhang等[17]的方法进行单糖组成分析;以半乳糖为标准品,利用蒽酮硫酸显色法[18]对纯化后的发酵刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖和低温冻融刺麒麟菜多糖的总糖含量进行测定;参考赵凯等[19]的方法,利用3,5-二硝基水杨酸比色法测定还原糖含量;硫酸根含量参考Yu等[20]以K2SO4为标准品,利用Dodgson-Price法[21]进行测定;蛋白质含量参考Tang等[22]采用碧云天BCA蛋白检测试剂盒进行测定;利用鲎试剂内毒素检测试剂盒检测内毒素含量。
1.2.6 发酵刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖的物理性质分析
1.2.6.1 平均分子量的测定
参照Gong等[23]的方法利用高效凝胶渗透法(HPGPC),采用示差检测器,配制pH为6的20 mmol/L磷酸盐缓冲液为流动相,将标准品和样品按照2%(w/v)的浓度溶于磷酸盐缓冲液,分别进样于TSK-GELG4000 SWXL色谱柱,流速为0.4 mL/min,进样体积20 μL,对两种多糖样品的纯化产物的平均分子量进行测定。
1.2.6.2 溶解度的测定
称取纯化后的冻干样品200 mg置于烘干至恒重的15 mL离心管中,加入10 mL超纯水混合,室温下振荡30 min,使多糖样品充分溶解,将样液全部转移至50 mL容量瓶中,定容至刻度线后混匀。吸取10 mL于8000 r/min离心10 min,将上清液完全转入称量瓶中烘干,恢复至室温后称重。按照式(1)计算:
DSI(%)=(m2−m1)×5m0×100 (1) 式中:DSI溶解度(%);m0样品质量(g);m1称量瓶质量(g);m2烘干样品+瓶质量(g)。
1.2.6.3 比浓粘度的测定
在25 ℃恒温条件下,使用内径为0.7~0.8 mm的乌氏粘度计测定浓度为0.5 g/dL的L-ESP和F-ESP的比浓粘度(ηre),参照Liu等[24]的方法进行,每个样品独立测定5次,分别记录样液通过毛细管的时间,按照式(2)计算:
ηr=tt0;ηsp=ηr−η0η0;ηre=ηspC (2) 式中:t0纯水流经毛细管的时间(s);t样品流经毛细管的时间(s);η0纯水的粘度;ηr相对粘度;ηsp特性粘度;ηre比浓粘度(dL/g);C样品浓度(g/dL)。
1.2.6.4 扫描电镜分析
将多糖样品固定在载物台导电胶表面,将载物台转移至蒸金室,打开真空泵,达到真空度后,溅射仪喷金90 s,然后在放大倍数为500×、1000×、3000×条件下进行拍照,观察多糖样品的微观形貌。
1.2.7 发酵刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖的红外光谱分析
将样品与干燥的溴化钾以1:100比例混合后研磨,经手动压片后利用傅里叶红外光谱仪在400~4000 cm−1进行扫描[25]。
1.2.8 发酵刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖抗过敏活性评价
RBL-2H3细胞使用10% FBS-MEM在5% CO2,37 ℃下培养,并采用MTT试剂按照说明书检测不同浓度样品对细胞活力的影响;RBL-2H3细胞脱颗粒参考Zhang等[26]的方法,将RBL-2H3细胞计数后用10%的FBS-MEM稀释,按照5×104个/孔铺至96孔培养板,用终浓度0.1 μg/mL的anti-DNP-IgE敏化过夜,然后PBS洗涤一次,样品组加入不同浓度样品(10、25、50、100 μg/mL)的台氏缓冲液100 μL孵育1 h,然后向阳性组和样品组加入终浓度为0.5 μg/mL的DNP-BSA激发,阴性孔加入同体积的PBS缓冲液,1 h后收集上清,向板底加入含有0.1% TritionX-100的台氏缓冲液100 μL,裂解5 min,吹打均匀后吸取上清和裂解液各25 μL,置于黑色荧光板,加入100 μL 1.2 mmol/mL的β-氨基己糖苷酶底物,混匀后37 ℃孵育30 min,检测激发波长360 nm,发射波长450 nm条件下的吸光度值。β-氨基己糖苷酶抑制率按照式(3)、(4)计算:
脱颗粒效率(%)=OD上清OD上清+OD裂解×100 (3) 脱颗粒抑制率(%)=阳性脱颗粒效率−样品脱颗粒效率阳性脱颗粒效率−阴性脱颗粒效率×100 (4) 1.3 数据处理
实验结果均重复三次以上,数据以平均值±标准差(Mean ± SD)表示。采用SPSS 20.0软件中的图基检验(Tukeytest)进行差异显著性分析,P<0.05为差异显著,P<0.01为差异极其显著。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素实验结果
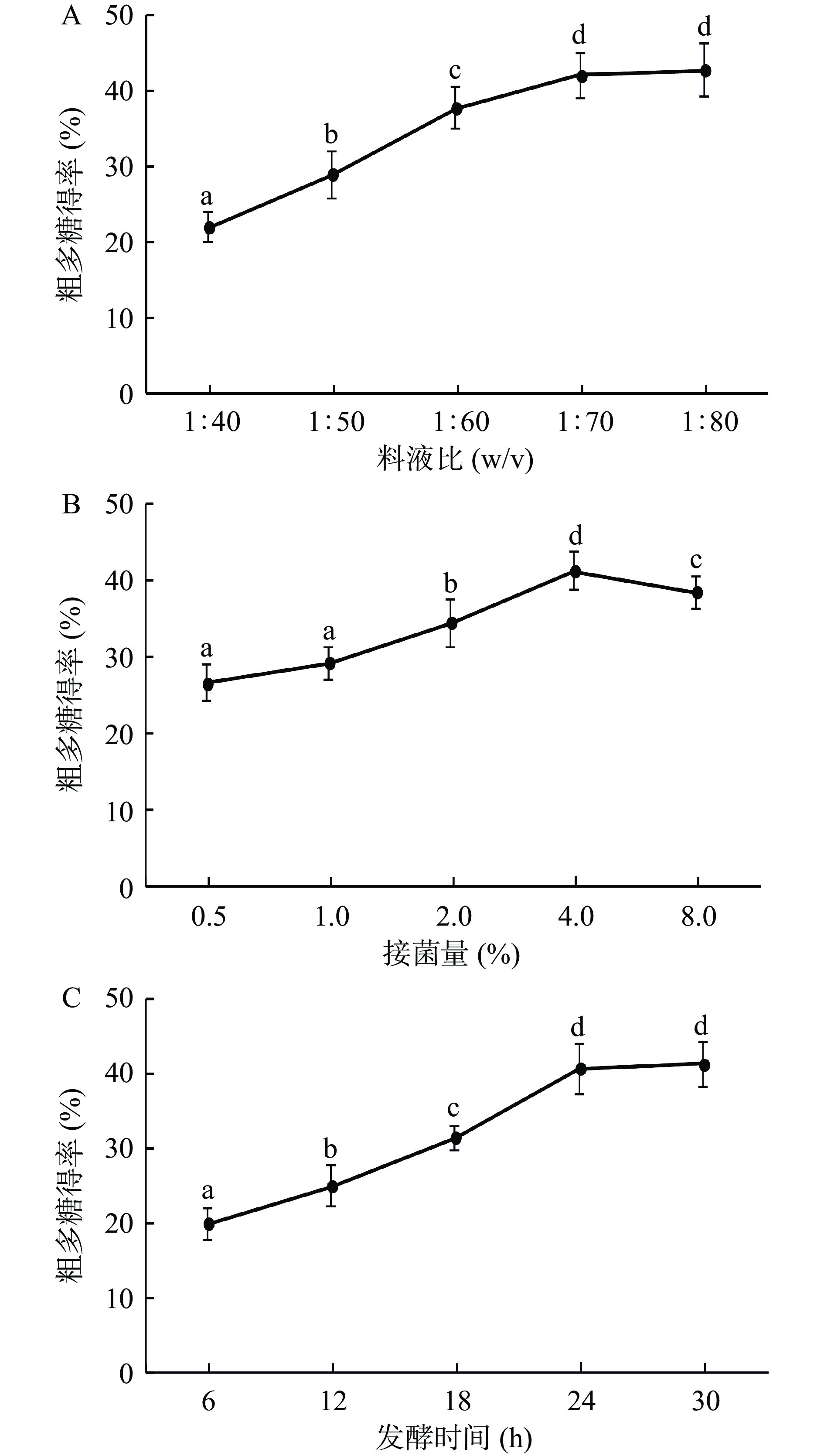
图1A所示,料液比不断增大,粗多糖得率呈现先快速增长后平缓的趋势,分析是因为料液比增大导致内外渗透压以及溶液饱和度的变化,当料液比为1:40时溶液极易达到饱和,且粘稠度高,不易于多糖的进一步析出,当液体体积不断增大至1:80,刺麒麟菜粉末与发酵液接触面积增大,多糖溶出率也随之上升,到达工艺上限。但料液比为1:70和1:80时,多糖得率差异不显著(P>0.05),因此选择1:70作为后续试验条件。
图1B所示,得率随着接菌量的增大逐渐升高,接菌量为4%时达到峰值,当扩大至8%时,得率明显下降,分析是因为鼠李糖乳杆菌能够以刺麒麟菜中某些糖类为碳源,利用了一部分可代谢的糖,从而导致最终得率的下降,这也印证了刺麒麟菜可能具有益生元特性,也有大量文献对此进行了报道[27-29]。
刺麒麟菜皮层最外2~3层多为小型薄壁细胞,内容物较少,向内逐渐增大[30],而发酵前期主要分解了外侧小型薄壁细胞的初生壁,随着发酵时间增长,内层较大的薄壁细胞被分解,大量内容物析出,得率显著提高,如图1C所示,当发酵时间不断增长至30 h时得率达到峰值,但与24 h差异不显著(P>0.05)。
2.2 响应面法优化发酵刺麒麟菜粗多糖制备工艺
响应面试验根据 Box-Benhnken原理利用DesignExpert 12软件进行试验设计,称量冻干后的所有固形物并计算多糖得率,结果如表2所示。
表 2 发酵制备刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖响应面试验设计及结果Table 2. Experimental design and results of response surface for preparation of F-ESP试验号 A料液比 B接菌量(%) C发酵时间(h) 多糖得率(%) 1 1:60 2 24 25.33 2 1:80 2 24 34.07 3 1:60 8 24 33.01 4 1:80 8 24 34.77 5 1:60 5 18 31.29 6 1:80 5 18 37.75 7 1:60 5 30 34.92 8 1:80 5 30 33.92 9 1:70 2 18 29.97 10 1:70 8 18 34.01 11 1:70 2 30 32.58 12 1:70 8 30 36.43 13 1:70 5 24 40.93 14 1:70 5 24 38.92 15 1:70 5 24 39.92 16 1:70 5 24 40.59 17 1:70 5 24 39.63 采用Design-Expert 12软件对表2结果进行多元回归拟合,得到多糖得率对料液比(A)、接菌量(B)、发酵时间(C)的二次多项式回归模型:
Y= 40.00+2A+2.03B+0.6038C−1.75AB−1.87AC−0.0475BC−3.49A2−4.71B2−2.04C2
如表3所示,相关系数R2为模型与总和的比值=272.80/281.95=0.9675,表示模型拟合性能良好,且失拟检验P值大于0.05,表明模型未失拟,模型P值远远小于0.05,说明各因素与响应值的线性关系十分显著,模型F值为23.20,说明该模型有意义,上述结果表明回归二次模型建立成功,可用于评价发酵刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖的工艺条件。根据ANOVA分析数据差异项,接菌量和液料比的变化对多糖得率的影响显著差异(P<0.01),根据各因素的F值判断主次因素并进行排序:接菌量>液料比>发酵时间。综合上述数据和分析,拟合出发酵刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖最佳工艺条件为料液比1:72.3、接菌量5.5%、发酵时间24.2 h,预测值为40.41%。为便于操作,条件参数设置为料液比1:70,接菌量5%,发酵时间24 h,按照该条件独立重复制备三次的粗多糖得率均值为41.70%±2.0%,与预测值相符合,且显著大于冻融法的得率(33.52%±2.71%)。
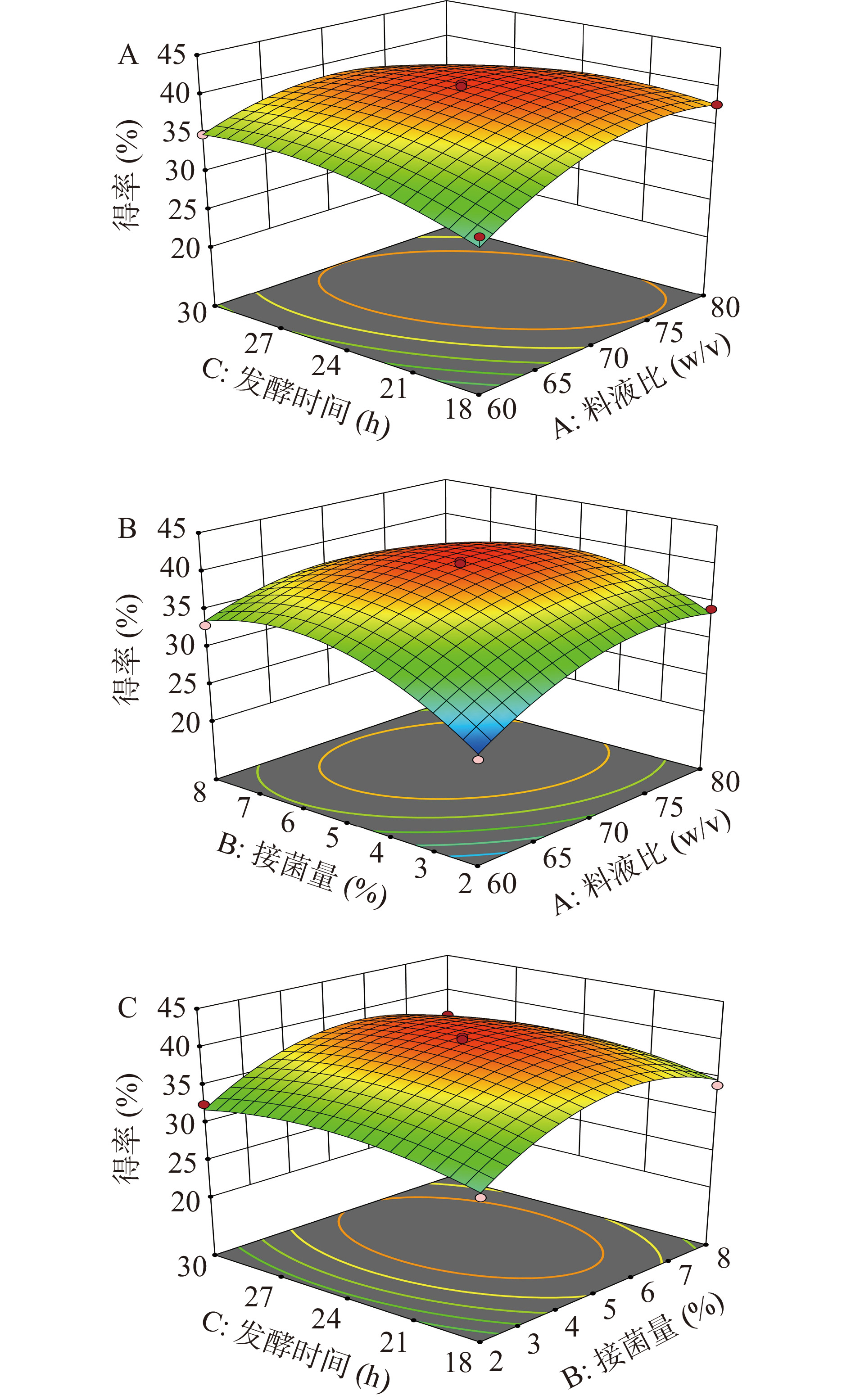
表 3 回归模型的方差分析Table 3. Analysis of variance of regression model来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 差异 模型 272.80 9 30.31 23.20 0.0002 ** A 31.84 1 31.84 24.37 0.0017 ** B 33.09 1 33.09 25.32 0.0015 ** C 2.92 1 2.92 2.23 0.1789 * AB 12.18 1 12.18 9.32 0.0185 * AC 13.91 1 13.91 10.65 0.0138 * BC 0.009 1 0.009 0.0069 0.9361 A² 51.29 1 51.29 39.25 0.0004 ** B² 93.52 1 93.52 71.57 < 0.0001 ** C² 17.48 1 17.48 13.38 0.0081 ** 残差 9.15 7 1.31 失拟 6.62 3 2.21 3.50 0.1287 不显著 误差 2.52 4 0.6307 总和 281.95 16 注:*为差异显著(P<0.05),**为差异极其显著(P<0.01)。 如图2所示,响应曲面映射在等高线上的图形越接近椭圆表明差异越显著,越接近圆越不显著。
根据表3和图2A结合判断,料液比和发酵时间相互作用显著(P<0.05),分析可能是因为料液比一定时,发酵时间的增加导致多糖的逐渐溶出,使得多糖得率先增加再平缓,当发酵时间一定时,料液比同样决定了多糖的溶出量以及刺麒麟菜纤维内部和溶液的浓度差;图2B可以看出料液比与接菌量的响应曲面较陡峭,结合表3中可知AB交互项对多糖得率的影响显著(P<0.05),说明料液比与接菌量的交互作用对多糖得率影响较大;接菌量和发酵时间的等高线图曲面比较平缓(图2C),交互作用不显著(P>0.05)。
2.3 发酵刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖的分离纯化
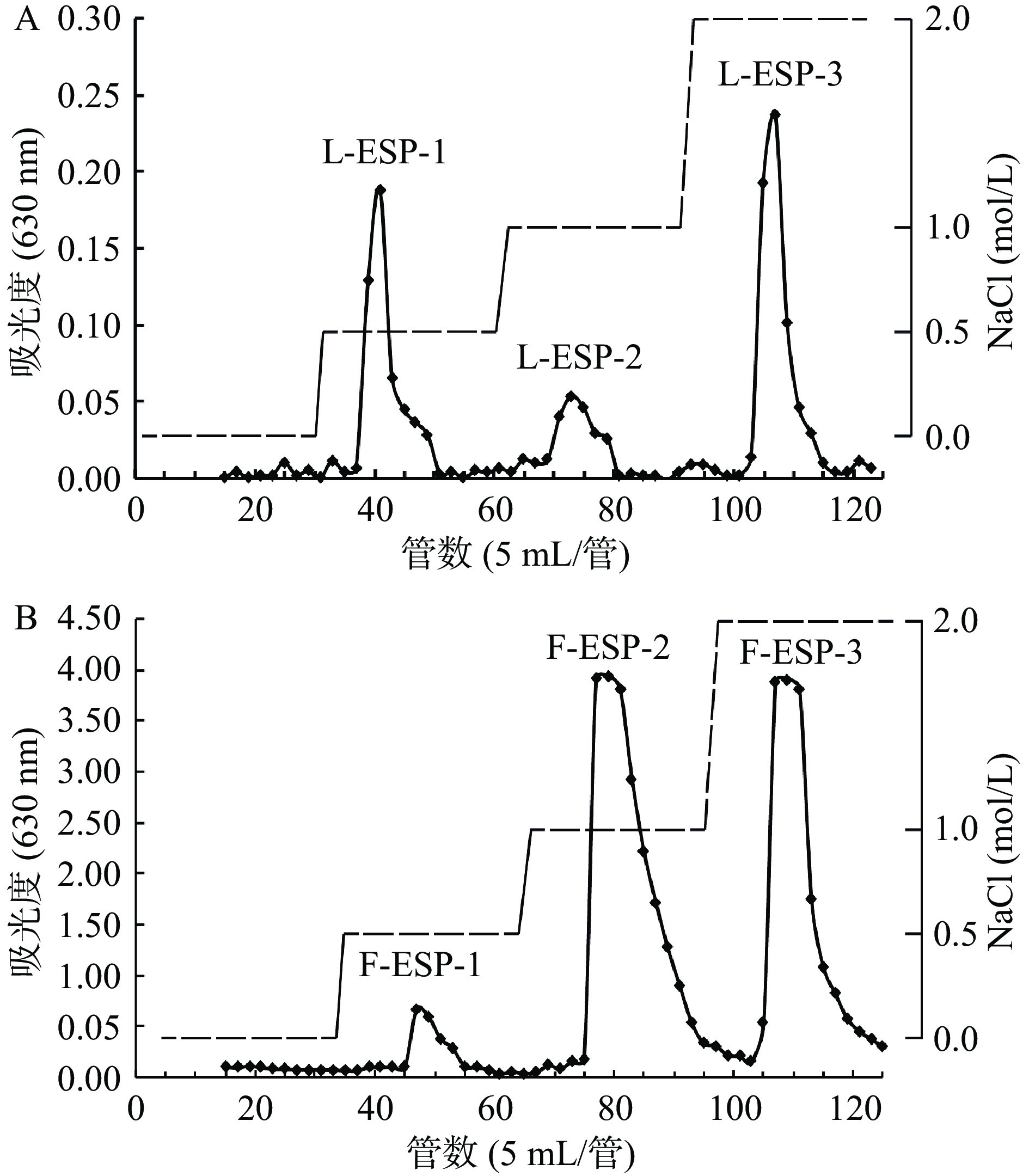
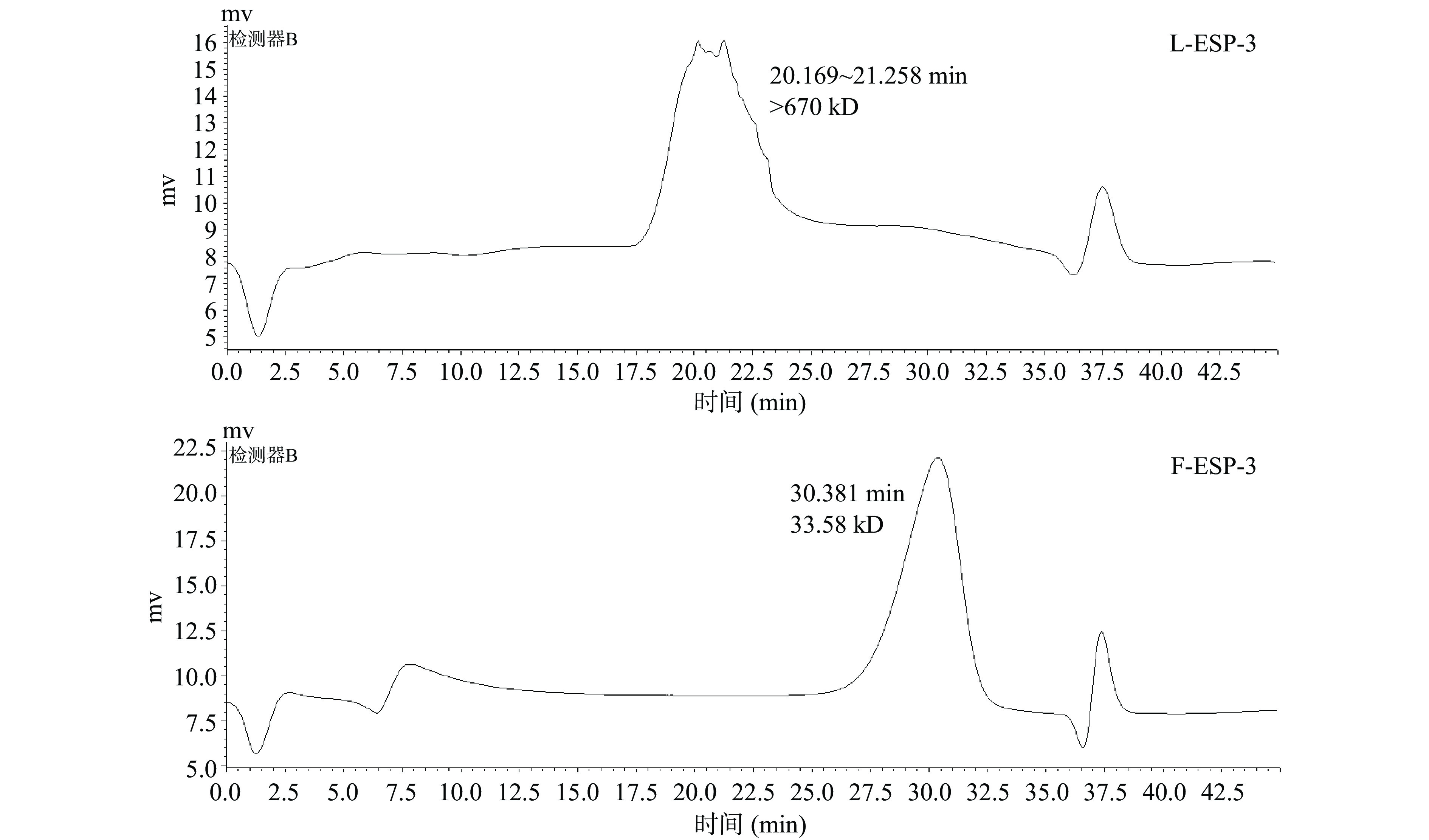
如图3所示,图3A为冻融法制备的L-ESP洗脱曲线,图3B为鼠李糖乳杆菌发酵制备的F-ESP洗脱曲线,将两种粗多糖上样于DEAE-52层析柱,经过0、0.5、1、2 mol/L的NaCl溶液阶段洗脱,测定总糖含量绘制洗脱曲线,各得到3个组分,命名为L-ESP-1、L-ESP-2、L-ESP-3,F-ESP-1、F-ESP-2、F-ESP-3。据报道硫酸根的存在能够显著提高植物多糖的生物活性[31],因此对三个组分的硫酸根含量进行测定,并结合得率选取L-ESP-3和F-ESP-3作为后续实验的样品。
2.4 发酵刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖的化学成分分析
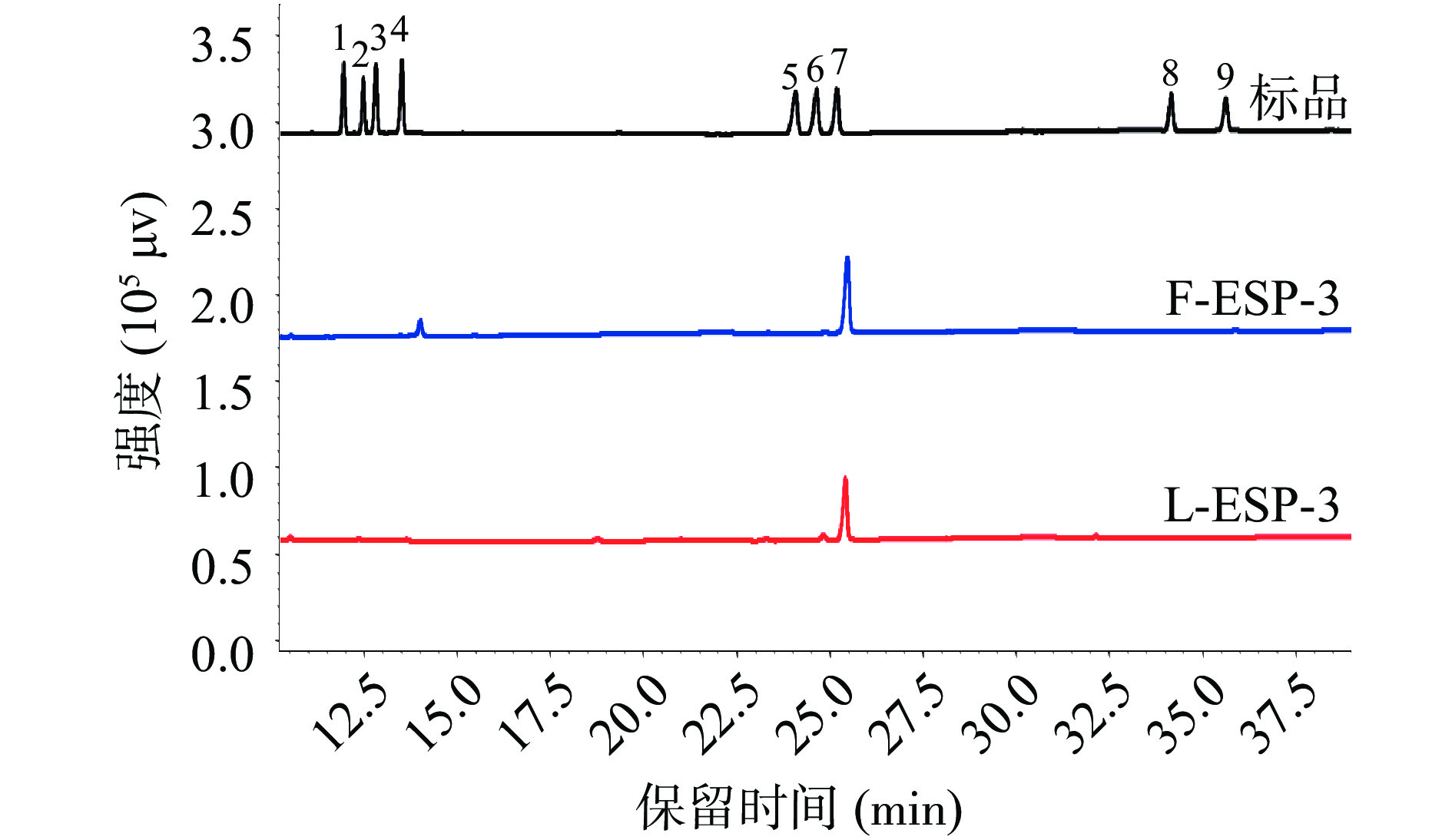
将L-ESP-3与F-ESP-3经三氟乙酸水解后还原乙酰化得到用于检测的糖醇乙酰酯衍生物,利用气相色谱法进行单糖组成的检测。取九个单糖标准品混合处理后测得标品的气相色谱图,如图4所示,与标准品的保留时间对比发现:L-ESP-3主要成分为半乳糖(91.14%)、含少量木糖(1.53%)与葡萄糖(7.33%),F-ESP-3在仪器精度范围内只检出半乳糖,未检出其他单糖。说明鼠李糖乳杆菌发酵消耗了葡萄糖并进一步转化为半乳糖,改变了F-ESP-3的单糖组成。Gao等[32]同样发现,植物乳杆菌发酵使苦瓜中葡萄糖含量降低,半乳糖含量升高。
如表4所示,L-ESP-3与F-ESP-3的总糖含量均达到98%左右,证明两种方法均得到了纯度较高的刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖,F-ESP-3的还原糖含量为7.87%±0.09%较L-ESP-3(1.45%±0.10%)极显著提升(P<0.01);二者硫酸根含量分别为28.76%±2.23%和28.40%±1.40%,硫酸根结构均未被破坏,说明这两种方法均能够保护多糖的硫酸根。同时发酵法还提高了刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖中还原糖的比例,乳酸菌发酵的酸性环境有效去除一部分蛋白质,且内毒素含量小于0.03 EU/mg,符合中华人民共和国药典标准[33]。
表 4 刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖化学组成成分表Table 4. Chemical composition of Eucheuma spinosum sulfate polysaccharides化学成分 L-ESP-3 F-ESP-3 总糖(%) 98.74±1.07 97.77±1.1 还原糖(%) 1.45±0.10 7.87±0.09** 硫酸根(%) 28.76±2.23 28.40±1.40 蛋白质(%) 1.22±0.21 1.01±0.11 内毒素(EU/mg) <0.03 <0.03 注:对同一行之间的数据进行显著性分析,**为差异极其显著(P<0.01)。 2.5 发酵刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖的物理性质分析
分子量测定结果如图5所示,L-ESP-3分子量大于670 kD,与陈玉芳等[16]得到的刺麒麟菜多糖分子量相似(690.12 kD);F-ESP-3的分子量为33.58 kD明显降低,分析可能是因为鼠李糖乳杆菌属于乳酸菌,乳酸菌在代谢过程中可以产生大量胞外酶系,如纤维素酶、果胶酶、淀粉酶等,这些非特异性酶能够随机降解多糖糖苷键[34]。同时也有相关报道认为发酵的酸性环境能够使复杂多聚糖水解为低聚糖,导致分子量进一步降低[35]。孙菁雯[36]利用发酵复合酶解法制备的铜藻和龙须菜多糖<3 kD的组分含量上升,表明多糖被降解,本研究获得了相似的结果。
经计算,L-ESP-3溶解度为56.51%±3.8%,F-ESP-3的溶解度为89.33%±3.1%;L-ESP-3和F-ESP-3的比浓粘度分别为3.85±0.25 dL/g和0.01±0.002 dL/g(P<0.01),由此可知,益生菌发酵法制备的刺麒麟菜多糖黏度极显著降低,溶解度极显著提高。有研究表明聚合物溶液的粘度较高的原因在于当分子链长度远大于溶剂分子,加上溶剂化作用,使其在流动时受到较大的内摩擦阻力,分子量大,分子链缠结越严重,使流动阻力变大,粘度升高[37]。所以分子量的降低可能是F-ESP黏度降低的主要影响因素。
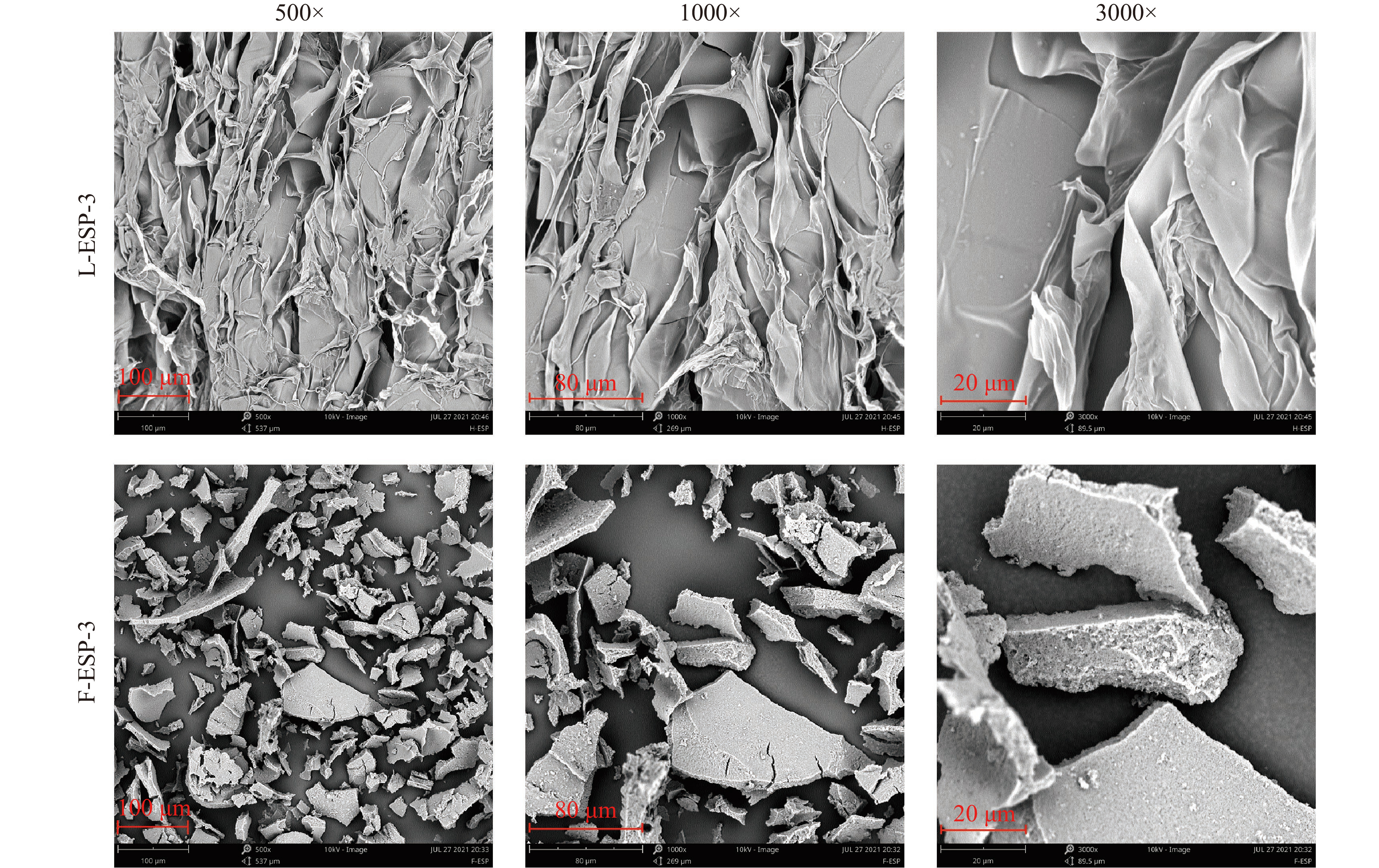
如图6所示,L-ESP-3的微观结构整体呈片状,3000倍放大后,可以看到结构非常完整且表面光滑致密,而F-ESP-3微观结构截然不同,呈现不规则颗粒状,3000倍放大后,发现表面粗糙有裂纹,内部结构具有大量孔隙。刺麒麟菜多糖作为卡拉胶多糖的一种,属于天然高分子凝胶,有研究报道,天然高分子凝胶的表面粗糙度增加可能是因为糖链间一般通过氢键连接,当糖苷键断裂后,导致糖链间氢键交联密度变小,畴结构变大[38]。
2.6 发酵刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖的红外光谱分析
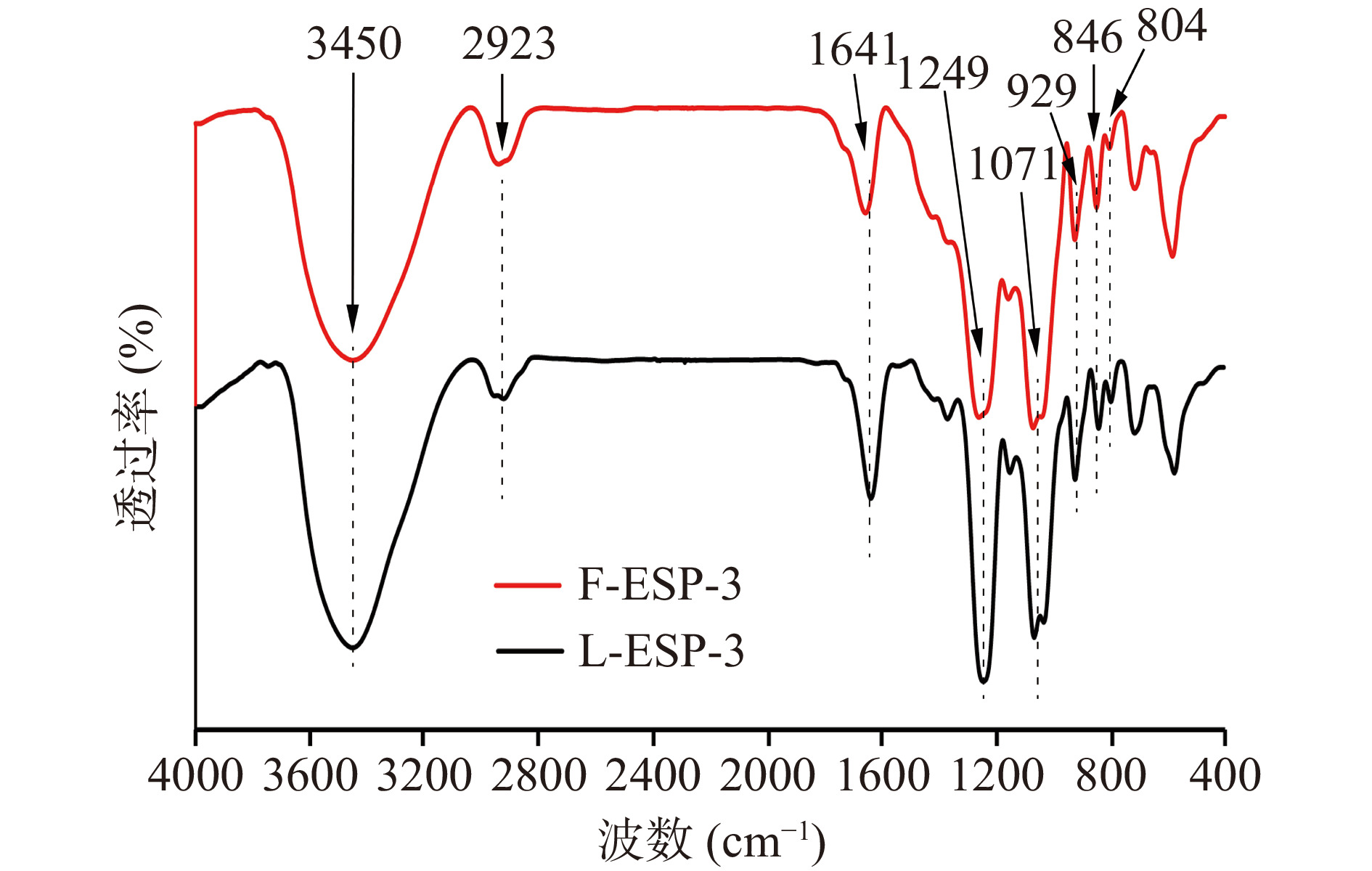
如图7所示,在特征谱带区3450 cm−1为O-H的伸缩振动,2923 cm−1为C-H的伸缩振动[39],这部分为多糖类的特征吸收,1641 cm−1为C=O的特征吸收[40],在指纹区1249 cm−1为O=S=O的伸缩振动,说明该多糖含有硫酸酯基[41],在1071cm−1处的特征吸收说明在主链中存在吡喃半乳糖,929 cm−1为C-O上的3,6内醚半乳糖残基的特征吸收[42];846 cm−1为吡喃糖环C4上的C-O-SO3的特征吸收[43],成苷的半缩醛羟基为α构型[44],804 cm−1为吡喃糖环C2上的C-O-SO3的特征吸收[43],这与ι-卡拉胶的特征光谱相似[45]。综上所述,两种方式制备的多糖结构相似,发酵并未改变多糖的糖链结构,F-ESP-3是一种含3,6内醚半乳糖残基的α硫酸吡喃糖。
2.7 发酵刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖的抗过敏活性评价
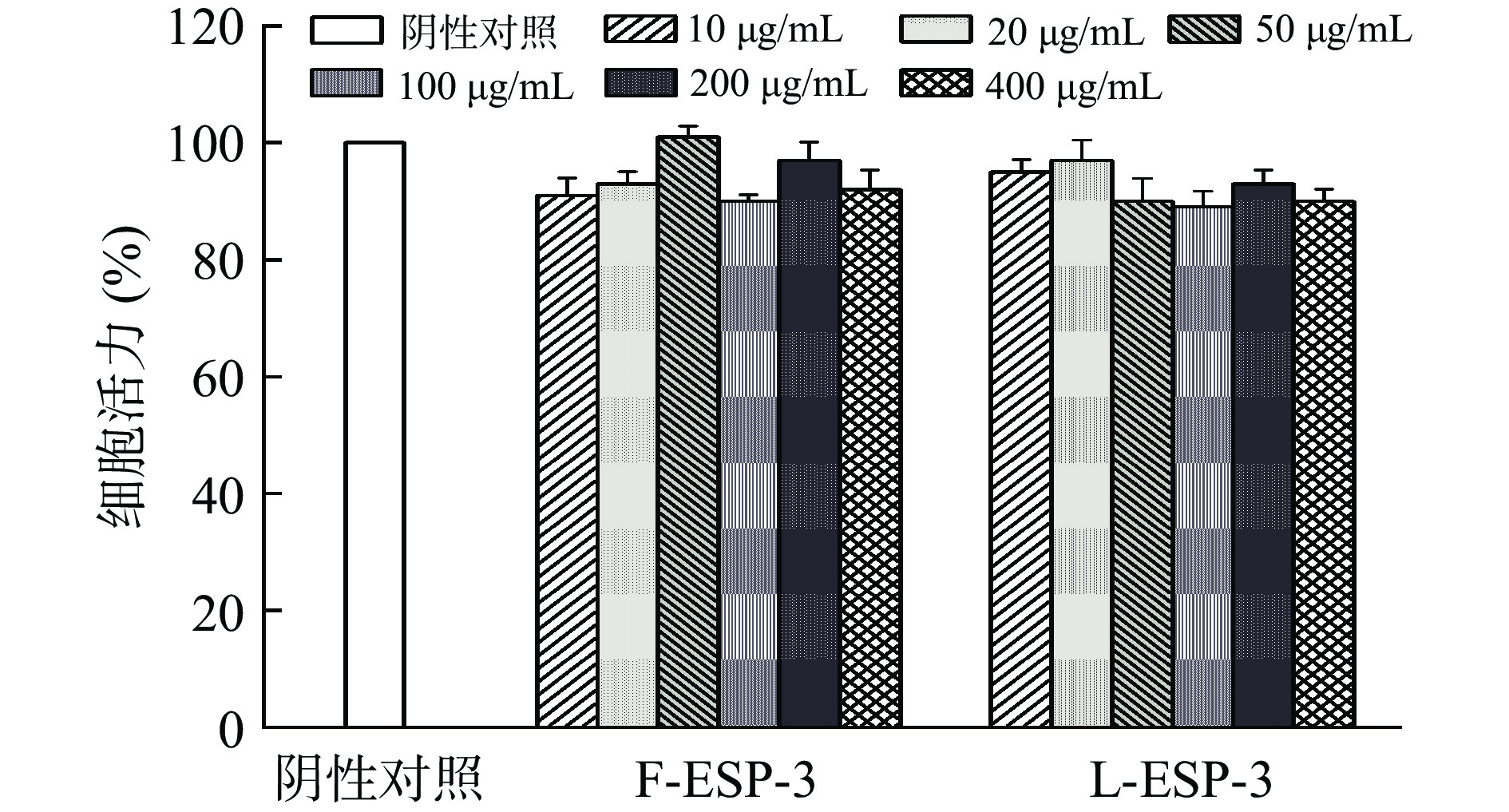
如图8所示,在10~400 μg/mL浓度范围内,L-ESP-3和F-ESP-3均无明显细胞毒性,且RBL-2H3细胞活力均在90%以上,说明对细胞活力无显著影响(P>0.05)。
肥大细胞在效应阶段受到致敏原刺激后脱颗粒,β-氨基己糖苷酶的大量释放是肥大细胞脱颗粒的经典标志,可以引发体内炎症风暴,导致严重的过敏反应,而抑制β-氨基己糖苷酶释放可以有效缓解过敏症状[46]。大鼠嗜碱性粒细胞与肥大细胞相似,受抗原刺激同样释放β-氨基己糖苷酶,并被广泛用作在细胞水平上研究过敏反应的替代和可靠模型[47]。如表5所示,L-ESP-3和F-ESP-3两个样品组均可以抑制β-氨基己糖苷酶的释放,抑制率均大于30%,呈浓度依赖,但F-ESP-3较L-ESP-3展现出更好的抑制活性,说明发酵刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖通过抑制β-氨基己糖苷酶的释放进一步发挥抗过敏活性。
表 5 刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖抑制β-氨基己糖苷酶释放的活性评价Table 5. The activity of Eucheuma spinosum sulfate polysaccharides in inhibiting the release of β-hexosaminidase样品浓度(μg/mL) β-hex抑制率(%) L-ESP-3 F-ESP-3 10 35.30±0.41a 35.74±1.12a 25 35.42±0.52a 41.05±1.07c 50 37.41±1.49b 45.37±0.45d 100 37.49±1.92b 47.81±0.17e 注:不同字母表示所列数据两两之间具有显著性差异,P<0.05为差异显著。 3. 结论与讨论
通过单因素实验和Box-Behnken响应面优化,鼠李糖乳杆菌发酵制备刺麒麟菜粗多糖最佳条件为:料液比1:70,接菌量5%,发酵时间24 h,主次因素排序为接菌量>液料比>发酵时间,最佳条件下粗多糖得率为41.70%±2.00%;纯化后的F-ESP-3总糖含量为97.77%±1.1%,主要单糖成分为半乳糖,硫酸根含量为28.40%±1.40%,F-ESP-3还原糖含量(7.87%±0.09%)对比L-ESP-3的还原糖含量(1.45%±0.10%)极显著提高(P<0.01);F-ESP-3分子量(33.58 kD)较L-ESP-3(>670 kD)极显著降低(P<0.01),溶解度为(89.33%±3.1%)对比L-ESP-3的溶解度(56.51%±3.8%)极显著提高(P<0.01),在相同浓度下,F-ESP-3的比浓粘度为(0.01±0.002 dL/g)对比L-ESP-3的比浓粘度(3.85±0.25 dL/g)极显著降低(P<0.01);二者在微观形态上,L-ESP-3呈现均匀片状结构,表面光滑结构致密,而F-ESP-3呈现不规则颗粒状,表面粗糙且内部具有孔隙结构;红外结构上二者较为相似,均含有硫酸酯基和3,6内醚半乳糖残基,成环方式为α构型吡喃糖环,指纹区呈现ι-卡拉胶型多糖的特征吸收。同时F-ESP-3的β-氨基己糖苷酶抑制活性高于L-ESP-3,呈浓度依赖。
综上所述,鼠李糖乳杆菌发酵的方式并没有破坏多糖的链环结构和硫酸基团,因为多糖的分子量和微观结构的疏松多孔化,导致多糖骨架链间的氢键相互作用改变,亲水基团外露,分散性能提高,从而提高溶解度,降低粘度。同时,分子量的降低进一步提高了F-ESP-3透过细胞膜的能力,提高了生物利用度,从而更好地抑制RBL-2H3细胞释放β-氨基己糖苷酶,展现出良好的抗过敏活性。由于发酵多糖的糖苷键连接方式、空间构象、取代基团之间的非共价相互作用及抗过敏具体作用机理尚不清楚,因此对于发酵多糖高级结构和抗过敏活性之间的关系以及抗过敏作用靶点还需要进一步深入研究。
-
表 1 响应面试验设计的因素及水平
Table 1 Factors and level of response surface test design
水平 因素 A料液比(w/v) B接菌量(%) C发酵时间(h) −1 1:60 2 18 0 1:70 5 24 1 1:80 8 30 表 2 发酵制备刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖响应面试验设计及结果
Table 2 Experimental design and results of response surface for preparation of F-ESP
试验号 A料液比 B接菌量(%) C发酵时间(h) 多糖得率(%) 1 1:60 2 24 25.33 2 1:80 2 24 34.07 3 1:60 8 24 33.01 4 1:80 8 24 34.77 5 1:60 5 18 31.29 6 1:80 5 18 37.75 7 1:60 5 30 34.92 8 1:80 5 30 33.92 9 1:70 2 18 29.97 10 1:70 8 18 34.01 11 1:70 2 30 32.58 12 1:70 8 30 36.43 13 1:70 5 24 40.93 14 1:70 5 24 38.92 15 1:70 5 24 39.92 16 1:70 5 24 40.59 17 1:70 5 24 39.63 表 3 回归模型的方差分析
Table 3 Analysis of variance of regression model
来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 差异 模型 272.80 9 30.31 23.20 0.0002 ** A 31.84 1 31.84 24.37 0.0017 ** B 33.09 1 33.09 25.32 0.0015 ** C 2.92 1 2.92 2.23 0.1789 * AB 12.18 1 12.18 9.32 0.0185 * AC 13.91 1 13.91 10.65 0.0138 * BC 0.009 1 0.009 0.0069 0.9361 A² 51.29 1 51.29 39.25 0.0004 ** B² 93.52 1 93.52 71.57 < 0.0001 ** C² 17.48 1 17.48 13.38 0.0081 ** 残差 9.15 7 1.31 失拟 6.62 3 2.21 3.50 0.1287 不显著 误差 2.52 4 0.6307 总和 281.95 16 注:*为差异显著(P<0.05),**为差异极其显著(P<0.01)。 表 4 刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖化学组成成分表
Table 4 Chemical composition of Eucheuma spinosum sulfate polysaccharides
化学成分 L-ESP-3 F-ESP-3 总糖(%) 98.74±1.07 97.77±1.1 还原糖(%) 1.45±0.10 7.87±0.09** 硫酸根(%) 28.76±2.23 28.40±1.40 蛋白质(%) 1.22±0.21 1.01±0.11 内毒素(EU/mg) <0.03 <0.03 注:对同一行之间的数据进行显著性分析,**为差异极其显著(P<0.01)。 表 5 刺麒麟菜硫酸多糖抑制β-氨基己糖苷酶释放的活性评价
Table 5 The activity of Eucheuma spinosum sulfate polysaccharides in inhibiting the release of β-hexosaminidase
样品浓度(μg/mL) β-hex抑制率(%) L-ESP-3 F-ESP-3 10 35.30±0.41a 35.74±1.12a 25 35.42±0.52a 41.05±1.07c 50 37.41±1.49b 45.37±0.45d 100 37.49±1.92b 47.81±0.17e 注:不同字母表示所列数据两两之间具有显著性差异,P<0.05为差异显著。 -
[1] SALEHI B, SHARIFI-RAD J, SECA A M L, et al. Current trends on seaweeds: Looking at chemical composition, phytopharmacology, and cosmetic applications[J]. Molecules,2019,24(22):4182. doi: 10.3390/molecules24224182
[2] WANG X L, HE L W, MA Y C, et al. Economically important red algae resources along the Chinese coast: History, status, and prospects for their utilization[J]. Algal Research,2020,46:101817. doi: 10.1016/j.algal.2020.101817
[3] YARNPAKDEE S, BENJAKUL S, KINGWASCHARAPONG P, et al. Physico-chemical and gel properties of agar from Gracilaria tenuistipitata from the lake of Songkhla, Thailand[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2015,51:217−226. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.05.004
[4] KANG J, JIA X, WANG N F, et al. Insights into the structure-bioactivity relationships of marine sulfated polysaccharides: A review[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021:107049. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107049
[5] PANGHAL A, JANGHU S, VIRKAR K, et al. Potential non-dairy probiotic products-A healthy approach[J]. Food Bioscience,2018,21:80−89. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2017.12.003
[6] 益生菌科学研究十大热点及行业发展建议[J]. 中国食品学报, 2020, 20(9): 337-344. Ten hotspots of probiotic scientific research and suggestions for industry development [J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2020, 20(9): 337-344.
[7] QIN H A, HUANG L, TENG J W, et al. Purification, characterization, and bioactivity of Liupao tea polysaccharides before and after fermentation[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,353:129419. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129419
[8] WAN Y J, HONG T, SHI H F, et al. Probiotic fermentation modifies the structures of pectic polysaccharides from carrot pulp[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2021,251:117116. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117116
[9] ZHU Y Y, JIANG J, YUE Y, et al. Influence of mixed probiotics on the bioactive composition, antioxidant activity and appearance of fermented red bayberry pomace[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2020,133(12):110076.
[10] TIAN W N, DAI L W, LU S M, et al. Effect of Bacillus sp. DU-106 fermentation on Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide: Structure and immunoregulatory activities[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,135:1034−1042. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.203
[11] LIU Y X, FANG H T, LIU H Y, et al. Goji berry juice fermented by probiotics attenuates dextran sodium sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis in mice[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2021,83:104491. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2021.104491
[12] 苏娜, 伊丽, 吉日木图. 鼠李糖乳杆菌GG发酵驼乳与牛乳的发酵特性和降糖活性比较[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(24):14−19. [SU N, YI L, JIRIMUTU. Comparison of fermentation characteristics and hypoglycemic activity between camel milk and milk fermented by Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(24):14−19. [13] 于配配, 方孝贤, 何鑫平, 等. 海藻植物发酵液饮料的研制[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(21):224−228. [YU P P, FANG X X, HE X P, et al. Development of seaweed fermented beverage[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(21):224−228. [14] WU S C, WANG F J, PAN C L. The comparison of antioxidative properties of seaweed oligosaccharides fermented by two lactic acid bacteria[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Technology-Taiwan,2010,18(4):537−545.
[15] ZHANG Z H, FAN S T, HUANG D F, et al. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum NCU116 fermentation on Asparagus officinalis polysaccharide: Characterization, antioxidative, and immunoregulatory activities[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2018,66(41):10703−10711. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b03220
[16] 陈玉芳, 陈鑫, 郑华, 等. 冷冻法提取刺麒麟菜多糖工艺优化及性质分析[J]. 食品科技,2018,43(12):224−229. [CHEN Y F, CHEN X, ZHENG H, et al. Optimization of extraction process and property analysis of polysaccharide from Eucheuma spinosum by freezing method[J]. Food Science and Technology,2018,43(12):224−229. [17] ZHANG Z S, ZHANG Q B, WANG J, et al. Regioselective syntheses of sulfated porphyrans from Porphyra haitanensis and their antioxidant and anticoagulant activities in vitro[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2010,79(4):1124−1129. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.10.055
[18] MORRIS D L. Quantitative determination of carbohydrates with dreywood's anthrone reagent[J]. Science,1948,107(2775):254−255. doi: 10.1126/science.107.2775.254
[19] 赵凯, 许鹏举, 谷广烨. 3, 5-二硝基水杨酸比色法测定还原糖含量的研究[J]. 食品科学,2008(8):534−536. [ZHAO K, XU P J, GU G Y. Study on the determination of reducing sugar content by colorimetry with 5-dinitrosalicylic acid[J]. Food Science,2008(8):534−536. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2008.08.127 [20] YU G, ZHANG Q Z, WANG Y B, et al. Sulfated polysaccharides from red seaweed Gelidium amansii: Structural characteristics, anti-oxidant and anti-glycation properties, and development of bioactive films[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,119:106820. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.106820
[21] DODGSON K S, PRICE R G. A note on the determination of the ester sulphate content of sulphated polysaccharides[J]. The Biochemical Journal,1962,84:106−110. doi: 10.1042/bj0840106
[22] TANG W, SHEN M Y, XIE J H, et al. Physicochemical characterization, antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Mesona chinensis Benth and their protective effect on injured NCTC-1469 cells induced by H2O2[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2017,175:538−546. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.08.018
[23] GONG G P, FAN J B, SUN Y J, et al. Isolation, structural characterization, and antioxidativity of polysaccharide LBLP5-A from Lycium barbarum leaves[J]. Process Biochemistry,2016,51(2):314−324. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2015.11.013
[24] LIU B, LIU Q M, LI G L, et al. The anti-diarrhea activity of red algae-originated sulphated polysaccharides on ETEC-K88 infected mice[J]. RSC Advances,2019,9(5):2360−2370. doi: 10.1039/C8RA09247H
[25] CHEN R Z, LUO S J, WANG C X, et al. Effects of ultra-high pressure enzyme extraction on characteristics and functional properties of red pitaya (Hylocereus polyrhizus) peel pectic polysaccharides[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,121:107016. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107016
[26] ZHANG Y F, LIU Q M, LIU B, et al. Dihydromyricetin inhibited ovalbumin-induced mice allergic responses by suppressing the activation of mast cells[J]. Food & Function,2019,10(11):7131−7141.
[27] ZHENG L X, CHEN X Q, CHEONG K L. Current trends in marine algae polysaccharides: The digestive tract, microbial catabolism, and prebiotic potential[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,151:344−354. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.168
[28] HAN R, PANG D R, WEN L R, et al. In vitro digestibility and prebiotic activities of a sulfated polysaccharide from Gracilaria lemaneiformis[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2020,64:103652. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2019.103652
[29] LI M M, SHANG Q S, LI G S, et al. Degradation of marine algae-derived carbohydrates by Bacteroidetes isolated from human gut microbiota[J]. Marine Drugs,2017,15(4):92. doi: 10.3390/md15040092
[30] LU W J, YANG Z F, CHEN J, et al. Recent advances in antiviral activities and potential mechanisms of sulfated polysaccharides[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2021,272:118526. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118526
[31] 潘迎捷. 水产辞典[M]. 上海: 上海辞书出版社, 2007: 284-353. PAN Y J. SHUICHANCIDIAN[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Lexicographical Publishing House, 2007: 284-353.
[32] GAO H, WEN J J, HU J L, et al. Momordica charantia juice with Lactobacillus plantarum fermentation: Chemical composition, antioxidant properties and aroma profile[J]. Food Bioscience,2019,29:62−72. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2019.03.007
[33] 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典三部[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020: 335−716. Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China[M]. Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Publishing House, 2020: 335−716.
[34] CUI Y H, QU X J. Genetic mechanisms of prebiotic carbohydrate metabolism in lactic acid bacteria: Emphasis on Lacticaseibacillus casei and Lacticaseibacillus paracasei as flexible, diverse and outstanding prebiotic carbohydrate starters[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2021,115:486−499.
[35] CHANDARAJOTI K, XU Y, SPARKENBAUGH E, et al. De novo synthesis of a narrow size distribution low-molecular-weight heparin[J]. Glycobiology,2014,24(5):476−486. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwu016
[36] 孙菁雯. 发酵酶解法制备两种海藻多糖及其保湿抗氧化活性研究[D]. 烟台: 烟台大学, 2021. SUN J W. Preparation of polysaccharides from two kinds of seaweed by fermentation and enzymatic hydrolysis and their moisturizing and antioxidant activities[D]. Yantai: Yantai University, 2021.
[37] TOGRUL H. Flow properties of sugar beet pulp cellulose and intrinsic viscosity-molecular weight relationship[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2003,54(1):63−71. doi: 10.1016/S0144-8617(03)00146-2
[38] DASKHAN G C, JAYARAMAN N. Increased glycosidic bond stabilities in 4-C-hydroxymethyl linked disaccharides[J]. Carbohydrate Research,2011,346(15):2394−2400. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2011.08.030
[39] JIANG J Y, KONG F S, LI N S, et al. Purification, structural characterization and in vitro antioxidant activity of a novel polysaccharide from Boshuzhi[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2016,147:365−371. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.04.001
[40] SEHRAWAT N, YADAV M, SINGH M, et al. Probiotics in microbiome ecological balance providing a therapeutic window against cancer[J]. Seminars in Cancer Biology,2021,70:24−36. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.06.009
[41] LAJILI S, AMMAR H H, MZOUGHI Z, et al. Characterization of sulfated polysaccharide from Laurencia obtusa and its apoptotic, gastroprotective and antioxidant activities[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,126:326−336. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.12.089
[42] XIAO Q, AN D, ZHANG C, et al. Agar quality promotion prepared by desulfation with hydrogen peroxide[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,145:492−499. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.12.206
[43] PEREIRA L, AMADO A M, CRITCHLEY A T, et al. Identification of selected seaweed polysaccharides (phycocolloids) by vibrational spectroscopy (FTIR-ATR and FT-Raman)[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2009,23(7):1903−1909. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2008.11.014
[44] USOV A I. Chapter 4-polysaccharides of the red algae[M]//HORTON D. Advances in Carbohydrate Chemistry and Biochemistry. 2011, 65: 115−217.
[45] PAULA G A, BENEVIDES N M B, CUNHA A P, et al. Development and characterization of edible films from mixtures of κ-carrageenan, ι-carrageenan, and alginate[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2015,47:140−145. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.01.004
[46] LAZKI-H P, KLEIN O, SAGI-EISENBERG R. The actin cytoskeleton and mast cell function[J]. Current Opinionin Immunology,2021,72:27−33. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2021.03.002
[47] MA J, TONG P Y, CHEN Y J, et al. The inhibition of pectin oligosaccharides on degranulation of RBL-2H3 cells from apple pectin with high hydrostatic pressure assisted enzyme treatment[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,371:131097. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131097
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 张全通,郑尧,杨柳,张帅帅,郭全友. 计算机视觉结合卷积神经网络快速检测南极磷虾粉中的虾青素含量. 食品工业科技. 2025(03): 11-18 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 刘鑫,马本学,李玉洁,陈金成,喻国威. 基于改进YOLOv7-ByteTrack的干制哈密大枣缺陷检测与计数系统. 农业工程学报. 2024(03): 303-312 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 贾雅欣,李传峰,罗华平,吴明清. 基于边缘轮廓定积分测量红枣体积的研究. 塔里木大学学报. 2024(01): 75-83 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 朱丽娟. 基于机器视觉的红枣裂纹特征提取. 科技风. 2024(10): 17-19 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 吴思,诸定莲,鲁梦瑶,万以磊,高亮亮,陈龙,汤卫荣,吴文彪. 基于机器视觉的大闸蟹自动分级分选设备研究与开发. 扬州大学学报(农业与生命科学版). 2024(04): 137-146 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 汤文祺,曹玉华,李应果. 基于机器视觉的一品红自动分级方法研究. 现代农业装备. 2024(05): 53-58 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 赵晓梅,李洪港. 基于X射线图像的金属腐蚀深度估计方法. 山东冶金. 2023(05): 25-27 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 蒋平. 一种快速红枣表面缺陷识别方法. 大众标准化. 2023(23): 55-57 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(13)





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:



