3D Printing of Fungus-Chicken Bone Powder Mixed Gel System and Its Texture Modification
-
摘要: 本文以木耳-鸡骨粉混凝体系为原料,采用3D打印技术来制造形状诱人、营养丰富的质构调整型产品。首先研究了不同骨粉添加比例对混凝体系流变和3D打印特性的影响,并通过低场核磁共振(LF-NMR)、傅立叶变换红外光谱(FTIR)等手段对相关机理进行探讨。结果表明,随着鸡骨粉含量增加,混凝体系的屈服应力、黏度和储能模量(G')降低,当鸡骨粉:木耳粉=2:8时,3D打印效果最佳。随后通过3D打印技术调控打印样品的内部结构(填充模式和填充比)研究其对质构特性的影响,发现样品的内部结构显著(P<0.05)影响其硬度、粘附性、胶着性和坚实度。该研究可为调整内部结构,实现质构定制化3D打印食品提供参考。Abstract: In this study, the fungus-chicken bone meal coagulation system was used to manufacture texture adjustment products with attractive shape and rich nutrition using 3D printing technology. Firstly, the effects of different bone powder addition ratios on the rheology and 3D printing characteristics of the coagulation system were studied, and the related mechanisms were discussed through low field nuclear magnetic resonance (LF-NMR) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). Results showed that, with the content of chicken bone meal increased, the yield stress, viscosity and storage modulus (G') decreased. When the ratio of chicken bone meal:fungus powder=2:8, the mixed gel system illustrated best 3D printing performance. Subsequently, the internal structure (filling mode and filling ratio) of the printed sample was controlled by 3D printing technology to study its effect on the textural properties. Results indicated that the internal structure significantly (P<0.05) affected the hardness, adhesion, adhesiveness and firmness of the sample. This study could provide useful information for the texture modification of customized 3D printed food.
-
Keywords:
- 3D printing /
- chicken bone powder /
- fungus powder /
- textural properties
-
3D打印技术是一种快速成型技术,其基于计算机数字技术,将物料按照所设计的3D打印模式进行逐层叠加,最后完成三维实体的构造[1]。该技术可以应用于食品领域中,实现个性化设计、特殊人群膳食定制[2]等,满足人们对食品营养和形状的需求,并且可以通过设计食品的内部结构来调整食品的质构特性[3]。
现阶段,我国人口老龄化程度持续加深,饮食是实现健康老龄化、提升老年人生活品质的重要一环。黑木耳是一种胶质食用菌,具有良好的口感、营养和药用价值,如具有抗氧化、抗肿瘤、降血脂和预防高血压、高血糖等作用[4-7],对老年人健康有益。然而,黑木耳弹性较强,不易咀嚼吞咽,市场上常见的适合于老年人食用的木耳类产品往往以粉末形式存在,但这类产品外观形态欠佳,难以引起食欲。因此,本研究拟以木耳粉为原料,以3D打印为手段构建能够引起食欲的质构调整型产品。另外,骨质疏松也已经成为影响老年人身体健康的慢性疾病之一[8],补钙是防治骨质疏松的主要方法之一,通过添加骨粉和纯牛奶也可以达到一定的补钙作用。目前,3D打印食品的研究侧重于物料性质和3D打印特性之间的关系,对食品内部结构与质构特性间的联系的研究很少。本研究首先构建木耳-鸡骨粉混合凝胶体系,研究不同配方对混凝体系的流变特性和3D打印特性,并探究相关机理,确定最优配方。然后,通过3D打印技术调整食品的内部结构,进一步研究了其对质构特性的影响,为开发质构定制化3D打印食品提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
黑木耳粉(蛋白质7.1 g/100 g,脂肪1.9 g/100 g,碳水化合物61.5 g/100 g) 安徽宝丰生物科技有限公司;鸡骨粉 陕西柏科生物科技有限公司;脱脂纯牛奶 内蒙古伊利实业集团股份有限公司;黄原胶 中国青岛Usolf化学科技有限公司。
JJ-1A 数显电动搅拌器 天津鑫博得仪器有限公司;CSE 1挤出型3D打印机 杭州时印科技有限公司;AR-2000 ex流变仪 TA Co., Ltd,UK;MiceoMR20-030V-1低场核磁共振分析仪(23.2 MHz) Numag Electric Co.,中国苏州;Thermo. Ltd.傅里叶变换红外光谱仪 San Jose,California,USA。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 木耳-鸡骨粉/混合凝胶体系的制备
通过预实验确定粉料混合物(木耳粉和鸡骨粉)与纯牛奶的比例为1:4。首先将鸡骨粉与木耳粉分别按0:10、1:9、2:8、3:7、4:6的比例混匀,再加入0.5%(W/W)黄原胶继续混匀,然后加入纯牛奶。使用电动搅拌器搅拌2 min,使其充分混合,再将混合物于80 ℃水浴30 min。最后将混合物室温放置2 h后使用。
1.2.2 流变特性分析
参照Liu等[9]的方法使用流变仪测试样品的流变特性。平板直径为40 mm,测试间距为1000 μm。测试时,在平板周围覆盖一层薄薄的硅油,以避免水分散失。在每次测试之前,在测试温度下平衡5 min,以使样品达到稳定状态。黏度测试时,剪切速率范围为0.1~100 s−1,温度为25 ℃。样品的屈服特性在25 ℃下通过振荡应力扫描测试进行的,应力在1 Hz下在1~2000 Pa之间变化。振荡应变测试是在25 ℃,1 Hz下进行的,应变范围0.01%~100%。
1.2.3 低场核磁共振(LF-NMR)分析
样品的水分状态由LF-NMR分析仪测定[10],磁体温度为32 ℃,磁场强度为0.5 T。首先使用自由感应衰减(FID)方法进行校准,然后使用Carr-Purcell-Meiboom-Gill (CPMG) 序列来确定质子衰变参数。每次测试约5 g样品,先用一层薄薄的塑料薄膜包装并放入玻璃管中,然后将玻璃管插入NMR分析仪中。CPMG序列中使用的参数设置如下:90°脉冲时间6.52 μs,180°脉冲时间12 μs,采样点数TD=29992,接收机带宽SW=100 kHz,回波数3000,累加次数NS=4,等待时间TW=3000 ms,应用核磁共振分析软件的SIRT算法将CPMG衰减曲线转化为横向弛豫时间(T2),进行10万次迭代拟合。每次测量进行三次。
1.2.4 傅里叶变换红外(FT-IR)光谱分析
首先将不同配方的样品冷冻干燥,在FT-IR 分析之前储存在干燥器中,以避免水分含量的干扰。使用配备有氘化三甘氨酸硫酸盐检测器的 FT-IR 光谱仪进行测试。将冻干样品研磨成粉末,与KBr(1:100,v/v)混合,室温下在4000~400 cm−1的波数范围内测定。每次测量进行三次。
1.2.5 3D打印特性分析
本试验3D打印模型为高20 mm,外径30 mm,内径20 mm的中空圆柱体,以评估不同配方下样品的3D打印适应性。3D打印温度为室温(25±1) ℃,喷嘴直径1.55 mm,打印速度25 mm/s,填充方式为直线型,填充率100%。分别记录打印完成时和60 min后样品的状态和尺寸。
1.2.6 3D打印样品内部结构对其质构特性的影响
1.2.6.1 3D打印
本试验通过3D打印设计样品的内部结构来调整其质构特性。3D打印模型为高30 mm,直径30 mm的实心圆柱体,填充模式设定为Rectilinear(直线型),Honeycomb(蜂窝状),Octagram spiral(八角螺旋)三种,填充比为40%,60%,80%,外周层数2层,喷嘴直径1.55 nm,打印速度25 mm/s。在室温下打印,每个实验条件下至少打印7个样品,用于质构特性分析。
打印完成后,可以先测定样品的尺寸特征(高度、直径),同时记录每个样品的重量以便计算孔隙率。孔隙率的计算采用体积置换法[11],首先测得样品的密度,然后用样品的重量除以密度得到样品体积。根据公式计算孔隙率:孔隙率(%)=(V1−V2)/V1×100,V1指设计模型的体积(21.21 cm3),V2是所得3D打印样品的体积。
1.2.6.2 质构特性
采用质构仪对样品进行全质构分析。测试前先用1 kg的砝码进行校准。选用圆柱形探头P/75(直径为75 mm),在全质构模式下测定样品的硬度和胶粘性。测试参数为:测试前速度5.0 mm/s,测试中和测试后速度均为2.0 mm/s,压缩应变45%,触发力10.0 g,温度为室温(25±1)℃,重复测定 3次。
在Return-to-start模式下,利用圆柱形探头(P/0.5R,直径≈13mm)测定样品的坚实度(firmness)。应力-应变(力-时间)曲线的最高点为坚实度(firmness)[9]。测试参数如下:试验前速度5.0 mm/s,试验中和试验后速度2 mm/s,压缩应变45%,触发力10.0 g。实验在室温(25±1)℃下进行,重复测定3次。
1.3 数据处理
使用Origin 9.0和Design-Expert 8.0对实验数据进行分析并绘制图形。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 流变特性
2.1.1 屈服应力
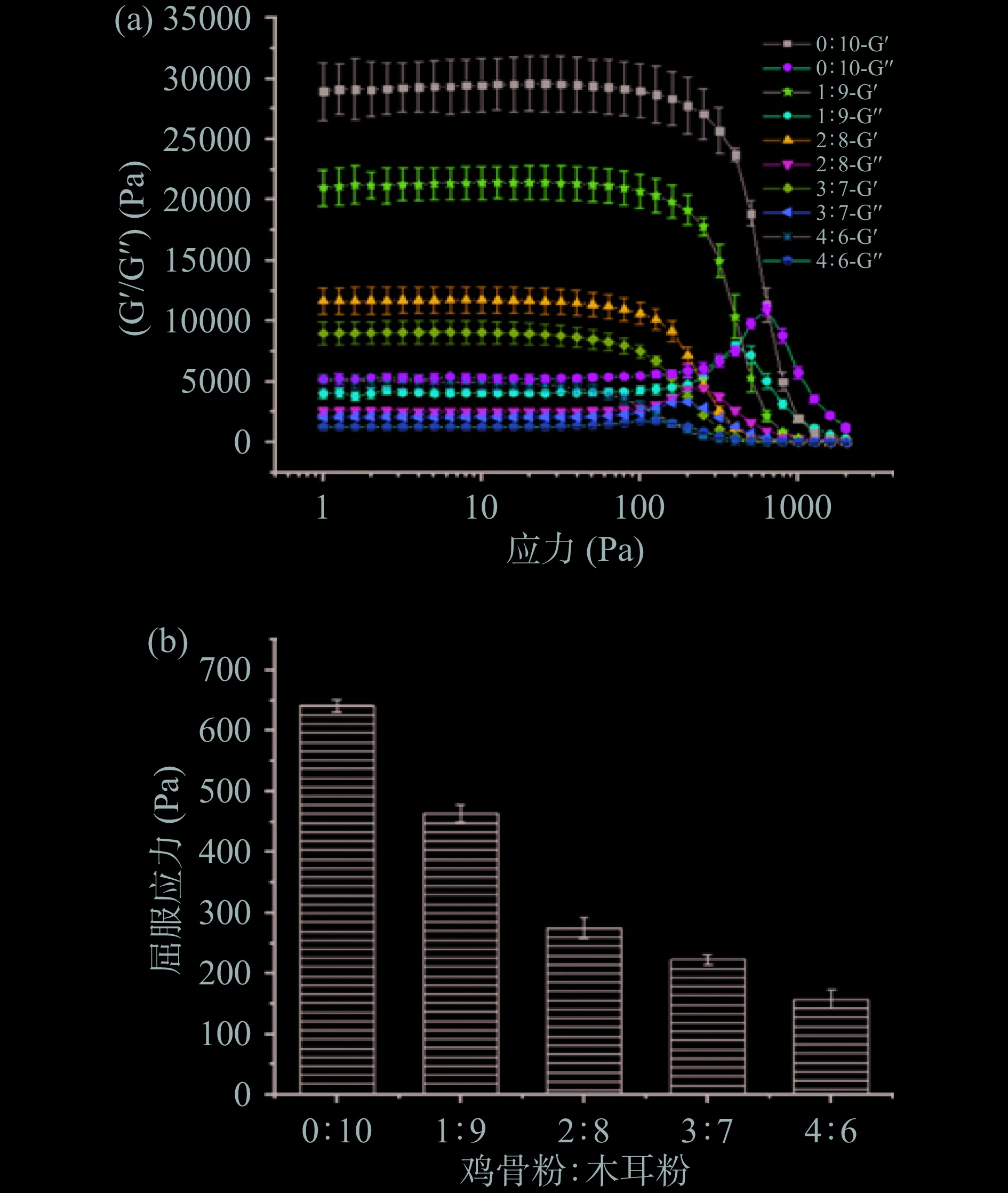
屈服应力对于确定3D打印过程中物料的挤出行为很重要[12-13]。屈服应力表示物料开始流动所需的最小力,低于最小力,物料将无法流动。研究表明在3D打印挤出时,物料应具有较低的屈服应力[14]。图1(a)表示了不同配方下木耳-鸡骨粉混凝体系的储能模量(G')和损耗模量(G")的变化。可以看到,随着应力增加,G'和G"先保持稳定,然后G'急剧下降,G"迅速上升,直到G'与G"相交,交点被定义为屈服应力。图1(b)为不同配方样品的屈服应力。没有鸡骨粉添加时,样品屈服应力为641.5 Pa,鸡骨粉与木耳粉比例为1:9时,屈服应力为463.5 Pa,鸡骨粉与木耳粉比例为2:8时,屈服应力为275 Pa,3:7时为223.5 Pa,4:6时为157.5 Pa。随着鸡骨粉含量的升高,物料的屈服应力降低,使其在3D打印挤出阶段的更容易挤出。
2.1.2 黏度和剪切稀化行为
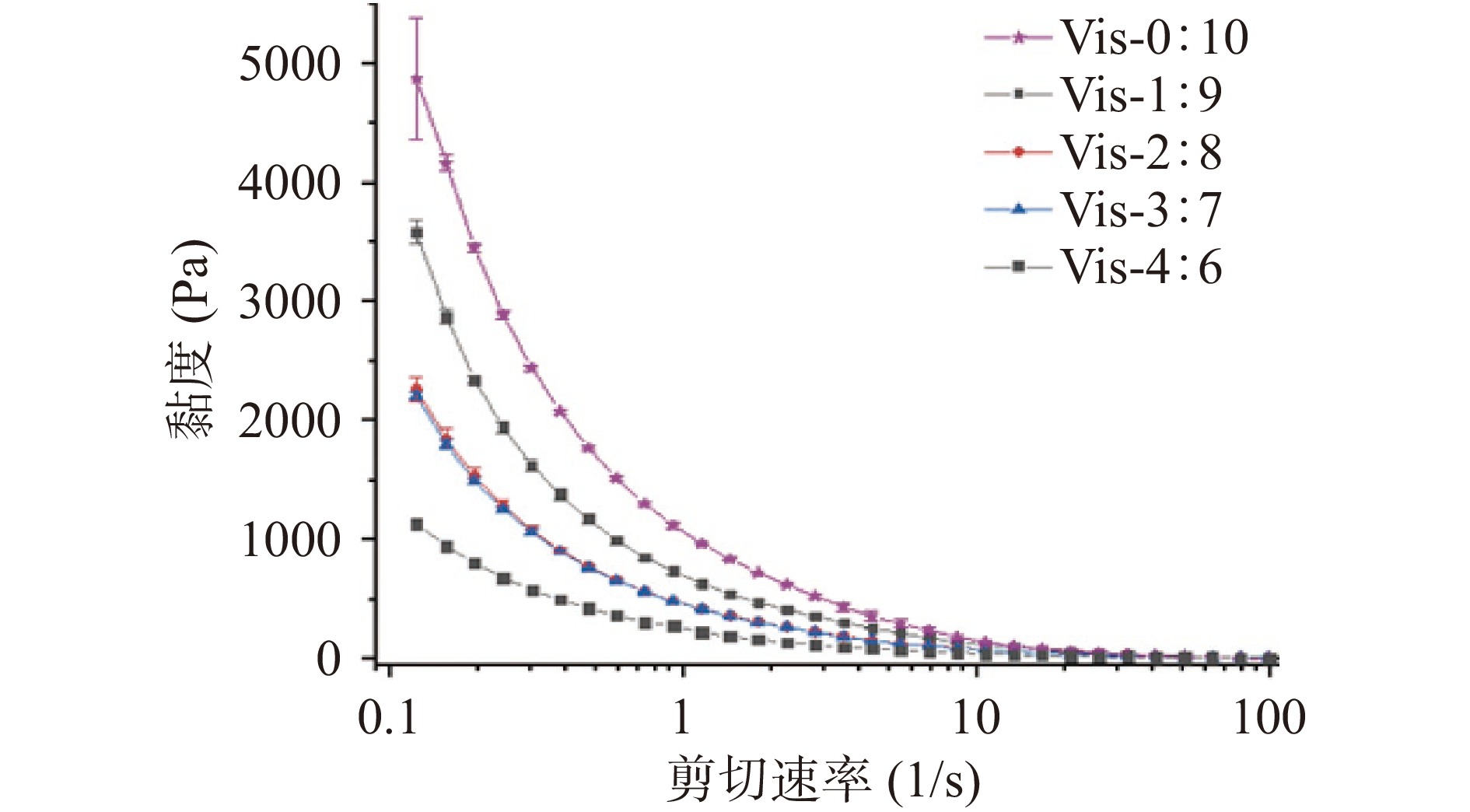
不同配方样品的黏度曲线如图2所示,各样品的黏度随着剪切速率的增加而下降,当剪切速率超过10 s−1后,各配方下样品的黏度没有明显差异,逐渐接近于零,这表明所有样品均呈现剪切稀化行为。剪切稀化行为对于3D打印十分重要,可以使食品样品在3D打印过程中易于挤出[15]。
为了进一步描述物料的剪切稀化行为,常用幂律模型来表示[16-17]。其中ƞ表示表观黏度,K表示稠度指数,γ̇ 表示剪切速率,n表示流动行为指数,牛顿流体的n=1,而n<1则将呈现剪切稀化,n越小表示剪切稀化行为变高[18-19]。表1为剪切速率为1、10、50 s−1时样品的黏度和幂律参数。可以看出,不同配方样品的流动行为指数n无显著差别。稠度指数K与3D打印过程中物料的挤出行为密切相关, K值过高将导致物料挤出困难和断线[20]。在只添加木耳粉情况下,K值最大,达到1029.87 Pa·sn,稠度较高。随骨粉添加量增高,K值越来越小,例如当鸡骨粉与木耳粉的比例为2:8时,K值降低为452.66 Pa·sn,当鸡骨粉与木耳粉的比例为4:6时,K值降低为248.183 Pa·sn,表明稠度越来越低,利于样品在3D打印过程中挤出。
表 1 剪切速率为1、10、50 s−1时样品的黏度和幂律参数Table 1. Viscosity of mixed gel system at 1, 10, 50 s−1 and power law related parameters配方
(鸡骨粉:木耳粉)η1 η10 η50 幂律方程 K(Pa·sn) n R2 0:10 971.70±11.92 146.90±5.21 15.73±2.74 1029.87±33.76 0.26±0.04 0.998 1:9 636.40±17.86 118.53±2.04 18.34±1.72 667.13±26.70 0.21±0.03 0.997 2:8 422.45±0.65 80.67±0.11 17.23±0.31 452.66±2.70 0.23±0.01 0.999 3:7 468.95±47.15 76.80±3.97 15.87±1.05 451.56±5.71 0.27±0.00 0.999 4:6 225.37±10.54 42.30±1.22 12.67±0.21 248.18±13.91 0.28±0.01 0.100 2.1.3 黏弹性行为
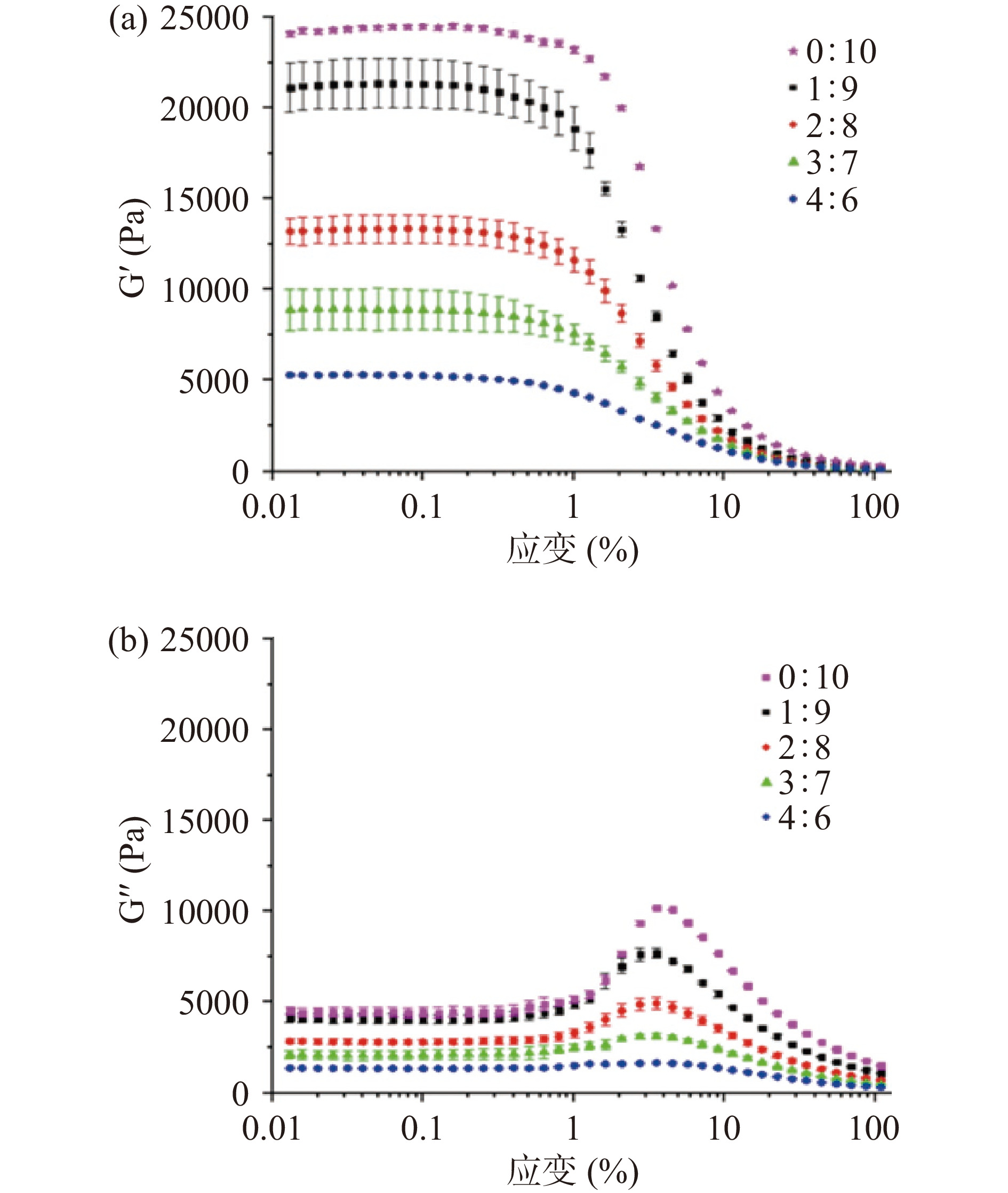
G'对3D打印样品的自支撑能力至关重要[21-22]。G'是指抵抗变形的能力和机械强度的类固体性质,物料具有足够机械强度和屈服应力时,其自支撑特性更好[23-24]。如图3所示,不同配方下的样品的G'均高于G",表明样品具有较好的弹性,并且具有一定的类固体特征。然而,随着鸡骨粉添加量增高,样品的G'变小,自支撑能力变差,影响3D打印样品的结构稳定性。G'过大或过小可能造成打印过程中出现断条或塌陷,合适的G'有助于混凝体系挤出后保持产品形状。
2.2 水分状态
物料的流变特性与水分的状态密切相关[25]。图4表示了在不同配方下混合凝胶体系的横向弛豫时间(T2)。T21在0.1~1 ms之间,为结合水,流动性差。T22在1~10 ms之间,为样品中不易流动水部分。弛豫时间大于10 ms的峰(T23)反映流动性较强的水,这部分水对物料的流变性质有较大影响[26]。鸡骨粉添加量为0的样品出现T23峰值时,弛豫时间短,表明样品的结构更紧密,流动性小。随鸡骨粉含量增加,弛豫时间变长,波谱右移,说明样品流动性变大。即在没有鸡骨粉添加时,水与木耳粉结合紧密,机械强度大。随着鸡骨粉含量的增加,水与粉料之间的结合变得相对疏松,机械强度和自支撑能力变差,这也与不同配方样品的G'和K值变化趋势相符合。
2.3 傅里叶变换红外光谱分析
傅里叶变换红外光谱可以检测氢键存在并间接比较其强度[27]。波数越低表明成分之间的相互作用越强。图5显示了不同配方下混合凝胶体系的特性峰值,所有样品出现类似的吸收峰,说明添加鸡骨粉后没有产生新的官能团。1050 cm−1附近的吸收带对应于糖类中C-O的伸缩振动。1650 cm−1附近的吸收带主要是因为木耳多糖中C=O。2900 cm−1附近产生的吸收峰是由于C-H的伸缩振动。对于所有样品来说,在3291~3311 cm−1附近出现的吸收峰是分子缔合羟基振动产生的,而且随着鸡骨粉添加量增加向较长波数偏移,表明氢键强度变弱。这可能可以用来解释随鸡骨粉添加量增加,样品机械强度降低这一现象,即鸡骨粉的加入削弱了混凝体系间氢键的强度,导致鸡骨粉加入过多时,3D打印的样品不能维持稳定结构。
2.4 3D打印效果
3D打印稳定性是评价3D打印产品品质的重要指标[28]。不同配方样品的3D打印效果如表2所示。随着鸡骨粉含量的增加,样品塌陷情况增强,同时,随着时间的推移样品出现轻微变形。实验中发现,当鸡骨粉:木耳粉为4:6时,样品塌陷严重,无法打印成型,当骨粉:木耳粉为3:7时,样品塌陷程度减弱,但仍然较软塌,易被破坏变形。这是因为样品具有相对较低的屈服应力和G',自支撑能力较差,不足以维持3D打印产品的形状。当鸡骨粉:木耳粉为2:8时,3D打印后的样品可以保持稳定,而且在3D打印过程中易于挤出,效果最佳。但是,当鸡骨粉:木耳粉为1:9和0:10时,物料的流动性下降,挤出的线条较生硬,有断条现象出现。
表 2 不同配方和不同储存时间的3D打印样品Table 2. 3D printed samples with different formulation and storage time打印后时间(min) 鸡骨粉:木耳粉 0:10 1:9 2:8 3:7 4:6 0 




60 




描述 无明显差别 无明显差别 无明显差别 无明显差别 明显塌陷 2.5 木耳-鸡骨粉混凝体系内部结构对质构特性的影响
综合上述实验结果,确定鸡骨粉:木耳粉=2:8为最优配方。接下来,以此配方研究样品内部结构对质构特性的影响。
2.5.1 3D打印尺寸特性和孔隙率
图6显示了3D打印模型在不同填充模式和填充比下的切片结果和实际打印出的样品。样品的密度为1.08±0.05 g/cm3,不同填充条件下3D打印圆柱样品的尺寸特性和孔隙率如表3所示。虽然打印样品的直径和高度与设计模型稍有偏差,但整体来看已经非常接近设计模型。可以看出填充模式和填充比影响3D打印样品的孔隙率。当填充比增加时,3D打印样品的孔隙率降低,例如直线型填充模式下,当填充比从40%增加至80%时,打印样品的孔隙率由37.57%下降到7.47%。不同的填充模式下,3D打印样品的填充比也不同。另外,试验中观察到当填充比较低时(40%),填充的物料较少,3D打印后的样品机械强度低,容易塌陷变形。对于直线型和蜂窝状填充的样品来说,当填充比达到80%时,已经看不到空隙,其孔隙率分别为7.47%和4.24%,可能是样品出现一定程度的压缩变形和挤出胀大现象[29]。总体来看,打印样品的实际填充比(100%-孔隙率)高于设定的填充比。比如当填充模式为蜂窝状,填充比为40%时,3D打印样品的孔隙率为28.97%,即实际填充比为71.03%,与设定的填充比有较大差异,这是因为3D打印软件所设定的填充比是样品内部的填充比,不包括外周层数部分。而且,目前3D打印切片软件常用于热塑性材料的打印,其参数主要是针对这些热塑性材料设计和优化而设置的,所以对于食品材料没有过多的考虑[30]。
表 3 不同填充条件下3D打印圆柱的尺寸特性和孔隙率Table 3. Dimensional properties and porosity of 3D printed cylindrical structure with different infill conditions填充条件
(填充模式-填充比)直径(mm) 高度(mm) 孔隙率(%) 打印模型 30 30 − 直线型-40% 29.17±0.09 29.25±0.04 37.57±0.02 直线型-60% 29.00±0.01 29.33±0.02 21.18±0.02 直线型-80% 30.17±0.04 29.50±0.03 7.47±0.01 蜂窝状-40% 29.83±0.04 29.33±0.04 28.97±0.02 蜂窝状-60% 30.00±0.06 29.58±0.03a 17.22±0.01 蜂窝状-80% 30.50±0.05 29.58±0.03 4.24±0.02 八角螺旋-40% 29.33±0.05 29.00±0.06 46.33±0.03 八角螺旋-60% 29.67±0.05 29.33±0.04 33.70±0.01 八角螺旋-80% 29.67±0.05 29.33±0.04 21.49±0.01 2.5.2 填充结构对质构特性的影响
表4显示了硬度、粘附性、弹性、内聚性、胶着性、坚实度的方差分析。可以看出填充比和填充模式对于3D打印样品的硬度、粘附性、胶着性和坚实度有极显著影响(P<0.01),对弹性和内聚性影响不显著(P>0.01)。图7显示了填充结构对3D打印样品质构特性的影响,与表4的结果一致。从图7中可以看出,样品的硬度随填充比的提高迅速增加,例如,直线型填充模式下,当填充比从40%提高到80%时,硬度从266.56 g增加到455.56 g。此外,填充模式也显著影响样品的硬度,在填充比相同时,填充模式为直线型时样品的硬度最大。比如填充比为80%时,直线型、蜂窝状、八角螺旋填充模式下,硬度分别为455.56、365.54、318.98 g。图7表明填充比和填充模式显著影响样品的粘附性,当填充模式相同时,随着填充比增加,样品的粘附性逐渐减低。样品的胶着性与填充结构的关系呈现出与硬度相同的变化趋势。填充比和填充模式显著影响样品的胶着性。样品的胶着性随着填充比和填充模式的变化而变化,比如在蜂窝状和直线型填充模式下,当填充比从40%提高到80%时,样品胶着性分别在66.73~105.34 N和64.40~102.82 N之间变化。填充模式为直线型时,样品胶着性最大,八角螺旋填充时,样品胶着性最小。同时,填充比和填充模式显著影响样品的坚实度。样品坚实度随填充比的提高而增加,以直线型为例,当填充比从40%增加到80%时,样品的坚实度从88.94 g增加到164.74 g。从表4中也可以看出,样品坚实度也随着填充模式的改变发生变化,与硬度和胶着性相同,在直线型填充模式下,样品的坚实度最大。然而,从图7中可以看出填充比和填充模式对于样品的弹性和内聚性并没有显著影响。
表 4 硬度、粘附性、弹性、内聚性、胶着性、坚实度的方差分析Table 4. Variance analysis of hardness, adhesiveness, springiness, cohesiveness, gumminess and firmness质构特性 差异来源 均方和 均方 P值 显著性 硬度 模型 186800.00 23354.49 <0.0001 极显著 A(填充比) 92844.45 46422.23 <0.0001 极显著 B(填充模式) 83205.02 41602.51 <0.0001 极显著 AB 10786.44 2696.61 0.0012 极显著 纯误差 6771.02 376.17 总离差 193600 粘附性 模型 553100 138300 <0.0001 极显著 A(填充比) 287900 144000 0.0002 极显著 B(填充模式) 265200 132600 0.0003 极显著 失拟度 36842.89 9210.72 0.5520 不显著 纯误差 212300 11791.84 总离差 802200 弹性 模型 0.00 不显著 纯误差 0.021 0.0022848 总离差 0.074 内聚性 模型 0.00 不显著 纯误差 0.012 0.0006391 总离差 0.023 胶着性 模型 10809.24 2702.31 <0.0001 极显著 A(填充比) 7058.80 3529.40 <0.0001 极显著 B(填充模式) 3750.43 1875.22 <0.0001 极显著 纯误差 799.82 44.43 总离差 11873.16 坚实度 模型 29693.99 3711.75 <0.0001 极显著 A(填充比) 21026.06 10513.03 <0.0001 极显著 B(填充模式) 7048.35 3524.18 <0.0001 极显著 AB 1619.58 404.90 <0.0001 极显著 纯误差 319.41 17.74 总离差 30013.40 3. 结论
本研究发现,随着鸡骨粉添加量的增加,屈服应力、黏度和G'降低。当鸡骨粉:木耳粉=2:8时,3D打印过程中物料容易挤出,且打印后的样品成型效果和稳定性最好。另外,样品的填充结构对硬度、粘附性、胶着性和坚实度具有显著影响,可通过改变填充结构实现对样品质构特性的调控,这可能为生产易于咀嚼的食品提供新的思路和手段。然而,本研究对质构特性的调控目前还比较粗糙,以后可进一步深入发掘内部结构参数与质构特性的定量关系及数学模型,并最终实现质构特性的定制化设计。
-
表 1 剪切速率为1、10、50 s−1时样品的黏度和幂律参数
Table 1 Viscosity of mixed gel system at 1, 10, 50 s−1 and power law related parameters
配方
(鸡骨粉:木耳粉)η1 η10 η50 幂律方程 K(Pa·sn) n R2 0:10 971.70±11.92 146.90±5.21 15.73±2.74 1029.87±33.76 0.26±0.04 0.998 1:9 636.40±17.86 118.53±2.04 18.34±1.72 667.13±26.70 0.21±0.03 0.997 2:8 422.45±0.65 80.67±0.11 17.23±0.31 452.66±2.70 0.23±0.01 0.999 3:7 468.95±47.15 76.80±3.97 15.87±1.05 451.56±5.71 0.27±0.00 0.999 4:6 225.37±10.54 42.30±1.22 12.67±0.21 248.18±13.91 0.28±0.01 0.100 表 2 不同配方和不同储存时间的3D打印样品
Table 2 3D printed samples with different formulation and storage time
打印后时间(min) 鸡骨粉:木耳粉 0:10 1:9 2:8 3:7 4:6 0 




60 




描述 无明显差别 无明显差别 无明显差别 无明显差别 明显塌陷 表 3 不同填充条件下3D打印圆柱的尺寸特性和孔隙率
Table 3 Dimensional properties and porosity of 3D printed cylindrical structure with different infill conditions
填充条件
(填充模式-填充比)直径(mm) 高度(mm) 孔隙率(%) 打印模型 30 30 − 直线型-40% 29.17±0.09 29.25±0.04 37.57±0.02 直线型-60% 29.00±0.01 29.33±0.02 21.18±0.02 直线型-80% 30.17±0.04 29.50±0.03 7.47±0.01 蜂窝状-40% 29.83±0.04 29.33±0.04 28.97±0.02 蜂窝状-60% 30.00±0.06 29.58±0.03a 17.22±0.01 蜂窝状-80% 30.50±0.05 29.58±0.03 4.24±0.02 八角螺旋-40% 29.33±0.05 29.00±0.06 46.33±0.03 八角螺旋-60% 29.67±0.05 29.33±0.04 33.70±0.01 八角螺旋-80% 29.67±0.05 29.33±0.04 21.49±0.01 表 4 硬度、粘附性、弹性、内聚性、胶着性、坚实度的方差分析
Table 4 Variance analysis of hardness, adhesiveness, springiness, cohesiveness, gumminess and firmness
质构特性 差异来源 均方和 均方 P值 显著性 硬度 模型 186800.00 23354.49 <0.0001 极显著 A(填充比) 92844.45 46422.23 <0.0001 极显著 B(填充模式) 83205.02 41602.51 <0.0001 极显著 AB 10786.44 2696.61 0.0012 极显著 纯误差 6771.02 376.17 总离差 193600 粘附性 模型 553100 138300 <0.0001 极显著 A(填充比) 287900 144000 0.0002 极显著 B(填充模式) 265200 132600 0.0003 极显著 失拟度 36842.89 9210.72 0.5520 不显著 纯误差 212300 11791.84 总离差 802200 弹性 模型 0.00 不显著 纯误差 0.021 0.0022848 总离差 0.074 内聚性 模型 0.00 不显著 纯误差 0.012 0.0006391 总离差 0.023 胶着性 模型 10809.24 2702.31 <0.0001 极显著 A(填充比) 7058.80 3529.40 <0.0001 极显著 B(填充模式) 3750.43 1875.22 <0.0001 极显著 纯误差 799.82 44.43 总离差 11873.16 坚实度 模型 29693.99 3711.75 <0.0001 极显著 A(填充比) 21026.06 10513.03 <0.0001 极显著 B(填充模式) 7048.35 3524.18 <0.0001 极显著 AB 1619.58 404.90 <0.0001 极显著 纯误差 319.41 17.74 总离差 30013.40 -
[1] GUO C F, ZHANG M, BHANDARIB. Model building and slicing in food 3D printing processes: A review[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 2019, 18(4): 1052-1069.
[2] RUBIO E, HURTADO S. 3D food printing technology at home, domestic application[J]. Fundamentals of 3D Food Printing and Applications,2019:289−329.
[3] LIU Z B, BHANDARI B, PRAKASH S, et al. Creation of internal structure of mashed potato construct by 3D printing and its textural properties[J]. Food Research International (Ottawa, Ont.),2018,111:534−543. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.05.075
[4] 周国华, 于国萍. 黑木耳多糖降血脂作用的研究[J]. 现代食品科技,2005(1):46−48. [ZHOU G H, YU G P, et al. Study on hypolipidemic effect of Auricularia auricularia polysaccharide[J]. Modern Food Science & Technology,2005(1):46−48. [5] 刘雅静. 黑木耳化学成分及药理活性研究[D]. 淄博: 山东轻工业学院, 2011. LIU Y J. Studies on the chemical components and pharamacological activities of Auricularia auricular [D]. Zibo: Qilu University of Technology, 2011.
[6] 孙畅, 姜明, 段旭彤, 等. 黑木耳的保健和药用价值以及开发前景分析[J]. 科技视界,2013(12):17−18. [SUN Ch, JIANG M, DUAN X T, et al. Summarizing the value of medical and healthth care and development prospect on Auricularia auricular[J]. Science & Technology Vision,2013(12):17−18. [7] 张燕燕, 刘新春, 王雪, 等. 黑木耳营养成分及生物活性研究进展[J]. 南方农业,2018,12(29):130−134. [ZHANG Y Y, LIU X C, WANG X, et al. Advances in studies on nutritional components and biological activities of Auricularia[J]. South China Agriculture,2018,12(29):130−134. [8] 白璧辉, 谢兴文, 李鼎鹏, 等. 骨质疏松症发病因素及其与中医体质相关性研究进展[A]. 中国中西医结合学会骨伤科专业委员会. 2019楚天骨科高峰论坛暨第二十六届中国中西医结合骨伤科学术年会论文集[C]//中国中西医结合学会, 2019: 2. BAI B H, XIE X W, LI D P, et al. Research progress on the pathogenesis of osteoporosis and its correlation with TCM constitution [A]. Professional Committee of Orthopedics and Traumatology of Chinese Association of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine. 2019 Chutian Orthopedics Summit Forum and the 26th Annual Conference of Chinese Integrated Traditional and Western Orthopedics [C]//Professional Committee of Orthopedics and Traumatology of Chinese Association of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine: Chinese Association of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine, 2019: 2.
[9] LIU Z B, ZHANG M, BHANDARIB, et al. Impact of rheological properties of mashed potatoes on 3D printing[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2018,220:76−82. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2017.04.017
[10] AHMAD M U, TASHIRO Y, MATSUKAWA S, et al. Gelation mechanism of surimi studied by 1H NMR relaxation measurements[J]. Journal of Food Science,2007,72(6):362−367. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2007.00411.x
[11] HUNG L, ZHANG M, MUJUMDAR A S, et al. Comparison of four drying methods for re-structured mixed potato with apple chips[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2011,103(3):279−284. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2010.10.025
[12] LIU Z B, BHANDARIB, PRAKASH S, et al. Linking rheology and printability of a multicomponent gel system of carrageenan-xanthan-starch in extrusion based additive manufacturing. Food Hydrocoll, 2019, 87: 413–424.
[13] KRISHNARAJ P, ANUKIRUTHIKA T, CHOUDHARY P, et al. 3D extrusion printing and post-processing of fibre-rich snack from indigenous composite flour[J]. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 2019, 12(10): 1776-1786.
[14] 刘振彬. 马铃薯泥及其淀粉混合凝胶体系的挤出型3D打印及后加工适应性研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2020. LIU Z B. Study on extrusion 3D printing and post-processing adaptability of mashed potato and its starchmixed gel system[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2020.
[15] DICK A, BHANDARI B, PRAKASH S. Printability and textural assessment of modified-texture cooked beef pastes for dysphagia patients[J]. Future Foods, 2021, 3,100006.
[16] REZENDE R A, BáRTOLO P J, MENDES A, et al. Rheological behavior of alginate solutions for biomanufacturing[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2009, 113(6): 3866−3871.
[17] SWEENEY M, CAMPBELL L L, HANSON J, et al. Characterizing the feasibility of processing wet granular materials to improve rheology for 3D printing[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2017, 52(22): 13040–13053.
[18] PAXTON N, SMOLAN W, BöCK T, et al. Proposal to assess printability of bioinks for extrusion-based bioprinting and evaluation of rheological properties governing bioprintability[J]. Biofabrication, 2017, 9(4): 044107.
[19] WILSON S A, CROSS L M, PEAK C W, et al. Shear-thinning and thermo-reversible nanoengineered inks for 3D bioprinting[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(50): 43449–43458.
[20] LIU Z B, ZHANG M, YE Y F. Indirect prediction of 3D printability of mashed potatoes based on LF-NMR measurements[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2020:287.
[21] SHAO Y, CHAUSSY D, GROSSEAU P, et al. Use of microfibrillated cellulose/lignosulfonate blends as Carbon precursors: Impact of hydrogel rheology on 3D printing[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2015,54(43):10575−10582.
[22] ZHANG M, VORA A, HAN W, et al. Dual-responsive hydrogels for direct-write 3D printing[J]. Macromolecules,2015,48(18):6482−6488. doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.5b01550
[23] ÁLVAREZ-CASTILLO E, OLIVEIRA S, BENGOECHEA C, et al. A rheological approach to 3D printing of plasma protein based doughs[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2021:288.
[24] GUO C F, ZHANG M, SAKAMON D. 3D extrusion-based printability evaluation of selected cereal grains by computational fluid dynamic simulation[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2020:286.
[25] AZAM R, ZHANG M, BHANDARI B, et al. Effect of different gums on features of 3D printed object based on vitamin-D enriched orange concentrate[J]. Food Biophysics,2018,13:250−262. doi: 10.1007/s11483-018-9531-x
[26] ASSIFAOUI A, CHAMPION D, CHIOTELLI E, et al. Characterization of water mobility in biscuit dough using a low-field 1H NMR technique[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2006,64(2):197−204. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2005.11.020
[27] SHALVIRI A, LIU Q, ABDEKHODAIE M J. et al. Novel modified starch-xanthan gum hydrogels for controlled drug delivery: Synthesis and characterization[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2009,79(4):898−907.
[28] LIU Z B, ZHANG M, BHANDARI B, et al. 3D printing: Printing precision and application in food sector[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2017,69:83−94.
[29] AL-MUSLIMAWI A, TAMADDON-JAHROMI HR, WEBSTER M F. Simulation of viscoelastic and viscoelastoplastic die-swell flows[J]. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics,2013,191:45−56. doi: 10.1016/j.jnnfm.2012.08.004
[30] SEVERINI C, AZZOLLINI D, ALBENZIO M, et al. On printability, quality and nutritional properties of 3D printed cereal based snacks enriched with edible insects[J]. Food Research International (Ottawa, Ont. ),2018,106:66−676.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 翟红旭,尹泽希,孙希云,李斌,李冬男,郭弘冰,张琦. 响应面法优化草莓混合凝胶3D打印配方. 食品工业科技. 2024(09): 147-158 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 邓亦秋,杜黎丹,董欣琳,吕欣,李玲,肖功年. TG酶对再制奶酪3D打印特性的影响. 中国食品学报. 2023(09): 120-128 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:



