Determination of the Effect of Different Stabilizers on the Stability of Passion Fruit Juice Based on Space and Time Resolved Extinction Profiles
-
摘要: 为了解决西番莲果汁稳定性差、易沉淀的问题,本研究以西番莲果汁为研究对象,使用基于空间-时间消光图谱技术的全自动稳定性分析仪以沉降速率、积分透射率和透射红外图谱为主要分析指标,判定稳定剂琼脂、羧甲基纤维素钠及这两种稳定剂复配对西番莲果汁稳定性的影响,选出相对适宜的单一稳定剂以及复配稳定剂的添加比例。结果表明:添加单一稳定剂的情况下,羧甲基纤维素钠(CMC-Na)相较琼脂各组的图谱线条更紧凑,线条走向更平稳,其整体稳定效果更好,而添加量为0.30%~0.35%的(CMC-Na)可获得单一稳定剂的最佳稳定效果,其沉降速率最低((0.0209±0.0003)%/s,(0.0181±0.0002)%/s);两种稳定剂复配情况下,随着CMC-Na含量的上升以及琼脂含量的降低,图谱中的线条越紧凑和平稳,果汁稳定性增强,最佳的复配添加配比为0.35% CMC-Na+0.15%琼脂和0.30% CMC-Na+0.20%琼脂,其沉降速率最低((0.0231±0.0004)%/s,(0.0209±0.0004)%/s)。上述发现可为西番莲果汁的开发和稳定体系的构建提供一定的科学依据。
-
关键词:
- 西番莲 /
- 稳定剂 /
- 羧甲基纤维素钠(CMC-Na) /
- 琼脂 /
- LUMI全功能稳定性分析仪
Abstract: In order to solve the problems such as poor stability and rapid precipitation of passion fruit juice, the influence of the different stabilizers on the stability of passion fruit juice was explored using the automatic stability analyzer based on the space and time resolved extinction profiles technology (STEP-Technology) in the current study. The sedimentation rate, the integral transmittance and transmission infrared spectrum were selected as the main indexes to determine the stabilizing effects of agar and/or sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC-Na) on the passion fruit juice stability. Results showed that, addition of CMC-Na resulted smoother light extinction curves compared to agar, indicating CMC-Na might exert better stabilizing effects when single stabilizer was used. The optimal stabilizing effect being obtained by addition of CMC-Na at 0.30%~0.35% with the lowest settlement rates ((0.0209±0.0003) %/s and (0.0181±0.0002) %/s, respectively) being recorded. When these two stabilizers were applied simultaneously, it was found that increase in CMC-Na and decrease in agar led to the smoother light extinction curves and enhanced stability of juice. The optimal stability were reached by addition of 0.35% CMC-Na+0.15% agar and 0.30% CMC-Na+0.20% agar, which showed the lowest settlement rates ((0.0231±0.0004) %/s and (0.0209±0.0004) %/s, respectively). These findings could provide a scientific basis for the development of passion fruit juice with improved stability.-
Keywords:
- Passiflora edulis /
- stabilizers /
- sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC-Na) /
- agar /
- LUMiSizer
-
西番莲是一种生长在热带、亚热带气候的草质藤本植物,属于西番莲科、西番莲属,学名Passiflora edulis[1]。西番莲作为一种独特浓缩香型的水果,含有香味物质达24种[2],糖酸比为7.5:1[3],酸甜可口,风味适宜,是很好的果汁加工原料,具有“饮料之王”、“果汁之王”的美誉[4]。同时,西番莲还被证实富含多种营养功能成分,包括有机酸(柠檬酸等)[5]、微量元素(铁、硒、锰等)[6]、氨基酸(谷氨酸等)[6]、维生素C[7]、酯类及萜烯类等[8],有抗焦虑、抗肿瘤[8]、抗炎作用[9]、预防心血管疾病[10]、缓解焦虑失眠[11]、减轻压力[12]、神经保护[13]等保健作用,具有用于进一步开发保健功能饮料的潜力。
虽然西番莲果汁饮料开发生产的前景良好,但是目前研究发现西番莲饮料常存在稳定性差、易产生沉淀、出现分层的问题,严重影响果汁的口感与外观,进而降低商品价值[14],因此进一步探索增强西番莲果汁的稳定性的方式成为了当前该领域重要的研究课题之一。目前在果汁饮料生产过程中适当添加稳定剂(如羧甲基纤维素钠(CMC-Na)及琼脂等)是有效提高其稳定性的常用方法,可以使果汁中介质密度分散,形成均匀稳定的溶液,从而提高饮品的口感及产品的质量[15]。
目前常用的果汁稳定性评价方法有:感官评价法[16]、自然沉淀率法[17]、离心沉淀率法[18-19],但上述测定方式均需要人为评测并需等待较长的静置时间,主观性强、效率低且较为繁琐。为解决上述难点,基于空间-时间消光图谱技术的全自动稳定性分析仪测定法[20]应运而生。该方法的测定原理是采用Stock定律和Beer-Lambert定律来对样品分离沉降过程监测[21]。根据Stock定律,液滴的运动速度与半径平方存在线性关系[22];而根据Beer-Lambert定律,单色光的吸光度与吸收物质的浓度之间存在线性关系[23]。从而该方法以离心分析方法模拟加速沉降过程并测定透光率变化,进而判断出产品的稳定性[24],目前已经被证实可用于研究悬浊液、乳状液等流体的稳定性测定及优化[25-26];还可以加速测量多种影响溶液稳定性的物理化学过程,如相分离速率、粒度分布和沉积物固结[27],从而确定造成其不稳定的原因。此外,该方法还具有能够在几乎任何浓度下测定样品稳定性的优点[25]。
基于此,本研究选择基于该原理的LUMi全自动稳定性分析仪,采用离心加速法模拟西番莲果汁在放置过程中的沉降速率,并通过检测其透光率的变化趋势,测定不同稳定剂在不同添加量及不同复配比例条件下对西番莲果汁稳定性的影响,从而优化得到可有效稳定西番莲果汁饮料的感官品质的稳定剂添加比例,进而为改良西番莲果汁饮料的生产提供一定的参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
西番莲原浆 果朝(广西)食品有限公司;羧甲基纤维素钠(300~800 mPa∙s) 国药集团化学试剂有限公司;琼脂 北京酷来搏科技有限公司。
JYL-C19V九阳厨房料理机 九阳股份有限公司;HWS-26电热恒温水浴锅 上海一恒科学仪器有限公司;SQP电子天平 赛多利斯科学仪器有限公司;LUMiSizer全功能稳定性分析仪 源顺国际有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 西番莲果汁制备
取适量西番莲果浆放入料理机中进行榨汁处理;榨汁完成后,使用200目的滤布对果汁进行过滤;为了提高过滤的效果,将过滤后的果汁继续使用滤布进行二次过滤,最终制得西番莲果汁样品。
1.2.2 稳定剂溶液的制备
根据宋华静[28-29]悬浮稳定剂的制备的方法,将稳定剂按2.5(w/v)比例加入40 ℃的纯净水至完全溶解。然后进一步稀释至实验所需浓度进行实验。
1.2.3 添加稳定剂的果汁样品制备
参考杜伟等[30]及陈毓滢等[31]的研究结果,结合实际对方案进行调整。配制成含有0.15%、0.20%、0.25%、0.30%、0.35%的琼脂的西番莲果汁每组各5 mL,用于测定单一稳定剂琼脂的稳定效果;配制成含有0.15%、0.20%、0.25%、0.30%、0.35%的CMC-Na的西番莲果汁每组各5 mL,用于测定单一稳定剂CMC-Na的稳定效果;设定复配稳定剂总添加量为0.50%[32],将CMC-Na与琼脂按0.25% CMC-Na+0.25%琼脂,0.15% CMC-Na+0.35%琼脂,0.35% CMC-Na+0.15%琼脂,0.30% CMC-Na+0.20%琼脂,0.20% CMC-Na+0.30%琼脂的比例进行配比用于后续测定分析。
1.2.4 稳定性分析方法
吸取425 μL的果汁放入类型为LUMi 2 mm,PC,Rect. Synthenic Cell(110-131)的试管中(2 mm×8 mm),全部注入样品后,依次放入LUMiSizer机器中,并通过在波长为865 nm的近红外光束对样品进行扫描分析。扫描参数设定为1倍的扫描光强、25 ℃及4000 r/min的转速扫描一个小时,每间隔30 s扫描一次,共计扫描120次,测定径向位置的函数[24]。扫描结束后,样品对应的空间-时间消光图谱、积分透射率及沉降速率结果通过全功能稳定性分析仪附带分析软件SEPView6进行分析。
1.3 数据处理
使用SEPViewer 6对结果进行处理分析,并使用GraphPad Prism8进行数据统计和差异显著性分析(P<0.05为显著)以及使用Origin 2019b进行图表的绘制。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 琼脂添加量对西番莲果汁稳定性的影响
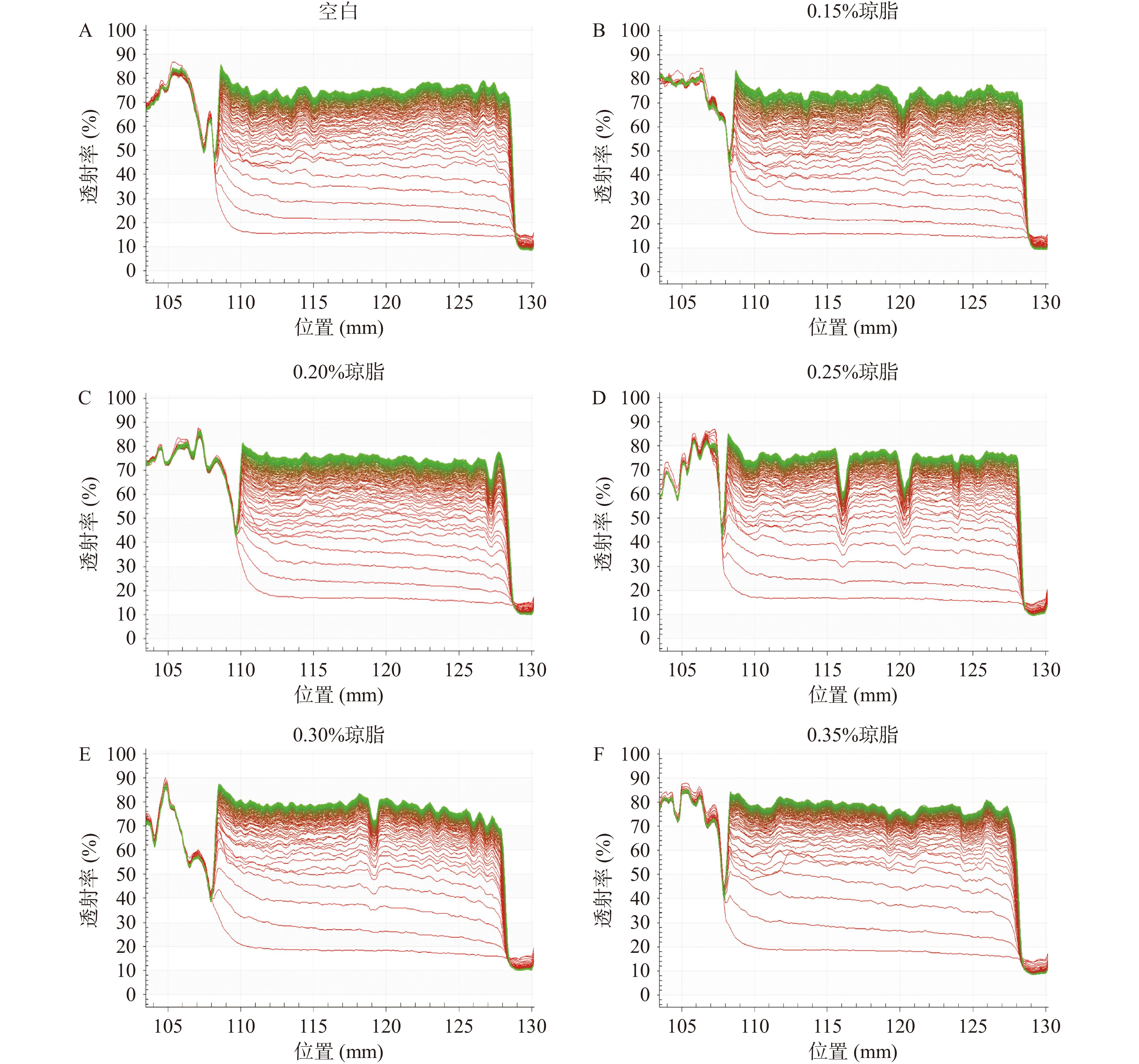
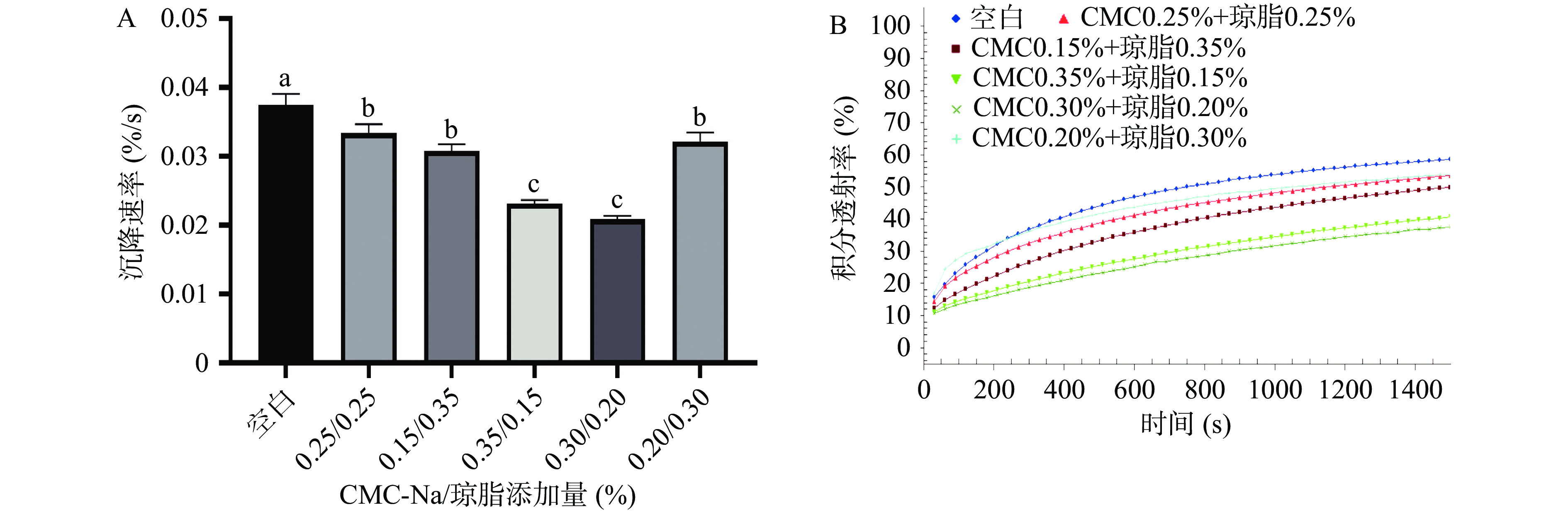
通过全自动稳定性分析仪对添加不同稳定剂的西番莲果汁样品进行检测分析,从而获得空间-时间消光图谱(图1)。该图谱反映了西番莲果汁样品透射率随样品位置不同及沉降时间延长所产生的变化。该图谱中图谱线条越紧凑,线条走向越平稳,则代表样品的稳定性越好。进一步通过对积分透射率做斜率可得沉降速率(积分透射率/时间,%/s),从而可对稳定性进行量化比较。沉降速率越低则代表沉淀出现的时间越晚,稳定性越好[30]。
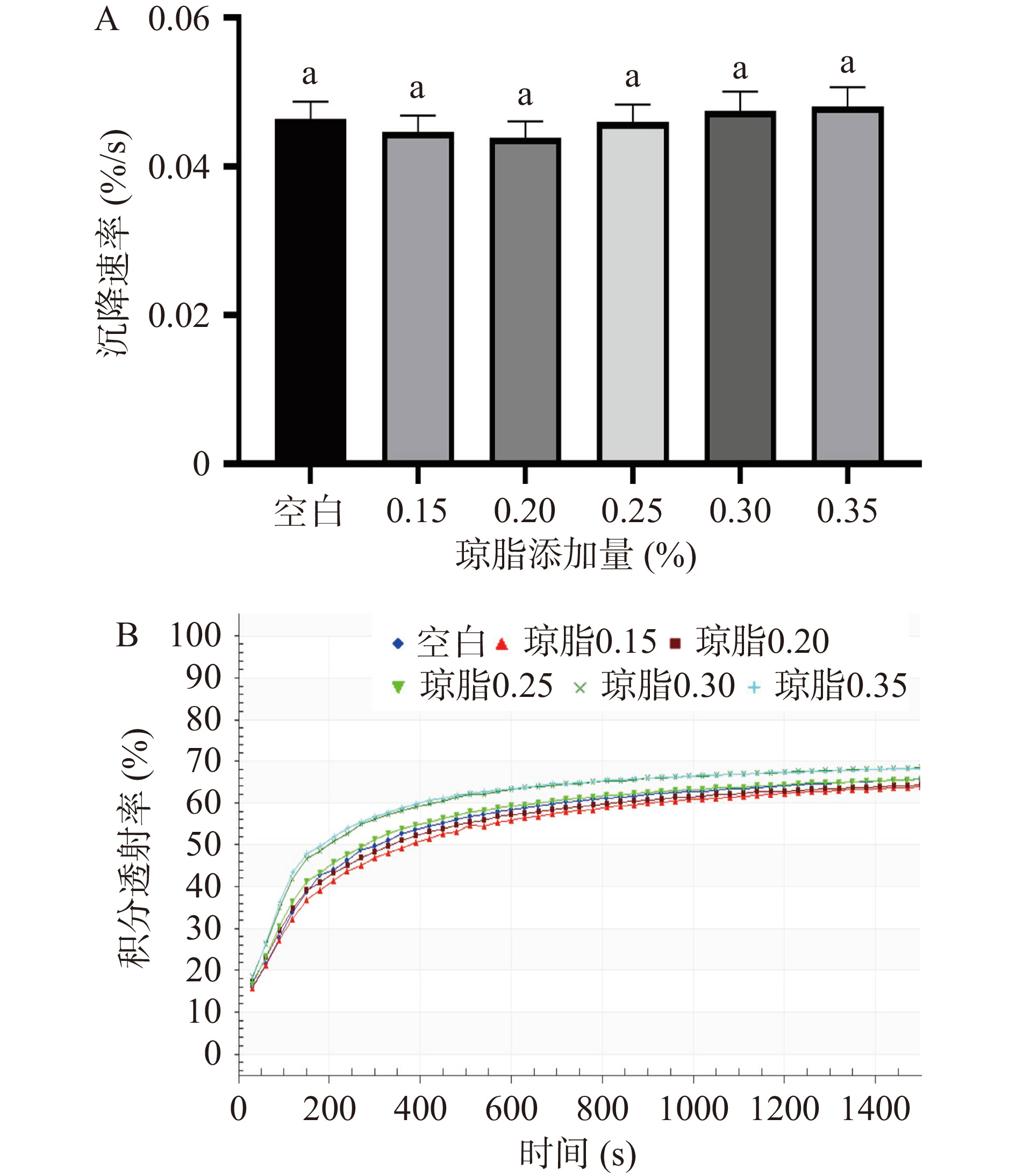
由实验所得到的空间-时间消光图谱(图1)可知,添加0.20%琼脂的西番莲果汁样品图谱线条之间最为紧凑,线条走向平稳,说明其稳定性较好;当琼脂含量增加,即当琼脂添加到0.25%时,图谱线条稀疏,线条波动较大,说明其稳定性较差。由沉降速率(图2A)及积分透射率(图2B)结果所示,添加0.15%和0.20%琼脂后西番莲果汁积分透射率及沉淀速率((0.0447±0.0018)%/s,(0.0439±0.0018)%/s)相较于空白组((0.0464±0.0019)%/s)有所降低,样品稳定性略有提升。但是,由图1和图2我们可以看到,琼脂各组与空白组的积分透射率以及图谱的变化差异并不明显,并且在沉降速率的对比中并无显著性的差异(P>0.05),说明添加琼脂后对西番莲果汁稳定性没有很大提升。而同时发现,当琼脂添加量过高(大于0.25%)时,琼脂的添加反而使得沉降速率上升甚至超过空白组,部分图谱出现不平整、突起的部分,说明琼脂的过量添加不仅不能起到增稠稳定的作用,反而可能造成稳定性的进一步破坏。这可能是由于过量添加的琼脂形成小颗粒凝结所导致的[33]。琼脂的空间凝胶网络形成的温度大约发生在40 ℃[34],即说明琼脂的凝胶温度约为40 ℃,而果汁样品在实验中温度逐渐降低,当温度降低到40 ℃及以下时琼脂会出现凝结并呈现颗粒状,从而加快了果汁的沉淀,导致西番莲饮料的稳定性下降。以上结果表明,琼脂较低浓度下添加可小幅度增加西番莲果汁的稳定性,但当添加量增加到一定浓度时反而使稳定性降低,其对于西番莲果汁的稳定性没有明显改善,不适合作为西番莲果汁的稳定剂。
2.2 CMC-Na添加量对西番莲果汁稳定性的影响
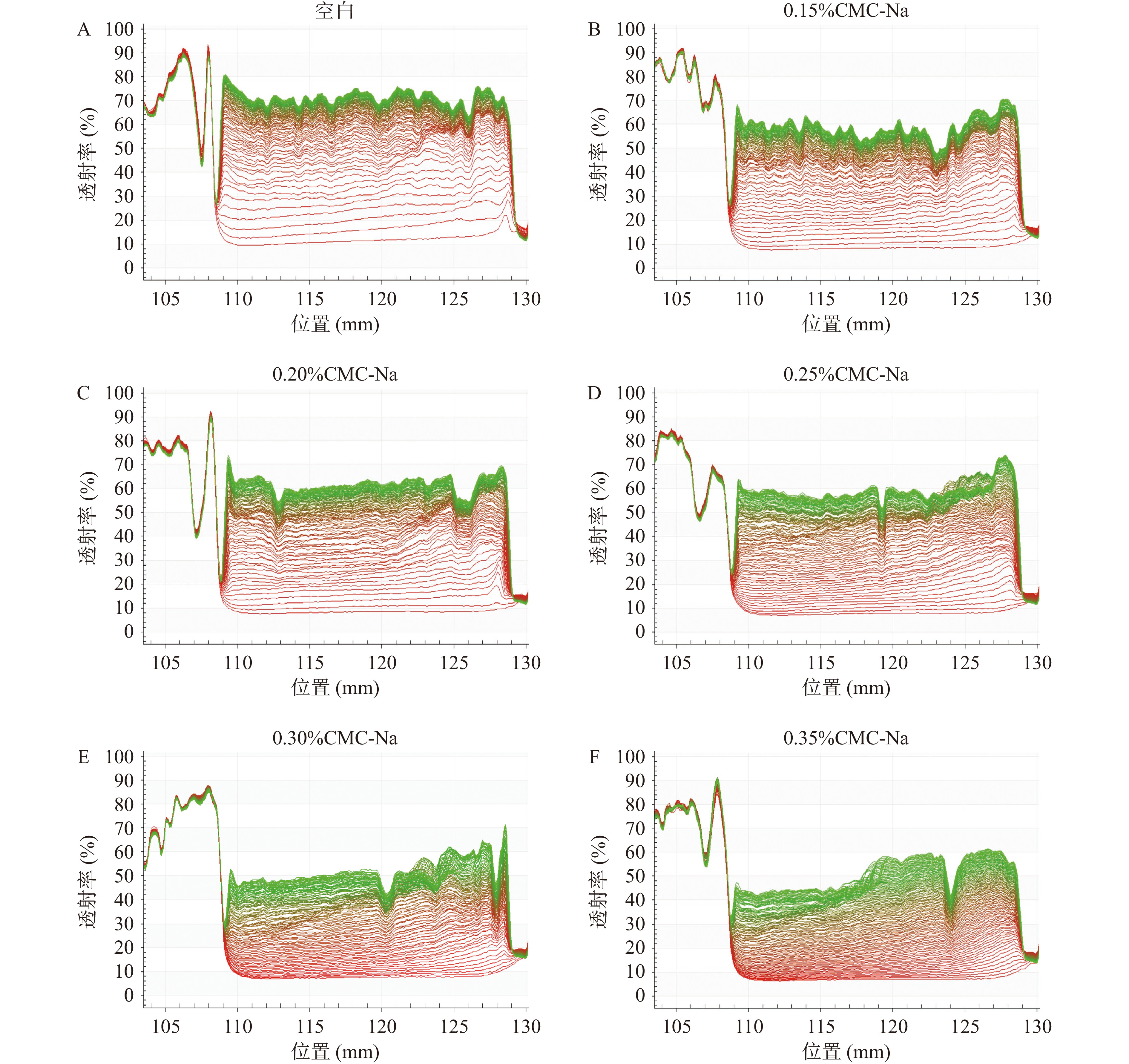
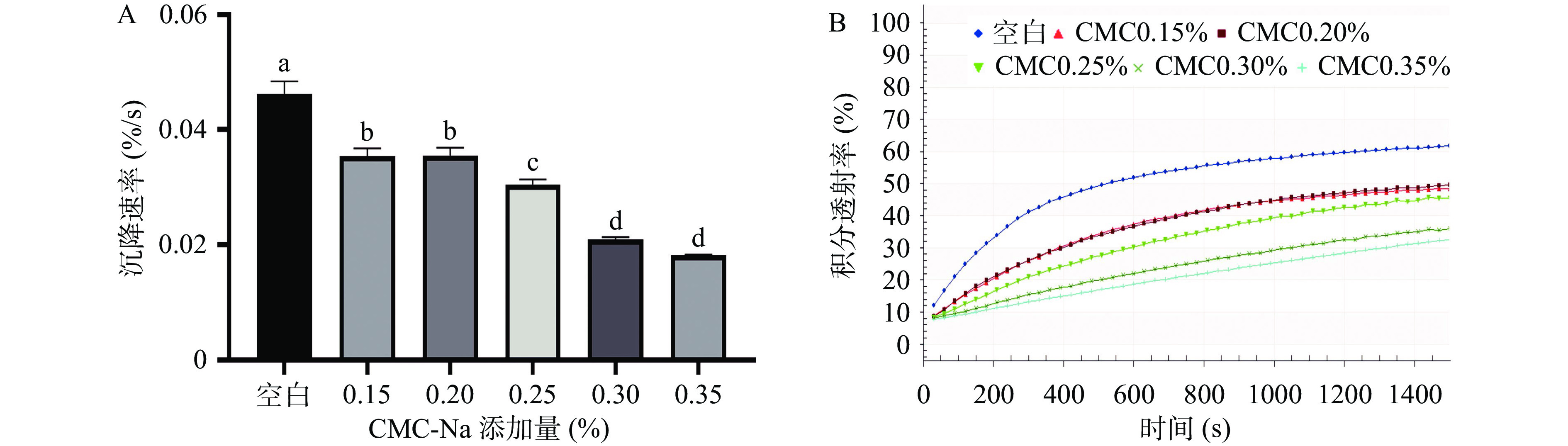
由空间-时间消光图谱(图3)所示,当CMC-Na的添加量为0.30%和0.35%时,图谱线条较其他组别更为紧凑,显示出更好的稳定性,且果汁稳定性与CMC-Na的添加量基本呈剂量依赖性增加。由沉降速率(图4A)和积分透射率(图4B)所示,添加CMC-Na的果汁样品的沉降速率以及积分透射率均低于空白组;尤其在沉降速率中,CMC-Na组别与空白组((0.0463±0.0018)%/s)有显著的差异性(P<0.05)。而在CMC-Na不同添加量的组间对比中,添加量为0.30%和0.35% CMC-Na的果汁样品的沉降速率为(0.0209±0.0003)%/s和(0.0181±0.0002)%/s,显著(P<0.05)低于其他添加比例,而这两种比例之间无显著性差异(P>0.05),因此添加0.30%和0.35% CMC-Na时对西番莲果汁稳定性的改善效果最好。这可能是因为CMC-Na作为高分子量的阴离子型聚合物[35],其分子中携带的阴离子负电荷通过结合易导致果汁中沉淀产生的物质,减少了果汁中絮状沉淀的发生,并促进果汁形成稳定性较好的悬浊液,最终提升了果汁的稳定性[3]。因此在单一稳定剂的实验中,0.30%和0.35% CMC-Na的添加使西番莲果汁呈现出最佳的稳定效果。
![]() 图 3 果汁中添加不同含量的CMC-Na的空间-时间消光图谱注:A:无添加CMC-Na(空白)的空间-时间消光图谱;B: CMC-Na添加量为0.15%的空间-时间消光图谱;C:CMC-Na添加量为0.2%的空间-时间消光图谱;D:CMC-Na添加量为0.25%的空间-时间消光图谱;E:CMC-Na添加量为0.30%的空间-时间消光图谱;F:CMC-Na添加量为0.35%的空间-时间消光图谱。Figure 3. Space and time resolved extinction profiles of passion fruit juice with different content of CMC-Na
图 3 果汁中添加不同含量的CMC-Na的空间-时间消光图谱注:A:无添加CMC-Na(空白)的空间-时间消光图谱;B: CMC-Na添加量为0.15%的空间-时间消光图谱;C:CMC-Na添加量为0.2%的空间-时间消光图谱;D:CMC-Na添加量为0.25%的空间-时间消光图谱;E:CMC-Na添加量为0.30%的空间-时间消光图谱;F:CMC-Na添加量为0.35%的空间-时间消光图谱。Figure 3. Space and time resolved extinction profiles of passion fruit juice with different content of CMC-Na2.3 复配稳定剂添加量对西番莲果汁稳定性的影响
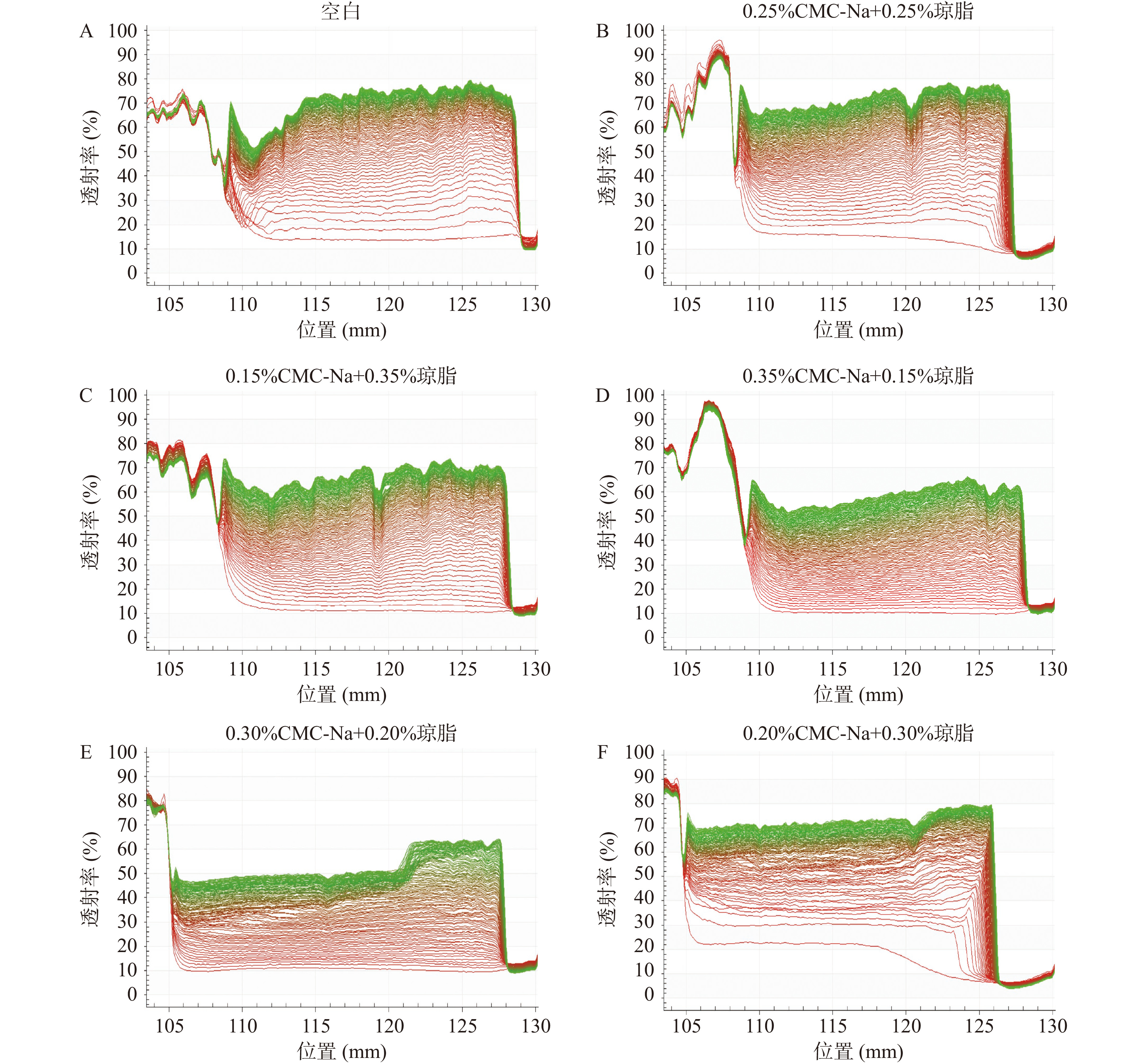
目前,市面上往往不是单一使用食品添加剂,而是将多种添加剂复配使用,通过协同增效更好发挥出稳定剂的作用,在保证产品品质的同时减少单种添加剂的使用量,以在实际生产中达到降低成本或者符合标准规定的目的[36]。故将CMC-Na与琼脂混合复配,通过实验分析得到这两种稳定剂的最佳复配比例,通过全自动稳定性分析仪分析得到的空间-时间消光图谱如图5所示。
![]() 图 5 果汁中添加不同比例的CMC-Na和琼脂的空间-时间消光图谱注:A:CMC-Na和琼脂均无添加(空白)的空间-时间消光图谱;B:添加量为0.25%CMC-Na+0.25%琼脂的空间-时间消光图谱;C:添加量为0.15%CMC-Na+0.35%琼脂的空间-时间消光图谱;D:添加量为0.35%CMC-Na+0.15%琼脂的空间-时间消光图谱;E:添加量为0.30%CMC-Na+0.20%琼脂的空间-时间消光图谱;F:添加量为0.20%CMC-Na+0.30%琼脂的空间-时间消光图谱。Figure 5. Space and time resolved extinction profiles of passion fruit juice with different content of CMC-Na and agar
图 5 果汁中添加不同比例的CMC-Na和琼脂的空间-时间消光图谱注:A:CMC-Na和琼脂均无添加(空白)的空间-时间消光图谱;B:添加量为0.25%CMC-Na+0.25%琼脂的空间-时间消光图谱;C:添加量为0.15%CMC-Na+0.35%琼脂的空间-时间消光图谱;D:添加量为0.35%CMC-Na+0.15%琼脂的空间-时间消光图谱;E:添加量为0.30%CMC-Na+0.20%琼脂的空间-时间消光图谱;F:添加量为0.20%CMC-Na+0.30%琼脂的空间-时间消光图谱。Figure 5. Space and time resolved extinction profiles of passion fruit juice with different content of CMC-Na and agar根据空间-时间消光图谱(图5)对比可知,添加量为0.35% CMC-Na+0.15%琼脂和0.30% CMC-Na+0.20%琼脂的图谱线条更为紧凑,线条较平缓。随着CMC-Na含量的上升,琼脂含量降低,西番莲果汁稳定性越好。当琼脂的含量增加时,西番莲饮料中的颗粒增多,分散率增高,这是由于琼脂的易凝结性质所导致的;而CMC-Na的含量增加时,琼脂的不利影响减弱,能更好的起到稳定的作用。0.35% CMC-Na+0.15%琼脂和0.30% CMC-Na+0.20%琼脂的积分透射率明显低于其他组(图6B)。由图6A所示,复配添加剂的所有组别沉降速率均显著(P<0.05)低于空白组,而0.35% CMC-Na+0.15%琼脂和0.30% CMC-Na+0.20%琼脂的速率为(0.0231±0.0004)%/s,(0.0209±0.0004)%/s显著(P<0.05)低于空白组((0.0375±0.0013)%/s)及其他各组同时这两种比例的复配添加剂沉降速率间无差异显著性(P>0.05)。因此,0.35% CMC-Na+0.15%琼脂和0.30% CMC-Na+0.20%琼脂这两种复配比例添加下的果汁样品稳定性最好。
2.4 单一及复配稳定剂添加量对西番莲果汁稳定性效果的对比
通过上述实验,筛选出了单一稳定剂及复配稳定剂的最佳添加量,为了进一步了解两者对西番莲果汁稳定性的改善效果之间是否有显著性差异,对比了最佳添加量的单一稳定剂及复配稳定剂与空白组的沉降速率之间的差异。如表1所示,添加了单一稳定剂的样品与添加了复配稳定剂的样品稳定性不同,单一稳定剂和复配稳定剂对沉降速率的改善效果间有显著性差异(P<0.05)。0.30%和0.35% CMC-Na的添加,使西番莲果汁的沉降速率下降程度更高,沉淀速度更慢,整体稳定性较添加0.35% CMC-Na+0.15%琼脂和0.30% CMC-Na+0.20%琼脂的果汁样品更好。这可以再一次说明,琼脂的加入不仅不能使西番莲果汁稳定性提升,反而会造成稳定性的进一步破坏,其不适合作为西番莲饮料的稳定剂。
表 1 不同浓度单一稳定剂和复配稳定剂对沉降速率的影响Table 1. Influence in settling rate of passion fruit juice with different content of single stabilize and compound stabilizer组别 与空白组比沉降速率下降(%/s) 0.30% CMC-Na 0.0254±0.0018a 0.35% CMC-Na 0.0282±0.0020a 0.35% CMC-Na+0.15%琼脂 0.0144±0.0010b 0.30% CMC-Na+0.20%琼脂 0.0166±0.0011b 注:不同小写字母标注表示组间差异显著(P<0.05)。 3. 讨论与结论
通过基于空间-时间消光图谱技术的全自动稳定性分析仪测定法,比较了不同比例的CMC-Na或琼脂作为增稠稳定剂对西番莲果汁饮料稳定性的影响。作为饮料中常用的稳定剂,CMC-Na具有良好的耐酸特性,常在酸性饮料中作为稳定剂使用,在水中的强溶解性使其可形成粘稠的溶液达到增稠稳定的效果,在蔬菜水果一类的饮料中能够有效地避免或者减轻沉淀出现,有助于其稳定性的提升,使感官品质得以保持、货架期得以延长[37-38]。而琼脂则能使固形物悬浮均匀,流动增加,爽滑口感且延长货架期[39]。通过本实验所获得的空间-时间消光图谱,对经过离心模拟加速沉降后的样品透光状态变化进行分析,从而有效克服了自然放置法观察仅通过重力作用下使果汁出现沉淀需要消耗大量实验时间的弊端,实验操作时间更短,同时得出的数据更易精确量化比较。
实验结果表明,在西番莲果汁中添加一定量的稳定剂,相较于未添加增稠稳定剂,可使得空间-时间消光图谱中线条更紧凑、平缓,表明果汁整体沉降速率得到降低,有效地改善果汁的稳定性,减少果汁沉淀的出现。其中适量添加CMC-Na或CMC-Na与琼脂按一定比例复配添加,可以显著降低西番莲果汁的沉降速率(P<0.05),从而确保果汁的均一性并改善果汁的感官品质。而琼脂对于果汁稳定性提升效果较为有限(P>0.05),因此相较琼脂,CMC-Na可能更适宜作为西番莲果汁的稳定剂。在单一添加CMC-Na时,最佳添加比例测得为0.30%~0.35%。而在复配稳定剂的实验中,添加了0.35% CMC-Na+0.15%琼脂和0.30% CMC-Na+0.20%琼脂的果汁样品与空白组相比也表现出更佳的稳定能力。但值得注意的是,相较单独添加0.30%~0.35%的CMC-Na而言,进一步复配琼脂未显现出明显的差异,这也符合单独稳定剂实验中所观察到的现象,即琼脂对西番莲果汁稳定性的提升效果较不明显,提示西番莲果汁饮料最佳的单一稳定剂为0.30%~0.35%的CMC-Na。这些结论可为西番莲这类热带果汁饮料的进一步研究与开发提供参考。
本研究中的西番莲果汁饮料仅添加调控增稠稳定剂的含量,未对其他添加剂进行添加,减少了其他因素对西番莲果汁饮料稳定性的影响,得出的实验结果较为准确,有一定的参考价值。但由于本研究只进行了理论值的研究,在实际中正式投入西番莲果汁饮料的生产还需要考虑产品的色泽、粘度、口感等方面的影响,以达到最佳的西番莲果汁饮料生产工艺配比。
-
图 3 果汁中添加不同含量的CMC-Na的空间-时间消光图谱
注:A:无添加CMC-Na(空白)的空间-时间消光图谱;B: CMC-Na添加量为0.15%的空间-时间消光图谱;C:CMC-Na添加量为0.2%的空间-时间消光图谱;D:CMC-Na添加量为0.25%的空间-时间消光图谱;E:CMC-Na添加量为0.30%的空间-时间消光图谱;F:CMC-Na添加量为0.35%的空间-时间消光图谱。
Figure 3. Space and time resolved extinction profiles of passion fruit juice with different content of CMC-Na
图 5 果汁中添加不同比例的CMC-Na和琼脂的空间-时间消光图谱
注:A:CMC-Na和琼脂均无添加(空白)的空间-时间消光图谱;B:添加量为0.25%CMC-Na+0.25%琼脂的空间-时间消光图谱;C:添加量为0.15%CMC-Na+0.35%琼脂的空间-时间消光图谱;D:添加量为0.35%CMC-Na+0.15%琼脂的空间-时间消光图谱;E:添加量为0.30%CMC-Na+0.20%琼脂的空间-时间消光图谱;F:添加量为0.20%CMC-Na+0.30%琼脂的空间-时间消光图谱。
Figure 5. Space and time resolved extinction profiles of passion fruit juice with different content of CMC-Na and agar
表 1 不同浓度单一稳定剂和复配稳定剂对沉降速率的影响
Table 1 Influence in settling rate of passion fruit juice with different content of single stabilize and compound stabilizer
组别 与空白组比沉降速率下降(%/s) 0.30% CMC-Na 0.0254±0.0018a 0.35% CMC-Na 0.0282±0.0020a 0.35% CMC-Na+0.15%琼脂 0.0144±0.0010b 0.30% CMC-Na+0.20%琼脂 0.0166±0.0011b 注:不同小写字母标注表示组间差异显著(P<0.05)。 -
[1] 张佳艳, 林欢, 秦战军. 西番莲果汁饮料的研制及其稳定性研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2016,37(18):62−66. [ZHANG J Y, LIN H, QIN Z J. Study on the technology and stability of passion fruit juice beverage[J]. Food Research and Development,2016,37(18):62−66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2016.18.015 ZHANG J Y, LIN H, QIN Z J. Study on the technology and stability of passion fruit juice beverage[J]. Food Research And Development, 2016, 37(18): 62-66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2016.18.015
[2] 龙倩倩. 西番莲果汁加工过程中香气成分变化[D]. 广州: 华南农业大学, 2018. LONG Q Q. Changes of aroma components in processing of passionflower juice[D]. Guangzhou: South China Agricultural University, 2018.
[3] 林碧敏, 黄苇, 鲍金勇. 西番莲果汁饮料的稳定性[J]. 食品工业,2006(2):5−7. [LIN B M, HUANG W, BAO J Y. Research on stability of passion fruit juice beverage[J]. The Food Industry,2006(2):5−7. LIN B M, HUANG W, BAO J Y. Research on stability of passion fruit juice beverage[J]. The Food Industry, 2006(2): 5-7.
[4] 张佳艳, 任仙娥. 西番莲果汁的研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发,2016,37(11):219−224. [ZHANG J Y, REN X E. Progress in research on passion fruit juice[J]. Food Research and Development,2016,37(11):219−224. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2016.11.052 ZHANG J Y, REN X E. Progress in research on passion fruit juice[J]. Food Research And Development, 2016, 37(11): 219-224. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2016.11.052
[5] 王琴飞, 李莉萍, 高玲, 等. 反相高效液相色谱法测定西番莲中的有机酸[J]. 热带作物学报,2015,36(8):1511−1517. [WANG Q F, ZHANG R L, XU L, et al. Analysis of organic acids in passion fruit by reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops,2015,36(8):1511−1517. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2015.08.025 WANG Q F, ZHANG R L, XU L, et al. Analysis of Organic Acids in Passion Fruit by Reverse Phase High Performance Liquid Chromatography [J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2015, 36(8): 1511-1517. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2015.08.025
[6] ZHU X, DUAN Z, YANG Y, et al. Development of passion fruit juice beverage[J]. IOP Conference Series:Earth and Environmental Science,2017,100:12080. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/100/1/012080
[7] XIE X, CHEN C, FU X. Study on the bioaccessibility of phenolic compounds and bioactivities of passion fruit juices from different regions in vitro digestion[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation,2021,45(1):e15056.
[8] MAMEDE A M G N, SOARES A G, OLIVEIRA E J, et al. Volatile composition of sweet passion fruit (Passiflora alata Curtis)[J]. Journal of Chemistry,2017,2017:3497216.
[9] DEWI N K, PUTRA I B, JUSUF N K. Passion fruit purple variant (Passiflora edulis Sims var. edulis) seeds extract 10% cream in acne vulgaris treatment: An open-label pilot study[J]. International Journal of Dermatology,2020,59(12):1506−1512. doi: 10.1111/ijd.15178
[10] PRASERTSRI P, BOORANASUKSAKUL U, NARAVORATHAM K, et al. Acute effects of passion fruit juice supplementation on cardiac autonomic function and blood glucose in healthy subjects[J]. Preventive Nutrition and Food Science,2019,24(3):245−253. doi: 10.3746/pnf.2019.24.3.245
[11] DOS REIS IZOLAN L, DA SILVA D M, OLIVEIRA H B L, et al. Sintocalmy, a passiflora incarnata based herbal, attenuates morphine withdrawal in mice[J]. Neurochemical Research,2021,46(5):1092−1100. doi: 10.1007/s11064-021-03237-w
[12] JANDA K, WOJTKOWSKA K, JAKUBCZYK K, et al. Passiflora incarnata in neuropsychiatric disorders—a systematic review: Nutrients[Z]. 2020: 12.
[13] TAL Y, ANAVI S, REISMAN M, et al. The neuroprotective properties of a novel variety of passion fruit[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2016,23:359−369. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2016.02.039
[14] 龚树立, 江彩秀, 文剑. 防止西番莲果汁饮料分层沉淀的研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,1994(3):41−43. [GONG S L, JIANG C X, WENG J. Study on preventing separation and sedimentation of passion fruit juice beverage[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,1994(3):41−43. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-990X.1994.03.009 GONG S L, JIANG C X, WENG J. Study on preventing separation and sedimentation of passion fruit juice beverage[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 1994(3): 41-43. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-990X.1994.03.009
[15] 王盼盼. 肉制品加工中使用的辅料——增稠剂[J]. 肉类研究,2011,25(2):29−35. [WANG P P. Ingredients in meat products: Thickeners[J]. Meat Research,2011,25(2):29−35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8123.2011.02.008 WANG P P. Ingredients in meat products: Thickeners[J]. MEAT RESEARCH, 2011, 25(2): 29-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8123.2011.02.008
[16] 杨平, 李业禄, 许青. 猕猴桃果汁稳定性的研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2017,38(10):73−76. [YANG P, LI Y L, XU Q. Study on the stability of the kiwi fruit juice[J]. Food Research and Development,2017,38(10):73−76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2017.10.016 YANG P, LI Y L, XU Q. Study on the stability of the kiwi fruit juice[J]. Food Research And Development, 2017, 38(10): 73-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2017.10.016
[17] 李娜. 红树莓果汁稳定性的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2010. LI N. Study on the stability of red raspberry juice[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2010.
[18] 张雪梅, 尹俊涛, 刘艳怀, 等. 蓝莓红树莓复合果汁的配方优化及稳定性研究[J]. 农产品加工,2021(4):13−16. [ZHANG X M, YIN J T, LIU Y H, et al. Study on formula optimization and stability of blueberry and red raspberry compound juice[J]. Farm Products Processing,2021(4):13−16. ZHANG X M, YIN J T, LIU Y H, et al. Study on formula optimization and stability of blueberry and red raspberry compound juice[J]. Farm Products Processing, 2021(4): 13-16.
[19] 苑园园, 季明月, 王子娇, 等. 桑葚红枣复合饮料的生产工艺优化及其稳定性研究[J]. 河北农业大学学报,2020,43(6):75−82. [YUAN Y Y, JI M Y, WANG Z J, et al. Study on optimization of processing technology and stability of mulberry and red jujube compound juice beverage[J]. Journal of Hebei Agricultural University,2020,43(6):75−82. YUAN Y Y, JI M Y, WANG Z J, et al. Study on optimization of processing technology and stability of mulberry and red jujube compound juice beverage[J]. Journal of Hebei Agricultural University, 2020, 43(6): 75-82.
[20] 夏君霞, 齐兵, 赵慧博, 等. 牛奶咖啡饮料的稳定性研究[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2020,31(3):92−100. [XIA J X, QI B, ZHAOH B, et al. Study on the stability of milk coffee drinks[J]. China Food Additives,2020,31(3):92−100. XIA J X, QI B, ZHAOH B, et al. Study on the stability of milk coffee drinks[J]. China Food Additives, 2020, 31(3): 92-100.
[21] 王莹, 王瑛瑶, 刘建学, 等. 低温花生粕蛋白制备及其饮料稳定性分析[J]. 食品科学,2014,35(20):26−30. [WANG Y, WANG Y Y, LIU J X, et al. Preparation of peanut protein isolate from low-temperature peanut meal, a byproduct from cold-pressed peanut oil production and its stability in beverage[J]. Food Science,2014,35(20):26−30. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201420006 WANG Y, WANG Y Y, LIU J X, et al. Preparation of peanut protein isolate from low-temperature peanut meal, a byproduct from cold-pressed peanut oil production and its stability in beverage[J]. Food Science, 2014, 35(20): 26-30. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201420006
[22] HOMAYOONFAL M, KHODAIYAN F, MOUSAVI M. Modelling and optimising of physicochemical features of walnut-oil beverage emulsions by implementation of response surface methodology: Effect of preparation conditions on emulsion stability[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,174:649−659. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.10.117
[23] MAMOUEI M, BUDIDHA K, BAISHYA N, et al. An empirical investigation of deviations from the Beer–Lambert law in optical estimation of lactate[J]. Scientific Reports,2021,11(1):13734. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-92850-4
[24] 王苏, 张景彬, 孙泽森, 等. 变性淀粉对酸性乳饮料稠度和稳定性的影响[J]. 中国乳品工业,2018,46(3):21−24. [WANG S, ZHANG J S, SUN Z S, et al. Effect of modified starch on consistency and stability of acid milk beverage[J]. China Dairy Industry,2018,46(3):21−24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2230.2018.03.006 WANG S, ZHANG J S, SUN Z S, et al. Effect of modified starch on consistency and stability of acid milk beverage[J]. China Dairy Industry, 2018, 46(3): 21-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2230.2018.03.006
[25] DETLOFF T, SOBISCH T, LERCHE D. Particle size distribution by space or time dependent extinction profiles obtained by analytical centrifugation (concentrated systems)[J]. Powder Technology,2007,174(1):50−55.
[26] PEREIRA I, ZIELIŃSKA A, FERREIRA N R, et al. Optimization of linalool-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles using experimental factorial design and long-term stability studies with a new centrifugal sedimentation method[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics,2018,549(1):261−270.
[27] LERCHE D, SOBISCH T, DETLOFF T. Determination of stability, consolidation and particle size distribution of liquid or semi-liquid food products by multisample analytical centrifugation[C]// Proceedings 4th International Symposium on Food Rheology and Structure (ISFRS). Zürich, Switzerland: 2006: 221−225.
[28] 律丹, 张智. 山楂果浆乳饮料工艺技术研究[J]. 黑龙江粮食,2014(3):53−55. [LÜ D, ZHANG Z. Study on the technology of hawthorn juice milk beverage[J]. Heilongjiang Grain,2014(3):53−55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6019.2014.03.028 LV D, ZHANG Z. Study on the technology of hawthorn juice milk beverage[J]. Heilongjiang Grain, 2014(3): 53-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6019.2014.03.028
[29] 宋华静, 韩小院, 孔瑾. 火龙果悬浮饮料的研制工艺[J]. 保鲜与加工,2018,18(5):112−117. [SONG H J, HAN X Y, KONG J. Development of pitaya suspended beverage[J]. Storage and Process,2018,18(5):112−117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6221.2018.05.020 SONG H J, HAN X Y, KONG J. Development of pitaya suspended beverage[J]. Storage and Process, 2018, 18(5): 112-117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6221.2018.05.020
[30] 杜伟, 黎庆宏, 陈渊, 等. 百香果-芒果复合饮料生产工艺及其稳定性研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2016,37(15):106−109. [DU W, LI Q H, CHEN Y, et al. The processing techniques and stability of the passionfruit and mango compound beverage[J]. Food Research and Development,2016,37(15):106−109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2016.15.025 DU W, LI Q H, CHEN Y, et al. The processing techniques and stability of the passionfruit and mango compound beverage[J]. Food Research And Development, 2016, 37(15): 106-109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2016.15.025
[31] 陈毓滢, 周雪松, 司卫丽. CMC-Na与几种胶体复配对山楂果肉型果汁饮料稳定性的影响[J]. 现代食品科技,2009,25(9):1070−1072. [CHEN Y Y, ZHOU X S, SI W L. Effect of mixtures of CMC and several colloids on the stability of hawthorn pulpy juice drink[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2009,25(9):1070−1072. CHEN Y Y, ZHOU X S, SI W L. Effect of mixtures of CMC and several colloids on the stability of hawthorn pulpy juice drink[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2009, 25(9): 1070-1072.
[32] 张松. 梨枸杞复合果汁加工工艺研究[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2019. ZHANG S. Study on processing technology of compound juice of pear and wolfberry[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2019.
[33] 董旭. 琼脂/海藻酸钠质构性能的研究[J]. 西部皮革,2020,42(3):104. [DONG X. Study on the texture properties of agar/sodium alginate[J]. West Leather,2020,42(3):104. DONG X. Study on the Texture Properties of Agar/Sodium Alginate[J]. West Leather, 2020, 42(3): 104.
[34] ASADOVA A, MASIMOV E A, IMAMALIYEV A R, et al. Spectrophotometric investigation of gel formation in water solution of agar[J]. Modern Physics Letters B,2020,34(14):2050147. doi: 10.1142/S021798492050147X
[35] 白永庆, 张璐. 食品增稠剂的种类及应用研究进展[J]. 轻工科技,2012,28(2):14−16. [BAI Y Q, ZHANG L. Study on the types and application rof food thickeners[J]. Light Industry Science and Technology,2012,28(2):14−16. BAI Y Q, ZHANG L. Study on the types and application rof food thickeners[J]. Light Industry Science and Technology, 2012, 28(2): 14-16.
[36] 谢小瑜, 陈奇, 覃俊达. 发酵型红枣米乳饮料的稳定性研究[J]. 轻工科技,2018,34(10):37−39. [XIE X Y, CHEN Q, QING J D. Study on the stability of fermented red jujube rice milk beverage[J]. Light Industry Science and Technology,2018,34(10):37−39. XIE X Y, CHEN Q, QING J D. Study on the stability of fermented red jujube rice milk beverage[J]. Light Industry Science and Technology, 2018, 34(10): 37-39.
[37] 李绍波, 卢文学. 聚葡萄糖对酸奶品质的影响[J]. 农业研究与应用,2011(1):27−29. [LI S B, LU W X. The effect of polydextrose on the quality of yogurt[J]. Agricultural Research and Application,2011(1):27−29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0764.2011.01.010 LI S B, LU W X. The Effect of polydextrose on the quality of yogurt[J]. Agricultural Research and Application, 2011(1): 27-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0764.2011.01.010
[38] 王淑梅, 王佳新. 增稠剂作用机制及其在食品加工中的应用[J]. 大连大学学报,2020,41(3):63−66. [WANG S M, WANG J X. The mechanism of thickener and its application in food processing[J]. Journal of Dalian University,2020,41(3):63−66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2395.2020.03.015 WANG S M, WANG J X. The mechanism of thickener and its application in food processing[J]. Journal of Dalian University, 2020, 41(3): 63-66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2395.2020.03.015
[39] 宋雪健, 王洪江, 张东杰. 琼脂在食品中的应用研究进展[J]. 现代农业科技,2017(12):267−268. [SONG X J, WANG H J, ZHANG D J. Research progress on application of agar in food[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology,2017(12):267−268. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2017.12.155 SONG X J, WANG H J, ZHANG D J. Research progress on application of agar in food[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017(12): 267-268. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2017.12.155
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 乔增辉,位璐璐,卢祺,史羽瑶,尹明雨,王锡昌. 保活方式对中华绒螯蟹活力和生理代谢的影响. 水产科学. 2025(01): 56-64 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张亮子,黄泽南,尤娟,刘茹,尹涛,马华威. 保活运输应激对水产动物肌肉品质影响的研究进展. 广东海洋大学学报. 2024(01): 35-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 阮记明,钟智威,黄建珍,温娇萍,王朝,傅雪军,王润萍. 克氏原螯虾低温休眠保活技术研究. 中国水产科学. 2024(07): 810-819 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李彤彤,赵玲,王善宇,刘淇,曹荣. 太平洋牡蛎活体冷藏过程中脂质及挥发性物质变化. 肉类研究. 2024(10): 23-29 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



