Research on Influencing Factors and Cleaning Effect of Forward Osmosis Membrane Fouling
-
摘要: 为研究正渗透(FO)浓缩过程中的膜通量衰减规律,本文以牛血清白蛋白(BSA)为特征污染物,研究了正渗透过程中原料液的离子强度及BSA浓度、膜方位等参数不同时FO膜的污染规律,以提高膜通量和截留率为目标,对驱动液的种类、浓度,料液流速进行了优化,并优化了适宜的膜清洗方案。结果表明:原料液中离子强度越大,FO膜的初始通量越低,但随着运行时间的延长,原料液BSA中含有盐离子时FO膜的通量高于纯BSA溶液的通量。BSA浓度越低,膜污染越轻,且FO模式(13.82±3.2 L/m2·h)的水通量高于PRO模式(5.08±2.1 L/m2·h),表明宜采取FO模式进行浓缩。在最佳操作条件下,即以1.5 mol/L NaCl为驱动液并控制料液流速为2.89 m/s时,FO膜通量达11.23±2.13 L/m2·h,BSA截留率97.83%,反向溶质通量Js为0.14 mol/m2·h。使用0.05% NaOH浸泡膜表面4 min,通量恢复率98.39%,多次使用及重复清洗后恢复率仍达98%以上,表明该膜具有良好的耐清洗性能,本研究将为从食品物料中回收蛋白质提供一定的技术参考。Abstract: In order to study the attenuation regularity of membrane flux in the process of forward osmosis (FO) concentration, the fouling rule of FO membrane affected by different parameters including ionic strength, BSA concentration in the feed and membrane orientation was studied with Bovine serum albumin (BSA) as the primary typical pollutants. In order to improve the membrane flux and rejection rate, the type and concentration of draw solution and the flow rate of feed solution were optimized and the appropriate membrane cleaning scheme was optimized. The results showed that the initial flux of FO membrane decreased with the increasing of ionic strength in feed solution, but the flux of FO membrane with BSA solution containing salt ions was higher than that of pure BSA solution as the running time went on. The lower the concentration of BSA, the lighter the membrane fouling was, and the water flux in FO mode (13.82±3.2 L/m2·h) was higher than that in PRO mode (5.08±2.1 L/m2·h), which indicated that FO mode should be adopted for concentration. Under the optimal operating conditions, the 1.5 mol/L NaCl as the draw solution and the flow rate of both feed and draw solution controlled at 2.89 m/s, FO flux was 11.23±2.13 L/m2·h, BSA retention rate was 97.83%, and reverse solute flux Js was 0.14 mol/m2·h. After the fouled membrane was immersed in 0.05% NaOH for 4 min, the flux recovery rate reached 98.39% and the flux recovery rate was still exceed 98% after reusing and cleaning many times, which indicated that the membrane had good cleaning resistance. This study would provide a certain technical reference for protein recovery from food materials.
-
Keywords:
- FO /
- membrane fouling /
- protein fouling /
- BSA /
- membrane cleaning
-
正渗透(FO)作为一种新型膜分离技术,是利用半透膜两侧溶液渗透压不同使水分子自发地从原料液(低渗透压)流向驱动液(高渗透压)[1-2],该过程无需外加压力,具有能耗低、浓缩倍数高、对杂质的截留能力强等优势[3],在海水淡化、污水和工业废水处理、军用应急水处理等领域均有一定规模的应用[4],同时FO在热敏性食品物料的浓缩等领域具有广阔的应用前景[5-8]。
虽然FO是公认的低污染膜分离技术,但内部浓差极化和膜污染仍是导致通量衰减的重要因素[9]。就提高FO膜水通量而言,目前正渗透技术的研究主要集中在汲取液的开发[10-11]、膜材料的设计以及膜结构优化[4,12-13],如使用水通道蛋白仿生材料[14]和氧化石墨烯[15]等嵌入到FO膜中以获得更高的水通量及脱盐率,然而有效控制膜污染是提高膜通量的重要手段。
FO过程中的膜方位、操作条件、水力条件和原料液性质等是影响FO膜污染形成与清除的重要因素[10,16-17],如Emily等[18]和Emadzaden等[19]的研究表明污染物可沉积在膜表面上或在水力作用下进入膜孔或微结构中,不同的膜方位(FO模式、PRO模式)对膜污染有不同影响。刘彩虹[20]研究发现,通过优化操作条件如运行速度、驱动液浓度等,可降低污染物对膜的污染。Zhao等[21]研究表明,原料液的离子强度、pH是影响FO膜污染的重要因素,原料液BSA中含有Ca2+时,将极大程度加剧膜污染且BSA对膜的污染随着Ca2+浓度和离子强度的增加而增大。FO膜污染的形成机理较复杂,特别是食品物料及其加工副产物中常含有大量的蛋白质、糖类、盐类等物质,在不同的操作条件下,有机物容易在膜表面或孔道内沉积[12,22-23]。另外,原料中盐类物质除了削弱FO两侧的渗透推动力之外,还容易在有机物间形成架桥作用加快膜污染[24]。目前大多数FO膜污染实验主要集中于研究单一因素的影响,对于原料为含盐有机物时的FO膜污染规律及相应的清洗方法的研究还鲜有报道。
本文系统研究影响FO膜BSA污染的因素,优化操作条件及适宜的膜清洗方案,旨在为FO在浓缩含有蛋白质和盐类物质的原料液和膜污染控制提供技术参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
醋酸纤维素(CTA)复合正渗透膜 温州莲华环保科技股份有限公司;氢氧化钠(NaOH)、无水氯化钙(CaCl2) 天津市大茂化学试剂厂;氯化钠(NaCl) 天津市鑫铂特化工有限公司;无水硫酸钠(Na2SO4)、柠檬酸三钠(C6H5Na3O7)、碳酸氢钠(NaHCO3)、乙醇(C2H5OH) 辽宁泉瑞试剂有限公司;牛血清白蛋白(BSA)、考马斯亮蓝G-250 福州飞净生物科技有限公司;磷酸(H3PO4) 沈阳市华东试剂厂;去离子水 食品学院中试车间提供。
JD4000-2电子天平 沈阳龙腾电子有限公司;WT3000-1JB-A齿轮泵 保定兰格恒流泵有限公司;JENCO 6350电导率仪 上海鑫嵩实业有限公司;79-1磁力加热搅拌器 常州市金坛大地自动化仪器厂;LZB-10流量计 沈阳北星仪表制造有限公司;T6新世纪紫外可见分光光度计 北京普析通用仪器有限责任公司。
1.2 实验装置
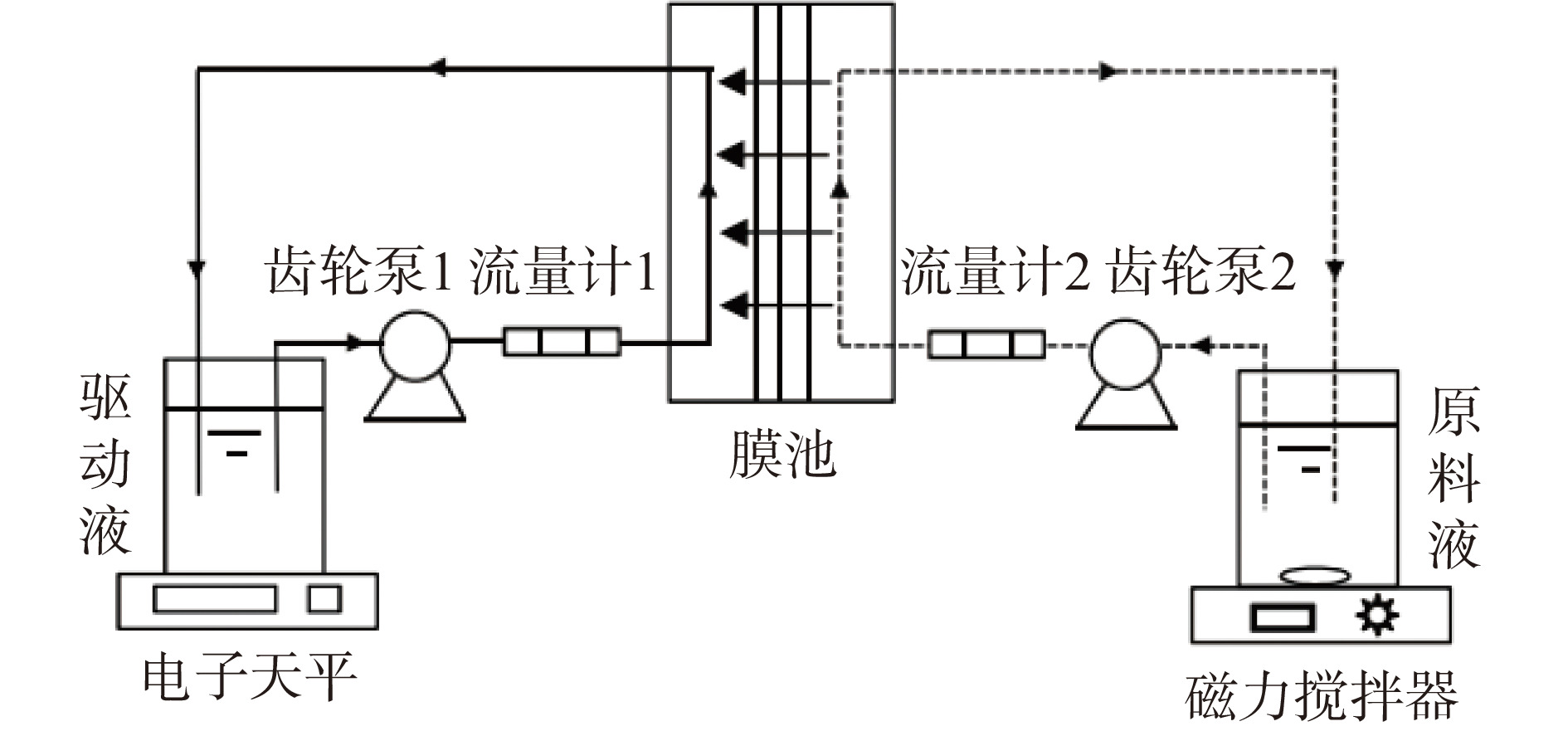
FO实验系统如图1,其有效膜面积为19.25 cm2(2.5 cm×7.7 cm)。膜池两侧分别为原料液和驱动液的矩形流道,在齿轮泵作用下同向、同速率循环流动。待流速稳定后,记录实验数据。
1.3 实验方法
1.3.1 原料液中离子强度和BSA浓度对膜污染的影响
食品加工后的废弃料液大多含有一定的渗透压,如灰水电导率约1.7 ms/cm[25],豆制品废水约为3.4 ms/cm[26]。本文参照上述实际废水配制了BSA和盐的混和物用于FO浓缩。
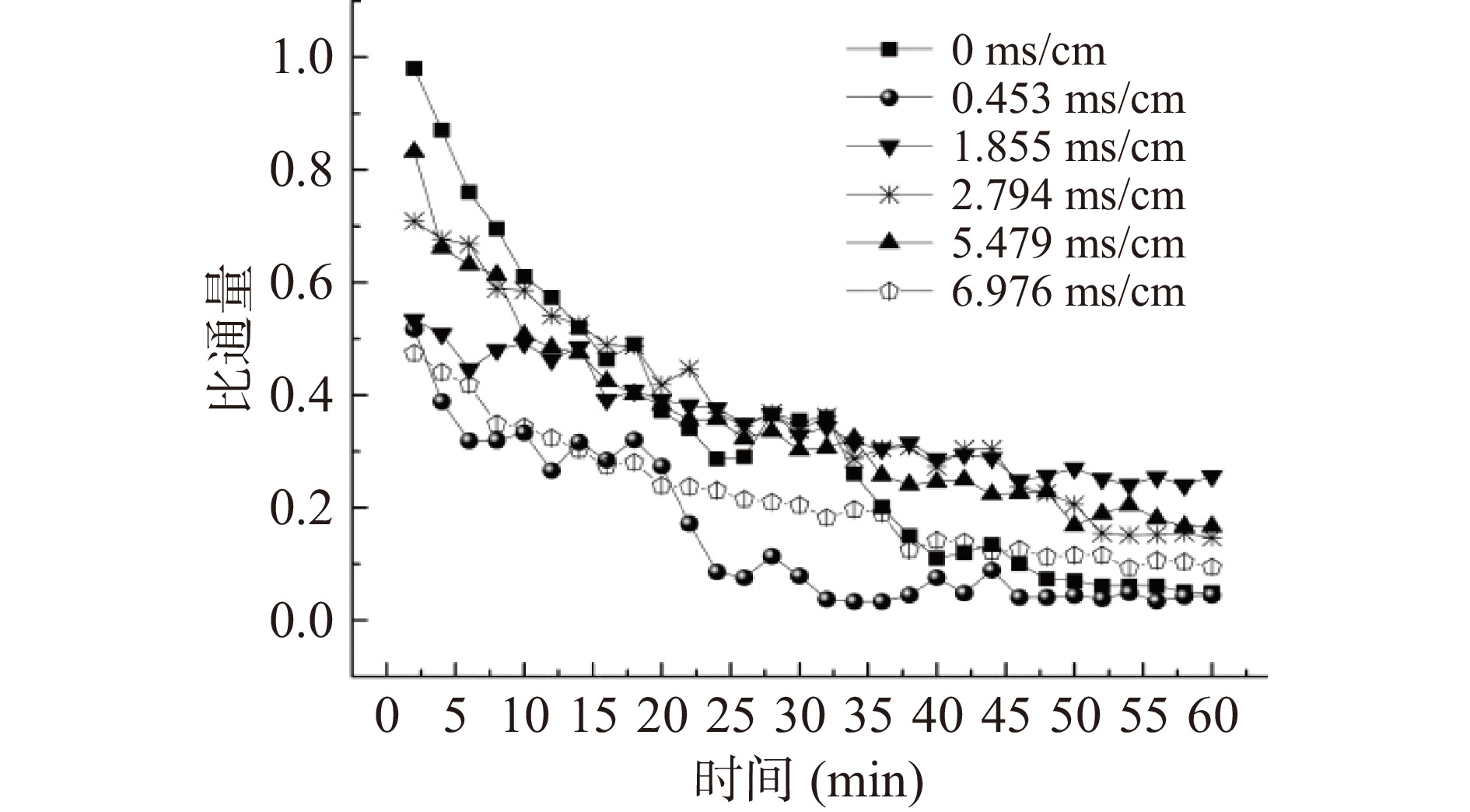
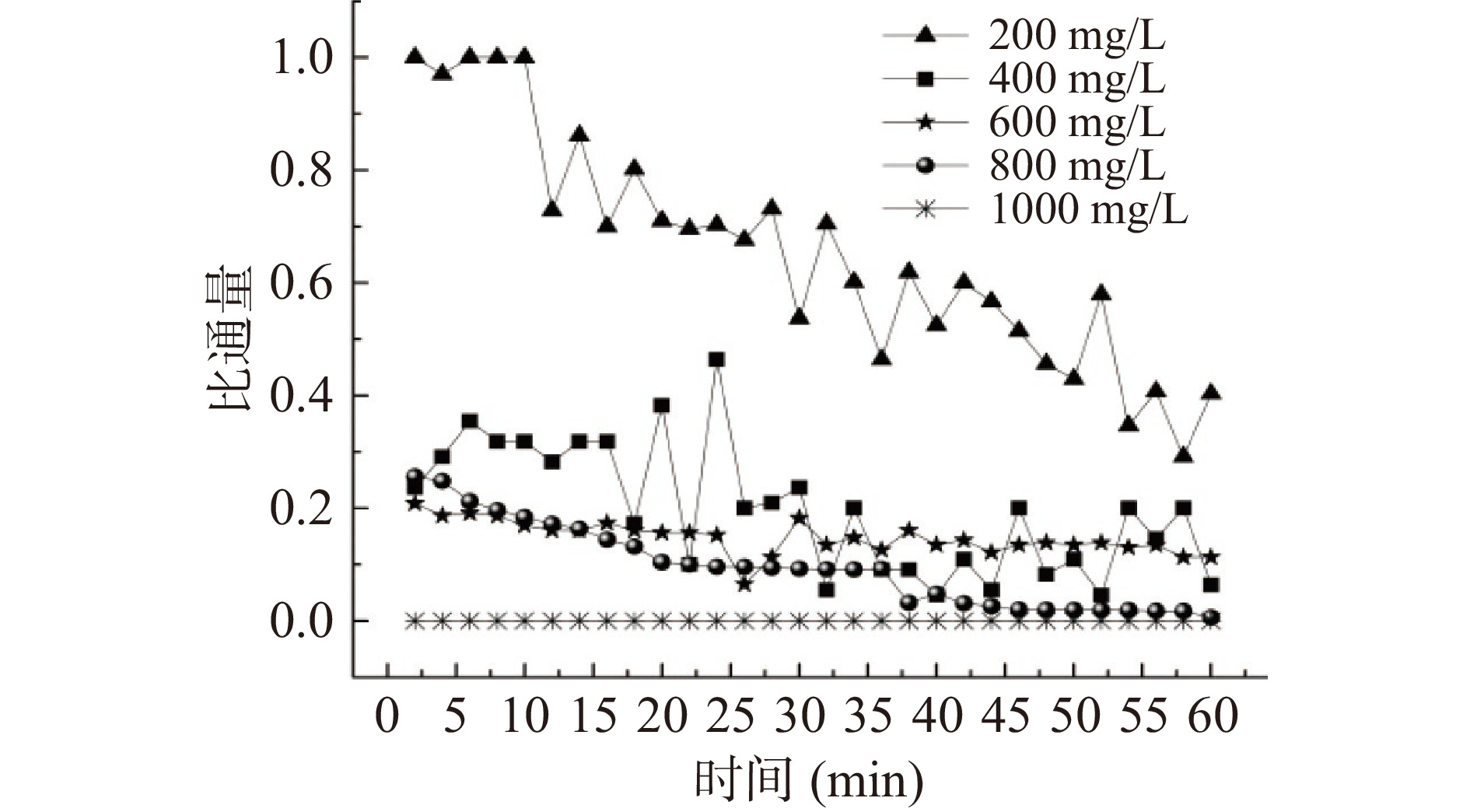
控制驱动液为1 mol/L NaCl,流速为2.89 m/s,在FO模式下操作。向含有一定浓度BSA(200 mg/L)的原料液中首先加入定量离子[27](1 mmol/L NaHCO3+1 mmol/L CaCl2),再分别继续添加NaCl至不同浓度(0、20、40、60和80 mmol/L),其对应电导率为(0.453、1.855、2.794、5.479和6.976 ms/cm),研究只含BSA的原料液和含有不同离子强度的BSA溶液对FO膜污染规律的影响;其次,在上述确定的NaCl添加量基础上,研究有机物BSA浓度(200、400、600、800、1000 mg/L)对FO膜污染规律的影响。
1.3.2 操作条件对通量及截留性能的影响
确定原料液成分(1 mmol/L NaHCO3+1 mmol/L CaCl2+20 mmol/L NaCl+200 mg/L BSA),以1 mol/L NaCl为驱动液,流速为2.89 m/s和FO模式为基本条件,研究膜方位(FO模式、PRO模式),驱动液的种类(Na2SO4、NaCl、C6H5Na3O7和CaCl2),驱动液浓度(0.5、1、1.5和2 mol/L),物料流速(2.16、2.89、3.61、4.33和5.05 m/s)对FO膜通量及BSA截留率的影响。
1.3.3 膜清洗
以浓度为200 mg/L的BSA溶液作为原料液,驱动液为1.5 mol/L NaCl溶液,按上述优化后的条件运行。利用物理(错流清洗、渗透回流清洗)和化学方法(0.05% NaOH)进行清洗,清洗后的FO膜以1.5 mol/L NaCl为驱动液,去离子水为原料液测定其通量恢复率。具体清洗条件如下:
错流清洗:在膜两侧以去离子水,在错流速度2.89 m/s的条件下分别清洗10、20、30 min后取出并用去离子水缓慢冲洗5次。
渗透回流清洗[28]:基于单因素实验结果筛选出汲取能力较强的驱动液种类,即以饱和氯化钙为驱动液,错流速度为2.89 m/s,分别清洗10、20、30 min,然后取出膜用去离子水缓慢冲洗5次。
化学清洗:将污染膜取出后在0.05% NaOH溶液中浸泡3、4、5 min,用去离子水冲洗至pH为7。
1.4 指标测定及计算
1.4.1 水通量
FO运行过程中驱动液质量的变化(JW),用公式(1)计算。
JW=ΔWSt (1) 式中:Jw表示水通量,L/m2·h;ΔW表示驱动液质量的增量,L;S表示膜的有效面积,m2;t表示运行时间,h。
1.4.2 比通量
比通量(%)=JJ0×100% (2) 式中:J0表示原膜初始纯水通量,L/m2·h;J表示污染膜实时通量,L/m2·h。
1.4.3 反向溶质通量
驱动液溶质反向扩散到料液中的量(JS),用公式(3)计算。
JS=ΔC×VtAt (3) 式中:JS表示反向溶质通量,mol/m2·h;ΔC表示原料液侧溶质浓度的增加量,mol/L;Vt表示t时刻原料液的体积,L;A表示膜的有效面积,m2;t表示渗透时间,h。
1.4.4 BSA截留率
蛋白质含量根据SN/T 3926-2014考马斯亮蓝法进行测定,以牛血清白蛋白标准液中的蛋白质含量为横坐标,吸光度值为纵坐标绘制标准曲线,得标准曲线方程为:y=5.49286x+0.0263,决定系数R2=0.99109。BSA的截留率按公式(4)计算。
BSA截留率(%)=(1−ρfρp)×100 (4) 式中:ρp表示原料液侧BSA浓度,mg/mL;ρf表示驱动液侧BSA浓度,mg/mL。
1.4.5 通量恢复率
通量恢复率按公式(5)计算:
通量恢复率(%)=JrJ0×100 (5) 式中:Jr表示膜清洗后的纯水通量,L/m2·h;J0表示纯水通量,L/m2·h。
1.5 数据处理
采用Excel 2010进行数据处理,用Origin 8.5进行图的绘制,用SPSS 19.0对膜方位的影响进行独立样本t检验。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 原料液成分对膜污染的影响
2.1.1 原料液中离子强度
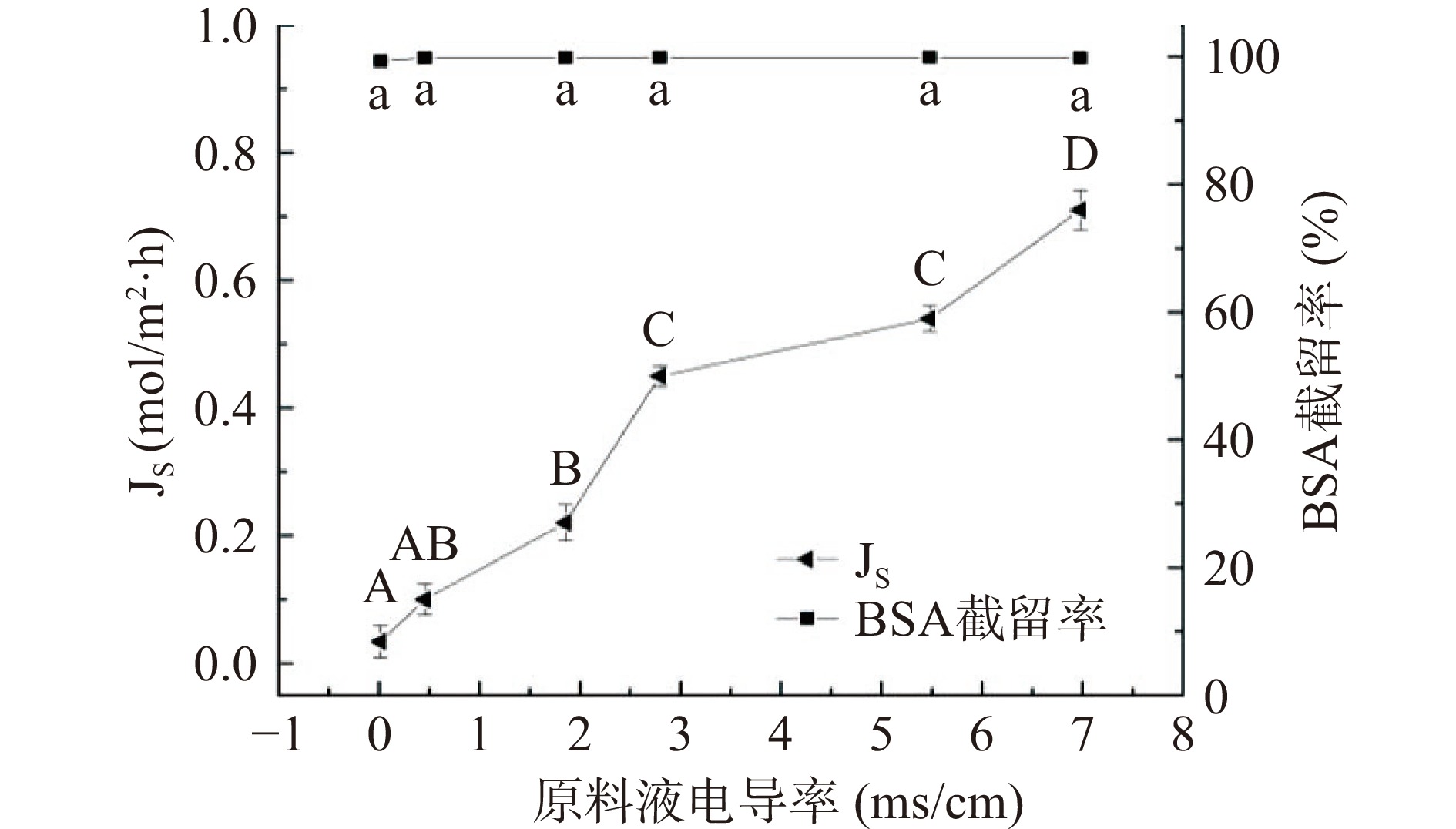
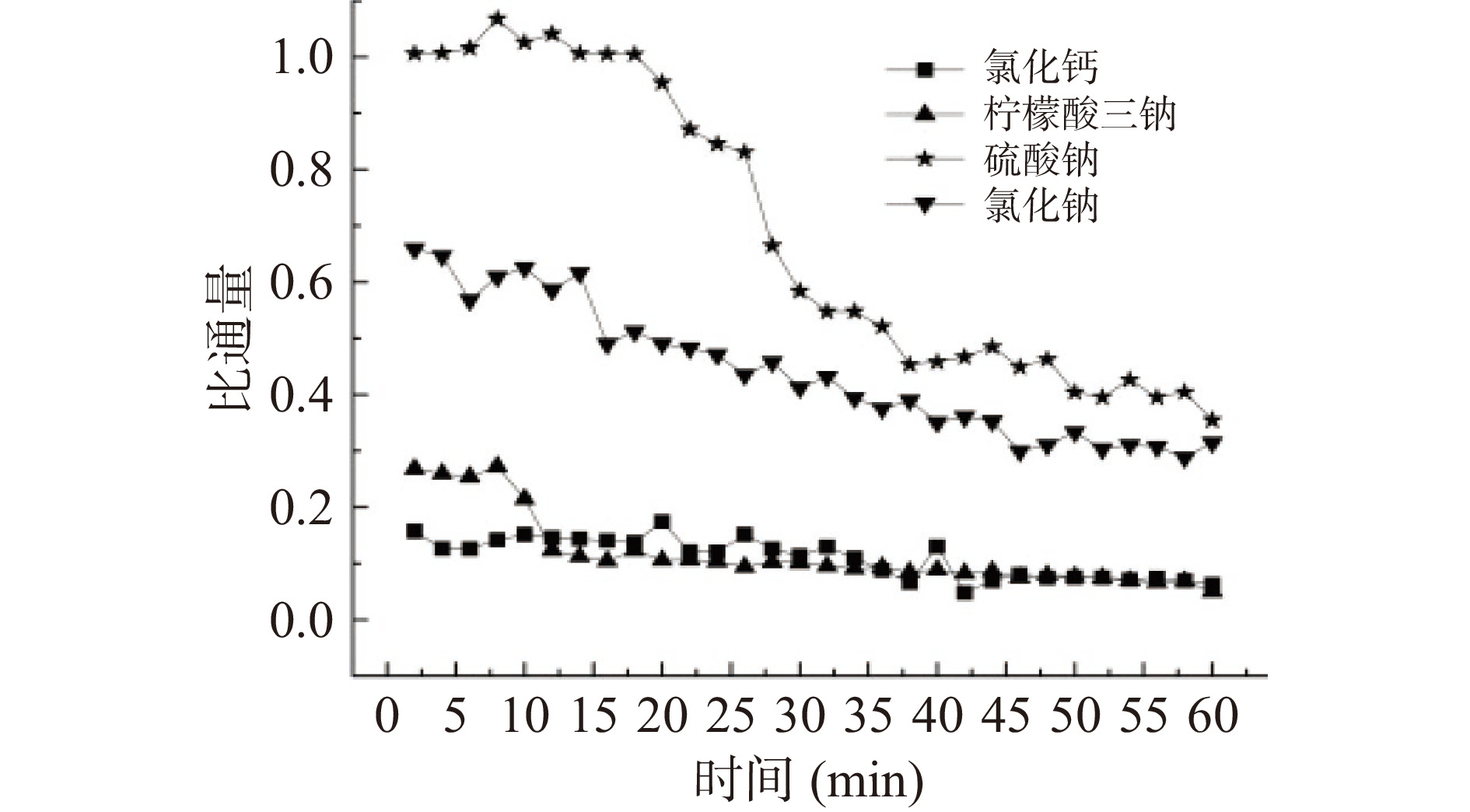
原料液中离子强度对膜通量的影响如图2所示。由图2可知,与纯BSA溶液相比,当原料BSA中加入不同浓度的NaCl时初始比通量会下降,这是由于原料液离子强度增大时,会降低膜两侧的有效渗透压差。但FO膜的稳定比通量随着NaCl的添加呈先增大后降低的趋势,其中电导率为1.855 ms/cm(20 mmol/L NaCl)时通量衰减比最小,即原料液BSA中含有一定浓度的盐离子可降低BSA的膜污染。当原料电导率值低于5.5 ms/cm时,可不对其脱盐直接进行FO处理。原料液中离子强度对反向溶质通量和BSA截留率的影响如图3所示。由图3可见,原料液侧离子强度不同时,BSA的截留率始终在99%以上,但随着原料中离子强度的增大,反向溶质渗透通量也随之增大,原因在于阴、阳离子的传输满足唐南平衡原理,程巍等[29]研究发现,驱动液中的离子除了经典的溶解-扩散机理外,还会以其他的方式进行传递,随着原料液离子浓度的增大,会降低膜对离子的选择性,进而增加了反向溶质通量。
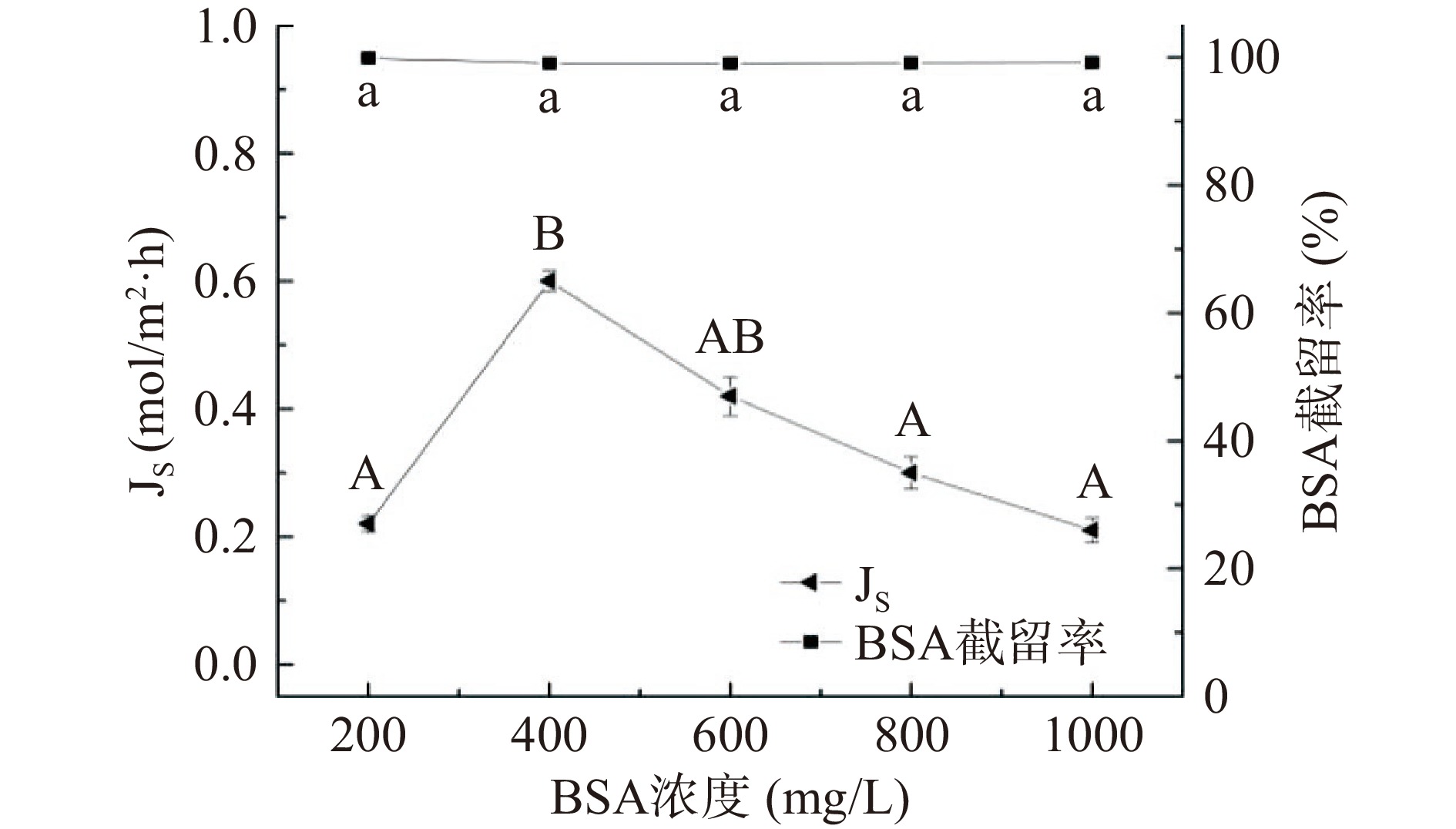
2.1.2 原料液中BSA浓度
按2.1.1的研究结果,将原料液BSA中添加20 mmol/L NaCl用于FO浓缩。由图4可知,随着原料液中BSA浓度的增大,比通量将逐渐降低,这是由于有机物浓度越高,越容易造成蛋白质在膜孔堵塞和表面吸附污染。BSA浓度为200 mg/L,比通量虽然很大但同时通量衰减速率也很快,这是由于试验初期,膜表面大量聚集无机盐和BSA,蛋白质质量浓度逐渐增大到其凝胶化浓度并形成结垢层,通量迅速下降。当浓度达到1000 mg/L时,比通量接近0,说明膜污染极其严重。如图5,FO膜对BSA的截留率基本不受其浓度的影响,始终接近100%。随BSA的浓度的增加,反向溶质通量呈先增大再降低的趋势,当BSA浓度为200 mg/L时,由于原料液的水通过膜扩散至驱动液侧,在较高水力作用下,使得膜孔多数被用来汲取水分子,则阻碍了盐离子的反向渗透。随着浓度的递增至400 mg/L时,水力作用减弱,故反向溶质通量增大。当BSA浓度继续增大到1000 mg/L,反向溶质通量反而降低,这是由于大量的BSA聚集在膜表面及孔道内部,阻碍了盐离子的反向扩散,故反向溶质通量降低。
2.2 操作条件对膜通量及截留性能的影响
2.2.1 膜方位的影响
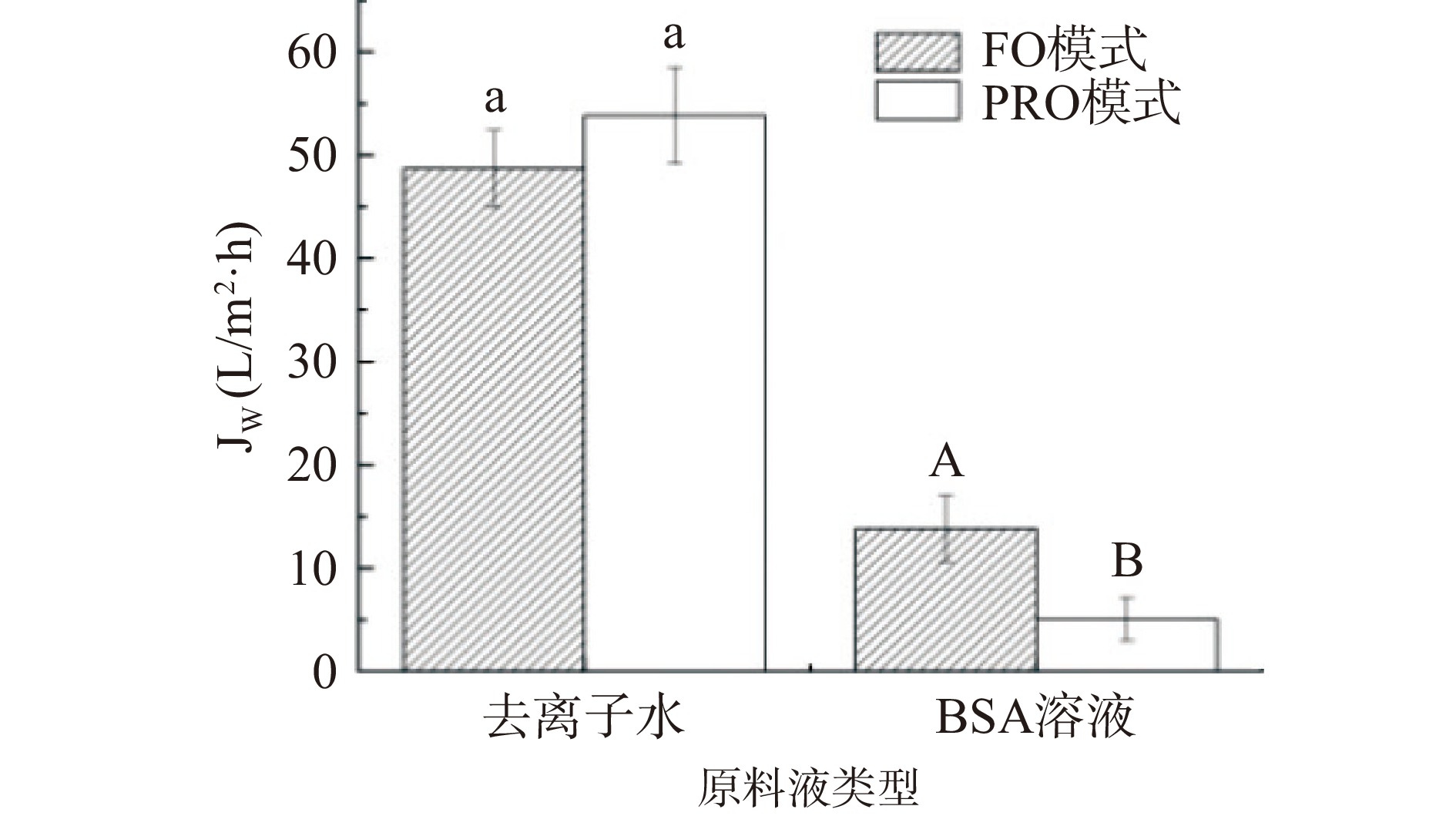
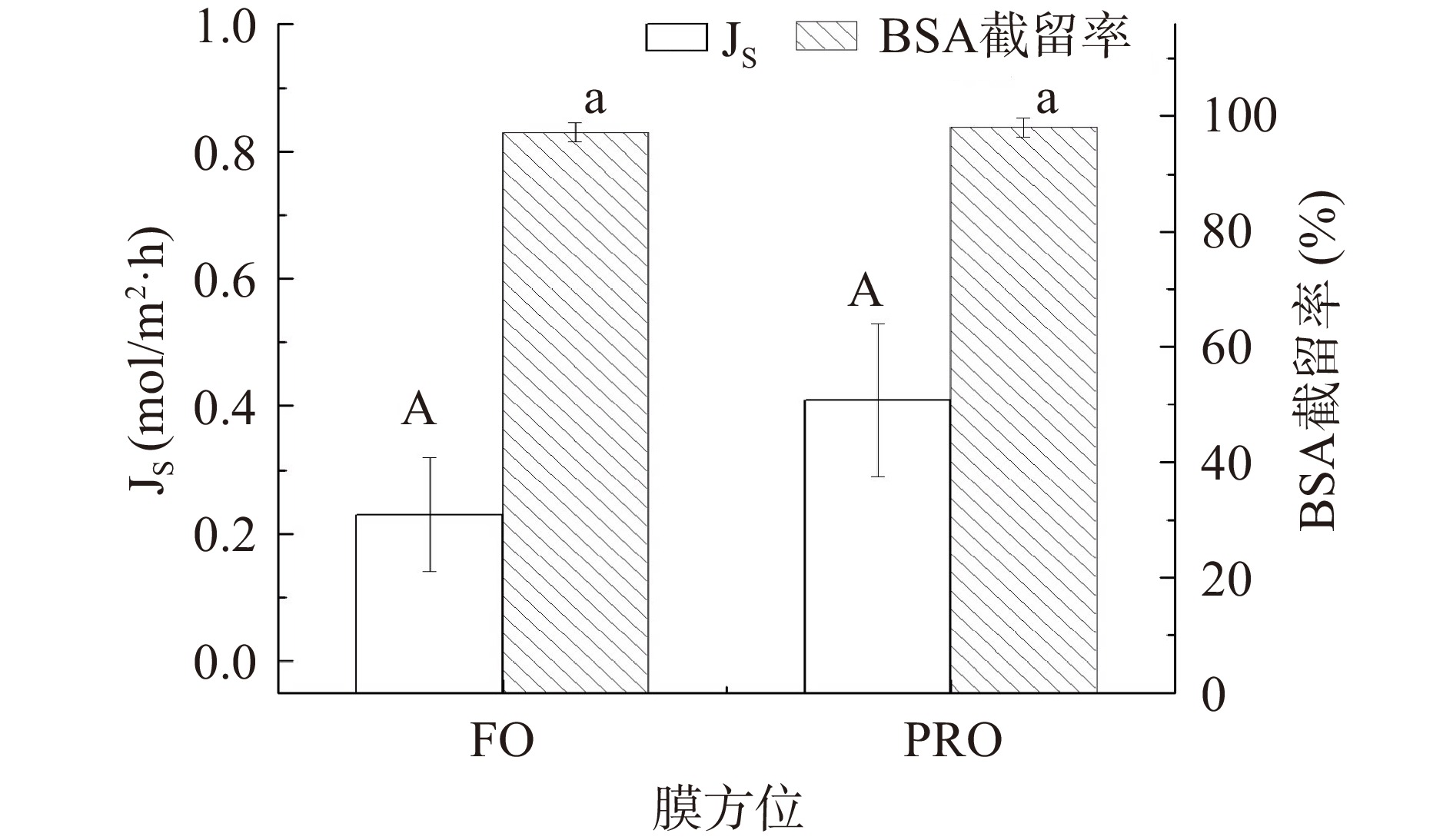
膜方位(FO模式与PRO模式)对FO过程的影响如图6~图8。从图6可知,当原料液为去离子水时,PRO模式水通量(53.83 L/m2·h)高于FO模式水通量(48.67 L/m2·h),与刘彩虹的研究结论一致[12]。将原料液换成污染物BSA后,水通量较纯水通量低,但FO模式水通量(13.82 L/m2·h)优于PRO模式水通量(5.08 L/m2·h),因PRO模式原料液中污染物易于进入多孔支撑层中并发生严重聚积,堵塞膜孔,增大了传质阻力[9,30],常将此现象归因于内浓差极化效应[31]。FO模式污染物在膜活性层表面积累,溶液错流产生平行膜表面剪切力能够去除一部分污染物,因此膜污染相对较轻;PRO模式溶液错流产生的剪切力主要在多孔支撑层以外区域起作用,支撑层内污染物几乎不受剪切力的影响,因此污染相对较重[28]。经独立样本t检验分析,当处理BSA溶液时,膜方位对水通量影响显著(P=0.036<0.05)且FO模式较优,与Zhou等[32]的试验结果类似。当处理BSA污染物时,由图7可知,FO模式反向溶质通量较低,两种模式下都有较高的BSA截留率,从图8可知,FO模式比通量较PRO模式高,浓差极化现象低,膜不易被污染。综上,膜的抗BSA污染试验中应选FO模式。
2.2.2 驱动液的影响
2.2.2.1 驱动液种类
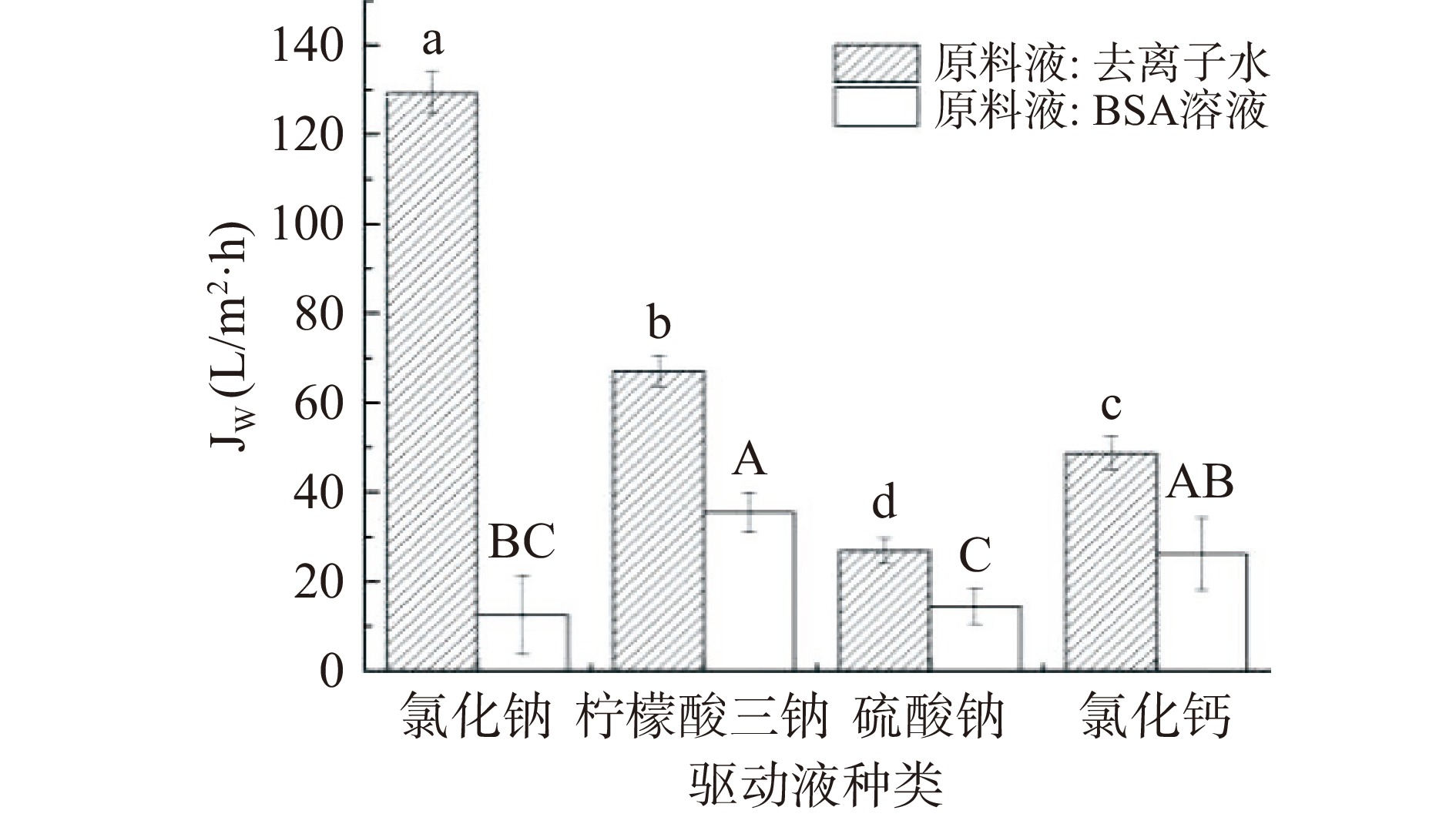
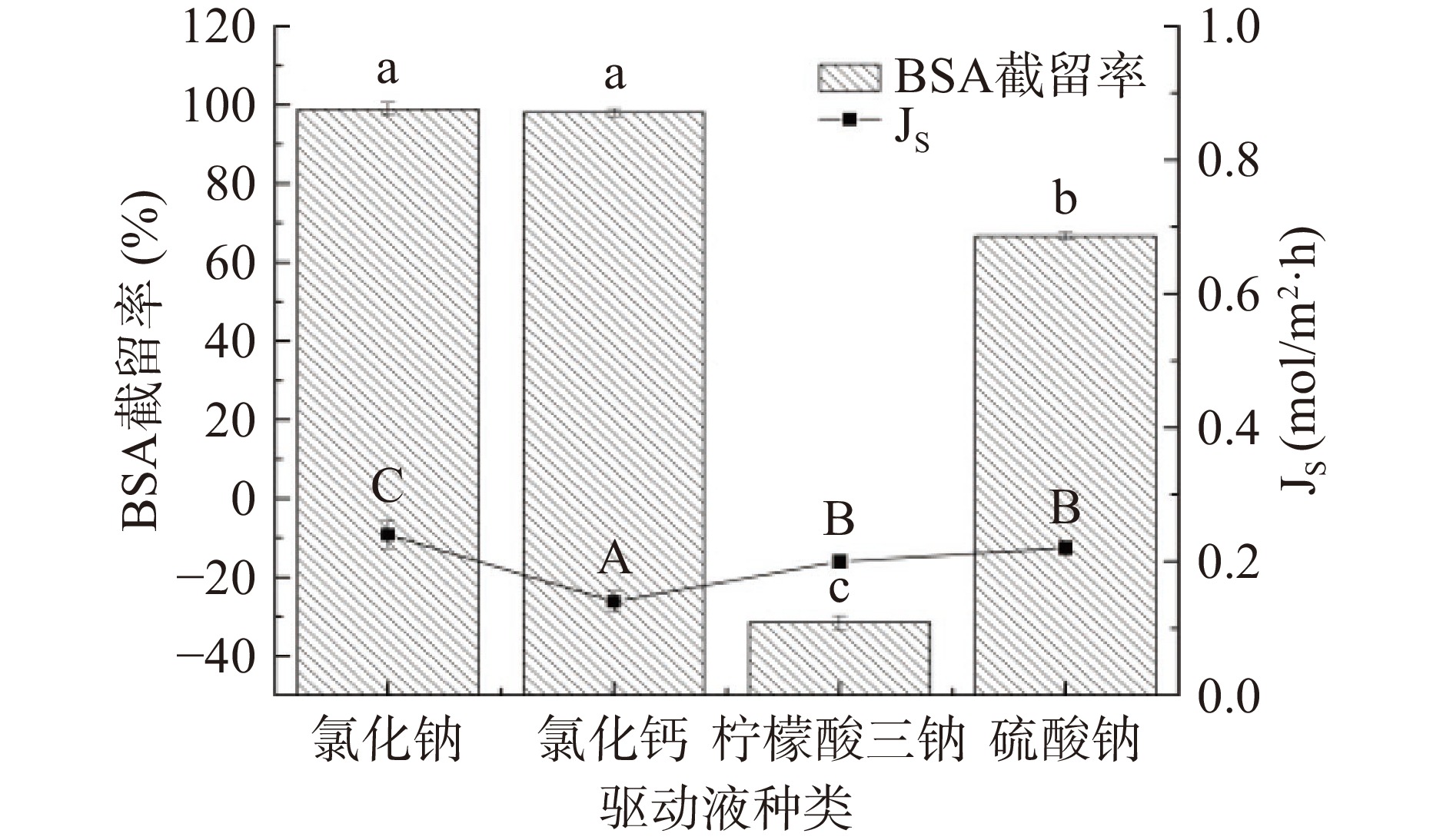
由图9可知,使用不同种类的驱动液时,膜通量始终是原料液BSA小于去离子水。这是由于BSA对FO膜产生了污染。比较而言,Na2SO4对应的水通量较低,Tan等[33]研究了14种无机驱动剂,研究结果也显示Na2SO4的驱动能力低于MgCl2和NaCl。由图10可知,四种驱动液的平均比通量由高到低顺序为Na2SO4、NaCl、C6H5Na3O7和CaCl2,这是由于驱动液对水的汲取能力不同,而汲取能力越大,越容易将BSA吸附在膜表面形成蓬松的薄层滤饼,导致膜污染加剧,通量下降较快,比通量降低。由图11可知,汲取液为CaCl2时反向溶质通量明显低于其他三种盐类,这说明Ca2+的水力半径较大,其反向扩散受到抑制[34]。使用驱动液种类不同时,BSA截留效果差异明显,驱动液为C6H5Na3O7时,截留效果不佳,而使用Na2SO4时,BSA截留率也仅为70%,NaCl和CaCl2的截留效果非常高,当驱动液正离子为Na+时,随着无机盐所含独立离子个数增加,截留率逐渐下降。而驱动液为氯化物时,阳离子(Na+、Ca2+)对截留率基本无影响,对BSA的截留率较高。使用NaCl时的平均比通量高于CaCl2,且膜污染小,因此选用NaCl为驱动液。
2.2.2.2 驱动液浓度
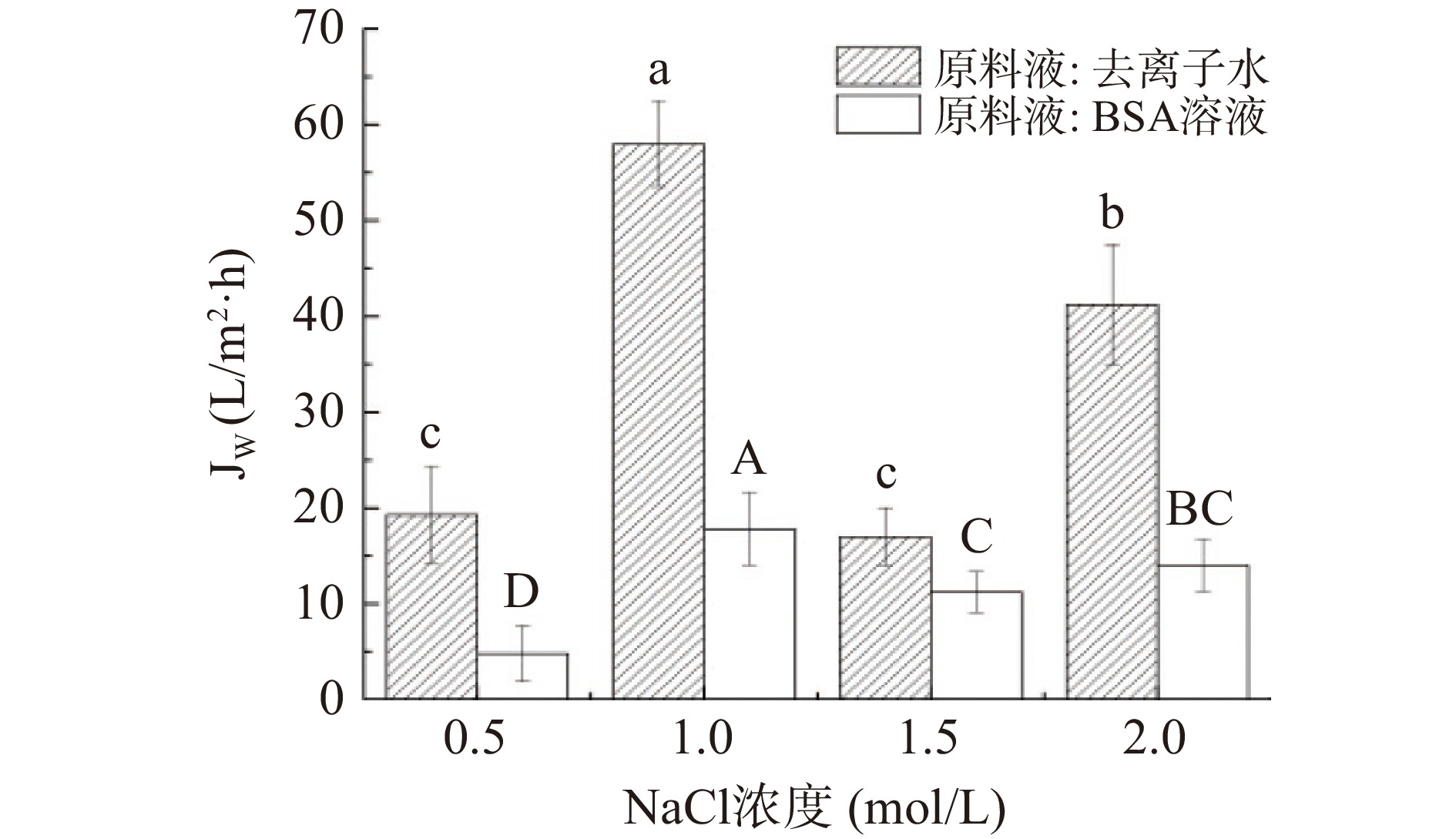
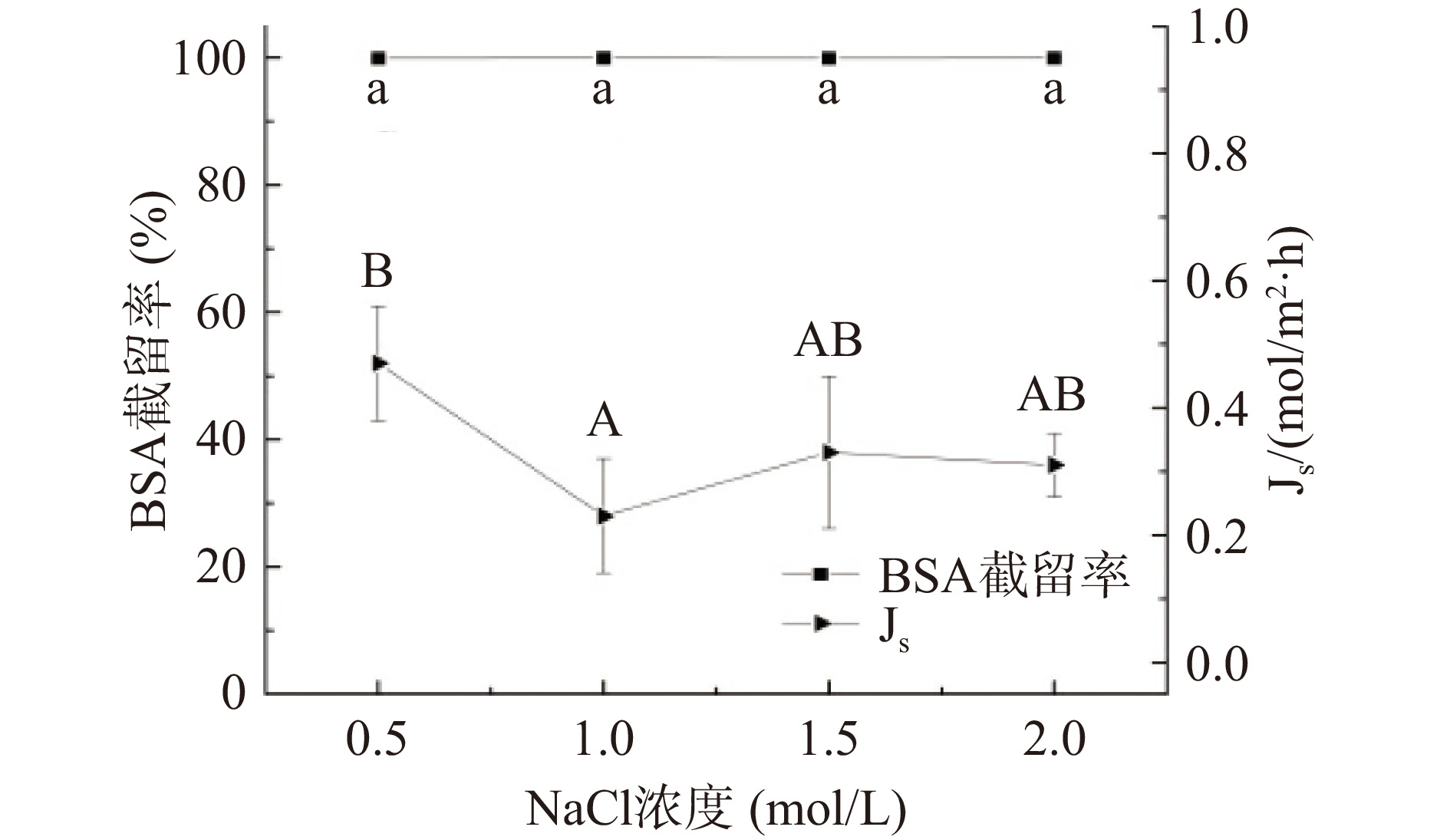
由图12可知,随着NaCl浓度增加,BSA试验中水通量先增大后减少,在1 mol/L时水通量较高为17.81 L/m2·h。原因在于低浓度时驱动能力弱,不足以提供更高的动力,使得水通量低;浓度过高时,污染物易在膜表面形成疏松的滤饼层,导致膜污染,水通量下降。如图13所示,比通量在1.5 mol/L浓度下较高,说明NaCl浓度在1.5 mol/L时,膜被BSA污染的程度低,可知,在FO过程中,水通量过高时,膜污染较为严重,比通量降低。Shan等[35]通过浓度梯度法,得到关于FO驱动液的临界浓度,当驱动液浓度低于临界浓度时,水通量基本维持稳定,膜污染较轻;当驱动液浓度高于临界浓度时,水通量下降速度较快,膜污染较严重。图14表明BSA的截留率(大于99%)和反向溶质通量受驱动液浓度影响较小。综上,将NaCl浓度选为1.5 mol/L。
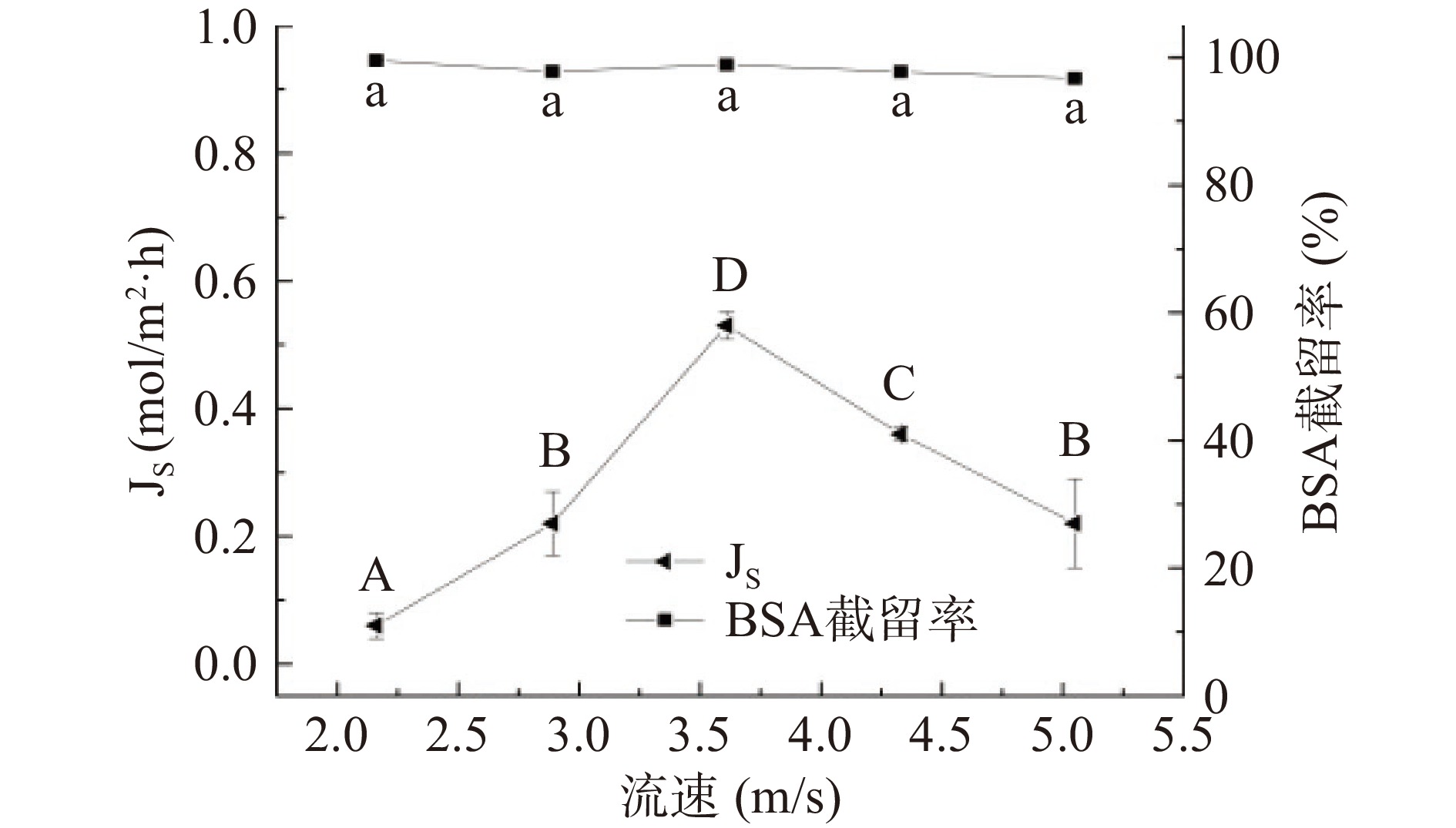
2.2.3 流速的影响
由图15可知,错流速度不同时,FO膜比通量下降程度不同。流速过低时,污染物在膜表面堆积,水通量低,合适流速可减少膜污染[36],增加膜表面的水流剪切力,降低污染物在膜表面的沉积,同时由于水流冲刷使致密活性层表面的污染层变薄,减轻浓差极化现象,使膜污染程度减小,流速在2.89 m/s时比通量较优。由图16~图17可知,当流速过高时,污染物加速与膜表面紧密接触的机会,部分膜孔被堵塞,也降低水通量。膜孔被堵塞同时BSA的截留率也随之增大,流速更大时,BSA分子会利用水流剪切力,穿过膜孔进入驱动液侧,进而降低膜对BSA的截留。随着流速的增大,反向溶质通量先增大后降低。综上确定流速为2.89 m/s。
2.3 FO膜清洗
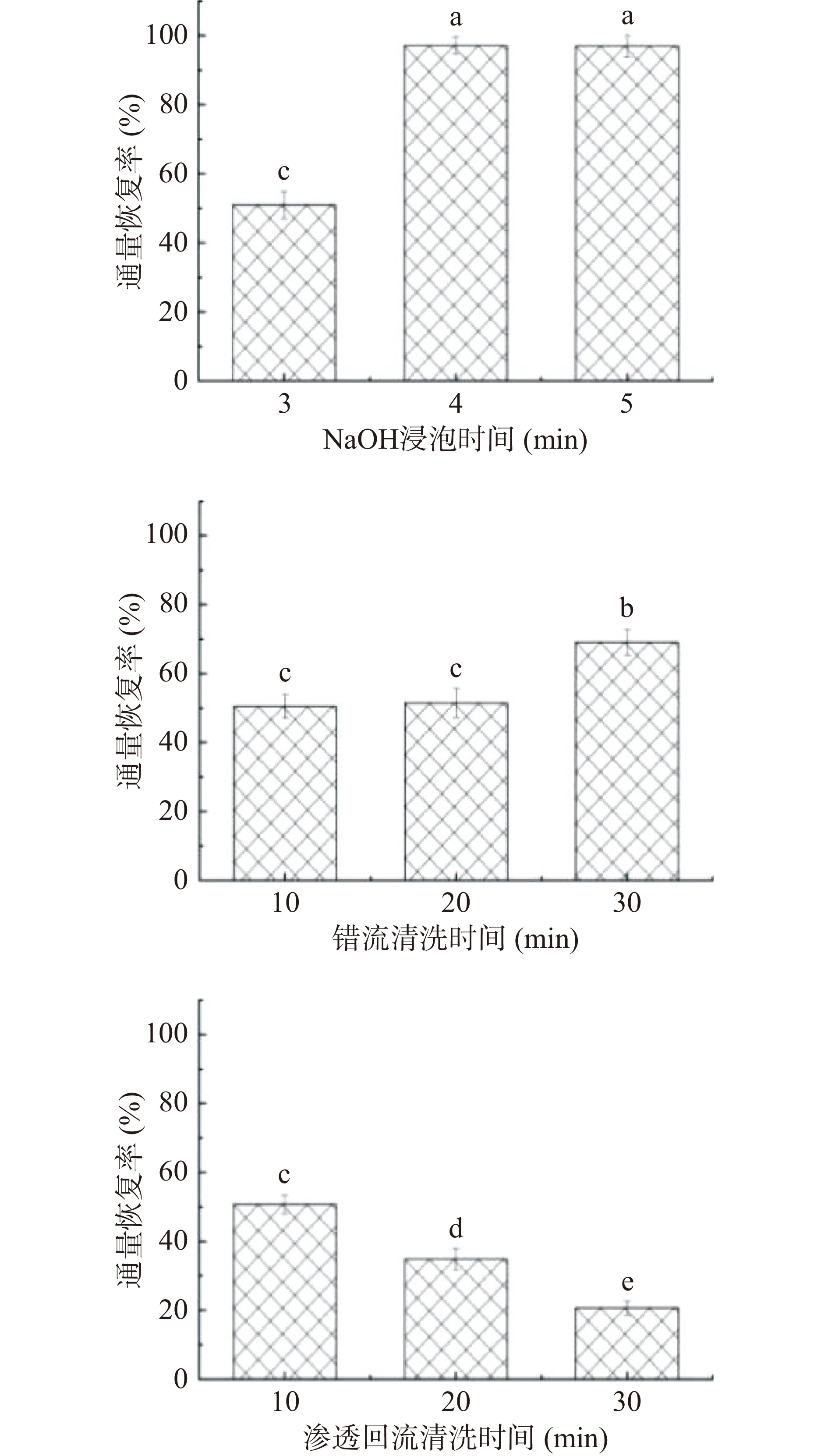
清洗后FO膜的通量恢复率如图18所示。
由图18可知,物理清洗方法中错流清洗优于渗透回流清洗,且错流清洗时间越长,通量恢复率逐渐增大,清洗30 min可使通量恢复约70%。但渗透回流清洗效果随着时间延长逐渐下降,可能由于驱动液侧饱和CaCl2溶液粘滞在膜表面,时间越长附着在膜面的CaCl2越多且不易去除,在进行通量恢复试验时,有效渗透压差降低,使得通量恢复率降低,Liu等[37]通过对放射性废水污染的膜清洗,得出错流清洗通量恢复至69%,可见,对于污染较为严重的膜,简单错流清洗显然达不到最佳效果。而化学清洗效果较为明显,仅仅4 min就能将膜通量恢复至约98%,超过4 min后,由于膜面的蛋白质溶解在NaOH中,过量的碱液将膜结构破坏致使通量恢复率增加。缪畅等[38]研究发现,蛋白质类、胶体类物质易吸附在膜表面或堵塞膜孔,pH10的NaOH清洗效果最佳。另外,较高的pH溶液中,由于羟基的出现,污染物官能团可以去质子化,负电性变得更强,这样会增加污染物之间排斥力,进而提高了清洗效果[39]。因此,经前期预实验确定0.05% NaOH浸泡4 min较为合适。
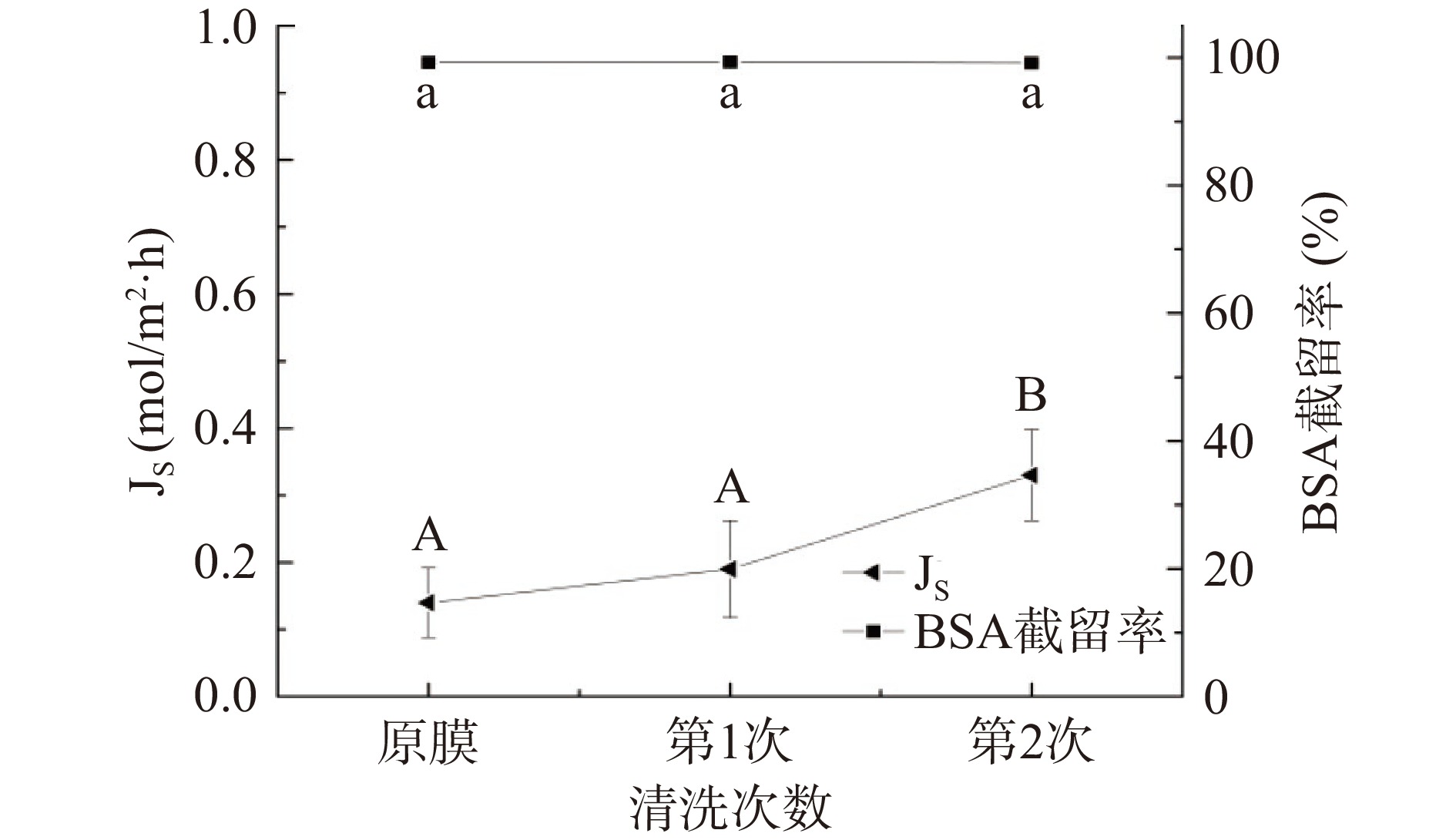
将FO膜片进行反复使用和清洗,由图19可知,随着FO的运行,比通量逐渐降低,经过0.05% NaOH清洗以后,膜初始比通量均有所提高,膜初始通量性能基本恢复。由图20可知,随着清洗次数的增加,反向溶质通量逐渐增大,第2次清洗后反向溶质通量(0.33 mol/m2·h)显著高于原膜(0.14 mol/m2·h)(P<0.05)和第1次清洗后反向溶质通量(0.19 mol/m2·h),本研究的反向溶质通量值介于吴思邈等[40]利用FO技术浓缩苹果汁时用的5 mol/L NaCl(1.49 mol/m2·h)和2 mol/L柠檬酸三钠(0.10 mol/m2·h)之间,且在此过程中膜的截留性能较为稳定。
3. 结论
本文研究了正渗透过程中原料液的离子强度及BSA浓度、膜方位等参数不同时FO膜的污染规律。原料液BSA中含有盐离子时FO膜的初始通量较低,但长时间运行时FO膜的通量高于纯BSA溶液的通量,反向溶质的扩散量在0.71 mol/m2·h以下,当原料电导率值低于5.5 ms/cm时,可不对其脱盐直接进行FO处理。且原料液中BSA的浓度越低,膜污染程度越轻。膜方位、驱动液种类和流速对水通量及反向溶质通量的影响较为显著,当处理含盐离子(1 mmol/L NaHCO3+1 mmol/L CaCl2+ 20 mmol/L NaCl)的BSA溶液最佳操作条件是以1.5 mol/L NaCl为驱动液并控制料液流速为2.89 m/s及FO模式下运行,此时FO膜通量达11.23±2.13 L/m2·h,BSA截留率97.83%、反向溶质扩散通量Js为0.14 mol/m2·h。对于蛋白质类污染物的最佳清洗方式为0.05% NaOH浸泡4 min,多次使用及重复清洗后恢复率仍达98%以上,表明该膜具有良好的耐清洗性能。
-
-
[1] 钱宇, 张忠国, 秦振平, 等. 阻垢剂PASP和DTPMP-Na7作为正渗透汲取液的比较研究[J]. 膜科学与技术,2019,39(1):101−109. [QIAN Y, ZHANG Z G, QIN Z P, et al. Comparative study on scale inhibitors PASP and DTPMP-Na7 as draw solution of forward osmosis process[J]. Membrane Science and Technology,2019,39(1):101−109. QIAN Y, ZHANG Z G, QIN Z P, et al. Comparative study on scale inhibitors PASP and DTPMP-Na7 as draw solution of forward osmosis process[J]. Membrane Science and Technology, 2019, 39(1): 101-109.
[2] 任潇, 王策, 李咏梅. 正渗透膜技术的研究与应用进展[J]. 环境污染与防治,2018,40(2):230−235. [REN X, WANG C, LI Y M. Research and application advances of forward osmosis membrane technology[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control,2018,40(2):230−235. REN X, WANG C, LI Y M. Research and application advances of forward osmosis membrane technology[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2018, 40(2): 230-235.
[3] 潘淑芳, 张珠鸿, 陈金垒, 等. 基于正渗透的膜集成工艺应用研究进展[J]. 水处理技术,2018,44(10):11−15,21. [PAN S F, ZHANG Z H, CHEN J L, et al. Research progress on the application of hybrid forward osmosis membrane systems[J]. Technology of Water Treatment,2018,44(10):11−15,21. PAN S F, ZHANG Z H, CHEN J L, et al. Research progress on the application of hybrid forward osmosis membrane systems[J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2018, 44(10): 11-15, 21.
[4] 齐亚兵, 张思敬, 杨清翠. 正渗透水处理技术研究现状及进展[J]. 现代化工,2021,41(8):52−57. [QI Y B, ZHANG S J, YANG Q C. Research status and progress on forward osmosis water treatment technologies[J]. Modern Chemical Industry,2021,41(8):52−57. QI Y B, ZHANG S J, YANG Q C. Research status and progress on forward osmosis water treatment technologies[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2021, 41(8): 52-57.
[5] NAYAK C A, RASTOGY N K. Comparison of osmotic membrane distillation and forward osmosis membrane processes for concentration of anthocyanin[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment,2010,16(1/2/3):134−145.
[6] SHALINI H N, NAYAK C A. Forward osmosis membrane concentration of raw sugarcane juice[M]. Singapore: Springer Singapore, 2016: 81-87.
[7] WANG Y N, WANG R, LI W, et al. Whey recovery using forward osmosis–evaluating the factors limiting the flux performance[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2017,533:179−189. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2017.03.047
[8] PEI J F, PEI S Y, WANG W J, et al. Athermal forward osmosis process for the concentration of liquid egg white: Process performance and improved physicochemical property of protein[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,312:1−9.
[9] 肖芹芹, 徐世昌, 王越, 等. 正渗透膜污染影响因素的研究与分析[J]. 化工进展,2018,37(1):359−367. [XIAO Q Q, XU S C, WANG Y, et al. Research and analysis on influencing factors of forward osmosis membrane fouling[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2018,37(1):359−367. XIAO Q Q, XU S C, WANG Y, et al. Research and analysis on influencing factors of forward osmosis membrane fouling[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2018, 37(1): 359-367.
[10] 赵频. 正渗透技术中驱动剂的选择及其膜污染的研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2018. ZHAO P. Study of draw solution selection and membrane fouling in forward osmosis[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2018.
[11] 李轻轻, 马伟芳, 聂超, 等. 正渗透汲取液类型及分离回收工艺研究进展[J]. 环境工程,2016,34(3):11−17. [LI Q Q, MA W F, NIE C, et al. Draw solution for forward osmosis processes: Types, separation and recovery process[J]. Environmental Engineering,2016,34(3):11−17. LI Q Q, MA W F, NIE C, et al. Draw solution for forward osmosis processes: Types, separation and recovery process[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2016, 34(3): 11-17.
[12] 刘彩虹. 聚酰胺复合膜功能层抗污染调控机制研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018. LIU C H. Antifouling modifications and mechanisms of surface functional layer of polyamide thin-film composite membranes[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018.
[13] LIN Y L, TSAI J Z, HUNG C H. Using in situ modification to enhance organic fouling resistance and rejection of pharmaceutical and personal care products in a thin-film composite nanofiltration membrane[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2019,26(33):34073−34084. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-3234-1
[14] 顾正阳, 龚超, 杨望臻, 等. 基于水通道蛋白的水处理仿生膜研究进展[J]. 化工进展,2018,37(3):1037−1046. [GU Z Y, GONG C, YANG W Z, et al. Recent progress on AQP based biomimetic membranes for water treatment[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2018,37(3):1037−1046. GU Z Y, GONG C, YANG W Z, et al. Recent progress on AQP based biomimetic membranes for water treatment[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2018, 37(3): 1037-1046.
[15] 赵永军. 纳米氧化石墨烯共混复合正渗透膜的制备与表征[D]. 上海: 东华大学, 2016. ZHAO Y J. Preparation and characterization of GO-polyamidenanocomposite forward osmosis membranes[D]. Shanghai: Donghua University, 2016.
[16] ENDRE N, IMRE H, EMILY W, et al. Effect of fouling on performance of pressure retarded osmosis (PRO) and forward osmosis (FO)[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2018,565:450−462. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2018.08.039
[17] MACHAWE M M, BHEKIE B M, ARNER R D V. Forward osmosis membrane performance during simulated wastewater reclamation: Fouling mechanisms and fouling layer properties[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering,2018,23:109−118. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2018.03.007
[18] EMILY W T, MARTIN M R, JOHN H L. In situ visualization of organic fouling and cleaning mechanisms in reverse osmosis and forward osmosis[J]. Desalination,2016,399:138−147. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2016.08.024
[19] EMADZADEN D, LAU W J, MATSUURA T, et al. The potential of thin film nanocomposite membrane in reducing organic fouling in forward osmosis process[J]. Desalination,2014,348:82−88. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2014.06.008
[20] 刘彩虹. 正渗透工艺特性及膜污染特征研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2013. LIU C H. Basic principles of forward osmosis and its membrane fouling behavior[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2013.
[21] ZHAO P, GAO B, YUE Q Y, et al. Fouling of forward osmosis membrane by protein (BSA): Effects of pH, calcium, ionic strength, initial permeate flux, membrane orientation and foulant composition[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment,2016,57(29):13415−13424. doi: 10.1080/19443994.2015.1060539
[22] EIJI I, NOBUYUKI K. Developments of blocking filtration model in membrane filtration[J]. Kona Powder and Particle Journal,2016,33(5):179−202.
[23] 赵淑真. 正渗透非热浓缩苹果浊汁的研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2021. ZHAO S Z. Forward osmosis process for nonthermal concentration of cloudy apple juice[D].Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2021.
[24] HEO J, HAN J, KIM Y, et al. Systematic study on calcium-dissolved organic matter interaction in a forward osmosis membrane-filtration system[J]. Journal of Korean Society of Water and Wastewater,2016,30(6):737−744. doi: 10.11001/jksww.2016.30.6.737
[25] 肖婷婷, 窦鹏佳, 王艳强, 等. 中空纤维正渗透膜浓缩灰水过程中的膜污染和清洗初探[J]. 膜科学与技术,2017,37(5):21−27. [XIAO T T, DOU J P, WANG Y Q, et al. Fouling and cleaning of hollow fiber forward osmosis membranes when concentrating grey water[J]. Membrane Science and Technology,2017,37(5):21−27. XIAO T T, DOU J P, WANG Y Q, et al. Fouling and cleaning of hollow fiber forward osmosis membranes when concentrating grey water[J]. Membrane Science and Technology, 2017, 37(5): 21-27.
[26] 刘宇, 张国治, 袁东振, 等. 豆制品废水综合利用现状[J]. 粮食与油脂,2015,28(3):22−25. [LIU Y, ZHANG G Z, YUAN D Z, et al. Fouling and cleaning of hollow fiber forward osmosis membranes when concentrating grey water[J]. Cereals & Oils,2015,28(3):22−25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2015.03.006 LIU Y, ZHANG G Z, YUAN D Z, et al. Fouling and cleaning of hollow fiber forward osmosis membranes when concentrating grey water[J]. Cereals & Oils, 2015, 28(3): 22-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2015.03.006
[27] 马藤, 王磊, 张慧慧, 等. 添加剂共混CA正渗透膜的制备及抗污染性研究[J]. 水处理技术,2017,43(10):68−71,75. [MA T, WANG L, ZHANG H H, et al. Preparation of CA forward osmosis membrane blended with additives and its anti-fouling performance[J]. Technology of Water Treatment,2017,43(10):68−71,75. MA T, WANG L, ZHANG H H, et al. Preparation of CA forward osmosis membrane blended with additives and its anti-fouling performance[J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2017, 43(10): 68-71, 75.
[28] 刘帅, 谢朝新, 周宁玉, 等. 正渗透膜污染及其清洗研究进展综述[J]. 净水技术,2015,34(4):23−30. [LIU S, XIE C X, ZHOU N Y, et al. Overview of research progress in membrane fouling and cleaning for forward osmosis membrane[J]. Water Purification Technology,2015,34(4):23−30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0177.2015.04.005 LIU S, XIE C X, ZHOU N Y, et al. Overview of research progress in membrane fouling and cleaning for forward osmosis membrane[J]. Water Purification Technology, 2015, 34(4): 23-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0177.2015.04.005
[29] 程巍, 吕兴霖, 刘乾亮, 等. 三醋酸纤维素正渗透膜的双向离子传质机制研究[J]. 中国给水排水,2019,35(13):67−71. [CHENG W, LV X L, LIU Q L, et al. Bidirectional transport of lons in cellulose triacetate forward osmosis membrane[J]. China Water & Wastewater,2019,35(13):67−71. CHENG W, LV X L, LIU Q L, et al. Bidirectional transport of lons in cellulose triacetate forward osmosis membrane[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2019, 35(13): 67-71.
[30] 王一博. 聚酰胺复合正渗透膜的结构与性能优化研究[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学, 2020. WANG Y B. Structure and property optimization of polyamide composite forward osmosis membrane[D]. Dalian: Dalian Maritime University, 2020.
[31] CHUYANG Y T, SHE Q H, WINSON C L L, et al. Fane. Coupled effects of internal concentration polarization and fouling on flux behavior of forward osmosis membranes during humic acid filtration[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2010,354(1):123−133.
[32] ZHOU Z Z, JIM Y L, CHUNG T S. Thin film composite forward-osmosis membranes with enhanced internal osmotic pressure for internal concentration polarization reduction[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2014,249:236−245. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.03.049
[33] TAN C H, NG H Y. A novel hybrid forward osmosis-nanofiltration (FO-NF) process for seawater desalination: Draw solution selection and system configuration[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment,2010,13(1−3):356−361. doi: 10.5004/dwt.2010.1733
[34] 吴晴. 正渗透过程中驱动溶质反渗规律研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2013. WU Q. Research on reverse permeation of draw solute in forward osmosis[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2013.
[35] SHAN Z, WANG Y N, FILICIA W, et al. Direct microscopic observation of forward osmosis membrane fouling by microalgae: Critical flux and the role of operational conditions[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2013,436:174−185. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2013.02.030
[36] 王根实. 基于膜面流场分析的正渗透性能研究及参数优化[D]. 天津: 天津工业大学, 2017. WANG G S. Research on forward osmosis performance and parameter optimization based on membrane flow field analysis[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin Polytechnic University, 2017.
[37] LIU X J, WU J L, HOU L A, et al. Fouling and cleaning protocols for forward osmosis membrane used for radioactive wastewater treatment[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Technology,2020,52(3):581−588. doi: 10.1016/j.net.2019.08.007
[38] 缪畅, 邱运仁. NF-RO组合膜处理大豆乳清废水[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2010,41(4):1623−1627. [LIAO C, QIU Y R. Treatment of soybean whey wastewater by NF and RO membrane[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology),2010,41(4):1623−1627. LIAO C, QIU Y R. Treatment of soybean whey wastewater by NF and RO membrane[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2010, 41(4): 1623-1627.
[39] WUI S A, TIRAFERRI A, CHEN K L, et al. Fouling and cleaning of RO membranes fouled by mixtures of organic foulants simulating wastewater effluent[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2011,376(1):196−206.
[40] 吴思邈, 陈建明, 王爱廉, 等. 正渗透技术浓缩苹果汁过程中反向溶质扩散的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(24):172−180. [WU S M, CHEN J M, WANG A L, et al. Study of reverse solute flux in apple juice concentration by forward osmosis[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(24):172−180. WU S M, CHEN J M, WANG A L, et al. Study of reverse solute flux in apple juice concentration by forward osmosis[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(24): 9.
-
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 于新海,李濛,周红昕,吴海英,姚文平. 大花卷丹的百合粗多糖提取工艺的研究与分析. 农业与技术. 2025(04): 41-44 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 何念武,董玉珊,朱姝俣. 连翘多糖提取工艺优化及抗氧化和抑菌活性研究. 商洛学院学报. 2024(02): 59-65 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王鑫,周卓,遇世友,岳振歌,修伟业,马永强. 甜玉米芯多糖纳米银的合成、表征及体外活性研究. 食品工业科技. 2024(13): 58-66 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 杨迎东,王伟东,张睿琪,冯秀丽,白一光,杨盼盼,周俐宏,李雪艳,胡新颖. 不同百合食药用功能指标检测分析. 沈阳农业大学学报. 2024(03): 276-284 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 伍乔,范茂清. 百合的研究进展. 中国食品工业. 2024(14): 132-134 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 陈强,王璐,徐峥嵘,罗金超,邓千千,方雨婷,李从虎,程旭. 玉米植物糖原超声辅助提取工艺优化及其生物活性评价. 食品工业科技. 2024(19): 177-186 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 康桥,孙越,刘梦瑶,赵保龙,李贺贺,王柏文,赵东瑞,孙宝国,孙金沅. 金铃子果皮多糖超声辅助提取工艺优化及其抗氧化和降糖活性研究. 食品工业科技. 2024(21): 164-173 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 藏颖,梁钟文,刘松,高丹,黄羽诺,李媚,刘红全. 雨生红球藻藻渣多糖提取条件优化及降血脂活性分析. 食品研究与开发. 2024(22): 102-110 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 于武华,桂明明,何平平,邓小燕. 百合的营养价值及加工技术研究进展. 食品安全导刊. 2024(35): 186-189 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 代琪,杨海媚,李林珍,叶俏波,罗霄,李及,叶俊龙. 不同品种百合的化学成分及药理作用研究进展. 中国药物评价. 2024(06): 459-463 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 许梦粤,曾长立,王红波. 药食同源植物多糖提取方法、结构解析和生物活性研究进展. 食品研究与开发. 2023(19): 216-224 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(10)





 下载:
下载:










 下载:
下载:
