Comparison of Change of Quality for Six High-quality Indica Rice during After-ripening
-
摘要: 后熟是粮食的特性之一,在后熟过程中,粮食籽粒会发生生理生化活动,其加工品质及食用品质在后熟完成后一般会改善,然而目前关于我国主要粮食作物之一稻谷的后熟研究较少。为探究籼稻的后熟期时长、后熟期间的具体活动状态、后熟期内的品质变化规律,实验以6种优质籼稻(隆两优534、黄华占、郢香丝苗、粤农丝苗、虾稻1号、A优442)为原料,在后熟期内定期对其品质进行检测,包括测定其生理生化指标(发芽率、电导率、出糙率、脂肪酸值)、糊化特性指标和不同酶活性(过氧化物酶、过氧化氢酶、α-淀粉酶)。结果表明,六类优质籼稻具有不同后熟时长,后熟期间6个品种优质籼稻的发芽率整体呈上升趋势,电导率呈波动的先上升后下降的趋势,出糙率呈波动上升趋势,脂肪酸值呈波动的先下降后上升趋势,过氧化物酶品种间有变化趋势的差异但整体呈波动下降趋势,过氧化氢酶活性除A优442外整体呈波动上升趋势、α-淀粉酶活性除黄华占以外呈现波动下降趋势,峰值粘度整体呈先波动的上升后下降的趋势。通过主成分分析进行品质评价,得分由高到低分别是A优442、隆两优534、虾稻1号、粤农丝苗、郢香丝苗、黄华占。Abstract: After-ripening is one of the characteristics of grain, physiological and biochemical activities will exist in grain during this period. Its processing quality and edible quality will generally be improved after the completion of ripening. However, there are few studies on after-ripening of rice, one of the main grain crops in China. The physiological and biochemical indexes (germination rate, conductivity, roughness and fatty acid value), gelatinization characteristics and different enzyme activities (peroxidase, catalase, α-amylase) of six types of high-quality indica rice (Longliangyou 534, Huanghuazhan, Yingxiangsimiao, Yuenongsimiao, Xiadao 1 and Ayou 442) were measured regularly during after-ripening period to investigate the after-ripening duration of indica rice, the specific activity state during the after-ripening period and the quality change rules during after-ripening period of indica rice. The results showed that six kinds of high quality indica rice had different after-ripening duration, 6 varieties at ripening time of germination rate rose on the whole, the conductivity was fluctuating downward trend after rising first, out of the roughness increased volatility, the fatty acid value decreased firstly then increased, peroxidase varieties had differences in trends but volatility declined on the whole, the activity of catalase showed a fluctuating upward trend except Ayou 442, the activity of α-amylase showed a fluctuating downward trend except Huanghuazhan, and the peak viscosity showed a fluctuating upward trend at first and then a decreasing trend. The quality evaluation was carried out by principal component analysis, and the scores from high to low were Ayou 442, Longliangyou 534, Xiadao 1, Yuenongsimiao, Yingxiangsimiao, Huanghuazhan.
-
Keywords:
- high-quality indica rice /
- after-ripening /
- quality change /
- pasting property /
- enzyme activity
-
粮食是满足人民温饱的重中之重,粮食、油料种子在田间收获后,需经过一段时间才能完成种子内部的变化,达到生理上的成熟,这种从收获成熟到生理成熟的过程称为后熟作用,此过程所经历的时间即为后熟期[1],在此期间,粮食的生理生化活动较为强烈,对入库之后的储粮安全造成潜在威胁。
在粮食领域中,有关后熟期的研究大都集中于小麦[2-4],根据前人研究表明,小麦在后熟期间其内部发生生理和生化变化,发芽率升高,加工和食用品质得以改善[5],新收获的小麦根据不同的品种,一般需要经过10~90 d的时间完成后熟期,此后小麦的降落数值及面筋指数有所增加,面团的流变学特性逐步改善[6]。粳米经过高温后熟处理,品质变化表现为直链淀粉和不溶性直链淀粉含量显著上升,蒸煮膨胀率增大,峰值粘度下降[7]。综上,粮食后熟期方面缺少籼稻类后熟期研究,而米粉加工企业仅凭生产经验选择贮藏一段时间的籼稻制作米粉,并未深入了解原料的差异性和适用性,难以保证米粉品质[8]。
为了确定不同品种优质籼稻的具体后熟时长,在后熟期间稻谷籽粒内部的生理活动变化、化学成分变化规律,为稻谷类后熟期研究提供参考与准确数据支撑,研究以6种优质籼稻(隆两优534、黄华占、郢香丝苗、粤农丝苗、虾稻1号、A优442)为实验材料于室温条件下贮藏,在收获后分别对发芽率、出糙率、电导率、脂肪酸值、糊化特性的指标、过氧化物酶活性、过氧化氢酶活动度以及降落数值进行测定,以期将关于籼稻后熟期品质比较的研究补充得更加系统完整,为稻谷收获后入库状态、对米粉等加工制品的进一步加工制作提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
隆两优534、黄华占、郢香丝苗、粤农丝苗、虾稻1号 于湖北省仙桃市收购;A优442 于湖北省咸宁市双溪桥镇收购;酚酞(指示剂)、无水乙醇(分析纯)、95%乙醇(分析纯)、愈创木酚(分析纯) 天津市科密欧化学试剂有限公司;十二水合磷酸氢二钠、磷酸二氢钾、30%过氧化氢 分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司;浓硫酸 分析纯,中国平煤神马集团开封东大化有限公司。
SHX-250B-Z型生化培养箱、GZX-9070MBE型数显鼓风干燥箱 上海博讯实业有限公司医疗设备厂;JSFM-1型粮食水分测试磨 成都施特威科技发展公司;AL204型电子分析天平 梅特勒-推利多仪器(上海)有限公司;THU358型砻谷机 佐竹机械有限公司;JXFM型锤式旋风磨 上海嘉定粮油仪器有限公司;JZDZ-I型脂肪酸值振荡器 国家粮食局成都粮食储藏科学研究所;T6型紫外可见分光光度计 北京普析通用仪器有限责任公司;Super-4型快速粘度仪 Newport scientific;FN1900型降落数值仪 杭州潜江仪器设备有限公司;80-2台式离心机 湖南凯达科学仪器有限公司;DX-1型电导率仪 杭州东星设备实验厂。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 实验设计
将6种收获的籼稻晾晒,至稻谷水分含量低于15%,存放于室温下(25 ℃)编织袋中,储存环境湿度维持在50%~70%,定期对实验指标进行测定,其中发芽率的测定间隔为3 d,其余检测指标间隔7 d。
1.2.2 水分含量测定
参考GB 5009.3-2016《食品中水分的测定105 ℃恒重法》[9]。
1.2.3 发芽率测定
参考GB/T 5520-2011《粮油检验发芽试验》[10]。
1.2.4 出糙率测定
参考GB/T 5495-2008《粮油检验稻谷出糙率检验》[11]。
1.2.5 电导率测定
称取5±0.2 g稻谷,置于100 mL离心管中,自来水冲洗3次,纯净水冲洗2~3次,滤纸吸干水分,添加50 mL纯净水,密封条件室温下浸泡24 h,期间摇匀2~3次,使用电导率仪测定。
1.2.6 脂肪酸值测定
脂肪酸值的测定参考GB/T 20569-2006《稻谷储存品质判定规则中的附录A测定脂肪酸值》[12]。
1.2.7 糊化特性测定
将实验原料均匀混合、除杂,经砻谷机脱壳后,所得净稻谷通过锤式旋风磨磨为粉状(可过80目筛),实验步骤参考GB/T 24852-2010《大米及米粉糊化特性的测定》[13]。
1.2.8 过氧化物酶(POD)活性的测定
1.2.8.1 粗酶液提取
称取1 g糙米粉置于研钵中,加10 mL 0.05 mol/L KH2PO4研磨均匀,倒入离心管中,4000 r/min离心10 min,取上清液备用。
1.2.8.2 反应混合液制备
取56 μL愈创木酚加入到pH6.0 1mol/L 100 mL的磷酸缓冲液中,在磁力搅拌器上以40 ℃加热搅拌20 min,冷却后加入38 μL 30%过氧化氢混匀,备用。
1.2.8.3 吸光度的测定
取1 mL酶液(空白加1 mL KH2PO4)和3 mL反应混合液于试管中,混匀后开始计时,在470 nm下测定吸光值,测定时长为5 min。
1.2.8.4 酶活性计算
每个样品3个平行,以每分钟OD470变化0.01为1个过氧化物酶活性单位(U)。
计算公式如下:
过氧化物酶(POD)活性(U)=ΔD470×VTW×VS×0.01 式中:ΔD470表示反应时间内吸光值的变化;W表示样品的质量,g;VT表示提取酶液总体积,mL;Vs表示测定时取酶液体积,mL。
1.2.9 过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性测定
参考GB/T 5522-2008《粮食油料过氧化氢酶活动度的测定》[14]。
1.2.10 α-淀粉酶活性测定
降落数值的变化可以表现稻谷中α-淀粉酶的活性变化,二者呈负相关。降落数值的测定方法参考GB/T 10361-2008《小麦、黑麦及其面粉,杜伦麦及其粗粒粉降落数值的测定》[15]。
1.3 数据处理
实验数据使用Excel2010整理,通过Origin2018软件进行图像绘制,采用SPSS19软件进行描述统计、相关性分析、主成分分析。描述统计分析采用Duncan法进行多重比较,相关性采用Pearson相关系数分析,主成分采用累计方差贡献率>80%提取主成分,将各组分得分相加,得出数据并进行排序。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 后熟期间水分含量的变化
如图1所示,在后熟期间,储藏籼稻水分含量在10%~15%之间波动,起初呈现下降趋势,之后呈现小幅度上升趋势,可能是起初稻谷水分较易迁移至表面散发,在后熟完成后,稻谷籽粒结构趋于完整紧密,水分不易散失、储藏环境湿度增加的原因。
2.2 后熟期间储藏特性的变化
2.2.1 后熟期间发芽率的变化
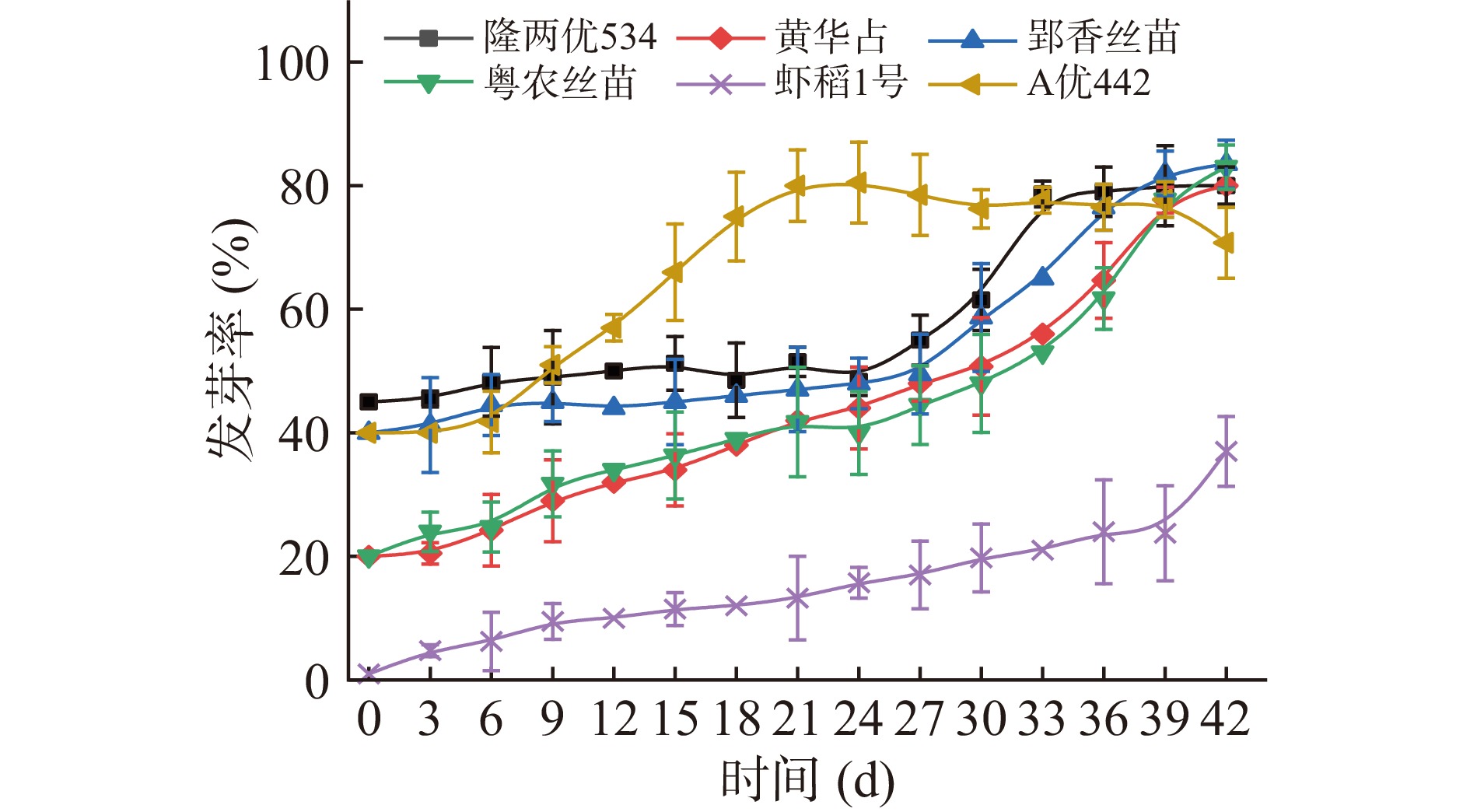
当粮食发芽率达到80%视为其完成后熟的标志。由图2、表1得知,六种优质籼稻拥有不同的后熟时间,除5号品种起始发芽率过低后熟未完成外,其余品种自收获之日起,发芽率呈现上升趋势,这是因为在后熟作用中,稻谷的种胚逐渐成熟,细胞内高分子化合物充分合成,也可能因为发芽抑制物质逐渐转化、消失,稻谷粒得到适宜的温度湿度而萌发[1]。根据图2所示,隆两优534与郢香丝苗、黄华占与粤农丝苗两组每组的增长数量与趋势基本一致,种子在收获后会经历休眠期,完成休眠期之后上涨速度加快。隆两优534在24~33 d中上升趋势明显,郢香丝苗为27~39 d;A优442于早期6~24 d上升趋势明显。相较一种粳稻(南粳46号)在后熟期间1~5 d呈迅速上升状态,7 d以后趋于平稳,快速完成后熟的情况,可能是品种之间的差异,以及后熟期的内源激素含量变化不同引起的[16]。
表 1 六种优质籼稻收获时间及后熟期Table 1. Harvesting time and post-ripening stage of six indica rice varieties编号 品种 收获时间 后熟期(d) 1 隆两优534 2020年10月11日 33 2 黄华占 2020年10月11日 42 3 郢香丝苗 2020年10月11日 39 4 粤农丝苗 2020年10月11日 42 5 虾稻1号 2020年10月11日 \ 6 A优442 2020年10月31日 21 2.2.2 后熟期间出糙率的变化
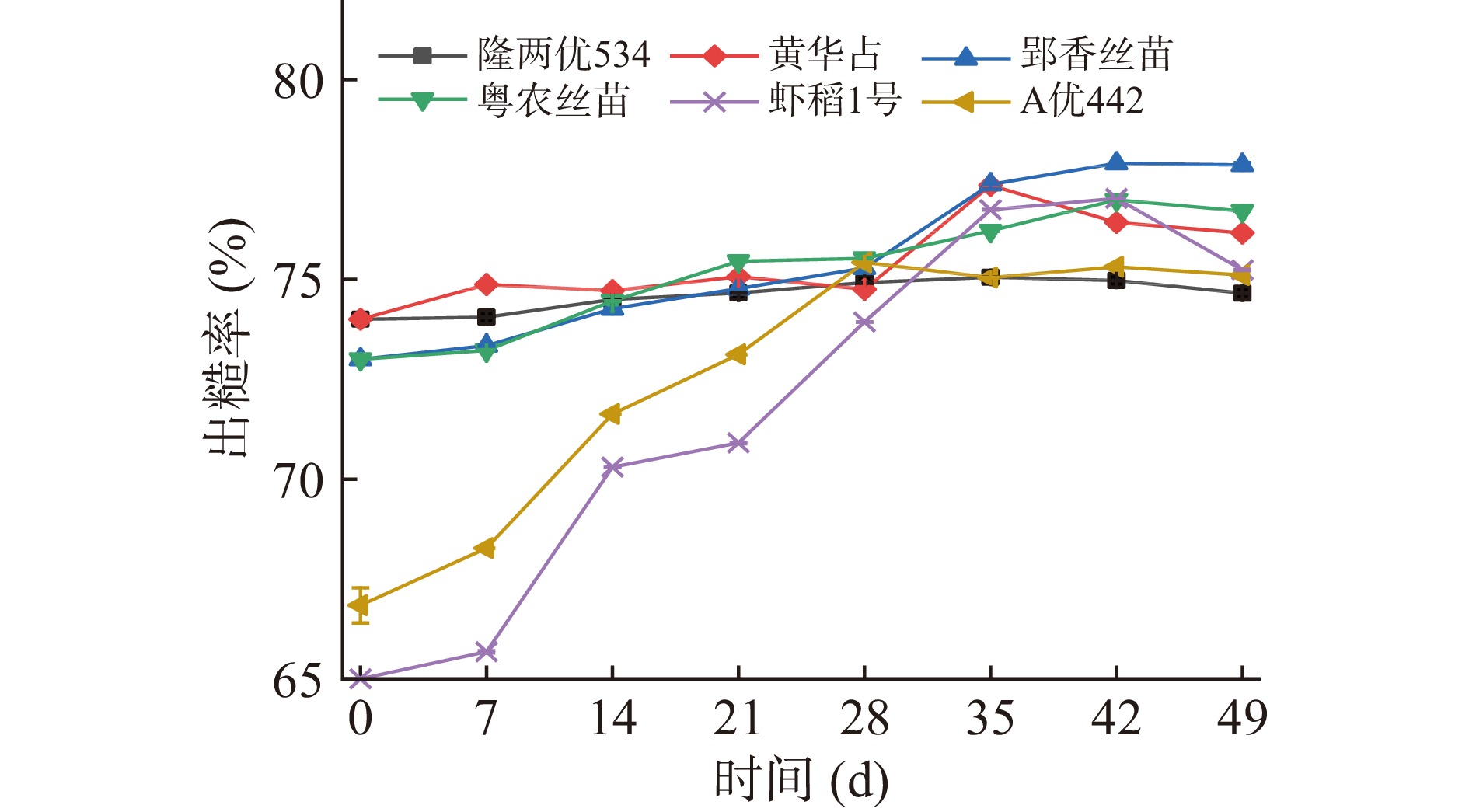
稻谷根据其出糙率划分为一等、二等、三等,直接反映稻谷加工品质的高低。如图3所示,随着籼稻后熟期的完成,隆两优534、黄华占、郢香丝苗、粤农丝苗发芽率增长趋势相似,出糙率增减范围在73%~77%内波动,隆两优534出糙率较缓的上升,至35 d左右开始下降;黄华占出糙率于0~35 d呈波动上升趋势后下降;郢香丝苗与粤农丝苗出糙率逐步上升同时至42 d达到最高峰;虾稻一号与A优442起始出糙率较低,但在后熟结束后其出糙率分别于42和28 d达到最大值为77.03%和75.42%。对六种优质籼稻的发芽率和出糙率进行pearson相关性分析,如表2所示,其中黄华占、郢香丝苗、粤农丝苗与虾稻一号品种其出糙率与发芽率存在相关性(P<0.05),说明随着籼稻后熟逐渐完成,稻谷籽粒越来越饱满,出糙率有明显提高,有利于稻谷后续加工。
表 2 六种优质籼稻在后熟期间出糙率与发芽率的相关性分析Table 2. Correlation analysis of roughness rate and germination rate of six high-quality indica rices during after-ripening period品种 隆两优534 黄华占 郢香丝苗 粤农丝苗 虾稻1号 A优442 Pearson相关性 0.441 0.854 0.888 0.832 0.924 0.734 显著性(双侧) 0.275 0.014 0.008 0.020 0.003 0.158 2.2.3 后熟期间电导率的变化
电导率是评价稻谷细胞膜完整度的评价指标,能够反映籼稻在新鲜程度上存在的差异[17]。如表3所示,电导率在稻谷后熟时期呈现不稳定波动的状态,其中隆两优534于28 d达到最高值,在后熟期完成(33 d)后电导率呈现稳定下降趋势;6种籼稻电导率同时于28 d达最大值,分别较起始增长37.20、39.35、41.80、36.67、36.25和32.90 μs/(cm·g),黄华占、郢香丝苗和虾稻一号的电导率在此以后呈现波动下降趋势,这可能是因为稻谷在后熟即将完成时,稻谷的细胞膜生长趋于完整,浸泡出的液体中稻谷成分较少渗出。
表 3 六种优质籼稻在后熟期间电导率的变化(μs/(cm·g))Table 3. Changes of electrical conductivity of six high-quality indica rices varieties during after-ripening period (μs/(cm·g))时间
(d)隆两优534 黄华占 郢香丝苗 粤农丝苗 虾稻一号 A优442 0 41.90±5.91a 34.50±2.29a 36.40±3.76a 36.43±1.53a 40.80±0.75a 40.00±2.35a 7 54.18±0.60ab 53.95±4.38b 53.67±6.97b 52.91±4.82b 63.38±3.44b 42.05±3.57a 14 68.27±5.69bc 65.55±6.15b 71.83±1.67de 59.50±4.10bc 67.15±0.35bc 67.65±3.32d 21 69.25±0.64bc 61.05±1.63b 62.23±2.85bcd 59.45±1.34bc 69.65±4.74bc 59.63±3.29b 28 79.10±4.81c 73.85±2.05c 78.20±1.55e 73.10±0.57d 77.05±5.59c 72.90±1.41c 35 72.95±4.60c 54.70±3.68b 54.10±1.31bc 53.00±2.97b 60.40±1.41b 65.63±4.96bc 42 73.90±1.41c 67.40±0.71bc 64.90±3.39cd 69.40±3.54cd 69.40±4.95bc 71.93±5.22c 49 74.00±1.98c 63.60±3.25b 61.10±0.99bcd 72.20±5.23d 64.77±3.57b 72.80±5.23c 注:同一列的相同字母表示差异不显著(P˃0.05);不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);表5同。 2.2.4 后熟期间脂肪酸值的变化
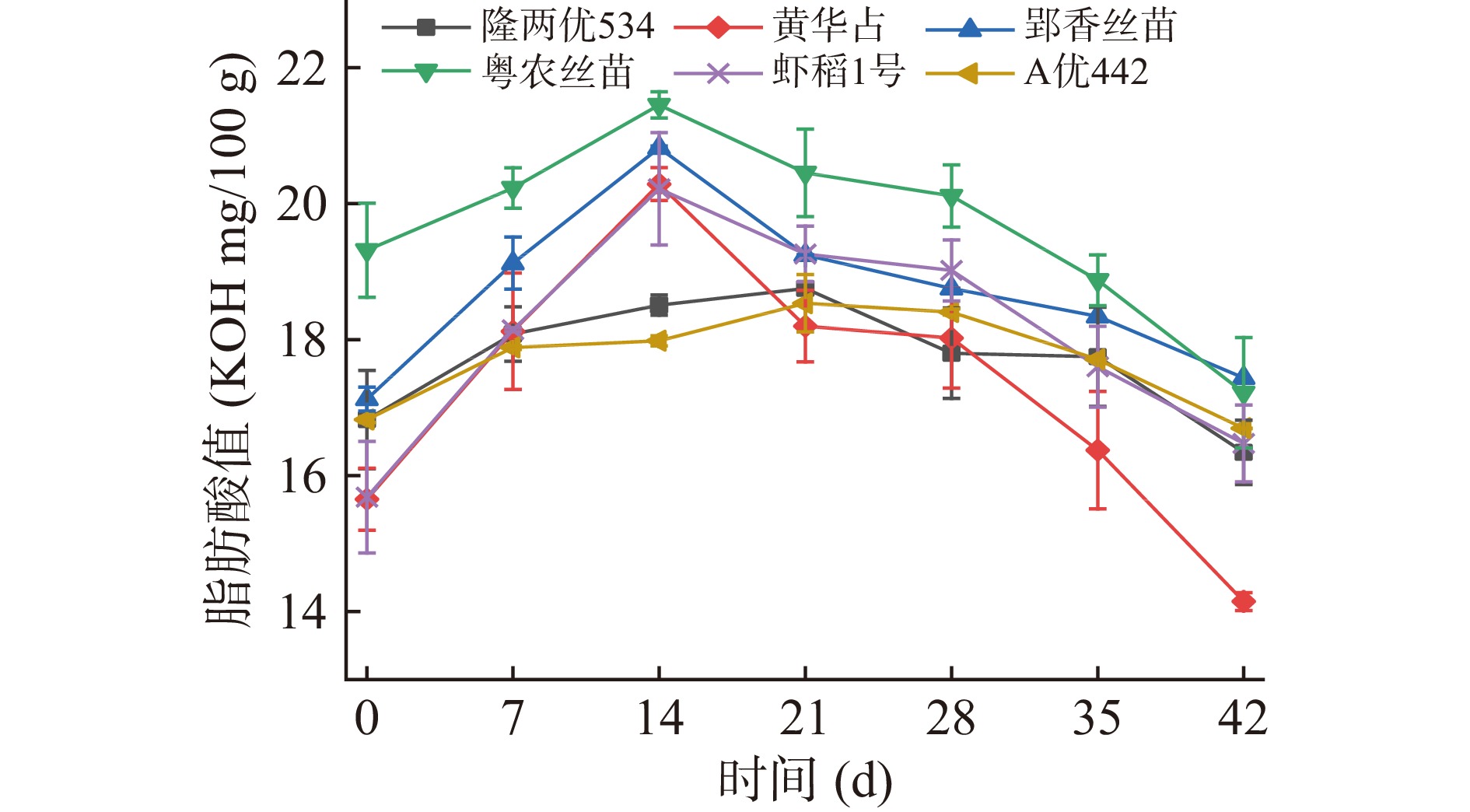
游离脂肪酸含量是判定稻谷品质的重要指标,反映粮食储藏品质的变化情况[18],稻谷在常规储藏情况下,稻谷中的脂肪会被水解成脂肪酸、甘油等物质,使储藏过程中的脂肪酸值增大,导致陈化变质[19]。如图4所示,隆两优534与A优442的脂肪酸值在21 d达到峰值,分别为18.75和18.53 mg/100 g,之后呈现下降趋势在42 d达到最小值分别为16.34和16.70 mg/100 g;黄华占、郢香丝苗、粤农丝苗、虾稻一号在14与42 d达到最大值与最小值。稻谷在后熟期间,脂肪酸值变化较大呈现先上升后下降的趋势,而稻谷储藏时,脂肪酸值一般呈现逐步上升的趋势[20],脂肪酸值的下降有可能是因为稻谷籽粒在后熟期间呼吸作用加强[21],稻谷中一部分脂肪酸作为呼吸作用的底物被利用发生反应提供能量,因此稻谷脂肪酸值在后熟期内存在下降趋势。
2.3 后熟期间糊化特性的变化
根据研究,稻谷的糊化特性可以直观反映出其直链淀粉含量高低[22],直链淀粉的含量和结构与稻谷的蒸煮品质食用品质有直接联系[23],用峰值粘度、最低粘度、回生值、和糊化温度值能较好反映稻米食味品质的优劣[24],因此可以作为优质稻谷的辅助指标[25]。六种优质籼稻(隆两优534、黄华占、郢香丝苗、粤农丝苗、虾稻1号、A优442)在后熟期间的糊化特性指标测定结果如表4所示。其中,隆两优534与黄华占峰值粘度在14 d达到最大值,郢香丝苗、粤农丝苗与虾稻一号在21 d达到最大值,A优442收获时为最大值,隆两优534达到六个品种中峰值粘度最大值为2305.0 cP。除A优442外其余品种的峰值粘度早后熟期整体呈现上升后下降的趋势,与研究一致[26],但根据研究[27],随着储藏时间的延长,峰值粘度呈现逐步上升的趋势,并无下降的趋势,不同于一般储藏,这可能是因为峰值粘度表示淀粉在升温过程中膨胀程度,灵敏地反映出淀粉颗粒的质量的好坏,而峰值粘度的变化与α-淀粉酶活性有关,酶解力大,淀粉结构松散,在糊化过程中膨胀程度较小,峰值粘度变小[28]。
表 4 六种优质籼稻在后熟期间的RVA特征值Table 4. RVA characteristics value of six indica rices varieties during after-ripening period时间
(d)峰值粘度
(cP)最低粘度
(cP)衰减值
(cP)最终粘度
(cP)回生值
(cP)峰值时间
(min)糊化温度
(℃)隆
两
优
5
3
40 2085±13b 968±12a 1117±1ab 1757±20a 790±8a 5.60±0.00a 82.68±0.04ab 7 2172±11c 1019±46a 1153±35bc 1969±52c 951±6e 5.80±0.10a 83.08±0.56abc 14 2305±0e 1055±35a 1250±35c 1979±25c 924±11cd 5.67±0.19a 82.25±1.77a 21 2229±6d 1029±56a 1202±50bc 1991±59c 962±3e 5.67±0.19a 83.00±0.57abc 28 2177±5cd 1022±34a 1155±30bc 1934±34bc 912±1c 5.66±0.12a 83.13±0.46abc 35 2207±17cd 1083±29a 1124±36ab 2024±30c 941±9de 5.82±0.18a 84.53±0.36bc 42 2224±24cd 1063±43a 1162±24bc 1962±53c 900±10c 5.73±0.17a 83.70±0.52abc 49 1995±25a 968±12a 1027±37a 1823±7ab 855±7b 5.73±0.17a 84.90±0.48c 黄华占 0 1494±45a 574±24 a 920±69a 1214±52a 640±76a 5.40±0.10a 75.88±1.66a 7 1948±40d 891±57c 1057±23b 2047±80d 1156±23f 5.94±0.09cd 76.68±0.53a 14 1971±50d 958±2c 1013±48ab 2014±18d 1057±16e 6.00±0.00d 77.08±0.04a 21 1901±26d 887±33c 1014±9ab 1953±47d 1066±15e 5.93±0.07cd 77.35±0.48a 28 1617±19b 679±18b 939±27a 1502±24bc 823±7cd 5.67±0.07abc 76.83±0.42a 35 1776±19c 755±40b 1021±23ab 1637±51c 883±12d 5.71±0.10bc 76.9±1.19a 42 1672±21b 677±19b 996±16ab 1415±28b 738±9b 5.56±0.08ab 76.53±0.32a 49 1679±15b 708±35b 971±39ab 1492±47b 785±13bc 5.66±0.12ab 77.63±0.46a 郢香丝苗 0 1234±25a 524±17a 710±8a 1186±37a 662±20a 5.70±0.04a 90.35±0.57b 7 1612±46c 715±140ab 897±47ab 1613±236bcd 898±96b 5.90±0.14a 91.13±0.53b 14 1422±71b 664±71ab 758±1ab 1435±119abc 771±48a 5.73±0.00a 90.35±0.57b 21 1752±27d 880±80bc 872±56bc 1854±108de 975±28b 6.00±0.18a 77.40±0.95a 28 1268±2a 577±24a 691±26a 1289±30ab 712±6a 5.74±0.09a 90.30±0.49b 35 1470±27b 1008±58c 462±45d 2005±67e 998±10b 5.82±0.10a 76.57±0.43a 42 1400±15b 965±20c 435±28d 1970±21e 1005±7b 5.80±0.07a 76.10±0.44a 49 1248±54a 852±85bc 396±43cd 1742±107cde 890±23b 5.69±0.14a 76.80±0.43a 粤农丝苗 0 1875±47c 910±45bc 965±3abcd 1695±59a 785±14a 5.77±0.05a 76.00±0.64a 7 2061±21d 1080±21d 981±0bcd 2234±30d 1154±9g 6.20±0.00c 90.65±0.00c 14 2044±16d 1006±26cd 1038±10d 2078±27c 1073±1f 6.00±0.10abc 89.45±0.49bc 21 2109±52d 1099±11d 1009±41cd 2196±15cd 1096±5f 6.09±0.03c 81.10±6.93ab 28 1673±20a 792±48a 881±28ab 1640±55a 848±7c 5.77±0.14ab 77.18±1.17a 35 1868±14c 941±19bc 927±14abc 1901±27b 960±11e 6.02±0.04bc 77.70±0.43a 42 1751±17ab 844±28ab 907±44ab 1658±30a 814±3b 5.78±0.08ab 76.70±0.52a 49 1826±14bc 947±51bc 879±38a 1853±60b 906±9d 5.98±0.10abc 77.93±0.78a 虾稻一号 0 1915±55a 896±34a 1019±21a 1758±40a 862±6a 5.70±0.04a 76.35±0.07a 7 2058±23a 1015±26a 1043±2a 2252±29c 1237±4d 6.04±0.05b 77.50±0.57a 14 2030±6a 956±56a 1074±50a 2053±66bc 1097±10bcd 5.87±0.09ab 76.78±0.60a 21 2080±32a 1019±55a 1061±24a 2212±67bc 1193±19cd 5.89±0.08ab 76.37±0.03a 28 1956±7a 932±18a 1025±11a 1968±23abc 1036±6b 5.84±0.05ab 76.25±0.00a 35 1920±18a 894±23a 1026±5a 1936±29ab 1043±7b 5.82±0.08ab 76.65±0.43a 42 2036±7a 967±41a 1069±34a 1956±35ab 990±8ab 5.76±0.08a 76.07±0.49a 49 2128±155a 990±98a 1138±105a 2074±194bc 1085±102bc 5.80±0.12ab 77.10±0.83a A优4
4
20 1831±8e 1310±5d 521±8b 2593±15e 1283±16d 5.98±0.04a 86.42±0.45a 7 1606±15c 1141±26bc 465±26ab 2430±6c 1290±31d 6.09±0.03a 89.33±0.53b 14 1509±5b 1049±18ab 460±13ab 2227±43b 1178±61abcd 5.97±0.05a 89.05±0.00b 21 1699±10d 1233±21cd 467±13ab 2495±31cd 1263±52cd 6.11±0.03a 89.83±0.06b 28 1467±17a 1009±34a 458±18ab 2123±12a 1114±45abc 5.93±0.12a 89.08±0.11b 35 1461±5a 1021±29a 439±33a 2069±23a 1048±51a 6.02±0.14a 89.33±0.98b 42 1598±18c 1158±38c 440±30a 2267±29b 1109±59ab 6.11±0.08a 89.60±0.95b 49 1732±10d 1306±57d 426±48a 2506±19d 1201±76bcd 6.20±0.18a 89.43±0.98b 注:不同品种在不同时间段位于同一列的相同字母表示差异不显著(P˃0.05);不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 A优442在49 d时最低粘度达到总品种最大值1306 cP;隆两优534在14 d衰减值达到总品种最大值1250cP;A优442在收获时最终粘度达到总品种最大值2593 cP;A优442在7 d回生值达到总品种最大值1290cP;隆两优534、郢香丝苗和A优442的峰值时间在α=0.05水平上无显著变化,粤农丝苗在21 d峰值时间达到总品种最大值6.09 min;郢香丝苗在7 d峰值温度达到总品种最大值91.13 ℃。
综上,在后熟期间,隆两优534品种在14 d时达到所有品种后熟期内的最大值,是稻米食味最佳的时期。而六种优质籼稻的糊化特性各指标出现差异,可能是其内部直链淀粉的组分含量与结构的不同的原因[29]。
2.4 后熟期间酶活性的变化
2.4.1 后熟期间过氧化物酶(POD)活性的变化
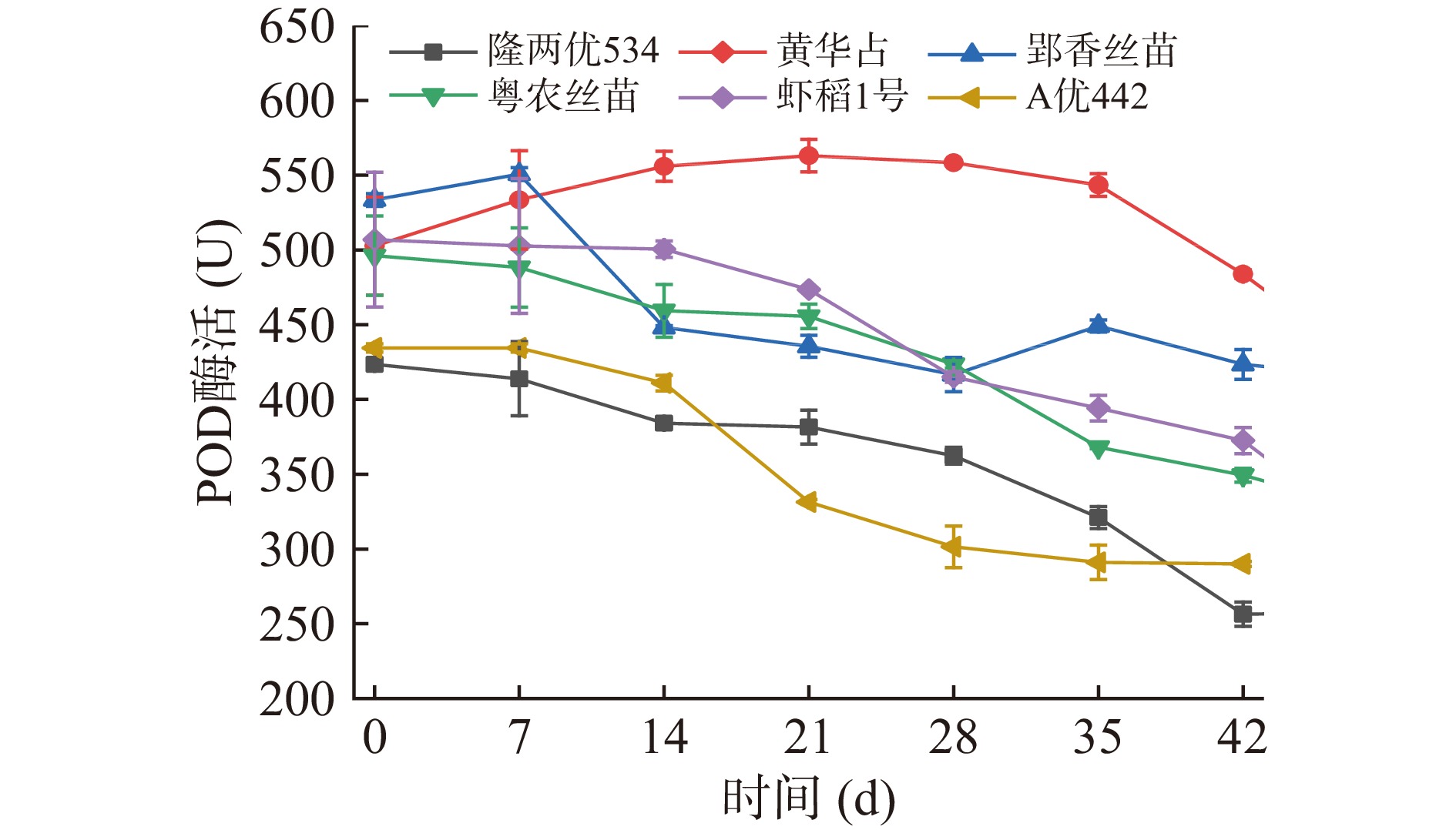
当稻谷中存在过氧化氢时,过氧化物酶能催化酚类与芳香族胺类发生氧化反应,生成物会使稻米产生不良气味。由图5得知,在后熟期间,隆两优534、粤农丝苗、虾稻一号和A优442的POD酶活呈现逐步下降趋势,分别较起初下降了167、147、134和144 U;黄华占的POD酶活呈现先上升至21 d达到最大值563 U而后下降至484 U的趋势;郢香丝苗的POD酶活整体呈现波动的下降趋势,在7 d达到最大值551 U而在28 d达到最小值417 U,隆两优534在后熟期间POD酶活变化最大,而黄华占的最小,说明稻谷籽粒在后熟过程中,过氧化物酶活性降低,会导致分解稻谷呼吸过程中所产生的对细胞存在伤害的过氧化物的能力下降,有害物质会在稻谷籽粒中累积,从而加速稻谷品质的劣变[30]。
2.4.2 后熟期间过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性的变化
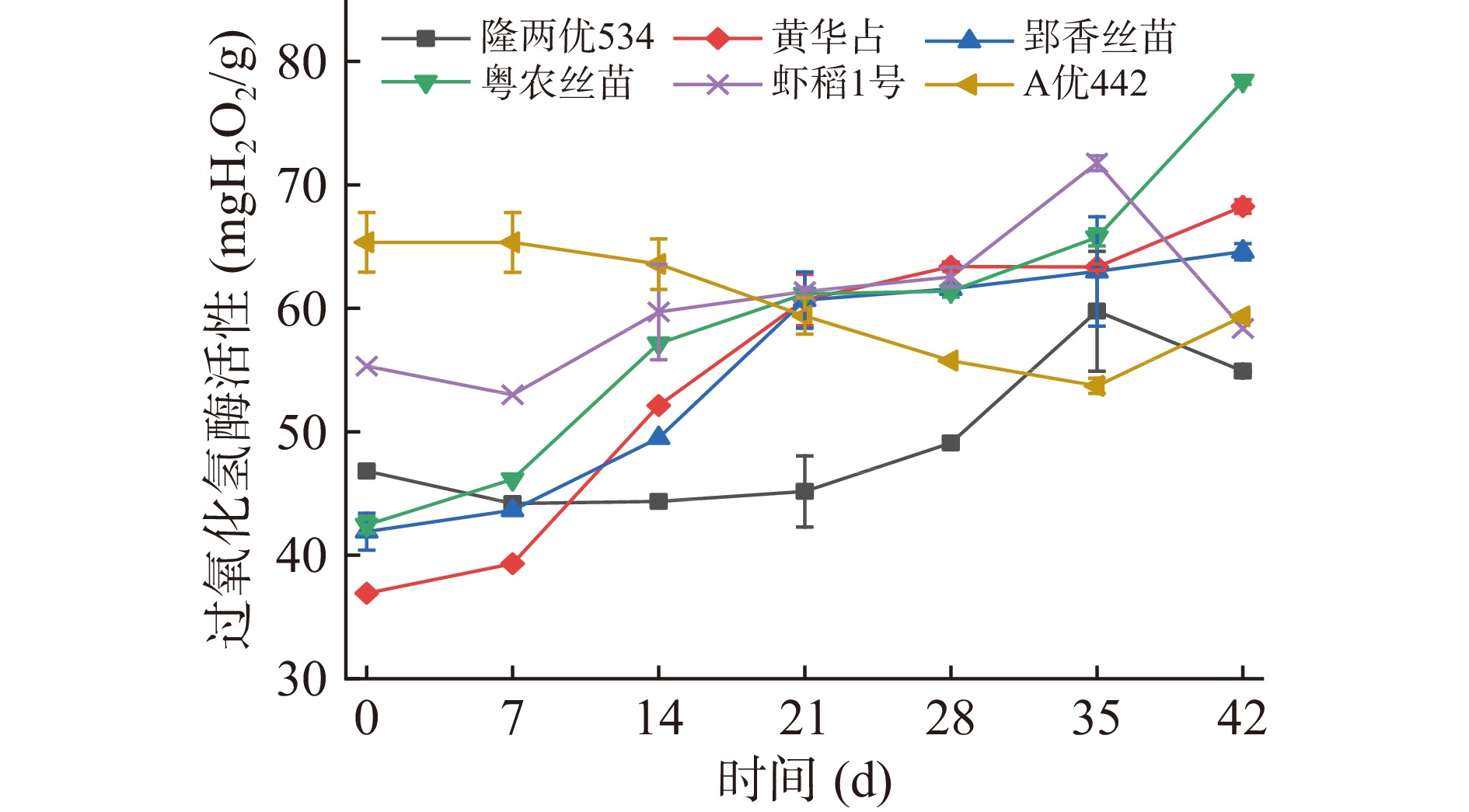
过氧化氢酶是生物体内活性氧防御系统的重要保护酶,可以有效阻止活性氧的积累,降低稻谷品质劣变速度[31]。如图6所示,隆两优534在后熟期0~33 d内呈现先下降后上升的趋势,整体于35 d达到最大值59.77 mg H2O2/g,较起始增幅28.00%;黄华占、郢香丝苗、粤农丝苗整体均呈现上升趋势于42 d达到最大值,分别为68.25、64.59、78.43 mg H2O2/g,较起始增长84.86%、54.08%、84.72%;虾稻1号在35 d达到最大值71.77 mg H2O2/g,较起始增长29.74%;A优442在后熟期内呈现下降趋势,在第35 d达到最小值53.73 mg H2O2/g,较起始减少了17.77%;由图6得知,黄华占、郢香丝苗与粤农丝苗的过氧化氢酶活性趋势相似,呈现上升趋势。
2.4.3 后熟期间α-淀粉酶活性的变化
降落数值体现稻谷中α-淀粉酶的活性,二者呈负相关,从表5得知,隆两优534在21 d达最小值412 s与初始413 s在α=0.05水平上无显著差异,35 d达到最大值481 s较初始高出16.34%;黄华占在21 d达到最大值346 s,较初始高出33.08%;郢香丝苗呈现上升趋势,42 d时其降落数值为403 s,较初始高出76.92%;粤农丝苗在28 d达到最小值301s,在42 d达到最大值381s,但增减幅度较小,无显著差异(P>0.05);虾稻1号整体呈波动上升趋势,在35 d时达到最大值349 s;A优442呈现先下降后上升的趋势,42 d达到最大值,但较初始仅增长了10.68%。
表 5 六种优质籼稻在后熟期间降落数值的变化Table 5. Changes of Hagberg values of six high-quality indica rices during after-ripening period时间(d) 降落数值(s) 隆两优534 黄华占 郢香丝苗 粤农丝苗 虾稻一号 A优442 0 413±0a 260±7a 228±2a 332±1a 318±1a 403±1ab 7 427±0a 286±0b 251±12a 356±8a 327±3ab 368±1a 14 436±2a 324±11cd 303±11b 327±9a 321±2a 391±8ab 21 412±3a 346±0d 351±2c 345±5a 341±14ab 417±7ab 28 447±2ab 281±4ab 348±4c 301±7a 329±3ab 440±4b 35 481±4b 299±6b 363±6c 349±12a 349±7ab 442±8b 42 442±5ab 303±6bc 403±9d 381±1a 381±5b 446±9b 2.5 不同品种优质籼稻后熟期间时间与品质的相关性分析
由表6可以看出,在6种优质籼稻后熟过程中,所有品种发芽率与出糙率与时间呈显著(P<0.05)或极显著正相关(P<0.01),除黄华占外各个品种过氧化物酶活性与时间呈显著(P<0.05)或极显著负相关(P<0.01),除虾稻1号外各个品种过氧化氢酶活性与时间呈显著(P<0.05)或极显著正相关(P<0.01),糊化特性指标整体与时间的相关性在α=0.05水平上均不显著。
表 6 不同籼稻在后熟期间时间与品质的相关性Table 6. Correlation between time and quality of different indica rice during after-ripening period品质指标 品种 隆两优534 黄华占 郢香丝苗 粤农丝苗 虾稻一号 A优442 发芽率 0.90** 0.98** 0.89** 0.95** 0.95** 0.79* 出糙率 0.95** 0.82* 0.97** 0.98** 0.98** 0.94** 电导率 0.86* 0.65 0.52 0.72 0.60 0.84* 脂肪酸值 −0.25 −0.39 −0.17 −0.59 0.00 −0.03 过氧化物酶 −0.94** −0.09 −0.81* −0.97** −0.96** −0.95** 过氧化氢酶 0.78* 0.95** 0.95** 0.97** 0.63 −0.82* 降落数值 0.67 0.30 0.30 0.33 0.78 −0.85 峰值黏度 0.42 −0.07 0.03 −0.53 0.02 −0.59 最低粘度 0.78* −0.13 0.74 −0.46 −0.08 −0.50 衰减值 −0.03 0.15 0.74 −0.60 0.23 −0.84* 最终黏度 0.60 −0.17 0.70 −0.36 −0.05 −0.71 回生值 0.40 −0.20 0.63 −0.27 −0.04 −0.85* 峰值时间 0.41 −0.11 0.63 −0.25 −0.21 0.22 糊化温度 0.72 0.35 −0.75 −0.45 −0.50 0.64 注:*表示在α=0.05水平(双侧)上显著相关;**表示在α=0.01水平(双侧)上显著相关。 2.6 不同品种优质籼稻主成分综合评价
对不同品种的优质籼稻的发芽率、出糙率、电导率、脂肪酸值、过氧化物酶活性、过氧化氢酶活性、α-淀粉酶活性、峰值黏度、最低粘度、衰减值、最终黏度、回生值、峰值时间、糊化温度14个指标,进行主成分分析,综合评价不同品种优质籼稻后熟期品质的综合表现,所得的相关矩阵的特征值和方差贡献率如表7显示,14个指标中排名前5的综合指标的累积方差贡献率已达到100%,其中排名前三的综合指标,其方差贡献率分别是50.151%、22.556%、12.638%,累积方差贡献率达到85.346%,说明这3个综合指标可以代替原来14个单独指标,对不同品种优质籼稻后熟期品质进行综合评价。经标准化后的因子负荷矩阵见表8,以方差贡献率>80%的标准提取3个成分作为主成分,根据数据进行整合,综合评价得出评分,如表9所示,得分由高到低分别是A优442、隆两优534、虾稻1号、粤农丝苗、郢香丝苗、黄华占。
表 7 主成分特征值、方差贡献率和累积贡献率Table 7. Eigenvalues, variance contribution rates and cumulative contribution rates of principal components成分 初始特征值 提取因子的载荷平方和 特征根 方差
贡献率(%)累积方差
贡献率(%)特征根 方差
贡献率(%)累积方差
贡献率(%)1 7.021 50.151 50.151 7.021 50.151 50.151 2 3.158 22.556 72.707 3.158 22.556 72.707 3 1.769 12.638 85.346 1.769 12.638 85.346 4 1.378 9.843 95.189 5 0.674 4.811 100 表 8 三个主成分与品质指标的因子得分系数矩阵表Table 8. Rotated factor loading matrix of three principal components and quality indicators指标 主成分1 主成分2 主成分3 发芽率 0.033 −0.442 −0.67 出糙率 −0.841 −0.053 0.386 电导率 −0.431 0.842 0.043 脂肪酸值 0.821 −0.079 0.108 过氧化物酶活性 −0.779 −0.42 0.054 过氧化氢酶活性 −0.564 −0.139 −0.625 降落数值 0.722 0.575 −0.266 峰值黏度 0.265 0.957 0.059 最低粘度 0.962 −0.023 0.229 衰减值 −0.659 0.506 0.387 最终黏度 0.945 −0.173 0.274 表 9 不同优质籼稻后熟期综合得分Table 9. Main component scores of indica rice of different quality at maturity stage品种 综合得分 排名 隆两优534 1.532 2 黄华占 −2.132 6 郢香丝苗 −1.063 5 粤农丝苗 −0.872 4 虾稻1号 0.424 3 A优442 2.112 1 3. 结论
研究结果表示,六种优质籼稻在后熟过程中,发芽率均呈现上升趋势,A优442、隆两优534、郢香丝苗、黄华占与粤农丝苗完成后熟的时间分别为33、42、39、42、21 d,虾稻1号由于起始发芽率过低发芽率未达到80%;出糙率整体呈现波动的上升趋势,虾稻一号与A优442趋势最为明显较起始均有明显增长;电导率整体呈现波动的上升后下降的趋势,后熟期完成后,黄华占、郢香丝苗与虾稻一号为下降趋势,隆两优534较稳定;脂肪酸值整体呈现波动的为先上升后下降的趋势。
六种优质籼稻在后熟期的糊化特性,其指标中的峰值粘度呈现波动的先上升后下降在上升的趋势。黄华占的过氧化物酶活性整体呈现先上升后下降的趋势,郢香丝苗的过氧化物酶活性呈现波动的下降趋势,其余品种呈现下降趋势;过氧化氢酶活性除A优442外整体呈波动上升趋势;α-淀粉酶活性除黄华占以外呈现波动下降趋势。
在后熟过程中,发芽率、出糙率和过氧化氢酶活性与时间呈显著正相关,过氧化物酶活性与时间呈显著负相关,说明随着时间的增加,后熟逐渐完成,籽粒逐渐饱满,种子逐渐脱离休眠期,稻谷内部生理活性逐渐稳定。根据主成分分析对6种籼稻的品质进行评价,结果表明得分由高到低分别是A优442、隆两优534、虾稻1号、粤农丝苗、郢香丝苗、黄华占。
然而目前关于优质籼稻在后熟过程中蛋白质、脂类等大分子如何影响品质的研究较少,并且缺乏分子结构层面的变化及分子之间相互作用的研究,这些变化和相互作用对籼稻品质的影响需进一步深入研究。
-
表 1 六种优质籼稻收获时间及后熟期
Table 1 Harvesting time and post-ripening stage of six indica rice varieties
编号 品种 收获时间 后熟期(d) 1 隆两优534 2020年10月11日 33 2 黄华占 2020年10月11日 42 3 郢香丝苗 2020年10月11日 39 4 粤农丝苗 2020年10月11日 42 5 虾稻1号 2020年10月11日 \ 6 A优442 2020年10月31日 21 表 2 六种优质籼稻在后熟期间出糙率与发芽率的相关性分析
Table 2 Correlation analysis of roughness rate and germination rate of six high-quality indica rices during after-ripening period
品种 隆两优534 黄华占 郢香丝苗 粤农丝苗 虾稻1号 A优442 Pearson相关性 0.441 0.854 0.888 0.832 0.924 0.734 显著性(双侧) 0.275 0.014 0.008 0.020 0.003 0.158 表 3 六种优质籼稻在后熟期间电导率的变化(μs/(cm·g))
Table 3 Changes of electrical conductivity of six high-quality indica rices varieties during after-ripening period (μs/(cm·g))
时间
(d)隆两优534 黄华占 郢香丝苗 粤农丝苗 虾稻一号 A优442 0 41.90±5.91a 34.50±2.29a 36.40±3.76a 36.43±1.53a 40.80±0.75a 40.00±2.35a 7 54.18±0.60ab 53.95±4.38b 53.67±6.97b 52.91±4.82b 63.38±3.44b 42.05±3.57a 14 68.27±5.69bc 65.55±6.15b 71.83±1.67de 59.50±4.10bc 67.15±0.35bc 67.65±3.32d 21 69.25±0.64bc 61.05±1.63b 62.23±2.85bcd 59.45±1.34bc 69.65±4.74bc 59.63±3.29b 28 79.10±4.81c 73.85±2.05c 78.20±1.55e 73.10±0.57d 77.05±5.59c 72.90±1.41c 35 72.95±4.60c 54.70±3.68b 54.10±1.31bc 53.00±2.97b 60.40±1.41b 65.63±4.96bc 42 73.90±1.41c 67.40±0.71bc 64.90±3.39cd 69.40±3.54cd 69.40±4.95bc 71.93±5.22c 49 74.00±1.98c 63.60±3.25b 61.10±0.99bcd 72.20±5.23d 64.77±3.57b 72.80±5.23c 注:同一列的相同字母表示差异不显著(P˃0.05);不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);表5同。 表 4 六种优质籼稻在后熟期间的RVA特征值
Table 4 RVA characteristics value of six indica rices varieties during after-ripening period
时间
(d)峰值粘度
(cP)最低粘度
(cP)衰减值
(cP)最终粘度
(cP)回生值
(cP)峰值时间
(min)糊化温度
(℃)隆
两
优
5
3
40 2085±13b 968±12a 1117±1ab 1757±20a 790±8a 5.60±0.00a 82.68±0.04ab 7 2172±11c 1019±46a 1153±35bc 1969±52c 951±6e 5.80±0.10a 83.08±0.56abc 14 2305±0e 1055±35a 1250±35c 1979±25c 924±11cd 5.67±0.19a 82.25±1.77a 21 2229±6d 1029±56a 1202±50bc 1991±59c 962±3e 5.67±0.19a 83.00±0.57abc 28 2177±5cd 1022±34a 1155±30bc 1934±34bc 912±1c 5.66±0.12a 83.13±0.46abc 35 2207±17cd 1083±29a 1124±36ab 2024±30c 941±9de 5.82±0.18a 84.53±0.36bc 42 2224±24cd 1063±43a 1162±24bc 1962±53c 900±10c 5.73±0.17a 83.70±0.52abc 49 1995±25a 968±12a 1027±37a 1823±7ab 855±7b 5.73±0.17a 84.90±0.48c 黄华占 0 1494±45a 574±24 a 920±69a 1214±52a 640±76a 5.40±0.10a 75.88±1.66a 7 1948±40d 891±57c 1057±23b 2047±80d 1156±23f 5.94±0.09cd 76.68±0.53a 14 1971±50d 958±2c 1013±48ab 2014±18d 1057±16e 6.00±0.00d 77.08±0.04a 21 1901±26d 887±33c 1014±9ab 1953±47d 1066±15e 5.93±0.07cd 77.35±0.48a 28 1617±19b 679±18b 939±27a 1502±24bc 823±7cd 5.67±0.07abc 76.83±0.42a 35 1776±19c 755±40b 1021±23ab 1637±51c 883±12d 5.71±0.10bc 76.9±1.19a 42 1672±21b 677±19b 996±16ab 1415±28b 738±9b 5.56±0.08ab 76.53±0.32a 49 1679±15b 708±35b 971±39ab 1492±47b 785±13bc 5.66±0.12ab 77.63±0.46a 郢香丝苗 0 1234±25a 524±17a 710±8a 1186±37a 662±20a 5.70±0.04a 90.35±0.57b 7 1612±46c 715±140ab 897±47ab 1613±236bcd 898±96b 5.90±0.14a 91.13±0.53b 14 1422±71b 664±71ab 758±1ab 1435±119abc 771±48a 5.73±0.00a 90.35±0.57b 21 1752±27d 880±80bc 872±56bc 1854±108de 975±28b 6.00±0.18a 77.40±0.95a 28 1268±2a 577±24a 691±26a 1289±30ab 712±6a 5.74±0.09a 90.30±0.49b 35 1470±27b 1008±58c 462±45d 2005±67e 998±10b 5.82±0.10a 76.57±0.43a 42 1400±15b 965±20c 435±28d 1970±21e 1005±7b 5.80±0.07a 76.10±0.44a 49 1248±54a 852±85bc 396±43cd 1742±107cde 890±23b 5.69±0.14a 76.80±0.43a 粤农丝苗 0 1875±47c 910±45bc 965±3abcd 1695±59a 785±14a 5.77±0.05a 76.00±0.64a 7 2061±21d 1080±21d 981±0bcd 2234±30d 1154±9g 6.20±0.00c 90.65±0.00c 14 2044±16d 1006±26cd 1038±10d 2078±27c 1073±1f 6.00±0.10abc 89.45±0.49bc 21 2109±52d 1099±11d 1009±41cd 2196±15cd 1096±5f 6.09±0.03c 81.10±6.93ab 28 1673±20a 792±48a 881±28ab 1640±55a 848±7c 5.77±0.14ab 77.18±1.17a 35 1868±14c 941±19bc 927±14abc 1901±27b 960±11e 6.02±0.04bc 77.70±0.43a 42 1751±17ab 844±28ab 907±44ab 1658±30a 814±3b 5.78±0.08ab 76.70±0.52a 49 1826±14bc 947±51bc 879±38a 1853±60b 906±9d 5.98±0.10abc 77.93±0.78a 虾稻一号 0 1915±55a 896±34a 1019±21a 1758±40a 862±6a 5.70±0.04a 76.35±0.07a 7 2058±23a 1015±26a 1043±2a 2252±29c 1237±4d 6.04±0.05b 77.50±0.57a 14 2030±6a 956±56a 1074±50a 2053±66bc 1097±10bcd 5.87±0.09ab 76.78±0.60a 21 2080±32a 1019±55a 1061±24a 2212±67bc 1193±19cd 5.89±0.08ab 76.37±0.03a 28 1956±7a 932±18a 1025±11a 1968±23abc 1036±6b 5.84±0.05ab 76.25±0.00a 35 1920±18a 894±23a 1026±5a 1936±29ab 1043±7b 5.82±0.08ab 76.65±0.43a 42 2036±7a 967±41a 1069±34a 1956±35ab 990±8ab 5.76±0.08a 76.07±0.49a 49 2128±155a 990±98a 1138±105a 2074±194bc 1085±102bc 5.80±0.12ab 77.10±0.83a A优4
4
20 1831±8e 1310±5d 521±8b 2593±15e 1283±16d 5.98±0.04a 86.42±0.45a 7 1606±15c 1141±26bc 465±26ab 2430±6c 1290±31d 6.09±0.03a 89.33±0.53b 14 1509±5b 1049±18ab 460±13ab 2227±43b 1178±61abcd 5.97±0.05a 89.05±0.00b 21 1699±10d 1233±21cd 467±13ab 2495±31cd 1263±52cd 6.11±0.03a 89.83±0.06b 28 1467±17a 1009±34a 458±18ab 2123±12a 1114±45abc 5.93±0.12a 89.08±0.11b 35 1461±5a 1021±29a 439±33a 2069±23a 1048±51a 6.02±0.14a 89.33±0.98b 42 1598±18c 1158±38c 440±30a 2267±29b 1109±59ab 6.11±0.08a 89.60±0.95b 49 1732±10d 1306±57d 426±48a 2506±19d 1201±76bcd 6.20±0.18a 89.43±0.98b 注:不同品种在不同时间段位于同一列的相同字母表示差异不显著(P˃0.05);不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 5 六种优质籼稻在后熟期间降落数值的变化
Table 5 Changes of Hagberg values of six high-quality indica rices during after-ripening period
时间(d) 降落数值(s) 隆两优534 黄华占 郢香丝苗 粤农丝苗 虾稻一号 A优442 0 413±0a 260±7a 228±2a 332±1a 318±1a 403±1ab 7 427±0a 286±0b 251±12a 356±8a 327±3ab 368±1a 14 436±2a 324±11cd 303±11b 327±9a 321±2a 391±8ab 21 412±3a 346±0d 351±2c 345±5a 341±14ab 417±7ab 28 447±2ab 281±4ab 348±4c 301±7a 329±3ab 440±4b 35 481±4b 299±6b 363±6c 349±12a 349±7ab 442±8b 42 442±5ab 303±6bc 403±9d 381±1a 381±5b 446±9b 表 6 不同籼稻在后熟期间时间与品质的相关性
Table 6 Correlation between time and quality of different indica rice during after-ripening period
品质指标 品种 隆两优534 黄华占 郢香丝苗 粤农丝苗 虾稻一号 A优442 发芽率 0.90** 0.98** 0.89** 0.95** 0.95** 0.79* 出糙率 0.95** 0.82* 0.97** 0.98** 0.98** 0.94** 电导率 0.86* 0.65 0.52 0.72 0.60 0.84* 脂肪酸值 −0.25 −0.39 −0.17 −0.59 0.00 −0.03 过氧化物酶 −0.94** −0.09 −0.81* −0.97** −0.96** −0.95** 过氧化氢酶 0.78* 0.95** 0.95** 0.97** 0.63 −0.82* 降落数值 0.67 0.30 0.30 0.33 0.78 −0.85 峰值黏度 0.42 −0.07 0.03 −0.53 0.02 −0.59 最低粘度 0.78* −0.13 0.74 −0.46 −0.08 −0.50 衰减值 −0.03 0.15 0.74 −0.60 0.23 −0.84* 最终黏度 0.60 −0.17 0.70 −0.36 −0.05 −0.71 回生值 0.40 −0.20 0.63 −0.27 −0.04 −0.85* 峰值时间 0.41 −0.11 0.63 −0.25 −0.21 0.22 糊化温度 0.72 0.35 −0.75 −0.45 −0.50 0.64 注:*表示在α=0.05水平(双侧)上显著相关;**表示在α=0.01水平(双侧)上显著相关。 表 7 主成分特征值、方差贡献率和累积贡献率
Table 7 Eigenvalues, variance contribution rates and cumulative contribution rates of principal components
成分 初始特征值 提取因子的载荷平方和 特征根 方差
贡献率(%)累积方差
贡献率(%)特征根 方差
贡献率(%)累积方差
贡献率(%)1 7.021 50.151 50.151 7.021 50.151 50.151 2 3.158 22.556 72.707 3.158 22.556 72.707 3 1.769 12.638 85.346 1.769 12.638 85.346 4 1.378 9.843 95.189 5 0.674 4.811 100 表 8 三个主成分与品质指标的因子得分系数矩阵表
Table 8 Rotated factor loading matrix of three principal components and quality indicators
指标 主成分1 主成分2 主成分3 发芽率 0.033 −0.442 −0.67 出糙率 −0.841 −0.053 0.386 电导率 −0.431 0.842 0.043 脂肪酸值 0.821 −0.079 0.108 过氧化物酶活性 −0.779 −0.42 0.054 过氧化氢酶活性 −0.564 −0.139 −0.625 降落数值 0.722 0.575 −0.266 峰值黏度 0.265 0.957 0.059 最低粘度 0.962 −0.023 0.229 衰减值 −0.659 0.506 0.387 最终黏度 0.945 −0.173 0.274 表 9 不同优质籼稻后熟期综合得分
Table 9 Main component scores of indica rice of different quality at maturity stage
品种 综合得分 排名 隆两优534 1.532 2 黄华占 −2.132 6 郢香丝苗 −1.063 5 粤农丝苗 −0.872 4 虾稻1号 0.424 3 A优442 2.112 1 -
[1] 姜梅. 优质籼稻黄华占储藏品质变化规律的研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉轻工大学, 2016. JIANG M. Research on storage quality changes of high-quality indica Huanghuazhan[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan Polytechnic University, 2016.
[2] 吴俊男. 小麦籽粒后熟期间碳水化合物变化对小麦品质的影响和机理探究[D]. 郑州: 河南工业大学, 2018. WU J N. Study on effect and machanism of carbohydrate changes on wheat quality of wheat of during after-ripening[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan University of Technology, 2018.
[3] 王琦, 苏晓宇, 贾峰, 等. 不同后熟条件对强筋和弱筋小麦品质改善的研究[J]. 河南工业大学学报(自然科学版),2020,41(3):12−18,33. [WANG Q, SU X Y, JIA F, et al. Study on quality improvement of wheat with strong gluten and weak gluten under different post-ripening conditions[J]. Journal of Henan University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2020,41(3):12−18,33. [4] 耿瑞蝶. 新收获小麦后熟过程中面筋蛋白聚集特性变化及机理研究[D]. 郑州: 河南工业大学, 2020. GENG R D. Study on the change of gluten protein aggregation characteristics and mechanism during the post-ripening process of newly harvested wheat[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan University of Technology, 2020.
[5] 贾峰, 王金水, 殷海成, 等. 小麦后熟期及储藏过程中生理生化变化研究进展[J]. 河南工业大学学报(自然科学版),2013,34(2):105−110. [JIA F, WANG J S, YIN H C, et al. Research progress on physiological and biochemical changes of wheat during post-ripening and storage[J]. Journal of Henan University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2013,34(2):105−110. [6] 丁卫新. 新小麦“后熟期”前后品质变化规律的研究[J]. 现代面粉工业,2011,25(4):46−50. [DING W X. Study on the quality change rule of new wheat before and after “post-ripening stage”[J]. Modern Flour Industry,2011,25(4):46−50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5280.2011.04.013 [7] 王涛, 熊柳, 孙庆杰. 后熟对粳米直链淀粉含量及品质特性影响的研究[J]. 中国粮油学报,2009,24(11):9−11,46. [WANG T, XIONG L, SUN Q J. Effects of late ripening on amylose content and quality characteristics of japonica rice[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2009,24(11):9−11,46. [8] 莫西亚, 易翠平, 祝红, 等. 籼稻后熟对米粉品质的影响研究进展[J]. 食品与机械,2021,37(6):11−17. [MO X Y, YI C P, ZHU H, et al. Research progress on the effect of indica rice on the quality of rice noodles[J]. Food & Machinery,2021,37(6):11−17. [9] 国家粮食和物资储备局. 食品安全国家标准: 食品中水分的测定: GB 5009.3-2016[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. National Bureau of Grain and Material Reserves. National food safety standard: Determination of moisture in food: GB 5009.3-2016[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2016.
[10] 国家粮食局. 粮油检验: 发芽试验: GB/T 5520-2011[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2011. National Grain Administration. Grain and oil inspection: Germination test: GB/T 5520-2011[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2011.
[11] 国家粮食局. 粮油检验: 稻谷出糙率检验: GB/T 5495-2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008. National Grain Administration. Grain and oil inspection: Rice roughness inspection: GB/T 5495-2008[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2008.
[12] 国家粮食局. 稻谷储存品质判定规则: GB/T 20569-2006[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006. National Grain Administration. Rules for determining the quality of rice storage: GB/T 20569-2006[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2006.
[13] 国家粮食局科学研究院. 大米及米粉糊化特性测定: 快速粘度仪法: GB/T 24852-2010[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2010. Research Institute of National Grain Administration. Determination of gelatinization characteristics of rice and rice flour: Rapid viscometer method: GB/T 24852-2010[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2010.
[14] 国家粮食局. 粮油检验: 粮食、油料的过氧化氢酶活动度的测定: GB/T 5522-2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准化出版社, 2008. National Grain Administration. Grain and oil inspection: Determination of catalase activity of grain and oilseeds: GB/T 5522-2008[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2008.
[15] 国家粮食局. 小麦、黑麦及其面粉, 杜伦麦及其粗粒粉降落数值的测定 Hagberg-Perten法: GB/T 10361-2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008. National Grain Administration. Determination of falling value of wheat, rye and flour, durum wheat and semolina Hagberg-Perten method: GB/T 10361-2008[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2008.
[16] 杜文丽. 后熟处理破除水稻种子休眠的机理及休眠性相关QTL定位研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2015. DU W L. Research on the mechanism of post-ripening treatment to break dormancy of rice seeds and the mapping of QTLs related to dormancy[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2015.
[17] 熊宁, 李琦, 刘利, 等. 稻谷电导率测定方法的研究[J]. 粮油食品科技,2013,21(4):68−71. [XIONG N, LI Q, LIU L, et al. Study on the determination method of electric conductivity of rice[J]. Cereals, Oils and Food Science and Technology,2013,21(4):68−71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7561.2013.04.017 [18] NITHYA U, CHELLADURAI V, JAYAS D S, et al. Safe storage guidelines for durum wheat[J]. Journal of Stored Products Research,2011,47(4):328−333. doi: 10.1016/j.jspr.2011.05.005
[19] JIANG H, LIU T, CHEN Q. Dynamic monitoring of fatty acid value in rice storage based on a portable near-infrared spectroscopy system[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy,2020,240:118620. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2020.118620
[20] 周显青, 祝方清, 张玉荣, 等. 不同储藏年限稻谷的储藏特性、生理生化指标及其糊化特性分析[J]. 中国粮油学报,2020,35:108−114,124. [ZHOU X Q, ZHU F Q, ZHANG Y R, et al. Analysis on the storage characteristics, physiological and biochemical indexes and gelatinization characteristics of rice with different storage years[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2020,35:108−114,124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2020.12.018 [21] 孙君. 稻谷热物性参数测定及模拟验证研究[D]. 南京: 南京财经大学, 2017. SUN J. Measurement and simulation verification of thermal physical parameters of rice[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Finance and Economics, 2017.
[22] 陈丽, 马静, 亢玲, 等. 杂草稻稻米RVA谱特征值与外观品质及蒸煮食味品质性状的相关性分析[J]. 宁夏农林科技,2020,61(6):1−4. [CHEN L, MA J, KANG L, et al. Correlation analysis of rice RVA spectrum characteristic values with appearance quality, cooking and eating quality traits of weedy rice[J]. Ningxia Agriculture and Forestry Science and Technology,2020,61(6):1−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-204x.2020.06.001 [23] 陈书强. 粳稻米蒸煮食味品质与其他品质性状的典型相关分析[J]. 西北农业学报,2015,24(1):60−67. [CHEN S Q. Canonical correlation analysis between cooking and eating quality of japonica rice and other quality traits[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica,2015,24(1):60−67. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1004-1389.2015.01.011 [24] 朱满山, 顾铭洪, 汤述翥. 不同粳稻品种和DH群体稻米淀粉RVA谱特征与蒸煮理化指标及相关分析[J]. 作物学报,2007(3):411−418. [ZHU M S, GU M H, TANG S Z, et al. RVA spectra of rice starch in different japonica rice varieties and DH population and their correlation analysis on cooking physical and chemical indexes[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica,2007(3):411−418. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0496-3490.2007.03.010 [25] 鲁超, 龚克成, 李育娟, 等. 优质与高产水稻品种稻米品质和淀粉RVA谱特征值差异初探[J]. 上海农业科技,2019(1):22−23,32. [LU C, GONG K C, LI Y J, et al. Study on the difference of rice quality and starch RVA spectrum between high yield and high quality rice cultivars[J]. Journal of Shanghai Agricultural Science and Technology,2019(1):22−23,32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0106.2019.01.010 [26] 舒在习, 戴煌. 优质籼稻储藏期间稻米RVA特性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(2):112−119. [SHU Z X, DAI H. Research on RVA characteristics of high-quality indica rice during storage[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(2):112−119. [27] PARK C E, KIM Y S, PARK K J, et al. Changes in physicochemical characteristics of rice during storage at different temperatures[J]. Journal of Stored Products Research,2012,48:25−29. doi: 10.1016/j.jspr.2011.08.005
[28] 刘璐. 糙米绿色储藏实验研究[D]. 南京: 南京财经大学, 2011. LIU L. Experimental study on green storage of brown rice[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Finance and Economics, 2011.
[29] 陈飞, 张昌泉, 周少川, 等. 优质籼稻品种黄华占和扬稻6号稻米理化特性和淀粉精细结构比较[J]. 中国稻米,2021,27:14−19. [CHEN F, ZHANG C Q, ZHOU S C, et al. Comparison of physicochemical properties and starch fine structure of high-quality indica rice varieties Huanghuazhan and Yangdao No.6[J]. China Rice,2021,27:14−19. [30] 张玉荣, 周显青, 刘敬婉. 加速陈化对粳稻的营养组分及储藏、加工品质的影响[J]. 河南工业大学学报(自然科学版),2017,38(5):37−44. [ZHANG Y R, ZHOU X Q, LIU J W. Effects of accelerated aging on nutrient components, storage and processing quality of japonica rice[J]. Journal of Henan University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2017,38(5):37−44. [31] 刘慧, 周建新, 方勇, 等. 稻谷储藏过程中微生物及品质变化规律研究[J]. 中国粮油学报,2020,35(1):126−131. [LIU H, ZHOU J X, FANG Y, et al. Study on the variation of microorganism and quality of rice during storage[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2020,35(1):126−131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2020.01.021 -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 何怀叶,孔令辉,裴迅,周望庭,吴慕慈,张瑞,何静仁. 不同制备方法对魔芋飞粉蛋白质结构及功能特性的影响. 食品工业科技. 2025(07): 49-59 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 沈祥皓,陈昌威,付靖雯,杨柳莺,王则程,杨金玉,盘赛昆. 响应面分析法优化女贞子蛋白质提取工艺及功能性研究. 中国调味品. 2024(07): 1-9 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘聪,尹乐斌,邹文广,罗雪韵,杨学为. 响应面法优化辣椒籽蛋白提取工艺及其功能性质研究. 邵阳学院学报(自然科学版). 2023(06): 78-87 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)







 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
