Construction and Bioinformatics Analysis of TRPV4 Prokaryotic Expression Purification System
-
摘要: 目的:构建非选择性阳离子通道蛋白TRPV4的原核表达纯化系统,并对其进行生物信息学分析,为与该目标蛋白相关疾病的研究和药物活性成分筛选提供技术支持。方法:将人源TRPV4基因分别克隆至pET-28a(+)、pET-32a、pET-15b、pGEX-5X-1、pEX-4T和pGEX-6p-1等6种表达载体,并利用BL21和Rossetta两种大肠杆菌表达宿主构建TRPV4原核表达系统。采用谷胱甘肽亲和层析和镍柱亲和层析法分离纯化目标蛋白。通过生物信息学技术对目标蛋白进行分析,获得其相应的理化性质和结构参数。结果:利用pGEX-6p-1载体和Rossetta构建了GST-TRPV4和GST-TRPV4-6his融合蛋白原核表达系统。诱导表达目标蛋白的IPTG浓度为0.6 mmol/L时,GST-TRPV4融合蛋白有明显表达,IPTG浓度为0.4 mmol/L时,GST-TRPV4-6his融合蛋白有明显表达,表达温度均为18 ℃。纯化GST-TRPV4-6his融合蛋白时,咪唑溶液在100 mmol/L或200 mmol/L时可以得到完整的GST-TRPV4-6his融合蛋白。结论:本文首次在原核表达系统中成功构建和表达纯化了人源TRPV4离子通道蛋白,并利用生物信息学分析解析了该蛋白的理化性质,为后续高纯度大量表达和进一步研究奠定了良好的基础。Abstract: Objective: This study aimed to construct the prokaryotic expression and purification system of non-selective cation channel TRPV4 protein and to carry out bioinformatics analysis to provide technical support for the study of diseases related to the target protein and the screening of drug active ingredients. Methods: The human TRPV4 gene was cloned into pET-28a(+), pET-32a, pET-15b, pGEX-5X-1, pEX-4T and pGEX-6p-1, respectively, and the prokaryotic expression system of TRPV4 was constructed using two E.coli expression hosts, BL21 and Rossetta. The target protein was isolated and purified by glutathione affinity chromatography and nickel column affinity chromatography. The target protein was analyzed by bioinformatics technology to obtain its corresponding physical, chemical properties and structural parameters. Results: The prokaryotic expression system of GST-TRPV4 and GST-TRPV4-6his fusion proteins was constructed using pGEX-6p-1 vector and Rossetta. The GST-TRPV4 fusion protein was significantly expressed when the IPTG concentrationwas 0.6 mmol/L, and the GST-TRPV4-6his fusion protein was significantly expressed when the IPTG concentration was 0.4 mmol/L, and the expression temperature was 18 ℃. When GST-TRPV4-6his fusion protein was purified, the complete GST-TRPV4-6his fusion protein could be obtained by imidazole solution at 100 mmol/L or 200 mmol/L. Conclusion: In this paper, human TRPV4 ion channel protein was successfully constructed, expressed and purified in prokaryotic expression system for the first time, and the physicochemical properties of the protein were analyzed by bioinformatics, which laid a good foundation for subsequent high-purity mass expression and further study.
-
Keywords:
- TRPV4 /
- ion channel protein /
- prokaryotic expression /
- PGEX-6p-1 vector /
- Escherichia coli /
- bioinformatics
-
瞬时感受器电位离子通道香草素受体4 (Tran-sient receptor potential vanilloid 4,TRPV4)是一类参与多种生理功能的非电压依赖性阳离子选择性通道[1],在哺乳动物机体内分布非常广泛,在脑神经、心血管、胃肠道、骨、肺、膀胱、内皮血管、皮肤等器官均有明显表达[2]。TRPV4是一种多表达的门控离子通道,可因物理化学刺激所激活,这些刺激可使TRPV4通道打开,Ca2+和Na+等内流相应增加[3-4],参与机体的温度和渗透压等生理功能调节,从而参加一系列病理生理反应等[5]。在许多食品和保健品中或多或少都会有一些添加剂,而有些添加剂是抗生素或激素类物质,食用后可能会导致人体发热等不良反应,本研究中TRPV4正是对温度敏感的离子通道蛋白,对该离子通道蛋白的研究也可为食品或保健品中可能引起发热物质的类型或含量等研究提供相应的支持。研究表明,TRPV4激活时,通过诱导ATP释放引起慢性阻塞性肺疾病(COPD)的发生,且COPD患者肺组织中TRPV4表达明显增加[6]。TRPV4在胃肠道和银屑病等疾病中起重要作用,炎症环境既可激活TRPV4通道,又可增加TRPV4蛋白表达水平[7-8],其抑制剂具有消炎和治疗腹痛的潜在作用[9]。激活TRPV4可诱导黑色素瘤细胞的凋亡及坏死[10],可促进乳腺癌来源的内皮细胞(BTEC)迁移[11],而TRPV4特异性激动剂(GSK1016790A)与化疗药物顺铂联合应用可显著抑制肺癌[12]。当TRPV4被激活或抑制时,会在心血管、呼吸、消化、肿瘤等多种疾病病理生理过程、功能障碍和发生与发展过程中起重要作用,而TRPV4抑制剂可用于预防和治疗多种疾病。
TRPV4是871个氨基酸组成的六次跨膜蛋白,其氨基和羧基连接末端均位于细胞质中[13]。结构中的6次跨膜结构域(TM1~TM6)穿过脂质双分子层,TM5和TM6之间有一段疏水基团构成的孔通道环结构,此结构允许Ca2+及部分阳离子通过[14-18]。TRPV4氨基端具有多个结构,主要为六个锚蛋白重复序列(ANK1-6)、脯氨酸结构域(PRD)和磷酸肌醇结合位点(PIBS)[14]。每两个相邻的ANK存在反向平行螺旋,形成五个“手指”环结构,此结构主要参与TRPV4与蛋白质之间的相互作用[14,19],且ANK序列与TRPV4的活性非常接近,可能直接参与TRPV4和部分疾病的发生[19]。TRPV4羧基端具有多个结构域,钙调素结合域(CaM)、寡聚结构域(OMD)和PDZ-L结构域,这些结构可与细胞外蛋白之间进行相互作用。
本文通过不同质粒的构建表达和优化蛋白纯化方案,首次在原核系统大肠杆菌中成功构建和表达纯化了TRPV4离子通道蛋白,并进行了相应的生物信息学分析,获得了该离子通道蛋白的理化性质和结构信息等,为后续与该离子通道蛋白相关的生理和病理疾病以及以该目标蛋白为靶点的药物活性成分筛选等研究提供了良好的基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
TRPV4克隆模板GV144-TRPV4质粒 上海吉凯基因化学技术有限公司;大肠杆菌DH10B和Rossetta(DE3) 由武汉大学组合生物合成与新药发现教育部重点实验室孙宇辉课题组赠送;表达载体质粒pGEX-6p-1 由湖北医药学院生物医药研究院赠送;酵母提取物、胰蛋白胨 购自OXOID;氯化钠、咪唑 购自国药集团化学试剂有限公司;琼脂粉、琼脂糖 赛国生物科技有限责任公司;T4 DNA ligase Thermo公司;DNA聚合酶混合液 锐博生物科技有限公司;DNA纯化回收试剂盒、质粒小提试剂盒 天根生物科技有限公司;限制性内切酶BamHI和XhoI Takara公司; Ni-NTA填料 凯杰生物;Glutathione resin 金斯瑞;还原性谷胱甘肽 购自北京索莱宝;TRPV4抗体 Cell Signaling公司;ECL发光试剂盒 碧云天生物科技有限公司;本研究基因测序 由武汉擎科生物科技有限公司进行。
T100TM Thermal Cycler PCR仪、Mini-PROTEAN Tetra System蛋白电泳仪、Trans-Blot TurboTM蛋白转膜仪 伯乐生命医学产品有限公司;DHZ-D细菌摇床 苏州市培英实验设备有限公司;DYCP-31DN水平电泳仪 北京六一生物科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 引物的设计与合成
本研究前期从上海吉凯基因化学技术有限公司购买了以GV144为载体的含有人源TRPV4全段基因的过表达质粒,经过测序,该基因的氨基酸序列与NCBI Genebank 中收录的人源TRPV4的氨基酸序列(CCDS 9134.1)完全一致。因此,本研究所有克隆将以该质粒为模板。通过定点突变设计引物:
以pGEX-6p-1为载体构建GST-TRPV4融合蛋白表达质粒,分别在引物两端添加BamHI和XhoI酶切位点及相应的保护碱基,引物详细序列为TCGGGATCCATGGCGGATTCCAG/GGTCTCGAGCTAGAGCGGGGCGT。
以pGEX-6p-1为载体构建GST-TRPV4-6his融合蛋白表达质粒,分别在引物两端添加BamHI和XhoI酶切位点及相应的保护碱基,引物详细序列为TCGGGATCCATGGCGGATTCCAG/CCGCTCGAGCTAGTGATGATGATGATGATGGAGCGGGGCGT。
1.2.2 TRPV4原核表达质粒的构建与验证
以GV144-TRPV4过表达质粒为模板进行PCR扩增,获得TRPV4完整基因片段(2616 bp),提取相应载体质粒,分别对载体质粒和PCR扩增产物进行双酶切并利用DNA回收试剂盒进行纯化回收,然后利用T4 DNA ligase将线性化的载体质粒与暴露粘性末端的TRPV4基因在4 ℃冰箱中连接14 h。将酶连产物转化至DH10B感受态中得到转化子,通过扩大培养提取重组质粒,利用双酶切验证和测序(武汉擎科生物科技有限公司)鉴定重组质粒。
1.2.3 TRPV4蛋白的表达、纯化和Western Blot分析
1.2.3.1 蛋白表达
将1.2.2中验证正确的重组质粒转化至大肠杆菌Rossetta(DE3)感受态中获得转化子,转化子经扩大培养后提取质粒进行酶切验证,验证正确的即为含有TRPV4重组质粒的大肠杆菌Rossetta(DE3)。将上述大肠杆菌在培养基中划出单克隆,挑取单克隆接入液体LB培养基中,37 ℃,220 r/min培养过夜。按照1:100比例将培养过夜的菌液转接于液体LB培养基(50 μg/mL Amp,12.5 μg/mL Cml)中,继续培养至OD600 nm约为0.6。然后将其置于冰水混合物中预冷10 min以降低培养基温度,同时将摇床温度设置为18 ℃。向培养基中加入不同浓度的IPTG,随后置于18 ℃摇床中以220 r/min转速培养16~18 h以诱导蛋白质的表达[20-21]。
1.2.3.2 蛋白纯化
通过大型台式离心机收集菌体,并用Lysis Buffer洗涤菌体2次,最后用Lysis Buffer重悬菌体并在冰上置于超声细胞破碎仪中破碎大肠杆菌,以使细胞内的蛋白释放出来。破碎完成的菌体经过高速离心使溶液中的细胞器及残余的细胞沉降至底部,将上清液通过亲和层析柱纯化。GST-TRPV4融合蛋白纯化采用谷胱甘肽亲和层析法,GST-TRPV4-6his融合蛋白纯化采用镍柱亲和层析法,纯化步骤按照填料说明书进行。最后通过SDS-PAGE电泳检测各样品的纯度。
1.2.3.3 纯化蛋白的Western Blot分析
纯化后的GST-TRPV4-6his融合蛋白通过SDS-PAGE电泳分离后转移至PVDF膜上。TBST(含5%脱脂牛奶)封闭2 h后,TBST摇晃清洗3次(10 min/次)。然后将PVDF膜转移至含有TRPV4抗体(1:1000)的TBST中,4 ℃孵育过夜。TBST摇晃清洗3次(10 min/次)后转移PVDF膜至含有HRP标记的二抗TBST溶液中(1:2000),室温孵育1 h,TBST摇晃清洗4次(5 min/次)。最后利用ECL化学发光检测试剂盒和伯乐化学发光成像分析仪检测条带。
1.2.4 TRPV4蛋白生物信息学分析
利用在线软件Protparam分析蛋白的理化性质和一级结构;利用Protscale在线软件,选用默认的Kyte&Doolittle计算方法(window size: 13),分析蛋白的亲水性;利用TMHMMOL/L在线软件对蛋白序列进行跨膜结构分析;利用Signalp server在线软件对蛋白序列进行信号肽预测;通过在线软件NPS@:SOPMA secondary structure prediction分析蛋白的二级结构;通过SWISS-MODEL在线软件分析人源TRPV4蛋白的三维结构;利用SMART在线软件对人源TRPV4蛋白的结构域、后修饰位点以及潜在的交联蛋白进行分析。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 重组质粒的构建及鉴定
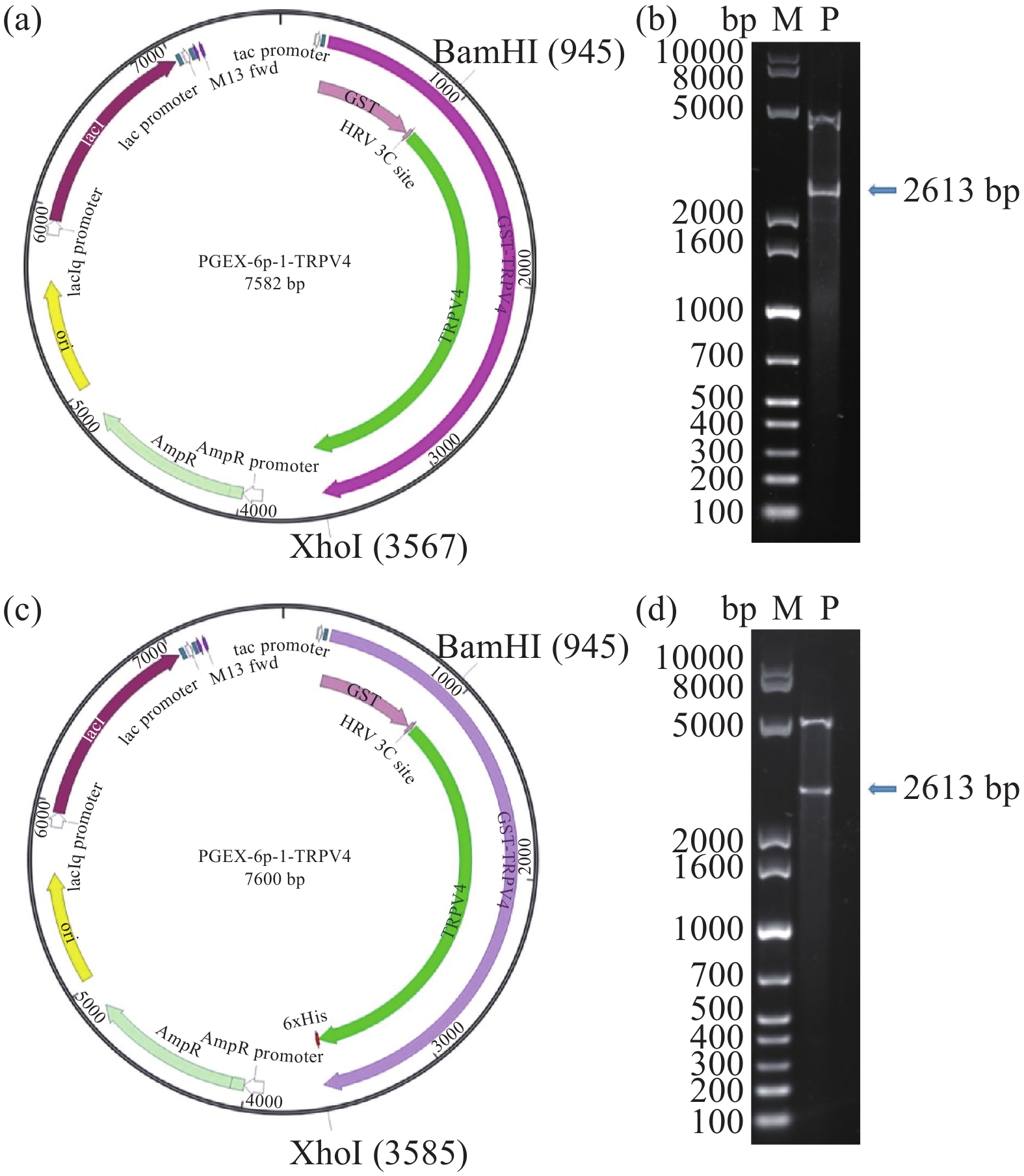
以GV144-TRPV4过表达质粒为模板进行PCR扩增,获得TRPV4完整基因片段。提取相应载体质粒,分别对载体质粒和PCR扩增产物进行双酶切并利用DNA回收试剂盒进行纯化回收,然后利用T4 DNA ligase将线性化的载体质粒与暴露粘性末端的TRPV4基因在4 ℃冰箱中连接14 h。将酶连产物转化至DH10B感受态中得到转化子,通过扩大培养提取重组质粒(图1a、1c),利用酶切验证(图1b、1d)和测序鉴定重组质粒大小正确、无碱基突变。除此之外,本研究也构建了包括pET-28a(+)-TRPV4、pET-32a-TRPV4、pET-15b-TRPV4、pGEX-5X-1-TRPV4和pEX-4T-TRPV4等质粒,但均未表达成功,所以未列出相关实验数据及附图。
2.2 TRPV4融合蛋白的表达、纯化及Western Blot鉴定
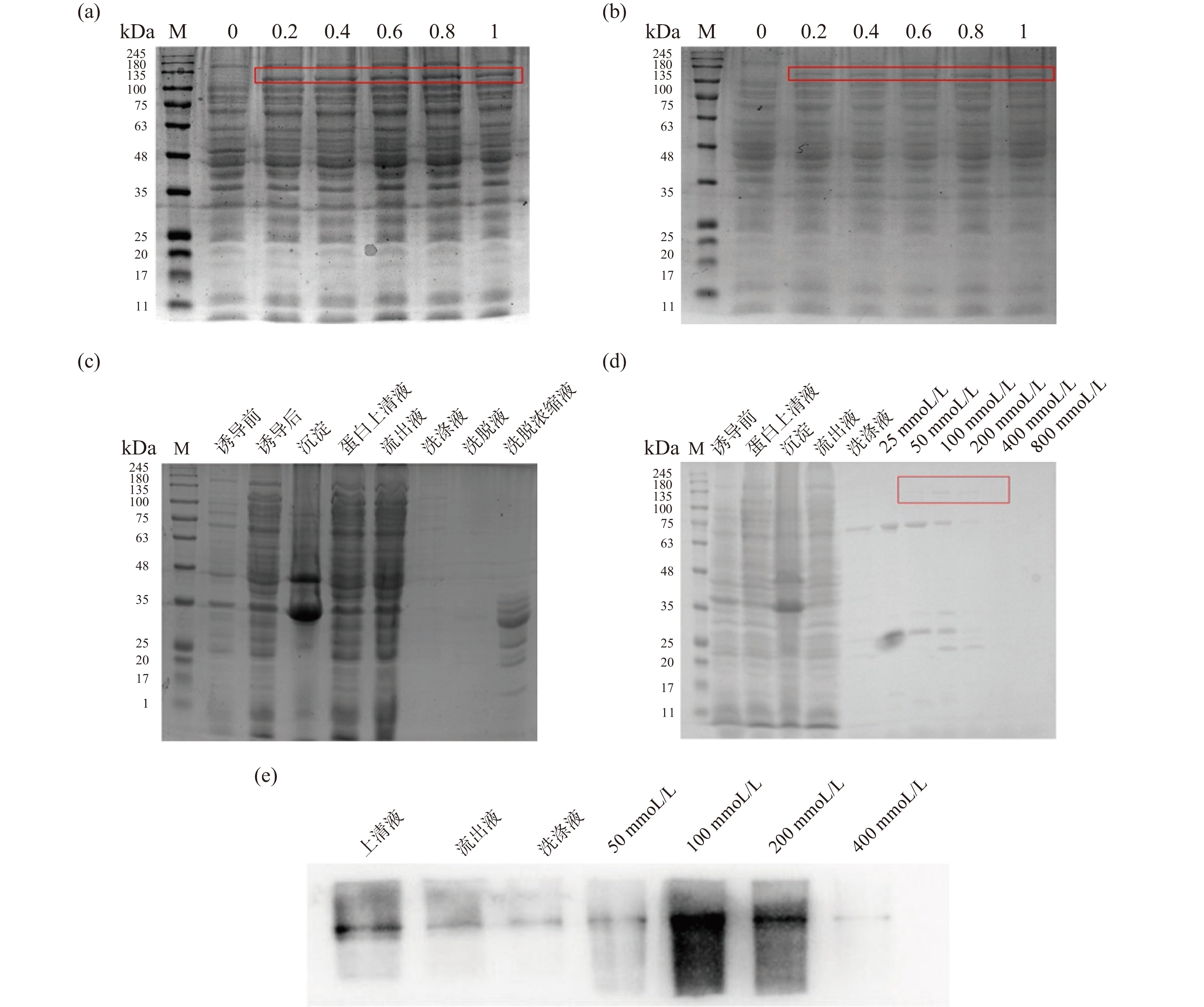
GST-TRPV4融合蛋白预测分子量125.1196 kDa,GST-TRPV4-6his融合蛋白预测分子量125.9425 kDa(蛋白分子量利用ENDMEMO在线软件分析)。按照1.2.3.1中方法分别表达两种融合蛋白(图2a、2b),结果显示在IPTG浓度为0.6 mmol/L时,GST-TRPV4融合蛋白有明显表达(图2a),在IPTG浓度为0.4 mmol/L时,GST-TRPV4-6his融合蛋白有明显表达(图2b)。对于GST-TRPV4融合蛋白,本研究利用谷胱甘肽亲和层析法进行纯化,结果显示经10 mL 20 mmol/L还原性谷胱甘肽溶液洗脱并浓缩后得到的是断裂蛋白,而不能得到完整的GST-TRPV4融合蛋白(图2c)。对于GST-TRPV4-6his融合蛋白,本研究采用镍柱亲和层析法进行纯化,结果显示(图2d)经100 mmol/L或200 mmol/L咪唑溶液洗脱后能得到完整的GST-TRPV4-6his融合蛋白,但是蛋白有部分发生断裂,经Western Blot检测,纯化蛋白确为TRPV4(图2e)。
![]() 图 2 融合蛋白的表达及纯化检测注:a: SDS-PAGE检测pGEX-6p-1-TRPV4/Rossetta(DE3)大肠杆菌在不同浓度IPTG的诱导表达情况(GST-TRPV4蛋白大小为125.1196 kDa);b: SDS-PAGE检测pGEX-6p-1-TRPV4-6his/Rossetta(DE3)大肠杆菌在不同浓度IPTG的诱导表达情况(GST-TRPV4-6his蛋白大小为125.9425 kDa);c: SDS-PAGE检测谷胱甘肽亲和层析法纯化的GST-TRPV4融合蛋白;d: SDS-PAGE检测镍柱亲和层析法纯化的GST-TRPV4-6his融合蛋白;e: Western Blot 检测镍柱亲和层析法纯化的GST-TRPV4-6his融合蛋白。Figure 2. Expression and purification of fusion protein
图 2 融合蛋白的表达及纯化检测注:a: SDS-PAGE检测pGEX-6p-1-TRPV4/Rossetta(DE3)大肠杆菌在不同浓度IPTG的诱导表达情况(GST-TRPV4蛋白大小为125.1196 kDa);b: SDS-PAGE检测pGEX-6p-1-TRPV4-6his/Rossetta(DE3)大肠杆菌在不同浓度IPTG的诱导表达情况(GST-TRPV4-6his蛋白大小为125.9425 kDa);c: SDS-PAGE检测谷胱甘肽亲和层析法纯化的GST-TRPV4融合蛋白;d: SDS-PAGE检测镍柱亲和层析法纯化的GST-TRPV4-6his融合蛋白;e: Western Blot 检测镍柱亲和层析法纯化的GST-TRPV4-6his融合蛋白。Figure 2. Expression and purification of fusion protein2.3 TRPV4蛋白的生物信息学分析
2.3.1 TRPV4蛋白的理化性质和一级结构分析
根据在线软件Protparam的分析(表1),TRPV4蛋白的分子式为C4450H6928N1176O1266S35,原子总量为13855,相对分子质量为98281.18,等电点(PI)为7.83,消光系数为114140 M−1cm−1(
A1mg/mL280nm =1.16),其在哺乳动物体外的半衰期为30 h,在酵母体内半衰期>20 h,在原核大肠杆菌体内半衰期>10 h,不稳定系数为43.23(>40为不稳定蛋白),脂肪系数为90.20,平均亲水系数(Grand average of hydropathicity,GRAVY)为−0.152,可能为亲水性蛋白。融合蛋白GST-TRPV4的相对分子质量为125105.34,等电点为6.76,不稳定系数为41.58,脂肪系数为90.15,平均亲水系数为−0.187。融合蛋白GST-TRPV4-6his的相对分子质量为125928.19,等电点为6.86,不稳定系数为41.41,脂肪系数为89.66,平均亲水系数为−0.204。根据以上分析,融合蛋白GST-TRPV4和GST-TRPV4-6his相较于TRPV4有更好的稳定性,且GST-TRPV4-6his 比GST-TRPV4更加稳定。表 1 蛋白的理化性质Table 1. Physicochemical properties of protein参数 TRPV4 GST-TRPV4 GST-TRPV4-6his 分子式 C4450H6928
N1176O1266S35C5680H8819
N1484O1607S48C5719H8861
N1499O1613S48原子总量 13855 17635 17737 相对分子量 98281.18 125105.34 125928.19 等电点 7.83 6.76 6.86 消光系数(M−1cm−1) 114140 157000 157000 哺乳动物体外半衰期(h) 30 30 30 酵母体内半衰期(h) >20 >20 >20 大肠杆菌体内半衰期(h) >10 >10 >10 不稳定系数 43.23 41.58 41.41 脂肪系数 90.20 90.15 89.66 平均亲水系数 −0.152 −0.187 −0.204 TRPV4蛋白序列中包含871个氨基酸,其中Asp(D)占5.6%,Arg(R)占6.0%,Glu(E)占5.3%,Lys(K)占5.2%,具体见表2。
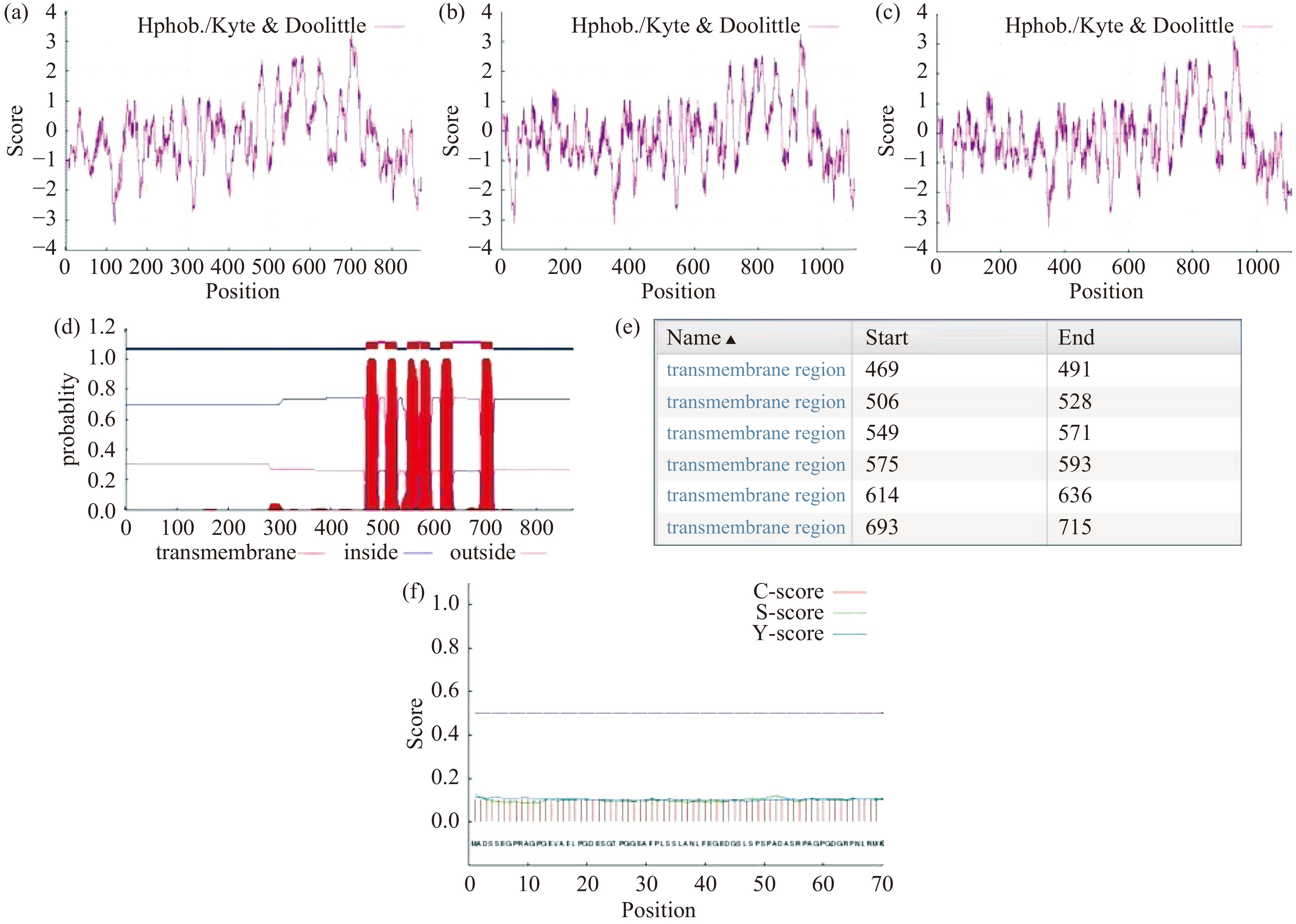
表 2 TRPV4蛋白质的氨基酸组成Table 2. Amino acid composition of TRPV4氨基酸 氨基酸 氨基酸 氨基酸 Ala(A) 6.0 Leu(L) 11.7 Arg(R) 6.0 Lys(K) 5.2 Asn(N) 4.6 Met(M) 2.5 Asp(D) 5.6 Phe(F) 5.3 Cys(C) 1.5 Pro(P) 6.2 Gln(Q) 2.4 Ser(S) 6.7 Glu(E) 5.3 Thr(T) 5.6 Gly(G) 6.7 Trp(W) 1.3 His(H) 1.8 Tyr(Y) 4.1 Ile(I) 5.1 Val(V) 6.5 TRPV4蛋白中带负电荷的氨基酸残基总数为95(Asp+Glu),带正电荷的氨基酸残基总数为97(Arg+Lys),正负电荷氨基酸残基总数比为1.02,GST-TRPV4和GST-TRPV4-6his融合蛋白正负电荷氨基酸残基总数比为0.98。利用Protscale在线软件,选用默认的Kyte & Doolittle计算方法(window size: 13),对三个蛋白的亲水性进行分析(图3a、3b、3c),结果显示TRPV4蛋白序列中,亲水区域多于疏水区域,而GST和六个连续组氨酸的融合增加了TRPV4蛋白的亲水性。利用TMHMMOL/L在线软件对TRPV4蛋白序列进行跨膜结构分析(图3d、3e),预测的跨膜螺旋数为6,膜内氨基酸数为131,且蛋白质的碳端和氮端都位于细胞膜内部。利用Signalp server在线软件对TRPV4蛋白序列进行信号肽预测,结果(图3f)显示原始剪切位点得分(C-score)为0.113,信号肽分数(S-score)为0.125,被结合的剪切位点分数(Y-score)为0.113,D值为0.052(小于信号肽基值0.45),因此,TRPV4无信号肽。
2.3.2 TRPV4蛋白的结构分析
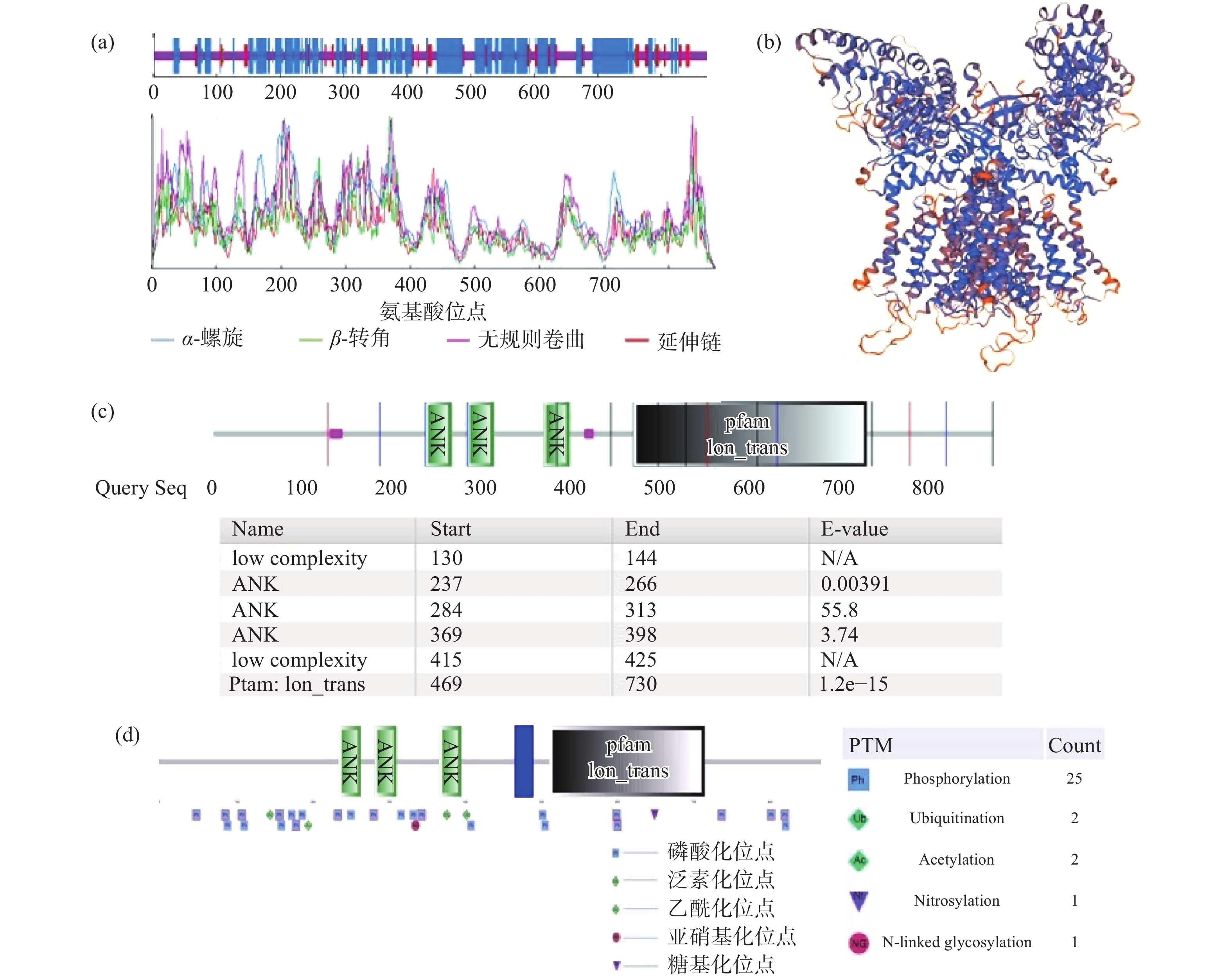
通过在线软件NPS@:SOPMA secondary structure prediction分析TRPV4蛋白的二级结构,结果显示该蛋白的二级结构包含45.35%的α-螺旋、9.64%的延伸链、4.25% β-转角和40.76%的无规则卷曲结构(图4a)。通过SWISS-MODEL在线软件分析人源TRPV4蛋白的三维结构(图4b),模板为热带爪蟾TRPV4蛋白,序列为6bbj. 1. A,相似度为79.43%,模型GMQE为0.57,QMEAN为−2.43。利用SMART在线软件对人源TRPV4蛋白的结构域进行分析(图4c),结果显示该蛋白包含3个ANK(Ankyrin repeats)结构域和一个离子通道(Ion-trans)结构域。
利用SMART在线软件对人源TRPV4蛋白的后修饰位点进行分析(图4d),结果显示,人源TRPV4蛋白的磷酸化位点有25个,泛素化位点有2个,乙酰化位点有2个,亚硝基化位点有1个,糖基化位点有1个,其具体位置见图4d。
2.3.3 TRPV4蛋白的交联分析
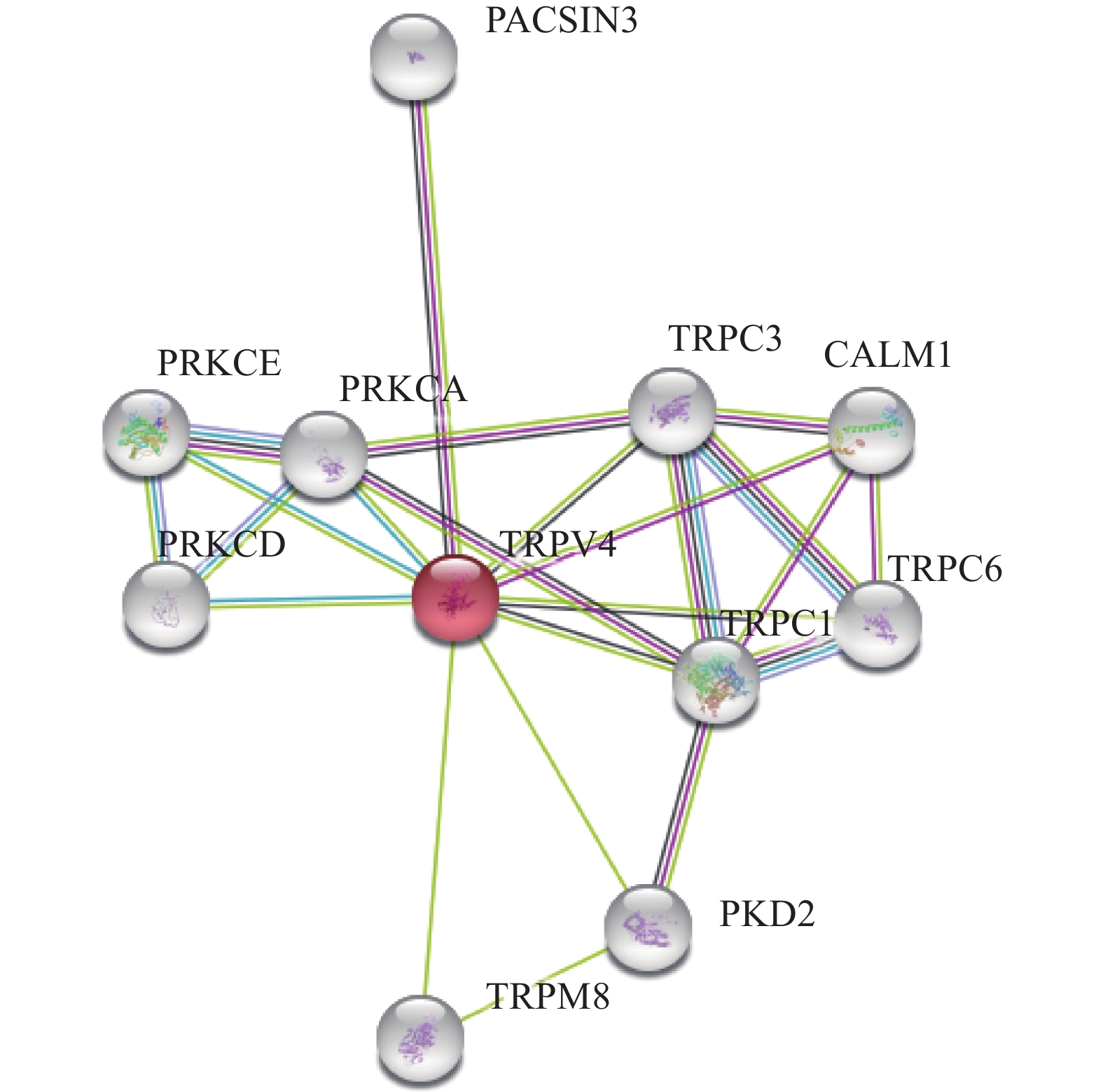
利用SMART在线软件对人源TRPV4蛋白在体内潜在的蛋白质交联作用进行分析。结果显示(图5),TRPV4与其他瞬时受体电位阳离子通道TRPC1、TRPM8、TRPC3以及TRPC6存在潜在的交联作用。除此之外,TRPV4在肾上皮初级纤毛中与阳离子通道蛋白Polycystin-2(PKD2)可以形成机械和热敏通道,而PKD1和PKD2可能通过共同的信号通路发挥作用,这对维持肾小管细胞的正常分化状态是必要的。Calmodulin-1(CALM1)可以通过钙结合调控大量酶、离子通道、水通道蛋白等,可能参与调控TRPV4离子通道的活性。神经元蛋白3中的蛋白激酶C和酪蛋白激酶底物PACSIN3参与胞吞作用,能够调节质膜蛋白的内化,其过表达后破坏了SLC2A1/GLUT1和TRPV4的内化,增加了细胞膜上SLC2A1/GLUT1和TRPV4的水平,也可能抑制TRPV4钙通道活性。PRKCA、PRKCE以及PRKCD均为钙离子依赖性蛋白激酶,在细胞粘附、运动、迁移、细胞周期等与细胞骨架蛋白相关的多个细胞过程的调控中起重要作用,在神经元生长和离子通道调控中也起至关重要的作用,可能参与TRPV4离子通道的定位及活性调控。
3. 讨论与结论
TRPV是哺乳动物体内瞬时受体电位(TRP)超家族香草素(Vanilloid)阳离子通道亚家族的简称,根据亚家族中成员对阳离子的选择性和对温度的敏感型分为两类:可感知温度刺激但对阳离子无明显选择性的TRPV1、TRPV2、TRPV3、TRPV4,不可感知温度刺激但具有显著的Ca2+离子选择性的TRPV5和TRPV6等[22-23]。在分布及功能上,TRPV1广泛分布于中枢神经系统(CNS)和外周神经系统(PNS),具备有害温度传感器(阈值约为43 ℃)和香草素受体的功能,激动剂为辣椒素、树脂毒素、花生四烯酸温度等,抑制剂为辣椒碱、钌红、碘树脂毒素、BCTC、PIP2;TRPV2广泛分布于中枢神经系统(CNS)和脾肺部,具备毒热温度传感器(阈值为52 ℃)和渗透压感受器的功能,受IGF-I、高温或PKA信号转导调控,抑制剂为钌红、La3+、SKF96365;TRPV3广泛分布于皮肤、中枢神经系统和外周神经系统,是温度感应通道,在感知范围(约33~39 ℃)内可明显感受温度的变化,抑制剂为钌红;TRPV4广泛分布于中枢神经系统(CNS)和脾肺部,具备温度传感器和渗透压感受器的功能,温度感知范围约为27~34 ℃,研究发现,在从小鼠皮肤分离出的角质形成层细胞原代培养实验中,环境温度的细微变化可激发TRPV4强烈的电信号,Trpv4-/-小鼠对热痛觉敏感性显著降低,TRPV4阳离子通道对温度或渗透压变化的灵敏度较高,GSK1016790A是TRPV4的强效激动剂,抑制剂为钌红、钆、镧;TRPV5和TRPV6广泛分布于肾、肠,在所有的TRPV亚家族中,仅有TRPV5和TRPV6对Ca2+具有显著的选择透过性(PCa/PNa>100),是Ca2+离子特异性通道,通道内的谷氨酸残疾、天冬氨酸残基为二价化合物提供丰富的结合位点,其功能受细胞内外的Ca2+离子浓度和钙调蛋白影响和调控,抑制剂为钌红和La3+等。
在结构上TRPV以四聚体的方式呈现,由四个亚基围绕离子通道对称排列,每个亚基都包含六个跨膜结构域。通常情况下,TRPV离子通道由四个相同的亚基(同源四聚体)构成,但最新的研究表明,已知的四个可感知温度刺激的TRPV1-4可相互组合构成四聚体(异源四聚体),但是构成TRPV离子通道的异源四聚体四个亚基之间如何识别、相互作用、感知刺激和调控阳离子通道的开闭等仍有待进一步研究,为了能更准确的阐明TRPV4温敏性的分子机制,解释TRPV4感知温度刺激时的状态变化,研究TRPV4在疾病发生发展中的作用等,TRPV4原核表达纯化系统的构建将有助于此类离子通道蛋白的功能研究和机制探索。
本研究为实现大分子多次跨膜蛋白高效表达与纯化,在原核表达系统中先后筛选了pET-28a(+)、pET-32a、pET-15b、pGEX-5X-1、pEX-4T、pGEX-6p-1等表达载体,也筛选了BL21或Rossetta两种大肠杆菌表达宿主,证明以pGEX-6p-1为载体构建的GST-TRPV4融合蛋白Rossetta表达系统能够表达TRPV4蛋白,而其他表达体系没有实现TRPV4原核表达。在原核表达系统构建中,该结果与生物信息学分析都表明GST融合蛋白的构建可增加目标蛋白在大肠杆菌体内的稳定性和亲水性,但在蛋白纯化过程中,发现GST-TRPV4融合蛋白在纯化过程中会发生断裂,以致纯化后无法获得完整的TRPV4融合蛋白,通过分析断裂片段发现每次纯化后断裂片段的大小及数量基本一致,因此,认为可能是TRPV4蛋白的某些固定位置存在不稳定性。同时,纯化使用的谷胱甘肽亲和层析介质,其基体表面的活性环氧基团密度较小,偶联的谷胱甘肽量较少,以致在蛋白纯化时时间过长,增加蛋白降解率;为了增加融合蛋白稳定性,在融合蛋白C端引入六个组氨酸,以此来增加蛋白稳定性,且可在目标蛋白纯化时使用更为高效快速的镍离子柱亲和层析法,从而大大减少融合蛋白在纯化过程中的不稳定因素。结果证明,相较于只有GST的融合蛋白,目标蛋白引入6个组氨酸后可通过镍离子柱亲和层析法成功纯化获得GST-TRPV4-6his完整融合蛋白。
本研究基于pGEX-6p-1载体构建的GST-TRPV4-6his重组质粒所表达的目标蛋白大约126 kDa,由于分子量较大和蛋白体外的不稳定性,获取的完整融合蛋白中仍有部分蛋白发生了降解,因此,后期将通过进一步分析该蛋白的不稳定序列,通过碱基突变等方式增强蛋白稳定性,从而获取大量高纯度的目标蛋白。并进一步将目标蛋白通过固定化的方式固载在载体上增加蛋白稳定性,并可将目标蛋白载体装填于色谱柱中来构建该蛋白的生物色谱,从而应用于药物与蛋白相互作用和药物活性成分筛选等应用研究。
-
图 2 融合蛋白的表达及纯化检测
注:a: SDS-PAGE检测pGEX-6p-1-TRPV4/Rossetta(DE3)大肠杆菌在不同浓度IPTG的诱导表达情况(GST-TRPV4蛋白大小为125.1196 kDa);b: SDS-PAGE检测pGEX-6p-1-TRPV4-6his/Rossetta(DE3)大肠杆菌在不同浓度IPTG的诱导表达情况(GST-TRPV4-6his蛋白大小为125.9425 kDa);c: SDS-PAGE检测谷胱甘肽亲和层析法纯化的GST-TRPV4融合蛋白;d: SDS-PAGE检测镍柱亲和层析法纯化的GST-TRPV4-6his融合蛋白;e: Western Blot 检测镍柱亲和层析法纯化的GST-TRPV4-6his融合蛋白。
Figure 2. Expression and purification of fusion protein
表 1 蛋白的理化性质
Table 1 Physicochemical properties of protein
参数 TRPV4 GST-TRPV4 GST-TRPV4-6his 分子式 C4450H6928
N1176O1266S35C5680H8819
N1484O1607S48C5719H8861
N1499O1613S48原子总量 13855 17635 17737 相对分子量 98281.18 125105.34 125928.19 等电点 7.83 6.76 6.86 消光系数(M−1cm−1) 114140 157000 157000 哺乳动物体外半衰期(h) 30 30 30 酵母体内半衰期(h) >20 >20 >20 大肠杆菌体内半衰期(h) >10 >10 >10 不稳定系数 43.23 41.58 41.41 脂肪系数 90.20 90.15 89.66 平均亲水系数 −0.152 −0.187 −0.204 表 2 TRPV4蛋白质的氨基酸组成
Table 2 Amino acid composition of TRPV4
氨基酸 氨基酸 氨基酸 氨基酸 Ala(A) 6.0 Leu(L) 11.7 Arg(R) 6.0 Lys(K) 5.2 Asn(N) 4.6 Met(M) 2.5 Asp(D) 5.6 Phe(F) 5.3 Cys(C) 1.5 Pro(P) 6.2 Gln(Q) 2.4 Ser(S) 6.7 Glu(E) 5.3 Thr(T) 5.6 Gly(G) 6.7 Trp(W) 1.3 His(H) 1.8 Tyr(Y) 4.1 Ile(I) 5.1 Val(V) 6.5 -
[1] GORETZKI B, GLOGOWSKI N A, DIEHL E, et al. Structural basis of TRPV4 N terminus interaction with syndapin/PACSIN1-3 and PIP2[J]. Structure,2018,26(12):1583−1593. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2018.08.002
[2] TSUNO N, YUKIMASA A, YOSHIDA O, et al. Discovery of novel 2′, 4′-dimethyl-[4, 5′-bithiazol]-2-yl amino derivatives as orally bioavailable TRPV4 antagonists for the treatment of pain: Part 1[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters,2016,26(20):4930−4935.
[3] BRIAN G L, EDWARD J B, DAVID J B. Recent advances in TRPV4 agonists and antagonists[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters,2020,30:127022.
[4] MARTINAC B, POOLE K. Mechanically activated ion channels[J]. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology,2018,97:104−107.
[5] PAIRET N, MANG S, KIECHLE T, et al. Differential modulation of transendothelial electrical resistance by TRPV4 agonists is mediated by apoptosis and/or necrosis[J]. Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports,2019,20:100672. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2019.100672
[6] BAXTER M, ELTOM S, DEKKAK B, et al. Role of transient receptor potential and pannexin channels in cigarette smoke-triggered ATP release in the lung[J]. Thorax:The Journal of the British Thoracic Society,2014,69(12):1080−1089.
[7] CENAC N, BAUTZOVA T, LE FAOUDER P, et al. Quantification and potential functions of endogenous agonists of transient receptor potential channels in patients with irritable bowel syndrome[J]. Gastroenterology,2015,149(2):433−444. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.04.011
[8] YAN J J, YE F, YING J, et al. Cimifugin relieves pruritus in psoriasis by inhibiting TRPV4[J]. Cell Calcium,2021,97:102429. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2021.102429
[9] FICHNA J, MOKROWIECKA A, CYGANKIEWICEZ A I, et al. Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 blockade protects against experimental colitis in mice: A new strategy for inflammatory bowel diseases treatment?[J]. Neurogastroenterology & Motility the Official Journal of the European Gastrointestinal Motility Society,2012,24(11):e557−e560.
[10] OLIVAN V A, GARCIA O A, LOZANO G J, et al. Pharmacological activation of TRPV4 produces immediate cell damage and induction of apoptosis in human melanoma cells and Ha Ca T keratinocytes[J]. PloS One,2018,13(1):e190307.
[11] FIORIO P A, ONG H L, CHENG K T, et al. TRPV4 mediates tumor-derived endothelial cell migration via arachidonic acid-activated actin remodeling.[J]. Oncogene,2012,31:200−212. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.231
[12] ADAPALA R K, THOPPIL R J, GHOSH K, et al. Activation of mechanosensitive ion channel TRPV4 normalizes tumor vasculature and improves cancer therapy[J]. Oncogene,2016,35:314−322. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.83
[13] SHIGEMATSU H, SOKABE T, DANEV R, et al. A 3.5-nm structure of rat TRPV4 cation channel revealed by Zernike phase-contrast cryoelectron microscopy[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry,2010,285(15):11210−11218. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.090712
[14] ZHAN L, LI J. The role of TRPV4 in fibrosis[J]. Gene,2018,642:1−8. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.10.067
[15] WORTLEY M A, BIRRELL M A, BELVISI M G. Drugs affecting TRP channels[J]. Pharmacology and Therapeutics of Asthma and COPD,2016,63:213−241.
[16] GARCIA E A, MRKONJIC S, JUNG C, et al. The TRPV4 channel[J]. Handb Exp Pharmacol,2014,222:293−319.
[17] SURESH K, SERVINSKY L, REYES J, et al. Hydrogen peroxide-induced calcium influx in lung microvascular endothelial cells involves TRPV4[J]. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol,2015,309(12):L1467−L1477. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00275.2015
[18] SCHERAGA R G, SOUTHERN B D, GROVE L M, et al. The role of transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 in pulmonary inflammatory diseases[J]. Frontiers in Immunology,2017,8:503. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00503
[19] LAMANDE S R, YUAN Y, GRESSHOFF I L, et al. Mutations in TRPV4 cause an inherited arthropathy of hands and feet[J]. Nature Genetics,2011,43(11):1142−1146. doi: 10.1038/ng.945
[20] LIU Y Z, CHEN X, LI Z Y, et al. Ansavaricin J, a new heterocyclic ring-fused streptovaricin from gene stvP5-deleted mutant of Streptomyces spectabilis CCTCC M2017417[J]. Chemistry & Biodiversity,2020,17(8):e1900713.
[21] LIU Y Z, CHEN X, LI Z Y, et al. Functional analysis of cytochrome P450s involved in streptovaricin biosynthesis and generation of anti-MRSA analogues[J]. ACS Chemical Biology,2017,12(10):2589−2597. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.7b00467
[22] SHIBASAKI K. TRPV4 activation by thermal and mechanical stimuli in disease progression[J]. Laboratory Investigation,2020,100:218−223. doi: 10.1038/s41374-019-0362-2
[23] HOSHI Y, OKABE K, SHIBASAKI K, et al. Ischemic brain injury leads to brain edema via hyperthermia-induced TRPV4 activation[J]. The Journal of Neuroscience,2018,38(25):5700−5709. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2888-17.2018
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:
