Optimization of Enzymatic Hydrolysis Process and Activity of ACE Inhibitory Peptides from Selenium-rich Moringa oleifera Leaves Protein
-
摘要: 以富硒辣木叶为原料提取富硒辣木叶蛋白,通过单因素实验和响应面优化富硒辣木叶蛋白血管紧张素转化酶(ACE)抑制肽的制备工艺,并对最优酶解物的ACE抑制活性、氨基酸组成和硒含量进行分析表征。结果表明,富硒辣木叶蛋白ACE抑制肽的最佳酶解条件为时间3 h,pH7.5、酶底比0.23%、底物浓度5.97%、温度39.2 ℃。该条件下制备的ACE抑制肽的ACE抑制活性较强(IC50=0.522 mg/mL),富含必需氨基酸(24.05%)和疏水性氨基酸(20.6%),其硒含量是辣木叶原料中硒含量的1.86倍。富硒辣木叶蛋白ACE抑制肽具有功能因子和天然食物的双重特性,此研究可为降血压药物及相关功能性食品的开发提供理论依据。Abstract: The selenium-rich Moringa oleifera leaves protein was extracted from the selenium-rich Moringa oleifera leaves. The preparation of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from selenium-rich Moringa oleifera leaves was optimized by single factor experiments and response surface method. The ACE inhibitory activity, amino acid composition and selenium content of the optimal enzymatic hydrolysate were analyzed and characterized. The results showed that the optimal hydrolysis conditions of ACE inhibitory peptides were as follows: time 3 h, pH7.5, enzyme to substrate ratio 0.23%, substrate concentration 5.97% and temperature 39.2 ℃. The ACE inhibitory peptides prepared under these conditions showed strong ACE inhibitory activity (IC50=0.522 mg/mL), rich in essential amino acids (24.05%) and hydrophobic amino acids (20.6%), and the selenium content was 1.86 times that of the raw material of Moringa oleifolia leaves. The ACE inhibitory peptides of selenium-rich Moringa oleifolia leaves protein had dual characteristics of functional factor and natural food. This study could provide theoretical basis for the development of antihypertensive drugs and related functional foods.
-
高血压是各种心脑血管疾病发生发展的主要病因之一,高血压患者是世界范围内患病人群中最大的一个群体,预计到2025年,发病人数将超过15亿[1-2]。血管紧张素转化酶(Angiotensin-converting enzyme,ACE)是调节血压和血管功能的重要因子。抑制ACE的活性可以有效阻止血管紧张素Ⅱ的生成,从而防治高血压。常见ACE抑制剂药物有卡托普利、苯那普利等,但临床上会有头痛、疲劳等不良反应[3-4]。寻求安全、无副作用的食源性ACE抑制活性成分成为近年研究的热点,比如从马氏珍珠贝肉蛋白[5]、牛乳酪蛋白[6]、大米[7]、龙须菜[8]、核桃[9]、松仁[10]等原料的酶解产物中已发现具有ACE抑制活性的多肽。
硒(Selenium,Se)是人体、动物体以及多种微生物体中各种重要生物学功能所必需的微量元素[11],也是许多酶的重要组成部分,具有保护血管、维持心脏正常等功能[12]。研究证实,富硒肽具有抗氧化、降血压、保肝、免疫调节等多种生理功能,比如从富硒糙米蛋白水解物中得到了对DPPH自由基、OH自由基和O2−自由基具有强抗氧化活性的硒肽[13]和富硒免疫调节肽[14];从富硒螺旋藻[15-16]和富硒茶[17]中分离鉴定出具有抑制ACE活性的硒肽。
辣木(Moringa oleifera Lam.)是一种生长在热带和亚热带的药食两用的植物[18]。2012年11月,我国卫生部批准辣木叶为新资源食品[19],被中国绿色食品发展中心认定为“国家首推绿色食品”[20]。辣木叶粉中蛋白质含量丰富,高达27.6%~35.4%[21-22],氨基酸种类多达19种(天冬氨酸、谷氨酸为主)[23],可媲美大豆,是一种值得开发利用的优质植物蛋白。但是,辣木叶蛋白体外消化率低且多作为动物饲料使用,造成资源的极大浪费[24]。研究表明,辣木叶蛋白及其酶解产物具有抗菌[25]、清除自由基能力和修复氧化损伤[26]以及改善高尿酸血症和代谢紊乱[27]等功能活性,但关于辣木叶蛋白肽对ACE抑制活性的研究报道较少。将硒的降血压作用与辣木叶肽的降血压作用相结合开发富硒辣木叶低聚肽产品,可能具有更好的降血压效果,但目前关于富硒辣木叶肽降血压的效果尚未报道。本研究以富硒辣木叶为原料,通过碱溶酸沉法提取富硒辣木叶蛋白,研究不同蛋白酶以及酶解工艺对于ACE抑制肽的制备及ACE抑制率的影响,采用响应面法明确最佳制备工艺,并对最优工艺条件下酶解物的ACE抑制活性、氨基酸组分和硒含量进行分析。本研究为辣木叶蛋白的深入研究提供参考依据,而且为富硒ACE抑制肽在功能性食品、医药领域的应用提供理论支持,以期促进富硒辣木叶的高值化利用。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
富硒辣木叶粉 由北部湾滨海富硒功能农业研究院提供;木瓜蛋白酶(20万U/g)、中性蛋白酶(10万U/g)、胃蛋白酶(300万U/g)、胰蛋白酶(25万U/g) 南宁庞博生物工程有限公司;血管紧张素转化酶(ACE)、N-[3-(2-呋喃基)丙烯酰]-L-苯丙氨酰-甘氨酰-甘氨酸(N-[3-(2-furyl)acryloyl]-L-phenyalanyl-glycyl-glycine,FAPGG)、羟乙基哌嗪乙磺酸(HEPES) 美国Sigma-Aldrich公司;其他化学品和试剂 均为分析纯。
2300多功能酶标仪 PerkinElmer公司;HH-4数显恒温水浴锅 金坛市华城海龙实验仪器厂;L530台式低速自动平衡离心机 湖南湘仪实验室仪器开发有限公司;FD-1型冷冻干燥机 海门市其林贝尔仪器制造有限公司;DH5000BII电热恒温培养箱 天津泰斯特仪器有限公司;pH计 上海佑科仪器有限公司;电子天平 梅特勒-托利多仪器(上海)有限公司; AFS-9530原子荧光光度计 北京海光仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 富硒辣木叶蛋白的提取
基于碱溶酸沉原理,参考祝素莹等[28]方法提取富硒辣木叶蛋白,并进行部分改进。称取一定量富硒辣木叶粉,用0.01 mol/L NaOH溶液配成辣木叶粉溶液(料液比1:20)在45 ℃条件下水浴3 h后,4000 r/min下离心10 min,收集上清液。用HCl调整pH至4.5,室温静置10~20 min,4000 r/min下,弃上清得到蛋白质沉淀,−40 ℃冷冻干燥24 h后即得富硒辣木叶蛋白粉。
1.2.2 富硒辣木叶蛋白ACE抑制肽的制备
参考赵爽等[29]的方法并略作修改。以ACE抑制活性为指标,将富硒辣木叶蛋白粉加入蒸馏水配制成一定浓度的蛋白质溶液,调节pH,加入一定量的酶,恒温水浴摇床酶解3 h后于沸水浴灭酶10 min,冷却至室温,4000 r/min下离心20 min,上清液即为含ACE抑制肽的酶解液。
1.2.3 单因素实验
选取4种蛋白酶并在其最适的条件下对富硒辣木叶蛋白进行酶解,分别为木瓜蛋白酶(pH6.5,55 ℃)、中性蛋白酶(pH7,45 ℃)、胃蛋白酶(pH2,37 ℃)、胰蛋白酶(pH8,37 ℃)。在底物浓度为3%,酶底比为0.3%,酶解3 h,灭酶,离心,取酶解液测定ACE的抑制率,选择合适的蛋白酶。
单因素基础条件设为:酶解温度3 h,pH8,底物浓度3%和酶底比0.3%。在最适酶的基础上,其他单因素实验采用改变一个因素,固定其他因素不变的方式,分别探究酶解温度(27、32、37、42、47 ℃),pH(7、7.5、8、8.5、9),底物浓度(1%、3%、5%、7%)和酶底比(0.1%、0.2%、0.3%、0.4%、0.5%)对酶解物ACE抑制活性的影响。
1.2.4 响应面优化试验
在单因素实验的基础上,以底物浓度(A)、酶底比(B)和温度(C)三个因素为自变量,以ACE抑制率为响应值,选择Design-Expert V8.0.6.1软件的Box-Behnken设计并进行三因素三水平的响应面试验,确定酶解富硒辣木叶蛋白的最优工艺条件。响应面因素与水平设计见表1。
表 1 响应面试验因素水平表Table 1. Factors and levels table of response surface experiment因素 水平 −1 0 1 A 底物浓度(%) 3 5 7 B 酶底比(%) 0.2 0.3 0.4 C 温度(℃) 32 37 42 1.2.5 ACE抑制率的测定
采用FAPGG法测定ACE抑制率[30]。缓冲液和反应物分别为80 mmol/L pH8.3的HEPES-NaOH(含0.3 mol/L NaCl)和缓冲液配制的1 mmol/L FAPGG。将酶解液用超纯水稀释30倍,在酶标板孔中依次加入40 μL待测样品、50 μL底物和10 μL ACE溶液(0.1 U/mL),振荡10 s后,快速放入酶标仪中测定340 nm下的吸光度,记为A1,而后37 ℃孵育30 min后测定吸光值为A2。计算ΔA,ΔA = A1−A2,以单位时间内吸光度值的变化表ACE酶活性。以缓冲液代替待测样品作空白对照。按照式(1)计算ACE抑制率:
ACE抑制率(%)=(1−ΔAaΔAb)×100 (1) 式(1)中:ΔAb为加入缓冲液时吸光度在30 min内的变化;ΔAa为加入抑制剂时吸光度在30 min内的变化。
1.2.6 最优酶解物ACE抑制活性测定
将最优酶解条件下的上清液冷冻干燥后,使用HEPES缓冲液(pH8.3)配制成不同浓度样品溶液(0.1、0.25、0.5、1、2 mg/mL),测定ACE抑制率。IC50定义为ACE抑制率达50%时的多肽质量浓度(mg/mL),用SPSS 21.0统计软件的概率单位法计算。
1.2.7 氨基酸组成测定
将最优酶解条件下制备的富硒辣木叶ACE抑制肽冷冻干燥,获得的冻干粉即为测定样品。参照GB 5009.124-2016《食品中氨基酸的测定》,以外标法检测样品液中17种氨基酸的浓度[31]。
1.2.8 硒含量的测定
根据国家标准GB 5009.93-2017《食品中硒的测定》,采用氢化物原子荧光光谱法(HG-AFS)测定富硒辣木叶原料,富硒辣木叶提取蛋白和富硒辣木叶ACE抑制肽中的总硒含量[32]。称取适量样品置于锥形瓶中,用10 mL浓硝酸和高氯酸混合物(v/v,9:1)在150 ℃下消化2.5 h,冷却后,加入5 mL 6 mol/L盐酸将样品中六价硒还原成四价硒。冷却后,用超纯水将消化后的溶液稀释至25 mL,然后将10 mL的溶液转移到反应容器中,其中加入2 mL 6 mol/L盐酸和1 mL 10% (w/w)铁氰化钾,混匀待测,同时做空白对照。
仪器条件为:负高压280 V,硒灯电流80 mA,原子化器高度8 mm,载气流量为300 mL/min;屏蔽气流量为800 mL/min,读数时间12 s,延迟时间3 s,重复测定3次,测定样品硒含量。
1.3 数据处理
实验数据均以平均值±标准偏差表示,采用SPSS 21.0统计学软件,多组数据间进行单因素方差分析(One-AVOVA中的Duncan’s test)。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素实验
2.1.1 蛋白酶的筛选
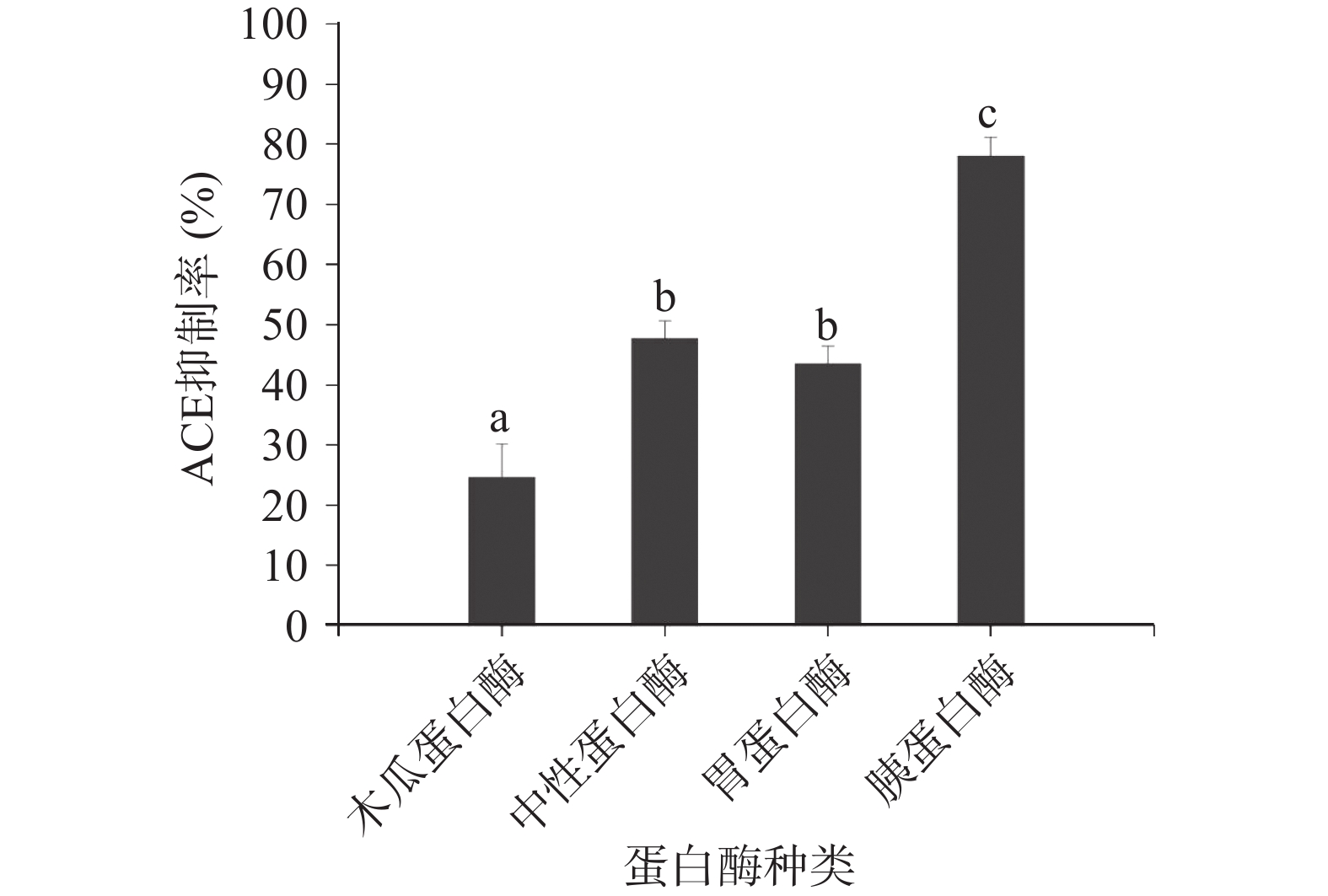
由于不同种类蛋白酶的作用位点不同,酶解获得的多肽片段也不相同,表现出的体外ACE抑制活性存在差异[28]。由图1可知,在各自适宜的条件下,不同蛋白酶酶解物对ACE抑制活性有显著的影响(P<0.05),ACE抑制率由高到低依次为胰蛋白酶(78.01%)>中性蛋白酶(47.64%)>胃蛋白酶(43.46%)>木瓜蛋白酶(24.61%)。这说明富硒辣木叶蛋白结构更适宜胰蛋白酶发挥作用,能够有效释放更多目标肽段,后续实验采用胰蛋白酶为ACE抑制肽制备酶。Sun等[33]报道,经胰蛋白酶水解的黄斑海蜇蛋白显示出最强的ACE抑制活性。余虹等[8]也发现经胰蛋白酶水解的龙须菜蛋白水解物对ACE的抑制能力最强。据报道,C末端Arg或Lys的存在能增强ACE抑制效价[34-36],由于胰蛋白酶其酶切位点优先在精氨酸和赖氨酸处裂解,因此胰蛋白酶水解产生的肽段C末端位置为精氨酸或赖氨酸,这可能是其酶解肽段活性较强的原因。
2.1.2 酶解温度对酶解效果的影响
由图2可知,在其他因素固定不变的条件下,酶解温度对ACE抑制活性有显著的影响(P<0.05),随着酶解温度的升高,ACE抑制率先增加后降低,酶解温度为37 ℃时,ACE抑制率达到最大值79.49%。可能由于此时酶活性较高,能更有效地水解蛋白质,释放具有抑制ACE活性的肽分子,当温度继续升高时,可能影响蛋白酶活性,进而使ACE抑制率降低[37-38],因此选用ACE抑制效果最佳的37 ℃进行后续实验。
2.1.3 pH对酶解效果的影响
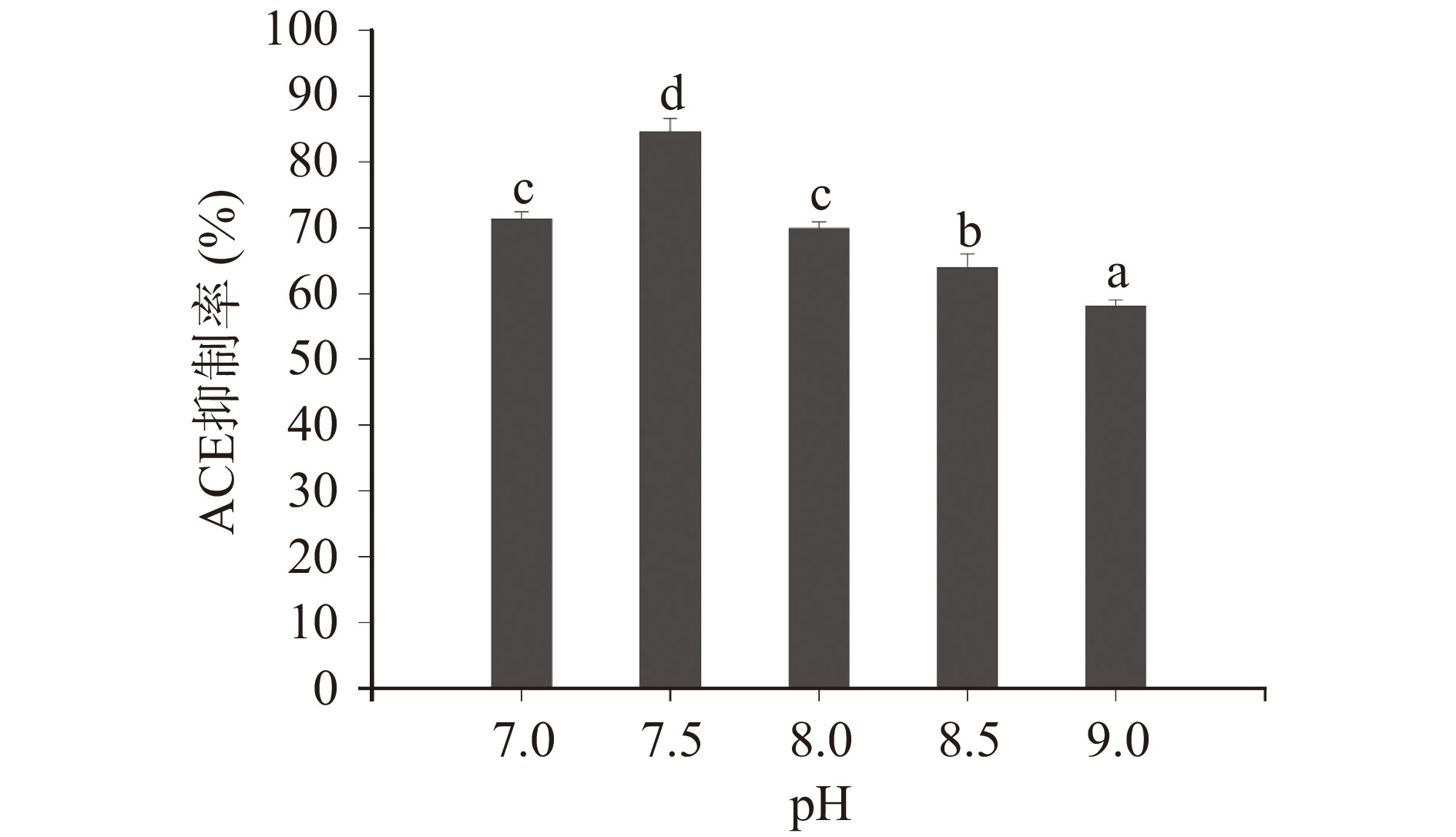
由图3可知,pH对富硒辣木叶肽的ACE抑制活性影响呈先升后降的趋势,在pH7.5处达到最高值(84.56%,P<0.05)后逐渐下降。pH是影响酶解效果的重要因素,它的影响体现在蛋白酶构象、酶与蛋白质的结合状态等方面,pH过高或过低都不利于更好的酶解效果[39-40]。在对魔芋ACE抑制肽[41]和榛子粕ACE抑制肽[42]等研究中也观察到类似变化,随着pH变化所呈现的先升后降的趋势与此吻合。因此,确定最适pH为7.5。
2.1.4 底物浓度对酶解效果的影响
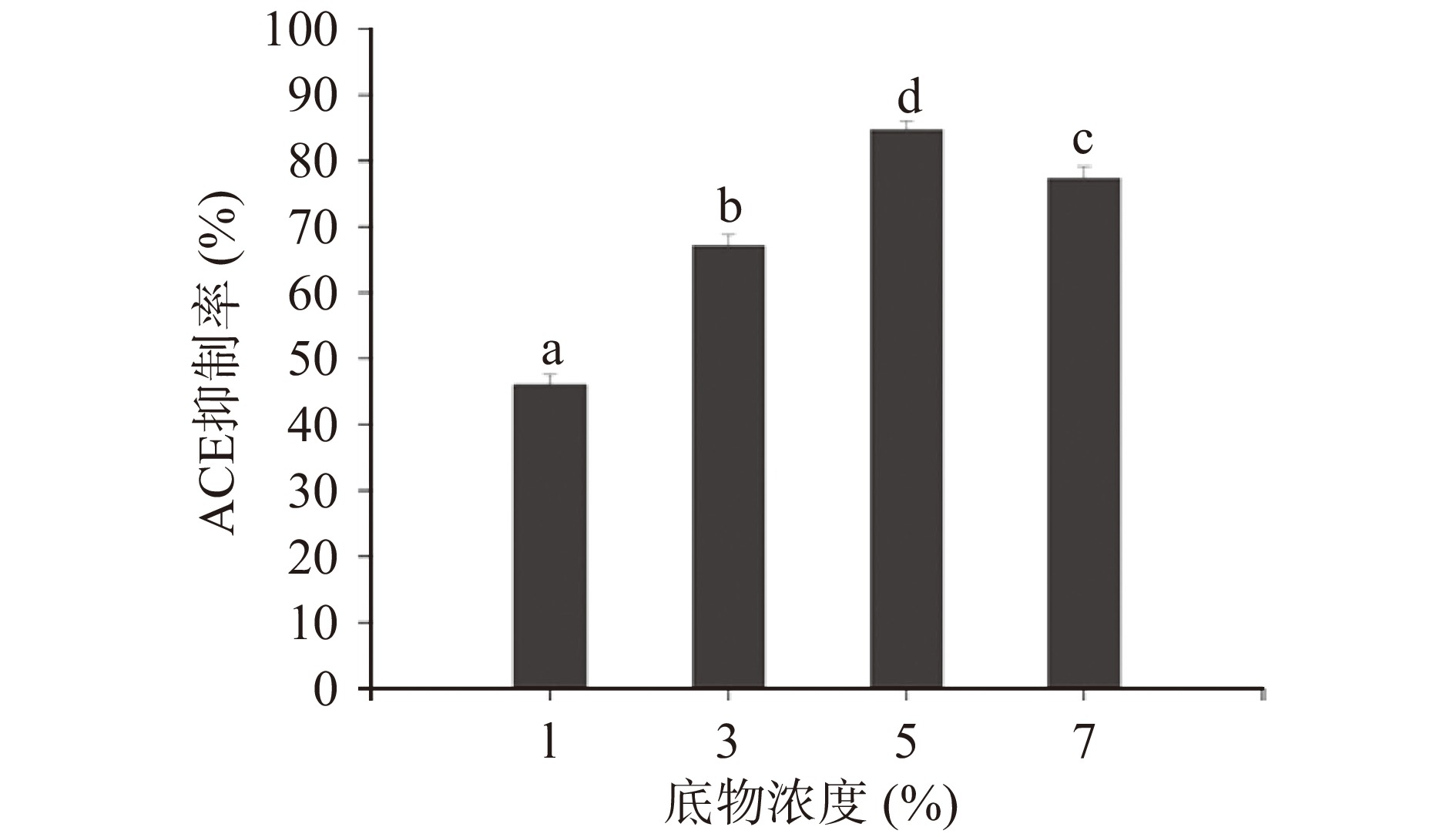
由图4可知,底物浓度对ACE抑制活性有显著的影响(P<0.05),在考察底物浓度范围内,酶解产物ACE抑制活性呈先上升后下降的趋势。当酶解底物浓度为5%时,酶解得到的富硒辣木叶多肽产物具有最高的ACE抑制活性,为84.65%。当底物浓度继续增大,抑制率反而降低,一方面可能没有足够的酶催化底物反应,另一方面酶解液过于粘稠,影响蛋白质的自由扩散,影响酶解效率[42-43]。最终选取底物浓度5%为最佳反应条件。
2.1.5 酶底比对酶解效果的影响
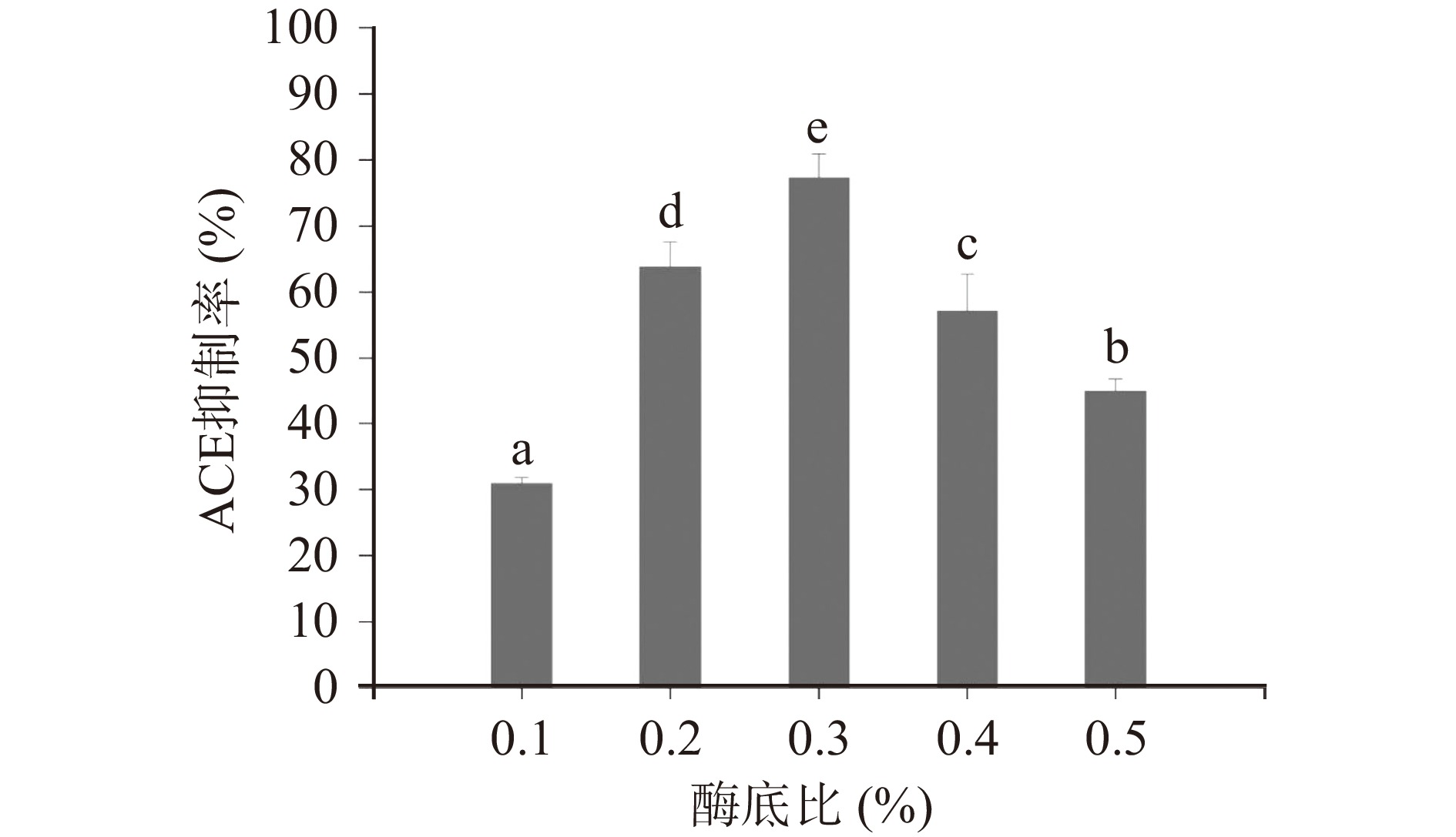
如图5所示,酶底比对ACE抑制活性有显著的影响(P<0.05),酶解产物的ACE抑制活性呈先增强后减弱的趋势,当酶底比为0.3%时,ACE抑制率达到最大,为77.18%,后再增加酶用量,ACE抑制活性下降,可能是过量的蛋白酶将具有活性的多肽继续降解为活性低甚至无活性的小肽,而且还会造成不同程度的资源浪费[44-46]。因此在进行酶底比的选择时,不仅要求考虑其对酶解效果的影响,还需考虑资源浪费和经济成本等方面。因此,最佳酶解酶底比为0.3%。
2.2 响应面试验
2.2.1 Box-Benhnken试验设计及结果
在单因素基础上,以底物浓度(A)、酶底比(B)和温度(C)三个因素为自变量,以ACE抑制率为响应值,利用利用Box-Behnken中心组合试验进行三因素三水平试验,对酶解条件进行优化。响应面试验结果见表2,方差分析结果见表3。
表 2 响应面设计方案及结果Table 2. Design and results of the response surface experiment试验号 因素 ACE抑制率(%) A底物浓度(%) B酶底比(%) C温度
(℃)1 0 0 0 89.23 2 0 0 0 87.79 3 0 −1 −1 83.48 4 1 −1 0 82.76 5 −1 1 0 82.05 6 −1 0 −1 69.12 7 0 0 0 84.92 8 −1 −1 0 69.12 9 0 0 0 85.3 10 1 1 0 73.43 11 0 1 −1 76.3 12 0 1 1 84.2 13 0 −1 1 88.79 14 0 0 0 89.95 15 1 0 −1 82.76 16 1 0 1 84.92 17 −1 0 1 71.99 表 3 响应面二次模型方差分析Table 3. Analysis of variance for response surface quadratic model方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F P 显著性 模型 649.00 9 72.11 4.33 0.0331 * A-底物浓度 124.74 1 124.74 7.50 0.0290 * B-酶底比 8.34 1 8.34 0.50 0.5018 C-温度 41.59 1 41.59 2.50 0.1579 AB 123.88 1 123.88 7.44 0.0294 * AC 0.13 1 0.13 0.01 0.9331 BC 1.68 1 1.68 0.10 0.7602 A2 289.82 1 289.82 17.41 0.0042 * B2 22.30 1 22.30 1.34 0.2850 C2 15.91 1 15.91 0.96 0.3607 残差 116.50 7 16.64 失拟项 95.94 3 31.98 6.22 0.0548 不显著 纯误差 20.56 4 5.14 总和 765.50 16 注:*:P<0.05,表示差异显著。 2.2.2 回归方程的建立与检验
利用软件(Design Expert V 8.0.6.1)对表2的实验结果进行拟合,得到二次多项回归方程:Y=87.44+3.95A−1.02B+2.28C−5.57AB−0.18AC+0.65BC−8.30A2−2.30B2−1.94C2。
对拟合出的回归模型进行显著性检验(见表3),该模型的F值为4.33,P=0.0331<0.05,表明该模型较显著,失拟项P=0.0548>0.05,不显著。说明未知因素对试验结果的影响较小;即该模型在被研究的整个回归区域内拟合较好,可用于预测酶解产物的ACE抑制率,所得二次回归方程可用于拟合三个参数和响应值间的关系[47-48]。
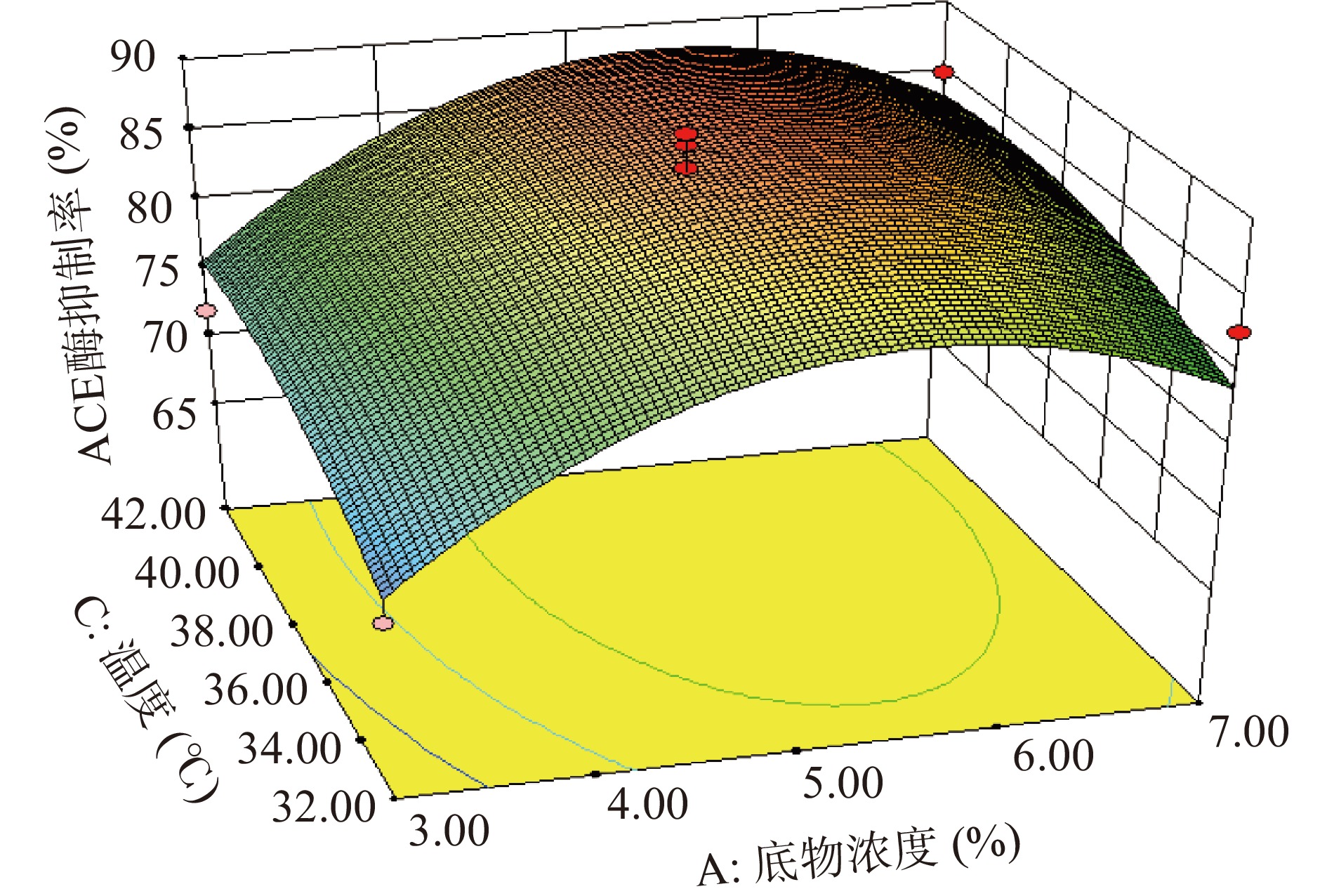
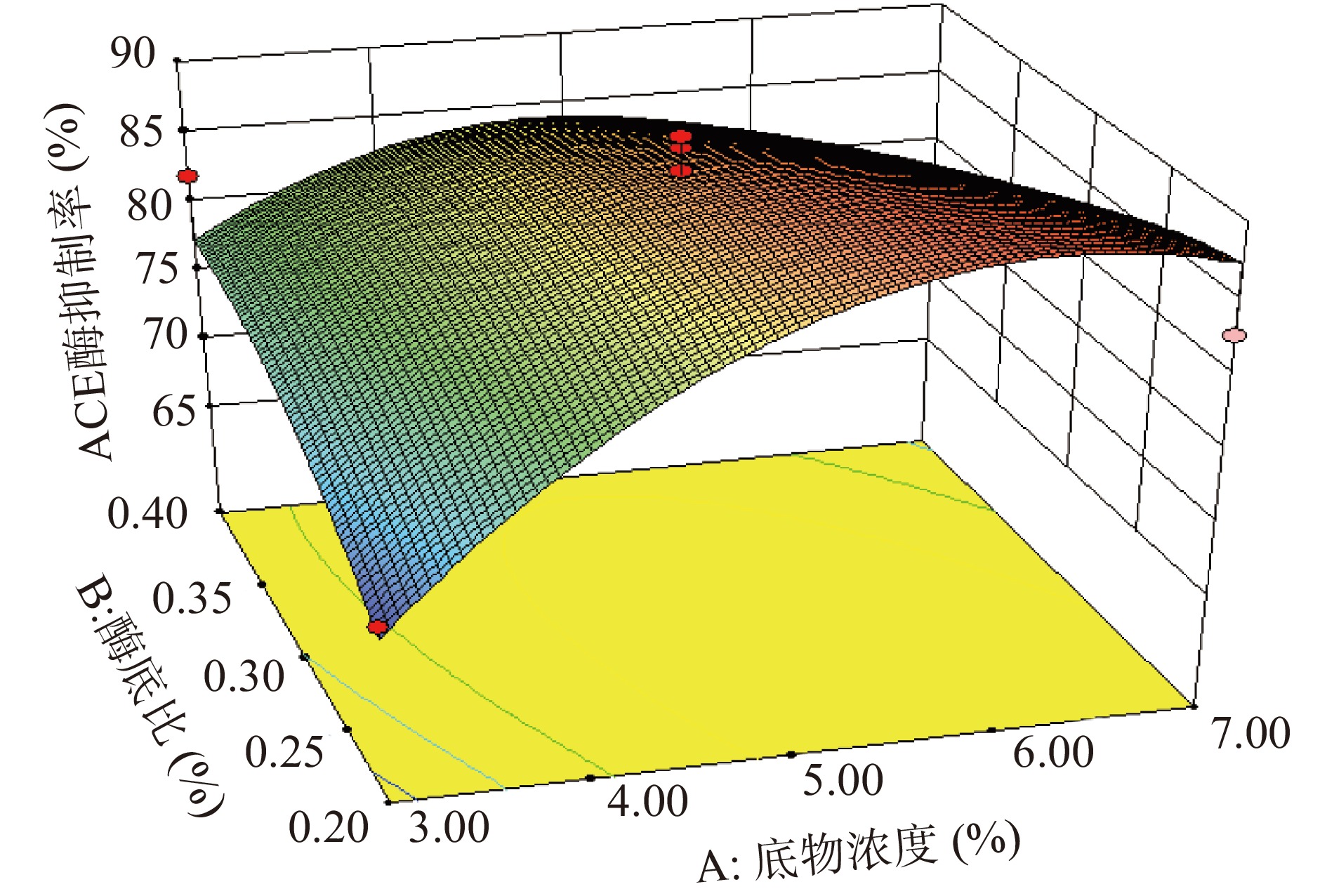
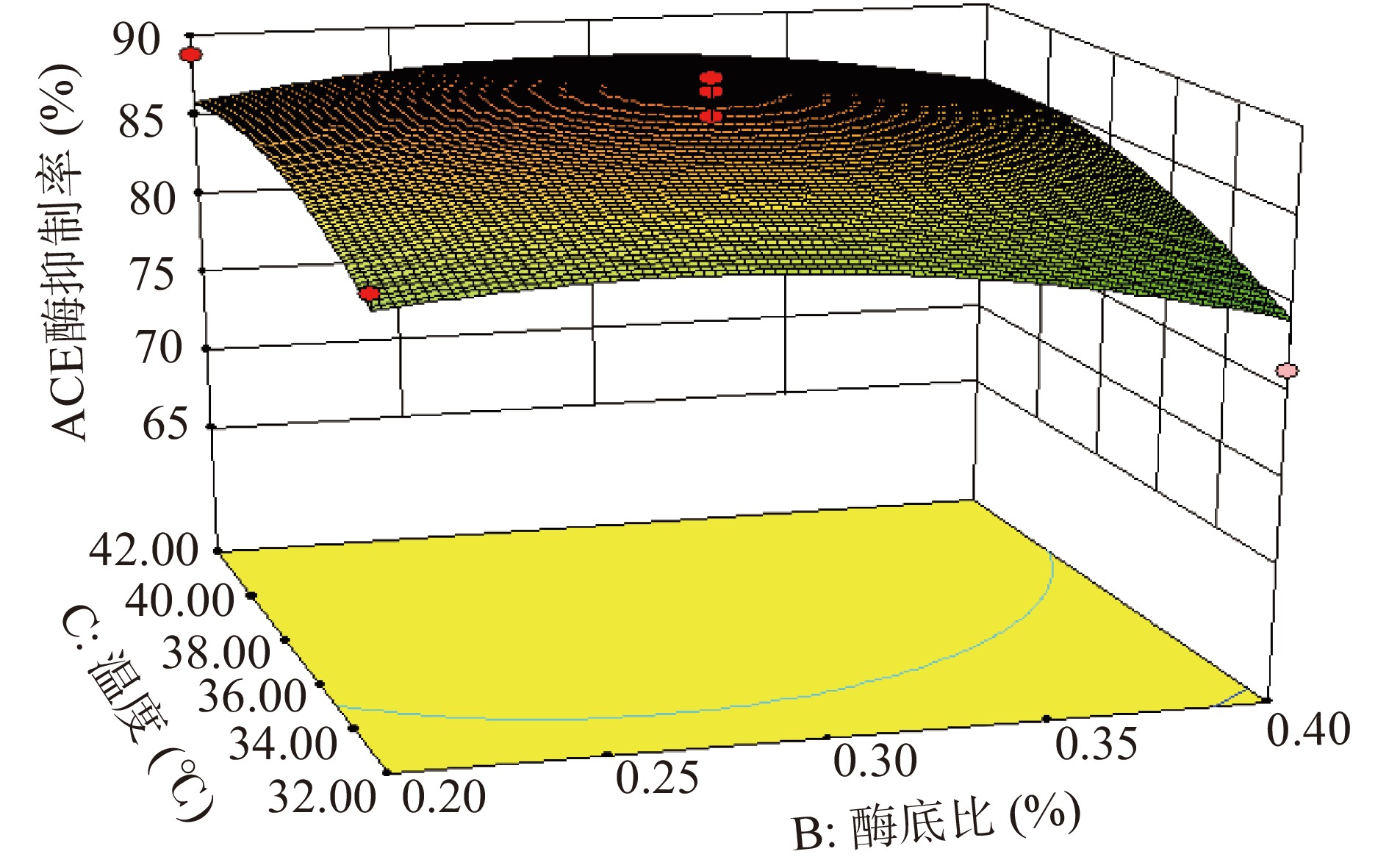
观察单个变量以及变量间两两组合的P值,发现单个变量中底物浓度对响应值的影响最为显著,酶底比及温度对响应值的影响不显著;根据P值推测三个因素对酶解液ACE抑制率的影响程度为:底物浓度>温度>酶底比。二次项中AB的P=0.0294<0.05,说明底物浓度和酶底比间的交互作用对ACE抑制率存在显著影响。变异系数(Coefficient of Variance,CV)反映模型的置信度,CV值越低模型的置信度越高[49];当变异系数<10%时,模型是可靠的[50],本实验的CV值为5%,说明模型方程能够很好地反映真实的实验值。综上,本实验所得出的模型有较好的可靠性,可以应用于后续的预测之中。响应面交互作用(图6~图8)结果表明,AB对抑制率的影响显著,其他因素交互作用不显著。
通过Design-Expert V 8.0.6.1软件分析及预测,得到胰蛋白酶酶解富硒辣木叶蛋白制备ACE抑制肽的最佳工艺参数:底物浓度5.97%、酶底比0.23%、温度39.2 ℃。对最优工艺进行验证,将酶解参数设定为底物浓度5.97%、酶底比0.23%、温度39.2 ℃,酶解时间3 h,pH7.5,酶解产物的实际ACE抑制率为88.97%,接近预测值89.27%,说明该回归模型对试验结果的分析预测准确。
2.3 富硒辣木叶蛋白肽ACE抑制活性分析
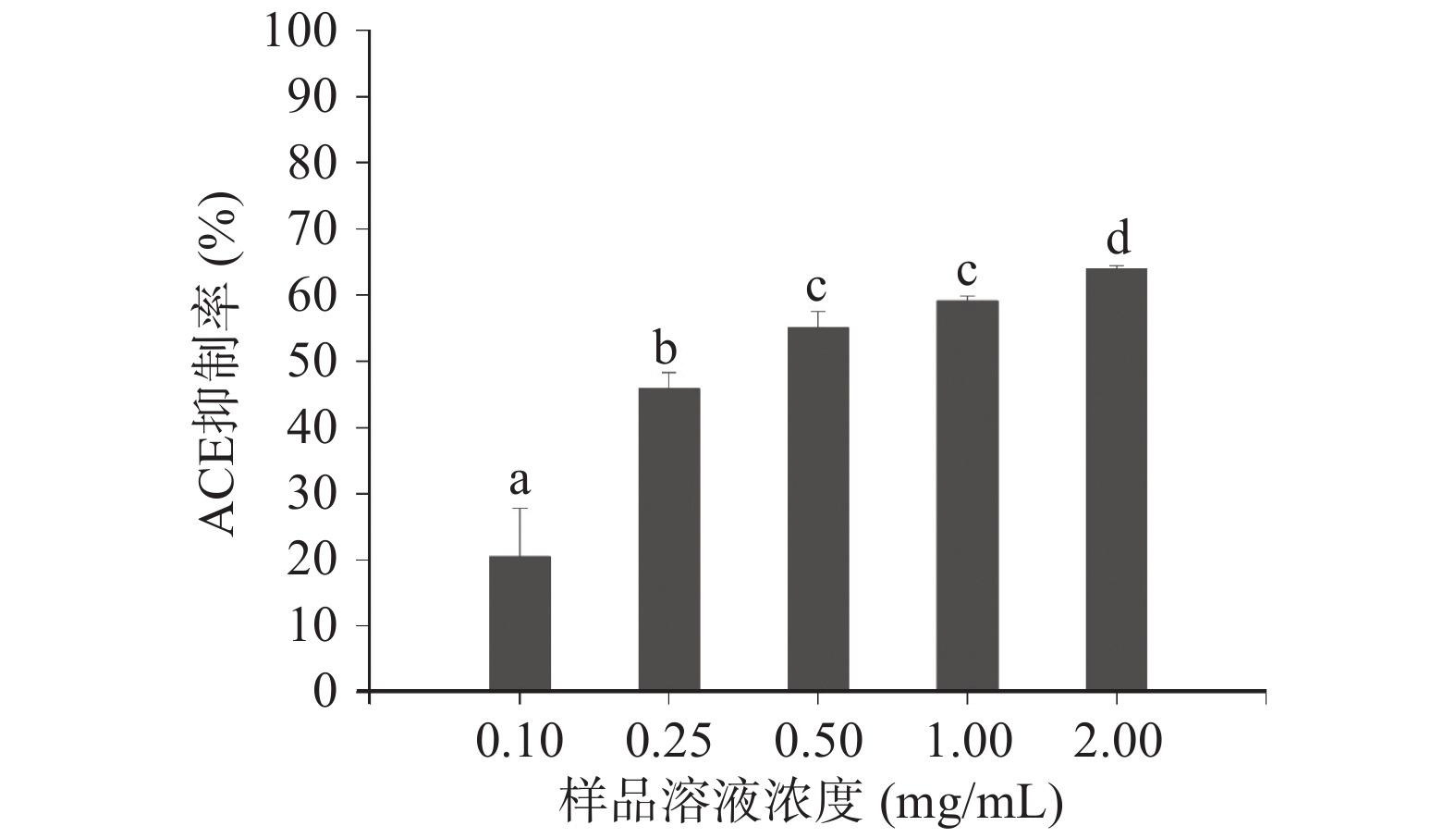
图9可见,ACE抑制率与样品的浓度呈现正相关关系,浓度的升高会提高ACE抑制率,呈现剂量依赖性。在样品溶液浓度为0.5 mg/mL时,ACE抑制率已经超过50%;在浓度达到2 mg/mL时,ACE抑制率达到了65.98%;利用SPSS软件得到该条件下富硒辣木叶ACE抑制肽的IC50为0.522 mg/mL。封张萍等[51]通过胰蛋白酶水解大米蛋白制备ACE抑制肽,测得经大孔树脂吸附后大米ACE抑制肽的IC50值为1.571 mg/mL。Wang等[52]用响应面法优化毛虾的发酵工艺,检测所得到发酵产物的ACE抑制能力,在最优发酵条件下发酵产物的IC50值为3.370 mg/mL。综上,酶解制备的富硒辣木叶蛋白ACE抑制肽在还未进行进一步分离纯化时便具有较好的ACE抑制能力,预计后续通过进一步筛选可以得到ACE抑制效果更好的单体。
2.4 氨基酸组成分析
富硒辣木叶蛋白酶解物的氨基酸组成见表4。在17种氨基酸中有7种人体必需氨基酸,占比为24.05%。单种氨基酸谷氨酸含量最多,占比7.89%,其次为占比6.31%的天冬氨酸,这一结果和大蒜降压肽[31]以及鱼类和贝类的降压肽[53-54]中的结果相似。此外,研究表明降血压肽分子中的疏水性氨基酸较为重要,其侧链可与ACE受体紧密结合,因而ACE抑制活性较强[55-56]。Miyoshi等[57]研究表明,ACE倾向于与含有疏水性氨基酸的底物结合。另外组成多肽的氨基酸亲疏水性和多肽的立体化学构象影响其ACE抑制肽的活性,这是受到ACE的C端结构域为疏水性环境所影响的[58];并且多肽中疏水性氨基酸的含量以及所在位置对多肽的空间结构也会存在影响,因此疏水性氨基酸的含量会对ACE抑制肽的活性造成重大影响[59]。实验分析也表明,富硒辣木叶蛋白酶解物的疏水性氨基酸含量较高,达20.6%,这与其较高的ACE抑制活性具有密切联系。
表 4 富硒辣木叶蛋白酶解物的氨基酸组成Table 4. Amino acid composition of Se-enriched M. oleifera leaves protein hydrolysate氨基酸种类 含量(%) 天冬氨酸(Asp) 6.31±0.16 苏氨酸(Thr) 3.09±0.01 丝氨酸(Ser) 2.91±0.08 谷氨酸(Glu) 7.89±0.12 甘氨酸(Gly) 3.48±0.44 丙氨酸(Ala) 3.81±0.10 胱氨酸(Cys) 0.19±0.02 缬氨酸(Val) 4.05±0.11 蛋氨酸(Met) 1.10±0.04 异亮氨酸(Ile) 3.03±0.25 亮氨酸(Leu) 5.52±0.31 酪氨酸(Tyr) 2.77±0.17 苯丙氨酸(Phe) 3.60±0.08 组氨酸(His) 2.10±0.02 赖氨酸(Lys) 3.30±0.05 精氨酸(Arg) 3.10±0.11 脯氨酸(Pro) 3.54±0.04 疏水性氨基酸含量 20.6±0.42 碱性氨基酸含量 8.5±0.36 必需氨基酸含量 24.05±0.40 总氨基酸 59.79±0.52 注:疏水性氨基酸:Val,Ile,Leu,Ala,Phe,Met,Pro,Trp;碱性氨基酸:Arg,His,Lys;必需氨基酸:Thr,Val,Met,Ile,Leu,Phe,Lys。 2.5 硒含量分析
由表5可知,富硒辣木叶原料,富硒辣木叶提取蛋白和富硒辣木叶ACE抑制肽中硒含量分别为9.84、16.32、18.31 mg/kg。这一结果说明富硒辣木叶中的硒元素主要与蛋白结合,并且酶解工艺优化研究使硒含量在活性肽中进一步富集。与其他富硒产品相比,辣木叶中的硒含量是一些富硒大米的58倍[60],辣木叶蛋白的硒含量是富硒玉米籽蛋白的2倍[61],且富硒辣木叶肽的硒含量是富硒大米肽的7.8倍[62],表明富硒辣木叶是一种硒含量较高的植物资源。有关研究发现,硒可以通过直接清除氧自由基、构成谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶、保护血管内皮细胞等机制防治高血压与冠心病[12],所以硒的含量也可能是影响酶解产物ACE抑制活性的重要因素之一。因此硒蛋白及其原料辣木叶粉制备的含硒ACE抑制肽将是辣木叶中极具开发潜力的含硒生物活性物质。
表 5 不同样品的硒含量Table 5. Se content of different samples样品名称 硒含量(mg/kg) 富硒辣木叶 9.84±0.23 富硒辣木叶提取蛋白 16.32±0.08 富硒辣木叶ACE抑制肽 18.31±0.10 3. 结论
通过碱溶酸沉法提取制备富硒辣木叶蛋白,在单因素实验基础上,采用响应面设计进行试验优化,确定胰蛋白酶酶解富硒辣木叶蛋白制备ACE抑制肽的最佳工艺条件为:pH7.5、底物浓度5.97%、酶底比0.23%、温度39.2 ℃,酶解时间3 h,此时ACE抑制率为88.97%。并对最优酶解条件下得到的酶解液冻干粉进行体外ACE抑制率测定,结果显示富硒辣木叶蛋白酶解物具有较强的ACE抑制能力(IC50=0.522 mg/mL);氨基酸分析结果表明,该酶解物的天冬氨酸、谷氨酸含量及疏水性氨基酸含量丰富;同时富硒辣木叶蛋白制备的ACE抑制肽的硒含量丰富(18.31 mg/kg)。本研究为富硒辣木叶在相关功能性食品领域的开发提供了理论依据。
-
表 1 响应面试验因素水平表
Table 1 Factors and levels table of response surface experiment
因素 水平 −1 0 1 A 底物浓度(%) 3 5 7 B 酶底比(%) 0.2 0.3 0.4 C 温度(℃) 32 37 42 表 2 响应面设计方案及结果
Table 2 Design and results of the response surface experiment
试验号 因素 ACE抑制率(%) A底物浓度(%) B酶底比(%) C温度
(℃)1 0 0 0 89.23 2 0 0 0 87.79 3 0 −1 −1 83.48 4 1 −1 0 82.76 5 −1 1 0 82.05 6 −1 0 −1 69.12 7 0 0 0 84.92 8 −1 −1 0 69.12 9 0 0 0 85.3 10 1 1 0 73.43 11 0 1 −1 76.3 12 0 1 1 84.2 13 0 −1 1 88.79 14 0 0 0 89.95 15 1 0 −1 82.76 16 1 0 1 84.92 17 −1 0 1 71.99 表 3 响应面二次模型方差分析
Table 3 Analysis of variance for response surface quadratic model
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F P 显著性 模型 649.00 9 72.11 4.33 0.0331 * A-底物浓度 124.74 1 124.74 7.50 0.0290 * B-酶底比 8.34 1 8.34 0.50 0.5018 C-温度 41.59 1 41.59 2.50 0.1579 AB 123.88 1 123.88 7.44 0.0294 * AC 0.13 1 0.13 0.01 0.9331 BC 1.68 1 1.68 0.10 0.7602 A2 289.82 1 289.82 17.41 0.0042 * B2 22.30 1 22.30 1.34 0.2850 C2 15.91 1 15.91 0.96 0.3607 残差 116.50 7 16.64 失拟项 95.94 3 31.98 6.22 0.0548 不显著 纯误差 20.56 4 5.14 总和 765.50 16 注:*:P<0.05,表示差异显著。 表 4 富硒辣木叶蛋白酶解物的氨基酸组成
Table 4 Amino acid composition of Se-enriched M. oleifera leaves protein hydrolysate
氨基酸种类 含量(%) 天冬氨酸(Asp) 6.31±0.16 苏氨酸(Thr) 3.09±0.01 丝氨酸(Ser) 2.91±0.08 谷氨酸(Glu) 7.89±0.12 甘氨酸(Gly) 3.48±0.44 丙氨酸(Ala) 3.81±0.10 胱氨酸(Cys) 0.19±0.02 缬氨酸(Val) 4.05±0.11 蛋氨酸(Met) 1.10±0.04 异亮氨酸(Ile) 3.03±0.25 亮氨酸(Leu) 5.52±0.31 酪氨酸(Tyr) 2.77±0.17 苯丙氨酸(Phe) 3.60±0.08 组氨酸(His) 2.10±0.02 赖氨酸(Lys) 3.30±0.05 精氨酸(Arg) 3.10±0.11 脯氨酸(Pro) 3.54±0.04 疏水性氨基酸含量 20.6±0.42 碱性氨基酸含量 8.5±0.36 必需氨基酸含量 24.05±0.40 总氨基酸 59.79±0.52 注:疏水性氨基酸:Val,Ile,Leu,Ala,Phe,Met,Pro,Trp;碱性氨基酸:Arg,His,Lys;必需氨基酸:Thr,Val,Met,Ile,Leu,Phe,Lys。 表 5 不同样品的硒含量
Table 5 Se content of different samples
样品名称 硒含量(mg/kg) 富硒辣木叶 9.84±0.23 富硒辣木叶提取蛋白 16.32±0.08 富硒辣木叶ACE抑制肽 18.31±0.10 -
[1] WU J J, XIE D W, CHEN X J, et al. Inhibitory mechanism of a substrate-type angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide[J]. Process Biochemistry,2019,79:97−104. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2018.12.018
[2] 陈秋銮, 陈雪芹, 马倩, 等. 酶解法制备牡丹籽ACE抑制肽及其稳定性[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(19):149−156. [CHEN Q L, CHEN X Q, MA Q, et al. Preparation and stability of ACE inhibitory peptides from peony seed meal by enzymatic hydrolysis[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(19):149−156. [3] HANAFI M A, HASHIM S N, YEA C S, et al. High angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity of alcalase-digested green soybean (Glycine max) hydrolysates[J]. Food Research International,2018,106:589−597. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.01.030
[4] LEE S Y, HUR S J. Antihypertensive peptides from animal products, marine organisms, and plants[J]. Food chemistry,2017,228:506−517. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.02.039
[5] 李姣, 苏继磊, 陈敏, 等. 马氏珍珠贝肉蛋白水解特征及其ACE抑制肽的筛选[J]. 食品科学,2021:1−13. [LI J, SU J L, CHEN M, et al. Hydrolysis characterization of Pinctada fucata (P. fucata) meat protein and screening for the ACE inhibitory peptides[J]. Food Science,2021:1−13. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20210108-084 [6] 姜瞻梅, 田波, 吴刚, 等. 酶解牛乳酪蛋白制备ACE抑制肽的研究[J]. 中国食品学报,2007(6):39−43. [JIANG Z M, TIAN B, WU G, et al. Studies on the preparation of ACE inhibitory peptides from enzymic hydrolysate of milk casein[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2007(6):39−43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7848.2007.06.007 [7] CHEN J W, LIU S S, YE R, et al. Angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory tripeptides from rice protein hydrolysate: purification and characterization[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2013,5(4):1684−1692. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2013.07.013
[8] 余虹, 操德群, 何艳丽, 等. 龙须菜蛋白酶解制备ACE抑制肽的工艺优化[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2019,38(2):133−139. [YU H, CAO D Q, HE Y L, et al. Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis conditions for production of ACE inhibitory peptides[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology,2019,38(2):133−139. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2019.02.019 [9] WANG C, TU M L, WU D, et al. Identification of an ACE-inhibitory peptide from walnut protein and its evaluation of the inhibitory mechanism[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2018,19(4):1156. doi: 10.3390/ijms19041156
[10] LIU X Q, MIAO X Y, WU D, et al. Purification and identification of ACE-inhibiting peptides from wild pine nut peptide fractions (PNPF)[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2018,244(6):979−988. doi: 10.1007/s00217-017-2987-y
[11] 贾蕾, 向极钎, 殷红清, 等. 生物活性硒肽的研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2021(15):346−355. [JIA L, XIANG J Q, YIN H Q, et al. Research progress of bioactive selenium-containing peptides[J]. Food Science,2021(15):346−355. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200428-368 [12] 时盼盼, 王芙蓉. 微量元素硒与高血压、冠心病相关性研究进展[J]. 社区医学杂志,2018,16(1):77−79. [SHI P P, WANG F R. Research progress on the correlation between selenium and hypertension and coronary heart disease[J]. Journal of Community Medicine,2018,16(1):77−79. [13] LIU K L, ZHAO Y, CHEN F S, et al. Purification and identification of Se-containing antioxidative peptides from enzymatic hydrolysates of Se-enriched brown rice protein[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,187:424−430. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.04.086
[14] FANG Y, CHEN X, LUO P Z, et al. The correlation between in vitro antioxidant activity and immunomodulatory activity of enzymatic hydrolysates from selenium-enriched rice protein[J]. Journal of Food Science,2017,82(2):517−522. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.13595
[15] 高冬芳, 张逸波, 凌钦婕, 等. 富硒螺旋藻多肽对血管紧张素转化酶的抑制作用[J]. 食品科学,2011,32(7):7−1. [GAO D F, ZHANG Y B, LING Q J, et al. Angiotensin convert enzyme inhibition of peptides derived from water soluble total protein of selenium-enriched Spirulina platensis[J]. Food Science,2011,32(7):7−1. [16] 王韵, 蔡智辉, 张逸波, 等. 富硒螺旋藻蛋白水解多肽的制备及其对ACE活性的抑制作用[J]. 现代食品科技,2013,29(7):1574−1579. [WANG Y, CAI Z H, ZHANG Y B, et al. Preparation of polypeptides by hydrolysis of selenium-enriched Spirulina protein and their inhibitory activity for angiotensin-converting enzyme[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2013,29(7):1574−1579. [17] 杜梦珂. 富硒碱性茶蛋白ACE抑制肽的制备、分离纯化及结构鉴定[D]. 上海: 上海师范大学, 2018. DU M K. Study on the preparation, purification and identification of ACE inhibitory activity peptides from se-enriched tea protein[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Normal University, 2018.
[18] 张能荣. 辣木的成分和药理[J]. 办公自动化,2018,23(2):17−21. [ZHANG N R. The composition and pharmacology of Moringa[J]. Office Informatization,2018,23(2):17−21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-001X.2018.02.004 [19] 汪泰, 顾文宏, 何军, 等. 辣木新资源食品研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(8):364−368. [WANG T, GU W H, HE J, et al. Advance of Moringa oleifera food as a new resource[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(8):364−368. [20] 冉隆中. 现代辣木生物学[M]. 昆明: 云南科技出版社, 2015. RAN L Z. Biology of modern Moringa oleifera[M]. Kunming: Yunnan Science and Technology Press, 2015.
[21] 郭刚军, 胡小静, 徐荣, 等. 辣木叶酶法水解提取蛋白质工艺优化[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(5):194−199. [GUO G J, HU X J, XU R, et al. Process optimization of protein extraction from Moringa oleifera leaf by enzymatic hydrolysi[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(5):194−199. [22] 巩思佳, 康澳, 陈可菁, 等. 辣木叶的营养、功能及应用研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技, 2021: 1−12. DOI: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020100030. GONG S J, KANG A, CHEN K J, Research progress on nutrition, function and application of Moringa Oleifera leaves[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021: 1−12. DOI: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020100030.
[23] 郭妍. 辣木叶植物化学物质分析及体外生物活性研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2018. GUO Y. Analysis of plant chemical constituents and in vitro bioactivity of Moringa oleifera leaves[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2018.
[24] FALOWO A B, MUKUMBO F E, IDAMOKORO E M, et al. Multi-functional application of Moringa oleifera Lam. in nutrition and animal food products: A review[J]. Food Research International,2018,106:317−334. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2017.12.079
[25] 康丹丹, 李照莹, 董浩澜, 等. 辣木叶蛋白质酶解产物的制备及其抗菌活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(8):114−119. [KANG D D, LI Z Y, DONG H L, et al. Preparation of enzymatic hydrolysis products from Moringa oleifera leaves protein and its antibacterial activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(8):114−119. [26] LIU L Z, ZHU Q Y, ZHAO M M, et al. Purification of peptide fraction with antioxidant activity from Moringa oleifera leaf hydrolysate and protective effect of its in vitro gastrointestinal digest on oxidatively damaged erythrocytes[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2019,54(1):84−91.
[27] TIAN Y C, LIN L Z, ZHAO M M, et al. Xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity and antihyperuricemic effect of Moringa oleifera Lam. leaf hydrolysate rich in phenolics and peptides[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2021,270:113808. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.113808
[28] 祝素莹, 朱瑜, 张银志, 等. 复合蛋白酶水解核桃粕制备血管紧张素转化酶抑制肽工艺优化[J]. 食品研究与开发,2020,41(17):56−63. [ZHU S Y, ZHU Y, ZHANG Y Z, et al. Optimization of complex protease hydrolysis for preparation of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from walnut dregs[J]. Food Research and Development,2020,41(17):56−63. [29] 赵爽, 刘昆仑, 陈复生. 酶法制备富硒糙米抗氧化肽的研究[J]. 河南工业大学学报(自然科学版),2017,38(5):5−10. [ZHAO S, LIU K L, CHEN F S. Preparation of antioxidant peptides from Se-enriched brow rice by enzymatic hydrolysis[J]. Journal of Henan University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2017,38(5):5−10. [30] 骆琳, 丁青芝, 马海乐. 96孔板法用于高通量血管紧张素转化酶抑制剂体外检测[J]. 分析化学,2012,40(1):129−134. [LUO L, DING Q Z, MA H L. Establishment ofin vitro high-throughput activity detection method for angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors based on 96 well plates[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry,2012,40(1):129−134. [31] 宋凯强, 刘鹏莉, 郑振佳, 等. 大蒜降压肽的制备及超滤分离[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(19):73−80. [SONG K Q, LIU P L, ZHENG Z J, et al. Preparation and ultrafiltration separation of garlic antihypertensive peptide[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(19):73−80. [32] 曾钰鹏, 易嘉鸣, 李瑶璐, 等. 辣木富硒低糖酸奶的加工工艺研究[J]. 食品与发酵科技,2020,56(5):22−29. [ZENG Y P, YI J M, LI Y L, et al. Study on processing technology of Moringa oleifera selenium-enriched low-sugar yogurt[J]. Food and Fermentation Sciences & Technology,2020,56(5):22−29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-506X.2020.05.004 [33] SUN Z L, QIN H L, CAO D, et al. Optimization of hydrolysis conditions for the isolation of angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from Rhopilema hispidum[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China,2018,17(6):1458−1464. doi: 10.1007/s11802-018-3666-8
[34] 侯成杰, 聂彩清, 王彦茜, 等. α-乳白蛋白源ACE抑制肽快速筛选及验证[J]. 食品科学,2020:1−12. [HOU C J, NIE C Q, WANG Y Q, et al. Accurate screening and verification of α-lactalbumin-derived ACE inhibitory peptides[J]. Food Science,2020:1−12. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20201012-094 [35] GU Y Y, MAJUMDER K, WU J P. QSAR-aided in silico approach in evaluation of food proteins as precursors of ACE inhibitory peptides[J]. Food Research International,2011,44(8):2465−2474. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2011.01.051
[36] JING P, QIAN B J, HE Y W, et al. Screening milk-derived antihypertensive peptides using quantitative structure activity relationship (QSAR) modelling and in vitro/in vivo studies on their bioactivity[J]. International Dairy Journal,2014,35(1):95−101. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2013.10.009
[37] 张杨, 胡磊, 汪少芸, 等. 响应面优化酶解法制备蒲公英籽蛋白抗氧化肽工艺[J]. 食品工业科技,2016,37(5):258−262. [ZHANG Y, HU L, WANG S Y, et al. Optimization of enzymolysis technology for preparation of antioxidant peptides from dandelion seeds-derived proteins by response surface methodology[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2016,37(5):258−262. [38] 殷海洋, 刘振春, 张世康, 等. 响应面优化超声波辅助酶法提取油莎豆ACE抑制肽的工艺[J]. 食品工业科技,2021:1−10. [YIN H Y, LIU Z C, ZHANG S K, et al. Response surface optimization of ultrasonic-assisted enzymatic extraction of ACE inhibitory peptides from cyperus esculentus[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021:1−10. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020100130 [39] QU W J, MA H L, PAN Z L, et al. Preparation and antihypertensive activity of peptides from Porphyra yezoensis[J]. Food Chemistry,2010,123(1):14−20. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.03.091
[40] 马倩, 潘梦莹, 陈秋銮, 等. 奇亚籽蛋白酶解制备抗氧化肽的工艺优化[J]. 食品研究与开发,2021,42(3):122−129. [MA Q, PAN M Y, CHEN Q L, et al. Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis of chia seed protein to prepare antioxidant peptides[J]. Food Research and Development,2021,42(3):122−129. [41] 毛跟年, 周亚丽, 贺磊, 等. 魔芋ACE抑制肽酶法制备工艺研究[J]. 食品工业,2017,38(1):99−102. [MAO G N, ZHOU Y L, HE L, et al. Enzymatic preparation of konjac ACE inhibitory peptides[J]. The Food Industry,2017,38(1):99−102. [42] 殷金莲, 靳毓. 酶解法制备榛子粕ACE抑制肽工艺研究[J]. 中国油脂,2020,45(1):68−72. [YIN J L, JIN Y. Preparation of ACE inhibitory peptide from hazelnut meal by enzymatic hydrolysis[J]. China Oils and Fats,2020,45(1):68−72. doi: 10.12166/j.zgyz.1003-7969/2020.01.015 [43] 安婷婷, 陈丽美, 邓长春, 等. 翡翠贻贝降血压肽酶解制备工艺研究[J]. 安徽农业科学,2020,48(10):137−140. [AN T T, CHEN L M, DENG C C, et al. Study on the enzymatic hydrolysis of antihypertensive peptide from Perna viridis[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2020,48(10):137−140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2020.10.037 [44] HUANG L, LIU B, MA H, et al. Combined effect of ultrasound and enzymatic treatments on production of ACE inhibitory peptides from wheat germ protein[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation,2014,38(4):1632−1640. doi: 10.1111/jfpp.12125
[45] 徐杨林, 严宏孟, 高蕾, 等. 苦杏仁醇溶蛋白酶解抗氧化肽的制备工艺优化[J]. 现代食品科技,2021,37(6):201−210. [XU Y L, YAN H M, GAO L, et al. Optimizing antioxidant peptide preparation using the proteolysis of the prolamins produced by Prunus dulcis var. amara[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2021,37(6):201−210. [46] 吴红洋, 姜太玲, 胡惠茗, 等. 响应面法优化酶解花椒籽蛋白制备降血压肽工艺[J]. 食品科学,2014,35(21):180−185. [WU H Y, JIANG T L, HU H M, et al. Response surface methodology for optimization of hydrolysis conditions for preparing antihypertensive peptides Sichuan pepper (Zanthoxylum bungeanum) seed protein[J]. Food Science,2014,35(21):180−185. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201421035 [47] SIN H N, YUSOF S, SHEIKH A H N, et al. Optimization of hot water extraction for sapodilla juice using response surface methodology[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2005,74(3):352−358.
[48] 李莉, 张赛, 何强, 等. 响应面法在试验设计与优化中的应用[J]. 实验室研究与探索,2015,34(8):41−45. [LI L, ZHANG S, HE Q, et al. Application of response surface methodology in experiment design and optimization[J]. Research and Exploration in Laboratory,2015,34(8):41−45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7167.2015.08.011 [49] 代文亮, 程龙, 陶文沂. 响应面法在紫杉醇产生菌发酵前体优化中的应用[J]. 中国生物工程杂志,2007,27(11):66−72. [DAI W L, CHENG L, TAO W Y. Application of response surface methodology in optimization of precursors for taxol production by Fusarium mairei K178[J]. China Biotechnology,2007,27(11):66−72. [50] 肖怀秋, 李玉珍, 林亲录, 等. Box-Behnken响应面优化冷榨花生粕酶解制备花生肽工艺[J]. 中国粮油学报,2014,29(10):106−111. [XIAO H Q, LI Y Z, LIN Q L, et al. Optimization of polypeptide preparation parameters from cold-pressed peanut meal by Box-Behnken response surface methodology[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2014,29(10):106−111. [51] 封张萍, 岳阳, 刘东红, 等. 大米ACE抑制肽制备工艺优化和生物活性研究[J]. 食品科技,2021,46(2):210−217. [FENG Z P, YUE Y, LIU D H, et al. Optimization of preparation and bioactivity of rice ACE inhibitory peptides[J]. Food Science and Technology,2021,46(2):210−217. [52] WANG Y K, HE H L, CHEN X L, et al. Production of novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides by fermentation of marine shrimp Acetes chinensis with Lactobacillus fermentum SM 605[J]. Biotechnologically Relevant Enzymes and Proteins,2008,79(5):785−791.
[53] ARIHARA K, NAKASHIMA Y, MUKAI T, et al. Peptide inhibitors for angiotensin I-converting enzyme from enzymatic hydrolysates of porcine skeletal muscle proteins[J]. Meat Science,2001,57(3):319−324. doi: 10.1016/S0309-1740(00)00108-X
[54] 毋瑾超, 汪依凡, 方长富. 贻贝蛋白酶解降血压肽的降压活性及相对分子质量与氨基酸组成[J]. 水产学报,2007(2):165−170. [WU J C, WANG Y F, FANG C F. Antihypertensive function and relative molecular weight as well as component of amino acids of antihypertensive peptide prepared from protein of mytilus coruscus[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China,2007(2):165−170. [55] 王泽奇, 杨双盼, 冉旭. 大鲵肌肉ACE抑制肽的制备及其稳定性[J]. 食品工业,2020,41(4):123−127. [WANG Z Q, YANG S P, RAN X. The preparation ACE inhibitory peptide from by Andrias davidianus by mixture design and its stability[J]. The Food Industry,2020,41(4):123−127. [56] MATSUI T, MATSUFUJI H, SEKI E, et al. Inhibition of angiotensin I-converting enzyme by Bacillus licheniformis alkaline protease hydrolyzates derived from sardine muscle[J]. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,1993,57(6):922−925. doi: 10.1271/bbb.57.922
[57] MIYOSHI S, ISHIKAWA H, KANEKO T, et al. Structures and activity of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in an alpha-zein hydrolysate[J]. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry,1991,55(5):1313−1318.
[58] 林凯, 韩雪, 张兰威, 等. ACE抑制肽构效关系及其酶法制备的研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(3):261−270. [LIN K, HAN X, ZHANG L W, et al. Progress in structure-activity relationship and enzymatic preparation of ACE inhibitory peptides[J]. Food Science,2017,38(3):261−270. [59] XUE L, YIN R X, HOWELL K, et al. Activity and bioavailability of food protein-derived angiotensin-I-converting enzyme-inhibitory peptides[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety,2021,20(2):1150−1187. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12711
[60] 刘波, 孟辉. 微波消解-氢化物发生原子荧光法测定保健食品中的硒含量[J]. 湖北农业科学,2008(2):223−225. [LIU B, MENG H. Determination of selenium in healthy food by hydride generation-atomic fluorescence spectrometry method[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences,2008(2):223−225. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0439-8114.2008.02.032 [61] 王真真. 富硒玉米蛋白水解物的制备、醒酒活性及结构研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2013. WANG Z Z. Preparation, activity and structures of se-enriched corn protein hydrolysates facilitating alcohol metabolism[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2013.
[62] 秦芸, 石沛霖, 刘维维, 等. 富硒大米肽体内抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(17):305−309. [QIN Y, SHI P L, LIU W W, et al. Antioxidant activity of the selenium-riched rice peptides in vivo[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(17):305−309.





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



