Research Progress of Mitochondrial-Mediated Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) Antioxidation
-
摘要: 二十二碳六烯酸(docosahexaenoic acid,DHA)是人体必需的ω-3多不饱和脂肪酸(polyunsaturated fatty acid,PUFA),在深海鱼油和海洋微藻中高度富集。线粒体是细胞的“能量工厂”,DHA可调节线粒体的功能和生物合成,发挥抗氧化、抗炎、抗癌等作用。本文主要就DHA调节线粒体抗氧化能力及其作用机制的研究进展进行综述,阐述DHA在消除活性氧(reactive oxygen species,ROS)、调节线粒体生物合成和功能方面的作用以及线粒体微小RNA(microRNA,miRNA)介导的DHA抗氧化表观遗传调控机制,为DHA相关产品的开发应用提供依据。
-
关键词:
- ω-3多不饱和脂肪酸 /
- 二十二碳六烯酸 /
- 线粒体 /
- 抗氧化 /
- 表观遗传
Abstract: Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is an essential omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) for human body, which is highly rich in deep sea fish oil and marine microalgae. Mitochondria are the energy factory of cells. Mitochondrial functions and biogenesis can be regulated by DHA which exhibits antioxidation, anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer activities. This article reviews the research progress of mitochondrial-mediated DHA antioxidation and the possible underlying mechanism. The effects of DHA in eliminating reactive oxygen species (ROS) and regulating mitochondrial biogenesis and functions, as well as the microRNA-mediated DHA antioxidant epigenetic mechanism are addressed, which may provide evidence for better DHA product exploration and application.-
Keywords:
- ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid /
- docosahexaenoic acid /
- mitochondria /
- antioxidation /
- epigenetics
-
活性氧(reactive oxygen species, ROS)是体内一类氧的单电子还原产物,包括超氧阴离子(O2−·)、羟自由基(·OH)和过氧化氢(H2O2)等。在线粒体进行细胞呼吸时,电子传递链(electron transport chain,ETC)复合物I和复合物III会产生O2−·、·OH等自由基。少量的自由基对细胞信号传导至关重要,但过量的自由基会引起线粒体损伤和氧化应激,进而引发心血管疾病、阿尔茨海默症等多种氧化相关疾病[1]。线粒体不仅是ROS产生的主要场所,还是ROS消除的主要细胞器,在细胞能量代谢、氧化还原平衡以及通透性转换中起重要调控作用[2-3]。
随着人们保健意识的增强,天然食源性抗氧化剂的开发利用逐渐成为当今一大热点。ω-3多不饱和脂肪酸(polyunsaturated fatty acids,PUFA)是人体必需的脂肪酸,主要包括α-亚麻酸(ALA)、二十碳五烯酸(EPA)、二十二碳五烯酸(DPA)以及二十二碳六烯酸(DHA)等长链不饱和脂肪酸[4]。DHA是典型的ω-3多不饱和脂肪酸,在深海鱼油和海洋微藻中高度富集。具有抗炎、抗癌、降血脂、免疫调节以及预防心血管疾等功效,DHA在食品保健、医学等领域得到了广泛应用[5-6]。此外,DHA有较强的抗氧化活性,可通过对多个信号通路的调节保护细胞免受氧化损伤:(1)通过ERK1/2信号通路激活线粒体自噬保护肝细胞免受氧化损伤[7];(2)激活PI3K/Akt信号通路,增强细胞抗氧化能力并维持细胞完整性[8];(3)激活NADPH氧化酶/ROS/Nrf2通路,诱导ARPE-19细胞表达血红素氧合酶-1,保护细胞免受氧化损伤[9-10]。
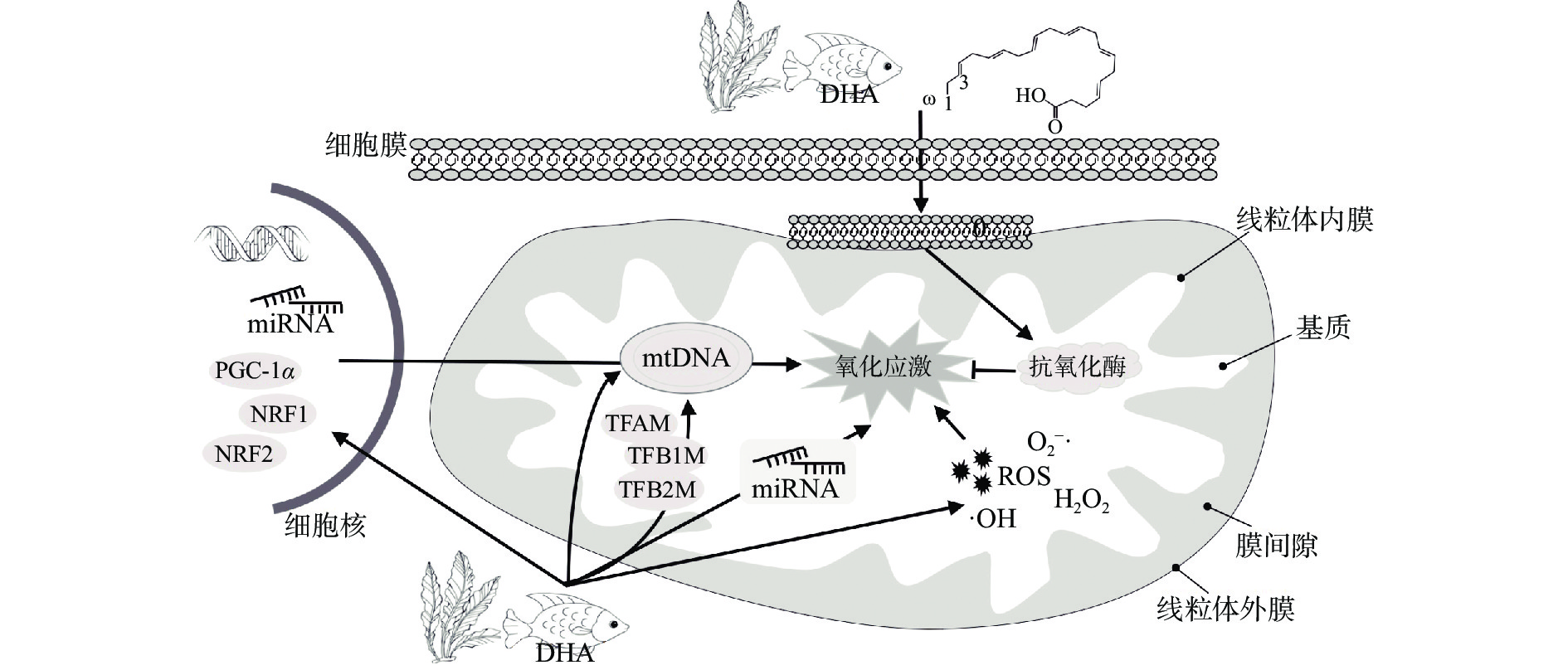
DHA因含有羧基结构,能与细胞及线粒体双层膜上的磷脂结合,影响膜蛋白的功能和脂筏信号传导[11-12]。人体补充鱼油12周后,富含DHA和EPA的ω-3 PUFA会渗入到线粒体膜中,导致线粒体膜上总磷脂、DHA和EPA的含量大大提高[13]。DHA可通过对线粒体的调控来影响细胞的生理活动。线粒体也是DHA调节氧化应激的主要靶点。线粒体介导DHA抗氧化作用的可能途径如图1所示。作为一种可以起防御作用的PUFA,DHA能够对抗体内自由基引起的氧化应激,提高抗氧化酶活性或表达,消除线粒体产生的ROS,调节细胞的氧化还原状态[2,14-15];DHA也可通过对细胞核及线粒体转录因子的调控促进线粒体生物合成并参与线粒体的表观遗传调控,增强线粒体功能[16-18]。作为一种食源性的抗氧化剂,DHA的抗氧化功能及应用已有不少报道,但其具体作用机理,特别是表观遗传的调控作用尚不明确。本文将围绕DHA对线粒体的调节及作用机制的研究进展进行综述,特别阐述线粒体表观遗传介导的调节机制,探讨DHA的抗氧化分子作用机理,为靶向线粒体的DHA膳食营养补充剂的开发利用提供依据。
1. DHA调节线粒体抗氧化酶的表达及活性
细胞内源性抗氧化系统(包括抗氧化酶和非酶抗氧化剂)可将有毒物质代谢成无害的副产物,代表着抵御这些有毒反应物的第一道防线。内源性抗氧化酶是生物体内抵抗自由基的主要成员,主要包括超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD)、过氧化氢酶(catalase,CAT)、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(glutathione peroxidase,GPx)、HO-1和维生素C等[19]。正常生理条件下,细胞的抗氧化系统可以保护细胞免受氧化损伤,而当环境因素改变导致氧分子氧化和O2−·产生时,特异性位于线粒体基质的锰型超氧化物歧化酶(Mn-SOD)可自身氧化还原O2−·产生H2O2,从而产生高活性的·OH,·OH可氧化胞内的DNA、RNA、蛋白质、脂质等物质,引起氧化应激并造成细胞损伤[20-21]。DHA能够通过作用SOD、CAT和GPx等酶来增加抗氧化活性,将H2O2转化为H2O,从而降低氧化损伤。因此,DHA可通过对线粒体抗氧化酶的调节来提高细胞的抗氧化能力。
DHA对线粒体抗氧化酶的调节方式是不同的,包括:a.提高抗氧化酶表达水平:DHA可通过诱导炎症细胞中CAT酶的表达降低ROS含量,减轻细胞氧化损伤[22];还可通过提高SOD和GPx酶的表达,预防H2O2诱导的PC12细胞氧化损伤[14];b.增强抗氧化酶的活性:DHA可通过增强红细胞中SOD和CAT酶的活性,降低患心血管疾病的风险[15];还可提高大脑中SOD和GPx酶活性,提高大脑组织的抗氧化性能,减轻神经元损伤[23-24]。前期研究发现,DHA可能通过上调线粒体中抗氧化酶基因(SOD2、CAT和GPx1)的表达水平,提高抗氧化酶的活性[16]。因此,DHA可能通过提高抗氧化酶活性或表达,改善氧化应激,发挥抗氧化作用。但也有研究显示,DHA对抗氧化酶有抑制作用。在HCC细胞中DHA可使谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4(GPx4)失活,促进细胞凋亡[25];DHA可降低卵巢癌细胞中SOD和GPx4的蛋白表达,引起脂质过氧化促进细胞凋亡[26]。在不同细胞系中DHA调节抗氧化酶的方式及效应不同,反映了不同体系中DHA作用机制的区别。DHA对线粒体抗氧化酶的具体调节机制仍有待明确。本文在总结DHA对线粒体抗氧化酶调节作用的基础上,进一步对DHA消除ROS、调节线粒体生物合成和稳态以及线粒体表观遗传调控作用的研究进展进行综述,阐述线粒体介导的DHA抗氧化分子机制,为揭示食品抗氧化剂的分子作用机制提供依据。
2. DHA抑制线粒体ROS的产生
ROS主要来源于线粒体呼吸链,其在生物系统中具有“双刃剑”效应:正常生理状态下其产生与清除处于动态平衡,此时较低生理浓度的ROS对正常的细胞信号传导起到至关重要的作用,还可上调抗氧化基因的表达以抵消氧化应激的影响;当外界条件改变打破这一平衡时,会导致其含量超过生理限度,此时,较高生理浓度和较长时间的ROS暴露除了对DNA、脂类和蛋白质等细胞大分子造成损伤外,还会破坏细胞结构,从而引起氧化损伤甚至导致细胞死亡[27]。
膳食补充ω-3 PUFA,特别是DHA,会影响线粒体膜磷脂结构和线粒体抗氧化功能。DHA进入细胞后可结合到线粒体膜上,维持正常线粒体结构并改变线粒体膜磷脂组成,从而影响线粒体膜通透性转换孔(mitochondrial permeability transition pore,MPTP)开放,减少质子泄露,抑制ROS产生[28-29]。在线粒体中参与ROS生成的主要酶系统是呼吸链,而呼吸链电子流动速率受ATP合成速率的限制,更准确的说是受特定偶联位点、即呼吸复合物Ⅰ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ的质子运输速率(Δp)限制。Δp的电成分即为跨膜电位(Δψm),提高Δψm可有效减少ROS产生。本团队的前期研究发现,DHA在HepG2细胞中可提高Δψm,降低ROS产生[30]。因此,DHA能通过多种途径降低细胞内线粒体的ROS水平并影响线粒体呼吸链,对细胞起一定的保护作用。DHA的作用方式包括:a.上调抗氧化酶基因表达,降低ROS水平,减少氧化应激,维持线粒体功能[31-32];b.影响反向电子传递,降低线粒体内膜的去极化,从而抑制反向电子传递依赖性ROS的产生[33];c.减弱MPTP对Ca2+的敏感性,减少MPTP瞬时开放来抑制ROS的产生[34];d.调节线粒体呼吸传递链,改善线粒体功能,抑制线粒体ROS的产生,消除ROS并维持正常的细胞代谢过程。但是,DHA通过调节线粒体ROS水平发挥抗氧化效用的结果还存在一些争议,具体机制也有待进一步明确。
3. DHA调节线粒体的生物合成和稳态
线粒体是ROS合成和消除的主要场所,对氧化应激极其敏感。当ROS的生成能力超过抗氧化防御能力时,过多的ROS攻击线粒体DNA(mtDNA),可能导致mtDNA损伤并伴随代谢功能紊乱[35]。线粒体并非单个作用的细胞器,可通过严格调控线粒体生物合成来维持其功能。线粒体合成涉及多个过程,包括mtDNA的复制和转录、翻译以及线粒体的融合、裂变、自噬等过程。线粒体能够通过生物合成产生新的线粒体,通过裂变自噬等清除功能失调的个体,还能通过融合作用产生连续的网络,修复受损个体、恢复活性从而维持代谢效率[36-38]。因此,维持正常的线粒体生物合成及稳态对细胞的抗氧化能力至关重要。不少研究表明,DHA参与线粒体的合成和稳态调节,对维持细胞正常生理活动、修复损伤的线粒体以及维持正常的线粒体形态和功能等起到一定的促进作用[39-40]。
3.1 DHA对线粒体生物合成的调节
线粒体生物合成包括mtDNA的复制、转录和翻译等,是一个受细胞核和线粒体相关因子严格调控的过程。多数线粒体转录调节因子可在DNA复制和转录水平调节线粒体生物合成,改善线粒体数量及质量,进而增强细胞对有害应激源的耐受阈值,在氧化应激调控中起重要作用。如过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ辅激活因子-1α(PGC-1α)是线粒体再生的一个重要调节因子,它可与调节线粒体生物合成所需的基因协同诱导线粒体生物合成并提高线粒体呼吸效率[41];细胞核呼吸因子(NRF1和NRF2)是线粒体生物合成调控网络的关键组成部分,控制编码细胞色素c和细胞色素c氧化酶亚基的基因表达;线粒体转录因子A(TFAM)及线粒体转录因子B1和B2(TFB1M和TFB2M)参与调节细胞色素氧化酶1-3(COX1-3)基因的转录,对线粒体DNA复制、转录和稳态维持发挥重要作用[42]。
DHA可通过多种方式调节线粒体的生物合成,特别是mtDNA的转录:a.DHA可提高C2C12成肌细胞的mtDNA拷贝数和PGC-1α启动子活性,促进NRF1、NRF2和TFAM表达,提高mtDNA复制和转录[43];b.DHA通过诱导PGC-1α及与线粒体融合相关的蛋白质的表达,提高线粒体的数量[44-45];c.DHA通过上调脑源性神经营养因子(BDNF)激活线粒体生物合成,维持正常的线粒体功能[46]。前期研究发现在HepG2细胞中DHA能增加mtDNA拷贝数、提高线粒体转录因子的表达[16]。
3.2 DHA对线粒体稳态的调节
线粒体是高度动态的双膜细胞器,线粒体稳态对其功能至关重要。在抵抗外界刺激的同时,细胞衍生出多种机制对自身受损或功能失调的线粒体进行修复或清除,以维持线粒体稳态并发挥正常的功能。线粒体为适应各种应激条件,通过不断分裂和融合促使其形成一个相互连接的网络结构,清除功能失调的个体,维持细胞正常生理活动的过程称为线粒体动力学[47]。该过程受线粒体融合蛋白1和2(MFN1和MFN2)、视神经萎缩蛋白-1(OPA1)和线粒体分裂蛋白-1(DRP1)等共同调控。DHA可能通过以下方式调节线粒体稳态:a.调控分裂融合蛋白的表达影响线粒体动态平衡,提高线粒体质量,维持其稳态。DHA可促进MFN1、MFN2和OPA1的表达,增强线粒体融合程度,限制DRP1的线粒体定位,从而有效降低线粒体损伤[39,48];b.修复损伤的线粒体维持其稳态。Zhang等[40]发现DHA可修复失衡的线粒体分裂和融合状态,增加整合线粒体的数量,维持线粒体稳态,提高细胞抗氧化能力。DHA对受损的线粒体表现出较强的修复及改善效果,有助于维持正常的线粒体功能,提高其抗氧化能力。
4. 线粒体表观遗传介导的DHA抗氧化作用
线粒体也受表观遗传调控。DHA可通过以下几种表观遗传调节方式影响线粒体功能或生物合成:a.调节DNA甲基化水平使电子传递链(ETC)上相关基因的转录减弱,导致ETC功能受损[49];b.参与调节组蛋白的化学修饰影响线粒体合成相关基因的表达及氧化磷酸化进程[50-51];c.调控microRNA(miRNA)表达影响线粒体能量代谢、细胞凋亡、分裂/融合等过程[52]。miRNA表达调控对线粒体功能及生物合成具有重要调节作用,线粒体内也存在大量的miRNA。DHA对miRNA、特别是线粒体miRNA的调控正引起日益关注。因此,本文主要从miRNA调控的角度探讨DHA的抗氧化机制。如表1所示,有不少miRNA靶向调控线粒体基因,在不同细胞系中发挥氧化应激调节作用(表1)。大多数线粒体miRNA由核基因编码形成,后被转运到线粒体基质中,在转录后水平调节线粒体蛋白表达进而影响线粒体功能。这些线粒体miRNA在氧化磷酸化、ATP合成、ROS形成以及脂肪酸代谢等多种过程发挥重要作用[60-61]。Das等[53]首次发现miR-181c可进入线粒体调节COX1和ROS水平,最终导致电子转运链复合物IV重塑和线粒体功能障碍;线粒体miR-1靶向线粒体编码的COX1、COX3、ND1和ATP8的mRNA,调节其翻译,但具体机制仍有待阐明[62]。鉴于miRNA对线粒体生物合成和功能的影响,进一步探讨线粒体内miRNA的活性及其作用机制对阐释线粒体的氧化应激调节具有重要的意义。
表 1 已知的靶向线粒体基因的miRNA氧化应激调节作用Table 1. Function of miRNAs that target mitochondrial genes in oxidative stressmiRNA 名称 靶基因 功能 细胞类型 文献 miR-181c 细胞色素c氧化酶1(COX1) 促氧化 大鼠心肌细胞(NRVMs) [53] miR-210 线粒体凋亡诱导因子3(AIFM3) 抗氧化 人胚胎肾细胞(HEK293) [54] miR-210 铁硫簇蛋白(ISCU) 促氧化 人乳腺癌(MCF7)和
结直肠癌(HCT116)细胞[55] miR-133b 谷胱甘肽S-转移酶(GSTP1) 促氧化 人宫颈癌细胞(Hela) [56] miR-145 细胞死亡调节因子(BNIP3) 抗氧化 大鼠心肌细胞(NRVMs) [57] miR-23b 脯氨酸氧化(POX) 抗氧化 人肾细胞(HREPC)和人肾癌细胞(TK10) [17] miR-335 超氧化物分解酶2(SOD2) 促氧化 大鼠腹膜间皮细胞(RPMCs) [58] miR-338 细胞色素c氧化酶4(COX4) 促氧化 大鼠颈神经细胞(RSCG) [59] 随着DHA氧化应激调节作用研究的深入,有越来越多的证据显示线粒体miRNA可通过以下几种方式介导DHA的抗氧化作用:a.受DHA调节的miRNA直接影响线粒体抗氧化酶的表达。如miR-23b靶向脯氨酸氧化酶(POX)降低ROS水平,DHA可提高miR-23b的表达,改善细胞抗氧化能力降低ROS[17-18]。b.受DHA 调节的miRNA通过影响线粒体稳态调节ROS的生成。如在哺乳动物中,miR-34a靶向调节Bcl-2的表达,影响线粒体的分裂融合,减缓线粒体氧化应激[63-64]。DHA在U266癌细胞及HepG2细胞中均能调节miR-34a的表达,而miR-34a对线粒体基因的表达有一定调控作用[65]。c.受DHA调节的miRNA调控线粒体自噬、降低ROS水平。自噬诱导剂肽(BECN1)是miR-30a的靶基因,在恢复线粒体自噬减轻线粒体功能障碍中起重要作用[66-68],补充DHA可上调肥胖雌性大鼠心肌中的miR-30a表达,提示DHA可通过调节miR-30a的水平影响线粒体自噬,降低氧化应激。本团队研究发现有多种受DHA调节的线粒体miRNA参与细胞的氧化应激调控。因此,DHA作为有效的抗氧化剂可通过调节miRNA的表达来增强细胞的抗氧化能力。受DHA调控的miRNA对线粒体的调节机制的探索可为揭示表观遗传介导的抗氧化分子作用机理提供证据。
5. 结论与展望
线粒体作为细胞产能的主要场所,在细胞的生理活动中起着重要作用。线粒体一旦受损或氧化应激过强会引发线粒体功能障碍,甚至引发各种疾病。近年来国内外关于DHA对线粒体调控的研究日益增多。这不仅有利于阐明DHA调节线粒体抗氧化作用的机制,也为线粒体氧化相关疾病(如神经退行性疾病、心血管疾病等)的预防和治疗提供了新思路。DHA通过对线粒体的功能、生物合成及表观遗传等多种途径的调节提高细胞抗氧化能力,降低氧化损伤。但DHA的调节作用也还有很多未解决的问题,如DHA是如何进到线粒体或细胞核调节线粒体合成基因的表达;DHA是否及如何调节线粒体miRNA表达;核基因组编码的miRNA如何进入线粒体以及线粒体基因组编码的miRNA如何加工成熟等问题都还未得到解决。线粒体miRNA对线粒体的靶向调节机制仍是当下待解决的问题。DHA是否可通过线粒体其它表观遗传方式的调控影响线粒体的抗氧化功能也有待探索。
人体所需DHA主要通过食物摄取,在食品中添加DHA不仅可解决人体DHA摄入量不足的问题,还在改善视力、预防老年痴呆、防治心血管疾病等方面起到重要作用[69]。改善居民膳食DHA摄入量偏低的状况是促进平衡膳食工作的重要内容,但DHA并不是摄入越多越好。如母体补充过量的DHA会影响胎儿肌肉发育,促进后代肌肉脂肪组织沉积[70]。DHA生物活性及其作用机制的探索将为抗氧化相关疾病的预防和治疗提供依据,也将进一步推动婴幼儿配方产品、休闲产品和膳食补充剂等DHA相关产品的开发与应用。相关产品中DHA的添加量和添加形式,以及产品摄取方式等都是DHA开发应用中需要关注的问题。同时,DHA对线粒体分子调节机制的明确也将为靶向线粒体的精准膳食调控提供依据,推动营养靶向设计、精准营养供给技术的发展。
-
表 1 已知的靶向线粒体基因的miRNA氧化应激调节作用
Table 1 Function of miRNAs that target mitochondrial genes in oxidative stress
miRNA 名称 靶基因 功能 细胞类型 文献 miR-181c 细胞色素c氧化酶1(COX1) 促氧化 大鼠心肌细胞(NRVMs) [53] miR-210 线粒体凋亡诱导因子3(AIFM3) 抗氧化 人胚胎肾细胞(HEK293) [54] miR-210 铁硫簇蛋白(ISCU) 促氧化 人乳腺癌(MCF7)和
结直肠癌(HCT116)细胞[55] miR-133b 谷胱甘肽S-转移酶(GSTP1) 促氧化 人宫颈癌细胞(Hela) [56] miR-145 细胞死亡调节因子(BNIP3) 抗氧化 大鼠心肌细胞(NRVMs) [57] miR-23b 脯氨酸氧化(POX) 抗氧化 人肾细胞(HREPC)和人肾癌细胞(TK10) [17] miR-335 超氧化物分解酶2(SOD2) 促氧化 大鼠腹膜间皮细胞(RPMCs) [58] miR-338 细胞色素c氧化酶4(COX4) 促氧化 大鼠颈神经细胞(RSCG) [59] -
[1] ONUKWUFOR J O, BERRY B J, WOJTOVICH A P. Physiologic implications of reactive oxygen species production by mitochondrial complex I reverse electron transport[J]. Antioxidants,2019,8(8):285. doi: 10.3390/antiox8080285
[2] 李兴太, 纪莹. 线粒体氧化应激与天然抗氧化剂研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2015,36(7):268−277. [LI X T, JI Y. Recent advances in mitochondrial oxidative stress and natural antioxidants[J]. Food Science,2015,36(7):268−277. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201507049 LI X T, JI Y. Recent Advances in mitochondrial oxidative stress and natural antioxidants[J]. Food Science, 2015, 36(7): 268-277. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201507049
[3] 黄文铅, 余杭, 郑一惠, 等. 线粒体相关的细胞信号分子与心血管疾病[J]. 生命科学,2018,30(7):771−778. [HUANG W Q, YU H, ZHENG Y H, et al. Mitochondrial-associated cellular signaling molecules and cardiovascular diseases[J]. Chineses Bulletin of Sciences,2018,30(7):771−778. HUANG W Q, YU H, ZHENG Y H, et al. Mitochondrial-associated cellular signaling molecules and cardiovascular diseases[J]. Chineses Bulletin of Sciences, 2018, 30(7): 771-778.
[4] SHAHIDI F, AMBIGAIPALAN P. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and their health benefits[J]. Annual Review of Food Science and Technology,2018,9(25):345−381.
[5] 杨贤庆, 吕军伟, 林婉玲, 等. DHA功能特性以及抗氧化性研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2014,35(2):390−394. [YANG X Q, LYU J W, LIN W L, et al. Research progress in biological function and antioxidative activity of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2014,35(2):390−394. YANG X Q, LV J W, LIN W L, et al. Research progress in biological function and antioxidative activity of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2014, 35(2): 390-394.
[6] 韩丽荣, 魏硕名, 王旭锋, 等. 二十二碳六烯酸免疫调节活性[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(3):206−212. [HAN L R, WEI S M, WANG X F, et al. Immunomodulatory activity of docosahexaenoic acid[J]. Food Science,2018,39(3):206−212. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201803032 HAN L R, WEI S M, WANG X F, et al. Immunomodulatory activity of docosahexaenoic acid[J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(3): 206-212. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201803032
[7] CHEN J, WANG D, ZONG Y, et al. DHA protects hepatocytes from oxidative injury through GPR120/ERK-mediated mitophagy[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2021,22(11):5675. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115675
[8] HALAPIN N A, BAZAN N G. NPD1 induction of retinal pigment epithelial cell survival involves PI3K/Akt phosphorylation signaling[J]. Neurochemical Research,2010,35(12):1944−1947. doi: 10.1007/s11064-010-0351-8
[9] 刘薇, 王红霞, 王立魁, 等. COX-2/Nrf2/ARE信号通路与体内外的抗炎、抗氧化作用机理[J]. 生命科学,2011,23(10):1027−1033. [LIU W, WANG H X, WANG L K, et al. COX-2 and Nrf2/ARE signaling pathways in anti-inflammation and antioxidation in vivo and in vitro[J]. Chineses Bulletin of Sciences,2011,23(10):1027−1033. LIU W, WANG H X, WANG L K, et al. COX-2 and Nrf2/ARE signaling pathways in anti-inflammation and antioxidation in vivo and in vitro[J]. Chineses Bulletin of Sciences, 2011, 23(10): 1027-1033.
[10] 刘越峰, 罗卫民, 张勇, 等. DHA激活NADPH氧化酶/ROS/Nrf2通路诱导ARPE-19细胞表达HO-1[J]. 中国免疫学杂志,2016,32(5):644−647. [LIU Y F, LUO W M, ZHANG Y, et al. Docosahexaenoic acid induces retinal pigment epithelial cells expression of heme oxygenase-1 by activation of NADPH oxidase/ROS/Nrf2[J]. Chinese Journal of Immunology,2016,32(5):644−647. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2016.05.009 LIU Y F, LUO W M, ZHANG Y, et al. Docosahexaenoic acid induces retinal pigment epithelial cells expression of heme oxygenase-1 by activation of NADPH oxidase /ROS /Nrf2[J]. Chinese Journal of Immunology, 2016, 32(5): 644-647. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2016.05.009
[11] CALDER P C. Docosahexaenoic acid[J]. Advances in Nutrition,2016,7(6):1139−1411. doi: 10.3945/an.116.012963
[12] FAN Y Y, FUENTES N R, HOU T Y, et al. Remodelling of primary human CD4+ T cell plasma membrane order by n-3 PUFA[J]. British Journal of Nutrition,2018,119(2):163−175. doi: 10.1017/S0007114517003385
[13] GERLING C J, MUKAI K, CHABOWSKI A, et al. Incorporation of omega-3 fatty acids into human skeletal muscle sarcolemmal and mitochondrialmembranes following 12 weeks of fish oil supplementation[J]. Frontiers in Physiology,2019,29(10):348.
[14] CLEMENTI M E, LAZZARINO G, SAMPAOLESE B, et al. DHA protects PC12 cells against oxidative stress and apoptotic signals through the activation of the NFE2L2/HO-1 axis[J]. International Journal of Molecular Medicine,2019,43(6):2523−2531.
[15] LLUÍS L, TALTAVULL N, MUÑOZ-CORTÉS M, et al. Protective effect of the omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids: Eicosapentaenoic acid/Docosahexaenoic acid 1: 1 Ratio on cardiovascular disease risk markers in rats[J]. Lipids in Health and Disease,2013,12(1):140. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-12-140
[16] LI G L, LI Y Y, XIAO B P, et al. Antioxidant activity of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and its regulatory roles in mitochondria[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2021,69(5):1647−1655. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c07751
[17] LIU W, ZABIRNYK O, WANG H, et al. MiR-23b targets proline oxidase, a novel tumor suppressor protein in renal cancer[J]. Oncogene,2010,29(35):4914−4924. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.237
[18] HANNAFON B N, CARPENTER K J, BERRY W L, et al. Exosome-mediated microRNA signaling from breast cancer cells is altered by the anti-angiogenesis agent docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)[J]. Molecular Cancer,2015,14(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0400-7
[19] HE L, HE T, FARRAR S, et al. Antioxidants maintain cellular redox homeostasis by elimination of reactive oxygen species[J]. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry,2017,44(2):532−553. doi: 10.1159/000485089
[20] APOSTOLOVA N, VICTOR V M. Molecular strategies for targeting antioxidants to mitochondria: Therapeutic implications[J]. Antioxidants and Redox Signaling,2015,22(8):686−729. doi: 10.1089/ars.2014.5952
[21] GARREL C, ALESSANDRI J M, GUESNET P, et al. Omega-3 fatty acids enhance mitochondrial superoxide dismutase activity in rat organs during post-natal development[J]. International Journal of Biochemistry and Cell Biology,2012,44(1):123−131. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2011.10.007
[22] SONG E A, LIM J W, KIM H. Docosahexaenoic acid inhibits IL-6 expression via PPAR γ-mediated expression of catalase in cerulein-stimulated pancreatic acinar cells[J]. International Journal of Biochemistry and Cell Biology,2017,88:60−68. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2017.05.011
[23] 王鹏, 曲丽辉, 谢金鹿, 等. DHA对沙鼠全脑缺血/再灌注诱导的海马神经元凋亡的影响[J]. 哈尔滨医科大学学报,2015,49(6):475−479. [WANG P, QU L H, XIE J L, et al. Effects of DHA on hippocampal neuronal apoptosis following global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in gerbils[J]. Journal of Harbin Medical University,2015,49(6):475−479. WANG P, QU L H, XIE J L, et al. Effects of DHA on hippocampal neuronal apoptosis following global cerebral ischemia /reperfusion in gerbils[J]. Journal of Harbin Medical University, 2015, 49(6): 475-479.
[24] 蒋利和, 马博, 谢正轶, 等. 二十二碳六烯酸对老年大鼠脑组织抗氧化和脂肪酸的影响[J]. 食品科学,2011,32(13):284−288. [JIANG L H, MA B, XIE Z Y, et al. Effect of DHA on antioxidation and fatty acids in aged rat brain[J]. Food Science,2011,32(13):284−288. JIANG L H, MA B, XIE Z Y, et al. Effect of DHA on antioxidation and fatty acids in aged rat brain[J]. Food Science, 2011, 32(13): 284-288.
[25] OU W, MULIK R S, ANWAR A, et al. Low-density lipoprotein docosahexaenoic acid nanoparticles induce ferroptotic cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Free Radical Biology and Medicine,2017,112:597−607. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.09.002
[26] DING W Q, LIND S E. Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase plays a role in protecting cancer cells from docosahexaenoic acid-induced cytotoxicity[J]. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics,2007,6(4):1467−1474. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0608
[27] SINGH A, KUKRETI R, SASO L, et al. Oxidative stress: A key modulator in neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Molecules,2019,24(8):1583. doi: 10.3390/molecules24081583
[28] STANLEY W C, KHAIRALLAH R J, DABKOWSKI E R. Update on lipids and mitochondrial function: Impact of dietary n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids[J]. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care,2012,15(2):122−126. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e32834fdaf7
[29] MADINGOU N, GILBERT K, TOMARO L, et al. Comparison of the effects of EPA and DHA alone or in combination in a murine model of myocardial infarction[J]. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids,2016,111:11−16. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2016.06.001
[30] SCHÖNFELD P, WOJTCZAK L. Fatty acids as modulators of the cellular production of reactive oxygen species[J]. Free Radical Biology and Medicine,2008,45(3):231−241. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.04.029
[31] 李霏, 李晓曦, 尹元琴. DHA对UVB和砷引起的DNA损伤的预防作用[J]. 临床肿瘤学杂志,2019,24(3):193−200. [LI F, LI X X, YIN Y Q. Preventive effect of DHA on DNA damage induced by UVB and arsenic[J]. Chinese Clinical Oncology,2019,24(3):193−200. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0460.2019.03.001 LI F, LI X X, YIN Y Q. Preventive effect of DHA on DNA damage induced by UVB and arsenic[J]. Chinese Clinical Oncology, 2019, 24(3): 193-200. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0460.2019.03.001
[32] 刘越峰, 罗卫民, 张勇, 等. 二十二碳六烯酸抑制氧化应激状态下人视网膜色素上皮细胞凋亡[J]. 中国病理生理杂志,2016,32(3):504−509. [LIU Y F, LUO W M, ZHANG Y, et al. Docosahexaenoic acid protects human retinal pigment epithelial cells against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Pathophysiology,2016,32(3):504−509. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4718.2016.03.019 LIU Y F, LUO W M, ZHANG Y, et al. Docosahexaenoic acid protects human retinal pigment epithelial cells against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Pathophysiology, 2016, 32(3): 504-509. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4718.2016.03.019
[33] NORDMANN C, STROKIN M, SCHÖNFELD P, et al. Putative roles of Ca2+-independent phospholipase A2 in respiratory chain-associated ROS production in brain mitochondria: Influence of docosahexaenoic acid and bromoenol lactone[J]. Journal of Neurochemistry,2014,131(2):163−176. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12789
[34] O'SHEA K M, KHAIRALLAH R J, SPARAGNA G C, et al. Dietary omega-3 fatty acids alter cardiac mitochondrial phospholipid composition and delay Ca2+-induced permeability transition[J]. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology,2009,47(6):819−827. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2009.08.014
[35] QUAN Y, XIN Y, TIAN G, et al. Mitochondrial ros-modulated mtdna: A potential target for cardiac aging[J]. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity,2020,2020:1−11.
[36] SHIRIHAI O S, SONG M, DORN G. How mitochondrial dynamism orchestrates mitophagy[J]. Circulation Research,2015,116(11):1835−1849. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.306374
[37] HAEUSSLER S, KOHLER F, WITTING M, et al. Autophagy compensates for defects in mitochondrial dynamics[J]. Public Library of Science genetics,2020,16(3):e1008638.
[38] GOLPICH M, AMINI E, MOHAMED Z, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction and biogenesis in neurodegenerative diseases: Pathogenesis and treatment[J]. CNS Neuroscience Therapeutics,2017,23(1):5−22. doi: 10.1111/cns.12655
[39] BUSQUETS-CORTES C, CAPÓ X, MARTORELL M, et al. Training enhances immune cells mitochondrial biosynthesis, fission, fusion, and their antioxidant capabilities synergistically with dietary docosahexaenoic supplementation[J]. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity,2016,2016:8950384.
[40] ZHANG T, WU P, ZHANG J H, et al. Docosahexaenoic acid alleviates oxidative stress-based apoptosis via improving mitochondrial dynamics in early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage[J]. Cellular and Molecular Neurobiollogy,2018,38(7):1413−1423. doi: 10.1007/s10571-018-0608-3
[41] POPOV L D. Mitochondrial biogenesis: An update[J]. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine,2020,24(9):4892−4899. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15194
[42] PICCA A, LEZZA A M. Regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis through TFAM-mitochondrial DNA interactions: Useful insights from aging and calorie restriction studies[J]. Mitochondrion,2015,25(2015):67−75.
[43] LEE M S, SHIN Y, MOON S, et al. Effects of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid on mitochondrial DNA replication and PGC-1 alpha gene expression in C2C12 muscle cells[J]. Preventive Nutrition and Food Science,2016,21(4):317−322. doi: 10.3746/pnf.2016.21.4.317
[44] XU Y, WAHLBERG K, LOVE T M, et al. Associations of blood mercury and fatty acid concentrations with blood mitochondrial DNA copy number in the seychelles child development nutrition study[J]. Environment International,2019,124:278−283. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.01.019
[45] ROSSIGNOLI C P, DECHANDT C R P, SOUZA A O, et al. Effects of intermittent dietary supplementation with conjugated linoleic acid and fish oil (EPA/DHA) on body metabolism and mitochondrial energetics in mice[J]. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry,2018,60:16−23. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.07.001
[46] KWAK Y S, LIM S Y. The combined impacts of docosahexaenoic acid, endurance physical exercise, and prolonged fasting on brain function[J]. Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation,2018,14(4):540−544. doi: 10.12965/jer.1836298.149
[47] 郑凯, 杨梅桂, 闫朝君, 等. 线粒体动力学与细胞凋亡[J]. 中国细胞生物学学报,2019,41(8):1467−1476. [ZHENG K, YANG M G, YAN Z J, et al. Mitochondrial dynamics and apoptosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Cell Biology,2019,41(8):1467−1476. ZHENG K, YANG M G, YAN Z J, et al. Mitochondrial dynamics and apoptosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Cell Biology, 2019, 41(8): 1467-1476.
[48] DARWESH A M, JAMIESON K L, WANG C, et al. Cardioprotective effects of CYP-derived epoxy metabolites of docosahexaenoic acid involve limiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation1[J]. Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology,2019,97(6):544−556. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2018-0480
[49] MOHAMMAD G, RADHAKRISHNAN R, KOWLURU R A. Epigenetic modifications compromise mitochondrial DNA quality control in the development of diabetic retinopathy[J]. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science,2019,60(12):3943−3951. doi: 10.1167/iovs.19-27602
[50] MATILAINEN O, QUIROS P M, AUWERX J. Mitochondria and epigenetics-crosstalk in homeostasis and stress[J]. Trends in Cell Biology,2017,27(6):453−463. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2017.02.004
[51] PHAM T X, BAE M, LEE Y, et al. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional repression of histone deacetylases by docosahexaenoic acid in macrophages[J]. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry,2018,57:162−169. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.03.002
[52] GEIGER J, DALGAARD L T. Interplay of mitochondrial metabolism and microRNAs[J]. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences,2016,74(4):631−646.
[53] DAS S, FERLITO M, KENT O A, et al. Nuclear miRNA regulates the mitochondrial genome in the heart[J]. Circulation Research,2012,110(12):1596−1603. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.267732
[54] MUTHARASAN R K, NAGPAL V, ICHIKAWA Y, et al. MicroRNA-210 is upregulated in hypoxic cardiomyocytes through Akt- and p53-dependent pathways and exerts cytoprotective effects[J]. American Journal of Physiology Heart and Circulatory Physiology,2011,301(4):H1519−H1530. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01080.2010
[55] FAVARO E, RAMACHANDRAN A, MCCORMICK R, et al. MicroRNA-210 regulates mitochondrial free radical response to hypoxia and krebs cycle in cancer cells by targeting iron sulfur cluster protein ISCU[J]. Public Library of Science One,2010,5(4):e10345.
[56] PATRON J P, FENDLER A, BILD M, et al. MiR-133b targets antiapoptotic genes and enhances death receptor-induced apoptosis[J]. Public Library of Science One,2012,7(4):e35345.
[57] LI R, YAN G, LI Q, et al. MicroRNA-145 protects cardiomyocytes against hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced apoptosis through targeting the mitochondria apoptotic pathway[J]. Public Library of Science One,2012,7(9):e44907.
[58] BAI X Y, MA Y, DING R, et al. MiR-335 and miR-34a promote renal senescence by suppressing mitochondrial antioxidative enzymes[J]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology,2011,22(7):1252−1261. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2010040367
[59] ASCHRAFI A, KAR A N, NATERA-NARANJO O, et al. MicroRNA-338 regulates the axonal expression of multiple nuclear-encoded mitochondrial mRNAs encoding subunits of the oxidative phosphorylation machinery[J]. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences,2012,69(23):4017−4027. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1064-8
[60] 王艺霏, 敖翔, 刘英, 等. 线粒体miRNA及其生物学功能[J]. 中国细胞生物学学报,2018,40(7):1247−1252. [WANG Y F, AO X, LIU Y, et al. Mitochondrial miRNAs and their biological functions[J]. Chinese Journal of Cell Biology,2018,40(7):1247−1252. doi: 10.11844/cjcb.2018.07.0366 WANG Y F, AO X, LIU Y, et al. Mitochondrial miRNAs and their biological functions[J]. Chinese Journal of Cell Biology, 2018, 40(7): 1247-1252. doi: 10.11844/cjcb.2018.07.0366
[61] 谭佳, 肖晨, 陈金娜, 等. MiRNA调控线粒体功能的研究进展[J]. 生命的化学,2020,40(2):250−255. [TAN J, XIAO C, CHEN J N, et al. Research progress of miRNA on mitochondrial function[J]. Chemistry of Life,2020,40(2):250−255. TAN J, XIAO C, CHEN J N, et al. Research progress of miRNA on mitochondrial function[J]. Chemistry of Life, 2020, 40(2): 250-255.
[62] ZHANG Y, XU H. Translational regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis[J]. Biochemical Society Transactions,2016,44(6):1717−1724. doi: 10.1042/BST20160071C
[63] ROLLAND S G, CONRADT B. New role of the BCL2 family of proteins in the regulation of mitochondrial dynamics[J]. Current Opinion in Cell Biology,2010,22(6):852−858. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2010.07.014
[64] ZHAO Y, WANG X. MiR-34a targets BCL-2 to suppress the migration and invasion of sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Oncology Letters,2018,16(5):6566−6572.
[65] DAI X, LI M, GENG F. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid enhance dexamethasone sensitivity in multiple myeloma cells by the p53/miR-34a/Bcl-2 Axis[J]. Biochemistry,2017,82(7):826−833.
[66] EGAN B T, VICZENCZOVA C, SZEIFFOVA B B, et al. Obesity-associated alterations in cardiac connexin-43 and PKC signaling are attenuated by melatonin and omega-3 fatty acids in female rats[J]. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry,2019,454(1−2):191−202. doi: 10.1007/s11010-018-3463-0
[67] VAN B E, RIOUFOL G, POUILLOT C, et al. Outcome impact of coronary revascularization strategy reclassification with fractional flow reserve at time of diagnostic angiography: Insights from a large French multicenter fractional flow reserve registry[J]. Circulation,2014,129(2):173−175. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.006646
[68] WANG J J, BIE Z D, SUN C F. Long noncoding RNA AK088388 regulates autophagy through miR-30a to affect cardiomyocyte injury[J]. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry,2019,120(6):10155−10163. doi: 10.1002/jcb.28300
[69] 黄菊华, 李蕴成. DHA的功能及在食品添加中的应用研究[J]. 中国食物与营养,2014,20(4):76−79. [HUANG J H, LI X C. Functions of DHA and its application in food addictives[J]. Food and Nutrition in China,2014,20(4):76−79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9577.2014.04.020 HUANG J H, LI X C. Functions of DHA and its application in food addictives[J]. Food and Nutrition in China, 2014, 20(4): 76-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9577.2014.04.020
[70] HSUEH T Y, BAUM J I, HUANG Y. Effect of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid on myogenesis and mitochondrial biosynthesis during murine skeletal muscle cell differentiation[J]. Frontiers in Nutrition,2018,5:15. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2018.00015
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 黄素艳,曹荣,刘楠,孙永,周德庆,王珊珊. 提取方式对微拟球藻蛋白理化性质和功能特性的影响. 食品工业科技. 2025(01): 87-96 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 陈亭菊,刘远超,蔡曼君,郭慧阳,陈少丹,吴清平,胡惠萍. 食药用菌蛋白质研究现状及应用. 食用菌学报. 2024(02): 113-126 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



