Study on the Absorption of Heavy Metal Ion Pb2+ by the Low Methoxy Pectin from Sunflower Heads
-
摘要: 重金属污染由于缺乏有效的治理方法而对公众健康有严重威胁,为了开发吸附重金属离子的生物新材料,本文以向日葵盘为原料提取天然的低酯化果胶LAHP,并研究LAHP对水溶液中Pb2+的吸附性能、优化LAHP吸附Pb2+的条件。采用草酸溶液80 oC提取、乙醇沉淀的方法获得LAHP,产率为14.68%±0.76%。质量分析显示LAHP符合国家质量标准对食品添加剂果胶的要求,结构分析说明LAHP主要由半乳糖醛酸(GalA,86.34%)组成,甲酯化度为23.93%±1.57%,分子量为257 kDa,是天然的低酯化果胶。LAHP对Pb2+的吸附能力受果胶用量、溶液pH、吸附温度和干扰离子等因素的影响,优化确定了LAHP吸附Pb2+的最佳条件:果胶添加量为30 mg/L(Pb2+浓度为11.0 mg/L)、溶液的pH=8.0、处理温度30 ℃。LAHP对Pb2+的最大吸附量为44.57±2.50 mg/g,二价金属离子会在一定程度上影响LAHP对Pb2+的吸附能力。因此,从向日葵盘中提取的低酯果胶是一种良好的天然重金属吸附剂,具有广阔的应用前景。Abstract: Heavy metal pollution poses a serious threat to public health due to lacking of effective treatment methods. In order to develop new biological materials for adsorption of heavy metal ions, the natural low-methoxyl pectin (termed LAHP) was extracted from dried heads of sunflower in this study. The adsorption capacity of LAHP for Pb2+ in aqueous solution was studied and the conditions for the adsorptions were optimized. LAHP was extracted by oxalic acid solution at 80 oC and precipitated by ethanol with the yield of 14.68%±0.76%. The composition analysis showed that LAHP met the requirements of national quality standard for pectin as a food additive. The structure analysis showed that LAHP was natural low-methoxyl pectin, which was mainly composed of galacturonic acid (GalA, 86.34%) with a low degree of methyl esterification (23.93%±1.57%) and high molecular weight (257 kDa). The adsorption capacity of Pb2+ by LAHP was affected by the amount of pectin, pH of solution, temperature and interference ions. The optimal conditions for the adsorption of Pb2+ were determined as follows: pectin dosage was 30 mg/L (concentration of Pb2+ was 11.0 mg/L), pH of solution was 8.0, and the temperature was 30 ℃. The maximum adsorption capacity of LAHP for Pb2+ was 44.57±2.50 mg/g, and would be reduced to some extent affected by divalent metal ions. Therefore, the low-methoxyl pectin from sunflower heads would be a kind of natural heavy metal adsorbent, which had a wide application prospect.
-
Keywords:
- sunflower heads /
- low-methoxyl pectin /
- heavy metal /
- lead /
- adsorption capacity
-
重金属在自然环境中普遍存在,特别是工业排放的废水中往往含有大量的重金属离子。众所周知,重金属如Hg、Pb、Cr、Ni、Cu、Cd、Zn等在生物体内容易积累,被人体吸收后超过所适应的浓度时,不同元素间固有的比例被破坏,会对人体的健康产生危害[1]。随着科技和工业的发展,向环境中释放的Pb2+不断增加,由于其毒性、在食物链中的富集作用和在生态系统中的持久性,对环境和公众健康构成了极大的威胁[2]。过量重金属进入人体后,将导致机体器官受损,引发心血管疾病,产生慢性或急性中毒,且重金属中毒对人体的危害是多器官、多系统、多指征、终生不可逆的[3]。
重金属污染防治一直是国际环保界的难点和研究热点,多年来已发展出若干技术,如过滤、化学沉淀、吸附、电沉积和膜处理系统等[4]。但是这些方法都有其固有的优点和局限性,在处理重金属超标废水时,大多数方法或比较昂贵,或效率较低,至今尚未找到普适有效的治理方法[5]。如何消除重金属的危害并有效地回收贵重金属是当今环境保护工作面临的突出问题。近年来,聚合物与重金属离子结合的研究成果显著,已广泛应用于核化学、电化学、湿法冶金和环境保护等领域,其作用原理主要是利用聚合物分子的三维结构来螯合去除重金属离子[6]。应用这种方法,有毒的重金属离子被去除,无害的离子被释放到环境中。最好的螯合金属离子的材料是生物聚合物,如纤维素[7]、海藻酸盐[8]、壳聚糖[9]和果胶[10]等,主要来源于农业副产物,具有来源广、成本低、天然无毒等特点,在重金属污染废水处理中很有吸引力,具有广阔的应用前景。
果胶(pectin)是广泛存在于高等植物中的一种酸性离子多糖,主要由D-半乳糖醛酸残基(D-GalA)通过α-(1→4)糖苷键连接构成[11-12]。果胶作为食品添加剂(凝胶剂、增稠剂、乳化剂和稳定剂)[13-15]和药用辅料[16],已广泛应用于食品和医药行业。果胶分子中GalA的羧基有不同程度的甲酯化修饰,根据甲酯化度(Degree of Methylation,DM)的不同可将果胶分为高酯化果胶(HMP)和低酯化果胶(LMP)[17]。与HMP相比,LMP对Pb2+等重金属离子的亲和力更大[18]。但是,目前商品LMP主要是由酸或碱处理HMP生产而来,不仅产品的生产成本较高,而且在反应过程中很容易造成果胶分子的降解,影响其性能。向日葵是我国重要的油料作物,脱籽后的向日葵盘作为农业废料常被丢弃或焚烧,不仅会污染空气,还会造成资源的浪费。成熟的向日葵盘中富含天然的低酯化果胶,含量高达15%~25%[19]。本论文首次研究了农业废弃物向日葵盘中的低酯化果胶对重金属离子Pb2+的吸附性能,摸索果胶吸附Pb2+的最佳条件。大规模应用该果胶吸附去除工业废水中的重金属离子,不仅能够充分利用自然资源、避免大量焚烧农业废料造成环境污染,还将为吸附、回收重金属离子提供一种安全稳定有效的新型方法,具有重要的经济效益和社会效益。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
向日葵盘 购自山西省五寨县;铅标准储备液 由国家钢铁材料测试中心钢铁研究总院提供;0.22 μm针头滤器(JET),Pb(NO3)2、HCl、NaOH、NaCl、CaCl2、草酸、乙醇等其他试剂 均为国产分析纯。
2zebuit700P 型火焰原子吸收分光光度计 德国耶拿分析仪器股份公司;PHS-3C酸度计 杭州雷磁分析仪器厂;HSS-1数字式超级恒温水浴槽 上海精宏实验设备有限公司;十功能自动煎药机 北京东华原医疗设备有限责任公司;ZMF-320G 多级闪蒸仪 河南智晶生物科技发展有限公司;LC-4012低速离心机 安徽中科中佳科学仪器有限公司;HC-2062高速离心机 安徽中科中佳科学仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 向日葵盘低酯化果胶的提取
按照课题组前期[20-22]优化确定的方法,提取向日葵盘低酯化果胶LAHP。具体操作简述如下:称取干燥的向日葵盘250 g,切成小块后加水浸泡过夜,弃去上清,加入5 L 0.2%草酸,80 ℃提取1 h,120目尼龙布过滤,收集滤液,再向滤渣中加入5 L 0.2%草酸重复提取一次,收集滤液。将两次提取的滤液合并,浓缩至1 L左右,离心(4500 r/min,15 min),取上清进行乙醇沉淀:边搅拌边加入4倍体积的95%乙醇,使溶液中乙醇浓度达80%左右,静置4 h,离心(4500 r/min,15 min),收集沉淀。向沉淀中加入1 L蒸馏水复溶,离心(4500 r/min,15 min),取上清,用同样的方法再次醇沉,收集沉淀。将沉淀依次用95%乙醇和无水乙醇洗涤2次后,置于真空干燥箱中室温干燥,得淡棕色粉末状果胶样品LAHP。
1.2.2 向日葵盘低酯化果胶的质量分析
按照中华人民共和国国家标准(GB 25533-2010)对食品添加剂果胶的质量要求[23],依次测定向日葵盘低酯化果胶LAHP的干燥失重、灰分、酸不溶灰分、总半乳糖醛酸、甲酯化度、重金属Pb的含量。
1.2.3 向日葵盘低酯化果胶的结构分析
采用酸水解-PMP衍生化-HPLC检测的方法,测定LAHP的单糖组成[22]。取2 mg果胶样品依次用1 mL 1 mol/L的盐酸-甲醇溶液80 ℃水解反应16 h、0.5 mL 2 mol/L三氟乙酸(TFA)120 ℃水解反应1 h,加入无水乙醇,60 ℃水浴蒸干。向水解产物中加入0.5 mL 1-苯基-3-甲基-5-吡唑啉酮(PMP)溶液和0.5 mL 0.3 mol/L NaOH溶液,充分溶解,70 ℃水浴反应30 min。离心(10000 r/min,5 min),取上清,并向其中加入0.05 mL 0.3 mol/L HCl溶液和0.05 mL蒸馏水,振荡混匀,加入1 mL三氯甲烷,萃取除去过量的PMP,水层用0.22 μm滤膜过滤,备测。应用高效液相色谱系统(HPLC)测定LAHP的单糖组成:取10 μL样品上样于DIKMA Inertsil ODS-3色谱柱(4.6 mm×150 mm),选择Shimadzu HPLC系统(SPD-10AVD紫外光检测器),检测波长为245 nm,流速为1.0 mL/min,流动相为乙腈:PBS=17.5:82.5(V/V)。
应用傅里叶变换红外光谱法(FT-IR)检测LAHP在400~4000 cm−1范围内的红外吸收光谱。
应用高效凝胶渗透色谱法(HPGPC)分析LAHP的分子量及其分布情况[21]。将0.22 μm滤膜过滤后的20 μL 4 mg/mL果胶溶液上样于TSK-gel G-4000 PWXL色谱柱,流动相为0.2 mol/L NaCl,流速为0.5 mL/min,检测系统为Shimadzu LC-10ATVP高效液相色谱,采用RID-10A示差折射检测器进行检测,Shimadzu CLASS-Vp工作站进行数据处理和分析。
1.2.4 向日葵盘低酯化果胶吸附铅离子的实验研究
1.2.4.1 果胶用量对LAHP吸附铅离子性能的影响
用超纯水溶解Pb(NO3)2配制成Pb2+浓度为22 mg/L的溶液,备用。移取10 mL Pb2+溶液于烧杯中,并向各烧杯中加入10 mL不同浓度的LAHP溶液,使果胶的终浓度分别为5、10、15、20、30、40、50、60、70、80和100 mg/L。用0.5 mol/L HCl或NaOH调节溶液pH至6.0,30 ℃恒温搅拌(200 r/min)40 min。吸附结束后,采用0.45 μm水系滤膜过滤,取滤液稀释,用原子吸收分光光度计测定溶液中Pb2+的含量,并计算LAHP对Pb2+的平衡吸附量Qe和Pb2+的去除率β。
1.2.4.2 pH对LAHP吸附铅离子性能的影响
移取1.2.4.1中配制的Pb2+溶液10 mL于烧杯中,加入60 mg/L LAHP溶液10 mL,并用0.5 mol/L HCl或NaOH调节溶液pH至2.0、3.0、4.0、5.0、6.0、7.0、8.0、9.0和10.0,30 ℃恒温搅拌(200 r/min)40 min。吸附结束后,用0.45 μm滤膜过滤,取滤液,稀释,用原子吸收分光光度计测定溶液中Pb2+的含量,并计算LAHP对Pb2+的平衡吸附量Qe和Pb2+的去除率β。
1.2.4.3 温度对LAHP吸附铅离子性能的影响
移取1.2.4.1中配制的Pb2+溶液10 mL于烧杯中,加入60 mg/L LAHP溶液10 mL,采用0.5 mol/L HCl或NaOH调节溶液pH至8.0,分别于不同温度(20、30、40、50、60和80 ℃)下恒温搅拌(200 r/min)40 min。吸附结束后,采用0.45 μm滤膜过滤,取滤液,稀释,应用原子吸收分光光度计测定溶液中Pb2+的含量,并计算果胶对Pb2+的平衡吸附量Qe和Pb2+的去除率β。
1.2.4.4 干扰离子对LAHP吸附铅离子性能的影响
移取1.2.4.1中配制的Pb2+溶液10 mL于烧杯中,分别添加不同浓度的干扰离子(离子种类:Na+、Ca2+,干扰离子与Pb2+的质量浓度比分别为1:0.5、1:1和1:2),并加入10 mL 60 mg/L的LAHP溶液,采用0.5 mol/L HCl或NaOH溶液调节pH至8.0,30 ℃恒温搅拌(200 r/min)40 min。吸附结束后,用0.45 μm滤膜过滤,取滤液,稀释,用原子吸收分光光度计测定溶液中Pb2+的含量,并计算果胶对Pb2+的平衡吸附量Qe和Pb2+的去除率β。
1.2.4.5 平衡吸附量Qe和Pb2+去除率β的计算
a. 平衡吸附量Qe的计算
按照下述公式(1)计算各实验组中LAHP对Pb2+的平衡吸附量Qe[24]。
(1) 式中,Qe为吸附达平衡时果胶对Pb2+的吸附量(mg/g);V为加入Pb2+溶液的体积(L);C0为吸附前溶液中Pb2+的初始浓度(mg/L);Ce为吸附平衡后溶液中Pb2+的浓度(mg/L);m为果胶的用量。
b. Pb2+去除率β的计算
按照下述公式(2)计算各实验组中Pb2+的去除率β[25]。
(2) 式中,β为果胶处理后,Pb2+的去除率(%);C0为吸附前溶液中Pb2+的初始浓度(mg/L);Ce为吸附平衡后溶液中Pb2+的浓度(mg/L)。
1.3 数据处理
采用SPSS 20.0软件进行数据分析,采用OriginPro 8.0软件进行作图,实验数据以“平均值±标准偏差”(Mean±SD)表示。组间分析采用t检验,P<0.05表示两组之间具有显著性差异,P<0.01表示两组之间具有极显著性差异。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 向日葵盘低酯化果胶的提取及质量分析
从向日葵盘中提取得到淡黄褐色絮状果胶样品(LAHP),得率为14.68%±0.76%。按照国家质量标准对食品添加剂果胶的要求,对LAHP进行质量分析,结果如表1所示。从表1中可以看出,LAHP的各项指标均达到了国家质量标准的要求。其中,灰分含量为3.21%±0.17%,低于采用六偏磷酸钠溶液提取获得的果胶的灰分含量[26-27];总半乳糖醛酸的含量高达86.34%±4.25%,与文献[28-29]中的结果一致;而甲酯化度为23.93%±1.57%,说明LAHP为天然的低酯化果胶。因此,向日葵盘是一种天然低酯化果胶的优质来源,采用草酸溶液提取法可以获得收率较高、品质较好的天然低酯化果胶。
表 1 向日葵盘低酯化果胶的质量分析Table 1. Quality analysis of low methoxyl pectin from sunflower heads项目 GB 25533-2010指标 LAHP 干燥失重(%) ≤12 7.15±0.38 灰分(%) ≤5 3.21±0.17 酸不溶灰分(%) ≤1 0.42±0.03 总半乳糖醛酸含量(%) ≥65 86.34±4.25 重金属含量(mg/kg) ≤5 0.34±0.04 酯化度(%) 23.93±1.57 2.2 向日葵盘低酯化果胶的结构分析
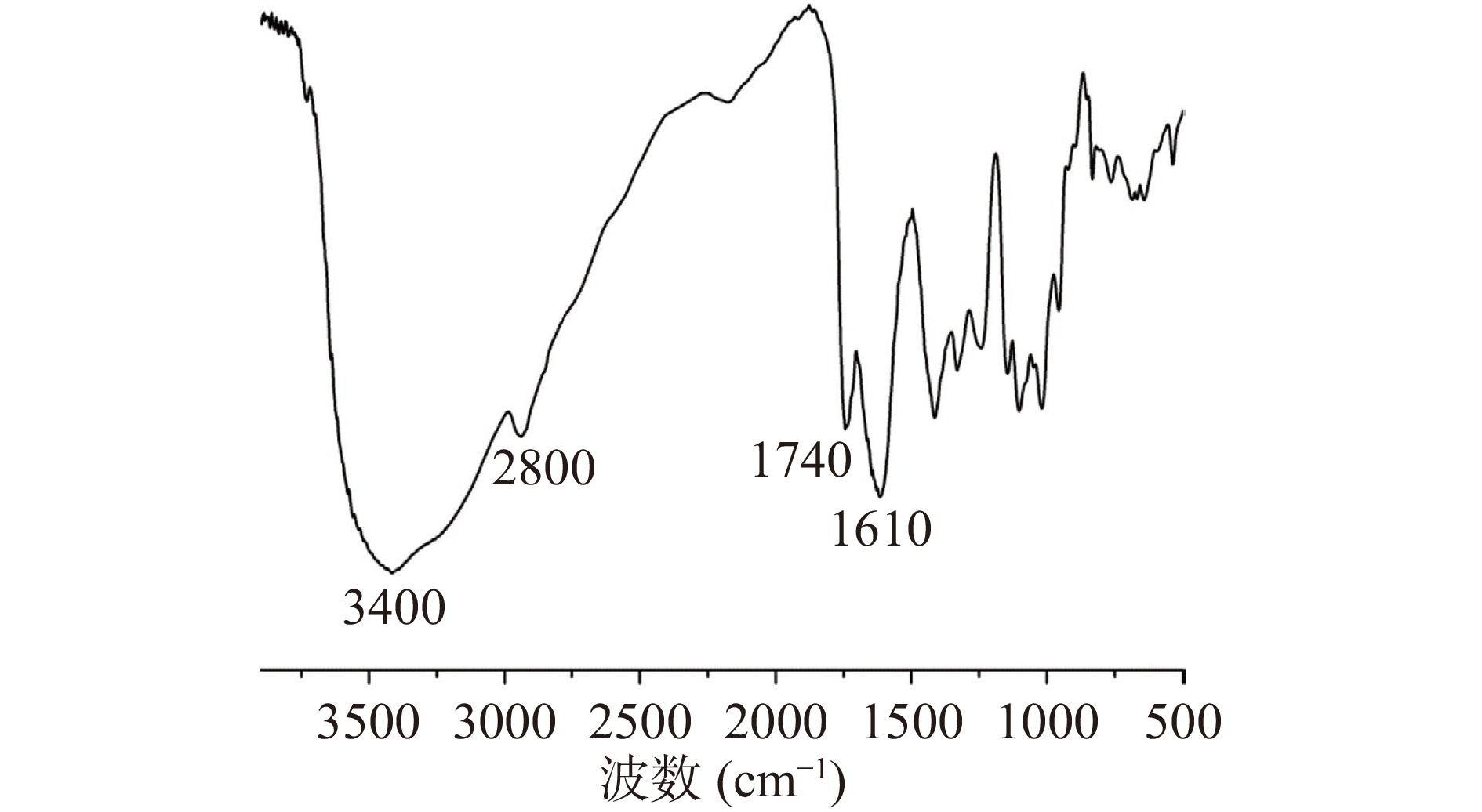
单糖组成分析显示,LAHP主要由半乳糖醛酸(GalA,86.34%)组成,与质量分析的结果一致,此外,还含有少量的鼠李糖(Rha,6.5%)、半乳糖(Gal,2.5%)和阿拉伯糖(Ara,3.6%),其中Rha与GalA的比值为0.074,推测LAHP的结构主要为同型半乳糖醛酸聚糖(Homogalacturonan, HG)。而且,LAHP中不含有葡萄糖(Glc),说明在提取过程中没有混入纤维素和淀粉样葡聚糖等杂质,进一步证明该提取方法能够获得质量较好的向日葵盘果胶。采用FT-IR分析LAHP的结构特征,结果如图1所示。LAHP分别在3400和2800 cm−1处有羟基的伸缩振动特征吸收峰和C-H的伸缩和弯曲振动吸收峰[30],在1740和1610 cm−1处的吸收峰分别对应于酯化羧基和游离羧基的伸缩振动特征峰[31]。而且1740和1610 cm−1处的峰面积比与果胶分子中酯化羧基和游离羧基的数目之比正相关[32],即果胶的甲酯化度与A1740/(A1740+A1610)成正比。据此推测LAHP的甲酯化度为25%,与质量分析得到的结果相符,此结果稍低于应用草酸铵提取的向日葵盘果胶[28-29],稍高于应用柠檬酸钠提取的向日葵盘果胶[33]。因此,采用本文的提取方法能够获得向日葵盘中的天然低酯化果胶。
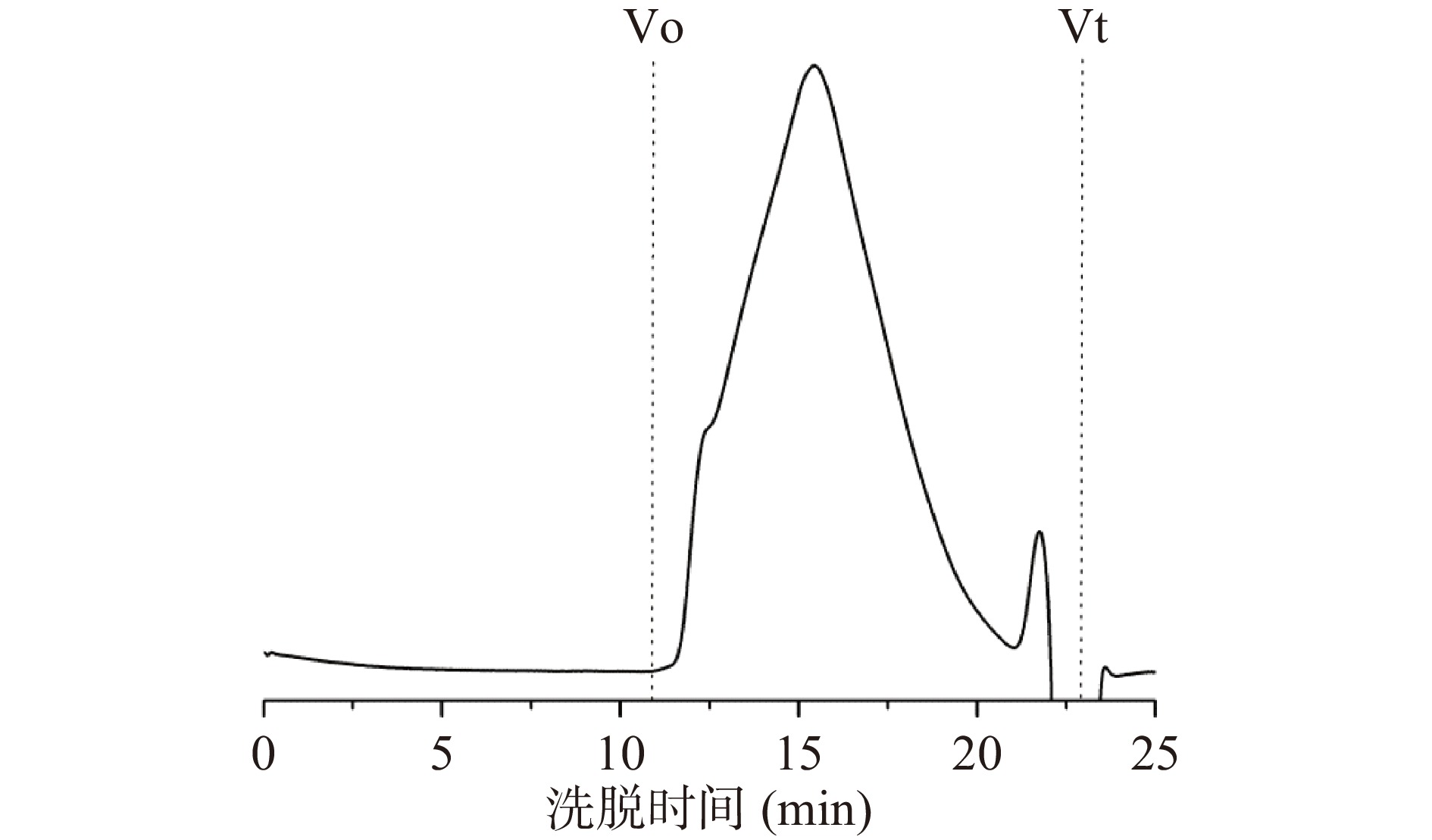
采用HPGPC分析LAHP的分子量,结果如图2所示。LAHP呈分布范围较宽的吸收峰,最高吸收值出现在15.42 min处,根据标准右旋葡聚糖校准的曲线计算LAHP的分子量为257 kDa。此结果低于草酸铵提取的向日葵盘果胶的分子量(605.6 kDa)[29],高于六偏磷酸钠溶液提取的果胶(39~52 kDa)[26]和亚临界水萃取法提取的果胶(11.5 kDa)[34],而与柠檬酸钠提取获得的果胶(256.40 kDa)[33]基本一致。这可能是因为向日葵盘的来源和贮藏时间以及提取溶液、温度等条件均会影响果胶的分子量。
2.3 向日葵盘低酯化果胶吸附铅离子的研究
吸附剂的用量、溶液pH、吸附温度及干扰离子等条件均会影响LAHP对重金属离子的吸附性能。本研究分析了这四种吸附因素对LAHP吸附Pb2+的平衡吸附量Qe和Pb2+去除率β的影响。
2.3.1 果胶用量对吸附铅离子性能的影响
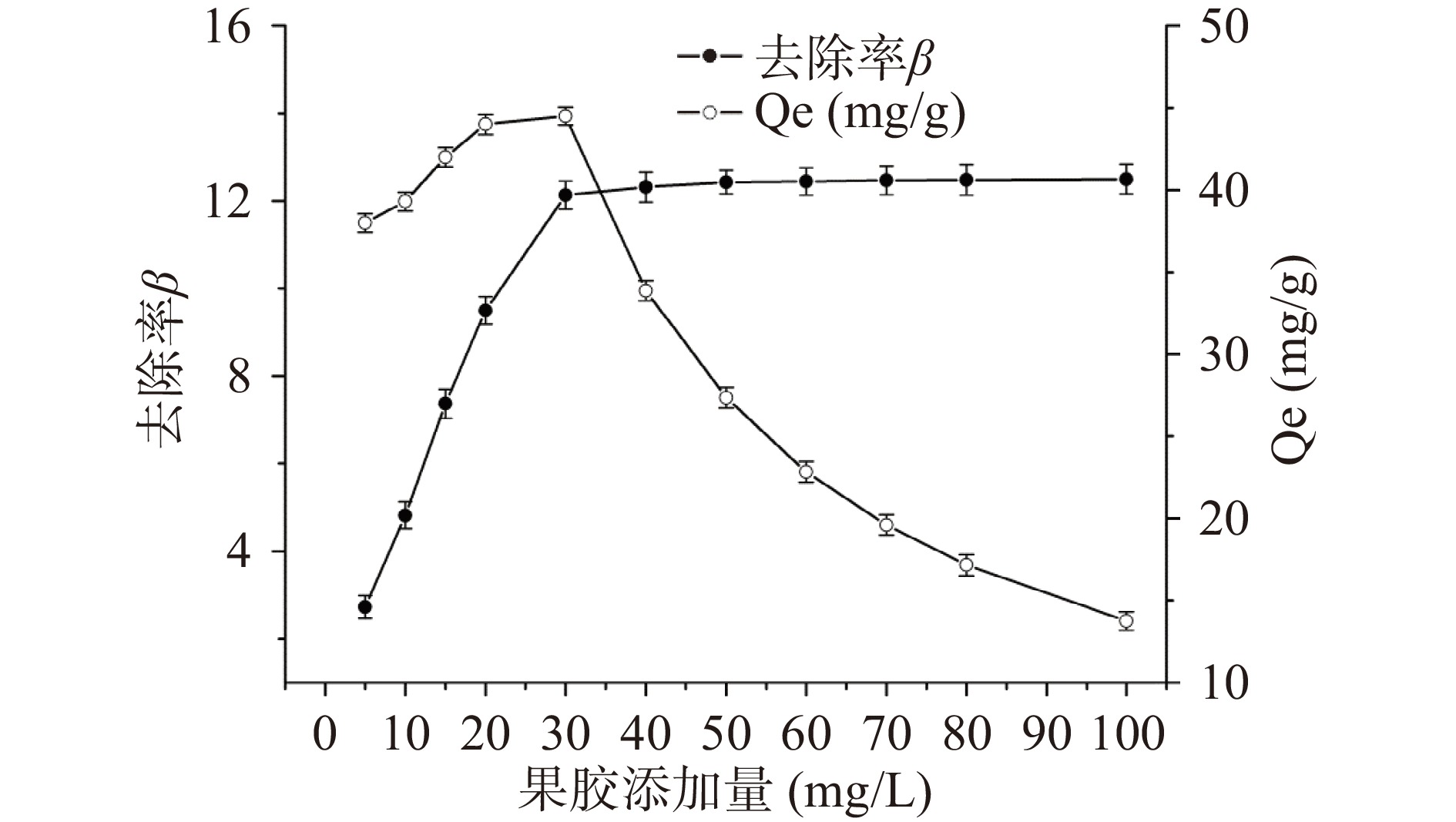
固定溶液中Pb2+的浓度,向其中加入终浓度不同的LAHP,分析LAHP的用量对Pb2+的吸附量Qe和去除率β的影响,结果如图3所示。随着LAHP用量的增加,LAHP对Pb2+的吸附量先增加后减少,而Pb2+的去除率β则先逐渐增加后保持不变,当LAHP的添加量为30 mg/L时,Pb2+的吸附量最大,为44.57±2.50 mg/g。这可能是因为随着果胶用量的增加,LAHP与Pb2+的接触面积不断增加,果胶的活性吸附点也不断增加,但Pb2+的量不变,使得单位质量的果胶吸附Pb2+减少,所以吸附量不断降低[35]。因此,从节约资源的角度考虑,LAHP吸附水溶液中Pb2+(11.0 mg/L)的最佳用量为30 mg/L。
2.3.2 溶液pH对果胶吸附铅离子性能的影响
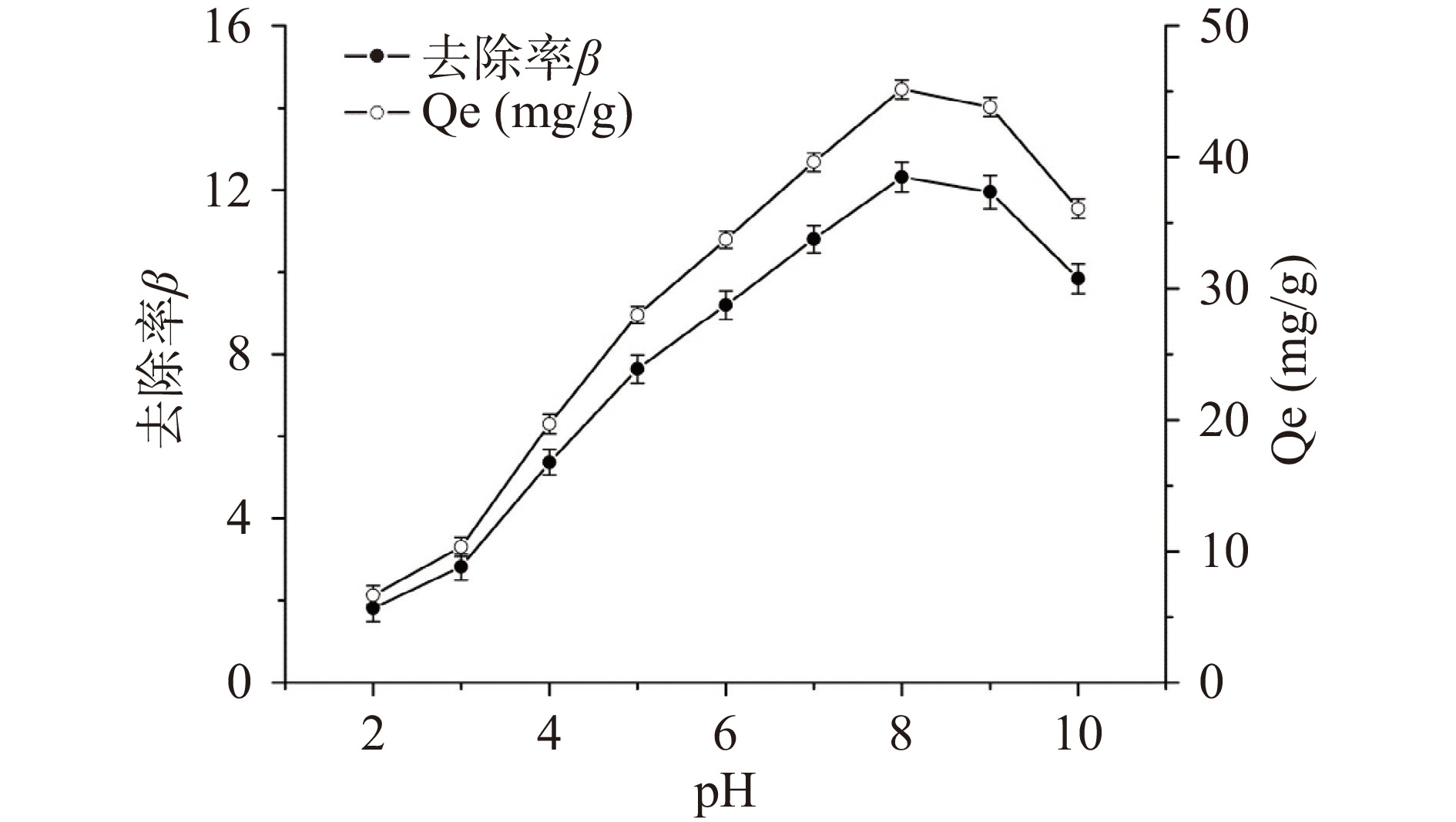
溶液的pH对果胶吸附重金属的性能影响较大,一方面会影响金属离子的存在形式,另一方面会影响吸附材料表面官能团的结构和电荷情况,图4显示了LAHP在不同pH溶液中对Pb2+的吸附情况。总体而言,随着溶液pH的增加,LAHP对Pb2+的吸附性能呈先增大后减少的趋势,在pH=8.0时达到最大吸附量。当pH小于8.0时,随着溶液pH的升高,LAHP对Pb2+的吸附量Qe和去除率β都逐渐增加,这可能是由于pH越低,果胶分子中羧基质子化的比例越高,重金属离子结合位点的数量就越少[18]。当pH高于8.0时,随着pH的升高,LAHP对Pb2+的吸附性能反而降低,可能是因为碱性溶液导致果胶分子变得不稳定,而且溶液中的Pb2+会形成不可溶的氢氧化物[36]。因此,LAHP吸附水溶液中Pb2+(11.0 mg/L)的最佳pH为8.0。
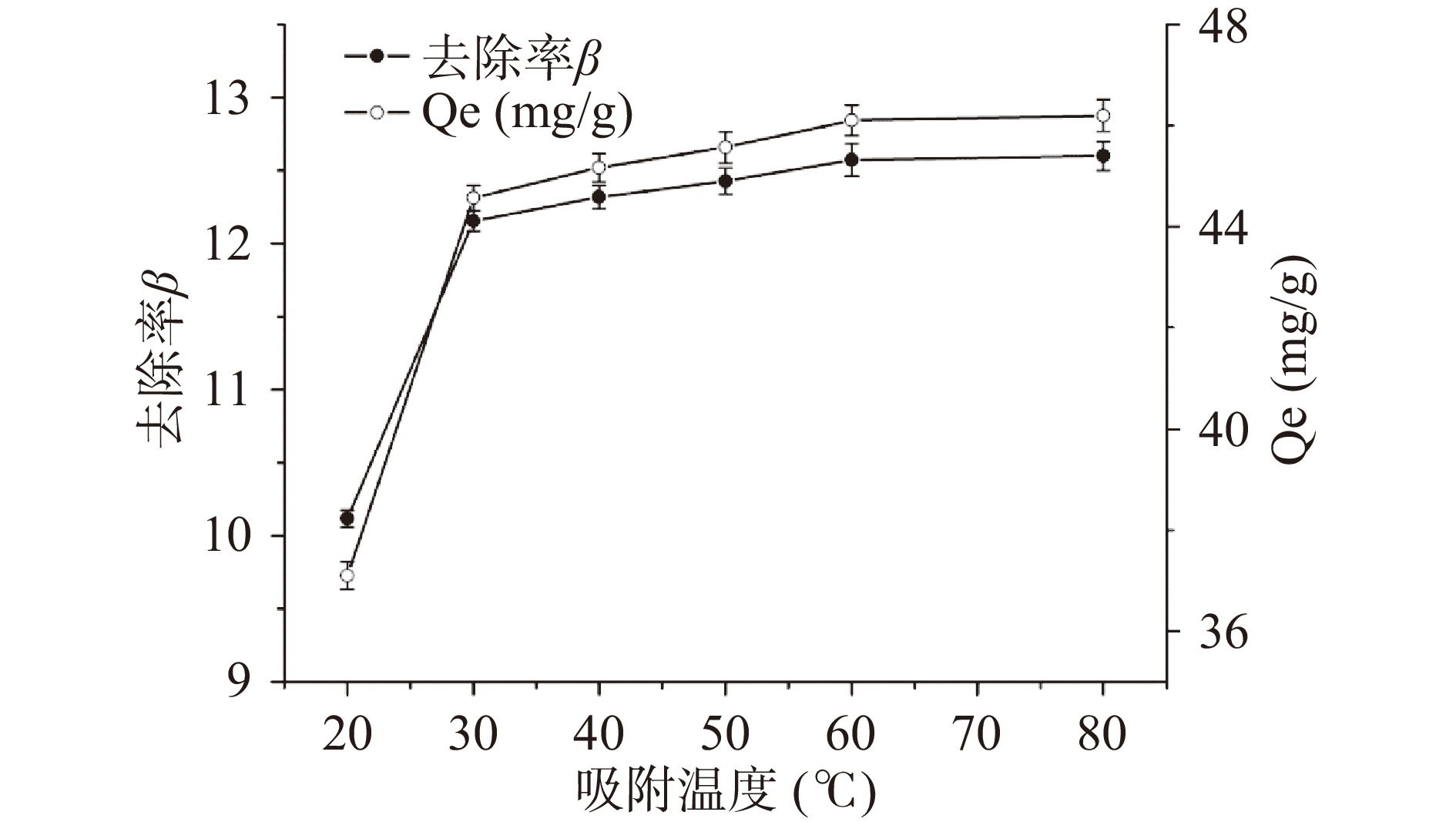
2.3.3 吸附温度对果胶吸附铅离子性能的影响
在20~80 ℃温度范围内检测了LAHP对Pb2+的吸附能力,结果如图5所示。当吸附温度低于30 ℃时,随温度的升高,LAHP对Pb2+的吸附量Qe和Pb2+的去除率β均迅速增加;当吸附温度高于30 ℃时,随温度的升高,Qe和β的增加速率变得较为缓慢;当温度高于60 ℃时,Qe和β几乎不随温度的升高而增加。虽然当吸附温度为60 ℃时,LAHP对Pb2+的吸附量才能达到最大值(46.10%±0.31%),但是为了节约能源,在应用LAHP吸附水溶液中Pb2+时,吸附温度可以设置为30 ℃,此时果胶对Pb2+的吸附容量为44.57±0.25 mg/g。
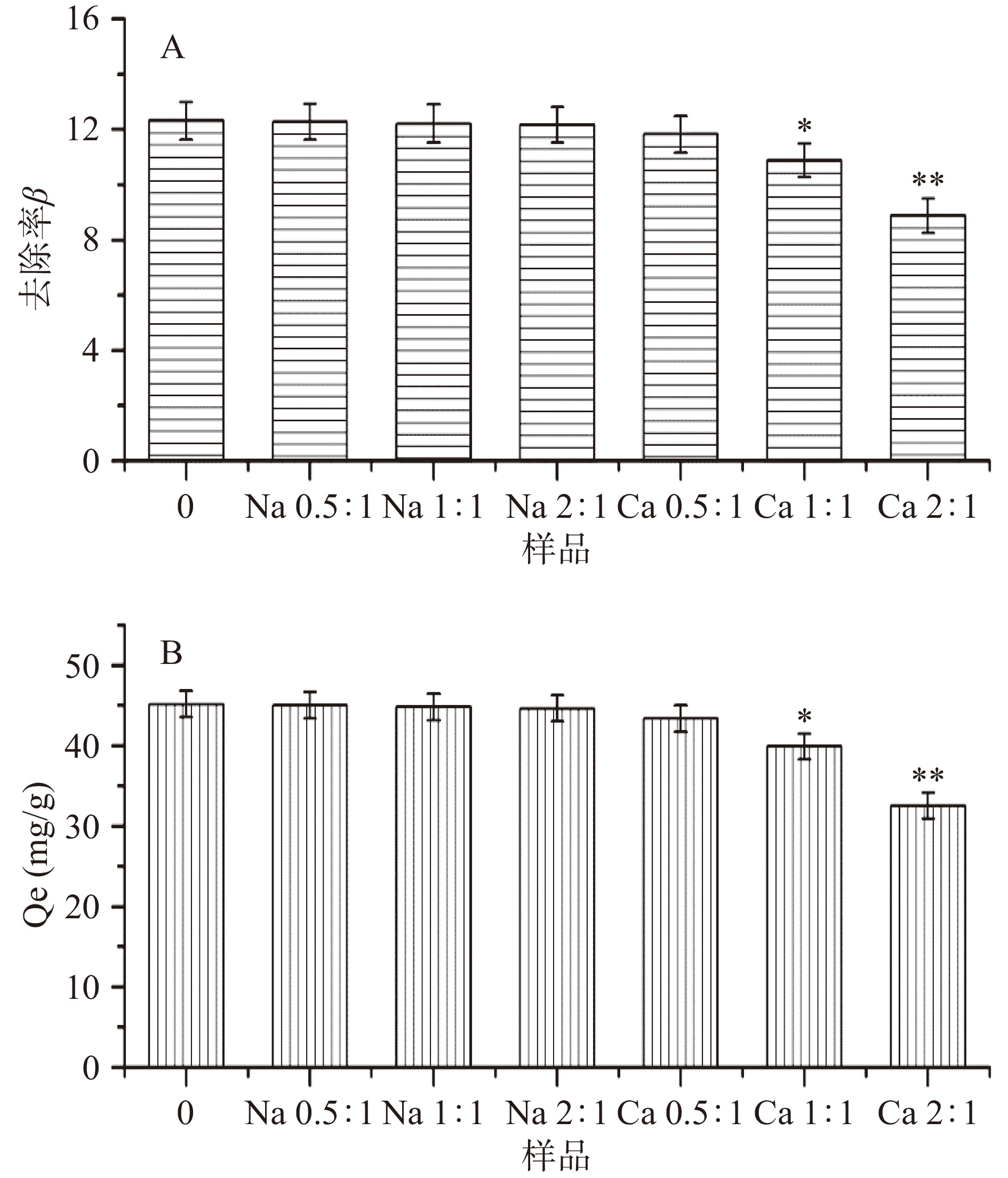
2.3.4 干扰离子对果胶吸附铅离子性能的影响
实际环境污染水样中常常是有害重金属离子与多种阴阳离子共存的,其他的阳离子是否会影响LAHP对重金属离子的吸附性能,也是一个需要考虑的重要问题。因此,本实验设计向Pb2+溶液中添加干扰离子Na+和Ca2+(与Pb2+的质量比依次控制为0.5:1、1:1和2:1)以研究其对LAHP吸附Pb2+性能的影响,结果如图6所示。Na+和低浓度的Ca2+不影响LAHP对Pb2+的吸附性能,当Ca2+与Pb2+的质量比高于1:1时,LAHP对Pb2+的吸附量和Pb2+的去除率均降低,而且随Ca2+浓度的增加,两者的降低程度也增加。因此,推测LAHP吸附Pb2+的作用机制是利用果胶分子中的-COO−与Pb2+形成“蛋盒”络合物结构而吸附去除Pb2+的[18]。一价的Na+不影响“蛋盒”结构的形成,因此几乎不影响LAHP的重金属吸附能力;而二价的Ca2+能够与果胶分子形成“蛋盒”结构[37],占据Pb2+的结合位点,从而导致果胶分子对Pb2+的吸附能力降低。
3. 讨论
果胶是一类酸性多糖,主要由D-吡喃型半乳糖醛酸(D-GalpA)通过α-1,4糖苷键连接构成。甲酯化度DM是果胶的重要性能指标,影响着果胶的凝胶性、流变性和增稠性等性质[32,38],如高酯化果胶(HMP)在可溶性糖含量≥60%、pH为2.6~3.4时形成非可逆的凝胶[39],分子间的疏水作用和氢键是其形成凝胶的主要作用力;而低酯化果胶(LMP)与Ca2+等二价金属离子交联即可形成凝胶,不受糖含量、pH的影响[40],两者之间的桥联作用是其形成凝胶的主要作用力。目前,商品果胶主要是以橘皮、苹果渣、柚皮、橙皮和柠檬皮等农业副产物为原料提取的,这些果胶均为HMP。而商品LMP一般是由酸或碱处理HMP转化而来,价格较高,而且容易造成果胶分子的降解、影响果胶的性能[26]。向日葵盘中富含天然的LMP[19-22,41],但是目前脱籽后的向日葵盘常被丢弃或焚烧,不仅会污染环境,还会造成资源浪费。本论文采用草酸溶液提取、乙醇沉淀的方法提取向日葵盘中的天然低酯化果胶LAHP,收率达14.68%±0.76%。质量分析显示,LAHP符合国家质量标准对食品添加剂果胶的各项质量要求,具有较高的安全性。结构分析显示,LAHP的GalA含量较高、甲酯化度较低、分子量较高,是一种天然的低酯化果胶。本论文的研究不仅可以丰富商品果胶的种类和来源,还有助于充分利用自然资源、减少环境污染。
重金属污染对公众健康有严重威胁,即使在低浓度时也有很大的毒性,在食物链中积累增加,并在环境中稳定存在[2]。Pb2+是工业上最常用的重金属之一,工业废水和土壤中的Pb2+含量不断升高,对人民特别是儿童的健康构成了严重威胁。一些生物聚合物如果胶,可用于去除工业废水中的重金属离子[10,24-25,42]。其机理是金属离子可以与果胶分子中作为结合位点的未酯化羧基结合形成“蛋盒”结构,而所谓的“蛋盒”结构即果胶分子中4~6个结构单元的活性羧基与一个金属离子形成的络合结构[43]。前人的研究证实果胶对金属的吸附量与果胶的化学结构有关,并随酯化度的增加而降低[42,44]。这是因为HMP中的大部分GalA残基与甲基酯化,阻止其与金属离子的相互作用[45],而LMP则被认为是更有效的金属结合剂[18]。本文选择向日葵盘中的天然低酯化果胶LAHP作为重金属吸附剂,并进一步研究了果胶用量、溶液pH、温度、时间和干扰离子等吸附条件对LAHP吸附Pb2+性能的影响。吸附时间对LAHP吸附Pb2+的影响较小,在1 min时即达到最大吸附量的90%以上,这是因为低酯化果胶与金属离子形成“蛋盒”络合结构的速度非常快[43]。溶液的pH对LAHP的Pb2+吸附性能影响较大,这是因为溶液的pH影响果胶分子中羧基的电离程度[46],去质子化的羧基是Pb2+的结合位点。因此,随着溶液pH的升高,LAHP羧基的去质子化程度增加,其对Pb2+的吸附量也随之增加。但是pH过高会导致果胶分子的降解[47]和Pb2+不溶性氢氧化物的形成[36]。干扰离子对果胶吸附Pb2+性能的影响情况进一步证明LAHP吸附Pb2+是通过形成“蛋盒”络合结构而实现的,二价的Ca2+能够与果胶形成“蛋盒”结构[44],从而与Pb2+竞争果胶分子中的金属结合位点,使得果胶对重金属的吸附量降低;而一价的Na+不与果胶形成“蛋盒”结构,不影响果胶的重金属吸附性能。因此,本研究获得的低酯化果胶作为重金属吸附剂可以安全、有效地去除水体中的Pb2+。
4. 结论
采用草酸溶液80 ℃提取、乙醇沉淀和常规干燥的方法从向日葵盘中提取获得果胶LAHP,其半乳糖醛酸含量为86.34%±4.25%,酯化度为23.93%±1.57%,分子量为257 kDa,是天然的低酯化果胶。LAHP对Pb2+的吸附性能受果胶用量、溶液pH、吸附温度及干扰离子的影响。确定了LAHP吸附Pb2+的最佳条件:果胶用量为30 mg/L(Pb2+浓度为11.0 mg/L)、溶液的pH=8.0、处理温度为30 ℃,此时LAHP对Pb2+的吸附量为44.57±2.50 mg/g。Na+等一价金属离子不影响LAHP吸附Pb2+的性能,而较高浓度的二价金属离子Ca2+等会在一定程度上影响LAHP对Pb2+的吸附能力。因此,推测LAHP除去重金属离子的作用机制可能是Pb2+与果胶分子中的-COO-形成“蛋盒”结构而络合除去。本文的研究为开发安全、有效的重金属吸附剂提供了思路,具有较好的理论意义和实际应用价值。但是,本文对LAHP吸附Pb2+机制的研究还不完善,果胶分子的结构如分子量、甲酯化度、分支度等对其重金属吸附性能的影响有待后续进一步的研究。
-
表 1 向日葵盘低酯化果胶的质量分析
Table 1 Quality analysis of low methoxyl pectin from sunflower heads
项目 GB 25533-2010指标 LAHP 干燥失重(%) ≤12 7.15±0.38 灰分(%) ≤5 3.21±0.17 酸不溶灰分(%) ≤1 0.42±0.03 总半乳糖醛酸含量(%) ≥65 86.34±4.25 重金属含量(mg/kg) ≤5 0.34±0.04 酯化度(%) 23.93±1.57 -
[1] PUJARI M, KAPOOR D. Heavy metals in the ecosystem: Sources and their effects[J]. Heavy Metals in the Environment,2021:1−7.
[2] DAS D, CHAKRABORTY S, BHATTACHARJEE C, et al. Biosorption of lead ions (Pb2+) from simulated wastewater using residual biomass of microalgae[J]. Desalination & Water Treatment,2016,57(10):4576−4586.
[3] 叶萌祺, 杜宗军, 陈冠军. 食品中重金属去除技术研究进展[J], 现代食品科技, 2017, 33(10): 308−318 YE Mengqi, DU Zongjun, CHEN Guanjun. Advance of the removal technology of heavy metals in foods[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2017, 33(10): 308−318.
[4] MOSTAFAZADEH A K, BENGUIT A T, CARABIN A, et al. Development of combined membrane filtration, electrochemical technologies, and adsorption processes for treatment and reuse of laundry wastewater and removal of nonylphenolethoxylates as surfactants[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering,2019,28:277−292. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.02.014
[5] 孙宁, 王兆苏, 卢然, 等. “十三五”重金属污染综合防治思路和对策研究[J]. 环境保护科学,2016,42(2):1−7. [SUN Ning, WANG Zhaosu, LU Ran, et al. Study of ideas and countermeasures of comprehensive prevention and control of heavy metal pollution during the 13th five-year plan period[J]. Environmental Protection Science,2016,42(2):1−7. [6] WURMFREDERIK R. Binding matters: Binding patterns control the degradation of phosphorus-containing polymers[J]. Green Materials,2016,4(4):135−139. doi: 10.1680/jgrma.16.00016
[7] 殷晓春, 思广慧, 师玉卓, 等. 纳米纤维素的改性及其吸附重金属离子的应用研究[J]. 高分子通报,2019,11:15−25. [YIN Xiaochun, SI Guanghui, SHI Yuzhuo, et al. A Review on adsorption of heavy metal ions by modified nanocellulose-based materials[J]. Polymer Bulletin,2019,11:15−25. [8] 郑国围, 魏方方, 杨万文, 等. 海藻酸钙复合物凝胶对水中铅和汞重金属离子的吸附性能研究[J]. 轻工科技,2017(7):90−91. [ZHENG Guowei, WEI Fangfang, YANG Wanwen, et al. Study on the adsorption capacity of calcium alginate complex gel for lead and mercury in water[J]. Light Industry Science and Technology,2017(7):90−91. [9] 唐凯. 壳聚糖基吸附剂去除水中重金属离子的研究进展[J]. 应用化工,2019,48(7):1749−1753. [TANG Kai. Research progress on removal of heavy metal ions in water by chitosan adsorbent[J]. Applied Chemical Industry,2019,48(7):1749−1753. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2019.07.054 [10] 王学栋, 李娅, 戴涛涛, 等. 果胶/聚间苯二胺凝胶珠的制备和表征及其对铅(II)吸附性能的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,15:85−95. [WANG Xuedong, LI Ya, DAI Taotao, et al. Study on preparation and characterization of pectin/poly-m-phenylenediamine gel bead and its adsorption performance on lead (II)[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,15:85−95. [11] NOREEN A, NAZLI Z I H, AKRAM J, et al. Pectins functionalized biomaterials; a new viable approach for biomedical applications: A review[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2017,101:254−272. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.03.029
[12] WILLATS W, KNOX J P, MIKKELSEN J D. Pectin: New insights into an old polymer are starting to gel[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2006,17(3):97−104.
[13] LIEW S Q, CHIN N L, YUSOF Y A, et al. Comparison of acidic and enzymatic pectin extraction from passion fruit peels and its gel properties[J]. Journal of Food Process Engineering,2016,39(5):501−511. doi: 10.1111/jfpe.12243
[14] QI P X, CHAU H K, HOTCHKISS A, et al. Molecular characterization of interacting complexes and conjugates induced by the dry-state heating of β-lactoglobulin and sugar beet pectin[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2019,91:10−18. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.01.010
[15] 胡晓波, 李梦圆, 刘咏, 等. 不同提取方法对橙皮果胶乳化特性的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(21):187−194. [HU Xiaobo, LI Mengyuan, LIU Yong, et al. Effect of different extraction methods on emulsification properties of pectins from orange peel[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2019,45(21):187−194. [16] HUQ T, VU K D, RIEDL B, et al. Development of probiotic tablet using alginate, pectin, and cellulose nanocrystals as excipients[J]. Cellulose,2016,23(3):1967−1978. doi: 10.1007/s10570-016-0905-2
[17] GUO Xiaobing, GUO Xiaoming, MENG Hecheng, et al. Influences of different pectins on the emulsifying performance of conjugates formed between pectin and whey protein isolate[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,123:246−254.
[18] KHOTIMCHENKO M, KOVALEV V, KHOTIMCHENKO Y. Equilibrium studies of sorption of lead (II) ions by different pectin compounds[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2007,149(3):693−699. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.04.030
[19] KIM W J, SOSULSKI F, CAMPBELL S J. Formulation and characteristics of low-ester gels from sunflower pectin[J]. Journal of Food Science,2010,43(3):746−749.
[20] 彭晓夏. 向日葵盘果胶的分析及果胶甲酯化方法的研究[D]. 长春: 东北师范大学, 2016 PENG Xiaoxia. Study on pectin from sunflower head and the methyl-esterification of pectin[D]. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, 2016.
[21] PENG Xiaoxia, YANG Guang, SHI Yun, et al. Box-Behnken design based statistical modeling for the extraction and physicochemical properties of pectin from sunflower heads and the comparison with commercial low-methoxylpectin[J]. Scientific Reports,2020,10:3595. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-60339-1
[22] PENG Xiaoxia, YANG Guang, YUE Qi, et al. The film-forming characterization and structural analysis of pectin from sunflower heads[J]. International Journal of Polymer Science,2021(3):1−12.
[23] 中华人民共和国卫生部. 中华人民共和国国家标准GB 25533-2010 食品安全国家标准食品添加剂果胶[S]. Ministry of health of the people’s republic of China. The state standard of the people’s republic of China GB25533-2010 National food safety standard food additive pectin[S].
[24] 冯宁川, 郭学益, 梁莎, 等. 皂化改性橘子皮生物吸附剂对重金属离子的吸附[J]. 环境工程学报,2012,6(5):1467−1472. [FENG Ningchuan, GUO Xueyi, LIANG Sha, et al. Adsorption of heavy metal ions by saponified orange peel[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2012,6(5):1467−1472. [25] 王晓波, 车海萍, 陈海珍, 等. 榴莲壳内皮果胶多糖和黄酮对重金属吸附作用的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2011(25):129−131,135. [WANG Xiaobo, CHE Haiping, CHEN Haizhen, et al. Study on pectin polysaccharides and flavonoids extraction of durian inner shell on adsorption capacity of heavy metals[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2011(25):129−131,135. [26] IGLESIAS M T, LOZANO J E. Extraction and characterization of sunflower pectin[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2004,62(3):215−223. doi: 10.1016/S0260-8774(03)00234-6
[27] SAHARI M A, AKBARIAN A, HAMEDI M. Effect of variety and acid washing method on extraction yield and quality of sunflower head pectin[J]. Food Chemistry,2003,83(1):43−47. doi: 10.1016/S0308-8146(03)00034-7
[28] WANG Kun, HUA Xiao, YANG Ruijin, et al. Hydrodynamic behavior and gelling properties of sunflower head pectin in the presence of sodium salts[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2014,36:238−244. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2013.09.011
[29] HUA Xiao, WANG Kun, YANG Ruijin, et al. Rheological properties of natural low-methoxyl pectin extracted from sunflower head[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2015,44:122−128. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2014.09.026
[30] PATIL S N, PARADESHI J, CHAUDHARI P B, et al. Bio-therapeutic potential and cytotoxicity assessment of pectin-mediated synthesized nanostructured cerium oxide[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology,2016,180(4):1−17.
[31] YAPO B M, LEROUGE P, THIBAULT J F, et al. Pectins from citrus peel cell walls contain homogalacturonans homogenous with respect to molar mass, rhamnogalacturonan I and rhamnogalacturonan II[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2007,69(3):426−435. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2006.12.024
[32] CHATJIGAKIS A K, PAPPAS C, PROXENIA N, et al. FT-IR spectroscopic determination of the degree of esterification of cell wall pectins from stored peaches and correlation to textural changes[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,1998,37(4):395−408. doi: 10.1016/S0144-8617(98)00057-5
[33] KANG Jiaqi, HUA Xiao, YANG Ruijin, et al. Characterization of natural low-methoxyl pectin from sunflower head extracted by sodium citrate and purified by ultrafiltration[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,180:98−105. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.02.037
[34] MA Xuemei, JING Jing, WANG Jingbao, et al. Extraction of low methoxyl pectin from fresh sunflower heads by subcritical water extraction[J]. ACS Omega,2020,5(25):15095−15104. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c00928
[35] 周宇, 何媛, 周文俊. 果胶对钯的吸附及其在有机合成中的应用[J]. 应用化学,2015,32(12):1402−1409. [ZHOU Yu, HE Yuan, ZHOU Wenjun. Adsorption of palladium by pectin and its application in organic synthesis[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry,2015,32(12):1402−1409. doi: 10.11944/j.issn.1000-0518.2015.12.150207 [36] 田月月, 胡沁蕊, 孔祥珍, 等. 水溶性大豆多糖体外吸附Pb2+的研究[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2018,37(4):50−54. [TIAN Yueyue, HU Qinrui, KONG Xiangzhen, et al. In vitro binding of lead by soybean soluble polysaccharides[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology,2018,37(4):50−54. [37] BORGOGNA, MASSIMILIANO, SKJåK-BRæK, et al. On the initial binding of alginate by calcium ions. The tilted egg-box hypothesis[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry B,2013,117(24):7277−7282. doi: 10.1021/jp4030766
[38] LöFGREN C, HERMANSSON A-M. Synergistic rheological behaviour of mixed HM/LM pectin gels[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2007,21(3):480−486. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2006.07.005
[39] GENOVESE D B, YE A, SINGH H. High methoxyl pectin/apple particles composite gels: effect of particle size and particle concentration on mechanical properties and gel structure[J]. Journal of Texture Studies,2010,41(2):171−189. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-4603.2010.00220.x
[40] CáRDENAS A, GOYCOOLEA F M, RINAUDO M. On the gelling behaviour of ‘nopal’ (Opuntiaficus indica) low methoxyl pectin[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2008,73(2):212−222. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2007.11.017
[41] MIYAMOTO A, CHANG K C. Extraction and physicochemical characterization of pectin from sunflower head residues[J]. Journal of Food Science,2010,57(6):1439−1443.
[42] 梁瑞红, 李鹏琳, 贺小红, 等. 不同酯化度的柑橘果胶对Pb2+的吸附作用影响及其机理研究. 食品工业科技, 2018, 39(6): 13−18 LIANG Ruihong, LI Penglin, HE Xiaohong, et al. Effects of citrus pectin with different degree of esterification on adsorption of Pb2+ and its mechanism[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2018, 39(6): 13−18.
[43] WAI W W, ALKARKHI A, EASA A M. Comparing biosorbent ability of modified citrus and durian rind pectin[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2010,79(3):584−589. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.09.018
[44] KHOTIMCHENKO M, MAKAROVA K, KHOZHAENKO E, et al. Lead-binding capacity of calcium pectates with different molecular weight[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2017,97:526−535. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.01.065
[45] MANUNZA B, DEIANA S, PINTORE M, et al. Interaction of Ca2+ and Na+ ions with polygalacturonate chains: A molecular dynamics study[J]. Glycoconjugate Journal,1998,15(3):297−300. doi: 10.1023/A:1006905314435
[46] FISHMAN M L, CHAU H K, QI P X, et al. Characterization of the global structure of low methoxyl pectin in solution[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2015,46:153−159. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2014.12.021
[47] PENG Xiaoxia, YANG Guang, FAN Xingchen, et al. Controlled methyl-esterification of pectin catalyzed by cation exchange resin[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2016,137:650−656. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.11.005







 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



