Effects of Theabrownin from Pu-erh Tea on Differentially Expressed Genes in the Liver of MS Rats during Growth
-
摘要: 为探讨普洱茶茶褐素对代谢综合征大鼠生长过程中的差异表达基因信息的影响,研究基于前期已获得的高质量代谢综合征大鼠肝脏转录组数据,用Short Time-series Expression Miner(STEM)软件,先对差异基因(DEGs)进行趋势分析,然后对显著上调和下调趋势包含的DEGs进行GO和KEGG富集分析。趋势分析结果显示3009个DEGs共聚类在7个显著基因表达模式。其中,493个DEGs聚类在1个显著上调趋势(profile19);248个DEGs聚类在1个显著下调趋势(profile0)。GO富集分析结果显示,显著上调趋势包含DEGs富集于40个GO条目,显著下调趋势包含DEGs富集于35个GO条目,富集基因数最多的均为细胞,其次是细胞零件和细胞进程。KEGG代谢通路富集分析结果显示,MS大鼠灌胃不同剂量茶褐素(TB)后Gnpda2、Ugp2、Cyp7a1、Sec11a、Sec61a1、Per3、Gmppa、Spcs3基因表达量呈现出直线增加的形式,说明随TB浓度的增加,这些基因表达量也随之增加;而Ste2、Mpv17l、Elovl5、Cry1、Plin2、Angptl4、Cyp4a8、Eci1、Pex11a、Cyp26b1、Cyp26a1、Crat、Pmvk、Cyp2d4、Acot5、Akr1c1、Acot4基因表达量呈现出递减的模式,说明TB对这些基因的表达有线性抑制作用。本研究揭示了TB对MS大鼠的肝脏基因表达谱和基因差异表达信息,TB影响肝脏基因表达的规律,为阐明普洱茶茶褐素降血糖、血脂的分子机制提供参考。Abstract: In order to explore the differential expression gene information of theabrownin from Pu-erh tea (TB) on the growth-process of metabolic syndrome rats (MS). The study was based on high quality transcriptomic data obtained from metabolic syndrome rats’ liver, and the Short Time-series Expression Miner (STEM) software was used to analyze the trend of differential genes (DEGs). Then the significant trends were be analyzed by GO and KEGG enrichment. The results showed that 3009 DEGs copolymer classes in 7 significant gene expression patterns. Among them, 493 DEGs clustered in 1 significant upward trend (profile19); 248 DEGs clustered in 1 significant downward trend (profile0). The results of GO enrichment analysis showed that the significant upward trend contains DEGs enriched in 40 GO entries and the significant downward trend contains DEGs enriched in 35 GO entries. And the largest number of enriched genes were all cells, followed by cell parts and cell processes. The results of KEGG metabolic pathway enrichment analysis showed that Gnpda2, Ugp2, Cyp7a1, Sec11a, Sec61a1, Per3, Gmppa and Spcs3 gene expression in MS rats showed a linear increase after gavage different doses of TB. As the TB concentration increased, the expression of these genes also increased. However, the expression of Ste2, Mpv17l, Elovl5, Cry1, Plin2, Angptl4, Cyp4a8, Eci1, Pex11a, Cyp26b1, Cyp26a1, Crat, Pmvk, Cyp2d4, Acot5, Akr1c1, Acot4 genes showed a decreasing pattern, indicated that the expression of these genes had a linear inhibitory effect on the expression of these genes. This experiment provides TB liver gene expression profile and gene differential expression information to MS rats, reveals the gene expression rules, and provides reference and contrast for further exploration of the molecular mechanism of hypoglycemic and lipid-lowering of theabrownin from Pu-erh tea in the future.
-
普洱茶茶色素属于天然色素,指从普洱茶中提取的一类水溶性酚性色素,包括茶黄素(TF)、茶红素(TR)、茶褐素(TB)等,其主要活性成分茶褐素是在普洱茶发酵过程中大量形成的[1]。现有多篇文献报道茶褐素具有降血糖、降血脂、减肥、防止动脉硬化、预防脂肪肝、抗氧化等功效[2-5]。赵丹等[6]的研究表明,茶褐素能够调节高糖饮食大鼠糖脂代谢关键酶活性,加速高糖饮食大鼠脂质代谢,降低高糖饮食大鼠胰岛损伤的程度。张婷婷等[7]的研究表明,普洱茶茶褐素具有抑制高糖饮食大鼠血糖升高及体重增加的功效。高斌等[8]研究发现,普洱茶茶褐素可显著增强高脂饮食大鼠肝脏和附睾脂肪组织HSL活性及其mRNA的表达,对大鼠降血脂效果明显。WU等[9]研究发现,灌胃茶褐素与荡秋千结合可显著改善代谢综合征大鼠血脂状态并预防大鼠肥胖和胰岛素抵抗。
之前关于茶褐素的研究主要是茶褐素对单一的高脂或高糖饮食大鼠的影响,茶褐素对于高脂高糖高盐饮食大鼠的研究几乎没有。近年来,人们的饮食、生活方式发生了很大改变,含有丰富脂肪、糖分以及能量食品越来越多,高脂高糖高盐饮食很难避免,而长期高脂高糖高盐饮食是引发代谢综合征(MS)的主要因素之一。MS是一组以肥胖、高血糖(糖尿病(diabetes mellitus,DM)或糖调节异常(impaired glucose regulation,IGR))、血脂异常(高甘油三酯和(或)低高密度脂蛋白胆固醇)以及高血压等聚集发病,是糖尿病及心血管疾病的重要复杂危险因素,影响着全身各个系统,严重降低了人民生活质量,缩短寿命。研究显示,MS发病率在全球呈上升趋势,已经成为严重威胁人群健康的公共卫生问题[10]。
本文主要基于前期[9]已获得的高质量代谢综合征大鼠肝脏转录组数据,通过趋势分析,GO(gene ontology)和KEGG(Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes)代谢通路(Pathway)富集分析,对高脂高糖高盐饮食大鼠肝脏差异表达基因(DEGs)进行转录组学分析,为深入探讨普洱茶茶褐素预防代谢综合征,降血糖、血脂的分子机制奠定基础,也为普洱茶的开发利用提供科学依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
凤庆牌普洱茶熟茶 购自云南春茗茶业有限责任公司(产品标准:GB/T 14456.2;生产日期:2012年);实验动物 由昆明医科大学实验动物中心提供(实验动物许可证:SCXK(滇)K2015-0002),选择SPF级雄性SD大鼠,体重160~180 g,外观符合健康标准;无水乙醇、无水乙醚(分析纯) 天津市化学试剂三厂;RT-PCR试剂 TRAN公司;逆转录试剂盒 Fast Quantity RT Kit(KR106) TIANGEN公司。
Nanodrop RNA质量检测仪、Forma900 −80 ℃冰箱、Mk3酶标仪、CT15RE冷冻离心机 Thermo Scientific;G2940CA Bioanalyzer 2100 美国Agilent科技;HiSeqTM 2000 基因测序仪、ABI Step One Plus荧光定量PCR仪 美国Illumina。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 普洱茶茶褐素样品的制备
普洱茶熟茶茶样→10倍蒸馏水(95 ℃)浸提2次,每次30 min→过滤→合并滤液→减压浓缩(65 ℃,0.07 MPa)→乙醇(滤液:无水乙醇=1:4,V/V)醇沉6 h→离心(4000 r/min,20 min)→收集沉淀→蒸馏水溶解→真空冷冻干燥→粗茶褐素(供试样)(茶褐素含量[11]:75.3%)。
1.2.2 实验动物的分组与饲喂管理
1.2.2.1 饲养方法及管理
大鼠在空调动物饲养室中同室群笼饲养,自由摄食,自由饮水。每天换一次垫料、鼠笼,清洗饮水瓶。每天定时通风,环境温度控制在(20±2)℃,湿度45%~60%。基础饲料配方/(g/kg):玉米350、麦麸250、豆粕250、鱼粉80、酵母20、骨粉20、乳清粉10、盐5、菜油5、矿物添加剂1、复合维生素0.3、蛋氨酸1.3、赖氨酸0.7、鱼肝油0.5。高脂高盐高糖饲料配方(g/kg):基础饲料620、猪油100、蛋黄粉100、胆固醇15、胆盐5、食盐10、白砂糖150。
1.2.2.2 实验动物组别设计
所有大鼠首先全部饲喂基础饲料,自由摄食、饮水,喂养1周以适应环境和饲喂方式,1周后根据TC(总胆固醇)、TG(甘油三酯)、GLU(葡萄糖)水平,随机分为5组,每组12只大鼠,分别为正常对照组、MS模型组、低、中、高剂量茶褐素组。适应期7 d结束后进入为期63 d的干预期,除正常对照组外,其他组别大鼠均食用高脂高盐高糖饲料,并每天自由饮用质量分数15%果糖。
1.2.2.3 灌胃剂量
低剂量为0.281 g/kg·bw,中剂量为0.562 g/kg·bw,高剂量为1.124 g/kg·bw。按照每组实验动物的体质量,称取一定量的受试物,溶于3 mL蒸馏水中,每日经口一次性灌胃,正常对照组和MS模型组给予等量蒸馏水灌胃[12-13]。
1.2.3 大鼠生理指标的测定
体重、TG(甘油三酯)、FPG(空腹血糖)的测定同参考文献[7]。
1.2.4 肝脏转录组学研究
肝脏组织的制备:干预期结束后将大鼠脱颈椎处死,解剖,将肝脏样品置于无菌试管内,分别命名为正常对照组(A1)、MS模型组(B1)、TB低剂量组(E1)、TB中剂量组(F1)、TB高剂量组(G1),并迅速用液氮冷冻转移至-80 ℃超低温冰箱贮存以备检测。
大鼠肝脏组织RNA的提取采用TRIzol法[9];TotalL RNA质量检测采用AgiLent 2100 BioanaLyzer,测序样品要求浓度>200 ng/µL,总量>20 µg,OD260/OD280≥1.8,28S/18S≥1.0;cDNA文库的构建:样品提取总RNA后,用带有Oligo(dT)的磁珠富集mRNA,向得到的mRNA中加入fragmentation buffer使其片断成为短片段,再以片断后的mRNA为模板,用6碱基随机引物(random hexamers)合成cDNA第一链,并加入缓冲液、dNTPs、RNase H和DNA Polymerase I合成cDNA第二链,经过QiaQuick PCR试剂盒纯化并加EB缓冲液洗脱经末端修复、加碱基A,加测序接头,再经琼脂糖凝胶电泳回收目的大小片段,并进行PCR扩增[9],从而完成整个文库制备工作;采用Illumina HiSeqTM 2000测序(cDNA文库的构建和Illumina HiSeqTM 2000测序由广州基迪奥公司完成)。
1.3 基因趋势分析
利用ShortTime-series Expression Miner[14]软件对所有DEGs进行趋势分析,获得显著性和非显著性基因表达模式。并对各个趋势中的基因进行GO/KEGG功能富集分析,通过假设检验计算得到P-value。得到的P-value通过FDR校正后[15],以Q-value≤0.05为阈值,满足此条件的GO term和Pathway,定义为在该趋势中显著富集的GO term和Pathway。
1.4 数据处理
DEGs的GO分类、KEGG Pathway富集分析及表达量聚类分析利用WEGO[16]对显著上调和下调趋势中的DEGs进行GO分类。利用Blastalla将显著上调和下调趋势中的DEGs比对KEGG数据库(www.genome.jp/kegg/),进行Pathway富集分析。利用在线分析工具Omics Share(http://www.omicshare.com/tools/index.php/Home/Index/index.html)对DEGs进行表达量聚类分析。为验证测序数据的可靠性,随机选取6个DEGs进行实时荧光定量PCR(RT-PCR)验证。反应按照KR106 Fast Quant RT Kit操作说明书进行。本实验进行3次生物学重复和3次技术重复。
其它数据以“平均值±标准差”表示,所有数据先进行Grubbs检验,以排除过失误差;经G检验合格的数据,采用SPSS 22.0,用邓肯氏法进行显著性分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 普洱茶茶褐素对代谢综合征大鼠生理指标的影响
由表1可以看出,适应期结束时,各实验组之间大鼠生理指标不具有统计学差异(P>0.05),干预期结束时,MS模型组的体重、甘油三酯(TG)、空腹血糖(FPG)值均显著高于正常对照组(P<0.05),表明代谢综合征(MS)大鼠模型建立成功。TB中、高剂量组和正常对照组之间大鼠体重不具有统计学意义(P>0.05),而MS模型组大鼠体重显著高于TB中、高剂量组(P<0.05)。说明普洱茶茶褐素能够抑制MS大鼠体重的增长,在一定范围内随着灌胃剂量的增加,体重受抑制的程度增大。这表明中、高剂量茶褐素对大鼠有减肥作用。
表 1 普洱茶茶褐素对大鼠体重、甘油三酯和空腹血糖的影响Table 1. Effect of TB extracted from Pu-erh tea on the body weight, TG and FPG of rats体重(g) TG(mmol/L) FPG(mmol/L) 组别 适应期 干预期63 d 净增体重 适应期 干预期63 d 适应期 干预期63 d 正常对照组 199.03±13.48A 346.84±26.02AB 147.81±26.58AB 0.68±0.11A 0.49±0.08AB 6.19±1.74A 7.07±1.57A MS模型组 207.91±13.18A 393.93±34.45C 186.02±29.60C 0.78±0.12A 0.68±0.28C 5.39±1.74A 8.92±1.48C TB低剂量组 204.20±14.71A 367.78±28.60BC 163.58±32.00BC 0.74±0.12A 0.56±0.16BC 5.47±1.80A 8.57±1.28BC TB中剂量组 203.83±12.72A 346.21±30.52AB 142.39±33.21AB 0.80±0.24A 0.39±0.04A 5.61±1.62A 8.61±1.15BC TB高剂量组 208.31±16.30A 326.93±25.73A 118.61±22.38A 0.68±0.11A 0.46±0.06AB 5.96±1.60A 7.48±0.91AB 注:同列不同大写字母,表示具有统计学差异(P<0.05)。 干预期63 d后,TB中、高剂量组的TG水平与MS模型组相比具有统计学意义(P<0.05),同时与正常对照组相比无显著性差异(P>0.05);表明灌胃中、高剂量的普洱茶茶褐素能够有效地降低MS大鼠血清TG水平;正常对照组的FPG水平与MS模型组、TB中、低剂量组相比均具有统计学意义(P<0.05),与TB高剂量组相比不具有统计学意义(P>0.05);表明灌胃高剂量普洱茶茶褐素可预防高脂高糖高盐饮食大鼠FPG水平的升高(P<0.05)。
2.2 不同组别的大鼠肝脏组织差异表达基因统计
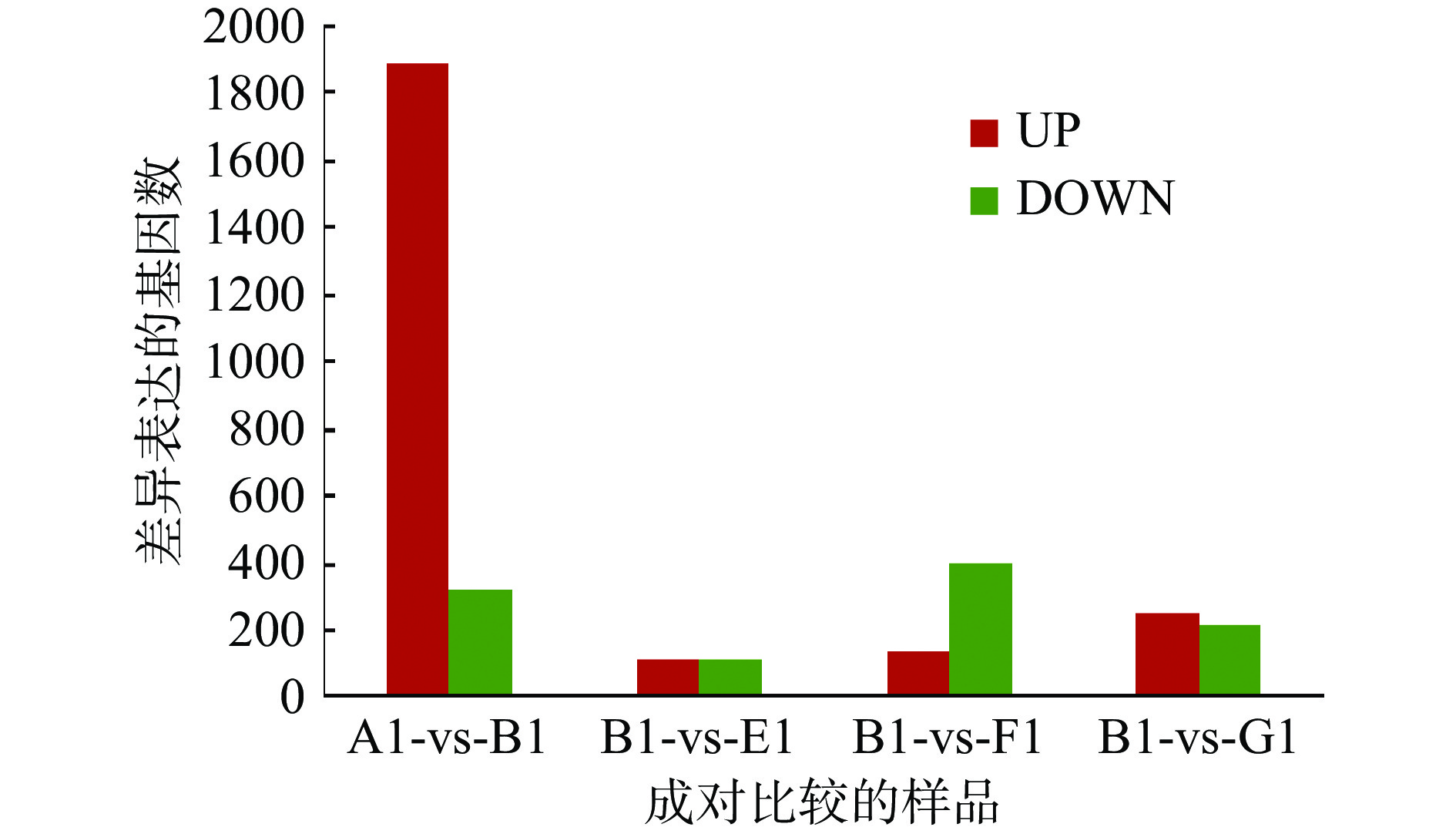
对5个组别所比对上的基因进行FPKM法定量,根据计算的基因表达量(FPKM值),计算该基因在不同样本间的差异表达倍数。然后,对差异检验的P-value作多重假设校正,通过控制FDR(false discovery rate)来决定P-value的域值。利用FDR与log2FC来筛选差异基因,筛选条件为FDR<0.05且|log2FC|>1。FDR值越小,差异倍数越大,表明表达差异越显著[15]。本试验5个组别,两两进行了基因差异表达统计分析,结果如下图1所示,样品间差异基因统计柱状图横坐标:成对比较的样品;纵坐标:差异表达的基因数;红色代表上调表达的差异基因;绿色代表下调表达的差异基因。
![]() 图 1 差异表达基因统计注:A1:正常对照组;B1:MS模型组;E1:TB低剂量组;F1:TB中剂量组;G1:TB高剂量组;表2同。Figure 1. The statistics of DEGs
图 1 差异表达基因统计注:A1:正常对照组;B1:MS模型组;E1:TB低剂量组;F1:TB中剂量组;G1:TB高剂量组;表2同。Figure 1. The statistics of DEGs如图1所示,正常对照组与MS模型组相比,有1886个基因上调表达,320个基因下调表达;MS模型组与TB低剂量组相比,有119个基因上调表达,112个基因下调表达;MS模型组与TB中剂量组相比,有133个基因上调表达,404个基因下调表达;MS模型组与TB高剂量组相比,有257个基因上调表达,213个基因下调表达。
2.3 普洱茶茶褐素对高脂高糖高盐饮食大鼠差异基因趋势的影响
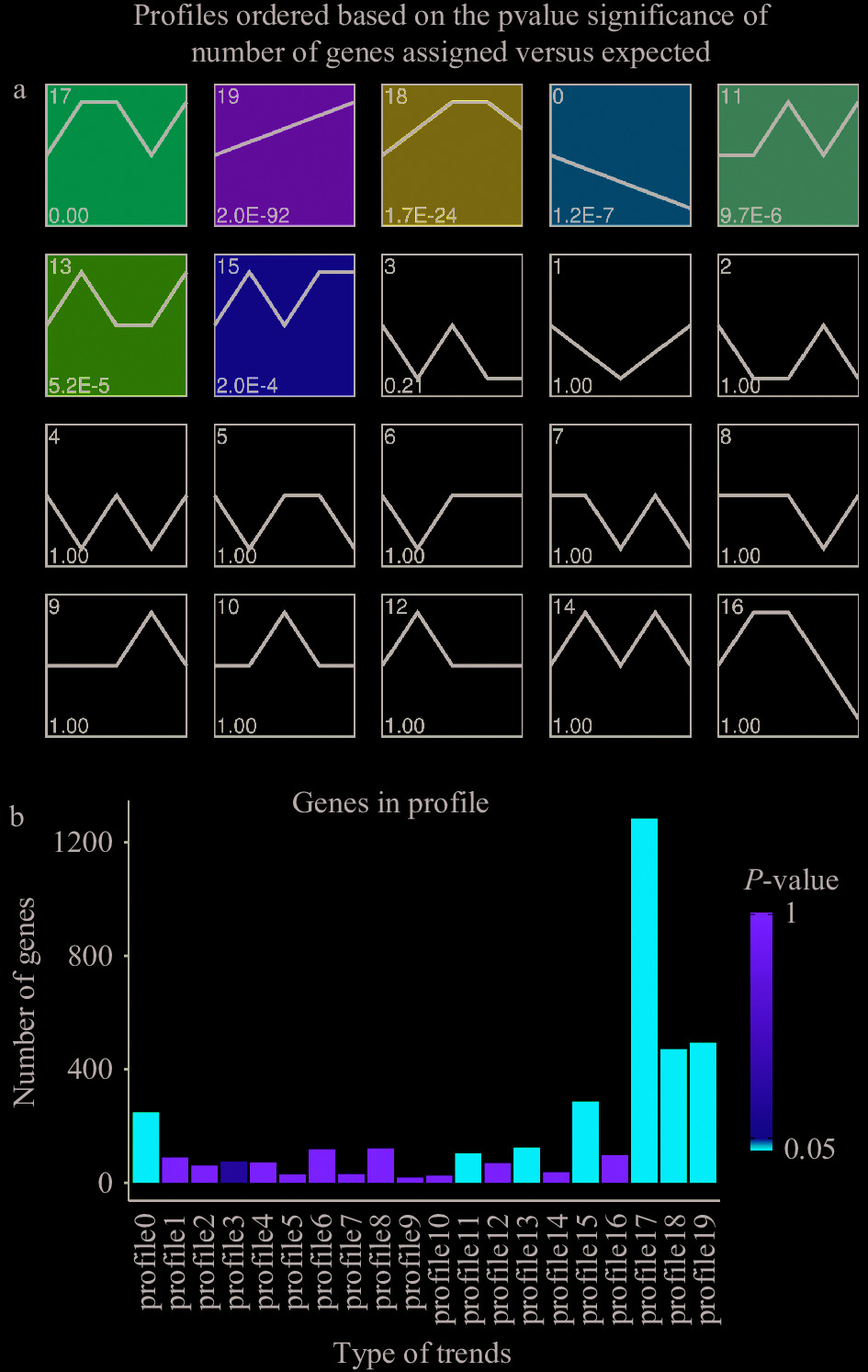
趋势分析是针对至少3个连续型样本的特点(样本间包含特定的处理剂量高低顺序)而对基因的表达模式进行聚类的方法。然后从聚类结果中挑选符合一定生物学特性的基因集,如表达量持续上升或持续下降[15]。这里通过基因表达水平的k-均值聚类,将所有的DEGs分为20种表达趋势(图2a),每种趋势的基因数不等,在这些趋势中,有7种表达显著(P<0.05),分别是profile0、profile11、profile13、profile15、profile17、profile18和profile19(图2b)。其中profile19和profile0显示相反的表达趋势(图2a和2b),profile19中含有的493个基因呈现出表达量直线增加的形式,说明在一定浓度范围内,这些基因的表达量随普洱茶茶褐素浓度的增加而增加;profile0中的248个基因表达量则以一直递减的模式呈现,说明茶褐素浓度对这些基因的表达有线性抑制作用。
![]() 图 2 差异表达基因聚类分析注:图2a大鼠差异表达基因所有趋势总图:每个趋势图左上方为趋势的ID,左下方为趋势中的P-value值;按P-value值排序,数值从小到大,黑线表示趋势线,横坐标为样品的编号(从左往右按照A1、B1、E1、F1、G1排列),纵坐标为log2(V(i)/V(0)),第i个样品的表达量与第1个样品的表达量的比值的log2值,带颜色的趋势块(P<0.05)为显著富集的趋势,不带颜色的趋势块为非显著富集的趋势块;图2b大鼠差异表达基因趋势基因数、P-value柱状图:图上柱子的高度代表基因数目,柱子的颜色代表P-value。Figure 2. Cluster analysis of differentially expressed genes
图 2 差异表达基因聚类分析注:图2a大鼠差异表达基因所有趋势总图:每个趋势图左上方为趋势的ID,左下方为趋势中的P-value值;按P-value值排序,数值从小到大,黑线表示趋势线,横坐标为样品的编号(从左往右按照A1、B1、E1、F1、G1排列),纵坐标为log2(V(i)/V(0)),第i个样品的表达量与第1个样品的表达量的比值的log2值,带颜色的趋势块(P<0.05)为显著富集的趋势,不带颜色的趋势块为非显著富集的趋势块;图2b大鼠差异表达基因趋势基因数、P-value柱状图:图上柱子的高度代表基因数目,柱子的颜色代表P-value。Figure 2. Cluster analysis of differentially expressed genes2.4 GO功能富集分析
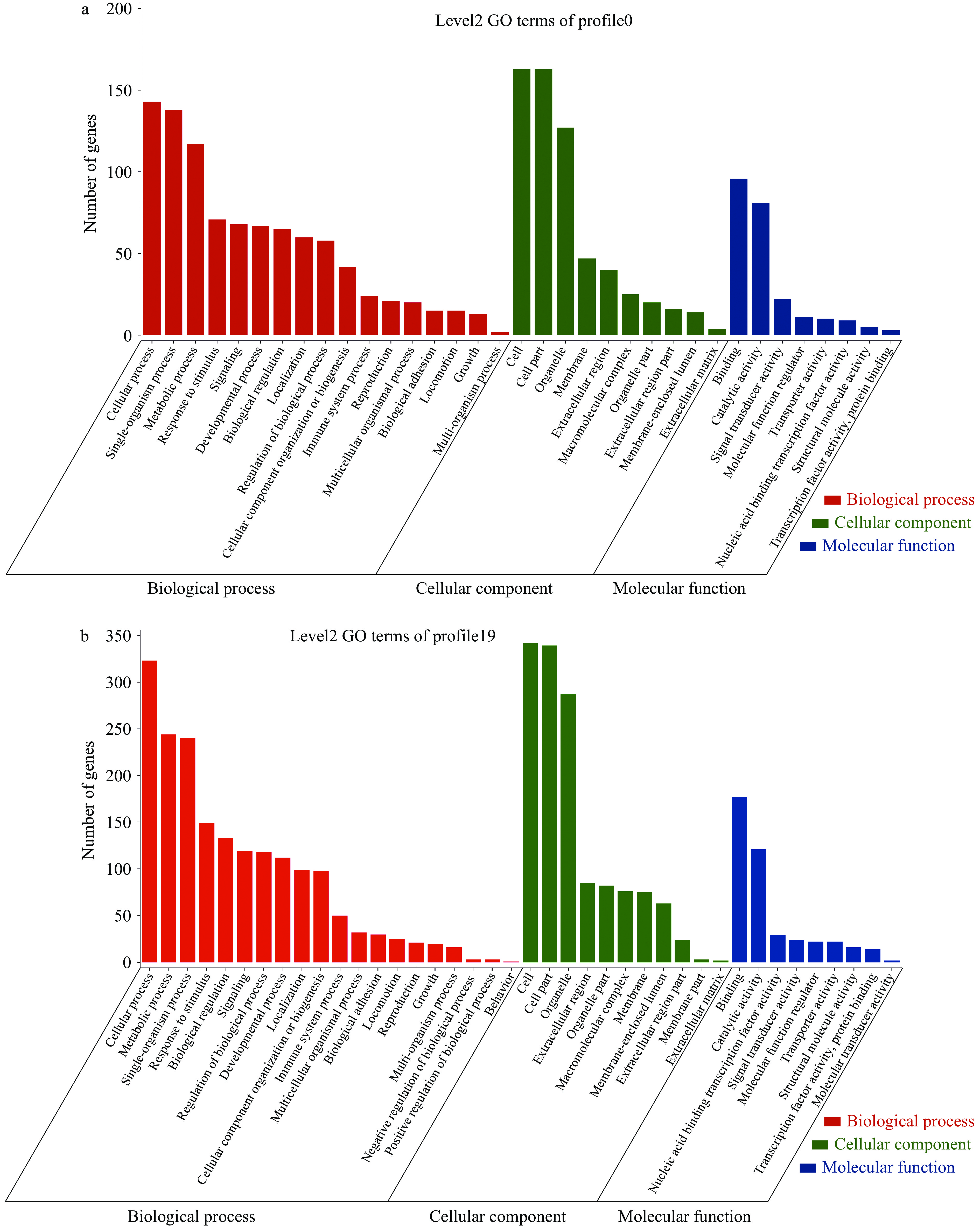
Gene Ontology(简称GO)是一个国际标准化的基因功能分类体系,提供了一套动态更新的标准词汇表来全面描述生物体中基因和基因产物的属性。GO总共有三个本体,分别描述基因的分子功能(MF,molecular function)、细胞组分(CC,cellular component)、参与的生物过程(BP,biological process)[17]。为显著趋势基因集群profile0和profile19(P<0.05)进行GO功能富集分析。
对profile0和profile19两种显著表达趋势所富集的MF、BP和CC进行了比较,结果表明,不同表达趋势基因的共同功能注释较多,即在profile0和profile19中MF、BP和CC中基因数虽差别明显,但所属功能基本一致。GO富集分析结果显示,显著下调趋势包含DEGs富集于35个GO条目上(图3a),富集基因数前十位的GO条目分别是cell(163 genes)、cell part(163 genes)、cellular process(143 genes)、single-organism process(138 genes)、organelle(127 genes)、metabolic process(117 genes)、binding(96 genes)、catalytic activity(81 genes)、response to stimulus(71 genes)、signaling(68 genes);显著上调趋势包含DEGs富集于40个GO条目上(图3b),富集基因数前十位的GO条目分别是cell(342 genes)、cell part(339 genes)、cellular process(323 genes)、organelle(287 genes)、metabolic process(244 genes)、single-organism process(240 genes)、binding(177 genes)、response to stimulus(149 genes)、biological regulation(133 genes)、catalytic activity(121 genes)。与profile0相比profile19多富集在5个GO条目上,分别是behavior,membrane part,molecular transducer activity,negative regulation of biological process,positive regulation of biological process。
2.5 Pathway富集分析
显著富集Pathway分析能准确的将基因定位在某个代谢途径中的某一个节点上,并确定差异表达基因参与的最主要生化代谢途径和信号转导途径[18]。不同趋势中Pathway相关基因的富集情况如图4所示。一个基因可以有许多不同的功能,同时,还可以在许多代谢通路中表现活跃。此外,一个基因可以直接或间接地减少或增加其他基因的表达。
由图4a可知,profile0显著富集的Pathway在Steroid hormone biosynthesis、PPAR signaling pathway、Fatty acid elongation、Biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids、Retinol metabolism、Peroxisome、Steroid biosynthesis、Fatty acid degradation等方面,主要是脂质代谢、内分泌系统、辅助因子和维生素的代谢、运输和分解代谢等相关的通路。
由图4b可知,profile19显著富集的Pathway在Protein export, Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism等方面,主要是脂质代谢、碳水化合物代谢、消化系统、内分泌系统、运输和分解代谢等相关的通路。
从profile0和 profile19显著富集的Pathway中筛选出表2的差异表达基因,其中,profile19中含有的Gnpda2、Ugp2、Cyp7a1、Sec11a、Sec61a1、Gmppa、Spcs3基因表达量呈现出直线增加的趋势,说明TB剂量增加,这些基因表达量也随之增加。profile0中含有的Ste2、Mpv17l、Elovl5、Cry1、Plin2、Angptl4、Cyp4a8、Eci1、Pex11a、Cyp26b1、Cyp26a1、Crat、Pmvk、Cyp2d4、Acot5、Akr1c1、Acot4基因表达量呈现出一直递减的模式,说明TB对这些基因的表达有线性抑制作用。
表 2 profile0和profile19中显著变化DEGs的注释信息Table 2. Annotation information for DEGs changed significantly in profile0 and profile19Gene ID profile FPKM值 Symbol KEGG_B_class A1 B1 E1 F1 G1 ENSRNOG00000001957 0 0 −0.76 −0.67 −0.94 −1.06 Ste2 Lipid metabolism ENSRNOG00000003285 0 −0.46 −0.9 −0.93 −1.52 Mpv17l Transport and catabolism ENSRNOG00000006331 0 −0.74 −0.54 −0.96 −1.34 Elovl5 Lipid metabolism; Global and Overview ENSRNOG00000007060 0 0.37 −0.41 −1.01 −1.27 Plin2 Endocrine system ENSRNOG00000007545 0 −0.54 −1.53 −2.09 −2.39 Angptl4 Endocrine system ENSRNOG00000008842 0 −1.34 −1.26 −1.53 −1.95 Cyp4a8 Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins; Sensory system;
Lipid metabolism; Endocrine system; Circulatory systemENSRNOG00000008843 0 −1.61 −1.74 −1.89 −1.9 Eci1 Lipid metabolism ENSRNOG00000015003 0 −1.89 −1.66 −2.25 −2.63 Pex11a Transport and catabolism ENSRNOG00000015076 0 −0.72 −0.72 −1.72 −2.04 Cyp26b1 Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins ENSRNOG00000016750 0 −1.18 −1.37 −1.22 −1.9 Cyp26a1 Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins ENSRNOG00000018145 0 −1.49 −1.71 −1.84 −2.06 Crat Transport and catabolism ENSRNOG00000020696 0 −1.21 −1.56 −1.47 −1.71 Pmvk Metabolism of terpenoids and polyketides;Transport and catabolism ENSRNOG00000032261 0 −1.91 −1.92 −1.54 −2.68 Cyp2d4 Nervous system;Lipid metabolism ENSRNOG00000032508 0 −0.24 −1.53 −1.3 −1.79 Acot5 Lipid metabolism ENSRNOG00000038331 0 −1.27 −1.46 −1.69 −1.6 Akr1c1 Lipid metabolism;Xenobiotics biodegradation and metabolism ENSRNOG00000046864 0 −1.28 −1.55 −1.62 −2 Acot4 Lipid metabolism ENSRNOG00000002177 19 0 0.92 1.51 1.41 1.74 Gnpda2 Carbohydrate metabolism ENSRNOG00000008079 0 0.37 0.25 0.97 1.11 Ugp2 Carbohydrate metabolism ENSRNOG00000009488 0 0.59 1.37 1.92 2.67 Cyp7a1 Digestive system;Lipid metabolism;Endocrine system ENSRNOG00000011029 0 0.68 0.71 0.78 1.01 Sec11a Folding, sorting and degradation ENSRNOG00000013743 0 0.8 0.96 1.1 1.1 Sec61a1 Transport and catabolism;Folding, sorting and degradation ENSRNOG00000019946 0 0.63 0.72 1.12 0.94 Gmppa Carbohydrate metabolism ENSRNOG00000038933 0 0.57 0.72 0.72 1.19 Spcs3 Folding, sorting and degradation 注:Ste2: estrogen sulfotransferase; Mpv17l: MPV17 mitochondrial inner membrane protein like; Elovl5: ELOVL fatty acid elongase 5; Plin2: perilipin 2; Angptl4: angiopoietin−like 4; Cyp4a8: cytochrome P450, family 4, subfamily a, polypeptide 8; Eci1: enoyl−CoA delta isomerase 1; Pex11a: peroxisomal biogenesis factor 11 alpha; Cyp26b1: cytochrome P450, family 26, subfamily b, polypeptide 1; Cyp26a1: cytochrome P450, family 26, subfamily a, polypeptide 1; Crat: carnitine O−acetyltransferase; Pmvk: phosphomevalonate kinase; Cyp2d4: cytochrome P450, family 2, subfamily d, polypeptide 4; Acot5: acyl−CoA thioesterase 5; Akr1c1: aldo−keto reductase family 1, member C1; Acot4: acyl−CoA thioesterase 4; Gnpda2: glucosamine−6−phosphate deaminase 2; Ugp2: UDP−glucose pyrophosphorylase 2; Cyp7a1: cytochrome P450, family 7, subfamily a, polypeptide 1; Sec11a: SEC11 homolog A, signal peptidase complex subunit; Sec61a1: Sec61 translocon alpha 1 subunit; Gmppa: GDP−mannose pyrophosphorylase A; Spcs3: signal peptidase complex subunit 3。 3. 讨论
ELOVL基因家族是在哺乳动物中发现的一类编码极长链脂肪酸延长酶的基因家族,已有报道ELOVL活性与人的肥胖显著相关[19]。本实验发现,相对于正常对照组,MS模型组及TB低、中、高剂量组的Elovl5基因表达量一直呈现线性递减的趋势,这可能是由于长期的高脂高糖高盐饮食阻碍了长链不饱和脂肪酸的合成。ACOT家族广泛分布于具有高脂肪酸氧化能力的组织中,通过ACOT酶催化的反应是在脂肪酸代谢中是非常重要的。哺乳动物中的ACOTs能够代谢多种化合物,包括短链、中链和长链酰基辅酶A、多不饱和脂肪酰辅酶A、支链酰基辅酶A和芳香族酰基辅酶A。这些化合物不仅在β-氧化和脂肪酸降解中得到运用,在炎症、离子通道开放、信号转导、脂质生物合成和基因调控中也起到作用[20]。本实验中,相对于正常对照组,MS模型组ACOT4、ACOT5的基因表达全部下调,可能影响了脂肪酸的氧化,导致高脂血症的形成。CYP4A8是脂质过氧化物酶,主要调控脂肪酸的氧化。相对于正常对照组,MS模型组和TB低、中、高剂量组CYP4A8的表达量一直呈现线性递减趋势。Angptl-4有多种功能,包括影响糖、脂代谢及血管生成等,还可以有效抑制LPL的作用,抑制血浆中Apo-B、乳糜微粒、VLDL中TG的分解等,有研究表明在小鼠体内Angptl-4可以促进肝脏对糖的摄取、改善胰岛素抵抗、促进糖异生以降低血糖,然而这种作用可能会造成高脂血症及脂肪肝[21]。本实验中,相对于MS模型组,TB低、中、高剂量组的Angptl-4的基因均下调,表明高脂高糖高盐饮食条件下,TB可能抑制Angptl-4基因表达,参与脂质代谢和促进血管结构发育。Cyp7a1是胆汁酸合成代谢经典途径的限速酶,催化胆固醇在肝脏分解为胆汁酸,属肝脏特异性微粒体细胞色素P450酶系。人体内近50%的胆固醇通过Cyp7a1的催化转化为胆汁酸排除体外,因此,Cyp7a1基因作为胆固醇合成通路中最重要的调控基因[22]。相对于MS模型组,TB低、中、高剂量组的Cyp7a1的基因均显著上调,表明高脂高糖高盐饮食条件下,TB能诱导Cyp7a1基因表达,促进胆固醇的分解代谢。综上所述,我们研究发现普洱茶茶褐素对高脂高糖高盐饮食大鼠具有减肥、降低大鼠血清FPG和TG水平的作用,其可能是通过上调Cyp7a1的基因表达,促进膳食中胆固醇的分解代谢,进而增加机体的能量消耗、降低体重,并预防大鼠肥胖。同时下调Angptl-4、Elovl5、CYP4A8的基因表达,来有效改善FPG和TG水平。本试验只对显著变化的基因进行分析,非显著变化包含的基因可能在TB对MS大鼠降血糖血脂功效方面也发挥一定的作用,有待于进一步深入研究。
4. 结论
大鼠长时间食用高脂高糖高盐饲料,对其肝脏的基因表达产生了显著的影响。灌胃不同剂量茶褐素干预后,相关基因的表达也呈现出剂量效应关系。从profile0和profile19显著富集的Pathway来看,MS大鼠灌胃不同剂量TB后Gnpda2、Ugp2、Cyp7a1、Sec11a、Sec61a1、Gmppa、Spcs3基因表达量呈现出直线上调;而Ste2、Mpv17l、Elovl5、Cry1、Plin2、Angptl4、Cyp4a8、Eci1、Pex11a、Cyp26b1、Cyp26a1、Crat、Pmvk、Cyp2d4、Acot5、Akr1c1、Acot4等基因表达量呈现直线下调。此外,普洱茶茶褐素对高脂高糖高盐饮食大鼠具有减肥、降低大鼠血清FPG和TG水平的作用,其作用机制可能是通过上调Cyp7a1的基因表达,加速膳食中胆固醇的分解代谢,进而增加机体能量消耗、降低体重,预防大鼠肥胖。同时下调Angptl-4、Elovl5、CYP4A8的基因表达,来有效改善FPG和TG水平。
-
图 1 差异表达基因统计
注:A1:正常对照组;B1:MS模型组;E1:TB低剂量组;F1:TB中剂量组;G1:TB高剂量组;表2同。
Figure 1. The statistics of DEGs
图 2 差异表达基因聚类分析
注:图2a大鼠差异表达基因所有趋势总图:每个趋势图左上方为趋势的ID,左下方为趋势中的P-value值;按P-value值排序,数值从小到大,黑线表示趋势线,横坐标为样品的编号(从左往右按照A1、B1、E1、F1、G1排列),纵坐标为log2(V(i)/V(0)),第i个样品的表达量与第1个样品的表达量的比值的log2值,带颜色的趋势块(P<0.05)为显著富集的趋势,不带颜色的趋势块为非显著富集的趋势块;图2b大鼠差异表达基因趋势基因数、P-value柱状图:图上柱子的高度代表基因数目,柱子的颜色代表P-value。
Figure 2. Cluster analysis of differentially expressed genes
表 1 普洱茶茶褐素对大鼠体重、甘油三酯和空腹血糖的影响
Table 1 Effect of TB extracted from Pu-erh tea on the body weight, TG and FPG of rats
体重(g) TG(mmol/L) FPG(mmol/L) 组别 适应期 干预期63 d 净增体重 适应期 干预期63 d 适应期 干预期63 d 正常对照组 199.03±13.48A 346.84±26.02AB 147.81±26.58AB 0.68±0.11A 0.49±0.08AB 6.19±1.74A 7.07±1.57A MS模型组 207.91±13.18A 393.93±34.45C 186.02±29.60C 0.78±0.12A 0.68±0.28C 5.39±1.74A 8.92±1.48C TB低剂量组 204.20±14.71A 367.78±28.60BC 163.58±32.00BC 0.74±0.12A 0.56±0.16BC 5.47±1.80A 8.57±1.28BC TB中剂量组 203.83±12.72A 346.21±30.52AB 142.39±33.21AB 0.80±0.24A 0.39±0.04A 5.61±1.62A 8.61±1.15BC TB高剂量组 208.31±16.30A 326.93±25.73A 118.61±22.38A 0.68±0.11A 0.46±0.06AB 5.96±1.60A 7.48±0.91AB 注:同列不同大写字母,表示具有统计学差异(P<0.05)。 表 2 profile0和profile19中显著变化DEGs的注释信息
Table 2 Annotation information for DEGs changed significantly in profile0 and profile19
Gene ID profile FPKM值 Symbol KEGG_B_class A1 B1 E1 F1 G1 ENSRNOG00000001957 0 0 −0.76 −0.67 −0.94 −1.06 Ste2 Lipid metabolism ENSRNOG00000003285 0 −0.46 −0.9 −0.93 −1.52 Mpv17l Transport and catabolism ENSRNOG00000006331 0 −0.74 −0.54 −0.96 −1.34 Elovl5 Lipid metabolism; Global and Overview ENSRNOG00000007060 0 0.37 −0.41 −1.01 −1.27 Plin2 Endocrine system ENSRNOG00000007545 0 −0.54 −1.53 −2.09 −2.39 Angptl4 Endocrine system ENSRNOG00000008842 0 −1.34 −1.26 −1.53 −1.95 Cyp4a8 Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins; Sensory system;
Lipid metabolism; Endocrine system; Circulatory systemENSRNOG00000008843 0 −1.61 −1.74 −1.89 −1.9 Eci1 Lipid metabolism ENSRNOG00000015003 0 −1.89 −1.66 −2.25 −2.63 Pex11a Transport and catabolism ENSRNOG00000015076 0 −0.72 −0.72 −1.72 −2.04 Cyp26b1 Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins ENSRNOG00000016750 0 −1.18 −1.37 −1.22 −1.9 Cyp26a1 Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins ENSRNOG00000018145 0 −1.49 −1.71 −1.84 −2.06 Crat Transport and catabolism ENSRNOG00000020696 0 −1.21 −1.56 −1.47 −1.71 Pmvk Metabolism of terpenoids and polyketides;Transport and catabolism ENSRNOG00000032261 0 −1.91 −1.92 −1.54 −2.68 Cyp2d4 Nervous system;Lipid metabolism ENSRNOG00000032508 0 −0.24 −1.53 −1.3 −1.79 Acot5 Lipid metabolism ENSRNOG00000038331 0 −1.27 −1.46 −1.69 −1.6 Akr1c1 Lipid metabolism;Xenobiotics biodegradation and metabolism ENSRNOG00000046864 0 −1.28 −1.55 −1.62 −2 Acot4 Lipid metabolism ENSRNOG00000002177 19 0 0.92 1.51 1.41 1.74 Gnpda2 Carbohydrate metabolism ENSRNOG00000008079 0 0.37 0.25 0.97 1.11 Ugp2 Carbohydrate metabolism ENSRNOG00000009488 0 0.59 1.37 1.92 2.67 Cyp7a1 Digestive system;Lipid metabolism;Endocrine system ENSRNOG00000011029 0 0.68 0.71 0.78 1.01 Sec11a Folding, sorting and degradation ENSRNOG00000013743 0 0.8 0.96 1.1 1.1 Sec61a1 Transport and catabolism;Folding, sorting and degradation ENSRNOG00000019946 0 0.63 0.72 1.12 0.94 Gmppa Carbohydrate metabolism ENSRNOG00000038933 0 0.57 0.72 0.72 1.19 Spcs3 Folding, sorting and degradation 注:Ste2: estrogen sulfotransferase; Mpv17l: MPV17 mitochondrial inner membrane protein like; Elovl5: ELOVL fatty acid elongase 5; Plin2: perilipin 2; Angptl4: angiopoietin−like 4; Cyp4a8: cytochrome P450, family 4, subfamily a, polypeptide 8; Eci1: enoyl−CoA delta isomerase 1; Pex11a: peroxisomal biogenesis factor 11 alpha; Cyp26b1: cytochrome P450, family 26, subfamily b, polypeptide 1; Cyp26a1: cytochrome P450, family 26, subfamily a, polypeptide 1; Crat: carnitine O−acetyltransferase; Pmvk: phosphomevalonate kinase; Cyp2d4: cytochrome P450, family 2, subfamily d, polypeptide 4; Acot5: acyl−CoA thioesterase 5; Akr1c1: aldo−keto reductase family 1, member C1; Acot4: acyl−CoA thioesterase 4; Gnpda2: glucosamine−6−phosphate deaminase 2; Ugp2: UDP−glucose pyrophosphorylase 2; Cyp7a1: cytochrome P450, family 7, subfamily a, polypeptide 1; Sec11a: SEC11 homolog A, signal peptidase complex subunit; Sec61a1: Sec61 translocon alpha 1 subunit; Gmppa: GDP−mannose pyrophosphorylase A; Spcs3: signal peptidase complex subunit 3。 -
[1] 秦谊, 龚加顺, 张惠芬, 等. 普洱茶茶褐素提取工艺及理化性质的初步研究[J]. 林产化学与工业,2009,29(5):95−98. [QIN Yi, GONG Jiashun, ZHANG Huifen, et al. Extraction technology of theabrownine from puerh tea and its physico-chemical properties[J]. Chemistry and Industry of Forest Products,2009,29(5):95−98. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2417.2009.05.018 [2] 陈婷. 普洱茶茶褐素降血脂功效及其作用机制研究[D]. 昆明: 云南农业大学, 2009, 25-50. CHEN Ting. Study on the hypolipidemic function and its mechanism of theabrowmin extracted from pu-erh tea[D]. Kunming: Yunnan Agricultural University, 2009, 25-50.
[3] 王秋萍, 龚加顺. “紫娟”普洱茶茶褐素对高脂饮食大鼠生长发育的影响[J]. 茶叶科学,2012,32(1):87−94. [WANG Qiuping, GONG Jiashun. Effect of theabrownin extracted from “Zijuan” pu-erh tea on growth of rats with hyperlipidemia food[J]. Journal of Tea Science,2012,32(1):87−94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2012.01.013 [4] PENG C, WANG Q, LIU H, et al. Effects of Zijuan pu-erh tea theabrownine on metabolites in hyperlipidemic rat feces by Py-GC/MS[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrol,2013,104:226−233. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2013.07.011
[5] 岳随娟, 刘建, 龚加顺. 普洱茶茶褐素对大鼠肠道菌群的影响[J]. 茶叶科学,2016,36(3):261−267. [YUE Suijuan, LIU Jian, GONG Jiashun. Effects of theabrownin extracted from Pu-erh tea on the intestinal flora[J]. Journal of Tea Science,2016,36(3):261−267. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2016.03.006 [6] 赵丹, 张婷婷, 彭春秀, 等. 普洱茶茶褐素对高糖饮食大鼠糖脂代谢关键酶及组织切片的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(15):298−303. [ZHAO Dan, ZHANG Tingting, PENG Chunxiu, et al. Effects of theabrowins extracted from pu-erh tea on key enzymes and tissue sections of glycolipid metabolism and with high sugar diet rats[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(15):298−303. [7] 张婷婷, 吴恩凯, 彭春秀, 等. 普洱茶茶褐素对高糖饮食大鼠血糖血脂指标的影响[J]. 食品科技,2018,43(7):53−59. [ZHANG Tingting, WU Enkai, PENG Chunxiu, et al. Effects of theabrownins extracted from pu-erh tea on blood glucose and blood lipid indexes of rats with high sugar diet[J]. Food Science and Technology,2018,43(7):53−59. [8] 高斌, 彭春秀, 龚加顺, 等. 普洱茶茶褐素对大鼠激素敏感性脂肪酶活性及其mRNA表达的影响[J]. 营养学报,2010,32(4):362−366. [GAO Bin, PENG Chunxiu, GONG Jiashun, et al. Effects of theabrownine in pu-erh tea on the hormone-sensitive lipase activity and mRNA expression in rat[J]. Acta Nutrimenta Sinica,2010,32(4):362−366. [9] WU Enkai, ZHANG Tingting, GONG Jiashun, et al. Theabrownin from pu-erh tea together with swinging exercise synergistically ameliorates obesity and insulin resistance in rats[J]. European Journal of Nutrition,2020,59:1937−1950. doi: 10.1007/s00394-019-02044-y
[10] 刘艺. 代谢综合征的危害和综合干预[J]. 中国城乡企业卫生,2020,1(1):37−39. [LIU Yi. Harm and comprehensive intervention of metabolic syndrome[J]. Chinese Journal of Urban and Iural Enterprise Hygieme,2020,1(1):37−39. [11] 吴恩凯, 王秋萍, 龚加顺, 等. 发酵方法对普洱茶茶褐素样品组成的影响[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(4):215−221. [WU Enkai, WANG Qiuping, GONG Jiashun, et al. Effect of fermentation methods on the abrownin composition of pu-erh tea[J]. Food Science,2019,40(4):215−221. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20171201-006 [12] 龚加顺, 陈文品, 周红杰, 等. 云南普洱茶特征成分的功能与毒理学评价[J]. 茶叶科学,2007,27(3):201−210. [GONG Jiashun, CHEN Wenping, ZHOU Hongjie, et al. Evaluation on the function and toxicity of extraction of characteristic components in Yunnan pu-erh tea[J]. Journal of Tea Science,2007,27(3):201−210. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2007.03.004 [13] 敬明武, 葛宇杰, 刘科亮. 茶色素胶囊对大鼠辅助调节血脂的研究[J]. 中国现代医生,2007,45(5):18−19. [JING Mingwu, GE Yujie, LIU Keliang. The explore of the effect of tea pigment capsule on assisting to adjust bloodfat of rat[J]. China Modern Doctor,2007,45(5):18−19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9701.2007.05.008 [14] ERNST J, BAR-JOSEPH Z. STEM: A tool for the analysis of short time series gene expression data[J]. BMC Bioinfprmatics,2006,7(1):1−11. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-1
[15] BENJAMINI Y, HOCHBERG Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B (Methodological),1995:289−300.
[16] YE J, FANG L, Zhang H, et al. WEGO: A web tool for plotting GO annotations[J]. Nucleic Acids Research,2006,34:W293−W297. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl031
[17] WHITE K P. Functional genomics and the study of development, variation and evolution[J]. Nat Rev Genet,2001,2(7):528−537. doi: 10.1038/35080565
[18] SHIRI Y, SOLOUKI M, EBRAHIMIE E, et al. Unraveling the transcriptional complexity of compactness in sistan grape cluster[J]. Plant Science,2018:198−208.
[19] PAN D A, LILLIOJA S, MILNER M R, et al. Skeletal muscle membrane lipid composition is related to adiposity and insulin action[J]. J Clin Invest,1995,96(6):2802−2808. doi: 10.1172/JCI118350
[20] HUNT M C, ALEXSON S E. Novel functions of acyl-CoA thioesterases and acyltransferases as auxiliary enzymes in peroxisomal lipid metabolism[J]. Prog Lipid Res,2008,47(6):405−421. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2008.05.001
[21] ZHENG Z, CHENG C, DONG R, et al. Advanced glycation end products upregulate angiopoietin-like protein 4 expression by activating the renin-angiotensin system in endothelial cells[J]. Biomedical Reports,2015,3(4):578−582. doi: 10.3892/br.2015.468
[22] 邢万佳, 高聆, 赵家军. 胆固醇7α-羟化酶CYP7A1表达及调控相关研究进展[J]. 世界华人消化杂志,2012,20(16):1439−1446. [XING Wanjia, GAO Ling, ZHAO Jiajun. Expression and regulation of cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase: An update[J]. World Chinese Journal of Digestology,2012,20(16):1439−1446. -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 蒋亚吉,丁雪梅,刘亚萍,孟金明. 风吹豆豉牛肉干加工工艺的研究. 粮食与油脂. 2023(12): 102-107 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 罗秋霞,何江红,刘倩,夏龙,李杨,张惠,程利思,刘承慈,苏雨婷,曾义星. 不同大米对八宝粥食用品质的影响. 粮食与食品工业. 2022(04): 33-36 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



