Active Components, Pharmacological Action and Application in Food Processing of Eucommia ulmoides Leaves
-
摘要: 杜仲富含大量活性成分,研究证明杜仲叶与杜仲皮有相同的药理作用,但未得到有效开发。本文整理已发表的杜仲叶相关文献,对其活性成分、药理作用及其在食品加工中的应用进行论述,以期为杜仲叶的精深加工和高值化开发奠定一定的理论基础。Abstract: Eucommia ulmoides is rich in a large number of active ingredients. Studies prove that the leaves and bark of Eucommia ulmoides have the same pharmacological effects, but it has not been effectively developed. In this paper, the active components, pharmacological effects and application in food processing of Eucommia ulmoides leaves are reviewed, so as to lay a theoretical foundation for deep processing and high-value development of Eucommia ulmoides leaves.
-
杜仲(Eucommia ulmoides Oliver),别名胶木,思连皮,丝棉皮,玉丝皮,为杜仲科杜仲属植物。在温暖湿润且常年放晴的环境中生长茂盛,具有一定的抗寒能力,是中国的特有种,大多在陕西、甘肃、河南、湖北等省区种植。其中陕西省略阳县是我国最大的杜仲基地县,2017年地存杜仲约3.9万公顷,1.29亿株,占全国总量的13%。杜仲自古以来被用作补药,具有补肝肾、安胎、抗炎杀菌以及增强体格等作用[1]。查阅大量资料发现杜仲的开发主要集中在杜仲皮和杜仲胶。20世纪80~90年代初期,市场上掀起“杜仲热”,人们对杜仲认知度上升,需求量增大,杜仲皮价格呈现持续上涨的局势,又因杜仲皮具有生长周期较长的特点,资源紧缺,无法进行大规模开发利用[2-3]。
据《中国药典》中记录,杜仲的药用部分为杜仲皮和叶[4],有研究发现,杜仲叶和杜仲皮有相似的活性成分,但含量有一定区别,且被证明有互补的趋势,在消炎、杀菌、降压等药理方面叶可替代皮[5-6]。杜仲叶并未得到有效开发,2019年杜仲叶被国家卫健委列入按照传统“既是食品又是中药材”的物质生产经营试点工作名单。本文通过归纳杜仲叶的活性成分以及药理作用,分析其在食品加工中的应用,旨在促进杜仲资源的合理利用,为未来杜仲叶开发利用及精加工提供宝贵建议。
1. 杜仲叶的活性成分
对杜仲叶不同药理活性的研究中,研究其活性成分是连接传统中草药理论和现代化医学的纽带。杜仲叶的活性成分集中于木质素类、环烯醚萜类、类苯丙素、黄酮类化合物[7]等。此外,杜仲叶还具有多种营养要素,如氨基酸、矿物质、胡萝卜素、脂肪等[8-9]。据研究可知,杜仲中的化学成分与含量在不同的部位和生长年限并不完全相同[10],其相应的活性功能的强弱也不完全一致。
1.1 木质素类
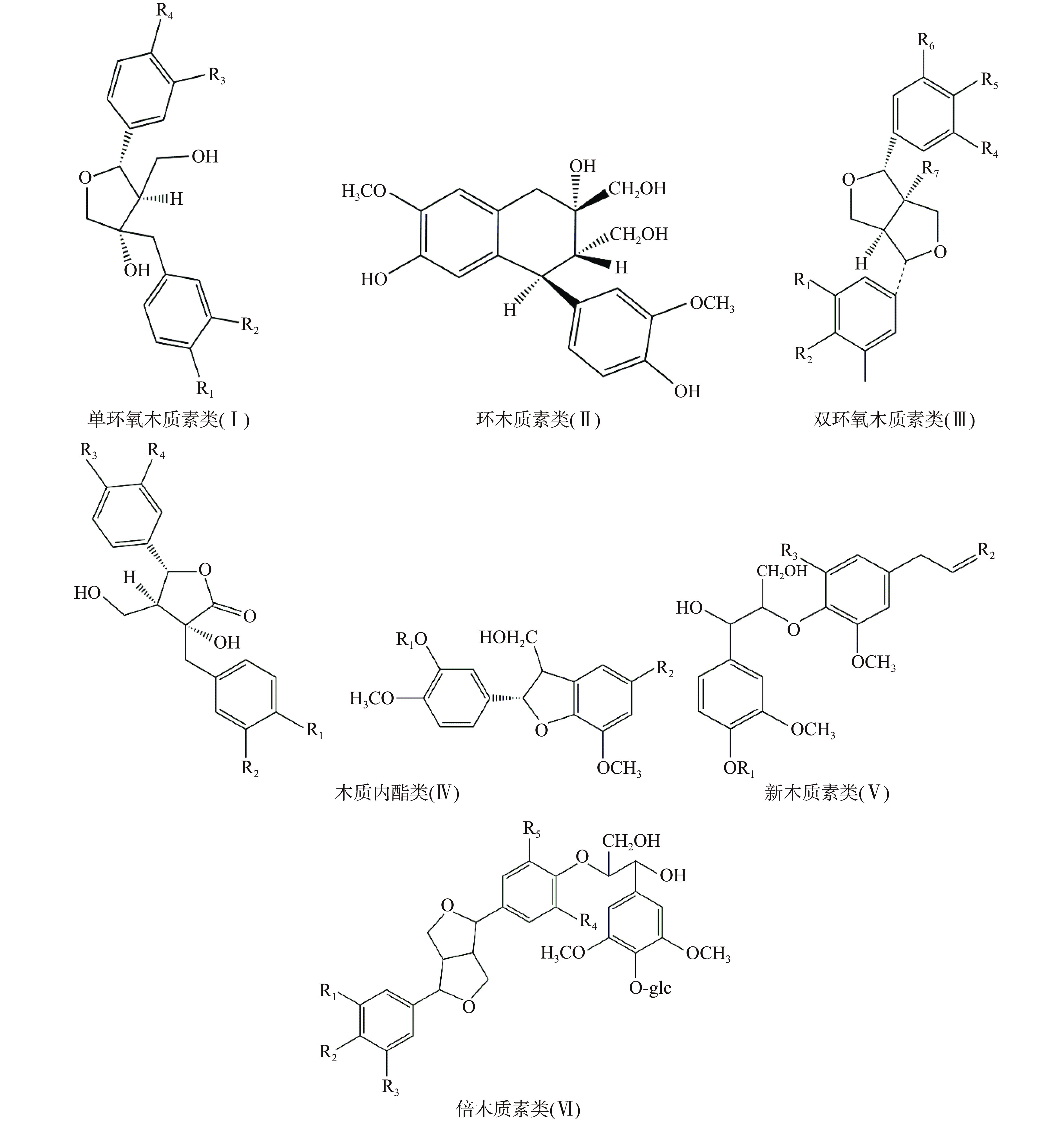
木质素是4-羟基苯丙素氧化组合偶联而产生的一大群芳香族聚合物的总称,具有保护细胞壁多糖不受微生物降解,赋予其耐腐性等功能[11]。根据化学结构的不同可将木质素类化合物分为单环氧木质素类(Ⅰ)、环木质素类(Ⅱ)、双环氧木质素类(Ⅲ)、木质内酯类(Ⅳ)、新木质素类(Ⅴ)和倍木质素类(Ⅵ)(图1)[3,12]。截至目前,已有32种木质素类化合物从杜仲的不同部位分离出[13],主要化学成分有杜仲素A、环橄榄脂素、松脂醇二葡萄糖苷、丁香脂素二葡萄糖苷等[14-17]。有研究发现化学结构为两个苯环对位的羟基的松脂醇丁香脂素二葡萄糖苷具有抗肿瘤、抗衰老、增强记忆力和较强的抑制环磷酸腺苷(cMAP)磷酸二酯酶的作用[18]。化雪艳[19]通过中性洗涤剂法测定杜仲叶中木质素含量为164.667 mg/g,约是杜仲皮的四倍。
1.2 环烯醚萜类
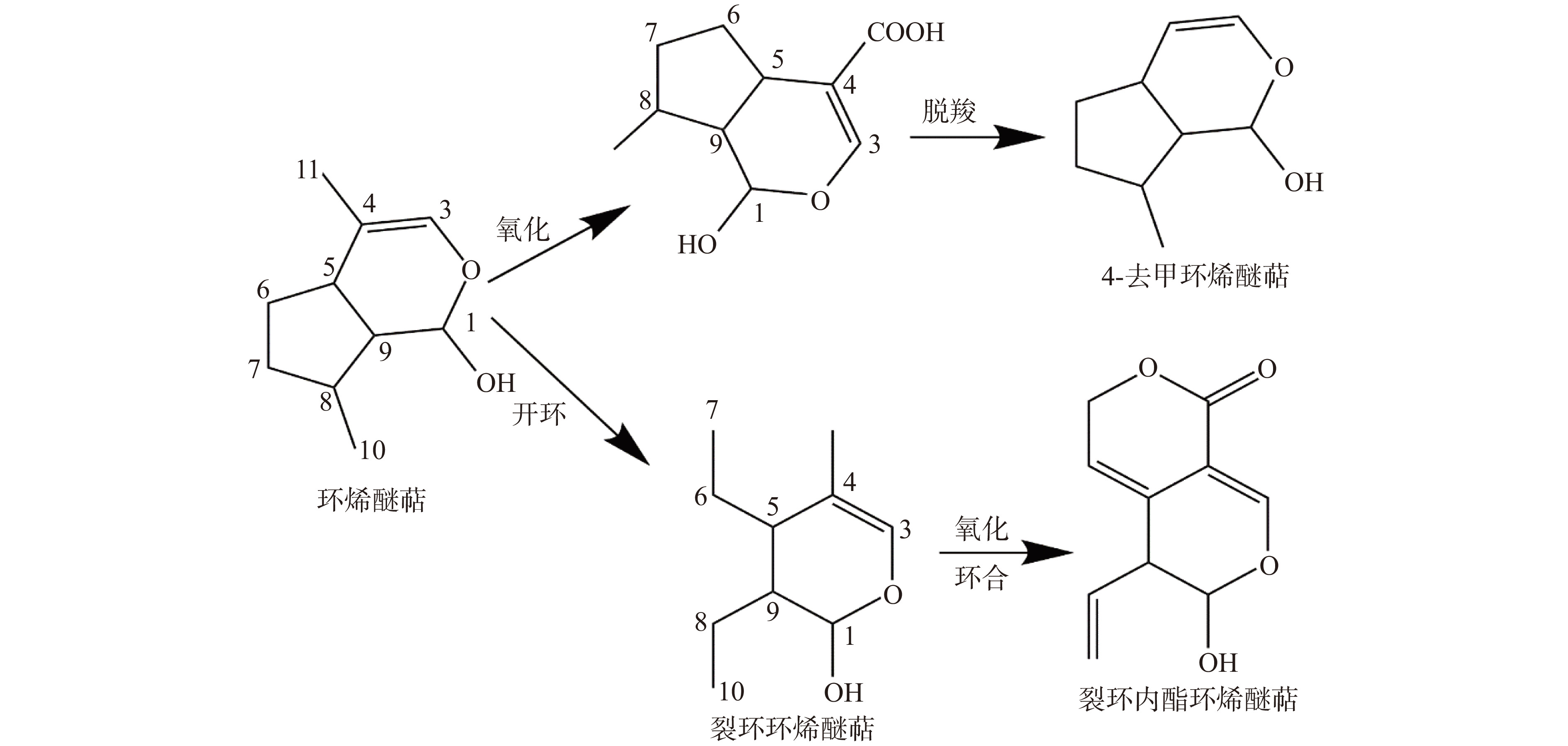
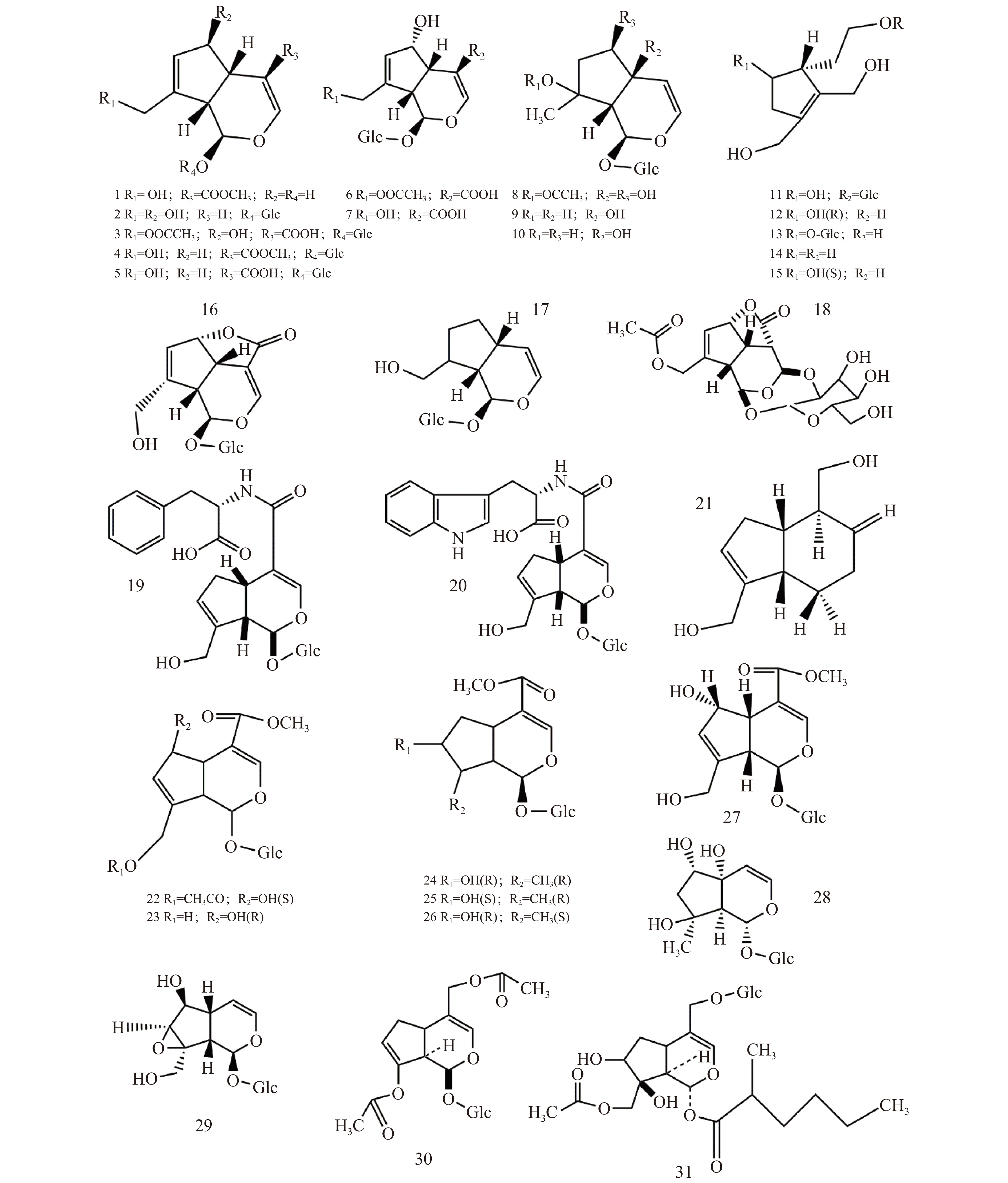
环烯醚萜类是蚁臭二醛的缩醛衍生物,在双子叶植物中含量较高。环氧化、羟基化以及由莽草酸途径得到的酯化的芳香酸使其骨架结构多样(图2)[20-21]。目前,已从杜仲的不同部位中分离得到30种环烯醚萜类化合物[3],主要存在于杜仲叶和杜仲皮中(表1),包括京尼平苷(Ⅰ)、京尼平苷酸(Ⅱ)、桃叶珊瑚苷(Ⅲ)、筋骨草苷(Ⅳ)(图3)、杜仲苷类和杜仲醇类[14,22-24]等,其中京尼平苷酸以其明显的消炎作用闻名。
序号 环烯醚萜类化合物 存在部位 1 京尼平 树皮 2 桃叶珊瑚苷 树皮 3 scandoside 10-O-acetate 树叶 4 京尼平苷 树皮 5 京尼平苷酸 树皮/树叶 6 车叶草苷酸 树叶 7 脱乙酰车叶草苷酸 树叶 8 哈帕苷丁酸脂 树皮 9 筋骨草甙 树皮 10 匍萄筋骨草甙 树皮 11 杜仲甙Ⅰ 树皮 12 杜仲醇 树皮/树叶 13 杜仲甙Ⅱ 树叶 14 去氧杜仲醇 树皮/树叶 15 Epieucommiol 树叶 16 车叶草苷 树叶 17 杜仲甙 树皮 18 Eucomoside A 树叶 19 Eucomoside B 树叶 20 Eucomoside C 树叶 21 栀二醇 树皮 22 交让木苷 树叶 23 鸡失藤甙甲酯 树叶 24 马线子苷 树叶 25 7-epi-loganin 树叶 26 8-epi-loganin 树叶 27 脱乙酰车叶草苷酸 树叶 28 哈巴苷 树皮 29 梓醇 树皮 30 杜仲甙C 树叶 31 杜仲甙D 树叶 1.3 苯丙素类
张威鹏等[25]采用高效液相色谱变波长-梯度洗脱法,以树龄和部位为变量,测得不同部位的杜仲中的苯丙素类含量。实验发现,在相同生长时期,杜仲叶中的苯丙素类成分含量最高,其次是干皮,最后是枝皮。杜仲叶中的苯丙素类含量随树龄的增长,整体出现减少的趋向。杜仲叶中苯丙素类的主要成分有绿原酸、咖啡酸、松柏苷、原儿茶酸、紫丁香苷,其中绿原酸因具有杀菌、消炎、抗衰老等多种药理作用,已被规定为某些药用植物的质量限定准则[26]。
1.4 黄酮类
杜仲中黄酮类物质含量较高,是检测杜仲质量的另一关键指标。黄酮类化合物在杜仲雄花和叶的分布较多,杜仲叶中总黄酮的含量高达10.05%[27]。陈景超等[28]通过比较杜仲叶中黄酮成分含量的不同提取方法得出酶解法提取效率最高,且此法不用任何有机溶剂,对人体较安全,可考虑工厂化。目前从杜仲中分离纯化出的黄酮类化合物共有36种,包含芦丁、山奈酚、槲皮素、紫云英苷、金丝桃苷等[3,29-30]。
1.5 多糖类
多糖是近年来新发现杜仲叶中的活性物质,含量丰富[27,31]。王莹等[27]研究发现,时间和地域对杜仲叶多糖含量有显著影响。张学俊等[32]对杜仲叶多糖结构进行解析,发现杜仲叶多糖由鼠李糖、D-岩藻糖、D-阿拉伯糖、D-木糖、D-葡萄糖、D-半乳糖六种单糖基组成。陈蕾[33]利用水提法和微波辅助法分别提取杜仲叶和皮中的多糖,结果发现杜仲叶和杜仲皮的多糖结构特性几乎没有差别,且不受提取方式的影响。
1.6 多酚类
酚类化合物是由一个羟基代替苯环上的氢原子形成的带有酚羟基的化合物。邓云云等[34]分别用60%的甲醇和60%的乙醇提取杜仲皮和叶中的总酚,得出杜仲叶中的多酚类化合物含量明显高于杜仲皮,分别是59.100和66.720 mg/g,杜仲皮中提取的总酚含量仅为8.729和7.414 mg/g。且总酚含量质量受气候因子、土壤因子及地理因子等生态因子的影响。影响杜仲叶品质的主导气候因子是温度及蒸发量。多酚类化合物含量随泥土中有效态铁、锌、锰、硼的含量增加而增加[35]。
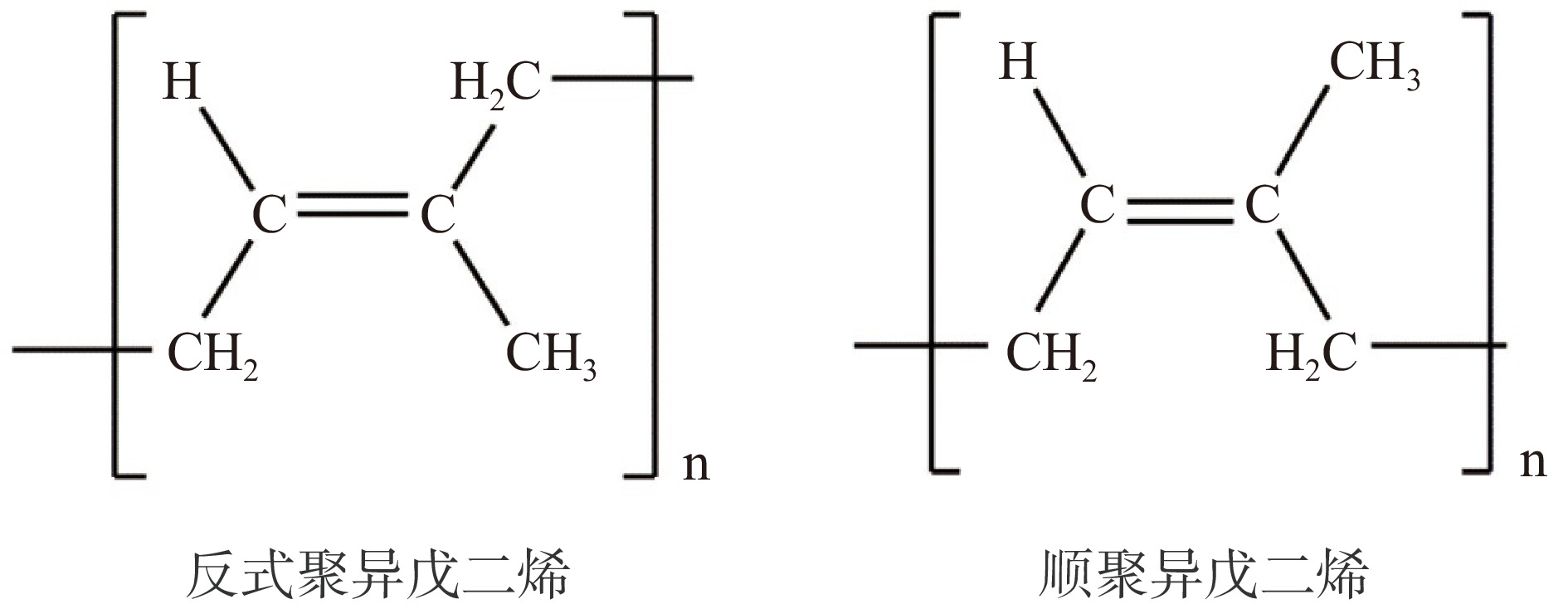
1.7 杜仲胶
杜仲胶是分子结构为反式聚异戊二烯的具有橡胶和塑料二重性的优异高分子材料,是橡胶的异构体,即顺聚异戊二烯(图4)。室温下坚韧,无色,可结晶,化学性质活泼,易氧化变成乳白色质地脆弱的物体。胶粘剂室温硬度高,常温成型,门尼粘度高,抗冲击强度高,热熔结合性能好,是一种具有前途的材料,在许多领域都有潜在的应用前景[36]。
1.8 其他
周芳等[37]采取气相色谱-质谱联用/选择性离子检测(GC-MS/SIM)方法对杜仲叶进行测定,共测出15种氨基酸,其中有七种为人体所必需的游离氨基酸。周利兵等[38]以此为基础分析不同产地杜仲叶的氨基酸含量发现,湖北省恩施州和云南省昆明市杜仲叶的氨基酸含量较高,湖南省常德市和重庆长寿杜仲叶的含量较低。除此之外,杜仲叶中还富含维生素、矿物质和胡萝卜素,其中钾、钠含量较高,约是杜仲皮的3倍 [3,31]。
2. 杜仲叶的药理作用
杜仲叶有多种保健功能,大量研究证明,杜仲叶具有抗氧化、抗炎杀菌、降压、降脂降糖、免疫调节、抗癌、抗衰老、抗骨质疏松等作用。
2.1 抗氧化作用
与杜仲皮、花和果实相比,杜仲叶具有更强的抗氧化活性[34,39]。杜仲叶中抗氧化成分较多,如环烯醚萜类化合物、酚类化合物、苯丙素类化合物、木质素类化合物、多糖和维生素等,其中酚类物质是植物中最活跃的抗氧化剂,其抑制自由基反应的作用机制不止一种,如改善机体抗氧化酶,多酚的金属螯合电位对铁和铜诱导的自由基反应起保护作用,酚羟基的氢与自由基结合等[40-42]。刘静[43]测定杜仲叶提取物对 O2 −·和·OH的清除率、对小鼠红细胞氧化溶血的影响和对各脏器丙二醛(Malondialdehyde,MDA)生成的抑制率,评价杜仲叶提取物的体外抗氧化作用,结果表明杜仲叶提取物具有显著的体外抗氧化能力。王翔等[44]实验证明杜仲叶提取物对ABTS+、·OH和DPPH·均有清除效果,其效果与总黄酮含量和酚类含量呈正相关。杜仲叶被证实有良好的抗氧化活性,作为天然抗氧化剂,在化妆品、食品、药品等领域极具应用前景。
2.2 抗炎杀菌作用
杜仲叶醇提物能够显著改善大鼠肝脏缺血再灌注引起的炎症反应,且效果优于杜仲皮,猜测环烯醚萜苷类成分可能是杜仲叶抗炎作用的主成分之一。杨志友等[45]以小鼠小胶质细胞(BV2)为研究对象证明杜仲叶中环烯醚萜苷类主成分京尼平苷酸(Geniposidic acid,GEN)具有抗炎杀菌性,当BV2小胶质细胞被激活释放大量炎症因子时,京尼平苷酸通过阻拦p38蛋白和p65蛋白的磷酸化,降低脂多糖(lipopolysaccharide,LPS)诱导的NO和促炎细胞因子白细胞介素-1β(interleukin-1β,IL-1β)、白细胞介素-6(interleukin-6,IL-6)、肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)的释放。此外,杜仲叶中作为环烯醚萜类化合物的桃叶珊瑚苷有明显的抗炎作用。桃叶珊瑚苷类化合物能够有效抑制炎症因子IL-6和白细胞介素-10(interleukin-10,IL-10)的释放,且对NO释放具有中等程度的抑制作用,同时抑制γ-干扰素(interferon γ,IFN-γ)磷酸化进而抑制其活性;还能作为核因子κB(nuclear factor kappa-B,NF-κB)的特异性抑制剂,起到抗炎的作用[46]。
绿原酸是杜仲叶中的主要抗炎杀菌成分之一。绿原酸对气单胞菌科、大肠杆菌、金黄色葡萄球菌、枯草芽孢杆菌、停球链球菌、沙门氏菌、乳房链球菌等均有一定的抑菌作用[47],同时,绿原酸也被证实有增加肠道菌群多样性、维持肠道菌群稳定的作用[48]。此外,杜仲叶提取物对黄曲霉和黑曲霉有良好的抑菌效果,且抑菌活性具有热稳定性[49]。
2.3 降压作用
医学实验证明,杜仲叶是最原始的降压药材。已知的杜仲叶的降压成分共有四类,分别为木质素类、苯丙素类、环烯醚萜类和黄酮类。其中,木质素类化合物的降压功能是杜仲中研究的较透彻的一种药理作用,李旭等[50]提取杜仲叶中绿原酸进行了降血压活性实验,得出杜仲叶中的绿原酸具有降压作用,且高剂量组的降压效果具有显著性。雷燕妮和张小斌[51]通过建立高血压大鼠模型并提取杜仲叶中总黄酮灌胃9 d,发现大鼠收缩压均有不同程度的降低,得出总黄酮对降血压有显著作用的结论。此外,杜仲叶中的2种环烯醚萜类化合物成分被证明具有降压效果[3]。
2.4 降血脂、血糖作用
我国古代百姓曾用杜仲叶泡水来治疗糖尿病,郎茜等[52]研究发现杜仲叶多糖具有一定的降血糖的作用,能降低糖尿病模型大鼠空腹血糖和尿素氮含量。同时,多糖浓度与半胱氨酸蛋白酶-3(Caspase-3)、p38蛋白及转化生长因子-β1(transforming growth factor-β,TGF-β1)等蛋白基因量的表达呈现负相关的关系,证明其具有良好的降血糖活性。乔红伟等[53]通过建立大鼠混合型高脂血症动物模型,灌胃30 d发现杜仲叶对大鼠具有辅助降血脂的作用。杜仲叶不仅有降糖降脂的作用,还对人体无任何毒副作用[54],因此杜仲叶作为新型天然药物的市场前景十分开阔,但其降糖降脂机制尚不明确,构效关系尚不清晰。
2.5 免疫调节作用
杜仲叶的大部分活性成分如多糖类、环烯醚萜类、黄酮类、维生素、微量元素及其浸取液等都被证明可以增强人体免疫力。徐贤柱等[55]采用水提的方式提取杜仲叶多糖,将其分为高中低三个剂量组并以生理盐水作为空白对照组,连续灌胃30 d后发现杜仲叶多糖可以增加小鼠脾脏重量和指数,提高其对免疫应答的能力。同时杜仲叶多糖不会影响胸腺,对胸腺的正常运作无抑制作用。叶颖霞等[56]实验研究发现杜仲叶多糖可以增加小鼠的胸腺和脾脏系数,提高血清中抗体的数量和巨噬细胞的吞噬功能的方式,以达到增强免疫力的目的。Yang等[57]的研究显示京尼平苷酸是调节细胞免疫和体液免疫方面的主要有效成分。同时,较高剂量杜仲叶可抑制小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞中NO和前列腺素E2的产生。袁带秀等[58]建立小鼠铅中毒模型后给予总黄酮治疗,测得模型小鼠免疫器官组织中MDA含量显著降低,总体抗氧化酶活性、超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD)、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(glutathione peroxidase,GSH-Px)显著上升,证明总黄酮对免疫系统的损坏有一定修复功能。腹腔巨噬细胞和单核巨噬细胞系统的活性能被杜仲的水提液和乙醇提取液激活,迟发型超敏反应还能被抑制,从而发挥双向调节细胞免疫的作用。杜仲叶的免疫调节目前研究较透彻,未来有望作为食品配料加入食品中,拓宽保健食品市场。
2.6 抗癌作用
栾芳菲等[59]采用噻唑蓝(MTT)比色法和流式细胞仪测定了杜仲叶提取物(EULE)对人结直肠癌细胞(HCT116)和人脐静脉内皮细胞(HUVEC)体外增殖和凋亡的影响,发现杜仲叶水提物具有阻抑细胞增殖、加速细胞凋亡的特点。在此基础上,张胜等[60]深入探究杜仲叶中主要活性成分对癌细胞的作用机制,发现在杜仲叶中含量较高的活性成分绿原酸和京尼平苷酸中,绿原酸有显著的加速细胞凋亡、遏制HCT116细胞生长的效果,且绿原酸属于酚酸,有多位学者曾实验证实酚酸可抗癌抗诱变。截至目前,癌症仍是人们的心头大患,而杜仲叶良好的抗癌活性为其未来临床应用奠定了基础。
2.7 抗衰老作用
杜仲叶主要通过增强免疫作用、清除自由基、促进胶原蛋白合成、减少其降解等方式达到抗衰老的目的。李小安等[61]利用向小鼠注射D-半乳糖的办法制成脑内单胺氧化酶B活力降低、脂褐质含量增加、细胞C3b受体花环结合率及免疫复合物花环结合率降低的小鼠亚急性衰老模型,结果表明杜仲叶浸膏粉具有抗衰老的作用,推测其作用机理可能是改善中枢神经递质、提高红细胞免疫力和抗氧化能力来引发抗衰老作用。赵晖[62]研究发现,杜仲中的京尼平苷酸、桃叶珊瑚苷等环烯醚萜单苷类物质呈剂量依赖性地加速胶原蛋白合成和皮肤角质层更新,延缓衰老的进程,且暂未发现任何不良影响。Li等[63]实验表明,桃叶珊瑚苷、京尼平苷酸、京尼平能促进大鼠衰老模型的胶原蛋白合成,促进形成肉芽肿,京尼平苷酸还能提高角质层更新率,对抗皮肤老化。张缓[64]研究发现,EUB-4(桃叶珊瑚苷)、EUB-2(车叶草苷)、EUB-17(Eucommia A)等对H2O2及UV损伤的人胚皮肤成纤维细胞株(ESF-1)都有显著保护作用。由此,将杜仲叶作为天然原料加入化妆品,开发出新型天然无害的植物精萃类化妆品具有重大现实意义。
2.8 抗骨质疏松作用
戴鹏等[65]制定详细的计划来评价杜仲叶醇提取物防治绝经后骨质疏松症的模型大鼠引起的骨质疏松症的能力后得出,杜仲叶具有打破骨代谢平衡的能力,拥有“强筋骨”的作用。杜仲叶防治骨质疏松的主要活性成分为木质素类、酚酸、黄酮类及苯丙素类等。杜仲叶可防止骨中钙和磷元素流失过多,使钙和磷元素在骨中沉积。此外,根据成骨细胞体外培养实验得出,杜仲叶提取物能加速骨细胞增殖,促进骨形成[66]。目前,应用于杜仲叶防治骨质疏松的临床试验研究较匮乏,有待考察。
2.9 其他作用
刘迪等[67]采用大孔吸附树脂法来获取杜仲叶粗提物,得到杜仲叶的树脂分离纯化产物具有抗疲劳的作用,且抗疲劳功效与多酚含量有关。中医常用杜仲来安胎。吕锦芳等[68]使空怀兔子宫分离,观察杜仲不同部位制得的水煎剂与其平滑肌运动性能的关系,发现杜仲各部位对子宫均有安胎作用;杜仲叶中大量的钾元素和桃叶珊瑚苷均能促进尿液分泌,具有利尿的作用[69];杜仲叶提取物还能保护小鼠的肝脏,加速机体恢复[70]。
3. 杜仲叶在食品加工中的应用
杜仲的药理作用在中国第一本药书《神农本草经》中就有记载,李时珍在《本草纲目》中也表示杜仲是十分珍贵的中药材,因此杜仲有“植物黄金”的美誉。杜仲浑身上下都是宝,杜仲叶作为食品原料在湖南省和河南省等地区均有食用历史,主要方法为杜仲嫩叶做菜、煮粥、制成杜仲茶或用榨取杜仲叶汁加入面团等,且截至目前无任何正常食用杜仲产生不良影响的报道。随药食同疗类食品的热度大增,人们逐渐将目光聚焦于资源丰富、营养价值高的杜仲叶的食品研发方面。
3.1 杜仲叶饮品
杜仲茶是杜仲食品类研究最多、生产最广泛的一类。20世纪80年代以来,日本首次掀起“杜仲茶”热潮,随后欧亚一些国家和地区也纷纷加入这波热度。值此浪潮,我国也开始制作杜仲茶,主要用于进出口[71]。实践发现,长期饮用具有减肥、美容、降压、治疗心律不齐、增强记忆、恢复体能等作用[72]。单用杜仲叶一种原料制成的杜仲茶,往往带有青涩的香味,引起部分消费者的不适。为了制成大众均能接受的茶饮,在纯杜仲茶中加入30%左右的茉莉花茶或中上档的乌龙茶,可有效改良茶香味。近期贵州省、陕西省等地生产的杜仲茶,都加入不同比值的茉莉花茶,香味较易于大众接受。
岳红等[72]以杜仲叶为主要原料,加入核桃仁,制作出一款甜味适中、适合中老年人长期饮用的核桃仁杜仲叶复合饮料。叶文峰等[73]在主原料为杜仲叶的基础上添加苹果汁等开发出了一款安全无毒、清爽可口的复合饮料。张志健等[74]将杜仲叶中加入蜂蜜、柠檬酸等辅料研制出一种口感酸甜的杜仲叶饮料。刘亮等[75]混合牛乳和杜仲茶粉制作出一款具有保健功能的酸奶,其色香味俱全,受到广泛好评。
3.2 其他食品
除上述食品外,有人将杜仲叶的浸膏粉作为添加剂,生产具有特定功能保健作用的食品,如杜仲饼干、杜仲糖、杜仲果冻等;有人将杜仲叶制成菜点食品并进行推广,成都某餐厅已投入实践,受到好评;还有人将其添加到主食中去,增加主食的营养保健性。特别是杜仲叶的抗衰老和对骨骼和肌肉中胶原蛋白的合成和分解作用,加以善用,可为太空食品的开发提供良好基础。
4. 展望
目前虽有多位学者提出杜仲叶和杜仲皮活性成分和药理作用相似,倡导大众将杜仲叶代替杜仲皮开发使用,但对于杜仲叶中各种活性成分的作用机制尚未明确,且应用于临床、食品、药品等领域缺乏安全性评价,需要进一步明确其作用机制,对其毒理学作用进行有效评价,为后续杜仲叶产业化开发奠定理论基础。本文整理多个实验发现杜仲叶和杜仲皮的活性成分含量有较大差别,因此想要杜仲叶完全替代杜仲皮的药理作用,还要明确杜仲叶的用量,对其进行定量研究。尽管杜仲叶作为药食同源物质已在广西等地设定试点,国家还应加强对杜仲叶开发的政策引导,扩大试点范围,加速其作为新资源食品应用市场的进程。此外,杜仲叶精深加工产品种类主要集中在饮品开发,种类较单一,各厂家与其不断美化产品外观、加强营销,不如将目光聚焦于开发杜仲叶产品种类,拓宽杜仲叶销路。
-
序号 环烯醚萜类化合物 存在部位 1 京尼平 树皮 2 桃叶珊瑚苷 树皮 3 scandoside 10-O-acetate 树叶 4 京尼平苷 树皮 5 京尼平苷酸 树皮/树叶 6 车叶草苷酸 树叶 7 脱乙酰车叶草苷酸 树叶 8 哈帕苷丁酸脂 树皮 9 筋骨草甙 树皮 10 匍萄筋骨草甙 树皮 11 杜仲甙Ⅰ 树皮 12 杜仲醇 树皮/树叶 13 杜仲甙Ⅱ 树叶 14 去氧杜仲醇 树皮/树叶 15 Epieucommiol 树叶 16 车叶草苷 树叶 17 杜仲甙 树皮 18 Eucomoside A 树叶 19 Eucomoside B 树叶 20 Eucomoside C 树叶 21 栀二醇 树皮 22 交让木苷 树叶 23 鸡失藤甙甲酯 树叶 24 马线子苷 树叶 25 7-epi-loganin 树叶 26 8-epi-loganin 树叶 27 脱乙酰车叶草苷酸 树叶 28 哈巴苷 树皮 29 梓醇 树皮 30 杜仲甙C 树叶 31 杜仲甙D 树叶 -
[1] 全熙宇, 彭湃, 文沛瑶, 等. 杜仲叶多糖、杜仲精粉、杜仲胶的提取分离及其性能分析[J]. 林产化学与工业,2019,39(2):122−128. [QUAN X Y, PENG P, WEN P Y, et al. Extraction and separation of Eucommia ulmoides leaf polysaccharides, Eucommia ulmoides powder, Eucommia ulmoides gum and their performance analysis[J]. Forest Products Chemistry and Industry,2019,39(2):122−128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2417.2019.02.018 QUAN X Y, PENG P, WEN P Y, et al. Extraction and separation of Eucommia ulmoides leaf polysaccharides, Eucommia ulmoides powder, Eucommia ulmoides gum and their performance analysis [J]. Forest Products Chemistry and Industry, 2019, 39(2): 122-128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2417.2019.02.018
[2] 李江月, 王建淇, 古云. 汉中市杜仲资源现状及开发利用对策[J]. 现代农业科技,2020,765(765):89−92. [LI J Y, WANG J Q, GU Y. Current situation and development and utilization countermeasures of Eucommia ulmoides in Hanzhong City[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology,2020,765(765):89−92. LI J Y, WANG J Q, GU Y. Current situation and development and utilization countermeasures of Eucommia ulmoides in Hanzhong City[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, No. 765(07): 89+92.
[3] WANG C, TANG L, HE J W, et al. Ethnobotany, phytochemistry and pharmacological properties of Eucommia ulmoides: A review[J]. The American Journal of Chinese Medicine,2019,47(2):259−300. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X19500137
[4] DAI X, HUANG Q, ZHOU B, et al. Preparative isolation and purification of seven main antioxidants from Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. (Du-zhong) leaves using HSCCC guided by DPPH-HPLC experiment[J]. Food Chemistry,2013,139(1-4):563−570. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.02.006
[5] 郭姝, 刘杰, 李娜, 等. 指纹图谱结合一测多评法评价杜仲叶代替杜仲皮的可行性[J]. 中药材,2020,43(4):896−902. [GUO S, LIU J, LI N, et al. Evaluation of the feasibility of replacing bark with leaves of Eucommia ulmoides by fingerprint combined with one measurement and multiple evaluation method[J]. Chinese Materia Medica,2020,43(4):896−902. GUO S, LIU J, LI N, et al. Evaluation of the feasibility of replacing bark with leaves of Eucommia ulmoides by fingerprint combined with one measurement and multiple evaluation method [J]. Chinese Materia Medica, 2020, 43(4): 896-902.
[6] 姚新生. 天然药物化学(第二版)[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 1988. YAO X S. Chemistry of natural medicines (second edition) [M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 1988.
[7] 姚丽娜. 杜仲的化学成分研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2010. YAO L N. Study on the chemical composition of Eucommia ulmoides [D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2010.
[8] 刘聪, 郭非非, 肖军平, 等. 杜仲不同部位化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J]. 中国中药杂志,2020,45(3):497−512. [LIU C, GUO F F, XIAO J P, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of different parts of Eucommia ulmoides[J]. Chinese Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2020,45(3):497−512. LIU C, GUO F F, XIAO J P, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of different parts of Eucommia ulmoides[J]. Chinese Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2020, 45(3): 497-512.
[9] 王亚洁, 何玉钰. 近年杜仲茶成分及工艺探讨[J]. 科学教育,2017(7):192−192. [WANG Y J, HE Y Y. Discussion on the ingredients and technology of Eucommia tea in recent years[J]. Science Education,2017(7):192−192. WANG Y J, HE Y Y. Discussion on the ingredients and technology of Eucommia tea in recent years[J]. Science Education, 2017(7): 192-192.
[10] 龚桂珍, 宫本红, 张学俊, 等. 杜仲叶和杜仲皮中化学成分的比较[J]. 西南大学学报:自然科学,2010,32(7):167−172. [GONG G Z, GONG B H, ZHANG X J, et al. Comparison of chemical components in Eucommia ulmoides leaves and Eucommia ulmoides bark[J]. Journal of Southwest University:Natural Science,2010,32(7):167−172. GONG G Z, GONG B H, ZHANG X J, et al. Comparison of chemical components in Eucommia ulmoides leaves and Eucommia ulmoides bark[J]. Journal of Southwest University: Natural Science, 2010, 32(7): 167-172.
[11] VANHOLME R, DEMEDTS B, MORREEL K, et al. Lignin biosynthesis and structure[J]. Plant Physiology,2010,153(3):895−905. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.155119
[12] 王娟娟, 秦雪梅, 高晓霞, 等, 杜仲化学成分、药理活性和质量控制现状研究进展[J]. 中草药, 2017, 48(15): 3228−3237. WANG J J, QIN X M, GAO X X, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents, pharmacological activity and quality control of Eucommia ulmoides[J]. Chinese Herbal Medicine, 2017, 48(15): 3228−3237.
[13] 栾庆祥. 杜仲化学成分和药理作用研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学,2016,44(9):153−156. [LUAN Q X. Research progress on the chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Eucommia ulmoides[J]. Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2016,44(9):153−156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2016.09.053 LUAN Q X. Research progress on the chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Eucommia ulmoides [J]. Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 44(9): 153-156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2016.09.053
[14] 赖娟华, 徐丽瑛, 饶华, 等. 杜仲叶化学成分和药理作用研究概况[J]. 实用中西医结合临床,2004,4(2):67−68. [LAI J H, XU L Y, RAO H, et al. Overview of research on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Eucommia ulmoides leaves[J]. Practical Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Clinic,2004,4(2):67−68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4040.2004.02.069 LAI J H, XU L Y, RAO H, et al. Overview of research on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Eucommia ulmoides leaves[J]. Practical Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Clinic, 2004, 4(2): 67-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4040.2004.02.069
[15] 李锟, 郝志友, 张翠利, 等. 杜仲化学成分研究[J]. 中药材,2016,36(9):46−48. [LI K, HAO Z Y, ZHANG C L, et al. Study on the chemical constituents of Eucommia ulmoides[J]. Chinese Medicinal Materials,2016,36(9):46−48. LI K, HAO Z Y, ZHANG C L, et al. Study on the chemical constituents of Eucommia ulmoides[J]. Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2016, 36(9): 46-48.
[16] 李健民, 徐艳明, 朱魁元, 等. 杜仲抗氧化生物活性研究进展[J]. 中医药学报,2010,38(2):137−139. [LI J M, XU Y M, ZHU K Y, et al. Research progress in antioxidative biological activity of Eucommia ulmoides[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2010,38(2):137−139. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2392.2010.02.056 LI J M, XU Y M, ZHU K Y, et al. Research progress in antioxidative biological activity of Eucommia ulmoides[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2010, 38(2): 137-139. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2392.2010.02.056
[17] 左月明, 张忠立, 李于益, 等. 杜仲叶木脂素类化学成分研究[J]. 时珍国医国药,2014,25(6):1317−1319. [ZUO Y M, ZHANG Z L, LI Y Y, et al. Study on the chemical constituents of lignans in Eucommia ulmoides leaves[J]. Shizhen Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica,2014,25(6):1317−1319. ZUO Y M, ZHANG Z L, LI Y Y, et al. Study on the chemical constituents of lignans in Eucommia ulmoides leaves[J]. LI Shi-zhen Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica, 2014, 25(6): 1317-1319.
[18] 管淑玉, 苏薇薇. 杜仲化学成分与药理研究进展[J]. 中药材,2003,26(2):124−129. [GUAN S Y, SU W W. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacology of Eucommia ulmoides[J]. Chinese Medicinal Materials,2003,26(2):124−129. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4454.2003.02.025 GUAN S Y, SU W W. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacology of Eucommia ulmoides [J]. Chinese medicinal materials, 2003, 26(2): 124-129. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4454.2003.02.025
[19] 化雪艳. 杜仲菌质制备及菌质烘焙食品研制[D]. 吉首: 吉首大学, 2014. HUA X Y. Preparation of Eucommia ulmoides bacterial and development of bacterial bake food [D]. Jishou: Jishou University, 2014.
[20] 王菲菲, 张聿梅, 郑笑为, 等. 环烯醚萜类化合物的结构和生物学活性研究进展[J]. 中国药事,2019,33(3):323−330. [WANG F F, ZHANG Y M, ZHENG X W, et al. Research progress on the structure and biological activity of iridoids[J]. Chinese Pharmaceutical Affairs,2019,33(3):323−330. WANG F F, ZHANG Y M, ZHENG X W, et al. Research progress on the structure and biological activity of iridoids[J]. Chinese Pharmaceutical Affairs, 2019, 33(3): 323-330.
[21] CHIKA, TAKAMURA, TETSUYA, et al. Iridoids from the green leaves of Eucommia ulmoides[J]. Journal of Natural Products,2007,70(8):1312−1316. doi: 10.1021/np0780046
[22] 高秀梅, 王虹, 苏艳芳, 等. 杜仲化学成分作为植物雌激素的新用途: 中国, 101647850A[P]. 2010-02-17. GAO X M, WANG H, SU Y F, et al. New uses of Eucommia ulmoides as phytoestrogens: China, 101647850A[P]. 2010-02-17.
[23] 贾智若, 朱小勇, 李兵, 等. 不同产地杜仲叶挥发油成分的GC-MS分析[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2013,19(19):118−122. [ JIA Z R, ZHU X Y, LI B, et al. GC-MS analysis of volatile oil from Eucommia ulmoides leaves from different origins[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Formulas,2013,19(19):118−122. JIA Z R, ZHU X Y, LI B, et al. GC-MS analysis of volatile oil from Eucommia ulmoides leaves from different origins[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Formulas, 2013, 19(19): 118-122.
[24] 马博, 张媛, 张达义, 等. 杜仲的化学成分及其药理作用研究进展[J]. 西部中医药,2013,26(12):153−159. [MA B, ZHANG Y, ZHANG D Y, et al. Research progress on the chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Eucommia ulmoides[J]. Western Traditional Chinese Medicine,2013,26(12):153−159. MA B, ZHANG Y, ZHANG D Y, et al. Research progress on the chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Eucommia ulmoides[J]. Western Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2013, 26(12): 153-159.
[25] 张威鹏, 朱雯, 张良, 等. 杜仲主要活性成分含量及其与树龄和部位的相关性[J]. 经济林研究,2020,38(3):46−57. [ZHANG W P, ZHU W, ZHANG L, et al. The content of main active components of Eucommia ulmoides and its correlation with tree age and position[J]. Economic Forest Research,2020,38(3):46−57. ZHANG W P, ZHU W, ZHANG L, et al. The content of main active components of Eucommia ulmoides and its correlation with tree age and position[J]. Economic Forest Research, 2020, 38(3): 46-57.
[26] 张子东, 付冬梅, 张威鹏, 等. HPLC法同时测定不同生长年限不同部位杜仲中5种苯丙素类成分[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(8):186−191. [ZHANG Z D, FU D M, ZHANG W P, et al. Simultaneous determination of 5 phenylpropanoids in different parts of Eucommia ulmoides with different growth years by HPLC method[J]. Food Science,2019,40(8):186−191. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20180417-231 ZHANG Z D, FU D M, ZHANG W P, et al. Simultaneous determination of 5 phenylpropanoids in different parts of Eucommia ulmoides with different growth years by HPLC method[J]. Food Science, 2019, 40(8): 186-191. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20180417-231
[27] 王莹, 阿来·赛坎, 邢亚楠, 等. 杜仲叶中总黄酮与总多糖的含量分析[J]. 应用化工,2016,45(3):550−552. [WANG Y, ALAI·SAIKAN, XING Y N, et al. Content analysis of total flavonoids and total polysaccharides in Eucommia ulmoides leaves[J]. Applied Chemical Industry,2016,45(3):550−552. WANG Y, ALAI·SAIKAN, XING Y N, et al. Content analysis of total flavonoids and total polysaccharides in Eucommia ulmoides leaves[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2016, 45(3): 550-552.
[28] 陈景超, 王彦宝. 杜仲叶中黄酮不同提取方法的比较[J]. 黑龙江科技信息,2011(21):20. [CHEN J C, WANG Y B. Comparison of different extraction methods of flavonoids in Eucommia ulmoides leaves[J]. Heilongjiang Science and Technology Information,2011(21):20. CHEN J C, WANG Y B. Comparison of different extraction methods of flavonoids in Eucommia ulmoides leaves[J]. Heilongjiang Science and Technology Information, 2011(21): 20.
[29] 张威鹏, 朱雯, 张良, 等. HPLC法同时测定不同采收年限及部位杜仲中5种黄酮类成分[J]. 黑龙江医药,2020,33(6):1267−1270. [ZHANG W P, ZHU W, ZHANG L, et al. Simultaneous determination of five flavonoids in Eucommia ulmoides in different harvest years and positions by HPLC method[J]. Heilongjiang Medicine,2020,33(6):1267−1270. ZHANG W P, ZHU W, ZHANG L, et al. Simultaneous determination of five flavonoids in Eucommia ulmoides in different harvest years and positions by HPLC method[J]. Heilongjiang Medicine, 2020, 33(6): 1267-1270.
[30] 张留记, 李宁, 屠万倩, 等. HPLC法同时测定杜仲叶中8种成分的含量[J]. 中国药房,2019,30(24):3383−3387. [ZHANG L J, LI N, TU W Q, et al. Simultaneous determination of the contents of 8 components in Eucommia ulmoides leaves by HPLC[J]. China Pharmacy,2019,30(24):3383−3387. ZHANG L J, LI N, TU W Q, et al. Simultaneous determination of the contents of 8 components in Eucommia ulmoides leaves by HPLC[J]. China Pharmacy, 2019, 30(24): 3383-3387.
[31] 王亮亮, 唐小兰, 王凯, 等. 杜仲的活性成分和保健功效及杜仲在食品加工中的应用[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2020,11(10):3074−3080. [WANG L L, TANG X L, WANG K, et al. Eucommia ulmoides active ingredients and health effects and its application in food processing[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection,2020,11(10):3074−3080. WANG L L, TANG X L, WANG K, et al. Eucommia ulmoides active ingredients and health effects and its application in food processing[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection, 2020, 11(10): 3074-3080.
[32] 张学俊, 伊廷金, 孙黔云, 等. 杜仲叶多糖的提取分离, 抗补体活性及结构研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2011,23(4):606−611. [ZHANG X J, YI T J, SUN Q Y, et al. Extraction, isolation, anti-complement activity and structure of polysaccharides from Eucommia ulmoides leaves[J]. Natural Products Research and Development,2011,23(4):606−611. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6880.2011.04.004 ZHANG X J, YI T J, SUN Q Y, et al. Extraction, isolation, anti-complement activity and structure of polysaccharides from Eucommia ulmoides Leaves [J]. Natural Products Research and Development, 2011, 23(4): 606-606. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6880.2011.04.004
[33] 陈蕾. 杜仲叶中多糖分子物的提取及其对运动人体免疫机能的影响[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学,2019,38(11):374−379. [CHEN L. Extraction of polysaccharide molecules from Eucommia ulmoides leaves and its effect on the immune function of exercise human[J]. Genomics and Applied Biology,2019,38(11):374−379. CHEN L. Extraction of polysaccharide molecules from Eucommia ulmoides leaves and its effect on the immune function of exercise human [J]. Genomics and Applied Biology, 2019, 38(11): 374-379.
[34] 邓云云, 张俊娥. 杜仲愈伤组织及其叶和皮的抗氧化活性及降血糖能力比较[J]. 分子植物育种,2019,17(3):1006−1010. [DENG Y Y, ZHANG J E. Comparison of antioxidant activity and hypoglycemic ability of Eucommia ulmoides Callus, its leaves and bark[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding,2019,17(3):1006−1010. DENG Y Y, ZHANG J E. Comparison of antioxidant activity and hypoglycemic ability of Eucommia ulmoides callus, its leaves and bark [J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2019, 17(3): 1006-1010.
[35] 彭密军, 彭胜, 王翔, 等. 杜仲叶中多酚类化合物含量与主要生态因子的相关性研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2018,30(5):823−831. [PENG M J, PENG S, WANG X, et al. Study on the correlation between the content of polyphenols in Eucommia ulmoides leaves and the main ecological factors[J]. Research and Development of Natural Products,2018,30(5):823−831. PENG M J, PENG S, WANG X, et al. Study on the correlation between the content of polyphenols in Eucommia ulmoides leaves and the main ecological factors[J]. Research and development of natural products, 2018, 30(5): 823-831.
[36] ZHANG X, CHENG C, ZHANG M, et al. Effect of alkali and enzymatic pretreatments of Eucommia ulmoides leaves and barks on the extraction of gutta percha[J]. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry,2008,56(19):62−65.
[37] 周芳, 刘韶, 邓梦如, 等. GC-MS/SIM法测定不同产地杜仲叶中的氨基酸[J]. 中南药学,2012,10(4):257−260. [ZHOU F, LIU S, DENG M R, et al. Determination of amino acids in Eucommia ulmoides leaves by GC-MS/SIM method[J]. Zhongnan Pharmacy,2012,10(4):257−260. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2981.2012.04.006 ZHOU F, LIU S, DENG M R, et al. Determination of amino acids in Eucommia ulmoides leaves by GC-MS/SIM method[J]. Zhongnan Pharmacy, 2012, 10(4): 257-260. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2981.2012.04.006
[38] 周利兵, 蒋才云, 蓝峻峰. 不同产地杜仲叶中氨基酸的化学计量分析[J]. 安徽农业科学,2020,48(19):180−181. [ZHOU L B, JIANG C Y, LAN J F. Stoichiometric analysis of amino acids in Eucommia ulmoides leaves from different origins[J]. Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2020,48(19):180−181. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2020.19.047 ZHOU L B, JIANG C Y, LAN J F. Stoichiometric analysis of amino acids in Eucommia ulmoides leaves from different origins[J]. Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(19): 180-181. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2020.19.047
[39] 钟淑娟, 杨欣, 李静, 等. 杜仲不同部位总黄酮含量及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中国药房,2017,28(13):1787−1790. [ZHONG S J, YANG X, LI J, et al. Study on content and antioxidant activity of total flavonoids from different parts of Eucommia ulmoides[J]. China Pharmacy,2017,28(13):1787−1790. doi: 10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2017.13.17 ZHONG S J, YANG X, LI J, et al. Study on content and antioxidant activity of total flavonoids from different parts of Eucommia ulmoides [J]. China Pharmacy, 2017, 28(13): 1787-1790. doi: 10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2017.13.17
[40] 陈辉. 杜仲及其提取物的生物学功能及其在养猪生产中的应用[J]. 广东饲料,2020,29(10):39−42. [CHEN H. The biological function of Eucommia ulmoides and its extracts and its application in pig production[J]. Guangdong Feed,2020,29(10):39−42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8613.2020.10.010 CHEN H. The biological function of Eucommia ulmoides and its extracts and its application in pig production[J]. Guangdong Feed, 2020, 29(10): 39-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8613.2020.10.010
[41] ZHANG Q, SU Y Q, ZHANG J F. Seasonal difference in antioxidant capacity and active compounds contents of Eucommia ulmoides oliver leaf[J]. Molecules,2013,18(2):44−48.
[42] YEN G C, HSIEH C L. Antioxidant activity of extracts from Du-zhong (Eucommia ulmoides) toward various lipid peroxidation models in vitro[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,1998,46(10):3952−3957. doi: 10.1021/jf9800458
[43] 刘静. 杜仲叶提取物的体外抗氧化作用[J]. 陕西教育学院学报,2007,23(2):65−67. [LIU J. Antioxidant effect of Eucommia ulmoides leaf extract in vitro[J]. Journal of Shaanxi Institute of Education,2007,23(2):65−67. LIU J. Antioxidant effect of Eucommia ulmoides leaf extract in vitro[J]. Journal of Shaanxi Institute of Education, 2007, 23(2): 65-67.
[44] 王翔, 胡凤杨, 杨秋玲, 等. 杜仲叶的营养评价及体外抗氧化活性分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(21):290−299. [WANG X, HU F Y, YANG Q L, et al. Nutritional evaluation andin vitro antioxidant activity analysis of Eucommia ulmoides leaves[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2019,40(21):290−299. WANG X, HU F Y, YANG Q L, et al. Nutritional evaluation and in vitro antioxidant activity analysis of Eucommia ulmoides leaves[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2019, 40(21): 290-299.
[45] 杨志友, 马智慧, 邓嘉航, 等. 药食同源植物杜仲叶中有效成分京尼平苷酸的抗炎作用研究[J]. 广东化工,2020,47(22):47−48. [YANG Z Y, MA Z H, DENG J H, et al. Study on the anti-inflammatory effect of geniposide, an active ingredient in the leaves of Eucommia ulmoides, a homologous plant for medicine and food[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry,2020,47(22):47−48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2020.22.018 YANG Z Y, MA Z H, DENG J H, et al. Study on the anti-inflammatory effect of geniposide, an active ingredient in the leaves of Eucommia ulmoides, a homologous plant for medicine and food[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2020, 47(22): 47-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2020.22.018
[46] 韩曼飞, 张刘强, 李医明. 天然桃叶珊瑚苷及其衍生物的化学结构和药理作用研究进展[J]. 中草药,2017,48(19):4105−4113. [HAN M F, ZHANG L Q, LI Y M. Research progress on the chemical structure and pharmacological effects of natural aucubin and its derivatives[J]. Chinese Herbal Medicine,2017,48(19):4105−4113. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2017.19.031 HAN M F, ZHANG L Q, LI Y M. Research progress on the chemical structure and pharmacological effects of natural aucubin and its derivatives[J]. Chinese herbal medicine, 2017, 48(19): 4105-4113. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2017.19.031
[47] 王宏军, 吴国娟, 李焕荣, 等. 金银花中绿原酸提取方法的筛选及其抑菌作用[J]. 北京农学院学报,2003,18(4):262−265. [WANG H J, WU G J, LI H R, et al. Screening of extraction methods of chlorogenic acid from honeysuckle and its antibacterial effect[J]. Journal of Beijing Agricultural College,2003,18(4):262−265. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3186.2003.04.007 WANG H J, WU G J, LI H R, et al. Screening of extraction methods of chlorogenic acid from honeysuckle and its antibacterial effect[J]. Journal of Beijing Agricultural College, 2003, 18(4): 262-265. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3186.2003.04.007
[48] 万凡, 侯扶江, 伊宝, 等. 绿原酸的生理功能及其在畜禽生产中的应用[J]. 动物营养学报, 2021, 33(5): 2416-2427. WAN F, HOU F J, YI B, et al. Physiological function of chlorogenic acid and its application in livestock production. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2021, 33(5): 2416-2427.
[49] 王红连, 张凌裳, 张东升, 等. 杜仲叶提取物对鲫鱼出血性病原菌抑菌试验的研究[J]. 饲料工业,2009,30(12):28−30. [WANG H L, ZHANG L S, ZHANG D S, et al. Study on the antibacterial test of Eucommia ulmoides leaf extract on the hemorrhagic pathogen of crucian carp[J]. Feed Industry,2009,30(12):28−30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-991X.2009.12.007 WANG H L, ZHANG L S, ZHANG D S, et al. Study on the antibacterial test of Eucommia ulmoides leaf extract on the hemorrhagic pathogen of crucian carp[J]. Feed Industry, 2009, 30(12): 28-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-991X.2009.12.007
[50] 李旭, 刘停, 陈时建, 等. 杜仲叶绿原酸提取工艺优化及对自发性高血压大鼠的降压作用[J]. 食品科学,2013,34(14):30−34. [LI X, LIU T, CHEN S J, et al. Optimization of extraction process of chlorogenic acid from Eucommia ulmoides leaf and its antihypertensive effect on spontaneously hypertensive rats[J]. Food Science,2013,34(14):30−34. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201314007 LI X, LIU T, CHEN S J, et al. Optimization of extraction process of chlorogenic acid from Eucommia ulmoides leaf and its antihypertensive effect on spontaneously hypertensive rats[J]. Food Science, 2013, 34(14): 30-34. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201314007
[51] 雷燕妮, 张小斌. 杜仲叶总黄酮降血压作用的研究[J]. 陕西农业科学,2016,62(5):6−8. [LEI Y N, ZHANG X B. Research on the effect of total flavonoids of Eucommia ulmoides on lowering blood pressure[J]. Shaanxi Agricultural Sciences,2016,62(5):6−8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0488-5368.2016.05.002 LEI Y N, ZHANG X B. Research on the effect of total flavonoids of Eucommia ulmoides on lowering blood pressure[J]. Shaanxi Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 62(05): 6-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0488-5368.2016.05.002
[52] 郎茜, 龚蕾, 叶婧, 等. 杜仲叶多糖对糖尿病大鼠的降血糖作用[J]. 现代食品科技,2020,36(10):27−32,78. [LANG Q, GONG L, YE J, et al. The effect of Eucommia ulmoides polysaccharide on reducing blood sugar in diabetic rats[J]. Modern Food Technology,2020,36(10):27−32,78. LANG Q, GONG L, YE J, et al. The effect of Eucommia ulmoides polysaccharide on reducing blood sugar in diabetic rats[J]. Modern Food Technology, 2020, 36(10): 27-32, 78.
[53] 乔红伟, 潘励山, 陈威, 等. 杜仲茶对大鼠的降血脂作用[J]. 中国比较医学杂志,2015,25(12):9−12. [QIAO H W, PAN L S, CHEN W, et al. The effect of Duzhong tea on lowering blood lipids in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Comparative Medicine,2015,25(12):9−12. QIAO H W, PAN L S, CHEN W, et al. The effect of Duzhong tea on lowering blood lipids in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Comparative Medicine, 2015, 25(12): 9-12.
[54] 王乙庚. 杜仲叶绿原酸和竹叶多糖降糖颗粒的研究[D]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学, 2015. WANG Y G. Studies on chlorogenic acid and polysaccharides from Eucommia ulmoides leaves [D]. Changsha: Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 2015.
[55] 徐贤柱, 饶华, 蔡险峰, 等. 杜仲叶多糖提取及对小鼠免疫功能影响研究[J]. 时珍国医国药,2013,24(3):541−542. [XU X Z, RAO H, CAI X F, et al. Extraction of polysaccharides from Eucommia ulmoides leaves and its effect on the immune function of mice[J]. Shizhen Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica,2013,24(3):541−542. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2013.03.011 XU X Z, RAO H, CAI X F, et al. Extraction of polysaccharides from Eucommia ulmoides leaves and its effect on the immune function of mice[J]. Shizhen Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica, 2013, 24(03): 541-542. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2013.03.011
[56] 叶颖霞, 林岚, 赵菊香, 等. 杜仲叶多糖对免疫抑制小鼠免疫功能的影响[J]. 中药材,2015,38(7):1496−1498. [YE Y X, LIN L, ZHAO J X, et al. The effect of Eucommia ulmoides leaf polysaccharides on the immune function of immunosuppressed mice[J]. Chinese Herbal Medicines,2015,38(7):1496−1498. YE Y X, LIN L, ZHAO J X, et al. The effect of Eucommia ulmoides leaf polysaccharides on the immune function of immunosuppressed mice[J]. Chinese herbal medicines, 2015, 38(07): 1496-1498.
[57] YANG G, KYOUNG SEO, LEE J H, et al. Suppression of splenic lymphocyte proliferation by Eucommia ulmoides and genipin[J]. Chem Biodivers,2015,12(4):538−546. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201400376
[58] 袁带秀, 刘梦姣, 聂红, 等. 杜仲总黄酮对铅中毒小鼠免疫器官抗氧化能力的影响[J]. 卫生研究,2016,45(4):643−647. [YUAN D X, LIU M J, NIE H, et al. The effect of total flavonoids of Eucommia ulmoides on the antioxidant capacity of the immune organs in lead poisoned mice[J]. Health Research,2016,45(4):643−647. YUAN D X, LIU M J, NIE H, et al. The effect of total flavonoids of Eucommia ulmoides on the antioxidant capacity of the immune organs in lead poisoned mice[J]. Health Research, 2016, 45(4): 643-647.
[59] 栾芳菲, 李湘洲, 黄丹, 等. 杜仲叶提取物对人结直肠癌细胞HCT116及抗血管生成活性的影响[J]. 林产化学与工业,2016,36(3):95−100. [LUAN F F, LI X Z, HUANG D, et al. Effects of Eucommia leaf extract on human colorectal cancer cell HCT116 and anti-angiogenesis activity[J]. Forest Products Chemistry and Industry,2016,36(3):95−100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2417.2016.03.014 LUAN F F, LI X Z, HUANG D, et al. Effects of Eucommia leaf extract on human colorectal cancer cell HCT116 and anti-angiogenesis activity[J]. Forest Products Chemistry and Industry, 2016, 36(03): 95-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2417.2016.03.014
[60] 张胜, 李湘洲, 刘子雷, 等. 杜仲叶活性成分对结肠癌细胞增殖与凋亡的影响[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2018,36(2):284−287. [ZHANG S, LI X Z, LIU Z L, et al. Effects of Eucommia leaf active components on proliferation and apoptosis of colon cancer cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2018,36(2):284−287. ZHANG S, LI X Z, LIU Z L, et al. Effects of Eucommia leaf active components on proliferation and apoptosis of colon cancer cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 36(2): 284-287.
[61] 李小安, 夏前明, 王秉文, 等. 杜仲叶浸膏粉抗衰老作用的研究[J]. 西部医学,2009,21(6):904−906. [LI X A, XIA Q M, WANG B W, et al. Study on the anti-aging effect of Eucommia ulmoides extract powder[J]. Western Medicine,2009,21(6):904−906. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3511.2009.06.007 LI X A, XIA Q M, WANG B W, et al. Study on the anti-aging effect of Eucommia ulmoides extract powder[J]. Western Medicine, 2009, 21(06): 904-906. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3511.2009.06.007
[62] 赵晖. 杜仲叶药理作用研究(Ⅰ)——抗衰老作用[J]. 国外医学(中医中药分册),2000(3):151−153,144. [63] LI Y, METORI K, KOIKE K, et al. Improvement in the turnover rate of the stratum corneum in false aged model rats by the administration of geniposidic acid in Eucommia ulmoides oliver leaf[J]. Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin,1999,22(6):528−585.
[64] 张缓. 杜仲抗皮肤衰老活性成分的筛选及其作用机制研究[D]. 开封: 河南大学, 2016. ZHANG H. Screening of anti-aging active ingredients of Eucommia ulmoides and its mechanism of action [D]. Kaifeng: Henan University, 2016.
[65] 戴鹏, 邓鸣涛, 张立超, 等. 杜仲叶对去势骨质疏松大鼠骨代谢的影响[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2012,18(12):1127−1130. [DAI P, DENG M T, ZHANG L C, et al. Effects of Eucommia ulmoides leaves on bone metabolism in ovariectomized osteoporotic rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Osteoporosis,2012,18(12):1127−1130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2012.12.015 DAI P, DENG M T, ZHANG L C, et al. Effects of Eucommia ulmoides leaves on bone metabolism in ovariectomized osteoporotic rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Osteoporosis, 2012, 18(12): 1127-1130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2012.12.015
[66] 饶华, 徐贤柱, 王曼莹. 杜仲叶总提取物治疗去势大鼠骨质疏松症的实验研究[J]. 江西医药,2014,49(2):100−102. [RAO H, XU X Z, WANG M Y. Experimental study of the total extract of Eucommia ulmoides in the treatment of osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats[J]. Jiangxi Medicine,2014,49(2):100−102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2238.2014.02.003 RAO H, XU X Z, WANG M Y. Experimental study of the total extract of Eucommia ulmoides in the treatment of osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats[J]. Jiangxi Medicine, 2014, 49(2): 100-102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2238.2014.02.003
[67] 刘迪, 尚华, 宋晓宇. 杜仲叶树脂分离纯化产物的抗疲劳功效[J]. 食品科学,2013,34(5):251−254. [LIU D, SHANG H, SONG X Y. Anti-fatigue effect of Eucommia ulmoides leaf resin separation and purification product[J]. Food Science,2013,34(5):251−254. LIU D, SHANG H, SONG X Y. Anti-fatigue effect of Eucommia leaf resin separation and purification product[J]. Food Science, 2013, 34(5): 251-254.
[68] 吕锦芳, 万文琴, 宁康健. 杜仲不同部位对兔离体子宫运动性能的影响[J]. 中国中医药科技,2004,11(5):292−293. [LV J F, WAN W Q, NING K J. The effect of different parts of Eucommia ulmoides on the motility of isolated rabbit uterus[J]. China Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology,2004,11(5):292−293. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7072.2004.05.018 LV J F, WAN W Q, NING K J. The effect of different parts of Eucommia ulmoides on the motility of isolated rabbit uterus[J]. China Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology, 2004, 11(5): 292-293. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7072.2004.05.018
[69] 刘静. 杜仲叶提取物对力竭运动及恢复小鼠肝脏和骨骼肌的保护作用[J]. 安徽农业科学,2012,40(18):9651−9652. [LIU J. The protective effect of Du-zhong leaf extract on exhaustive exercise and recovery of liver and skeletal muscle in mice[J]. Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2012,40(18):9651−9652. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2012.18.029 LIU J. The protective effect of Du-zhong leaf extract on exhaustive exercise and recovery of liver and skeletal muscle in mice[J]. Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 40(18): 9651-9652. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2012.18.029
[70] 黄友谊, 冀志霞, 杨坚. 杜仲茶开发现状[J]. 茶叶机械杂志,2001(2):22−24. [HUANG Y Y, JI Z X, YANG J. Development status of Du-zhong tea[J]. Tea Machinery Magazine,2001(2):22−24. HUANG Y Y, JI Z X, YANG J. Development status of Du-zhong tea[J]. Tea Machinery Magazine, 2001(2): 22-24.
[71] 陈斌, 程小东, 唐祖志. 杜仲的功能作用及其在食品中的应用前景[J]. 现代食品科技,1999(4):19−21. [CHEN B, CHENG X D, TANG Z Z. The functional role of Eucommia ulmoides and its application prospects in food[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,1999(4):19−21. CHEN B, CHENG X D, TANG Z Z. The functional role of Eucommia ulmoides and its application prospects in food[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 1999(4): 19-21.
[72] 岳红, 胡小玲, 管萍, 等. 杜仲、核桃保健型复合饮料的研制[J]. 林业科技,2001,26(1):58−60. [YUE H, HU X L, GUAN P, et al. Development of Eucommia and walnut health-care compound beverage[J]. Forestry Science and Technology,2001,26(1):58−60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9499.2001.01.022 YUE H, HU X L, GUAN P, et al. Development of Eucommia and walnut health-care compound beverage[J]. Forestry Science and Technology, 2001, 26(1): 58-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9499.2001.01.022
[73] 叶文峰, 楮维元, 席银华, 等. 杜仲叶复合保健饮料的研制[J]. 食品科学,2004,25(11):446−448. [YE W F, CHU W Y, XI Y H, et al. Development of Eucommia ulmoides compound health drink[J]. Food Science,2004,25(11):446−448. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2004.11.118 YE W F, CHU W Y, XI Y H, et al. Development of Eucommia ulmoides compound health drink[J]. Food Science, 2004, 25(11): 446-448. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2004.11.118
[74] 张志健, 李新生, 李建育. 杜仲叶饮料加工工艺研究[J]. 食品科技,2007,32(3):183−186. [ZHANG Z J, LI X S, LI J Y. Research on Eucommia leaf beverage processing technology[J]. Food Science and Technology,2007,32(3):183−186. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2007.03.051 ZHANG Z J, LI X S, LI J Y. Research on Eucommia leaf beverage processing technology[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2007, 32(3): 183-186. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2007.03.051
[75] 刘亮, 卢琪, 段加彩, 等. 杜仲茶酸奶的研制及茶粉、绿原酸对酸奶品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2010,31(12):114−118. [LIU L, LU Q, DUAN J C, et al. The development of Eucommia tea yogurt and the effects of tea powder and chlorogenic acid on the quality of yogurt[J]. Food Science,2010,31(12):114−118. LIU L, LU Q, DUAN J C, et al. The development of Eucommia tea yogurt and the effects of tea powder and chlorogenic acid on the quality of yogurt[J]. Food Science, 2010, 31(12): 114-118.
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 宋巧英. 超声辅助深共熔溶剂提取栀子黄酮及其对HepG2细胞的降血糖作用. 精细化工. 2024(10): 2223-2230 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 杨春晖,王文平,续丹丹,崔宇倩,鞠岩,许春艳,吕小婷. 不同原料酿造酱油功能成分及抗氧化活性比较. 食品工业科技. 2023(14): 318-325 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 白琨,李艳,蔡伟. 和田茴香籽总黄酮提取及体内抗氧化活性研究. 中国调味品. 2023(08): 199-202 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 周煜凡,冯疆涛,白冰瑶. 响应面法优化新疆纸皮核桃分心木中总黄酮提取工艺. 食品工业. 2023(09): 40-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 郑沛,文敏,刘秋叶,王潇,左亚杰. 半枝莲总黄酮提取工艺优化及抗氧化、抗肿瘤活性评价. 食品工业科技. 2023(23): 194-202 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 张晨,赵金,严俊杰,苗人云,林俊彬,李翔,周向荣,张攀,甘炳成. 响应面法优化黑皮鸡枞总黄酮提取工艺. 中国调味品. 2022(11): 138-143 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(8)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
