Study on the Therapeutic Effect of Morinda officinalis on HCT-116 Xenograft Tumor Model and the Underlying Mechanism
-
摘要: 目的:检测巴戟天对人源结肠癌细胞HCT-116移植瘤的抑制作用及初步探讨其作用机制。方法:于雄性裸鼠腋下注射人源结肠癌HCT-116细胞,建立移植瘤模型,随后采用巴戟天乙醇提取物(Ethanol extract of Morinda officinalis, EEMO)(12 mg/kg/d)和巴戟天生药(Crude drug of Morinda officinalis, CDMO)(200 mg/kg/d)为实验组进行灌胃给药,以5-氟尿嘧啶(5-Fluorouracil, 5-FU)为阳性药(30 mg/kg,每3 d给药一次,腹腔注射),以水(一次/d)为对照组,共四组(EEMO组、CDMO组、5-FU组和对照组),持续给药23 d。通过检测各干预组动物的肿瘤重量、肿瘤体积、肿瘤组织病理变化判断巴戟天的抑癌作用;通过检测肿瘤组织血管生成因子(VEGF)、缺氧诱导因子-1α(HIF-1α)和环氧化酶-2(COX-2)的表达水平以及巨噬细胞的极化趋势初步探讨其抑癌途径。结果:EEMO和CDMO能不同程度抑制小鼠移植瘤体积的增长(P<0.05)、降低移植瘤的重量(P<0.01)和降低血清前列腺素E2(PGE2)的水平(P<0.05)。蛋白免疫印迹和免疫组化的检测结果显示EEMO和CDMO可显著下调肿瘤组织VEGF、HIF-1α和COX-2的表达水平(P<0.01和P<0.05)。免疫荧光检测结果显示,EEMO和CDMO极显著增加iNOS的表达水平(P<0.01),并且极显著提高iNOS/CD206的比例(P<0.01)。结论:EEMO和CDMO对小鼠体内的移植瘤发生有抑制作用,可能与其下调VEGF、HIF-1α和COX-2/PGE2信号通路的表达、增强巨噬细胞向M1型极化有关。Abstract: Objective: To explore the inhibitive effect and underlying mechanism of Morinda officinalis (MO) on human colorectal cancer cell HCT-116 xenograft tumor model. Methods: Xenograft tumor model was established through transplanting human colorectal cancer cell into the armpits of male nude mice. Four groups were divided for appropriate administration, including ethanol extract of Morinda officinalis (EEMO) group (12 mg/kg/d), crude drug of Morinda officinalis (CDMO) group(200 mg/kg/d), 5-fluorouracil (30 mg/kg, once per three days) group, control group (water, once a day). The administration of drugs was lasted for 23 days. Tumor weight, tumor volume and pathological changes were detected. Protein expression of Hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α), Cyclooxygenase-2/Prostaglandin E2 (COX-2/PGE2) pathway and macrophage polarization were determined after the experiment. Results: Both EEMO and CDMO could significantly inhibited the weight and growth of HCT-116 xenograft tumor (P<0.01), lowered the content of PGE2 (P<0.05), reduced the expression of HIF-1α, COX-2 and VEGF in tumor (P<0.01 and P<0.05). Additionally, EEMO and CDMO could remarkably increase the ratio of M1-like macrophage phenotype in tumor microenvironment (P<0.01). Conclusion: MO exerted anti-tumor effect partly via inhibiting expression of HIF-1α, COX-2/PGE2 pathway and polarizing tumor-associated macrophages toward M1-like macrophage phenotype.
-
结肠癌是一种常见的消化道恶性肿瘤,为世界第三大癌症,严重威胁着人类生命健康[1-2]。中医认为,结肠癌的主要症候之一为脾肾阳虚。此外,不良饮食习惯和情绪的干扰,可导致胃肠受损,加速结肠癌病程的发展[3]。临床上对于结肠癌的治疗主要手段为根治性手术,并辅以放疗、化疗和中医治疗[4]。结直肠癌的化疗药物,如5-氟尿嘧啶和奥沙利铂,在对抗癌细胞的同时,也会对机体正常细胞造成一定程度的损伤,长期化疗可导致腹泻、口腔黏膜炎,更甚者会造成严重的后遗症,严重降低了患者的生活质量[5]。基于结直肠癌的发病过程时间较长,寻找适合长期服用并有抑制肿瘤生长效果的药物,具有较好的应用前景。
中医认为结肠癌的病机主要为:肠道蕴结湿热、火毒为病之标;肾亏、正气不足为病之本。故治疗结肠癌应当以清热利湿和补肾为主[6-8]。巴戟天是我国“四大南药”之一,属于药食同源、药理活性明确的中药,具有补肝肾、强筋骨、祛风湿的功效,因此,具有良好的开发前景[9]。关于巴戟天的抗肿瘤活性,最早的报道是来源于巴戟天醇提物抑制肿瘤形成的研究。该报道指出,巴戟天醇提物抑制肿瘤形成过程中的关键蛋白酶磷脂酰肌醇-3-活化醇素的活性,从而限制肿瘤的发生发展[10]。环烯醚萜苷类化合物作为巴戟天乙醇提取物的主要成分之一,其主要的单体成分包括具有抗肿瘤活性的水晶兰苷、香茅苷和骨化三醇A,三者均对诱导肿瘤发生发展的蛋白活化剂AP-1有明显的抑制作用[11]。然而,巴戟天的抗肿瘤活性是否可通过其他途径实现尚未有深入的探讨。
本课题组前期研究发现,巴戟天乙醇提取物对硫酸葡聚糖(Dextran sulfate,DSS)诱导的溃疡性结肠炎小鼠具有显著疗效,通过下调肠道促炎因子的分泌,有效缓解肠道炎症环境,改善小鼠肠道屏障受损[12]。众所周知,肠道长期处于炎性环境是诱发肠道癌变的重要因素[13]。基于此,探讨巴戟天是否能够作为对抗结直肠癌的潜在药物具有重要的现实意义。因此,本研究拟建立人源结肠癌HCT-116细胞移植瘤模型,探讨巴戟天是否具有抑制结直肠癌的作用,并初步探讨其可能的潜在干预机制。本研究结果为后续对于巴戟天应用结直肠炎、癌的预防应用提供了实验依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
雄性SPF级裸鼠(6~8周)40只,18~22 g 广东省医学实验动物中心,许可证号SCXK(粤)2019-0003;人源结肠癌HCT-116细胞 购于中国科学院细胞库。
巴戟天生药(盐制品) 购于深圳Lush有限责任公司,由广州中医药大学中药学院丁平教授鉴定和提供;巴戟天乙醇提取物 由广州中医药大学侯少贞课题组制备得到;5-氟尿嘧啶(5-FU) 购于广州瑞舒生物有限公司,批号:20190301;DAB显色试剂盒(20×) 购于北京中杉金桥生物技术有限公司,批号:K192421C;BCA蛋白浓度测定试剂盒 购于大连美仑生物科技有限公司,批号:MA0082-3-APR-12D;柠檬酸钠抗原修复液 购于博士德生物工程有限公司,批号:13K08A24;免疫组化试剂盒 购于北京博奥森生物技术有限公司,批号:AI07258834;Mouse PGE2 测定试剂盒 购于江苏酶免实业有限公司,批号:MM-0062M1;iNOS抗体 Affinity公司,批号:7913216;CD206抗体 R&D system公司,批号:WFT011801A;HIF-1α抗体 购于Affinity公司,批号:17v4560;COX-2抗体 购于SAB公司,批号:4813;VEGF抗体 购于武汉赛维尔生物科技有限公司,批号:LS194929;GAPDH小鼠单克隆抗体 购于Protein-tech公司,批号:10008047;超敏ECL化学发光试剂盒 购于碧云天公司,批号:P0018S。
BSA224S型电子天平 德国赛多利斯公司;500-151-30型电子数显游标卡尺 日本Mitutoyo公司;HP300组织脱水机、HBM-1型组织包埋机、TM-4000组织切片机、DL6M型冷冻低速离心机、MR-96A型全波长多功能酶标仪、DW86型−80 ℃超低温冰箱 美国Thermo Fisher公司;CU600型电热恒温水浴锅 中国中新医疗仪器有限公司;TGL-20M型高速冷冻离心机 中国常州金坛良友仪器有限公司;ZY-300型涡旋仪 浙江新丰医疗器械有限公司;HF-24M型全自动样品冷冻研磨仪 上海贺帆仪器有限公司;CKX-41-32型倒置型显微镜、CM-24-11型光学显微镜 日本Olympus公司;Zeiss LSM800型激光共聚焦显微镜 德国蔡司公司;SW-CJ-2F型双人双面型洁净工作台 南京晓晓仪器设备有限公司;MCO-20AIC型细胞培养箱 日本Sanyo仪器有限公司;165-8033型蛋白电泳仪、170-3848型Trans-Blot半干转印槽 美国Bio-rad公司;Tanon2500型全自动凝胶成像系统 上海天能科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 药物制备
巴戟天生药(盐制品)经干燥,超微粉碎获得;巴戟天乙醇提取物制备方法:将制取的巴戟天粉末用8倍量85%乙醇加热回流2 h,重复两次,合并两次提取液,回收溶剂,使用旋转蒸发器浓缩,得到的浓缩液在真空下冷冻干燥后得浸膏后低温烘干打粉,并存放于4 ℃冰箱。经检测,巴戟天乙醇提取物中环烯醚萜的主要活性成分为水晶兰苷,含量为2.12%[12]。
1.2.2 细胞准备
将储存于液氮罐的HCT-116细胞取出,在37 ℃恒温水浴锅中来回晃动快速解冻。将解冻的细胞转移至离心管中进行离心(1000 r/min),弃上清液,加入含有9%胎牛血清和1%青霉素-链霉素双抗的DMEM完全培养基,吹打均匀,而后将细胞悬液转移至细胞培养瓶中,置于细胞培养箱中培养(37 ℃,5% CO2)。细胞培养稳定后,加入胰酶消化液将细胞从瓶壁脱落,然后加入完全培养基终止消化。对细胞进行离心后计数,调整细胞密度为107个/mL,于每只裸鼠腋下接种0.2 mL细胞悬液,造实体瘤裸鼠模型。
1.2.3 动物实验
1.2.3.1 动物造模和分组
动物饲养于广州中医药大学实验动物中心SPF级别动物房,饲养温度为22~25 ℃,湿度:45%~55%,每日光照12 h,每天给予动物标准饲料自由食用和蒸馏水自由饮用。
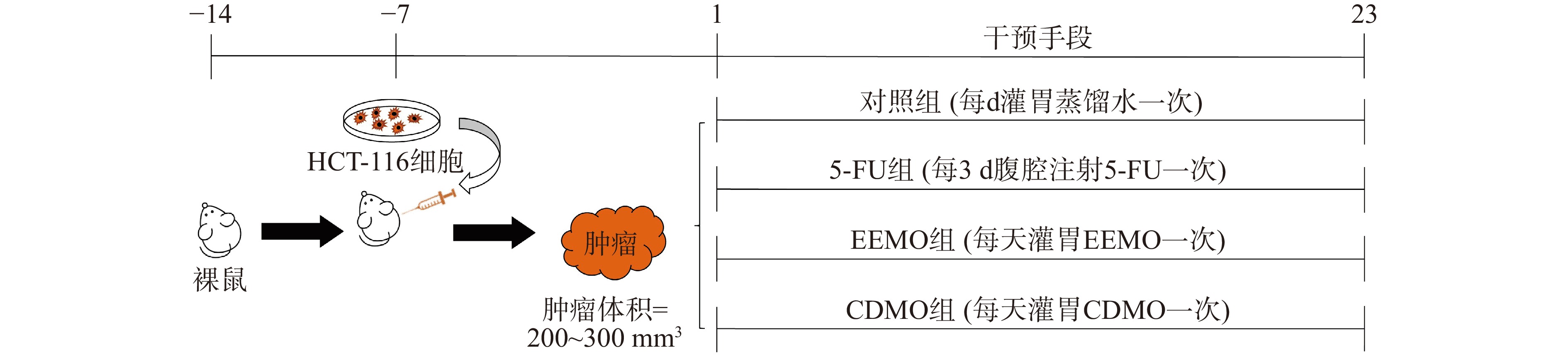
40只裸鼠于SPF级动物房适应性饲养一周后,腋下接种0.2 mL细胞密度为107个/mL的HCT-116细胞悬液,造成实体瘤动物模型。接种后24 h内将动物随机分为对照组和给药组。每天观察裸鼠状态并且记录小鼠的体重和肿瘤体积。每天使用电子游标卡尺量取小鼠腋下的肿瘤,以瘤体任意两点连线最长的长度为长径(a)以及垂直于a的最大长度为宽径(b),计算和记录肿瘤体积。肿瘤体积的计算公式:肿瘤体积=0.5×a×b2。裸鼠的造模流程可参见图1。
饲养一周后,剔除肿瘤增长过快或未形成肿块的动物;待裸鼠皮下肿瘤体积达到200~300 mm3,将全部裸鼠按肿瘤体积随机分组,分别为:对照组(Control group)、5-氟尿嘧啶组(5-FU group)(30 mg/kg,每3 d给药1次,腹腔注射给药),巴戟天乙醇提取物组(EEMO group,12 mg/kg/d,灌胃给药)、巴戟天生药组(CDMO group,200 mg/kg/d,灌胃给药),每组共有10只裸鼠。每5 d观察裸鼠状态并且记录小鼠的体重和肿瘤体积。对照组每天灌胃等体积蒸馏水和每3 d腹腔注射等体积蒸馏水,EEMO和CDMO组除每天灌胃相应药物外另每3 d腹腔注射等体积生理盐水。所有裸鼠均给予自由饮食饮水。实验进行至第23 d结束,对小鼠进行解剖,剖取肿瘤组织进行称量、记录重量和保存。
1.2.3.2 血液与肿瘤组织收集
实验结束后,对裸鼠进行乙醚麻醉,眼眶取血。4 ℃条件下以3500 r/min离心血液15 min得血清,血清保存于−80 ℃冰箱中备用。随后对小鼠进行脱颈椎法处死,并小心剖去皮下肿瘤组织,测量肿瘤重量,并拍照记录。取1/4肿瘤组织用于病理学检测,1/4肿瘤组织用于流式细胞术检测,剩余部分冻存于−80 ℃冰箱中备用。
1.2.4 体外指标检测
1.2.4.1 病理学检测
实验结束后,切取每个肿瘤的1/4浸泡于4 %甲醛。将浸泡4 %甲醛超过48 h的肿瘤组织,进行脱水、浸蜡、包埋等程序,切成4 μm薄片附载于粘附性载玻片上,将载玻片在60 ℃烘箱中烘烤2 h,随后使用组织自动染色机进行苏木精-伊红染色法(Hematoxylin-eosin staining, HE)染色,具体染色操作参考WANG等[14]的方法。对染色完成后的载玻片进行风干,用中性树脂和盖玻片进行封片操作,置于电子显微镜下观察和拍摄(200×和400×)。
1.2.4.2 Western blotting法检测VEGF、HIF-1α和COX-2的水平
剪取0.1 g肿瘤组织加入到含有预冷的混合裂解液(RIPA:PMSF=100:1)的EP管中,使用研磨仪进行组织匀浆,静置30 min。将匀浆液进行离心(12000 r/min,15 min),取上清,按BCA试剂盒说明书进行蛋白浓度测定。取每组等蛋白量的样品进行电泳和封闭后,加入VEGF、HIF-1α和COX-2一抗(1:1000),4 ℃孵育过夜。次日,回收一抗,用含0.5 %TBST的磷酸盐缓冲液洗涤后,分别加入二抗(1:3000),室温孵育2 h。回收二抗并洗涤后,使用ECL试剂盒在发光成像系统中显影成像,对条带进行拍摄记录。具体操作参考WANG等[14]的方法。GAPDH作为内参蛋白。后续使用Image J软件对条带进行定量分析。
1.2.4.3 VEGF、HIF-1α和COX-2的免疫组化检测
将附载肿瘤组织的载玻片放置烘箱内60 ℃烘烤2 h后进行脱蜡,用柠檬酸缓冲液进行抗原修复和3%过氧化氢消除内源性过氧化酶。按免疫组化试剂盒说明书要求对组织进行封闭,后孵育一抗VEGF、HIF-1α和COX-2(1:200),4 ℃孵育过夜。次日孵育相应的二抗以及辣根素酶试剂。DAB显色液避光显色,苏木素复染,再进行乙醇梯度浓度脱水,使用中性树胶和盖玻片进行封片。将载玻片置于电子显微镜下观察拍摄。具体操作参考ZONG等[15]的方法。使用Image J软件对相关蛋白的阳性表达进行分析。
1.2.4.4 巨噬细胞分型的免疫荧光法检测
将附载肿瘤组织的载玻片放置于烘箱内60 ℃烘烤2 h后,进行脱蜡和脱水操作,再使用柠檬酸缓冲液进行抗原修复和3%过氧化氢室温孵育30 min消除内源性过氧化酶。室温封闭1 h后,滴加一抗iNOS和CD206(1:200),4 ℃孵育过夜。次日滴加相应的二抗,避光孵育2 h。洗涤后滴加DAPI对细胞核染色,室温孵育3 min。避光条件下滴加抗荧光猝灭剂覆盖盖玻片,将样品置于激光共聚焦显微镜下观察和拍摄。具体操作参考ZONG等[15]的方法。使用ZEM软件对组织上相关蛋白的表达进行统计分析。
1.3 统计学处理
使用SPSS 25.0数据分析软件对实验结果进行统计分析,采用Graph Pad Prism 8.0对实验结果作图。组间差异比较采用单因素方差分析,当组间两两比较,方差齐则采用LSD检验,方差不齐则采用Dunnett T检验。P<0.05被认为差异具有统计学意义。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 巴戟天对小鼠移植瘤生长的影响
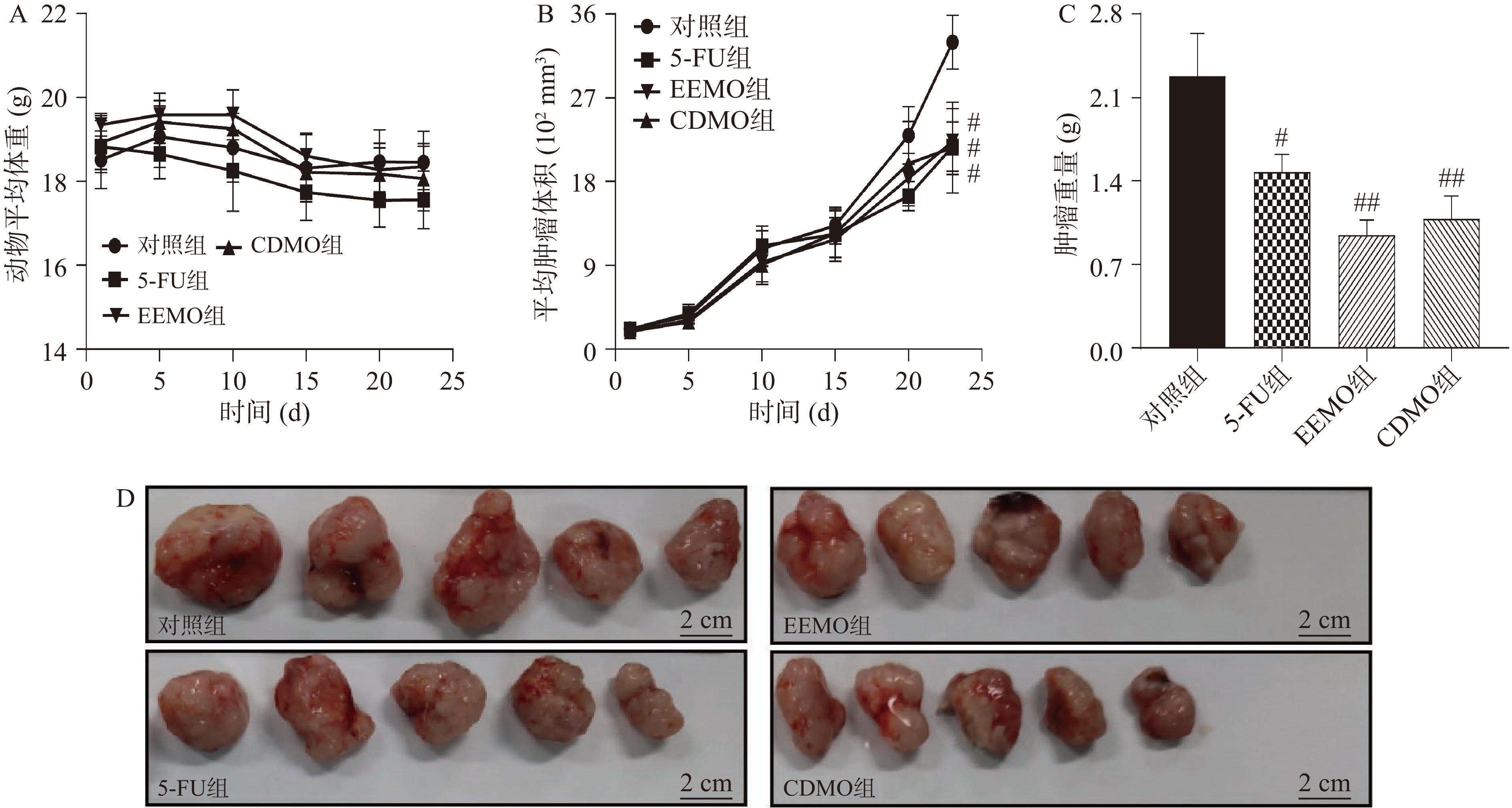
实验于第23 d结束,实验期间通过记录小鼠体重以及肿瘤体积的变化,反映小鼠状态的变化。实验结束后剖取小鼠体内肿瘤进行称量和拍照记录,可直观反映肿瘤的生长状况。与实验第1 d各组小鼠的平均体重相比,各组小鼠第23 d的平均体重均发生下降,但差异无统计学意义(P>0.05;图2A所示)。此外,随着实验的进行,各组动物平均肿瘤体积逐步增加。与对照组相比,5-FU组、EEMO组和CDMO组的肿瘤体积生长速度减缓(P<0.05;图2B所示)。剖取动物皮下的肿瘤,直观可见对照组肿瘤体积最大,各给药的肿瘤大小比对照组小;与对照组相比,5-FU(P<0.05)、EEMO(P<0.01)和CDMO(P<0.01)均能显著降低肿瘤重量;与5-FU组相比,EEMO和CDMO均能使肿瘤质量下降,但差异没有统计学意义(图2C和图2D所示)。结果表明,EEMO和CDMO能干预小鼠体内移植瘤的生长进程,降低肿瘤的生长速度,同时两者对肿瘤生长的抑制作用与5-FU相当。
2.2 巴戟天对小鼠移植瘤病理学的影响
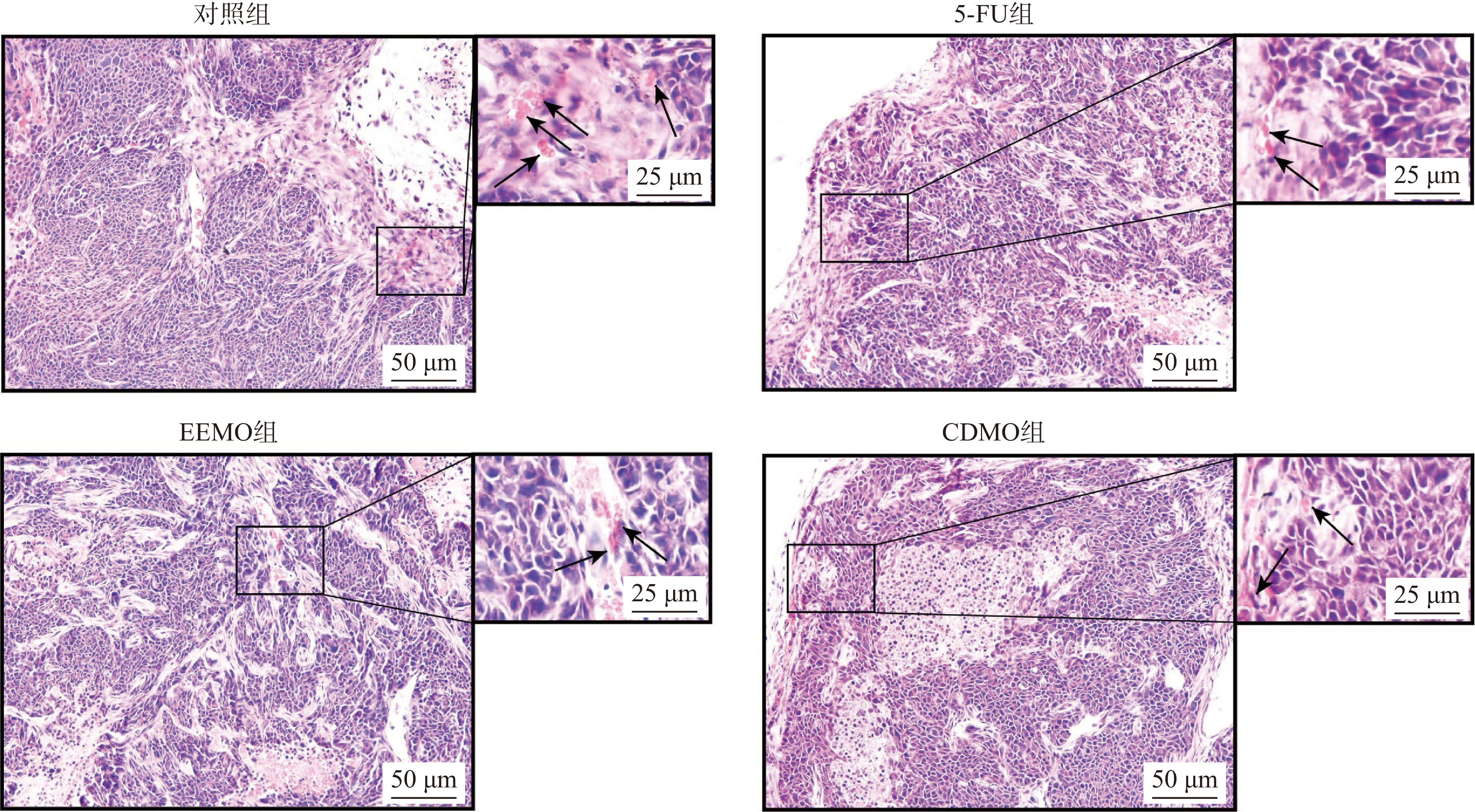
对移植瘤进行病理分析,观察EEMO和CDMO对肿瘤造成的病理学改变,可为进一步深入研究提供方向。从肿瘤病理结果可得,对照组肿瘤细胞生长状态良好,肿瘤细胞致密,肿瘤边缘有较多血管生成(黑色箭头所示)。与对照组相比,阳性药5-FU组、EEMO组和CDMO组动物的肿瘤生长状态良好,细胞较致密,但出现肿瘤细胞坏死区域,伴有轻微血管生成增加,且出现核碎裂(图3所示)。综合各组的病理学结果,可表明5-FU、EEMO和CDMO可能通过抑制肿瘤血管生成,从而抑制肿瘤生长进程,发挥抗肿瘤的作用。
2.3 巴戟天对小鼠移植瘤中VEGF的影响
VEGF是一种高度特异性的促进血管内皮细胞生长因子,对血管内皮细胞的增殖以及血管的生长有促进作用[16]。由检测结果可得,与对照组相比,5-FU(P<0.05)、EEMO(P<0.01)和CDMO(P<0.01)均能降低肿瘤VEGF表达量,差异具有统计学意义(图4A和图4B所示)。同时,免疫组化的结果显示,与对照组相比,5-FU(P<0.01)、EEMO(P<0.01)和CDMO(P<0.01)均能极显著下调肿瘤中VEGF的阳性表达(图4C和图4D所示)。此外,与5-FU组相比,EEMO组和CDMO组的VEGF表达均有下降,但差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)(图4C和图4D所示)。综合VEGF的检测结果,说明巴戟天可通过下调肿瘤VEGF的表达,发挥抗肿瘤血管生成的作用;该结果与病理组织检测结果相一致。
2.4 巴戟天对肿瘤组织巨噬细胞极化的影响
肿瘤相关巨噬细胞是浸润肿瘤组织的主要细胞群,其不同的分型(M1型巨噬细胞和M2型巨噬细)对肿瘤的发生发展进程有不同的作用[17]。其中,当肿瘤相关巨噬细胞分型趋向M1型巨噬细胞,表现为肿瘤杀伤和肿瘤血管抑制的作用;当巨噬细胞分型趋向M2型巨噬细胞,表现为肿瘤血管增生,促进肿瘤生长的作用[18]。免疫荧光的结果显示,与对照组相比,5-FU组、EEMO组和CDMO组肿瘤的M2型巨噬细胞标记物CD206表达水平有所下降,但是差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)(图5B所示)。与对照相比,5-FU组(P<0.01)、EEMO组(P<0.01)和CDMO组(P<0.01)移植瘤组织的M1型巨噬细胞标记物iNOS表达水平极显著上调(图5C所示)。将同一样本的iNOS荧光强度与CD206荧光强度作比值,统计分析可得5-FU组(P<0.01)、EEMO组(P<0.01)和CDMO组(P<0.01)的iNOS/CD206值与对照组相比极显著升高(图5D所示)。其中,与5-FU组相比,EEMO和CDMO均能提升iNOS/CD206值,但差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。由此可得,经EEMO和CDMO药物干预后,M1型巨噬细胞的分化比例升高,肿瘤相关巨噬细胞的分化趋势偏向于M1型巨噬细胞,从而能够解释肿瘤血管生成减少。
2.5 巴戟天对肿瘤组织HIF-1α和COX-2的表达影响
HIF-1α作为肿瘤微环境中的重要调节因子,可调节下游转录因子,促进肿瘤对肿瘤微环境的适应[19]。COX-2作为HIF-1α调节的下游转录因子,可提高PGE2的表达,介导炎症的发生发展和肿瘤血管的生成,对肿瘤细胞的增殖有促进的作用[20]。免疫组化检测结果表明,与对照组相比,5-FU组(P<0.01)、EEMO组(P<0.05)和CDMO组(P<0.05)的HIF-1α表达水平下降,差异具有统计学意义(图6A和图6C所示)。同时,与对照组相比,5-FU(P<0.01)、EEMO(P<0.01)和CDMO(P<0.01)均能极显著下调肿瘤COX-2的阳性表达(图6B和图6D所示)。结果说明EEMO和CDMO对肿瘤血管生成的影响可能与调节HIF-1α和COX-2的表达有关。
2.6 巴戟天对肿瘤组织HIF-1α和COX-2/PGE2信号通路的影响
COX-2/PGE2是经典的炎症信号通路。在肿瘤微环境中,COX-2/PGE2通路可刺激肿瘤细胞的生长和肿瘤血管的生成,从而加快肿瘤形成的进程[21]。对HIF-1α和COX-2/PGE2信号通路的表达做进一步做定量分析。从结果分析可得,与对照组相比,5-FU组(P<0.01)、EEMO(P<0.01)组和CDMO组(P<0.01)的HIF-1α和COX-2的蛋白表达量极显著下降(图7B和图7C所示)。此外,与对照组相比,5-FU组(P<0.01)、EEMO组(P<0.01)和CDMO(P<0.05)组肿瘤PGE2含量均下调(P<0.05)(图7D所示),差异具有统计学意义。检测结果进一步说明巴戟天可能是通过下调HIF-1α的表达,进而下调下游关键影响因子COX-2的表达,减少PGE2的分泌,达到抑制肿瘤细胞和肿瘤血管生成的作用。
3. 讨论
结肠癌作为常见的恶性肿瘤之一,其肿瘤细胞的异常增殖和生长会造成瘤体缺氧的现象,促使肿瘤细胞继续增长和转移[22]。缺氧诱导因子-1α(Hypoxia inducible factor-1α, HIF-1α)作为细胞缺氧反应的关键调节剂,调节下游多种靶点,协助肿瘤细胞适应肿瘤缺氧微环境,影响肿瘤的生长和发展[23-24]。由实验结果得知,巴戟天生药及其醇提物可致肿瘤细胞坏死区域增加,伴有轻微血管生成增加,且肿瘤血管生成的相关蛋白VEGF表达在药物干预后出现明显下降,提示巴戟天生药及其醇提物能够抑制肿瘤血管新生,推测其可能具有抑制HIF-1α活性的作用。
已有研究证明,HIF-1α在多种恶性肿瘤中通过调控COX-2的启动子,诱导COX-2生成[25-26]。COX-2参与肿瘤的恶性进程主要与催化花生四烯酸生成PGE2相关[27]。作为COX-2的关键催化产物,PGE2是一种与肿瘤发生发展密切相关的促炎介质[28-29]。HIF-1α和COX-2/PGE2信号通路的活化可抑制机体肿瘤免疫,加速肿瘤的恶性进程,促进肿瘤的发生发展[19-20]。目前,越来越多的研究结果证实HIF-1α和COX-2/PGE2可以干预肿瘤微环境血管新生和调节巨噬细胞的免疫抑制性[30-32]。在本研究中,巴戟天生药及其醇提物可明显抑制HIF-1α和COX-2/PGE2信号通路在肿瘤组织的阳性表达,且在蛋白水平方面也明显受到抑制,提示巴戟天生药及其醇提物可通过干预肿瘤细胞的HIF-1α表达,从而调控下游COX-2/PGE2信号通路的低表达,发挥对抗肿瘤的发生和发展。
肿瘤的形成与发展受多种因素的调控。巨噬细胞在肿瘤免疫抑制过程中充当重要的角色,并且通过不同的极化状态影响着肿瘤的发生发展[17-18]。巨噬细胞的极化分为经典激活的巨噬细胞(即M1型巨噬细胞)和替代激活的巨噬细胞(即M2型巨噬细胞)。M1型巨噬细胞和M2型巨噬细胞分别具有肿瘤杀伤性和免疫抑制性,而在肿瘤微环境中巨噬细胞主要呈现M2型巨噬细胞的特征,即表现为促进肿瘤血管的增生[33-34],进而促进肿瘤的生长和发展。在本研究中,巴戟天生药及其醇提物能够诱导肿瘤组织中M1型巨噬细胞的比例升高。这说明巴戟天还可能通过调控巨噬细胞向M1型巨噬细胞极化发挥抑癌作用。除此之外,对比巴戟天生药和巴戟天乙醇提取物两者的药效作用,尽管巴戟天乙醇提取物对肿瘤的发生发展干预作用比巴戟天生药药效略优,但二者之间的差距并无统计学意义。导致这种情况的发生可能是由于巴戟天乙醇提取物中的抗肿瘤成分与巴戟天生药相比更加集中。对于巴戟天生药和巴戟天乙醇提取物的比较需要更深入的实验分析进行研究。同时,巴戟天作为药食同源类中药材,其保健功效已经得到初步的开发和探索,龙碧波[35]研究发现巴戟天可明显改善负重游泳小鼠的疲劳指标,发挥抗疲劳作用;周月[36]发现巴戟天提取物联合γ-氨基丁酸和茶氨酸对抑郁患者精神躯体症状和睡眠质量有积极的疗效;石小琼[37]团队研究开发巴戟天为日常保健品和食品,如巴戟天口服液、巴戟天果脯和巴戟天果酒等。综上所述,开发巴戟天成为保健品食品依然具有非常大的潜力和市场。
综上,巴戟天可能通过抑制HIF-1α和COX-2/PGE2信号通路的活化,从而诱导巨噬细胞向M1型巨噬细胞极化,发挥抑制肿瘤血管新生的作用,从而影响结直肠癌移植瘤的发生和发展。
-
-
[1] SIEGEL R L, MILLER K D, GODING S A, et al. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020[J]. Ca Cancer J Clin,2020,70(3):145−164. doi: 10.3322/caac.21601
[2] THANIKACHALAM K, KHAN G. Colorectal cancer and nutrition[J]. Nutrients,2019,11(1):164−164. doi: 10.3390/nu11010164
[3] 张涛, 康向东. 中西医在结肠癌治疗中的研究进展[J]. 系统医学,2019,4(23):192−194. [ZHANG T, KANG X D. Research progress of traditional Chinese and Western medicine in the treatment of colon cancer[J]. Systems Medicine,2019,4(23):192−194. [4] HINZE L, LABROSSE R, DEGAR J, et al. Exploiting the therapeutic interaction of wnt pathway activation and asparaginase for colorectal cancer therapy[J]. Cancer Discov,2020,10(11):1690−1705. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-1472
[5] 张敬涛, 马艳, 白克运, 等. 炎性肠病相关结直肠癌动物模型研究进展[J]. 吉林中医药,2019,39(11):1528−1532. [ZHANG J T, MA Y, BAI K Y, et al. Animal models of inflammatory bowel disease-related colorectal cancer[J]. Jilin Journal of Chinese Medicine,2019,39(11):1528−1532. [6] 欧阳佳丽. 中医辨证护理联合中医治疗在晚期结肠癌患者的应用研究[J]. 江西中医药,2018,49(8):46−48. [OUYANG J L. Study on the application of traditional Chinese medicine syndrome differentiation nursing combined with traditional Chinese medicine treatment in patients with advanced colon cancer[J]. Jiangxi Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2018,49(8):46−48. [7] 莫淑婵, 田甜, 吴钟彪. 加味四君子汤辨证治疗结肠癌术后化疗的不良反应效果观察[J]. 辽宁中医杂志,2018,45(3):571−574. [MO S C, TIAN T, WU Z B. Effect of Jiawei Sijunzi Decoction in treatment of colon cancer after chemotherapy[J]. Liaoning Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2018,45(3):571−574. [8] 谢丽琼. 结肠癌“脾虚”病机的生物学基础探要[J]. 四川中医,2020,38(3):47−49. [XIE L Q. Biological basis exploration on "Spleen Deficiency" pathogenesis of colon cancer[J]. Journal of Sichuan of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2020,38(3):47−49. [9] 周妍妍, 周晓洁, 闫博文, 等. 巴戟天化学成分及药理作用的研究进展[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报,2021:1−11. [ZHOU Y Y, ZHOU X J, YAN B W, et al. Chemical components of pharmacological effect of Bajitian (Morindae officinalis Radix)[J]. Journal of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2021:1−11. [10] 徐吉银, 楚桐丽, 丁平. 巴戟天属植物环烯醚萜类化学成分和药理活性研究进展[J]. 广州中医药大学学报,2006(3):268−271. [XU J Y, CHU T L, DING P. Research progress on the chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of iridoids in Morinda officinalis[J]. Journal of Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2006(3):268−271. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3213.2006.03.025 [11] 沈燚, 张奇, 刘梦琴, 等. 巴戟天属植物环烯醚萜类化学成分及生物活性研究进展[J]. 药学实践杂志,2020,38(2):110−114. [SHEN Y, ZHANG Q, LIU M Q, et al. Research on chemical components and biological activities of the iridoids in Morinda genus[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice,2020,38(2):110−114. [12] JIAN L, LIANG J, HAO H, et al. The extracts of Morinda officinalis and its hairy roots attenuate dextran sodium sulfate-induced chronic ulcerative colitis in mice by regulating inflammation and lymphocyte apoptosis[J]. Front Immunol,2017,8:905. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00905
[13] FUJITA M, MATSUBARA N, MATSUDA I, et al. Genomic landscape of colitis-associated cancer indicates the impact of chronic inflammation and its stratification by mutations in the wnt signaling[J]. Oncotarget,2018,9(1):969−981. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22867
[14] WANG S Q, CUI S X, QU X J. Metformin inhibited colitis and colitis-associated cancer (cac) through protecting mitochondrial structures of colorectal epithelial cells in mice[J]. Cancer Biol Ther,2019,20(3):338−348. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2018.1529108
[15] ZONG S, LI J, YE Z, et al. Lachnum polysaccharide suppresses S180 sarcoma by boosting anti-tumor immune responses and skewing tumor-associated macrophages toward M1 phenotype[J]. Int J Biol Macromol,2020,144:1022−1033. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.09.179
[16] 肖剑波, 钟佳宁, 陈斌. 肿瘤微环境在肿瘤血管生成的研究进展[J]. 赣南医学院学报,2021,41(1):86−92. [XIAO J B, ZHONG J N, CHEN B. Research progress of tumor microenvironment in tumor angiogenesis[J]. Journal of Gannan Medical University,2021,41(1):86−92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5779.2021.01.017 [17] 刘怡辰, 向卉楠, 诸君, 等. 肿瘤相关巨噬细胞在肿瘤中作用的研究进展[J]. 肿瘤研究与临床,2021,33(2):149−153. [LIU Y C, XIANG H N, ZHU J, et al. Progress of tumor associated macrophages in tumors[J]. Cancer Research and Clinic,2021,33(2):149−153. [18] 贾瑞, 惠毅, 闫曙光, 等. 巨噬细胞m1/m2型极化与免疫炎症性疾病关系的研究进展[J]. 中国免疫学杂志,2021:1−22. [JIA R, HUI Y, YAN S G, et al. Research progress on relationship between macrophage M1/M2 polarization and immune inflammatory diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Immunology,2021:1−22. [19] 周文婷. Hif-1活性调控机制的研究进展[J]. 生理科学进展,2020,51(6):443−448. [ZHOU W T. Advances in the regulatory mechanisms of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 activity[J]. Progress in Physiological Sciences,2020,51(6):443−448. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0559-7765.2020.06.009 [20] 黎贵芸, 冯强, 胡雄, 等. COX-2/PGE2在肿瘤发生发展和重塑肿瘤微环境中的研究进展[J]. 中国肿瘤临床,2020,47(16):840−846. [LI G Y, FENG Q, HU X, et al. Research progress of COX-2/PGE2 in tumorigenesis and remodeling tumor microenvironment[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Oncology,2020,47(16):840−846. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8179.2020.16.643 [21] DONG X F, LIU T Q, ZHI X T, et al. COX-2/PGE2 axis regulates HIF2 alpha activity to promote hepatocellular carcinoma hypoxic response and reduce the sensitivity of sorafenib treatment[J]. Clin Cancer Res,2018,24(13):3204−3216. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-2725
[22] WENG M, FENG Y, HE Y, et al. Hypoxia-induced LIN28A mrna promotes the metastasis of colon cancer in a protein-coding-independent manner[J]. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology,2021:9.
[23] 刘烨, 高志海, 安燚. 结肠癌组织中转化生长因子-β1和缺氧诱导因子-1α及血管内皮生长因子的表达及临床意义[J]. 中国慢性病预防与控制,2019,27(5):352−355. [LIU Y, GAO Z H, AN Y. The expression and clinical significance of TGF-β1, HIF-1α and VEGF in colon cancer tissue[J]. Chinese Journal of Prevention and Control of Chronic Diseases,2019,27(5):352−355. [24] 朱雯霏, 洪兰. 缺氧诱导因子-1α在肿瘤中的表达研究进展[J]. 延边大学医学学报,2019,42(2):152−154. [ZHU W F, HONG L. Research progress on the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in tumors[J]. Journal of Medical Science Yanbian University,2019,42(2):152−154. [25] HUANG M, WANG L, CHEN J, et al. Regulation of COX-2 expression and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha is associated with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma patients post tace surgery[J]. Int J Oncol,2016,48(5):2144−2154. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3421
[26] HUGO H J, SAUNDERS C, RAMSAY R G, et al. New insights on COX-2 in chronic inflammation driving breast cancer growth and metastasis[J]. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia,2015,20(3-4):109−119. doi: 10.1007/s10911-015-9333-4
[27] WANG Q, LU D, FAN L, et al. COX-2 induces apoptosis-resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via the HIF-1alpha/PKM2 pathway[J]. Int J Mol Med,2019,43(1):475−488.
[28] 王彤, 邓炯. 前列腺素E2对肿瘤发生和转移作用的研究进展[J]. 癌症进展,2017,15(10):1131−1134. [WANG T, DENG J. Research progress on the effect of prostaglandin E2 on tumorigenesis and metastasis[J]. Oncology Progress,2017,15(10):1131−1134. [29] 陈艺萍, 潘建基. 环氧化物酶-2在肿瘤微环境中的作用研究进展[J]. 肿瘤学杂志,2019,25(11):990−994. [CHEN Y P, PAN J J. Research progress on roles of COX-2 in tumor microenvironment[J]. Journal of Chinese Oncology,2019,25(11):990−994. doi: 10.11735/j.issn.1671-170X.2019.11.B013 [30] MARITZA P G, IVÁN H, MANUEL V, et al. Ngf-enhanced vasculogenic properties of epithelial ovarian cancer cells is reduced by inhibition of the COX-2/PGE2 signaling axis[J]. Cancers,2019,11(12):1970. doi: 10.3390/cancers11121970
[31] HONG M, SHI H, WANG N, et al. Dual effects of chinese herbal medicines on angiogenesis in cancer and ischemic stroke treatments: Role of HIF-1 network[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology,2019,10:696. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00696
[32] SCHOOS A, GABRIEL C, KNAB V M, et al. Activation of HIF-1 α by δ-opioid receptors induces COX-2 expression in breast cancer cells and leads to paracrine activation of vascular endothelial cells[J]. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics,2019,370(3):480−489. doi: 10.1124/jpet.119.257501
[33] 张满, 胡旭东, 陶艳艳, 等. 中药提取物调控巨噬细胞极化研究进展[J]. 中国中医药信息杂志,2019,26(11):136−140. [ZHANG M, HU X D, TAO Y Y, et al. Research progress in regulation of macrophages polarization by TCM herbal extracts[J]. Chinese Journal of Information on TCM,2019,26(11):136−140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5304.2019.11.031 [34] 刘佳宁, 王鑫雅, 孙玥. 巨噬细胞极化对炎症性疾病影响的研究进展[J]. 生物化工,2020,6(1):112−115. [LIU J N, WANG X Y, SUN Y. Research progress on the effects of macrophage polarization in inflammatory diseases[J]. Biological Chemical Engineering,2020,6(1):112−115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0387.2020.01.033 [35] 龙碧波, 徐海衡, 张新定. 巴戟天抗疲劳药理活性的实验研究[J]. 时珍国医国药,2013,24(2):298−300. [LONG B B, XU H H, ZHANG X D. Anti-fatigue effect of Morinda offieinalis How[J]. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research,2013,24(2):298−300. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2013.02.019 [36] 周月. 巴戟天提取物联合γ-氨基丁酸/茶氨酸改善抑郁症状的研究[D]. 天津: 天津医科大学, 2020 ZHOU Y. Study on the ameliorates of Modinda officinalis extract combined with γ-aminobutyric acid/theanine on depressive symptoms[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin Medical University, 2020
[37] 石小琼, 章浩军, 王健, 等. 巴戟天保健食品开发初探[J]. 科技资讯,2010(35):208−209. [SHI X Q, ZHANG H J, WANG J, et al. Preliminary study on the development of Morinda officinalis health food[J]. Science & Technology Information,2010(35):208−209. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3791.2010.35.170





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
