Physicochemical Properties of ACE Inhibitory Peptides from Jujube Kernel by Enzymatic Method
-
摘要: 本研究将脱脂后的酸枣仁渣通过碱溶酸沉法提取得到酸枣仁蛋白,并通过中性蛋白酶和碱性蛋白酶复合酶解得到酸枣仁血管紧张素转化酶(ACE)抑制肽,以其为研究对象,对酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的理化性质进行研究。本文通过分析脱脂酸枣仁的基本营养成分和酶解后酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的氨基酸成分,从氨基酸方面论证酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的功能活性和营养价值。分子量分布、粒度分布、微观结构观察等试验立体论证酸枣仁蛋白的酶解效果。最后针对酸枣仁蛋白酶解前后的溶解度、热稳定性、持水性和持油性、起泡性和起泡稳定性、乳化性和乳化稳定性、感官特性等理化性质进行对比试验及分析研究。结果表明,脱脂酸枣仁蛋白质含量为(73.40±0.23) g/100 g,蛋白质含量较高。酸枣仁ACE抑制肽中必需氨基酸含量为36.48%,疏水性氨基酸含量占51.14%,且谷氨酸含量最高。酸枣仁ACE抑制肽分子量主要集中在1000~3000 Da,占97.50%,且多分散性指数为1.088,分子量分布较窄。粒度分布测定和扫描电镜对比酸枣仁蛋白和酸枣仁ACE抑制肽酶解前后蛋白质结构被打破,酶解充分。理化性质研究表明,酸枣仁ACE抑制肽较酶解前酸枣仁蛋白,热稳定性、溶解度、持水性、持油性、乳化稳定性都有显著提高,起泡性、起泡稳定性、乳化性显著降低。结果表明酸枣仁ACE抑制肽较酶解前理化性质均得到显著改善,相关理化性质的探明为开展后续应用研究奠定研究基础,为酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的生产应用提供理论依据。Abstract: In this study, the defatted jujube kernel residue was extracted by alkali solubilization and acid seperation method to obtain jujube kernel protein, and the angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptide was obtained by enzymatic hydrolysis of neutral protease and alkaline protease. Taking jujube kernel as the research object, the physicochemical properties of ACE inhibitory peptide were studied. In this paper, the functional activity and nutritional value of ACE inhibitory peptide in defatted jujube kernel were demonstrated from the aspect of amino acids by analyzing the basic nutrients of defatted jujube kernel and the amino acid composition of ACE inhibitory peptide in enzymolyzed jujube kernel. The enzymatic hydrolysis effect of jujube kernel protein was proved by molecular weight distribution, particle size distribution and microscopic structure observation. Finally, the physical and chemical properties of jujube seed, including solubility, thermal stability, water and oil retention, foaming and foaming stability, emulsification and emulsification stability, and sensory characteristics before and after proteolysis, were compared and analyzed. It was found that the protein content of defatted jujube kernel was (73.40±0.23) g/100 g, and the protein content was higher. The essential amino acid content and hydrophobic amino acid content in ACE inhibitory peptide of jujube kernel were 36.48% and 51.14%, and the content of glutamate was the highest. The molecular weight of ACE inhibitory peptides in Zizyphus jujube kernel was mainly in the range of 1000~3000 Da, accounting for 97.50%, and the polydispersity index was 1.088, indicating a narrow molecular weight distribution. The protein structure of jujube kernel was broken before and after enzymolysis of ACE inhibitory peptides, and the enzymolysis was sufficient. The study of physical and chemical properties showed that compared with the protein before enzymolysis, the thermal stability, solubility, water holding capacity, oil holding capacity and emulsification stability of the ACE inhibitory peptide of jujube kernel were significantly improved, while the foaming, foaming stability and emulsification ability significantly decreased(P<0.05). The results showed that the physicochemical properties of ACE inhibitory peptides in jujube kernel were significantly improved compared with those before enzymolysis(P<0.05). The discovery of related physicochemical properties laid a research foundation for the follow-up research, and provided a theoretical basis for the production and application of ACE inhibitory peptides in jujube kernel.
-
酸枣仁是将酸枣(Ziziphus jujuba Mill. var. spinosa)分离出果核,从果核中分离得到的种子[1],在华北地区、陕西、内蒙古等地产量丰富。酸枣仁被认定为药食同源食品,其中蛋白质含量约为36%,并含有三萜类、甾醇、酸枣仁皂甙等多种功能性物质[2],营养价值较高。酸枣仁有镇静、催眠、镇痛、敛汗、降压作用[3]。目前相关研究仅局限于药理作用下的酸枣仁黄酮、酸枣仁皂苷等成分研究[4],其蛋白相关的功能特性和理化性质却鲜有报道。
血管紧张素转化酶抑制肽,又称ACE(Angiotensin-I Converting Enzyme)抑制肽是一类可以抑制血管紧张素转化酶的小分子肽段,ACE抑制肽具有安全、高效、易吸收等优点[5-6]。世界上第一种ACE抑制剂是从南美蝮蛇的毒液中得到[7],而目前常见的降压药物如:卡托普利、赖诺普利等同样是从蛇的毒液中获取[8]。而目前从蛇的毒液中获取以外的天然ACE抑制肽来源主要有动物来源和植物来源,已发现的具有ACE抑制作用的植物源如:大豆、豌豆、玉米、小麦、魔芋、核桃、大蒜、苦瓜种子等[9-16];动物源如:蛋清、鲢鱼、猪血红等[17-19]。
近年来,从植物源ACE抑制肽的相关研究一直是研究热点。ACE抑制肽在实际生产应用时,其理化性质方面的研究极为重要。贺磊[20]通过酶解法制备魔芋ACE抑制肽,经分离纯化后,测定其理化性质,为指导工业生产提供理论依据。目前对于ACE抑制肽的相关研究较为普遍,但关于酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的理化性质研究尚且还是空白。本文分析了脱脂酸枣仁粉的基本营养成分和酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的氨基酸成分,通过分子量分布、粒度分布、微观结构观察等实验立体论证酸枣仁蛋白的酶解效果。最后针对酸枣仁蛋白酶解前后理化性质以及酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的实际生产应用进行了溶解度、热稳定性、持水性和持油性、起泡性和起泡稳定性、乳化性和乳化稳定性、感官特性等实验分析。本文主要从工艺的角度对酸枣仁粗多肽开展初步的研究与分析,以期为后续的分离纯化及活性研究提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
酸枣仁 河北省邢台市润玉食品有限公司提供;牛血清蛋白、考马斯亮蓝G-250 生化纯,北京奥博星生物技术有限公司;盐酸、氢氧化钠、氢氧化钾、硫酸铜、硫酸钾、十二烷基硫酸钠、葡萄糖 分析纯,天津市永大化学试剂有限公司;硼酸、硫酸、磷酸、苯酚 分析纯,天津欧博凯化工股份有限公司;石油醚 分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司;甲基红指示剂、溴甲酚绿指示剂、亚甲基红指示剂 分析纯,上海远慕生物科技有限公司;金龙鱼大豆油 食用级,嘉里粮油有限公司。
DF-101集热式恒温加热磁力搅拌器 巩义市予华仪器有限责任公司;HC-3018高速离心机 安徽中科中佳科学仪器有限公司;RT-25型气流式超微粉碎机 荣聪精密科技有限公司;LGJ-10D型冷冻干燥机 北京四环科学仪器厂有限公司;SPECTRO star Nano酶标仪 德国BMG LABTECH公司;MDSCQ200差式量热扫描仪 美国TA公司;L-8800氨基酸自动分析仪、Hitachi S-4800扫描电子显微镜 日本日立公司;RE52-AAA粒度分析仪 上海嘉鹏科技有限公司;UPT-K1800全自动凯氏定氮仪 北京优谱通用科技有限公司;MB90水分测定仪 美国奥豪斯公司;SXT-06索氏抽提器 上海本昂科学仪器有限公司;V-1600B分光光度计 上海美谱达仪器有限公司;KS-800KDE高功率超声波清洗器 宝鸡新宇光机电有限责任公司;JRA-35S均质仪 无锡杰瑞安仪器设备有限公司;ST2100实验室pH计 奥豪斯仪器(常州)有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 酸枣仁蛋白的制备
取200 g酸枣仁以液氮为冷源通入粉碎机,打粉1 min,过80目筛。将粗粉碎的酸枣仁粉放入气流式超微粉碎机,以液氮为冷源通入超微粉碎机,电流设置5 A,粉碎1 min,过150目筛,收集密封放入4 ℃冰箱备用[21]。
将粉碎好的酸枣仁粉与石油醚按料液比1:3(g/mL),50 ℃水浴浸提30 min,离心(4000 r/min、10 min)去除上清液,重复多次,直到上清液完全澄清透明,室温通风12 h,40 ℃干燥12 h,得到脱脂酸枣仁粉,收集密封放入−20 ℃冰箱备用。
称取1 g脱脂酸枣仁粉,按液料比32:1(mL/g)溶解于蒸馏水中,调节溶液pH11.4,51 ℃下水浴搅拌浸提58 min,离心(5000 r/min、20 min)得上清液,调节溶液pH至酸枣仁蛋白等电点即pH4.6,4 ℃静置2 h,离心(5000 r/min、15 min)得到酸枣仁蛋白沉淀,−70 ℃冷冻干燥24 h得到酸枣仁蛋白粉,置于−20 ℃冰箱备用。
1.2.2 酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的制备
称取1 g冻干后酸枣仁蛋白粉,按底物浓度为3.1%溶解于蒸馏水中,按酶添加量为6000 U/g加入中性蛋白酶和碱性蛋白酶,中性蛋白酶与碱性蛋白酶比例为2.1:1,调节溶液pH至7.5,于54 ℃下水浴搅拌浸提62 min,酶解过程中保持酶解液pH、温度不变。酶解结束后灭酶活,沸水浴10 min,待酶解液冷却至室温后,调节溶液pH至酸枣仁蛋白等电点即pH4.6,4 ℃静置2 h,离心(5000 r/min、15 min)得到酸枣仁ACE抑制肽沉淀,−70 ℃冷冻干燥24 h,置于−20 ℃冰箱备用。
1.2.3 脱脂酸枣仁基本成分测定
以脱脂酸枣仁粉为原料,测定基本成分。蛋白质测定:参照GB 5009.5-2016《食品中蛋白质的测定》[22],凯氏定氮法;水分测定:参照GB 5009.3-2016《食品中水分的测定》[23],直接干燥法;灰分测定:参照GB 5009.4-2016《食品中灰分的测定》[24],干法灰化法;粗脂肪测定:参照GB 5009.6-2016《食品中脂肪的测定》[25],索氏抽提法;粗纤维测定:参照GB/T 5009.10-2003《植物类食品中粗纤维的测定》[26];总糖测定:参照SN/T 4260-2015《出口植物源食品中粗多糖含量的测定》[27],苯酚-硫酸法。
1.2.4 氨基酸分析
称取过80目筛的酸枣仁ACE抑制肽冻干粉80 mg于反应釜中,加入10 mL,浓度为6 mol/L的HCl,密封于110 ℃烘箱水解24 h。取1 mL稀释50倍,用0.22 μm滤膜过滤至液相小瓶,于氨基酸自动分析仪测定。
1.2.5 分子量分布测定
以酸枣仁ACE抑制肽冻干粉为原料,采用凝胶渗透色谱法,测定酸枣仁ACE抑制肽分子量分布。凝胶渗透色谱测定条件:色谱柱:SB-806HQ;流动相:0.02%硝酸钠水溶液;流速:1 mL/min;柱温:40 ℃;进样体积:500 μL。
样品制备:样品溶解于质量分数为0.02%硝酸钠水溶液,配制质量浓度为3 mg/mL样品溶液,过0.45 μm滤膜。
1.2.6 粒度分布测定
以酸枣仁ACE抑制肽冻干粉和酸枣仁蛋白为原料,样品按1:10(W/W)用去离子水稀释,激光粒度分析仪的操作参数:分散模式为通用;颗粒折射率1.520;颗粒吸收率0.1;分散剂水;分散剂折射率:1.333;泵的转速2200 r/min。
1.2.7 微观结构观察
使用扫描电子显微镜观察酸枣仁ACE抑制肽和酸枣仁蛋白的微观结构。喷金处理,加速电压 30 kV。
1.2.8 热稳定性
以酸枣仁ACE抑制肽冻干粉和酸枣仁蛋白为原料,采用差示扫描量热法测定酸枣仁ACE抑制肽热稳定性,量取适量样品放入差示扫描量热仪分析仪专用铝盒中,将制备好的铝盒放入差示扫描量热仪分析仪中,检测条件为:采用氮气;气压为0.2 MPa;气体流量为20 mL/min;升温速率为10 ℃/min,从60 ℃上升到200 ℃。记录升温过程中样品的DSC曲线。采用专业软件记录和分析吸热曲线上的起始温度、终止温度、变性温度、和热焓值(ΔH)。
1.2.9 溶解度测定
以酸枣仁ACE抑制肽冻干粉和酸枣仁蛋白为原料,称取一定量样品溶解于蒸馏水中,配制2 mg/mL样品溶液,用1 mol/L氢氧化钠或盐酸溶液将溶液pH调节为2.0~10.0,搅拌混匀,离心(4000 r/min,20 min),上清液采用考马斯亮蓝法测定蛋白含量,用牛血清蛋白作标准曲线,样品溶解性的计算公式为:
溶解度(\%)=上清液中蛋白质质量总蛋白质质量×100 1.2.10 持水性和持油性的测定
以酸枣仁ACE抑制肽冻干粉和酸枣仁蛋白为原料,称取0.1 g样品与5 mL蒸馏水(大豆油)于离心管混溶,使用均质机混合,静置30 min,离心(4000 r/min,20 min),测量上清液体积,体积减少量即为持水量与持油量。
1.2.11 起泡性和起泡稳定性的测定
以酸枣仁ACE抑制肽冻干粉和酸枣仁蛋白为原料,称取一定量样品溶解于蒸馏水中,配制成5 mg/mL样品溶液,用1 mol/L的氢氧化钠或盐酸溶液将溶液pH分别调节为2.0、3.0、4.0、5.0、6.0、7.0、8.0、9.0、10.0,记录初始体积为V0 /mL,10000 r/min均质2 min,记录体积为V1 /mL,静置30 min,记录体积为V2 /mL。起泡性和泡沫稳定性计算公式为:
起泡性(\%)=V1−V0V0×100 起泡稳定性(\%)=V2−V0V0×100 1.2.12 乳化性和乳化稳定性
以酸枣仁ACE抑制肽冻干粉和酸枣仁蛋白为原料,称取一定量样品,配制成10 mg/mL样品溶液,用1 mol/L氢氧化钠或盐酸溶液调节溶液pH为2.0~10.0,取10 mL样品溶液加入3.0 mL大豆油,10000 r/min均质2 min,吸取底部50 μL乳状液,加入5 mL、0.1%十二烷基硫酸钠(SDS)溶液混匀,在500 nm波长处测定吸光度,记为A0。静置10 min后,再次用上述方法测定吸光度,记为A1。乳化性和乳化稳定性计算公式为:
乳化性(m2/g)=2.303×2×A0C×L×Φ×10000×N 乳化稳定性(min)=A0×ΔtA0−A1 式中:N表示稀释倍数;Φ表示油相的体积分数,%;L表示光程,cm;C表示调节pH后样品溶液中的蛋白质量浓度,g/mL;t表示时间,min。
1.2.13 感官特性
对制备出的酸枣仁ACE抑制肽和酸枣仁蛋白进行感官评定[20]。主要从色泽、性状、形态、气味等方面评定。
1.3 数据处理
所有试验均重复 3次,试验结果用平均值±标准差表示,使用OriginPro 8.0、SPSS Statistics 22.0对试验数据进行处理和分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 脱脂酸枣仁基本成分测定结果
由表1可知,脱脂酸枣仁蛋白质含量为(73.40±0.23)g/100 g,相关研究脱脂酸枣仁蛋白质含量为(68.93±0.30)g/100 g[28],说明该酸枣仁原料蛋白质含量高,经脱脂过程,蛋白质保存较好,利于开展后续研究。
表 1 脱脂酸枣仁主要成分(g/100 g)Table 1. Main ingredients of defatted jujube seed main ingredients (g/100 g)成分 总糖 脂肪 蛋白质 水分 灰分 脱脂酸枣仁 10.15±0.27 3.07±0.41 73.40±0.23 8.90±0.33 1.95±0.29 2.2 酸枣仁ACE抑制肽氨基酸分析结果
由表2可知,酸枣仁ACE抑制肽有较好的氨基酸组成,谷氨酸含量最高,其次是脯氨酸和亮氨酸,半胱氨酸含量最低。必需氨基酸含量占36.48%,含量较高,且缬氨酸、异亮氨酸、亮氨酸含量均达到联合国粮农组织和世界卫生组织(FAO/WHO)的儿童推荐标准[29],苏氨酸、缬氨酸、异亮氨酸、亮氨酸含量均达到成人推荐标准。其中必需氨基酸与非必需氨基酸的比值为0.5743,高于大豆蛋白(0.4804),属于优质蛋白。疏水性氨基酸含量占51.14%,且相关研究表明ACE抑制活性与疏水性氨基酸有关[30],侧面证明酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的ACE抑制活性。
表 2 酸枣仁ACE抑制肽氨基酸成分分析Table 2. Analysis of amino acid composition of ACE inhibitor peptide in jujube seed氨基酸种类 含量(g/100g) 占氨基酸总量百分比(%) 天冬氨酸(Asp) 4.54±0.12 7.03±0.19 苏氨酸(Thr) 1.60±0.04 2.48±0.06 丝氨酸(Ser) 2.87±0.02 4.45±0.03 谷氨酸(Glu) 11.03±0.08 17.09±0.12 甘氨酸(Gly) 3.27±0.05 5.07±0.08 丙氨酸(Ala) 2.30±0.03 3.56±0.05 半胱氨酸(Cys) 0.42±0.04 0.65±0.06 缬氨酸(Val) 4.41±0.14 6.83±0.22 甲硫氨酸(Met) 2.22±0.07 3.44±0.11 异亮氨酸(Ile) 4.66±0.03 7.22±0.05 亮氨酸(Leu) 7.49±0.13 11.60±0.20 酪氨酸(Tyr) 0.06±0.01 0.09±0.02 苯丙氨酸(Phe) 1.74±0.01 2.70±0.02 赖氨酸(Lys) 1.43±0.04 2.22±0.06 脯氨酸(Pro) 10.19±0.11 15.79±0.17 组氨酸(His) 1.37±0.03 2.12±0.05 精氨酸(Arg) 4.95±0.07 7.66±0.11 疏水性氨基酸 33.01±0.52 51.14±0.81 必需氨基酸 23.55±0.46 36.48±0.71 总氨基酸含量 64.55±1.02 注:氨基酸含量为100 g酸枣仁脱脂粉中氨基酸含量;Ala、Val、Leu、Ile、Phe、Pro、Met 为疏水性氨基酸;Thr、Met、Val、Lys、Ile、Leu、Phe为必需氨基酸。 2.3 酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的分子量分布测定结果
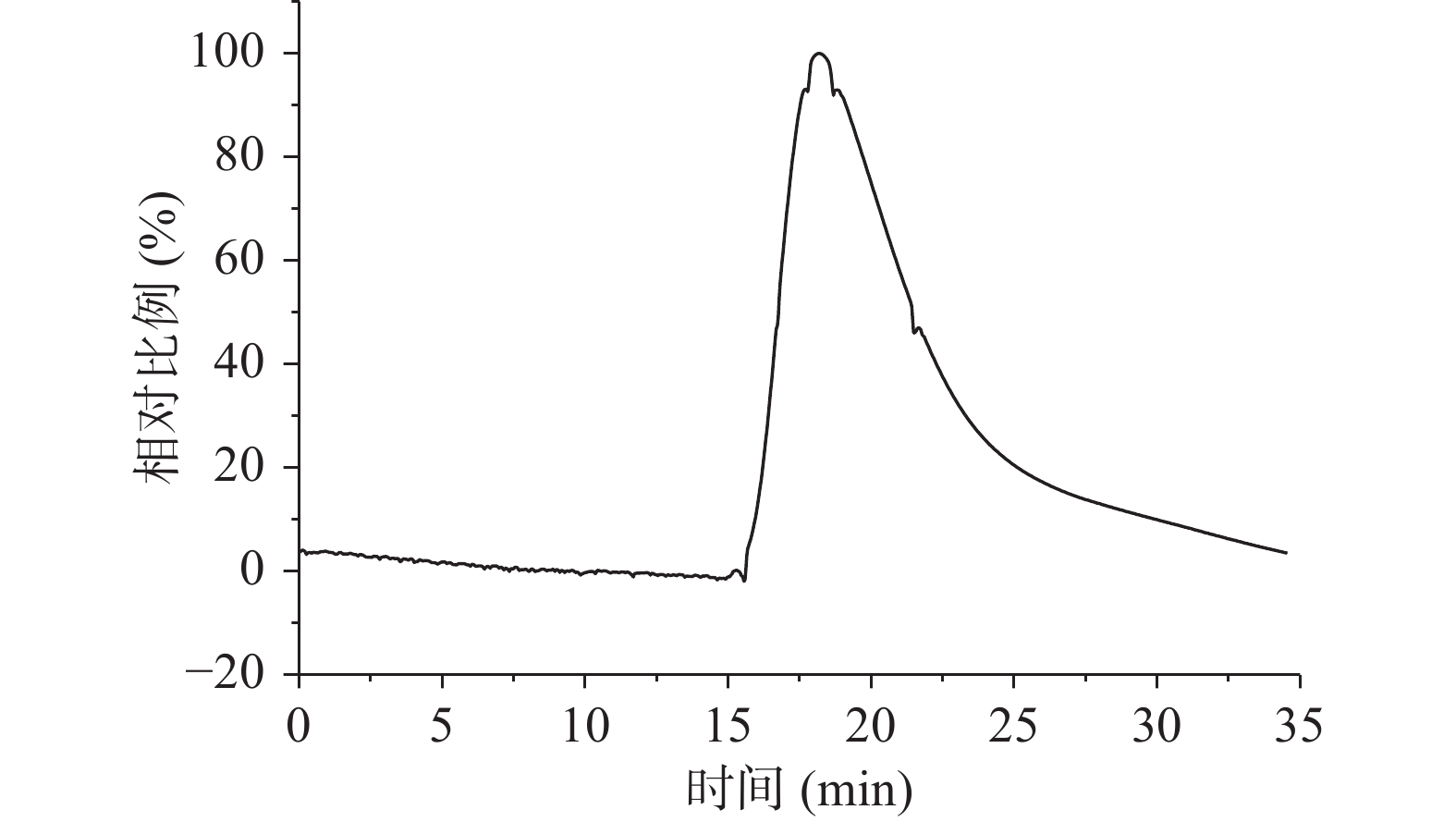
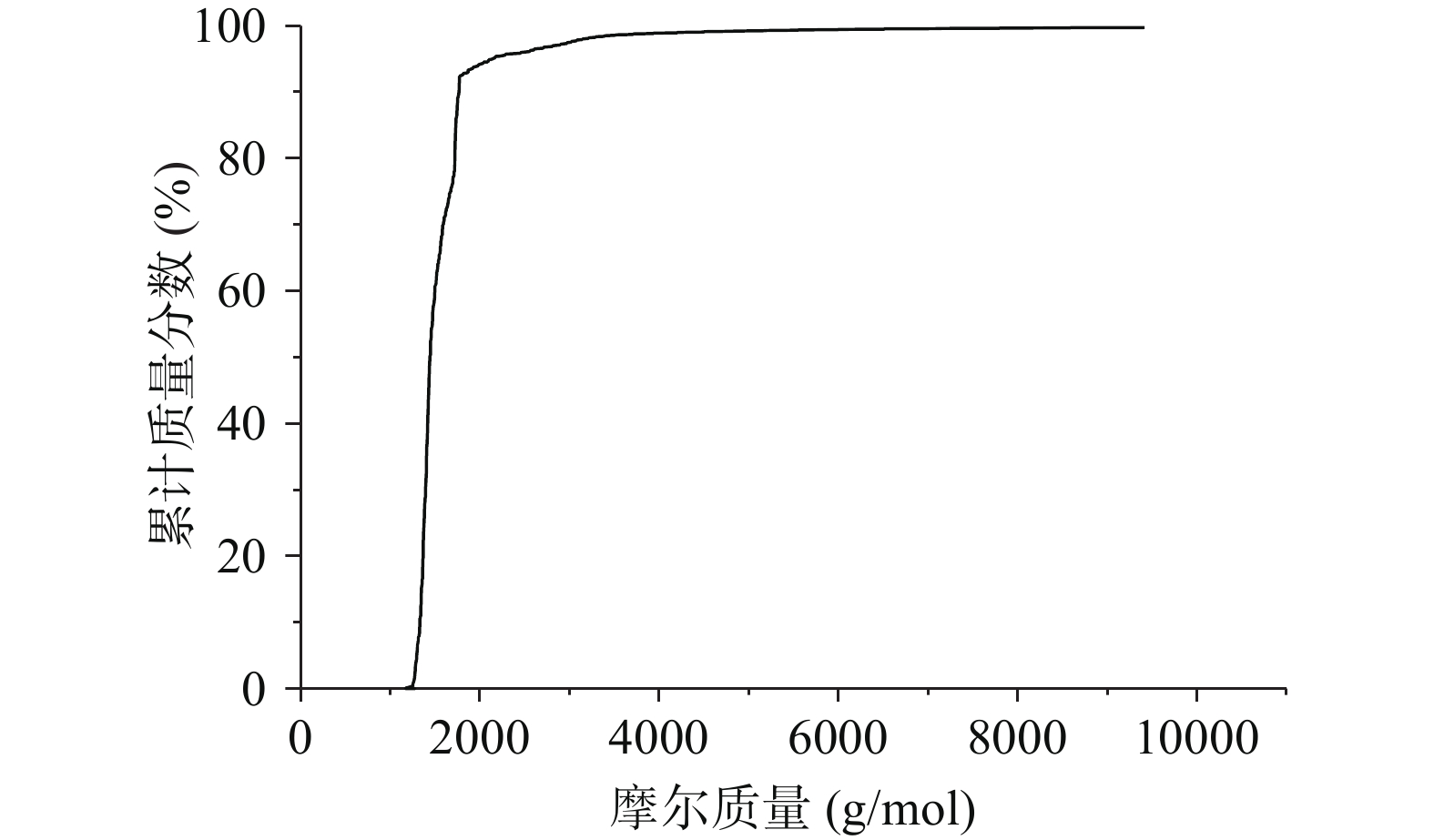
由图1、图2和表3可知,酸枣仁ACE抑制肽分子量主要集中在1000~3000 Da,占97.50%,符合相关研究表明具备降压效果的多肽分子量主要集中在1000~3000 Da[31-33]。由表4可知,数均分子量(Mn)表示分子量在1517 Da时,两侧分布的分子数量相同。重均分子量(Mw)表示分子量在1652 Da时,两侧有同等重量的分子分布。由于该聚合物分子量分布极窄,其峰值分子量(Mp)为1343 Da。而多分散性指数(Mw/Mn)为1.088,表明酶解后的酸枣仁ACE抑制肽分散聚合物链长相近,分子量分布极窄,也符合分子量分布结果。
表 3 酸枣仁ACE抑制肽分子量分布Table 3. Molecular weight distribution of ACE inhibitory peptides from jujube seed分子量分布 1000~3000(Da) 3000~5000(Da) 5000~10000(Da) 比例(%) 97.50 1.70 0.80 表 4 分子量表征结果Table 4. Molecular weight characterization results分子量表征 Mn Mw Mp Mz Mw/Mn 分子量 1517 Da 1652 Da 1343 Da 1591 Da 1.088 2.4 酸枣仁蛋白与酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的粒度分布测定结果
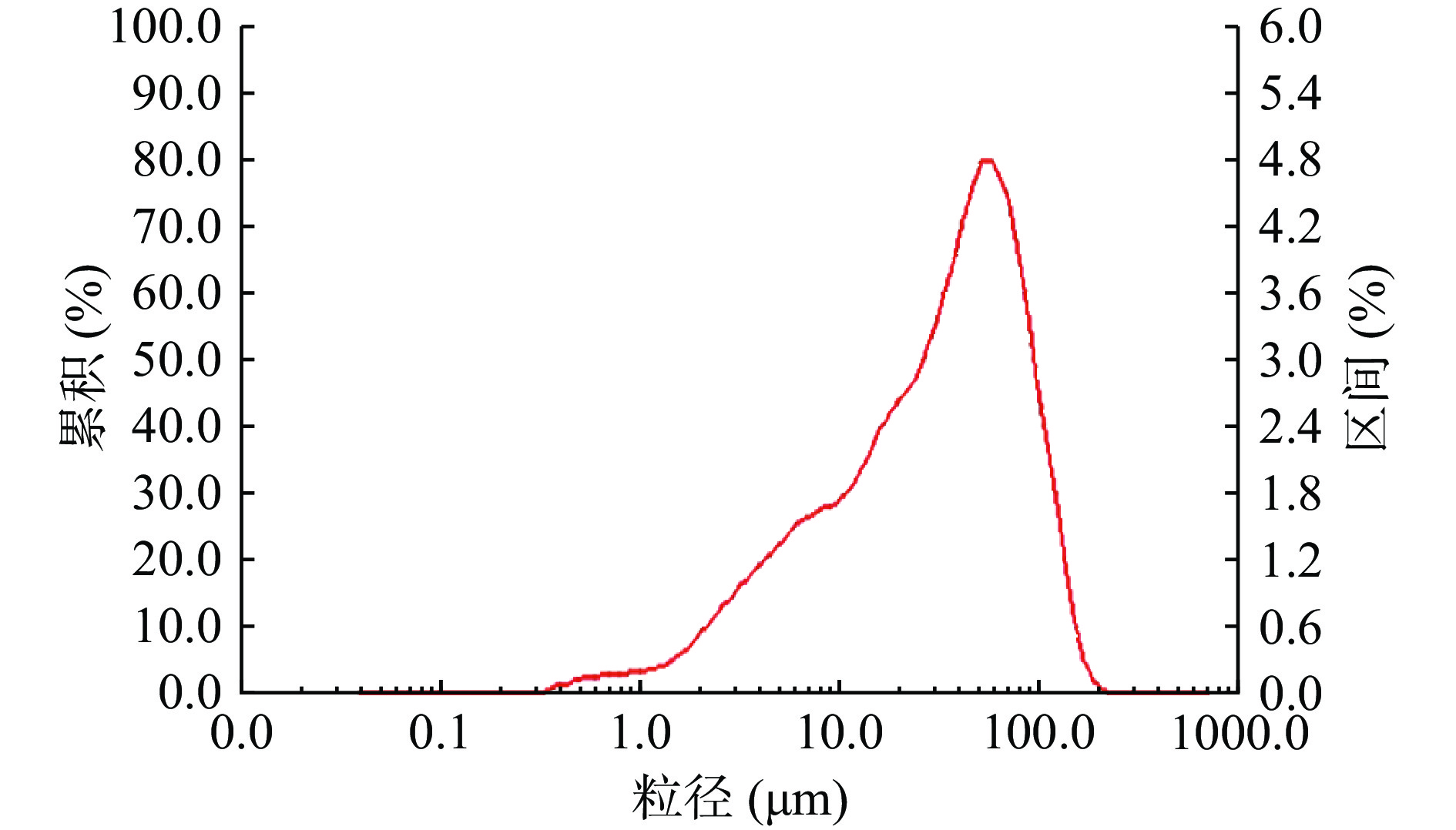
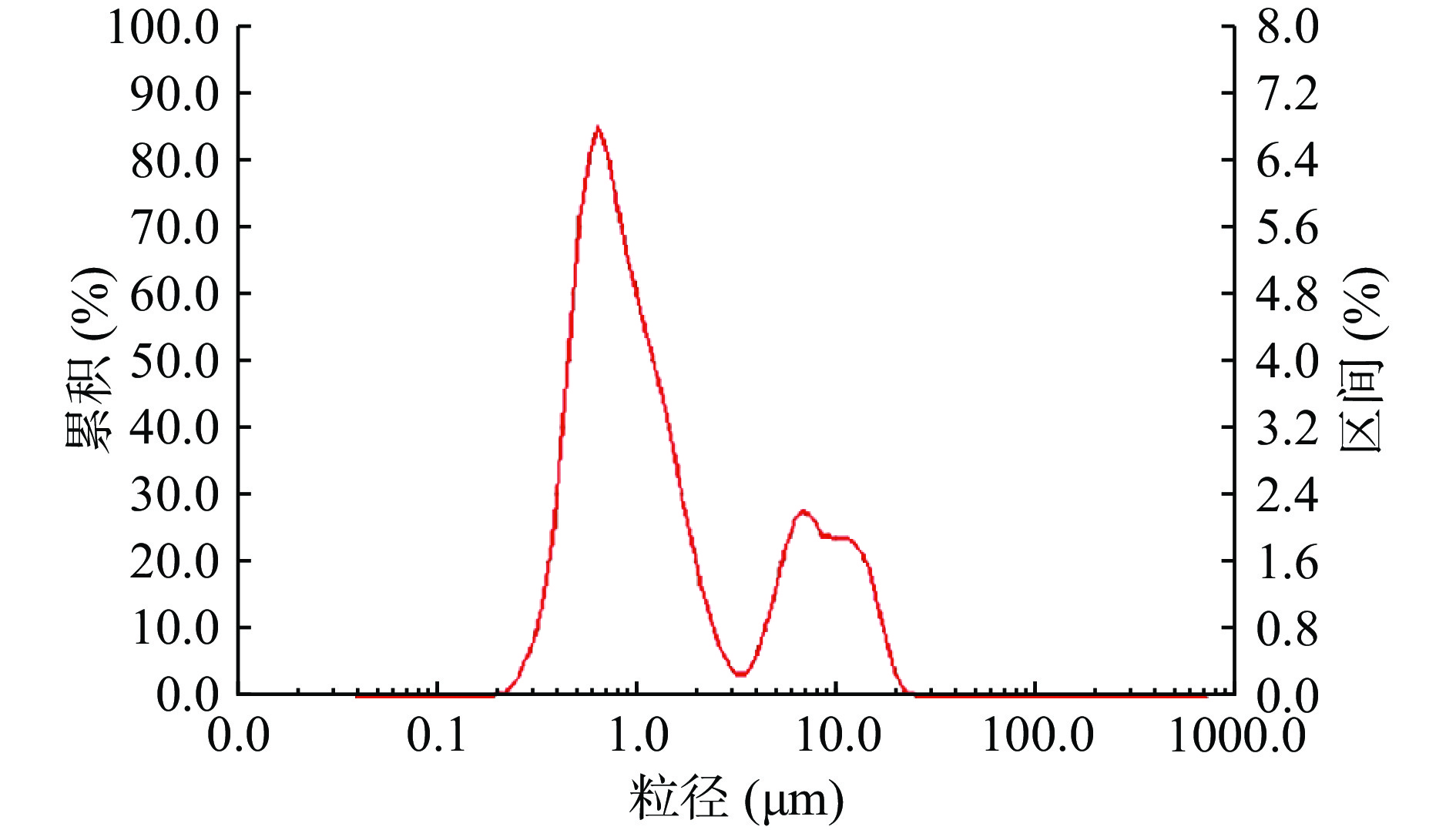
由图3、图4可知,酸枣仁蛋白粒径积累曲线在(50~60)μm处出现单峰,符合正态分布。而酸枣仁ACE抑制肽出现2个峰,分别在(0.6~0.7)μm和(6~7)μm,说明在酶解过程中,这两种粒径的酶解物较多,且酶解物粒径较酶解前减小。由表5可知,酸枣仁蛋白粒径特征值都明显高于酸枣仁ACE抑制肽,说明酶解充分。
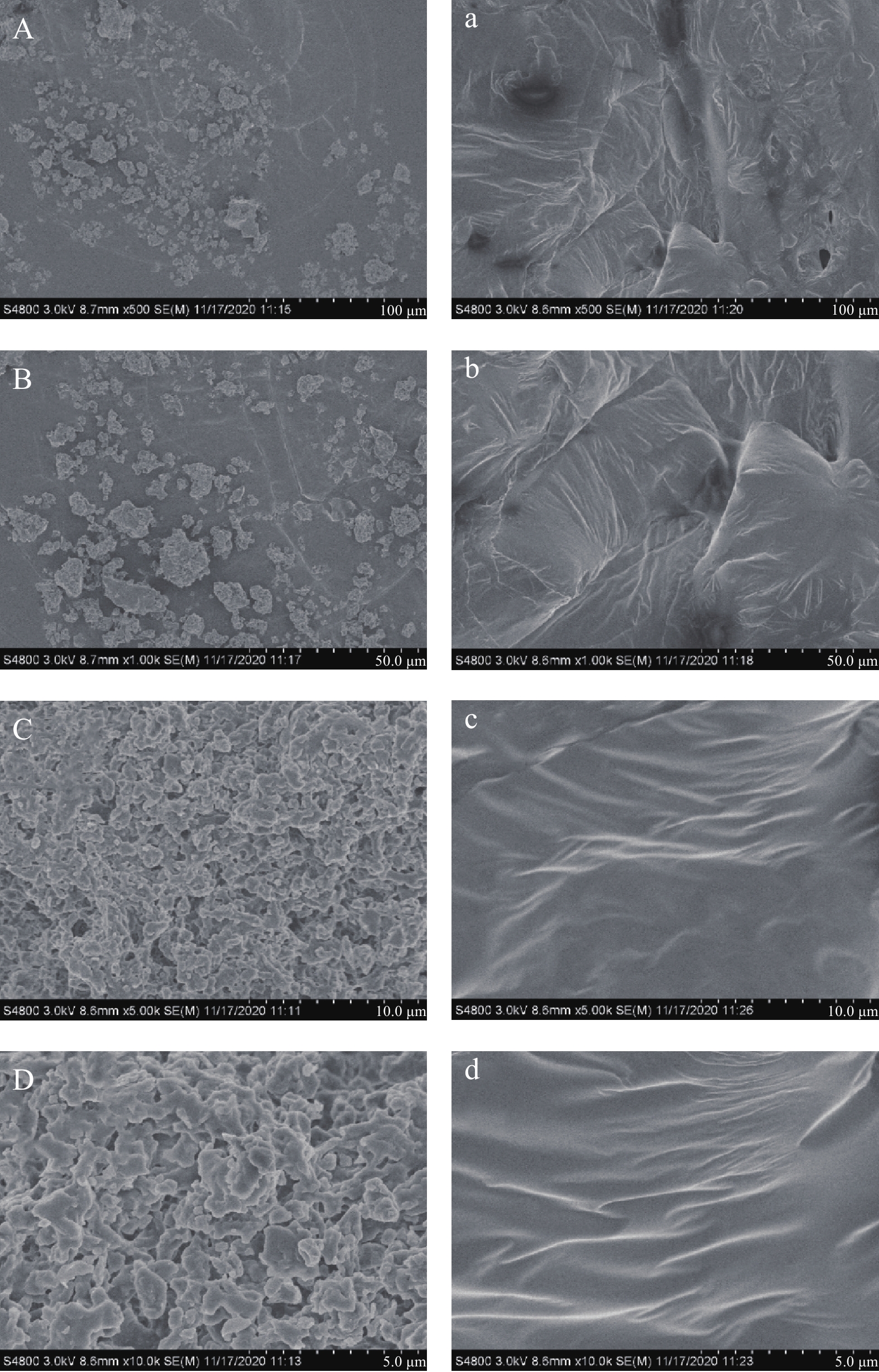
2.5 酸枣仁蛋白与酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的微观结构观察结果
扫描电镜在0.5、1、5、10 k倍视野下观察到酸枣仁蛋白和酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的表面微观结构如图5所示,酸枣仁蛋白在固体状态下是不规则的,表面有凸起,多孔性,呈铰链状聚合在一起,分子结构较大,酸枣仁蛋白分子之间交联程度低,未形成致密的网络状结构。酸枣仁ACE抑制肽通过酶解,蛋白结构被打破,片状结构消失,小颗粒的物质开始聚合,形成表面光滑、致密、略带褶皱,与粒径分析结果吻合,且与相关研究结果一致[34-35]。
表 5 酸枣仁蛋白与酸枣仁ACE抑制肽粒径特征值Table 5. Particle size characteristic values of jujube kernel protein and ACE inhibitory peptides in jujube kernel样品 中位粒径(D50)(μm) 面积平均粒径(μm) 体积平均粒径(μm) 酸枣仁蛋白 33.74 10.37 41.61 酸枣仁ACE抑制
肽冻干粉0.97 0.924 2.937 2.6 酸枣仁蛋白与酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的热稳定性结果
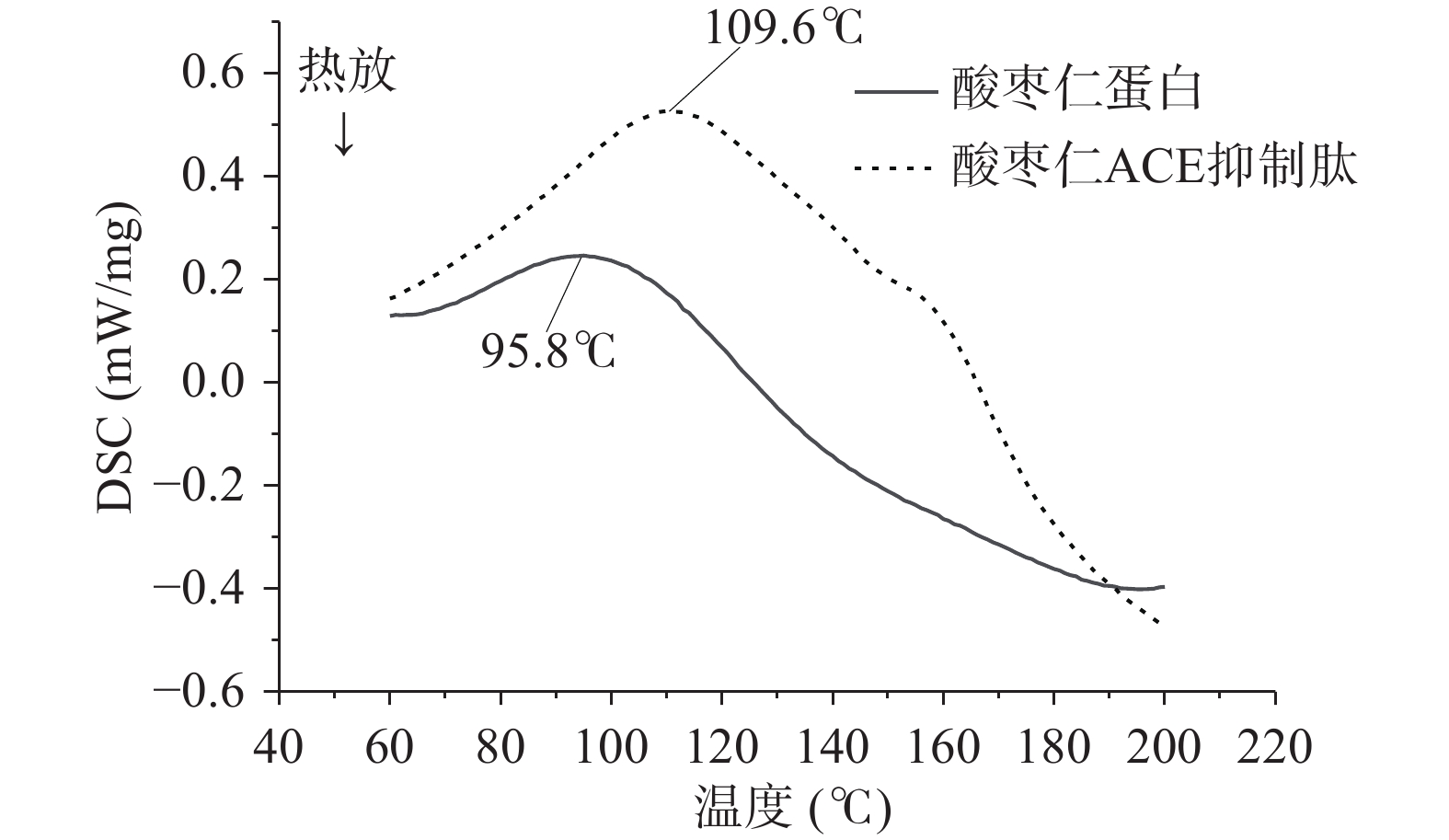
由图6和表6可知,酸枣仁蛋白和酸枣仁ACE抑制肽随着温度的升高,分子间链被打开,需要吸收热量,DSC逐渐曲线上升。酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的热变性温度为109.6 ℃,明显高于酸枣仁蛋白热变性温度95.8 ℃,说明酸枣仁ACE抑制肽热稳定性较好。热焓值(ΔH)反映蛋白质的变性状态,即蛋白质结构的维持能力、蛋白质有序结构、蛋白质的热稳定性[36]。酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的热焓值为19.6 J/g,明显高于酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的热焓值3.3 J/g ,由此得出酸枣仁ACE抑制肽比酸枣仁蛋白更稳定,对热敏感度相对较低,这可能与酶解过程中肽链的断开有关。
表 6 酸枣仁蛋白与酸枣仁ACE抑制肽热力学特征值Table 6. Thermodynamic characteristic values of jujube kernel protein and ACE inhibitory peptide in jujube kernel样品 起始温度(℃) 终止温度(℃) 变性温度(℃) 热焓值(ΔH)(J/g) 酸枣仁蛋白 82.2 106.8 95.8 3.3 酸枣仁ACE抑制肽冻干粉 85.2 128.9 109.6 19.6 2.7 酸枣仁蛋白与酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的溶解度测定结果
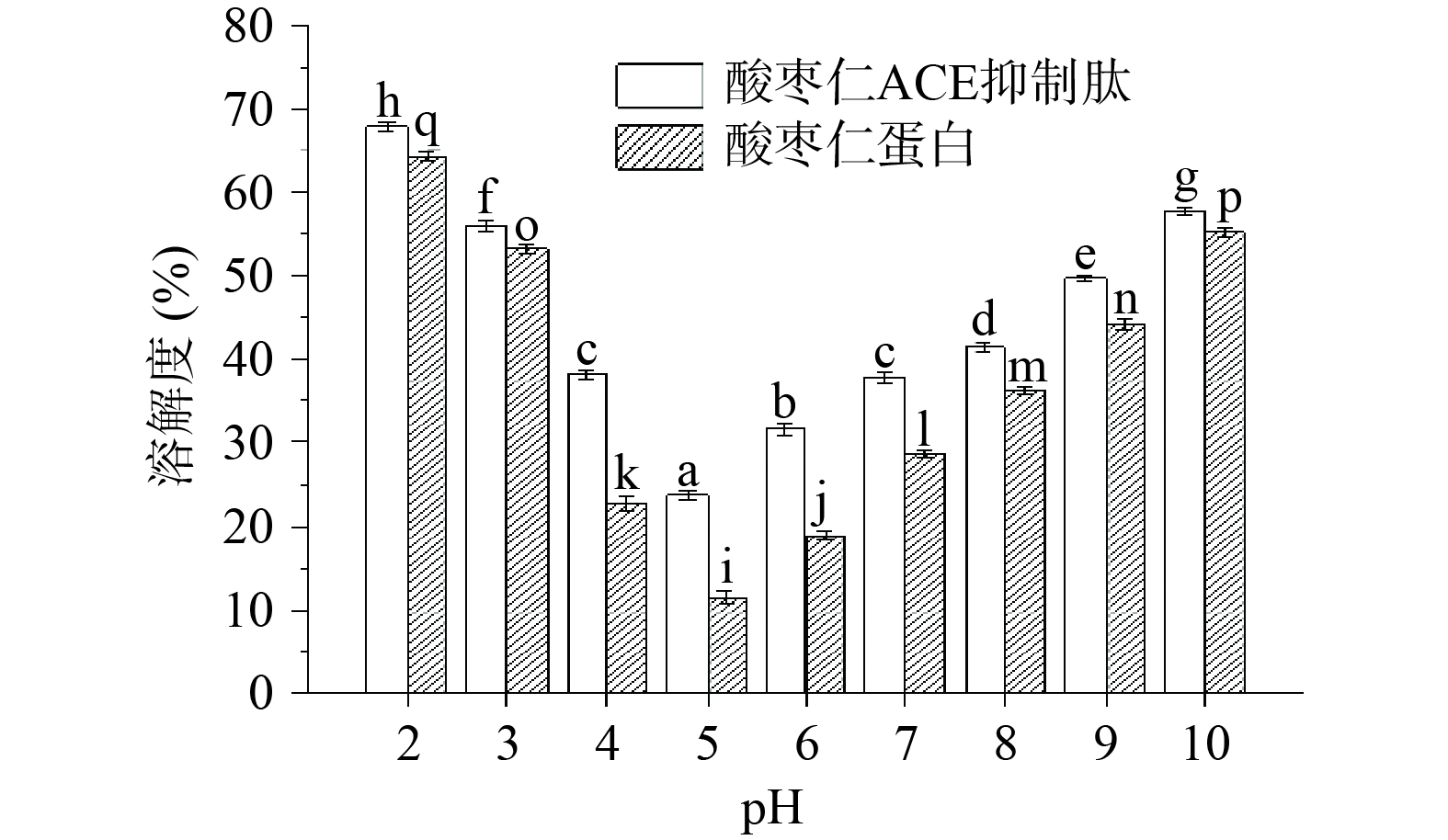
由图7可知,在接近等电点(pH5)处,酸枣仁蛋白和酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的溶解度最低,当远离等电点时,溶解度逐渐升高,与Jain[37]等研究得出溶解度曲线类似。因为在等电点时,蛋白质分子的净电荷为零,不存在相互作用力,颗粒易相互作用形成沉淀,此时溶解度最低,当溶液的pH逐渐远离等电点时,由于电荷作用,蛋白质产生相互作用力,且极易与水分子相互作用,从而改善并提高蛋白质的溶解度[38]。
而酸枣仁ACE抑制肽在不同pH下溶解度均高于酸枣仁蛋白,由于酶解过程使酸枣仁蛋白空间发生改变,肽链断裂,导致亲水性基团暴露,极性基团数量增加,从而使得蛋白质之间的疏水作用减弱,从而蛋白质与水的相互作用加强,利于蛋白质的溶解[39]。
2.8 酸枣仁蛋白与酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的持水性和持油性的测定结果
如表7所示,酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的持水性显著高于酸枣仁蛋白,是因为酸枣仁蛋白水解后,肽链被打开,暴漏出更多的亲水性基团[37]。酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的持油性明显高于酸枣仁蛋白,是因为酸枣仁ACE抑制肽比酸枣仁蛋白具有更多的非共轭链和疏水性物质[40-41]。
表 7 酸枣仁蛋白与酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的持水性和持油性Table 7. Water retention and oil retention of jujube kernel protein and ACE inhibitory peptides样品 持水性(mL/g) 持油性(mL/g) 酸枣仁蛋白 1.5±0.2 2.7±0.1 酸枣仁ACE抑制肽 21.5±0.5 5.1±0.2 2.9 酸枣仁蛋白与酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的起泡性和起泡稳定性测定结果
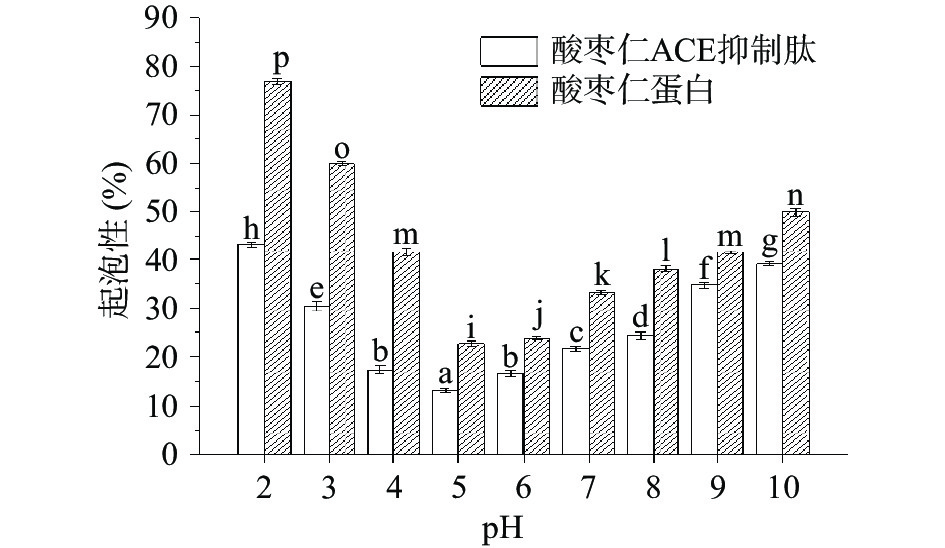
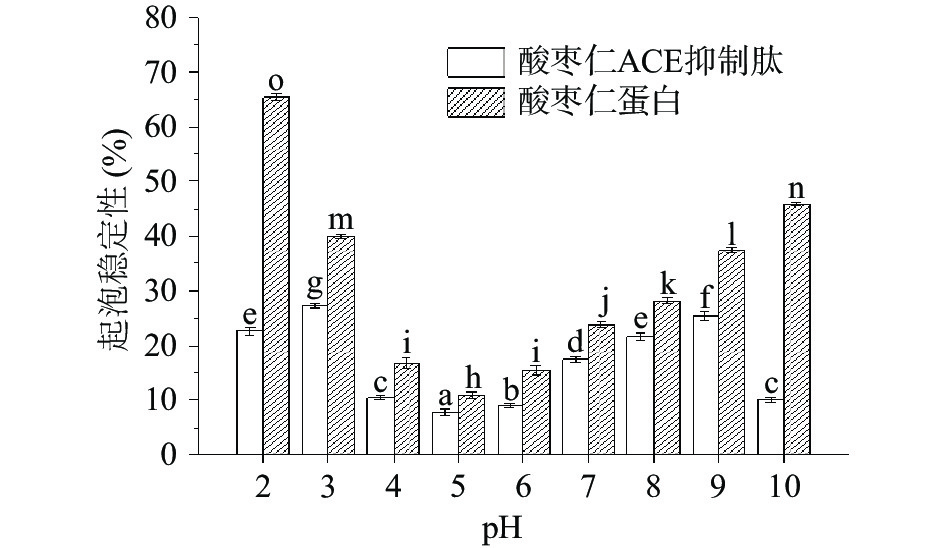
由图8、图9可知,酸枣仁ACE抑制肽起泡性和起泡稳定性在不同pH下均显著(P<0.05)小于酶解前的酸枣仁蛋白,这是因为蛋白质极性基团的数量和蛋白质相对分子质量是决定起泡能力的关键因素[41-42],酶解过程导致酸枣仁蛋白肽链断裂,相对分子质量减小,分子量降低,从而不利于泡沫的形成[43]。
2.10 酸枣仁蛋白与酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的乳化性和乳化稳定性测定结果
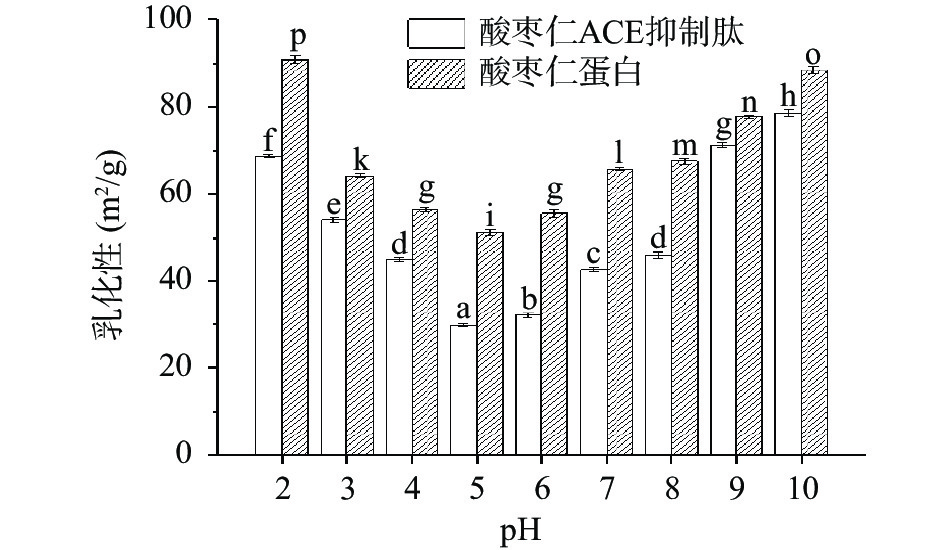
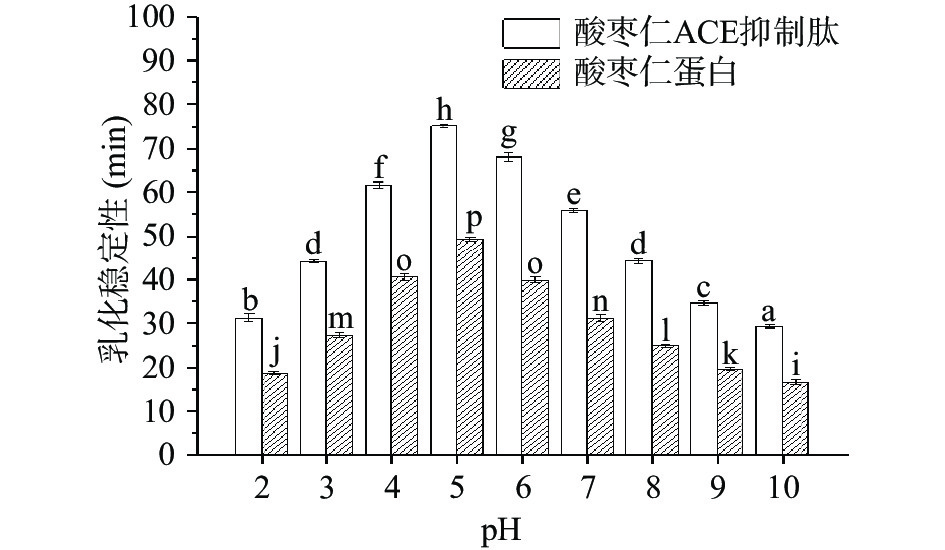
如图10、图11所示,不同pH下酸枣仁蛋白与酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的乳化能力和乳化稳定性变化。酸枣仁ACE抑制肽乳化能力显著(P<0.05)低于酸枣仁蛋白,而乳化稳定性却显著高于酸枣仁蛋白(P<0.05)。相关研究表明,肽链上至少要有20个以上的氨基酸残基才能有良好的乳化作用[44],酶解使酸枣仁蛋白空间结构改变,肽键断裂,蛋白相对分子质量减小,分子量降低,部分氨基酸残基缺失,不能降低界面张力,导致乳化性降低。酶解使蛋白质空间结构发生改变的同时暴露出疏水性基团和亲水性基团,不同基团与油相、水相相互作用,乳化稳定性得到提高[45]。
2.11 酸枣仁蛋白与酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的感官特性测定结果
酸枣仁蛋白与酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的感官特性测定结果如表8所示。酸枣仁ACE抑制肽冻干粉形态为结晶状粉末,相较于酸枣仁蛋白的片状粉末,颗粒更为细小,表明酶解充分。酸枣仁蛋白和酸枣仁ACE抑制肽在气味方面都为无味,有利于实际生产应用。
表 8 酸枣仁蛋白与酸枣仁ACE抑制肽感官特性结果Table 8. Sensory characteristics of jujube kernel protein and ACE inhibitory peptides from jujube kernel感官评价 酸枣仁蛋白 酸枣仁ACE抑制肽冻干粉 色泽 乳白色 浅褐色 性状 固体 固体 形态 片状粉末 结晶状粉末 气味 无味 无味 3. 结论
本文对脱脂酸枣仁的基本营养成分进行测定,蛋白质含量较高,脱脂过程蛋白质保存效果较好,有利于后续实验进行。酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的氨基酸组成中必需氨基酸含量较高,占36.48%,有利于人体营养需要,疏水性氨基酸含量占51.14%,侧面论证酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的有效降压效果。酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的分子量分布主要集中在1000~3000 Da,占97.50%;粒径分析表明酸枣仁蛋白酶解后,酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的中位粒径(D50)明显小于酸枣仁蛋白,且微观结构观察发现酶解后,酸枣仁ACE抑制肽表面呈现光滑、致密、略带褶皱,与粒径分析结果吻合。对比酸枣仁蛋白酶解前后理化性质,酸枣仁蛋白呈现乳白色、无味、片状粉末,而酸枣仁ACE抑制肽呈现浅褐色、无味、结晶状粉末。酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的溶解度、热稳定性、持水性和持油性均有显著提高(P<0.05);起泡性、起泡稳定性和乳化性得到改善,显著性降低(P<0.05);乳化稳定性提高。本文从基本理化指标对酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的酶解前后进行对比分析,以期为后续的实际应用提供参考依据,同时更为广泛的理化性质测定也有待后续试验展开。
-
表 1 脱脂酸枣仁主要成分(g/100 g)
Table 1 Main ingredients of defatted jujube seed main ingredients (g/100 g)
成分 总糖 脂肪 蛋白质 水分 灰分 脱脂酸枣仁 10.15±0.27 3.07±0.41 73.40±0.23 8.90±0.33 1.95±0.29 表 2 酸枣仁ACE抑制肽氨基酸成分分析
Table 2 Analysis of amino acid composition of ACE inhibitor peptide in jujube seed
氨基酸种类 含量(g/100g) 占氨基酸总量百分比(%) 天冬氨酸(Asp) 4.54±0.12 7.03±0.19 苏氨酸(Thr) 1.60±0.04 2.48±0.06 丝氨酸(Ser) 2.87±0.02 4.45±0.03 谷氨酸(Glu) 11.03±0.08 17.09±0.12 甘氨酸(Gly) 3.27±0.05 5.07±0.08 丙氨酸(Ala) 2.30±0.03 3.56±0.05 半胱氨酸(Cys) 0.42±0.04 0.65±0.06 缬氨酸(Val) 4.41±0.14 6.83±0.22 甲硫氨酸(Met) 2.22±0.07 3.44±0.11 异亮氨酸(Ile) 4.66±0.03 7.22±0.05 亮氨酸(Leu) 7.49±0.13 11.60±0.20 酪氨酸(Tyr) 0.06±0.01 0.09±0.02 苯丙氨酸(Phe) 1.74±0.01 2.70±0.02 赖氨酸(Lys) 1.43±0.04 2.22±0.06 脯氨酸(Pro) 10.19±0.11 15.79±0.17 组氨酸(His) 1.37±0.03 2.12±0.05 精氨酸(Arg) 4.95±0.07 7.66±0.11 疏水性氨基酸 33.01±0.52 51.14±0.81 必需氨基酸 23.55±0.46 36.48±0.71 总氨基酸含量 64.55±1.02 注:氨基酸含量为100 g酸枣仁脱脂粉中氨基酸含量;Ala、Val、Leu、Ile、Phe、Pro、Met 为疏水性氨基酸;Thr、Met、Val、Lys、Ile、Leu、Phe为必需氨基酸。 表 3 酸枣仁ACE抑制肽分子量分布
Table 3 Molecular weight distribution of ACE inhibitory peptides from jujube seed
分子量分布 1000~3000(Da) 3000~5000(Da) 5000~10000(Da) 比例(%) 97.50 1.70 0.80 表 4 分子量表征结果
Table 4 Molecular weight characterization results
分子量表征 Mn Mw Mp Mz Mw/Mn 分子量 1517 Da 1652 Da 1343 Da 1591 Da 1.088 表 5 酸枣仁蛋白与酸枣仁ACE抑制肽粒径特征值
Table 5 Particle size characteristic values of jujube kernel protein and ACE inhibitory peptides in jujube kernel
样品 中位粒径(D50)(μm) 面积平均粒径(μm) 体积平均粒径(μm) 酸枣仁蛋白 33.74 10.37 41.61 酸枣仁ACE抑制
肽冻干粉0.97 0.924 2.937 表 6 酸枣仁蛋白与酸枣仁ACE抑制肽热力学特征值
Table 6 Thermodynamic characteristic values of jujube kernel protein and ACE inhibitory peptide in jujube kernel
样品 起始温度(℃) 终止温度(℃) 变性温度(℃) 热焓值(ΔH)(J/g) 酸枣仁蛋白 82.2 106.8 95.8 3.3 酸枣仁ACE抑制肽冻干粉 85.2 128.9 109.6 19.6 表 7 酸枣仁蛋白与酸枣仁ACE抑制肽的持水性和持油性
Table 7 Water retention and oil retention of jujube kernel protein and ACE inhibitory peptides
样品 持水性(mL/g) 持油性(mL/g) 酸枣仁蛋白 1.5±0.2 2.7±0.1 酸枣仁ACE抑制肽 21.5±0.5 5.1±0.2 表 8 酸枣仁蛋白与酸枣仁ACE抑制肽感官特性结果
Table 8 Sensory characteristics of jujube kernel protein and ACE inhibitory peptides from jujube kernel
感官评价 酸枣仁蛋白 酸枣仁ACE抑制肽冻干粉 色泽 乳白色 浅褐色 性状 固体 固体 形态 片状粉末 结晶状粉末 气味 无味 无味 -
[1] 李强. 酸枣仁潜在效应成分研究[D]. 太原: 山西大学, 2017. LI Q. Study on potential effective components of jujube seed[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi University, 2017.
[2] 李续娥, 李维凤, 裴渭静. 酸枣仁与缅枣仁的蛋白质分析[J]. 中草药,2002,33(1):28−30. [LI X E, LI W F, PEI W J. Protein analysis of jujube seed and jujube seed[J]. Chinese Herbal Medicine,2002,33(1):28−30. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2670.2002.01.013 [3] 刘静, 李贞, 刘海英. 酸枣仁氨基酸组成分析及营养评价[J]. 食品研究与开发,2016,37(20):20−22. [LIU J, LI Z, LIU H Y. Analysis of amino acid composition and nutrition evaluation of jujube seed[J]. Food Research and Development,2016,37(20):20−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2016.20.006 [4] 黄之镨, 马伟光. 酸枣仁及活性物质的药理研究进展[J]. 中国民族民间医药,2018,27(3):57−60. [HUANG Z P, MA W G. Progress of pharmacological research on jujube seed and active substance[J]. Chinese national folk medicine,2018,27(3):57−60. [5] 操德群, 何艳丽, 余虹, 等. 海洋生物ACE抑制肽研究进展[J]. 核农学报,2017,31(5):927−937. [CAO D Q, HE Y L, YU H, et al. Research progress of ACE inhibitory peptides in marine organisms[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agriculture,2017,31(5):927−937. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2017.05.0927 [6] 李勇. 蚕蛹ACE抑制肽的制备及其ACE抑制活性的研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2012. LI Y. Preparation of ACE inhibitory peptide from silkworm chrysalis and study on its ACE inhibitory activity[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2012.
[7] FERREIRA S H. A Bradykinin-Potentiating Factor (BPF) present in the venom of Bothrops jararaca[J]. British Journal of Pharmacology and Chemotherapy,1965,24(1):163−169. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1965.tb02091.x
[8] JIMSHEENA V K, GOWDA L R. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides derived from arachin by simulated gastric digestion[J]. Food Chemistry,2011,125(2):561−569. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.09.048
[9] WENG T M, CHEN M T. Effect of two-step fermentation by Rhizopus oligosporus and Bacillus subtilis on protein of fermented soybean[J]. Food Science & Technology Research,2011,17(5):393−400.
[10] JAKUBCZYK A, KARA M, BARANIAK B, et al. The impact of fermentation and in vitro digestion on formation angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from pea proteins[J]. Food Chemistry,2013,141(4):3774−3780. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.06.095
[11] 刘志国, 陈江源, 王亚林, 等. 玉米醇溶蛋白酶解制备ACE抑制肽的研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2006,27(2):138−141. [LIU Z G, CHEN J Y, WANG Y L, et al. Study on preparation of ACE inhibitory peptide by zein glycolysis[J]. Food Research and Development,2006,27(2):138−141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2006.02.048 [12] ZHOU C, MA H, YU X, et al. Pretreatment of defatted wheat germ proteins (by-products of flour mill industry) using ultrasonic horn and bath reactors: Effect on structure and preparation of ACE-inhibitory peptides[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2013,20(6):1390−1400. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2013.04.005
[13] 毛跟年, 周亚丽, 贺磊, 等. 魔芋ACE抑制肽的分离纯化及活性检测[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2017,38(1):99−102. [MAO G N, ZHOU Y L, HE L, et al. Study on preparation technology of konjac ACE inhibitory peptidase[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2017,38(1):99−102. [14] LIU M, DU M, ZHANG Y, et al. Purification and identification of an ACE inhibitory peptide from walnut protein[J]. Chemical Reviews,2013,61(17):4097−4100.
[15] HAILE M A. Pretreatment of garlic powder using sweep frequency ultrasound and single frequency countercurrent ultrasound: Optimization and comparison for ACE inhibitory activities[J]. Ultrasonics - Sonochemistry,2015,23:109−115. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2014.10.020
[16] ANUGERAH D P. Screening, discovery, and characterization of angiotensin-I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from proteolytic hydrolysate of bitter melon seed proteins[J]. Journal of Proteomics,2015,128:424−435. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2015.08.018
[17] 于志鹏, 武思佳, 赵文竹, 等. 蛋清中ACE抑制肽的筛选及其作用机制(英文)[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(22):126−133. [YU Z, WU S J, ZHAO W Z, et al. Screening and mechanism of ACE inhibitory peptides in egg white[J]. Food Science,2019,40(22):126−133. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181109-118 [18] 尹歆, 邓放明. 鲢鱼蛋白制备ACE抑制肽的工艺优化[J]. 食品与机械,2012,28(2):147−151. [YIN X, DENG F M. Process optimization of preparation of ACE inhibitory peptide from silver carp protein[J]. Food & Machinery,2012,28(2):147−151. [19] 郑炯, 邓惠玲, 阚建全. 响应面法优化猪血红蛋白制备ACE抑制肽的酶解工艺条件[J]. 食品科学,2012,33(23):209−214. [ZHENG J, DENG H L, KAN J Q. Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis conditions for preparation of ACE inhibitory peptide from porcine hemoglobin by response surface methodology[J]. Food science,2012,33(23):209−214. [20] 贺磊. 魔芋ACE抑制肽制备技术及理化性质研究[D]. 西安: 陕西科技大学, 2017. HE L. Study on preparation technology and physicochemical properties of ACE inhibitory peptide from taro[D]. Xi’an: Shanxi University of Science and Technology, 2017.
[21] 谭力铭, 裴海生, 赵丹丹, 等. 超微冷冻粉碎处理下酸枣仁蛋白提取工艺优化[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(23):122−128. [TAN L M, PEI H S, ZHAO D D, et al. Optimization of extraction process of jujube kernel protein by ultrafine freezing pulverization[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(23):122−128. [22] 国家技术监督局. GB/T 5009.5-2016食品中蛋白质的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. State Bureau of Technical Supervision. GB/T 5009.5-2016, Determination of protein in food of national standard for food safety [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[23] 国家技术监督局. GB/T 5009.3-2016食品中水分的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. State Bureau of Technical Supervision. GB/T 5009.3-2016, Determination of moisture in food of the national standard for food safety [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[24] 国家技术监督局. GB/T 5009.4-2016食品中灰分的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. State Bureau of Technical Supervision. GB/T 5009.4-2016, Determination of ash content in food of national standard for food safety [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[25] 国家技术监督局. GB/T 5009.6-2016食品中脂肪的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. State Bureau of Technical Supervision. GB/T 5009.6-2016, Determination of fat in food of national standard for food safety [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[26] 国家技术监督局. GB/T 5009.10-2016植物类食品中粗纤维的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. State Bureau of Technical Supervision. GB/T 5009.10-2016, Determination of crude fiber in plant foods [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[27] 国家技术监督局. SN/T 4260-2015出口植物源食品中粗多糖含量的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2015. State Bureau of Technical Supervision. SN/T 4260-2015, Determination of crude polysaccharide content in exported plant-derived food [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2015.
[28] 赵节昌. 响应面法优化酸枣仁蛋白提取工艺[J]. 食品科学,2013,34(16):134−138. [ZHAO J C. Optimization of extraction process of jujube kernel protein by response surface methodology[J]. Food Science,2013,34(16):134−138. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201316027 [29] EGGUM B. Comments on report of a joint FAO/WHO expert consultation on protein quality evaluation, Rome 1990[J]. Zeitschrift für Ernährungswissenschaft,1991,30(2):81−88. doi: 10.1007/BF01610063
[30] LEE J K, HONG S, JEON J K, et al. Purification and characterization of angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from the rotifer, Brachionus rotundiformis[J]. Bioresource Technology,2009,100(21):5255−5259. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.05.057
[31] 王升光, 于帅, 孟凡刚, 等. 酶法制备大豆肽的相对分子量分布及降压作用研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(1):46−51. [WANG S G, YU S, MENG F G, et al. Study on relative molecular weight distribution and antihypertensive effect of soybean peptide prepared by enzymatic method[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(1):46−51. [32] LIU X, ZHANG M, SHI Y, et al. Production of the angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides and isolation of four novel peptides from jellyfish (Rhopilema esculentum) protein hydrolysate[J]. J Sci Food Agric,2016,96(9):3240−3248. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.7507
[33] 朱俊向, 于丁一, 宋玉凤, 等. 动物蛋白水解酶法制备南极磷虾多肽及其抗氧化活性[J]. 中国调味品,2019,44(4):104−107. [ZHU J X, YU D Y, SONG Y F, et al. Preparation and antioxidant activity of krill polypeptides from animal proteolytic enzymes[J]. Chinese Seasoning,2019,44(4):104−107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2019.04.022 [34] 韩晓燕, 包郁明, 辛凤姣, 等. 棉籽蛋白酶解物的制备及其抗菌活性[J]. 中国农业科学,2016,49(15):3019−3029. [HAN X Y, BAO Y M, XIN F J, et al. Preparation and antibacterial activity of cottonseed protease hydrolysate[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2016,49(15):3019−3029. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2016.15.016 [35] 苏银杰. 酪蛋白酶解特性的研究[D]. 郑州: 河南工业大学, 2013. SU Y J. Study on enzymatic hydrolysis characteristics of casein[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan University of Technology, 2013.
[36] 张维. 工业大麻籽蛋白的制备与功能特性研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2008. ZHANG W. Preparation and functional characteristics of hemp seed protein[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2008.
[37] JAIN A, PRAKASH M, RADHA C. Extraction and evaluation of functional properties of groundnut protein concentrate[J]. Journal of Food Science & Technology,2015,52(10):1−8.
[38] 许英一, 王宇, 林巍. 燕麦蛋白理化性质研究[J]. 安徽农业大学学报,2018,45(3):385−388. [XU Y Y, WANG Y, LIN W. Study on physicochemical properties of oat protein[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University,2018,45(3):385−388. [39] LI G H, LE G W, SHI Y H. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from food proteins and their physiological and pharmacological effects[J]. Nutrition Research,2004,24(7):469−486. doi: 10.1016/S0271-5317(04)00058-2
[40] TOMOTAKE H, SHIMAOKA I, KAYASHITA J, et al. Physicochemical and functional properties of buckwheat protein product.[J]. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry,2002,50(7):2125.
[41] ZHU K X, SUN R H, CHEN R C, et al. Comparison of functional properties and secondary structures of defatted wheat germ proteins separated by reverse micelles and alkaline extraction and isoelectric precipitation[J]. Food Chemistry,2010,123(4):1163−1169. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.05.081
[42] MUTILANGI W A M, PANYAM D, KILARA A. Functional properties of hydrolysates from proteolysis of heat-denatured whey protein isolate[J]. Journal of Food Science,2010,61(2):270−275.
[43] AGYARE K K, ADDO K, XIONG Y L. Emulsifying and foaming properties of transglutaminase-treated wheat gluten hydrolysate as influenced by pH, temperature and salt[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2009,23(1):72−81. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2007.11.012
[44] 蒋菁莉. 牦牛乳酪蛋白降血压肽酶法制备及功能评价[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2007. JIANG J L. Preparation and function evaluation of yak cheese proteinase-lowering peptidase[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2007.
[45] 李莹. 泥鳅蛋白源ACE抑制肽的酶法制备及其降压活性研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2012. LI Y. Enzymatic preparation of ACE inhibitor peptide from loach protein and its antihypertensive activity[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2012.
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 马晓青,孙皓岩,魏宝红,胡淑曼,杨文哲,杨雪. 紫贻贝酶解工艺及抗炎活性研究. 食品科技. 2024(01): 116-120 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 程钰,胡蓉,李强,蒋蕾,何跃辉,卢静,王淑军. 复合蛋白酶水解菲律宾蛤蜊及产物的生物学活性研究. 食品科技. 2024(06): 134-141 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 付雪媛,杜芬,孙呈浩,王明丽,王长伟. 蛤蜊肽的制备工艺优化及其增强免疫活性. 食品工业科技. 2023(09): 244-253 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 沈畅华,杨娟,张远红,曾晓房. 双酶酶解鸽胸肉工艺优化及抗氧化性评价. 食品与机械. 2023(04): 163-169 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 吴伟东,马诗淳,陈锐,周广平,邓宇. 厌氧角蛋白降解菌KD-1粗酶和商业蛋白酶酶解猪肉的功能与评价. 中国沼气. 2022(02): 47-53 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 李佳芸,王欣之,韦源青,卞慧敏,刘睿,吴皓. 马氏珍珠贝软体酶法制备降糖肽的工艺优化及肽段分析. 食品工业科技. 2021(22): 202-211 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)










 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
