Hepatoprotective Effects of Grape Seed Oil on Acute Liver Injury
-
摘要: 探究葡萄籽油对四氯化碳(CCl4)诱导小鼠急性肝损伤的保护作用。利用CCl4建立急性肝损伤模型,通过测定小鼠体重、食物和水摄入量,检测血清和肝组织相关指标,观察小鼠肝组织形态学变化,以评价葡萄籽油对小鼠急性肝损伤的保护作用。结果表明:与CCl4组相比,中、高剂量(10、20 mL/kg·d)葡萄籽油处理能有效降低肝损伤小鼠血清中谷草转氨酶(AST)、谷丙转氨酶(ALT)、乳酸脱氢酶(LDH)活性以及总胆固醇(TC)和甘油三酯(TG)含量(P<0.05),显著提高肝组织中谷胱甘肽(GSH)含量、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活力(P<0.05),并降低丙二醛(MDA)含量(P<0.05),明显改善病理损伤程度。综上所述,葡萄籽油对CCl4诱导小鼠急性肝损伤具有明显的保护作用,且剂量越高,保护作用越强。Abstract: The hepatoprotective effects of grape seed oil (GSO) against carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) induced acute liver injury in mice was investigated. The model of acute liver injury was induced by intraperitoneal injection of CCl4. The body weight and food and water intake were measured, the relevant indexes of serum and liver tissue were detected, and the pathological changes of liver tissues in mice were observed. The results showed that compared mice-treated with CCl4, the mice were oral administered middle dose (10 mL/kg·d) of GSO (MGSO) and high dose (20 mL/kg·d) of GSO (HGSO) could significantly reduce the activities of aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and the levels of total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG) (P<0.05) in serum, could significantly increase the activities of glutathione (GSH), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and reduce concentrations of malondialdehyde (MDA) (P<0.05), and could significantly improve the pathological changes of liver tissue. Therefore, GSO had significant hepatoprotective effects against CCl4 induced acute liver injury in mice, and the hepatoprotective effects was stronger with the increasing dose.
-
Keywords:
- hepatoprotective effects /
- grape seed oil /
- carbon tetrachloride /
- mice /
- acute liver injury
-
肝脏是脊椎动物腹腔内最大的腺体,具有清毒、凝血、免疫以及分泌胆汁等多种功能,参与蛋白、碳水化合物以及脂质等大部分代谢过程,因此,肝脏极易受到外源性物质的攻击,从而导致急性或慢性肝脏损伤[1-4]。近年来,随着人类生活方式和环境的改变,全球肝脏疾病的发病率逐年攀升,严重威害人类健康[5]。目前,临床上多采用化学合成的核苷类、维生素类预防和治疗肝脏疾病,虽然能控制或改善病症,但局限性较大[6]。因此,寻找一种高效的、无毒的功能性食物或药物已经成为肝脏保护领域的研究热点。
葡萄是葡萄属木质藤本植物,具有鲜食、榨汁和酿酒等多种用途,其中酿酒是葡萄的最主要利用方式,约占其总产量的80%[7]。葡萄经酿酒后会产生葡萄皮、果梗以及葡萄籽等一系列副产物,约占其加工量的25%[8]。葡萄籽是副产物中最主要的成分,含有多种对人体有益的成分,如脂质、蛋白质、维生素以及多酚等[9]。因此,对葡萄籽进行合理的开发利用不仅能减少残渣丢弃造成的资源浪费和环境污染,还能延长葡萄酒产业链从而增加经济效益[10]。葡萄籽油作为葡萄籽中最有益的成分,含有多种不饱和脂肪酸[11]、多酚[12-13]、植物甾醇[14]以及维生素[15]等物质,具有防辐射[16]、抑菌[17]、消炎[18]、抗氧化[19]以及降血糖[20]等多种生理功能。但关于葡萄籽油对小鼠急性肝损伤保护作用的研究未见报道。
因此,本文以葡萄籽油为研究对象,利用CCl4诱导小鼠急性肝损伤,探究葡萄籽油对小鼠急性肝损伤的保护作用,从而为后续葡萄籽油护肝作用的研究提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
雄性昆明种小鼠 72只,体重(40±2)g,生产许可证号:SCXK(豫)2017-0001 河南省实验动物中心;葡萄籽油、花生油 京东商城线上超市;联苯双酯 北京协和药厂;谷丙转氨酶(alanine aminotransferase, ALT)、谷草转氨酶(aspartate aminotransferase, AST)、乳酸脱氢酶(lactate dehydrogenase, LDH)、甘油三酯(triglyceride, TG)、总胆固醇(total cholesterol, TC)、丙二醛(malondialdehyde, MDA)、谷胱甘肽(glutathione, GSH)以及超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase, SOD)等试剂盒 南京建成生物工程研究所;四氯化碳 色谱级,上海苗克林生化有限公司。
AL204电子天平 梅特勒-托利多仪器(上海)有限公司;PM型行星球磨机 南京弛顺科技发展有限公司;7890B型气相色谱仪 美国安捷伦科技有限公司;LD5-10型低速离心机 北京京立离心机有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 葡萄籽油的脂肪酸组成测定
参照GB 5009.168-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品中脂肪酸的测定》测定葡萄籽油的脂肪酸组成。
气相色谱(GC)条件:柱子型号为HP-88(100 m×0.252 mm×0.2 μm),进样量1 μL,分流比为1:50,以高纯度氦气作为载气,进样口温度250 ℃,检测器温度280 ℃。升温程序:初温170 ℃,以4 ℃/min的速度升至220 °C,不保温,再以1 °C/min的速度升至240 ℃。
1.2.2 动物分组及模型建立
72只小鼠均分为6组,包括正常对照组-NC(10 mL/kg·d生理盐水),CCl4组-CCl4(10 mL/kg·d生理盐水),联苯双酯阳性对照组-BP(150 mg/kg·d联苯双酯),葡萄籽油低剂量组-LGSO(5 mL/kg·d葡萄籽油),葡萄籽油中剂量组-MGSO(10 mL/kg·d葡萄籽油),葡萄籽油高剂量组-HGSO(20 mL/kg·d葡萄籽油)。所有小鼠均在同一环境中每天灌胃1次,连续灌胃14 d。在第15 d时,除NC组小鼠注射花生油(5 mL/kg·d)外,其余各组小鼠均注射0.8% CCl4(5 mL/kg·d,CCl4溶于花生油中),注射完毕将所有小鼠严格禁食不禁水16 h。
1.2.3 小鼠体重与食物和水摄入量的测定
准确称量小鼠体重并对每组小鼠体重求平均值。每天监测小鼠食物和水摄入量,对每组小鼠在15 d内的食物和水摄入量取平均值。
1.2.4 血清指标的测定
实验结束后,从眼静脉采集血样,离心取上清以获得血清标本。根据试剂盒的操作说明测定ALT、AST和LDH活力以及TG和TC含量。
1.2.5 脏器指数的测定
小鼠脱臼处死后立即解剖获取肝脏,称其质量,按照下式计算脏器指数。
脏器指数(%)=肝脏质量(g)小鼠体重(g)×100 1.2.6 肝脏组织指标测定
利用液氮将肝脏组织快速冷冻,置于球磨机中,按照1:9的比例添加冷生理盐水(w/v)进行研磨,然后离心取上清。根据试剂盒的操作说明测定MDA、GSH含量以及SOD活力。
1.2.7 肝脏组织形态的检测
肝脏组织在4 ℃的条件用10%中性甲醛溶液固定48 h,然后经脱水、包埋、切片、染色等处理后利用显微镜进行病理学观察。
1.3 数据处理
利用GraphPad Prism 8作图,采用SPSS 20.0软件进行单因素方差分析,以Duncan-t检验比较组间差异,P<0.05代表差异显著,P<0.01代表差异极显著。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 葡萄籽油的脂肪酸组成
由表1可知,葡萄籽油中不饱和脂肪酸含量为86.16%,饱和脂肪酸含量为13.84%,其中人体必需脂肪酸亚油酸含量最高,占62.04%。贾雪峰等[21]研究表明,亚油酸具有降低胆固醇、抗炎、抗氧化、抗肿瘤以及防止动脉粥样硬化等多种功效。此外,吴正平[22]对金花葵籽油的不饱和脂肪酸(油酸、亚油酸)提纯,探究其对CCl4诱导小鼠急性肝损伤的保护作用,结果表明不饱和脂肪酸具有调血脂和护肝的作用。而葡萄籽油含有大量的不饱和脂肪酸,因此对人体十分有益。
表 1 葡萄籽油的脂肪酸组成Table 1. Fatty acids composition of grape seed oil成分 百分比(%) 癸酸 3.40 棕榈酸 6.59 棕榈油酸 0.14 硬脂酸 3.54 油酸 23.50 亚油酸 62.04 亚麻酸 0.48 山嵛酸 0.31 饱和脂肪酸 13.84 单不饱和脂肪酸 23.64 多不饱和脂肪酸 62.52 不饱和脂肪酸 86.16 2.2 葡萄籽油对CCl4损伤小鼠体重与食物和水摄入量的影响
由表2可知,在第15 d各组小鼠体重无显著性差异(P>0.05),表明在注射CCl4前,各组小鼠均正常生长,而注射CCl4后,因严格禁食,各组小鼠体重差异不显著。在食物摄入方面,与NC组相比,CCl4和BP组无显著性差异(P>0.05),而LGSO、MGSO和HGSO组差异显著(P<0.05),可能是因为小鼠将葡萄籽油消化吸收为机体提供能量[23],所以随着葡萄籽油服用剂量的增加,食物摄入量减少。在饮水量方面,与NC组相比,CCl4、BP、LGSO、MGSO组均无显著性差异(P>0.05),而HGSO组差异显著(P<0.05)。
表 2 葡萄籽油对CCl4损伤小鼠体重与食物和水摄入量的影响Table 2. Effects of grape seed oil on body weight and food and water intake of mice组别 体重(g) 食物摄入量 饮水量 第1 d 第15 d (g/rat/day) (mL/rat/day) NC 46.11±4.41a 57.58±4.36ab 8.75±1.55a 10.45±0.86ab CCl4 44.22±3.42a 54.34±2.59b 9.07±0.85ab 10.02±2.03b BP 44.88±2.51a 55.91±3.62ab 9.33±0.94a 11.21±1.05a LGSO 44.64±4.25a 58.82±4.41a 8.32±1.26b 10.03±1.23bc MGSO 45.37±5.21a 56.72±4.70ab 6.98±0.81c 9.65±1.36bc HGSO 45.60±3.76a 58.20±3.13a 5.64±1.54d 8.96±0.53c 注:同一列不同字母代表差异显著(P<0.05);表3同。 2.3 葡萄籽油对CCl4损伤小鼠血清指标的影响
由于细胞膜的选择透过性,ALT、AST以及LDH被细胞膜隔绝在肝细胞内,因此血清中三种酶的活力很低。然而当CCl4诱导小鼠肝损伤后,细胞膜完整性遭到破坏,导致ALT、AST以及LDH从细胞中渗出进入血液循环系统,使血清中三种酶活力显著升高,因此ALT、AST以及LDH可作为鉴定肝损伤程度的指标[24]。由表3可知,与NC组相比,CCl4组小鼠血清中ALT、AST以及LDH活力均显著提高(P<0.05),表明细胞膜遭到破坏,引起细胞内酶出现外泄现象,标志着小鼠肝脏受损,建模成功。而MGSO和HGSO组小鼠的ALT、AST以及LDH活力均显著低于CCl4组小鼠(P<0.05),表明葡萄籽油在一定程度上能够保护肝脏。此外,HGSO与BP组小鼠血清中ALT、AST以及LDH活力水平无显著差异(P>0.05),表明服用高剂量葡萄籽油(20 mL/kg·d)与联苯双酯(150 mg/kg·d)的保肝效果相当,但都不能使其恢复到正常状态。
表 3 葡萄籽油对CCl4损伤小鼠血清指标ALT、AST、LDH、TG和TC的影响Table 3. Effects of grape seed oil on ALT, AST, LDH, TG and TC levels in serum of mice组别 AST(U/L) ALT(U/L) LDH(U/L) TG(mmol/L) TC(mmol/L) NC 70.71±21.21c 28.04±2.36d 3978.47±108.35f 2.80±0.36c 6.27±0.27d CCl4 217.70±11.11a 257.48±48.61a 8384.14±497.11a 4.01±0.35a 11.22±0.69a BP 139.40±8.59b 126.32±21.10c 6123.82±141.76e 3.01± 0.34bc 7.62±0.57c LGSO 192.01±32.88a 202.31±28.02ab 7046.24±599.53bc 3.62±0.42ab 9.01±0.49b MGSO 168.69±23.22b 172.08±32.89bc 6703.33±178.52cd 3.33±0.85bc 8.70±1.05bc HGSO 149.53±7.27b 132.27±18.00c 6377.25±372.61de 3.12±0.23bc 7.69±0.73c CCl4诱导小鼠肝脏受损会导致蛋白质合成障碍,从而影响脂质代谢使血清中TG和TC大量积累,最终引发心血管疾病,因此TG和TC也是反映小鼠肝脏受损程度的重要指标[25]。由表3可知,CCl4组与NC组相比,小鼠血清中TG和TC含量显著升高(P<0.05),表明建模成功。MGSO和HGSO组与CCl4组相比,小鼠血清中TG和TC的含量显著降低(P<0.05),表明葡萄籽油能有效降低血清中TG和TC的浓度。此外,当葡萄籽油的服用剂量在5~20 mL/kg·d时,对肝脏的保护作用存在剂量效应,即服用剂量越高,保护效果越好。
2.4 葡萄籽油对CCl4损伤小鼠脏器指数的影响
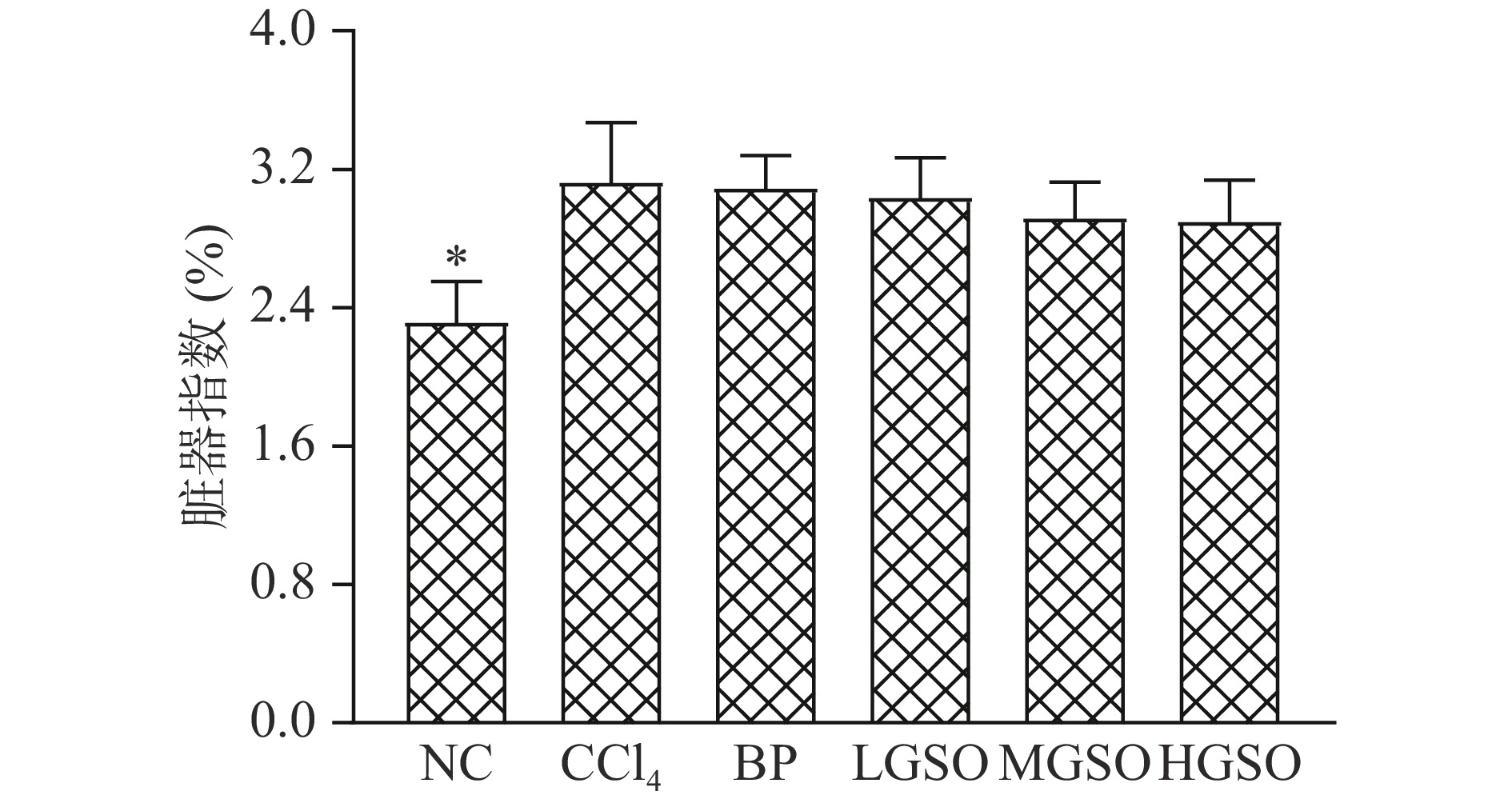
CCl4是诱导动物肝脏受损的典型毒物,能够破坏肝细胞膜的结构和功能,使其通透性增加,失去阻碍大分子物质回流到细胞膜内的能力,从而导致肝脏体积肿胀,质量增加[26-27]。由图1可知,CCl4组脏器指标显著高于NC组(P<0.05),表明CCl4组小鼠肝脏出现严重的肿胀现象。虽然BP、LGSO、MGSO和HGSO组的脏器指数在数值上均低于CCl4组,但均无显著性差异(P>0.05)。
![]() 图 1 葡萄籽油对小鼠脏器指数的影响注:*表示与CCl4组相比,差异显著(P<0.05);**表示与CCl4组相比,差异极显著(P<0.01);图2同。Figure 1. Effects of grape seed oil on liver index in mice
图 1 葡萄籽油对小鼠脏器指数的影响注:*表示与CCl4组相比,差异显著(P<0.05);**表示与CCl4组相比,差异极显著(P<0.01);图2同。Figure 1. Effects of grape seed oil on liver index in mice2.5 葡萄籽油对CCl4损伤小鼠肝脏抗氧化能力的影响
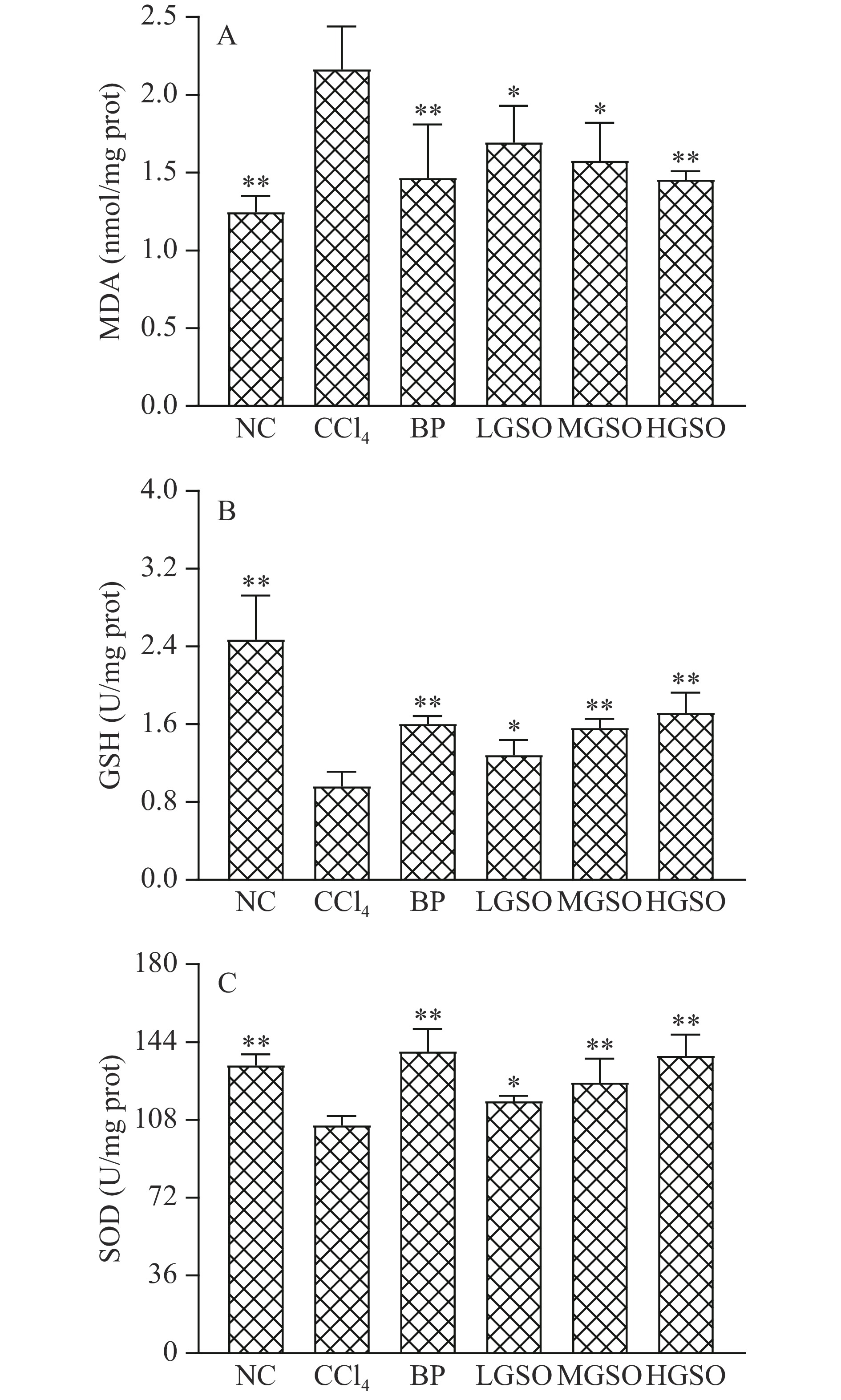
MDA是脂质过氧化反应的终产物,其含量可用来反映肝脏损伤的程度[28]。SOD是动物体重要的抗氧化酶,具有清除超氧阴离子并终止自由基链反应的作用,通常与GSH协同作用。首先SOD将细胞内外的活性氧自由基催化为H2O2和O2,然后GSH催化分解H2O2为H2O和O2[29-30]。由图2可知,与CCl4组相比,BP、LGSO、MGSO和HGSO组小鼠肝脏中SOD活力和GSH含量均显著升高(P<0.05),而MDA含量显著下降(P<0.05),且HGSO组与BP组的效果相当,表明葡萄籽油能显著提高小鼠肝细胞的抗氧化能力,且高剂量葡萄籽油(20 mL/kg·d)的增强效果与联苯双酯(150 mg/kg·d)相当。
2.6 葡萄籽油对CCl4损伤小鼠肝脏组织形态的影响
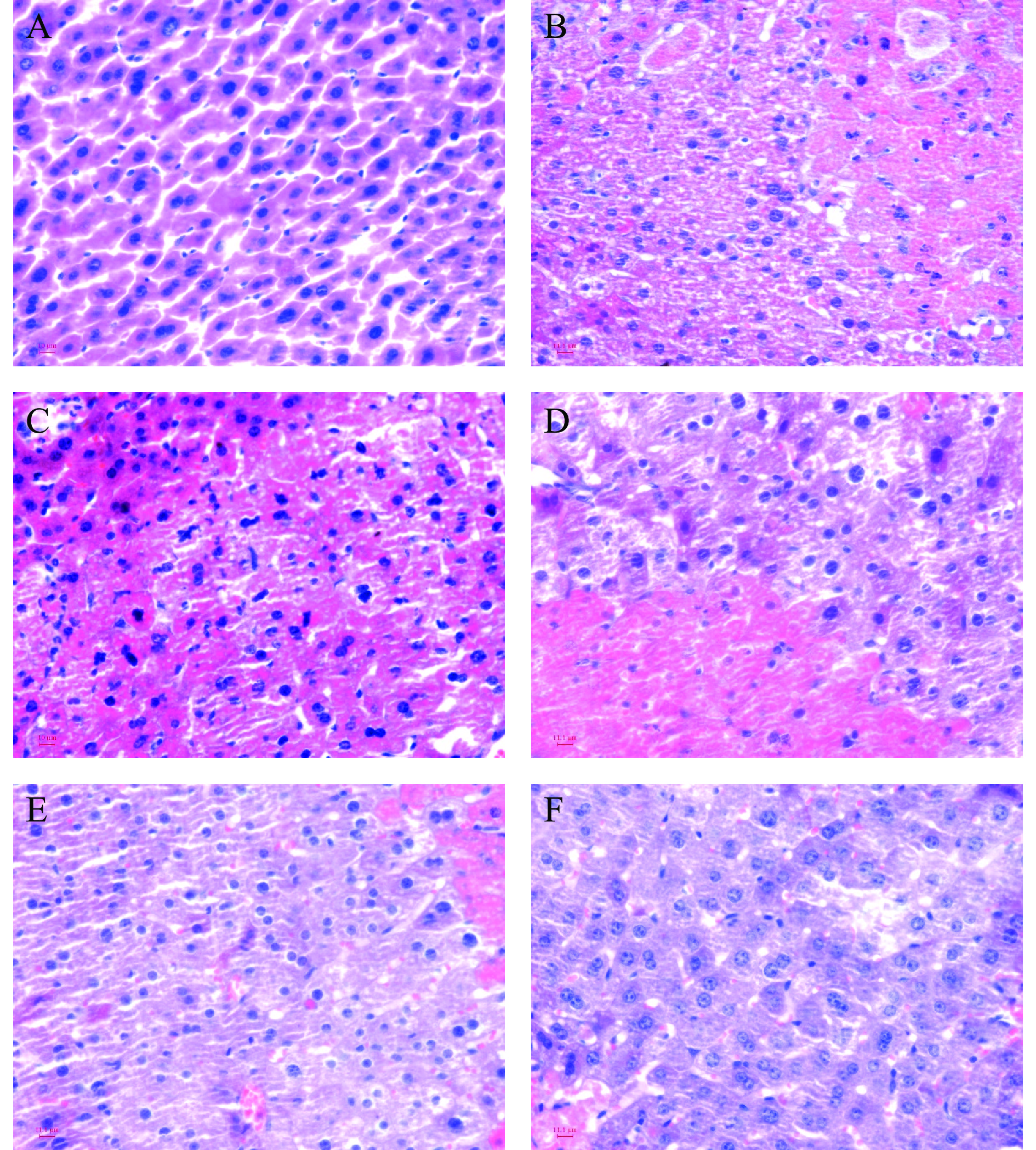
由图3A可知,NC组小鼠肝细胞结构完整,染色均匀,细胞分界清楚,核大且圆,肝窦正常。CCl4组(图3B)小鼠肝细胞发生脂肪变性,大部分肝窦消失,纤维组织增生,肝细胞肿胀,胞浆凝聚,细胞核萎缩,存在大量的细胞坏死和严重的炎性细胞浸润现象,表明建模成功。与CCl4组相比,BP、LGSO、MGSO和HGSO组(图3C、D、E、F)明显改善了小鼠肝细胞脂肪变性、炎性细胞浸润以及肝细胞坏死等现象,而且葡萄籽油剂量越高,改善肝细胞变性、肿胀以及坏死的效果越明显,恢复肝细胞结构、肝窦以及细胞核萎缩的能力越强。
3. 结论
本文以葡萄籽油为研究对象,通过CCl4诱导小鼠急性肝损伤,探究葡萄籽油对急性肝损伤的保护作用。结果表明,葡萄籽油中(10 mL/kg·d)、高(20 mL/kg·d)剂量组可有效抑制血清AST、ALT、LDH活性以及TG、TC浓度的升高(P<0.05),显著提高肝组织中GSH含量、SOD活力并减少MDA含量(P<0.05);同时明显改善CCl4造成的肝细胞变性、肿胀以及坏死等现象。表明葡萄籽油对CCl4诱导的小鼠急性肝损伤具有良好的保护作用,其机理可能与清除自由基、抑制炎症因子以及稳定细胞膜结构有关。因此,葡萄籽油具有成为一款保肝护肝产品的潜力。
-
图 1 葡萄籽油对小鼠脏器指数的影响
注:*表示与CCl4组相比,差异显著(P<0.05);**表示与CCl4组相比,差异极显著(P<0.01);图2同。
Figure 1. Effects of grape seed oil on liver index in mice
表 1 葡萄籽油的脂肪酸组成
Table 1 Fatty acids composition of grape seed oil
成分 百分比(%) 癸酸 3.40 棕榈酸 6.59 棕榈油酸 0.14 硬脂酸 3.54 油酸 23.50 亚油酸 62.04 亚麻酸 0.48 山嵛酸 0.31 饱和脂肪酸 13.84 单不饱和脂肪酸 23.64 多不饱和脂肪酸 62.52 不饱和脂肪酸 86.16 表 2 葡萄籽油对CCl4损伤小鼠体重与食物和水摄入量的影响
Table 2 Effects of grape seed oil on body weight and food and water intake of mice
组别 体重(g) 食物摄入量 饮水量 第1 d 第15 d (g/rat/day) (mL/rat/day) NC 46.11±4.41a 57.58±4.36ab 8.75±1.55a 10.45±0.86ab CCl4 44.22±3.42a 54.34±2.59b 9.07±0.85ab 10.02±2.03b BP 44.88±2.51a 55.91±3.62ab 9.33±0.94a 11.21±1.05a LGSO 44.64±4.25a 58.82±4.41a 8.32±1.26b 10.03±1.23bc MGSO 45.37±5.21a 56.72±4.70ab 6.98±0.81c 9.65±1.36bc HGSO 45.60±3.76a 58.20±3.13a 5.64±1.54d 8.96±0.53c 注:同一列不同字母代表差异显著(P<0.05);表3同。 表 3 葡萄籽油对CCl4损伤小鼠血清指标ALT、AST、LDH、TG和TC的影响
Table 3 Effects of grape seed oil on ALT, AST, LDH, TG and TC levels in serum of mice
组别 AST(U/L) ALT(U/L) LDH(U/L) TG(mmol/L) TC(mmol/L) NC 70.71±21.21c 28.04±2.36d 3978.47±108.35f 2.80±0.36c 6.27±0.27d CCl4 217.70±11.11a 257.48±48.61a 8384.14±497.11a 4.01±0.35a 11.22±0.69a BP 139.40±8.59b 126.32±21.10c 6123.82±141.76e 3.01± 0.34bc 7.62±0.57c LGSO 192.01±32.88a 202.31±28.02ab 7046.24±599.53bc 3.62±0.42ab 9.01±0.49b MGSO 168.69±23.22b 172.08±32.89bc 6703.33±178.52cd 3.33±0.85bc 8.70±1.05bc HGSO 149.53±7.27b 132.27±18.00c 6377.25±372.61de 3.12±0.23bc 7.69±0.73c -
[1] 伍沙沙, 王延, 徐婷, 等. 八月瓜对四氯化碳所致肝损伤小鼠的保护作用[J]. 安徽农业科学,2021,49(4):163−165,174. [WU S S, WANG Y, XU T, et al. Protective effect of Holboellia latifolia Wall. on liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2021,49(4):163−165,174. [2] 夏娜, 陈义磊, 陶海燕, 等. 药桑多糖对四氯化碳所致大鼠肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 食品科学,2015,36(13):247−251. [XIA N, CHEN Y L, TAO H Y, et al. Protective effect of polysaccharides from Morus nigra Linn. fruits on CCl4-induced liver damage in rats[J]. Food Science,2015,36(13):247−251. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201513046 [3] 胡力夫, 苏沛文, 冯微, 等. 大蒜提取物制备及其对四氯化碳诱导小鼠肝损伤的保护作用研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2020. HU L F, SU P W, FEN W, et al. Preparation of garlic extract and its protective effect on liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2020.
[4] 丁杰英, 李嘉斌, 郑妮. 滇黄精多糖对四氯化碳所致肝损伤大鼠氧化因子、凋亡因子的影响[J]. 广西医科大学学报,2020,37(10):1766−1771. [DING J Y, LI J B, ZHENG N. Effects of polysaccharide in Polygonatum kingianum on oxidative and apoptotic factors in rats with carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury[J]. Journal of Guangxi Medical University,2020,37(10):1766−1771. [5] 刘晓东, 温雯静, 赵志军. 多穗柯总黄酮对四氯化碳致小鼠急性肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 医药导报,2020,39(12):1626−1630. [LIU X D, WEN W J, ZHAO Z J. Protective effect of total flavonoids from Lithocarpus polystachyus Rehd. on CCl4-induced acute liver injury in mice[J]. Herald of Medicine,2020,39(12):1626−1630. [6] 黄小强, 丁辉, 刘顺和, 等. 马齿苋多糖对四氯化碳诱导的小鼠急性肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(23):315−319,324. [HUANG X Q, DING H, LIU S H, et al. Protective effect of purslane polysaccharide on CCl4 induced acute liver injury in mice[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(23):315−319,324. [7] FERNANDES L, CASAL S, CRUZ R, et al. Seed oils of ten traditional Portuguese grape varieties with interesting chemical and antioxidant properties[J]. Food Research International,2013,50:161−166. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2012.09.039
[8] 刘霞. 葡萄籽油的提取方法综述[J]. 河西学院学报,2020,36(5):75−79. [LIU X. Review on extraction methods of grape seeds oil[J]. Journal of Hexi University,2020,36(5):75−79. [9] BAIL S, STUEBIGER G, KRIST S, et al. Characterisation of various grape seed oils by volatile compounds, triacylglycerol composition, total phenols and antioxidant capacity[J]. Food Chemistry,2008,108(3):1122−1132. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.11.063
[10] 王灿, 杨晨露, 王华, 等. 葡萄籽油生理功能及应用综述[J]. 中外葡萄与葡萄酒,2020(6):66−71. [WANG C, YANG C L, WANG H, et al. Review on physiological function and application of grape seed oil[J]. Sino-Overseas Grapevine & Wine,2020(6):66−71. [11] 程碧君, 李天娇. 山葡萄籽油的脂肪酸组成研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2019,40(15):73−77. [CHENG B J, LI T J. Study on fatty acid composition of mountain grape seed oil[J]. Food Research and Development,2019,40(15):73−77. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2019.15.012 [12] DUBA K S, FIORI L. Supercritical CO2 extraction of grape seed oil: Effect of process parameters on the extraction kinetics[J]. Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2015,98:33−43. doi: 10.1016/j.supflu.2014.12.021
[13] ANDREA N, CARLA D P. Kinetic models for conventional and ultrasound assistant extraction of polyphenols from defatted fresh and distilled grape marc and its main components skins and seeds[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design,2020,156:1−12. doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2020.01.009
[14] 牛春艳, 孙静, 张健, 等. 超声波法提取葡萄籽甾醇的研究[J]. 广州化工,2016,44(14):65−66,98. [NIU C Y, SUN J, ZHANG J, et al. Optimization of ultrasound technology extraction parameters for phytosterol from grape seed[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry,2016,44(14):65−66,98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2016.14.025 [15] 周旭. 几种油溶性天然抗氧化剂在核桃油、葡萄籽油中的应用研究[J]. 中国油脂,2017,42(3):64−68. [ZOU X. Application of oil soluble natural antioxidants in walnut oil and grape seed oil[J]. China Oils and Fats,2017,42(3):64−68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7969.2017.03.013 [16] CASTILLO J, BENAVENTE-GARCÍA O, LORENTE J, et al. Antioxidant activity and radioprotective effects against chromosomal damage induced in vivo by X-rays of flavan-3-ols (procyanidins) from grape seeds (Vitis vinifera): Comparative study versus other phenolic and organic compounds[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2000,48:1738−1745. doi: 10.1021/jf990665o
[17] KANDASAMY M, NASIMUDDIN S, MALAYAN J, et al. A study on antibacterial effect of grape seed extracts in common clinical and dmg resistant isolates[J]. International Journal of Clinical Trials,2016,3(3):165−168. doi: 10.18203/2349-3259.ijct20162799
[18] ZHAO L, YAGIZ Y, XU C, et a1. Muscadine grape seed oil as a novel source of tocotrienols to reduce adipogenesis and adipocyte inflammation[J]. Food & Function,2015,6(7):2293−2302.
[19] XIA E Q, DENG G F, GUO Y J, et al. Bio1ogical activities of polyphenols from grapes[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2010,11(2):622−646. doi: 10.3390/ijms11020622
[20] AL-AWWADI N A, CAROLINE A, AURÉLIE B, et al. Extracts enriched in different polyphenolic families normalize increased cardiac NADPH oxidase expression while having differential effects on insulin resistance, hypertension, and cardiac hypertrophy in high-fructose-fed rats[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2005,53:151−157. doi: 10.1021/jf048919f
[21] 贾雪峰, 吴洪斌, 金新文, 等. 番茄籽油的提取及其影响因素和生理活性研究进展[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2013(1):203−207. [JIA X F, WU H B, JIN X W, et al. Review on the extraction and physiological activity of tomato seed oils[J]. China Food Additives,2013(1):203−207. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2513.2013.01.031 [22] 吴正平. 金花葵籽不饱和脂肪酸对实验性高脂血症大鼠血脂和肝功能的影响[J]. 中成药,2011,33(7):1245−1247. [WU Z P. Effect of the unsaturated fatty acids from Hibiscus manihot seeds on the blood lipid and liver function in experimental hyperlipidemia rats[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2011,33(7):1245−1247. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2011.07.045 [23] 叶展. 典型膳食油脂胃肠道消化吸收特性及其对肠道健康的影响研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2020. YE Z. Studies on characteristics of typical dietary oil gastrointestinal digestion and absorption, and their influences on gut health[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2020.
[24] 林文海. 芪苓散粗多糖对四氯化碳引起急性肝损伤雏鸡血清中ALT和AST的影响[J]. 福建畜牧兽医,2020,42(2):4−6. [LIN W H. Effect of Qilingsan crude polysaccharide on ALT and AST in serum of chickens with acute liver injury caused by carbon tetrachloride[J]. Fujian Journal of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine,2020,42(2):4−6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4331.2020.02.002 [25] 张扬, 朱彩平, 林杨楠, 等. 平菇多糖对四氯化碳诱导雄性昆明种小鼠肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(23):157−162. [ZHANG Y, ZHU C P, LIN Y N, et al. Hepatoprotective effect of Pleurotus ostreatus polysaccharides on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in male Kunming mice[J]. Food Science,2019,40(23):157−162. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181016-151 [26] 姚秀芬, 程栋, 王承明. 花生粗多糖对四氯化碳及酒精所致小鼠急性肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 食品科学,2011,32(9):261−266. [YAO X F, CHENG D, WANG C M. Hepatoprotective effect of crude peanut polysaccharide on carbon tetrachloride-or alcohol-induced acute liver injury in mice[J]. Food Science,2011,32(9):261−266. [27] 李晨曦. 芝麻籽粒成熟过程成分分析、多糖的提取及其功能性研究[D]. 郑州: 河南工业大学, 2020. LI C X. Component analysis of ripening process of sesame seeds, extraction of polysaccharides and functional study[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan University of Technology, 2020.
[28] WANG H L, SIT W H, TIPOE G L, et al. Differential protective effects of extra virgin olive oil and corn oil in liver injury: A proteomic study[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2015,74:131−138.
[29] SHABAN N Z, EL-KERSH M A, EL-RASHIDY F H, et al. Protective role of Punica granatum (pomegranate) peel and seed oil extracts on diethylnitrosamine and phenobarbital-induced hepatic injury in male rats[J]. Food Chemistry,2013,141(3):1587−1596. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.04.134
[30] 郑岳, 孙伟, 卢坤玲, 等. 龙葵多糖对四氯化碳致小鼠肝损伤的保护作用及其机制[J]. 山东医药,2016,56(8):23−25. [ZHENG Y, SUN W, LU K L, et al. Hepatoprotective effect and mechanism of nightshade polysaccharide on carbon tetrachloride -induced acute liver injury in mice[J]. Shandong Medical Journal,2016,56(8):23−25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2016.08.008 -
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 薛淑贞,梁婷,赵祥民,张家玮,汝应俊,唐德富. 葡萄籽提取物和有机铁对蛋鸡生产性能和蛋品质的影响. 饲料工业. 2025(04): 59-63 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 常安其,毛帅翔,柳广斌. 葡萄残渣的饲料化利用及其在羊生产中的应用研究进展. 中国畜牧兽医. 2024(11): 4842-4850 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 杨辉,胡雅婕. 活性包装薄膜对冷藏圣女果的保鲜效果研究. 农业科技与装备. 2024(05): 61-64 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王建康,郭诗琼,王静,魏丽娜,冯莉,黄峻榕,Fereidoon SHAHIDI. 浆果籽油的生物活性与应用研究进展. 食品与生物技术学报. 2024(10): 32-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 赵明洪,卢天明,刘莉,王启新,杨通,林娜,邱崇,钟田雨,郭秋岩,王继刚. 甘草减轻雷公藤多苷片所致肝损伤的作用机制. 中国实验方剂学杂志. 2023(05): 24-31 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 尚嘉毅,初柏君,赵文君,翟孟婷,王翔宇,马欲明,孙晴,孟祥永,陈吉江,张宇. 市售牛油果油和葡萄籽油品质研究. 中国油脂. 2023(06): 119-125+152 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 盖永强,蓝天婵,李金生,朴美子,李岩. 葡萄籽果冻的工艺. 食品工业. 2022(06): 107-110 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)






 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



