An Electrochemical Aptasensor for Detection of Aflatoxin M1 Based on Reduced Graphene Oxide
-
摘要: 本实验基于还原氧化石墨烯(RGO)构建了一种用于黄曲霉毒素M1(AFM1)检测的电化学适配体传感器。采用红枣汁还原氧化石墨烯(GO)制备RGO,RGO通过滴涂法修饰在玻碳电极(GCE)表面,利用电沉积法将纳米金修饰在RGO/GCE上,AFM1的适配体(Apt)通过Au-S键固定在AuNPs/RGO/GCE电极表面用于靶标AFM1的捕获。当AFM1存在时,AFM1与适配体特异性结合形成AFM1-Apt复合物,该复合物阻碍了电子的传递,导致电化学信号减弱。对RGO的制备条件进行优化,利用差示脉冲伏安法(DPV)监测电极表面的电化学信号,并对不同类型的毒素(黄曲霉毒素B1、黄曲霉毒素B2、赭曲霉毒素A和伏马毒素B1)、不同浓度的AFM1(1×10−7~5×10−4 ng/mL)以及羊乳样品进行检测以确定电化学适配体传感器的特异性、灵敏性和实用性。结果表明,GO:红枣汁=2:1(V:V),pH=11时所制备的RGO的导电能力最强。传感器的电信号与AFM1浓度的对数呈线性关系,检测范围为1×10−7~5×10−4 ng/mL,检测限为3.3×10−5 pg/mL,同时所建立的方法仅对AFM1的检测有响应,而对干扰毒素无响应,说明电化学适配体传感器的特异性良好。使用建立的AFM1电化学适配体传感器对羊奶中的AFM1含量进行测定,发现所构建的传感器具有很高的灵敏性和良好的选择性,有望应用于食品工业中真菌毒素的快速、准确检测当中。Abstract: In this study, a fast and sensitive electrochemical aptasensor for sensitive determination of AFM1 was successfully established based on reduced graphene oxide (RGO). RGO was prepared by reducing graphene oxide with jujube juice. The synthesized RGO was dropped onto the surface of GCE. AuNPs was modified on the surface of the RGO/GCE via electrodepositio. The thiolated aptamer (SH-Apt) of the AFM1 was immobilized on the surface of the AuNPs/RGO/GCE through strong Au-S bond. When AFM1 was present, AFM1 bound specifically to the aptamer forming Apt-AFM1 conjugates. The conjugates hindered electron transfer, causing a decrease of current signal. Differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) was used to monitor electrochemical signal. This electrochemical aptasensor was used to test aflatoxin B1 (AFB1), aflatoxin B2 (AFB2), ochratoxin A (OTA) and fumonisin B1 (FB1) to ensure the electrochemical aptasensor’s specificity. This electrochemical aptasensor was used to detect 1×10−7~5×10−4 ng/mL AFM1 to ensure the electrochemical aptasensor’s sensitivity. And this electrochemical aptasensor was used to detect goat milk to evaluate the practical use of electrochemical aptasensor. The results showed that RGO had the strongest conductivity when GO to jujube juice was 2:1 (V:V) and pH value was about 11. There was a good linear relationship between electrochemical signal and logarithm of AFM1 concentration in the range of 1×10−7~5×10−4 ng/mL with a low detection limit of 3.3×10−5 pg/mL. What’s more, the developed aptasensor was specific to AFM1 and did not respond to interfering mycotoxins, which suggested that the electrochemical aptasensor possessed an excellent selectivity for AFM1 detection. AFM1 electrochemical aptamer sensor was used to determine the content of AFM1 in goat milk. It was found that the sensor had high sensitivity and good selectivity, and it was expected to be applied to the rapid and accurate detection of mycotoxins in food industry.
-
Keywords:
- aflatoxin M1 /
- electrochemical aptasensor /
- reduced graphene oxide
-
黄曲霉毒素(AFS)是由黄曲霉和寄生曲霉产生的一类具有生物活性的次级代谢产物,其具有很高的毒性和很强的致癌能力[1]。在整个黄曲霉毒素家族中,黄曲霉毒素B1(AFB1)毒性最大、致癌能力最强,且在湿热的环境中,玉米、花生、坚果、棉籽等农产品极易被黄曲霉毒素B1污染,即使浓度较低,AFB1也会对人类和动物的健康构成严重的威胁,如免疫失调、黄疸、肝癌、肾癌和乳腺癌等[2-3]。黄曲霉毒素M1(AFM1)是黄曲霉毒素B1的代谢产物,当哺乳动物被喂食AFB1污染的饲料时,AFB1在肝酶细胞色素P450的参与下在肝脏中被羟基化为AFM1,随后分泌到哺乳动物的乳汁中[4-5]。AFM1耐高温,在常规的乳制品灭菌过程中(如巴氏灭菌)是相当稳定的,如果它存在于原料奶中,可能持续存在于供人类食用的最终产品中,考虑到人类,尤其是婴幼儿对乳制品的需求量较大。为了防止食品安全事件的发生,世界各国家对乳及乳制品中AFM1含量都制定了限量标准,中国和美国的限量为0.5 μg/kg,欧盟的规定更加严格为0.05 μg/kg。因此,AFM1检测方法对于防止其危害具有重要意义。
传统的黄曲霉毒素检测方法主要有薄层色谱法(TLC)、高效液相色谱法(HPLC)、液相色谱-串联质谱法(LC-MS)和酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA)。HPLC和LC-MS因其准确性和灵敏度高成为目前最常用的技术,然而这两种方法由于样品前处理复杂、仪器昂贵且需专业人员操作等缺点限制其应用。ELISA虽然操作简单,但是对于真菌毒素的定量检测易出现假阳性。
近年来,电化学适配体传感器因其特异性好、灵敏度高、操作简便等优点在抗生素、重金属、致病菌、毒素等检测中被广泛应用。对于高灵敏的电化学适配体传感器,纳米材料起了至关重要的作用。氧化石墨烯(GO)是一种具有代表性的单原子厚度(0.35~6 nm)、二维(2D)蜂窝晶格和sp2杂化碳晶体的碳纳米材料[6-7]。GO的碳原子层平面上以及边缘区域存在着大量的含氧官能团,如羟基、羧基和环氧基等[8],这些官能团的存在使得GO的化学性质比较活泼,容易与有机物结合反应。因此在使用时常通过还原法去掉其表面的官能团,常用的处理方法是化学还原法,如采用肼/肼衍生物或硼氢化钠作为还原剂,但是这种方法有其缺陷(还原过程中常常涉及到有毒化学物质)。近年来,产生了一个新的化学术语“绿色还原” ,它主要是一种以生物分子、微生物和植物提取物为还原剂的绿色纳米技术,在金属纳米颗粒的合成中得到了广泛的应用。其中涉及到纳米颗粒的生物还原、形成和稳定的化学成分主要有蛋白质、氨基酸、多糖、生物碱、醇类衍生物、多酚化合物、酶、螯合剂和维生素等生物分子[9-10],该技术也适用于氧化石墨烯的生物还原,得到的石墨烯(RGO)比表面积大、电子传递能力强。例如,Weng等[11]用绿茶提取物(绿茶提取物中含有多酚)还原氧化石墨烯。Kuila等[12]研究了胡萝卜根在制备石墨烯中的潜力。Kartick等[13]使用椰子汁建立了氧化石墨烯的绿色还原反应。Mahmoud等[14]通过玫瑰水还原氧化石墨烯,合成了单层还原氧化石墨烯纳米片,所得的RGO很容易分散在水中,悬浮稳定性很好,30 d后未见沉淀,且实验证明该材料在生物传感器的构建中具有良好的潜力。
红枣是鼠李科枣属植物的成熟果实,红枣富含多种营养物质,如氨基酸、维生素、矿物质、有机酸、碳水化合物等[15-17],此外还含有多糖、皂苷、生物碱、黄酮和三萜类等功能成分[18]。研究表明红枣中的酚类化合物(黄酮、花青素、酚酸类化合物)、还原性糖、维生素C等具有较强的抗氧化活性[19-21],抗氧化剂通常具有还原性,而红枣中天然抗氧化剂的存在可能显示出将枣汁作为绿色还原剂的巨大潜力。
本研究构建了一种绿色、简便及快速的电化学适配体传感器用于检测黄曲霉毒素M1。利用原红枣汁还原氧化石墨烯得到还原氧化石墨烯,在玻碳电极(GCE)表面滴涂还原氧化石墨烯,然后在氯金酸溶液中电沉积纳米金,巯基化的适配体通过Au-S键固定在电极表面,当待测液中存在靶标时,靶标与适配体的特异性结合阻碍了电极表面电子的传递,通过监测电极表面的电化学信号变化完成对AFM1的定量检测,该方法对于真菌毒素的快速检测具有一定的参考意义。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
红枣 狗头枣,华润万家超市(西安,陕西);羊乳样品 红星美羚乳业股份有限公司(西安,陕西);黄曲霉毒素B1(AFB1)、黄曲霉毒素B2(AFB1)、黄曲霉毒素M1(AFM1)、赭曲霉毒素A(OTA)、伏马毒素B1(FB1) 美国Sigma公司;三水合氯化金(HAuCl4·3H2O)、6-巯基-1-己醇(MCH)、柠檬酸三钠(99%)、铁氰化钾(k3[Fe(CN)6])、亚铁氰化钾(k4[Fe(CN)6])、石墨粉等试剂 阿拉丁试剂有限公司(上海,中国);高锰酸钾(KMnO4)、浓硫酸(H2SO4)、硝酸钠(NaNO3)、H2O2、甲醇 均为分析纯,天津科密欧化学试剂有限公司;巯基化的适配体 序列如下:AFM1适配体(Apt):3’-CAC CGA GAC ACT GCT AGA GAT TTT CCA CAT TTC TGT GTG TCC-(CH2)6-SH-5’(AFM1的适配体序列参考以下文献[22]),生工生物科技有限公司(上海,中国);实验用水 均为超纯水。
CHI660E电化学工作 上海辰华仪器有限公司;水浴锅 余姚市东方电子仪器厂;pH计 上海精密仪器仪表有限公司;LDZX-30KBS立式压力蒸汽灭菌器 上海申安医疗器械厂;恒温恒湿培养箱 赛福实验仪器公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 原枣汁、发酵枣汁、原枣汁和发酵枣汁中多酚的制备
1.2.1.1 原枣汁
取600 mL的蒸馏水加入到100 g干净且去核的狗头枣中,然后打浆、离心、过滤,得到的枣汁置于4 ℃的冰箱备用。
1.2.1.2 发酵枣汁
取600 mL的蒸馏水加入到100 g干净且去核的狗头枣中,然后打浆、离心、过滤,得到的枣汁于121 ℃的高压蒸汽灭菌锅中,灭菌20 min,枣汁灭完菌后放置于无菌室中,使其冷却至室温。然后按枣汁体积的1%的量接种植物乳杆菌,震荡混匀,在37 ℃发酵24 h,得到的浆液经离心、过滤得到发酵枣汁。
1.2.1.3 原枣汁中多酚的提取
取100 mL原枣汁,然后加入等体积的80%甲醇溶液(V/V),1000 W超声提取30 min,3000 r/min 离心10 min后收集上清液,重复提取3次,合并三次提取液,35 ℃旋转蒸发后用甲醇定容至100 mL,放置于4 ℃冰箱备用。
1.2.1.4 发酵枣汁中多酚的提取
使用100 mL的发酵枣汁,参照1.2.1.3步骤进行提取。
1.2.2 氧化石墨烯(GO)和还原氧化石墨烯(RGO)的制备
以石墨粉为原料,采用Hummers法制备氧化石墨烯(GO)[23-24]。具体步骤如下:在冰浴条件下,将2.0 g石墨粉和1.6 g硝酸钠与67.5 mL的浓硫酸(98%)混合均匀,然后加入9.0 g KMnO4并磁力搅拌40 min,撤去冰浴,继续搅拌48 h之后,缓慢加入560 mL去离子水,98 ℃保持30 min,然后加入适量H2O2(30%)还原残留的氧化剂至悬浮液变为亮黄色,然后8000 r/min离心,去除上清液后,用HCl(5%)溶液和去离子水洗涤、真空干燥即得GO。
将0.5 g制备好的GO分散在1 L的超纯水中超声30 min。然后将红枣汁与GO分散体混合,在80 ℃的水浴中加热8 h。反应后得到RGO用0.45 μm醋酸纤维素膜过滤并用超纯水清洗三次以除去杂质。在不同的pH(2,4.2,5,8,11)下重复合成,其中pH由HCl或NaOH溶液(0.1 mol/L)调节,GO与枣汁的比例(3:1,2:1,1:1,1:2,1:3,V/V)。所得GO和RGO的形貌及元素分布由环境扫描电镜(Quanta 200,FEI公司)进行表征。
1.2.3 电化学适配体传感器的构建
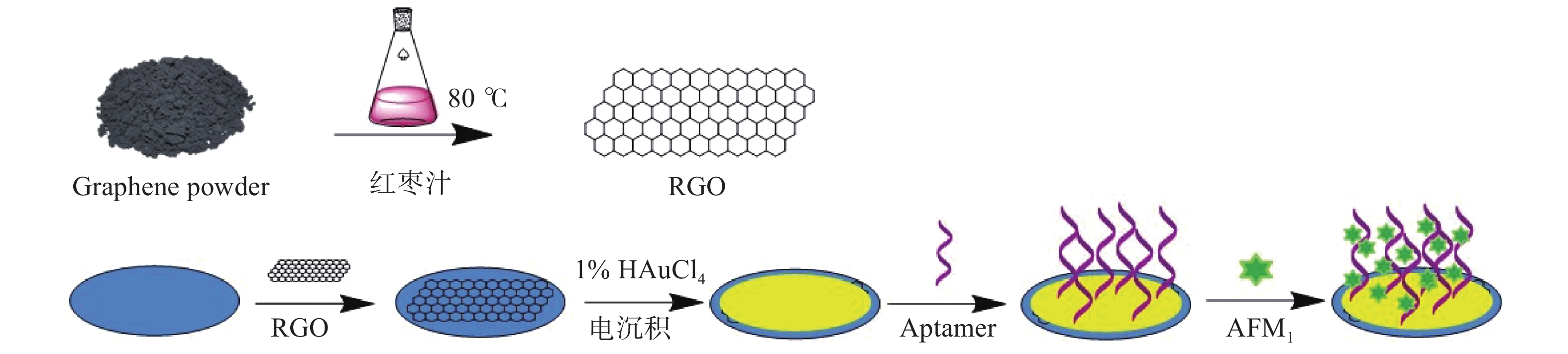
电化学适体传感器的构建步骤如图1所示。在修饰之前,采用0.05 μm的Al2O3粉末对所用的GCE进行打磨处理,然后在乙醇水溶液(1:1)中超声清洗5 min,最后采用氮气将电极表面吹干。在打磨好的电极表面滴涂上事先制备好的RGO(10 µL),用红外灯烘干。之后将电极浸入1% HAuCl4溶液中,采用i-t恒电位法电沉积纳米金,沉积电位为−0.2 V,沉积时间为40 s。随后将GCE电极浸入30 μL的Apt溶液中,室温下孵育40 min后用超纯水冲洗,以除去未结合的适配体,再将10 μL的MCH(2.0 mmoL/L)溶液滴涂于电极表面反应30 min,MCH不仅可以防止非特异性吸附,还能保持适配体的线性结构,有利于靶标与其结合。最后,将电极浸入不同浓度的黄曲霉毒素M1溶液中,于37 ℃下反应40 min后,用超纯水清洗。差分脉冲伏安法(DPV)记录电化学信号,实现对黄曲霉毒素M1的检测。
1.2.4 电化学检测
循环伏安法(CV),方波伏安法(SWV)和差分脉冲伏安法(DPV)测量均在CHI660E电化学工作站上进行,采用传统的三电极系统,GCE为工作电极,Ag/AgCl(饱和KCl溶液)为参比电极,铂丝为对电极。CV和SWV实验在5 mL 5 mmol/L [Fe(CN)6]3−/4−(含0.1 moL/L的KCl)溶液中进。DPV实验在0.01 moL/L的PBS(含0.02 moL/L的KCl,pH7.4)中进行。CV和SWV的扫描范围为-0.2~0.6 V,扫描速率为100 mV/s。DPV的初始电位为−0.2 V,终止电位为0.6 V,振幅为0.05 V,脉冲宽度为0.05 s。
1.2.5 样品的处理
根据文献[25-26]报道的方法对样品进行前处理。首先将25 mL的羊乳和10 mL以9000 r/min离心10 min,去掉上层脂肪,以离心管中部的水相作为样品,然后将2 mL样品与6 mL甲醇混合,所得的混合物超声处理30 mim后,用0.01 moL/L PBS稀释100倍,最后用0.22 μm的一次性过滤器过滤,得到的溶液用加入不同浓度的AFM1,用于实际样品的检测。
1.3 数据处理
每组实验重复三次,结果以平均值±标准差的形式表示,采用Origin 9.0作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 用不同材料还原石墨烯的试验条件的筛选
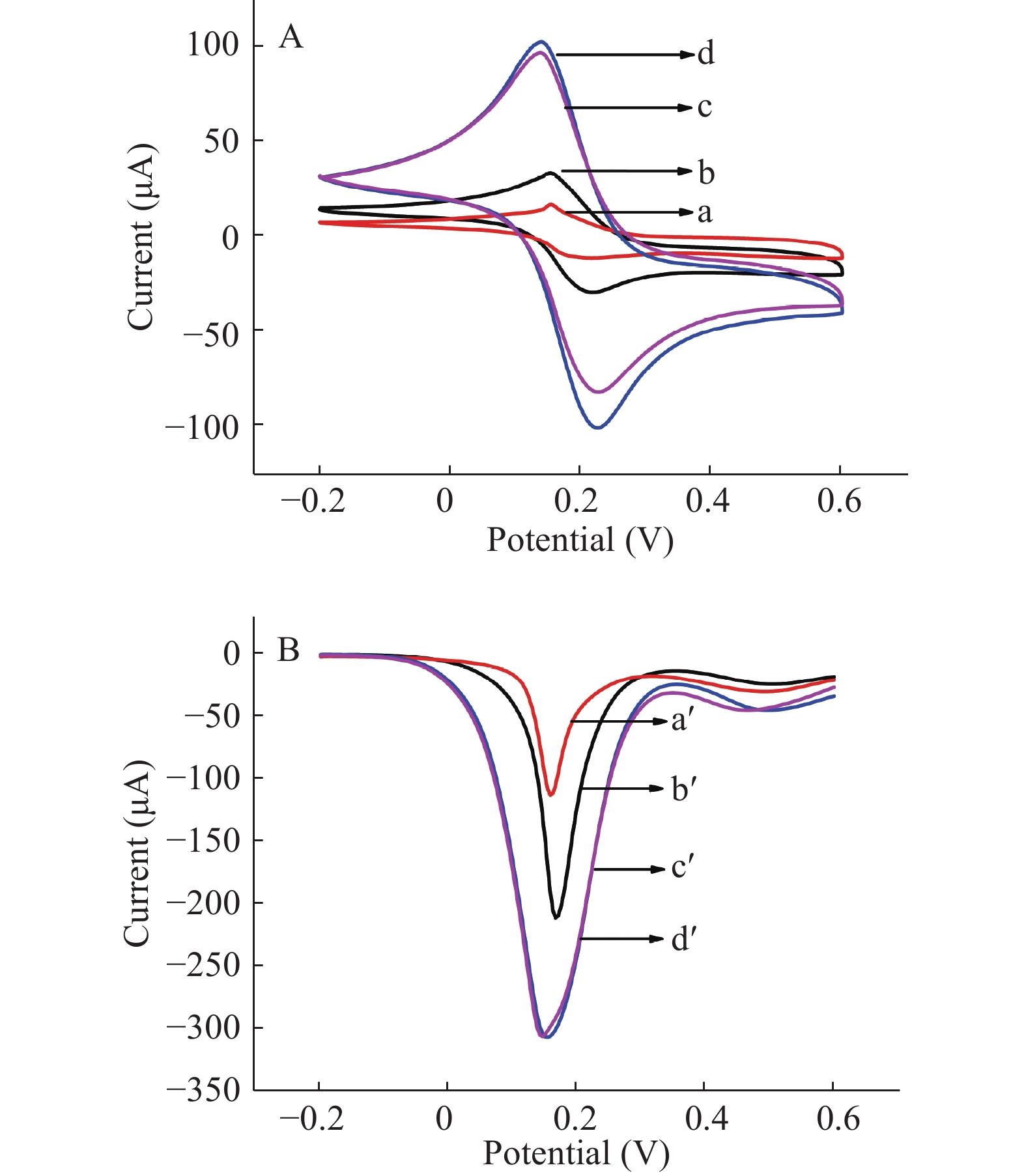
采用原红枣汁、发酵红枣汁、原红枣汁中多酚及发酵红枣汁中多酚分别对氧化石墨烯进行还原,然后将所得的RGO滴涂在金电极上,使用CV法和SWV法测量电极的峰电流值。在CV图中产生了一个氧化峰电位和一个还原峰电位,两峰电位差越大,表明电流值越高,RGO导电性越好。在SWV图中峰电流值绝对值越大,RGO导电性越好。如图2A和图2B所示,发酵红枣汁中的多酚还原GO获得的RGO导电性最差(曲线a,a'),其次是枣汁中的多酚(曲线b,b'),用发酵枣汁和原枣汁还原GO所得的RGO的导电性基本相同,(曲线c,d和c',d')。因此,考虑到实验的简便性,在接下来的实验中使用红枣汁作还原剂还原GO。
2.2 还原氧化石墨烯(RGO)的表征
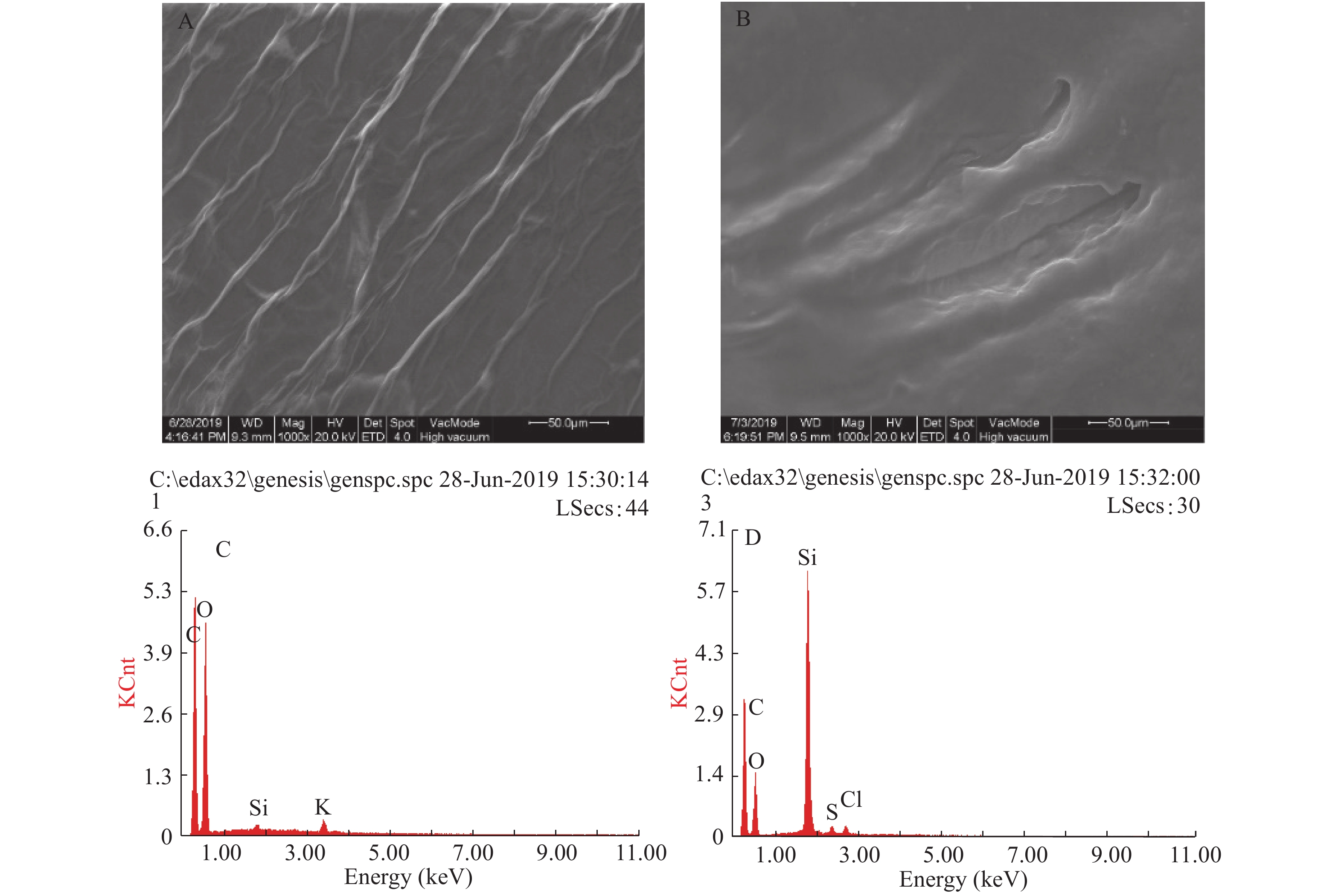
对于合成的GO和RGO,采用扫描电镜表征,从图3A可以看出,GO由彼此紧密相关的单个薄片组成,具有丝质和叶状结构。相比之下,RGO显示出比较平滑的结构(图3B),这可能是由于还原过程中枣汁中的多酚等还原性物质破坏了GO表面的官能团(如羧基、羟基、环氧基团等),从而使其变成比较平滑的结构[27]。
用EDS测定了GO和RGO的元素组成。如图3C所示,合成的氧化石墨烯同时含有C和O峰。Cl、S和K元素是由于合成氧化石墨烯的过程中所添加的试剂所致。在RGO(图3D)中C和O的比例相比GO明显减小,这是在还原的过程中,破坏了氧化石墨烯表面的含氧官能团,这证实了使用红枣汁成功地绿色合成了RGO。另外由于二氧化硅组成作为基底,Si的百分比仍然存在。
2.3 电化学适配体传感器构建过程的电化学表征
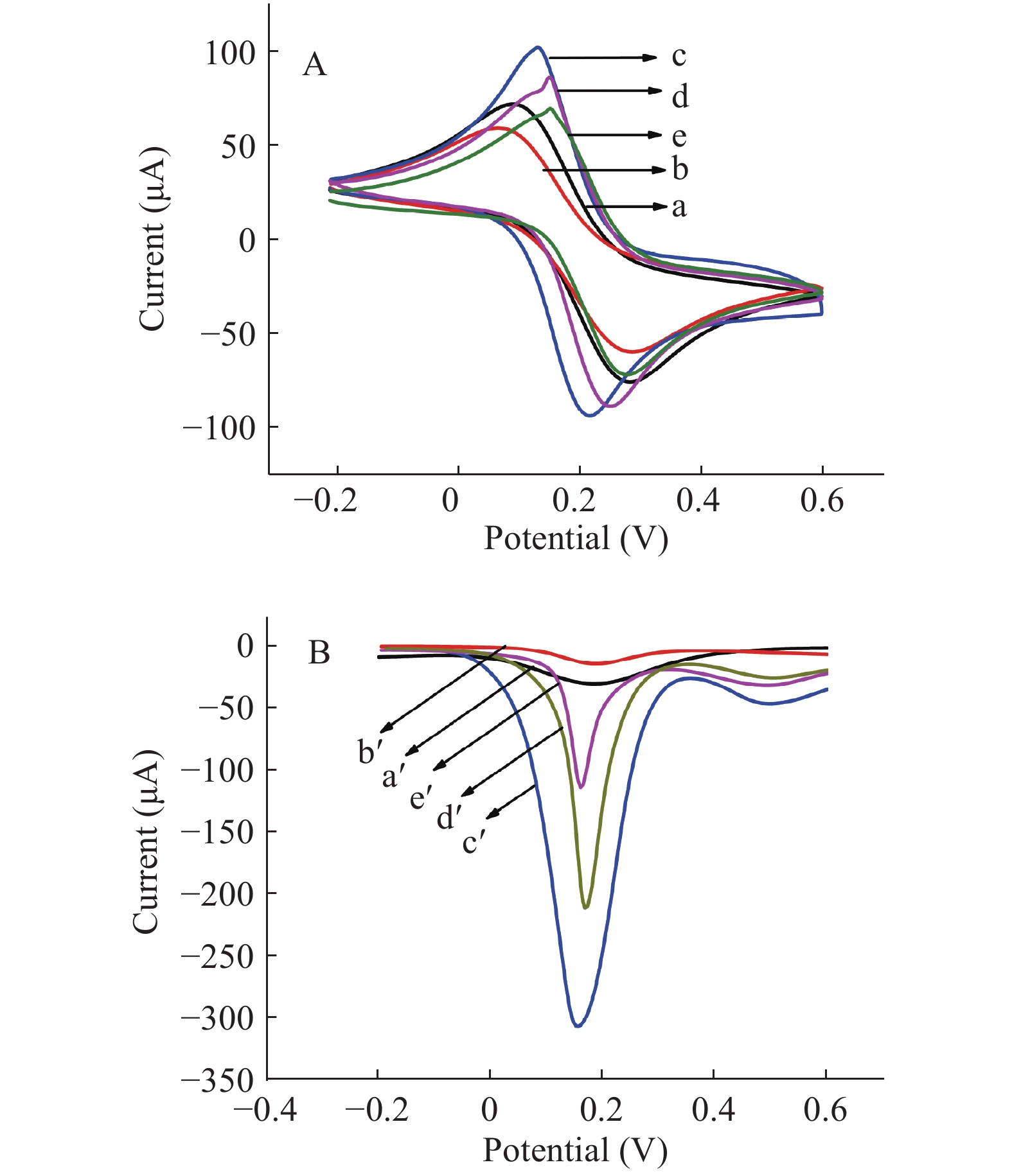
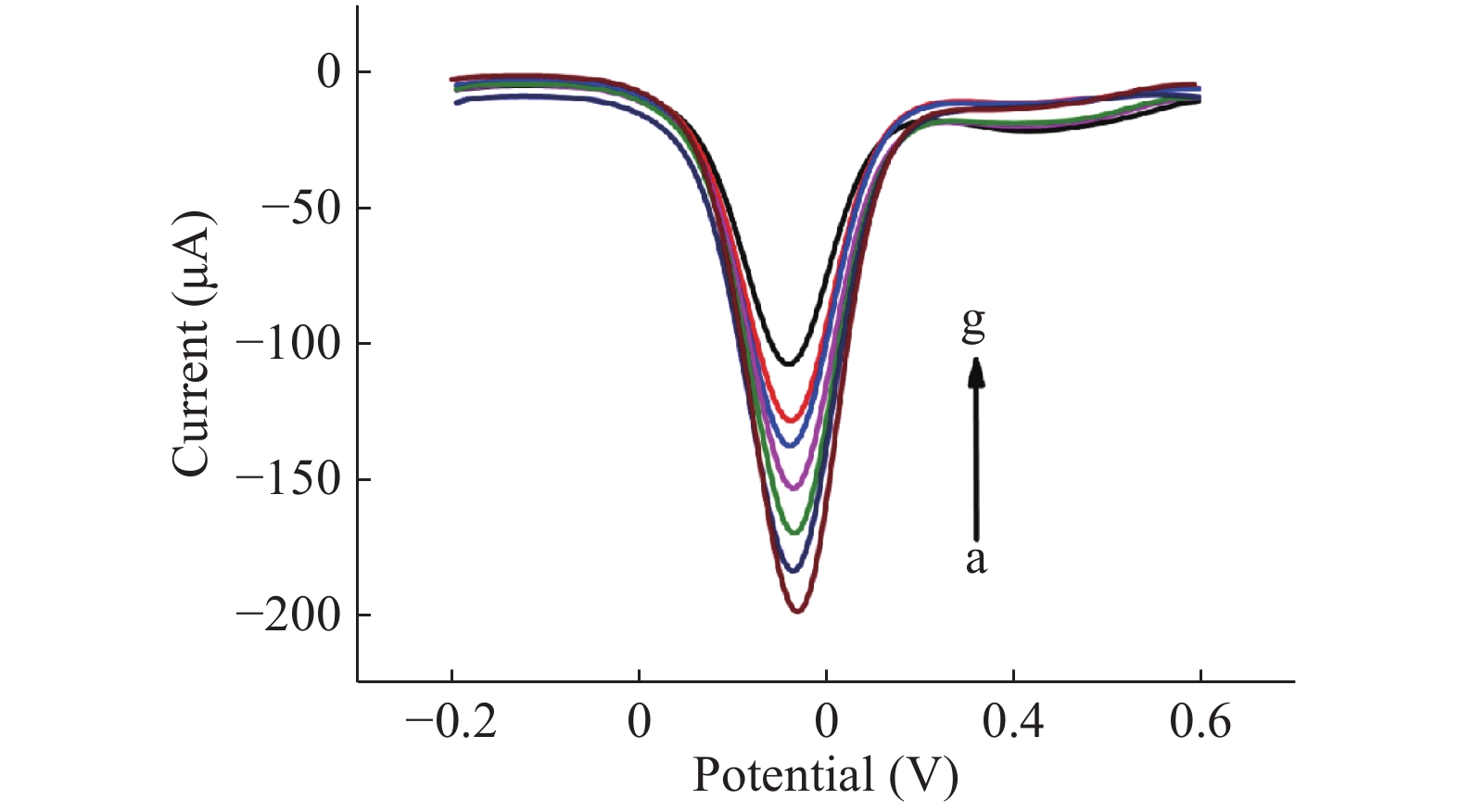
在传感器构建过程中,采用循环伏安法(CV)和方波伏安法(SWV)对电化学适体传感器进行表征。在CV中,电流值越高意味着阻抗越小,由图4A可知,裸GCE呈现一个较低的峰电流(曲线a),说明GCE不利于电子的转移。当在裸GCE上修饰上一层RGO后,峰电流进一步减弱(曲线b)。主要原因是RGO层含有大量带负电荷的COO−,它可以作为静电屏障,阻碍电子的传递,该结果与Gound等[28]报道的结果一致。当在电极上修饰纳米金后,由于AuNPs具有良好的导电性,促进了电子转移,导致峰电流明显增强(曲线c)。当将适配体修饰在电极上,峰电流减弱(曲线d),其原因可能是来自适配体的磷酸骨架所带的负电荷阻止了[Fe(CN)6]3−/4−离子到达电极表面,从而抑制了氧化还原反应的电子传递过程。当目标物AFM1存在时,AFM1与适配体的特异性结合导致空间位阻变大,从而进一步抑制了电子的转移过程。同时也采用SWV法进行验证,结果如图4B所示,由图可知CV法与SWV法所得出的结果一致,进一步证明该传感器构建成功。
2.4 不同条件对RGO导电性的影响
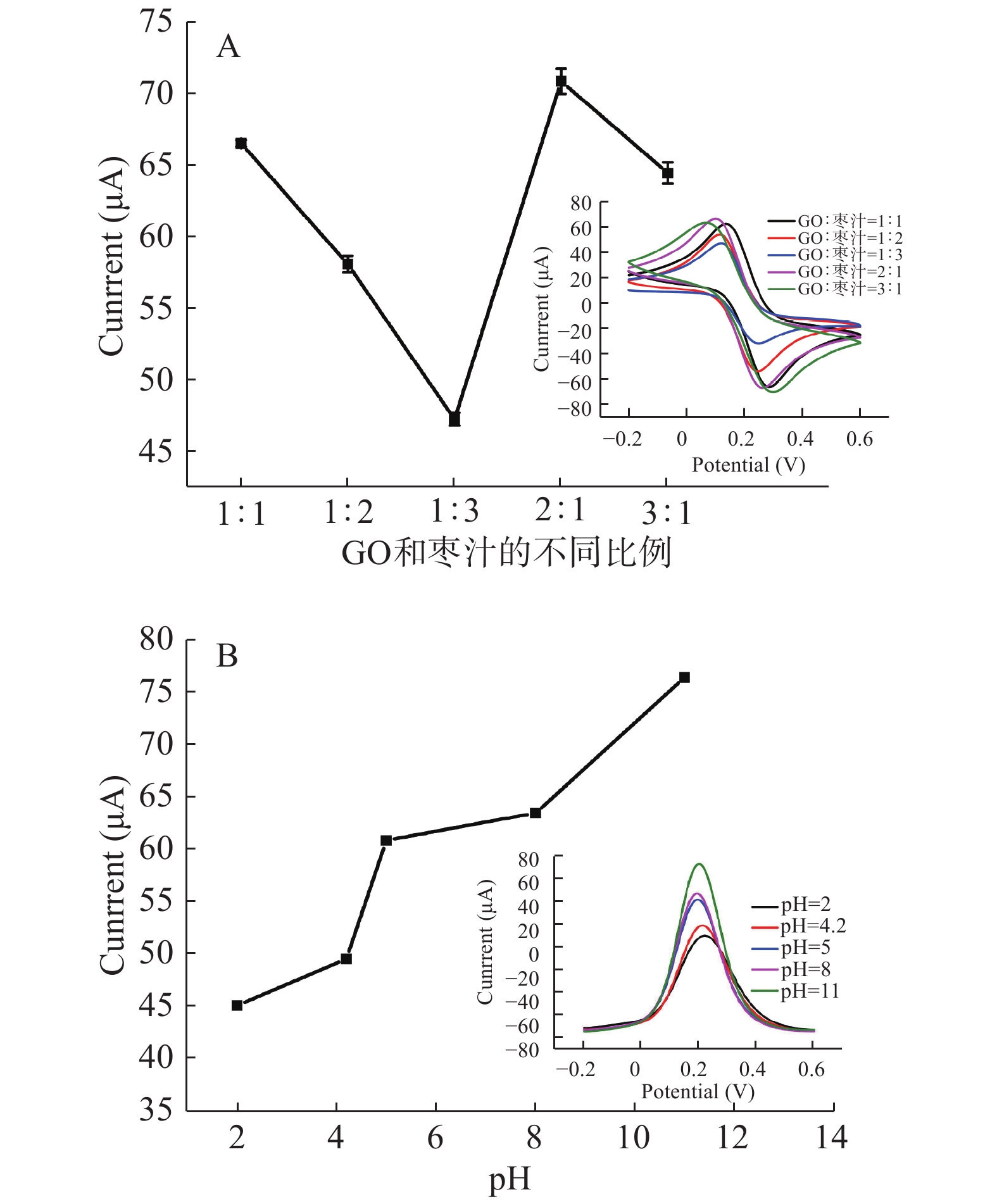
植物的不同部位,如叶子、果皮、根等,会产生不同的生化物质。这些物质主要含有生物分子,包括蛋白质、维生素、氨基酸、糖类、生物碱、果胶、醇类化合物、类黄酮和酶[29-30]。为了获得最佳试验性能,对不同比例的GO和红枣汁对制备的RGO的导电能力进行了测量,结果如图5A所示(采用CV法),当GO和红枣汁的比例是2:1时,所制备的石墨烯的导电能力最强。原因可能是枣汁的用量过少致使GO还原不完全,枣汁用量过多则GO易发生团聚,而且易在溶液中残留。
不同pH对所制备的RGO的导电能力的影响如图5B所示(采用SWV法),随着pH的增加,所制备的RGO的导电性增强,主要原因是GO表面的羟基会电离出氢离子,在碱性环境下氢氧根离子与氢离子作用,有利于GO的分散。而且,在碱性环境下,红枣中多酚中的结合态多酚会向游离态多酚转变,使游离态的酚含量增加,提高了枣汁的还原能力。
2.5 电化学适配体传感器的检测性能
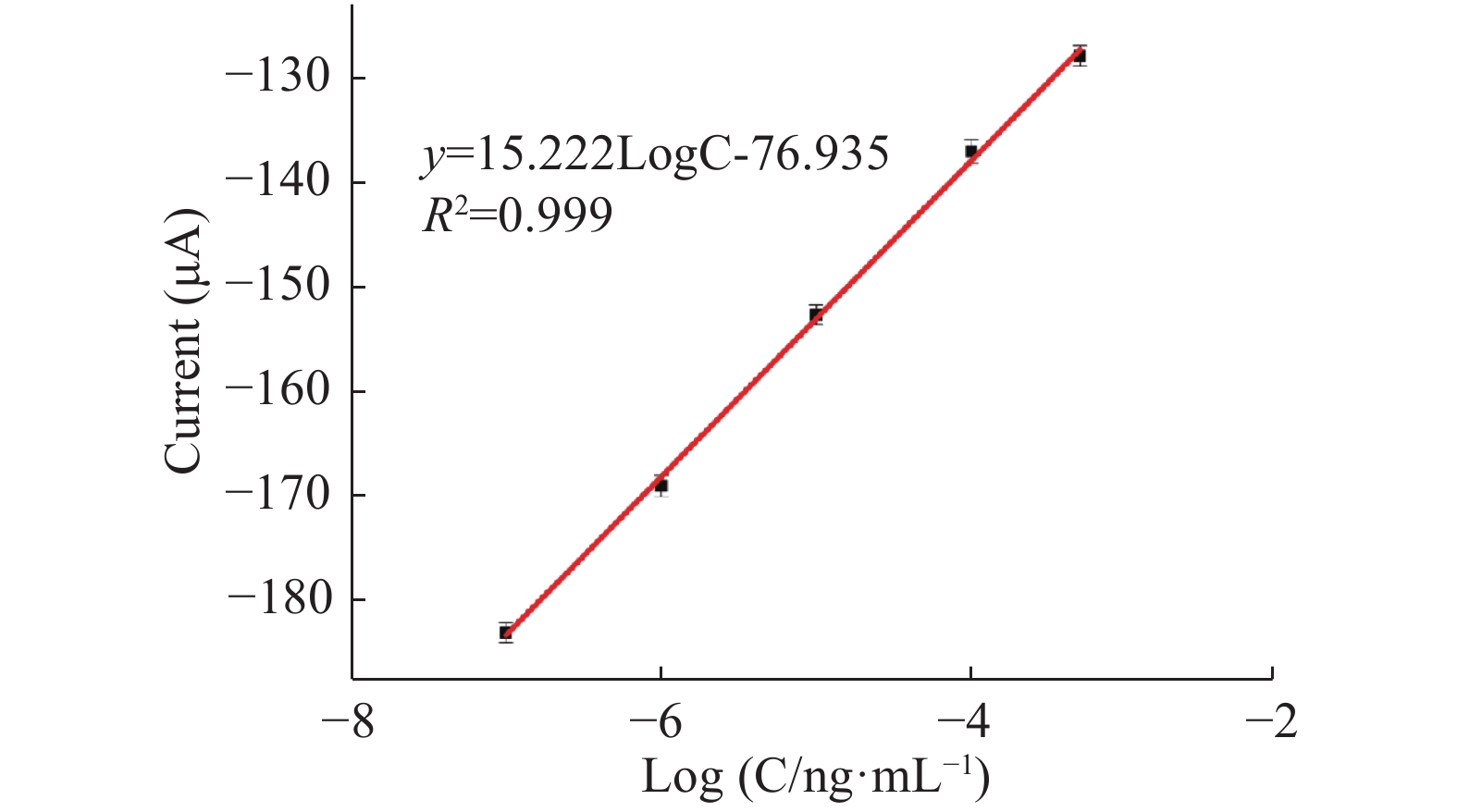
在最佳条件下,将构建好的传感器浸入不同浓度的AFM1,记录DPV电化学信号。从图6可以看出,随着AFM1浓度的增大,DPV电流明显减弱。在AFM1浓度为1×10−7~5×10−4 ng/mL时,传感器DPV曲线的峰电流值与AFM1浓度的对数呈线性关系,线性方程为I(μA)=15.222lgC−76.935,R2=0.999,检测限为3.3×10−5 pg/mL(LOD=3σ/n,σ为空白溶液的标准偏差,n为线性方程的斜率)[31](图7)。与文献中报道的其他方法相比较(表1),此方法具有较低的检测限和较宽的检测范围,尤其相较与HPLC法,此方法不仅样品前处理简单,而且检测限和检测范围完全符合国家要求。
表 1 本研究与报道的检测AFB1的方法的比较Table 1. Comparison of reported methods for the detection of AFB1黄曲霉毒素 检测方法 检测范围(ng/mL) 检测限(ng/mL) 参考文献 AFB1 高效液相色谱法 0.1~20 0.08 [32] 电化学适配体传感器 1×10−8~1×10−6 2×10−9 [33] 电化学适配体传感器 5~200 0.035 [34] 电化学适配体传感器 0.05~20 0.016 [35] 表面增强拉曼适配体传感器 0.0001~100 4×10-4 [36] AFM1 高效液相色谱法 0.05~5 0.02 [37] 电化学适配体传感器 0.002~0.6 9×10-4 [22] 电化学适配体传感器 0.002~0.15 1.15×10−3 [38] 电化学适配体传感器 0.006~0.06 1.98×10−3 [5] 荧光适配体传感器 0.0001~0.5 0.0194×10−3 [39] 电化学适配体传感器 1×10−7~5×10−4 3.3×10−8 本工作 2.6 电化学适配体传感器的特异性和稳定性
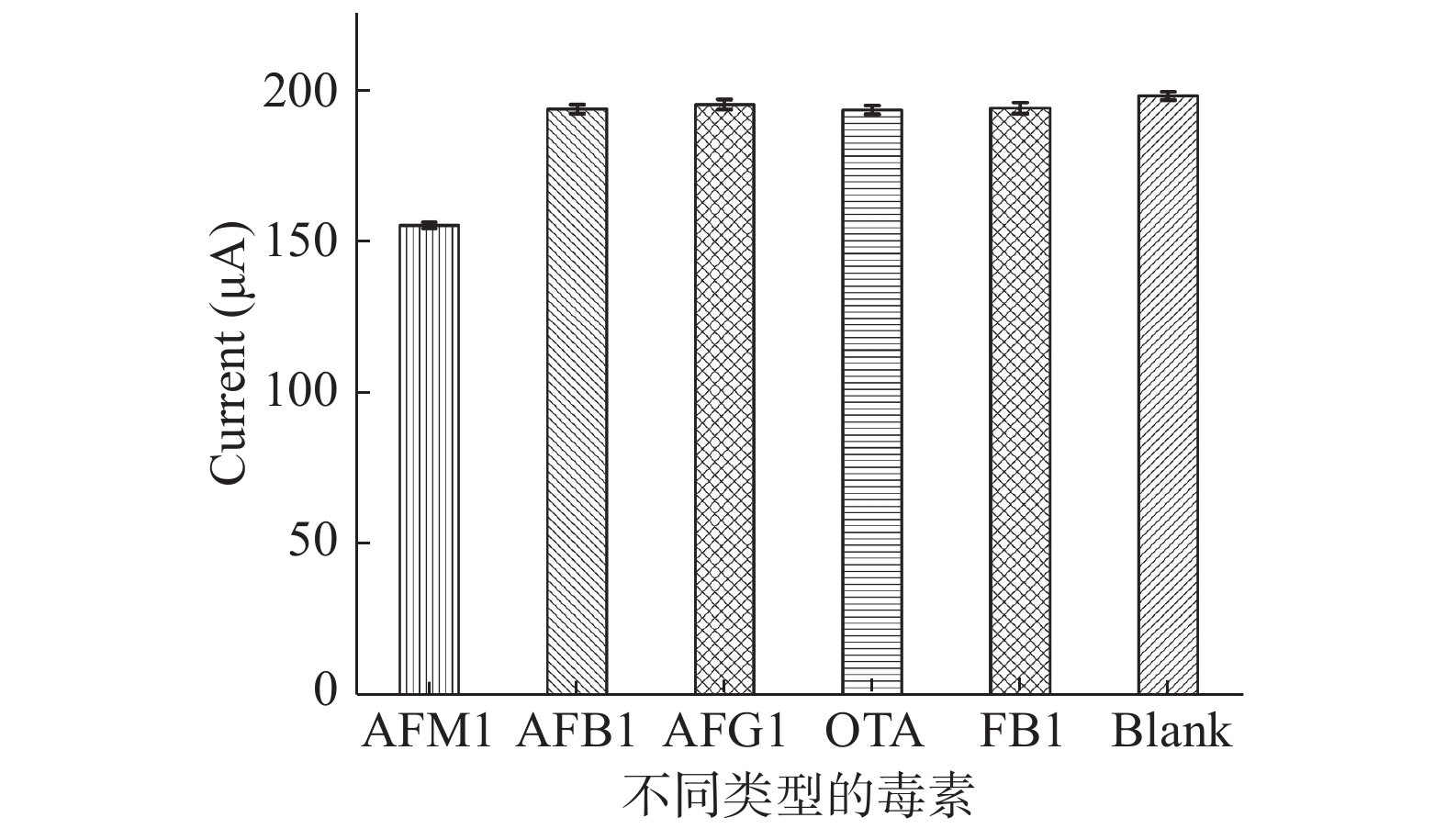
电化学适配体传感器的特异性是一个必须考虑的重要参数,为了测量传感器的特异性,在相同条件下对其它几种干扰物质(AFB1,AFG1,OTA,FB1)进行了检测,结果如图8所示,除了AFM1其他几种干扰物质的峰电流较强且与空白的峰电流基本一致,这表明该适配体传感器的特异性良好。
另外,为了验证传感器的稳定性,在相同条件下制备三根电极,将其在4 ℃条件储存15 d,每3 d测量其峰电流值。结果显示该传感器15 d后的峰电流值为初始值的93.8%。表明该电化学适配体传感器具有良好的稳定性。
2.7 在实际样品中的加标回收实验
为验证构建的AFM1电化学适配体传感器在实际样品中的可行性,在最佳条件下,对羊乳样品中进行了加标回收实验,结果如表2所示,回收率为85.8%~103%,RSD为5.05%~7.87%。由此可以判断该方法具有良好的准确度,在实际样品分析中具有潜在的应用价值。
表 2 羊乳样品中AFM1的检测回收率(n=3)Table 2. Recovery of AFM1 detection in goat milk (n=3)样品 添加量AFM1
(ng/mL)测得量
(ng/mL)回收率
(%)相对标准偏差
(%)1 1×10−4 1.03×10−4 103.0 6.82 2 1×10−5 8.58×10−6 85.8 7.87 3 1×10−6 9.36×10−7 93.6 5.05 3. 讨论与结论
常规的氧化石墨烯还原用肼、硼氢化钠等作为还原剂,都属于化学还原。红枣中的多酚、多糖均具有还原作用,在还原氧化石墨烯方面,两者效果相同,为节省资源和时间,选用原枣汁进行还原,具有“绿色还原”的优势。同时,还原氧化石墨烯作为一种典型的二维碳纳米材料,比表面积大,热稳定性好,将其滴涂在电极表面,可以使更多的AuNPs沉积在电极表面。AuNPs具有大的比表面积,良好的导电性,较好的生物相容性,其不仅可以促进电子转移,还为适配体的固定提供一个完美的平台。其次,AFM1和适配体的特异性识别能力确保了该传感器具有良好的选择性和稳定性。同时,由于该传感器的构建步骤简单,仅需三步,减少了实验过程中的一些系统误差。但是,该方法的局限性在于只能检测到一种毒素。因此,在今后的工作中将考虑通过新的策略同时检测多种毒素。
本研究成功构建了一种用于AFM1检测的电化学适配体传感器。在最佳条件下,该传感器对AFM1的检测范围为1×10−7~5×10−4 ng/mL,检测限为3.3×10−5 pg/mL。同时在羊乳样品中进行了加标回收实验,获得了满意的回收率。总之,该方法操作简便,成本低廉、灵敏度高、特异性好,有望应用于AFM1的定量检测当中,同时对食品工业中其它真菌毒素的检测提供一个良好的借鉴。
-
表 1 本研究与报道的检测AFB1的方法的比较
Table 1 Comparison of reported methods for the detection of AFB1
黄曲霉毒素 检测方法 检测范围(ng/mL) 检测限(ng/mL) 参考文献 AFB1 高效液相色谱法 0.1~20 0.08 [32] 电化学适配体传感器 1×10−8~1×10−6 2×10−9 [33] 电化学适配体传感器 5~200 0.035 [34] 电化学适配体传感器 0.05~20 0.016 [35] 表面增强拉曼适配体传感器 0.0001~100 4×10-4 [36] AFM1 高效液相色谱法 0.05~5 0.02 [37] 电化学适配体传感器 0.002~0.6 9×10-4 [22] 电化学适配体传感器 0.002~0.15 1.15×10−3 [38] 电化学适配体传感器 0.006~0.06 1.98×10−3 [5] 荧光适配体传感器 0.0001~0.5 0.0194×10−3 [39] 电化学适配体传感器 1×10−7~5×10−4 3.3×10−8 本工作 表 2 羊乳样品中AFM1的检测回收率(n=3)
Table 2 Recovery of AFM1 detection in goat milk (n=3)
样品 添加量AFM1
(ng/mL)测得量
(ng/mL)回收率
(%)相对标准偏差
(%)1 1×10−4 1.03×10−4 103.0 6.82 2 1×10−5 8.58×10−6 85.8 7.87 3 1×10−6 9.36×10−7 93.6 5.05 -
[1] Yugender G K, Catanante G L, Hayat A, et al. Disposable and portable electrochemical aptasensor for label free detection of aflatoxin B1 in alcoholic beverages[J]. Sensors and Actuators B Chemical,2015,235:466−473.
[2] Inoue T, Nagatomi Y, Uyama A, et al. Degradation of aflatoxin B1 during the fermentation of alcoholic beverages[J]. Toxins,2013,5(7):1219−1229. doi: 10.3390/toxins5071219
[3] Sugiyama K, Hiraoka H, Sugitakonishi Y. Aflatoxin M1 contamination in raw bulk milk and the presence of aflatoxin B1 in corn supplied to dairy cattle in Japan[J]. Shokuhinseigaku Zasshi Journal of the Food Hygienic Society of Japan,2008,49(5):352−359. doi: 10.3358/shokueishi.49.352
[4] Rodríguez-Blanco M, Ramos A J, Prim M, et al. Usefulness of the analytical control of aflatoxins in feedstuffs for dairy cows for the prevention of aflatoxin M1 in milk[J]. Mycotoxin Research,2019,36:11−22.
[5] Nguyen B H, Tran L D, Do Q P, et al. Label-free detection of aflatoxin M1 with electrochemical Fe3O4/polyaniline-based aptasensor[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: C,2013,33(4):2229−2234. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2013.01.044
[6] Mollarasouli F, Asadpour-Zeynali K, Campuzano S, et al. Non-enzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensor based on graphene quantum dots-chitosan/methylene blue hybrid nanostructures[J]. Electrochimica Acta,2017,246:303−314. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2017.06.003
[7] Linting Z, Ruiyi L, Zaijun L, et al. An immunosensor for ultrasensitive detection of aflatoxin B1 with an enhanced electrochemical performance based on graphene/conducting polymer/gold nanoparticles/the ionic liquid composite film on modified gold electrode with electrodeposition[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical,2012,174:359−365. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2012.06.051
[8] 凌强. 石墨烯负载金属氧化物复合材料的制备及应用研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2014. [9] Agharkar M, Kochrekar S, Hidouri S, et al. Trends in green reduction of graphene oxides, issues and challenges: A review[J]. Materials Research Bulletin,2014,59:323−328. doi: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2014.07.051
[10] Iravani S. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants[J]. Green Chemistry,2011,13(10):2638−2642. doi: 10.1039/c1gc15386b
[11] Weng X, Wu J, Ma L, et al. Impact of synthesis conditions on Pb(II) removal efficiency from aqueous solution by green tea extract reduced graphene oxide[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2019,359(2):976−981.
[12] Kuila T, Bose S, Khanra P, et al. A green approach for the reduction of graphene oxide by wild carrot root[J]. Carbon,2012,50(3):914−921. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2011.09.053
[13] Kartick B, Srivastava S K, Srivastava. Green synthesis of graphene[J]. Journal of Nanoence & Nanotechnology,2013,13(6):4320.
[14] Mahmoud A T, Behzad H. Green-synthesis of reduced graphene oxide nanosheets using rose water and a survey on their characteristics and applications[J]. Rsc Advances,2013,3(32):13365−13370. doi: 10.1039/c3ra40856f
[15] Song J, Bi J, Chen Q, et al. Assessment of sugar content, fatty acids, free amino acids, and volatile profiles in jujube fruits at different ripening stages[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,270(11):344−352.
[16] 王丽玲, 蒲云峰, 李雁琴, 等. 红枣中γ-氨基丁酸的研究进展[J]. 食品科学技术学报,2019,37(6):23−28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-6002.2019.06.004 [17] Wojdy O A, Figiel A, Legua P, et al. Chemical composition, antioxidant capacity, and sensory quality of dried jujube fruits as affected by cultivar and drying method[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,207:170−179. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.03.099
[18] Wang B N, Cao W, Gao H, et al. Simultaneous determination of six phenolic compounds in jujube by lc-ecd[J]. Chromatographia,2010,71(7-8):703−707. doi: 10.1365/s10337-010-1485-1
[19] Pawlowska A M, Camangi F, Bader A, et al. Flavonoids of Zizyphus jujuba L. and Zizyphus spina-christi (L.) willd (rhamnaceae) fruits[J]. Food Chemistry,2009,112(4):858−862. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.06.053
[20] 黄婉玉. 超滤对红枣汁理化性质和抗氧化活性的影响[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2010. [21] 王毕妮. 红枣多酚的种类及抗氧化活性研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2011. [22] Hamid J S, Mohammad R, Mohammad D N, et al. A novel electrochemical aptasensor for detection of aflatoxin M1 based on target-induced immobilization of gold nanoparticles on the surface of electrode[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2018,117:487−492. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2018.06.055
[23] Hummers W S, Offeman R E. Preparation of Graphitic Oxide[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society,1958,208:1334−1339.
[24] Allen M J, Tung V C, Kaner R B. Honeycomb carbon: A review of graphene[J]. Chemical Reviews,2009,110(1):132−145.
[25] Sharma A, Catanante G, Hayat A, et al. Development of structure switching aptamer assay for detection of aflatoxin M1 in milk sample[J]. Talanta,2016,158:35−41. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2016.05.043
[26] Dinçkaya E, Kınık Ö, Sezgintürk M K, et al. Development of an impedimetric aflatoxin m1 biosensor based on a DNA probe and gold nanoparticles[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2011,26(9):3806−3811. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2011.02.038
[27] 陈超, 段芳莉. 氧化石墨烯褶皱行为与结构的分子模拟研究[J]. 物理学报,2020,69(19):147−154. [28] Goud K Y, Hayat A, Catanante G, et al. An electrochemical aptasensor based on functionalized graphene oxide assisted electrocatalytic signal amplification of methylene blue for aflatoxin B1 detection[J]. Electrochimica Acta,2017,244:96−103. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2017.05.089
[29] Park Y, Hong Y N, Weyers A, et al. Polysaccharides and phytochemicals: A natural reservoir for the green synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles[J]. Nanobiotechnology Iet,2012,43(6):69−78.
[30] Iravani S. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants[J]. Green Chemistry,2014(13):2638−2650.
[31] Zeng Y Y, Zheng A X, Wu J, et al. Horseradish peroxidase and aptamer dual-functionalized nanoprobe for the amplification detection of alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase[J] Analytica Chimica Acta, 2015, 899: 100−105.
[32] Alguel I, Kara D. Determination and chemometric evaluation of total aflatoxin, aflatoxin B1, ochratoxin A and heavy metals content in corn flours from Turkey[J]. Food Chemistry,2014,157(15):70−76.
[33] Geleta G S, Zhao Z, Wang Z. A novel reduced graphene oxide/molybdenum disulfide/polyaniline nanocomposite-based electrochemical aptasensor for detection of aflatoxin B1[J]. Analyst,2018,143(7):1644−1649. doi: 10.1039/C7AN02050C
[34] Qian J, Ren C C, Wang C Q, et al. Gold nanoparticles mediated designing of versatile aptasensor for colorimetric/electrochemical dual-channel detection of aflatoxin B1[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2020,166:112443. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112443
[35] Li Y Y, Liu D, Zhu C X, et al. Sensitivity programmable ratiometric electrochemical aptasensor based on signal engineering for the detection of aflatoxin b1 in peanut[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2020,387:122001−122008. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.122001
[36] He H R, Sun D W, Pu H B, et al. Bridging Fe3O4@Au nanoflowers and Au@Ag nanospheres with aptamer for ultrasensitive sers detection of aflatoxin B1[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,324:126832. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126832
[37] 华宇, 高和杨, 聂兴娜, 周旌, 张大伟. 同位素内标-高效液相色谱-串联质谱法检测牛奶及奶粉中黄曲霉毒素M1[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2020,11(6):1978−1984. [38] Istamboulié G, Paniel N, Zara L, et al. Development of an impedimetric aptasensor for the determination of aflatoxin M1 in milk[J]. Talanta,2016,146:464−469. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2015.09.012
[39] Niazi S, Khan I M, Yu Y. et al. et al. A novel fluorescent aptasensor for aflatoxin m1 detection using rolling circle amplification and g-C3N4 as fluorescence quencher[J]. Sensors and Actuators B-Chemical,2020,315:128049. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2020.128049
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 杨帆,黄建辉,陈琛,关书会,刘广鹏,张岩. 乳及乳制品中黄曲霉毒素检测技术研究进展. 乳业科学与技术. 2023(03): 46-51 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 袁京磊. 黄曲霉毒素检测方法的研究进展. 现代食品. 2022(01): 14-16+20 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李凯. 电化学还原石墨烯及其在有机磷电化学传感器中的应用. 电子元器件与信息技术. 2022(04): 50-53+57 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张振宇,王勇. 乳与乳制品中黄曲霉毒素检测研究进展. 中国畜牧兽医. 2022(07): 2820-2830 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 许颖芬. 电化学氧化还原法降解卤代有机污染物的研究进展. 云南化工. 2021(11): 23-25 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



