In Silico Analysis of Novel DPP-IV Inhibitory Peptides Released from Camel Milk Lactoferrin and the Possible Pathways Involved in Diabetes Protection
-
摘要: 目的:结合生物信息学,从驼乳乳铁蛋白(Lactoferrin,LF)中筛选DPP-IV(Dipeptidyl peptidase IV,DPP-IV)抑制肽,并利用网络药理学探讨筛选肽段对糖尿病的潜在作用机制。方法:利用BIOPEP网站模拟酶切LF序列产生多条肽段,结合多肽数据库及分子对接筛选潜在的DPP-IV抑制肽,选择其中四条进行人工合成,验证其DPP-IV抑制活性,通过分子对接分析肽段与DPP-IV分子间相互作用方式,Lineweaver-Burk方法分析肽段抑制模式。选择抑制作用较强的GPQY进行网络药理学分析,预测其对糖尿病的潜在作用机制。采用Swiss Target Prediction和GeneCards数据库挖掘GPQY及糖尿病的作用靶点,String数据库获取蛋白与蛋白互作关系,Cytoscape 3.9.0软件构建PPI网络,DAVID数据库对靶点进行GO与KEGG通路富集分析。结果:筛选验证获得2条DPP-IV抑制GPQY和EACAF,其半抑制浓度(IC50)值分别为348.27±16.11和1024.89±19.67 μmol/L,抑制模式分析表明GPQY为竞争性抑制,EACAF为混合型抑制。分子对接结果显示两条肽段通过氢键、疏水作用和静电作用与DPP-IV结合。由PPI网络筛选到GPQY有STAT3、MMP9、SRC、MAPK1等25个核心作用靶点,KEGG通路富集显示GPQY防治糖尿病通路涉及IL-17信号通路、肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)信号通路、肾素-血管紧张素系统、细胞凋亡等。 结论:驼乳LF是DPP-IV抑制肽的良好来源,由其获得的四肽GPQY可通过多靶点、多通路参与炎症反应,影响细胞增殖分化等多方面防治糖尿病及其并发症。Abstract: Objective: To screen novel dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory peptides from camel milk lactoferrin (LF) combined with bioinformatics. Network pharmacology was used to explore the potential mechanism of action of screened peptides on diabetes. Methods: Multiple peptides were generated by simulated enzymatic cleavage of lactoferrin using the BIOPEP website. Screening target peptides by combining peptide databases and molecular docking. Four of them were selected for solid-phase synthesis to verify their DPP-IV inhibitory activity. Molecular docking was performed to analyze the interaction between the peptide and DPP-IV molecules, and the Lineweaver-Burk method was used to analyze the inhibition mode of the peptide. Then, GPQY with stronger inhibition was selected for network pharmacological analysis to predict its potential mechanism of action on diabetes. Furthermore, the active targets of GPQY and diabetes were mined from the Swiss Target Prediction and Gene Cards databases, and the String database was used to obtain protein-protein interaction relationships. The PPI networks were built by Cytoscape 3.9.0 software, and the DAVID database was exploited for enrichment analysis of GO and KEGG signaling pathways for key targets. Results: Two DPP-IV inhibitory peptides were obtained with semi-inhibitory concentration (IC50) values of 348.27±16.11 and 1024.89±19.67 μmol/L. Inhibition pattern analysis indicated competitive inhibition of GPQY and mixed-type inhibition of EACAF. Molecular docking results revealed two peptides bound to the active pocket of DPP-IV through hydrogen bonding, hydrophobic interactions and electrostatic interactions. From the PPI network analysis, GPQY had 25 core-acting targets, including STAT3, MMP9, SRC, and MAPK1. The enrichment results were based on KEGG pathways, which showed that GPQY was involved in the IL-17 signaling pathway, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) signaling pathway, renin-angiotensin system, apoptosis, etc. Conclusion: Camel milk lactoferrin is a good source of DPP-IV inhibitor peptide. GPQY could prevent diabetes and its complications through multiple targets and pathways involved in the inflammatory response and cell proliferation and differentiation.
-
糖尿病(Diabetes Mellitus,DM)是一种以持续性高血糖为特征的代谢性疾病,随着时间推进会导致心血管疾病、神经病变、肾功能衰竭等一系列并发症,主要表现为I型糖尿病(T1MD),II型糖尿病(T2MD)和妊娠型糖尿病(GDM)三种类型,其中II型糖尿病患者占到90% 以上[1]。T2DM显著的病理生理学特征为胰岛素调控葡萄糖代谢能力的下降(胰岛素抵抗)伴胰岛β细胞功能缺陷所导致的胰岛素分泌减少。二肽基肽酶4(Dipeptidyl peptidase IV,DPP-IV)是II型糖尿病代谢中一种关键酶,广泛表达于大多数组织和细胞中[2]。DPP-IV在体内会迅速降解胰高血糖素样肽-1(glucagon-like peptide-1, GLP-1)从而影响胰岛素分泌和血糖代谢,因此DPP-IV也是糖尿病治疗的一个关键因子[3-4],DPP-IV抑制剂成为糖尿病药物开发的一个重要方向。目前在全球上市的DPP-IV抑制剂超过10种,常见的有西格列汀(sitagliptin)、维格列汀(vildagliptin)、沙格列汀(saxagliptin)等,但这类药物都是人工合成药物,常会引发比较严重的副反应,如头疼、腹泻、尿路感染、肾脏负担等[5-6]。相比之下,食源性DPP-IV抑制肽因稳定性好,副作用小等优点而受到关注。
乳源是生物活性肽的广泛来源,驼乳是一种营养很高的小品种乳,富含多种功能性因子,其在辅助治疗糖尿病方面显示出巨大的潜力[7-8]。驼乳源DPP-IV抑制肽的研究相对较少,2017年Nongonierma首次报道了驼乳蛋白水解物对DPP-IV抑制作用,从中鉴定到两条新型DPP-IV抑制肽LPVPQ和WK,研究结果表明,相比牛乳,驼乳蛋白水解物具有更高的DPP-IV抑制率[9]。LF是驼乳中重要的功能性因子之一,有文献报道了LF和糖尿病及其并发症之间的潜在联系,例如胰岛素抵抗、炎症和肥胖症[10-12]。Khan等[12]首次在分子和细胞水平上分析驼乳LF和牛乳LF对肝癌细胞(HepG2)和人胚胎肾细胞(HEK293)中胰岛素受体活性和药理作用,表明LF是驼乳中抗糖尿病特性背后的潜在生物活性蛋白。Gamal Badr等[13]也发现驼乳源LF可提高II型糖尿病患者的胰岛素敏感性,并具有抗炎和免疫调节作用。由此推测驼乳LF可能是DPP-IV抑制肽的潜在来源,但目前关于驼乳LF源DPP-IV抑制肽的研究非常有限。
食源性DPP-IV抑制肽已成为国内外研究热点,然而常规方法筛查DPP-IV抑制肽耗时费力,随着科技手段的进步,模拟酶切和分子对接等生物信息学工具已被广泛应用于生物活性肽制备及筛选中。此外,网络药理学也作为一种有效工具应用于活性成分与疾病间作用机制的研究中[14]。基于此,本研究以驼乳LF为研究对象,模拟酶切产生多条肽段,结合文献报道,数据库比对及分子对接筛选DPP-IV抑制肽,选择其中4条进行人工合成验证其DPP-IV抑制率。随后,采用分子动力学和分子对接进一步揭示肽段与DPP-IV的作用机理。最后,选择DPP-IV抑制率较强的肽段进行网络药理学分析,进一步探究肽段防治糖尿病的潜在作用靶点及通路,为驼乳源DPP-IV抑制剂的研发提供研究基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
DPP-IV、Gly-Pro-pNA Sigma-Aldrich公司;Tris-HCl缓冲液 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;醋酸-醋酸钠缓冲液 北京谱析科技有限公司;合成肽段EACAF、GPQY、IWKL、FGR (纯度≥98%)生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司。
VictorX3酶标仪 美国珀金埃尔默股份有限公司;DRP-9162电热恒温培养箱 上海森信实验仪器有限公司;XP6电子天平 梅特勒-托利多公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 模拟酶切
驼乳LF序列由UniProt数据库获取(entry ID:Q9TUM0),其氨基酸序列长度为708。选择三组不同类型蛋白酶进行模拟酶切,包括三种胃肠消化酶胰蛋白酶、胰凝乳蛋白酶和胃蛋白酶,一种植物蛋白酶木瓜蛋白酶以及碱性蛋白酶和蛋白酶K两种微生物蛋白酶。胰蛋白酶、胃蛋白酶和碱性蛋白酶是文献中制备DPP-IV抑制肽常用的三种蛋白酶,此外还选择了胰凝乳蛋白酶、木瓜蛋白酶和蛋白酶K三种水解能力较强的蛋白酶水解驼乳LF,以产生更多新型肽段。驼乳LF序列在BIOPEP网站(https://biochemia.uwm.edu.pl/biopep-uwm/)进行模拟酶切。
1.2.2 DPP-IV抑制肽的筛选
1.2.2.1 Peptide Ranker评分
将1.2.1中所得肽段在Peptide Ranker(http://bioware.ucd.ie/~compass/biowareweb/)网站中进行生物活性可能性分析,肽段评分越高,则其具有生物活性的可能性越大。选择生物活性评分≥0.5的肽段作为潜在的目标活性肽[15],与多肽数据库BIOPEP、PeptideDB、SwePep、EROP Moscow、PepBank和文献中的生物活性肽进行比对,筛选出未报道的肽段进行下一步分析。
1.2.2.2 分子对接筛选
应用Discovery Studio2019软件中的Dock Ligands(CDOCKER)工具对肽段与DPP-IV(PDB ID:4A5S)进行半柔性分子对接,按照分子对接步骤设定相关参数,以-CDOCKER_ENERGY和-CDOCKER_INTERACTION_ENERGY为评分指标,筛选目标活性肽。“-CDOCKER_INTERACTION_ENERGY”值是受体与配体相互作用力的评分,“-CDOCKER_ENERGY”值是“-CDOCKER_INTERACTION_ENERGY”与分子内能的和,“-CDOCKER_ENERGY”值相对越高,表示配体和受体结合越紧密[15]。
1.2.3 目标肽段人工合成
采用固相法对筛选所得肽段进行人工合成(纯度≥98%),通过LC-MS和HPLC法确定肽段分子量和纯度(委托上海生工公司完成)。
1.2.4 DPP-IV抑制率测定
参考张颖的方法[16],采用发色底物法测定DPP-IV抑制率。所有试剂和样品均在Tris-HCl(100 mmol/L,pH8.0)缓冲液中稀释。将25 μL样品与25 μL底物(1.6 mmol/L)加入96孔酶标板,在37 ℃下孵育10 min,加入50 μL DPP-IV(8 U/L),于37 ℃反应60 min后加入100 μL醋酸钠缓冲液(1 mol/L,pH4.0)终止反应,使用酶标仪在405 nm下检测吸光值。测定不同浓度下样品的抑制率,并绘制样品浓度-抑制率函数图,确定IC50值(DPP-IV抑制率达到50%时的样品浓度)。
DPP-IV抑制率(%)=(1−(C−DA−B))×100 式中:A阴性对照,以Tris-HCl代替样品;B阴性空白对照,以Tris-HCl代替DPP-IV;C样品在405 nm处的吸光度;D样品空白对照,以Tris-HCl代替DPP-IV。
1.2.5 肽段作用机理分析
1.2.5.1 肽段抑制模式分析
采用Lineweaver-Burk方法研究了不同样品的抑制模式。底物浓度范围为0.1~2.0 mmol/L(最终浓度),样品浓度取IC50值的1/8和1/16,以不含抑制肽的样品作为阴性对照,于37 °C反应30 min后,使用酶标仪测定405 nm处的吸光值[3]。
1.2.5.2 分子对接探究肽段与DPP-IV作用位点与作用方式
利用Discovery Studio2019软件receptor-ligand Interactions模块中的Ligand Interactions (Interaction options),分析肽段与DPP-IV作用位点和相互作用方式,包括氢键、静电作用和疏水相互作用,并在analyze ligand poses条目下分析详细作用残基。
1.2.6 网络药理学分析
1.2.6.1 肽段对糖尿病潜在作用靶点预测
利用Swiss Target Prediction网站(http://www.swisstargetprediction.ch/)预测筛选所得肽段在体内的潜在作用目标。由Genecards数据库(https://www.genecards.org/)获取糖尿病相关基因靶点,关键词设定为“diabetes”。绘制维恩图(http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/Venn/),获取所选肽段与糖尿病作用靶点的交集。
1.2.6.2 PPI网络构建
将肽段对糖尿病的潜在作用靶点上传到STRING网站(https://cn.string-db.org/),属性选择“Homo sapiens”,置信度>0.7,获得蛋白与蛋白相互作用网络(Protein-protein interactions,PPI)。使用Cytoscape3.9.0软件修饰网络,CytoNCA插件计算网络拓扑参数,度值(Degree)用于评价节点在网络中的重要性,度值越大,说明节点在网络中越重要。
1.2.6.3 GO分析及KEGG通路富集分析
通过GO分析及KEGG通路富集分析进一步研究肽段对糖尿病保护作用的各种机制。将所选肽段的抗糖尿病作用靶点导入DAVID(https://david.nci fcrf.gov/home.jsp)平台,限定物种为“Homo sapiens”,P<0.05[17-18]。保存富集结果,利用微生信平台(http://www.bioinformatics.com.cn/)进行可视化分析。
1.3 数据处理
使用Excel2016处理DPP-IV活性验证数据,实验重复3次,结果表示为平均值±标准差。使用Origin2018软件绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 驼乳LF模拟酶切
BIOPEP平台模拟酶切驼乳LF序列生成肽段,利用Peptide Ranker网站对肽段进行生物活性可能性评分,从中筛选活性评分大于0.5的肽段,结果如表1。DPP-IV抑制肽的构效关系研究表明,大多数DPP-IV抑制肽结构中具有脯氨酸(Pro)和丙氨酸(Ala),尤其是肽段N端第二位是Pro和Ala时,一般具有DPP-IV抑制作用,此外疏水性氨基酸(Ala、Val、Ile、Leu、Met、Phe、Tyr 或 Trp)存在可增强与DPP-IV热点处残基的相互作用,从而使肽段抑制作用增强[19-21]。根据DPP-IV抑制肽的特征,在评分大于0.5的肽段中筛选符合DPP-IV抑制特征的肽段进行下一步分析。
表 1 模拟酶切结果Table 1. Simulation of digestion results蛋白酶种类 模拟酶解产
生肽段数目去除重复肽
段后数目特有肽
段数Peptide ranker
得分>0.5胰蛋白酶Trypsin
(EC3.4.21.4)75 73 72 23(32%) 胃蛋白酶pepsinpH1.3
(EC3.4.23.1)82 77 26 32(42%) 胰凝乳蛋白酶
Chymotrypsin
(EC3.4.21.1)125 110 49 33(30%) 木瓜蛋白酶papain
(EC3.4.22.2)186 144 114 35(24%) 碱性蛋白酶Subtilisin
(3.4.2.34)167 148 93 45(30%) 蛋白酶K proteinase K
(EC3.4.21.67)154 133 85 38(29%) 2.2 DPP-IV抑制肽的筛选
通过Peptide Ranker及DPP-IV抑制特征初步选定30条短肽(表2),将30条肽段在BIOPEP-UWM和PeptideDB等多肽数据库进行比对,有8条为已报道过的活性肽,其中7条是DPP-IV抑制肽。
表 2 筛选肽段Peptide ranker评分Table 2. Peptide ranker score for screening peptides序号 肽段 Peptide ranker评分 序号 肽段 Peptide ranker评分 1 GF1 0.994712 16 SGF 0.947492 2 RF1 0.986556 17 GDF 0.941533 3 AF1 0.973259 18 IPM1 0.845096 4 IW 0.944175 19 DAF 0.804969 5 CP 0.943255 20 CPN 0.780467 6 DW 0.933025 21 APG1 0.745179 7 GP1 0.905487 22 SPL 0.665423 8 CL 0.879917 23 PAL 0.631952 9 VW 0.802223 24 GAL 0.594888 10 AP1 0.626856 25 DPY 0.586633 11 SP1 0.514894 26 IWKL 0.733588 12 CRF 0.98469 27 GPQY 0.643377 13 RPF 0.977766 28 PPEPL 0.684494 14 FGR 0.967011 29 DPYKL 0.579245 15 GAF 0.954769 30 EACAF 0.634993 注:1为已报道的肽。 为进一步筛选DPP-IV抑制肽,使用Discovery Studio2019软件对22条肽段进行半柔性分子对接。IPI为迄今为止发现的抑制作用最强的DPP-IV抑制肽,以IPI作为对照,最佳对接姿势打分结果见表3。对接结果显示IPI “-CDOCKER_ENERGY”打分60.1427 kcal/mol,这与Wang等报道IPI打分结果(66.8307 kcal/mol)相近[22]。这22条肽段中有18条肽段-CDOCKER_ENERGY打分高于IPI,其中EACAF打分最高为102.042 kcal/mol,排名前五的肽段中,DAF与FGR两者“-CDOCKER_ENERGY”打分相近,但GAF“-CDOCKER_INTERACTION_ENERGY”评分低于IPI,因此在排名靠前的肽段中选择EACAF、IWKL、GPQY和FGR四条肽段进行人工合成。
表 3 分子对接打分表Table 3. Molecular docking scoring序号 肽段 -CDOCKER_ENERGY -CDOCKER_INTERACTION_
ENERGY1 EACAF 102.042 68.9447 2 IWKL 88.9743 79.7752 3 GPQY 84.6352 71.8239 4 DAF 81.4763 59.859 5 FGR 81.046 75.6303 6 GDF 80.4749 64.0784 7 DPYKL 75.5242 76.8073 8 GAF 74.7882 64.8822 9 GAL 73.5947 61.7327 10 SGF 73.5308 63.686 11 CRF 72.4341 68.7239 12 DPY 71.4961 63.9571 13 DW 68.2476 53.2253 14 IW 66.5734 63.7061 15 CPN 63.3028 65.4616 16 RPF 61.2769 71.9084 17 SPL 60.3406 67.1524 18 VW 60.2456 55.2833 19 IPI 60.1427 62.6373 20 PAL 57.1327 65.2958 21 PPEPL 54.4414 72.4935 22 CP 48.4354 53.0389 2.3 肽段抑制活性验证
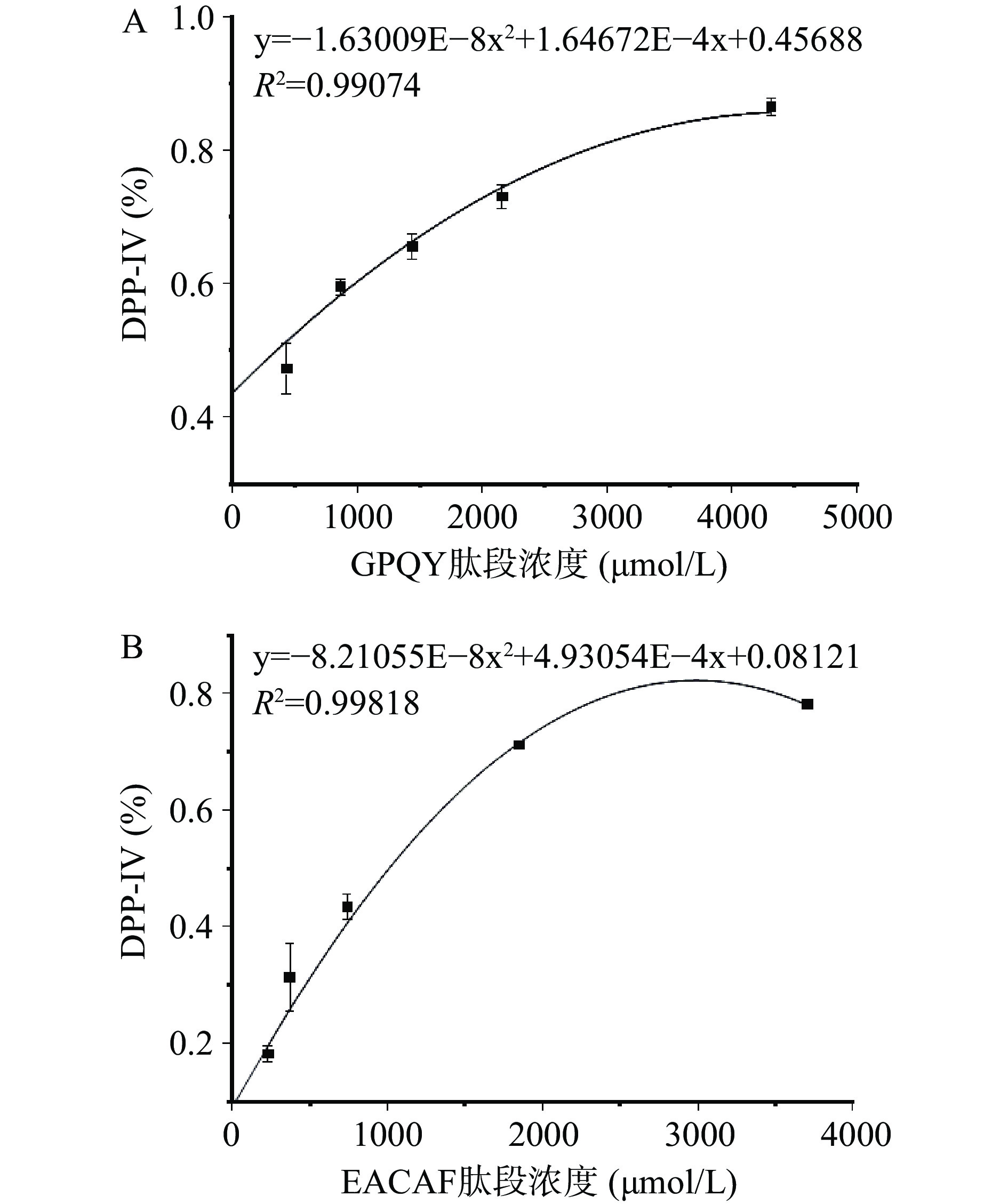
采用固相合成法对EACAF、GPQY、IWKL和FGR四条肽段进行合成,肽段的纯度和分子量由HPLC和LC-MS分析验证,结果如图1所示,四条肽段的纯度都大于98%,分子量大小分别为539.60、463.48、558.70和378.42。测定肽段IC50值判断肽段对DPP-IV抑制效果,IC50值越低,说明肽段对DPP-IV抑制效果越好。四条肽段中GPQY和EACAF对DPP-IV具有明显的抑制作用,根据抑制率函数图(图2)计算得IC50值分别为348.27±16.11 和1024.89±19.67 μmol/L。IWKL在浓度为2 mg/mL时抑制率仅有10.47%,抑制作用不明显,而FGR在2 mg/mL并未表现出抑制作用。表4列出了几种已报道的DPP-IV抑制肽,本研究所得GPQY抑制率与LPLPL相近[20],高于MPPLP、LP、ADF、GPFPILV[20,23];肽段EACAF抑制率略低,但仍高于Zhao等[24]由鸡蛋蛋白中获得的三肽ADF和MIR。对四条肽段的体外活性验证符合先前研究结果,EACAF和GPQY两条肽段N端的第二位分别为丙氨酸(A)和脯氨酸(Pro),根据对DPP-IV构效关系的研究,具有这类结构的肽段一般具有DPP-IV抑制活性[21,25]。
表 4 已报道的DPP-IV抑制肽的IC50值Table 4. IC50 values of the reported DPP-IV inhibitory peptides肽段 来源 DPP-IV IC50 参考文献 VPF 驼乳β-酪蛋白 55.1±5.8 μmol/L [3] YP 酪蛋白 658.1±8.0 μmol/L [20] LP 酪蛋白 712.5±11.0 μmol/L [20] LPLPL 酪蛋白 325.0±15.2 μmol/L [20] MPPLP 乳制品 490 μmol/L [23] ADF 鸡蛋肌球蛋白 16.83 mmol/L [24] MIR 鸡蛋肌球蛋白 4.86 mmol/L [24] MPVQA 驼乳蛋白 93.3±8.0 μmol/L [25] IPI κ-酪蛋白 3.5 μmol/L [26] IPV 鱼蛋白 5.61±0.20 μmol/L [27] LQP β-酪蛋白 118.1 μmol/L [28] GPFPILV 山羊乳酪蛋白 163.7±1.33 mmol/L [29] 2.4 肽段与DPP-IV的作用机理
2.4.1 肽段抑制模式分析
采用Lineweaver-Buck法对EACAF和GPQY两条肽段进行抑制模式分析,结果如图3所示:图中直线与Y轴的交点为最大初速Vm的倒数(1/Vm),与X轴的交点为Km(反应速度达到最大反应速度Vm一半时的底物浓度)的倒数(−1/Km)。GPQY表现为竞争性抑制模式,不同浓度线性回归曲线相较于Y轴正半轴,随着肽段浓度增大,最大初速度Vm保持不变,Km值增大。研究表明,Pro在DPP-IV抑制肽N端序列中所处位置的不同会直接影响其抑制模式,当Pro处于N端第二位时,由于其具有DPP-IV底物的类似结构,所以一般会与底物竞争性结合DPP-IV活性位点[21,30],如IPIQY、IPML、PYPY、YPYY、IPSK、EPVK和YPLR等均表现为竞争性抑制模式[3,28]。GPQY肽段N端第二位为Pro,与DPP-IV底物Gly-Pro-pNA具有相似的结构,说明GPQY可能与天然底物竞争性结合到DPP-IV的活性位点,从而发挥其生物效应。EACAF不同浓度线性回归曲线相交于第二象限,表现为竞争/非竞争混合型抑制模式,这意味着该肽段在抑制DPP-IV过程中是通过结合DPP-IV催化活性中心以及活性中心以外的点两种方式共同起作用[16,30]。在本研究中,相比EACAF,竞争性抑制肽段GPQY对DPP-IV表现出更好的抑制效果。
2.4.2 分子对接分析相互作用方式
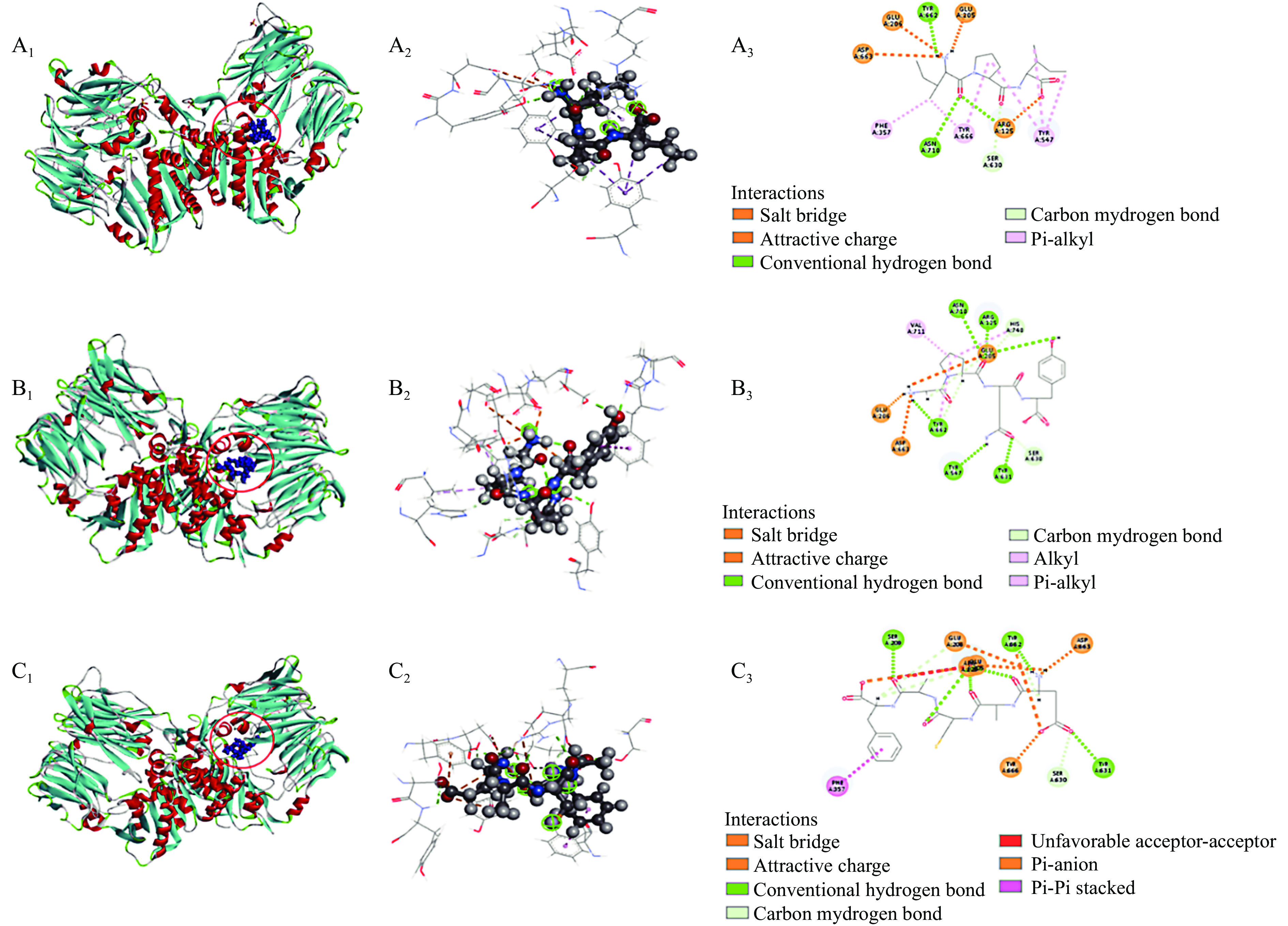
为了解肽段与DPP-IV分子间相互作用力,将2.2中分子对接结果进行深入分析,结果如图4和表5所示。图4展示了IPI(对照)、GPQY、EACAF与DPP-IV的分子对接图。由分子对接3D结构图中可看出EACAF和GPQY都能结合到DPP-IV的活性空腔内。小分子与大分子间结合程度强弱通常取决于对接过程中自由能的变化,所以两者之间的相互作用力对结合物的亲和程度和结合模式都有很大影响,如氢键、静电相互作用和疏水相互作用往往是有助于复合物结合的相互作用力[15]。从表5中可看到,GPQY与DPP-IV残基形成9个氢键,3个疏水作用和3个静电作用;EACAF与DPP-IV残基形成11个氢键,1个疏水作用和6个静电相互作用,GPQY和EACAF与DPP-IV的这三种作用力有助于两者结合物的结构稳定。
表 5 肽段与DPP-IV对接最佳构象相互作用力Table 5. Optimal conformational interaction force of peptide docking with DPP-IVPeptides
(肽键)-CDOCKER_ENERGY
(亲和力)Residues with Hydrogen bonds
(氢键)Residues with Hydrophobic
(疏水相互作用)Residues with Electrostatic
(静电相互作用)IPI 60.1427 Asn 710(2.85 Å)
Arg 125(2.67Å,2.59 Å)
Tyr 662 (2.04 Å)Phe 357(5.21 Å)
Tyr 547(5.06Å, 5.21Å, 5.01 Å)
Tyr 666(5.10Å, 5.15Å)Arg 125(2.07 Å)
Glu 205(1.76 Å)
Glu 206(2.59 Å)
Asp 663(4.68 Å)GPQY 84.6352 Arg 125(1.93 Å)
Glu 205(1.90Å,2.75 Å)
Tyr 547(2.65Å)
Ser 630(2.97 Å)
Tyr 631(1.89 Å)
Tyr 662(1.81 Å, 2.33 Å)
His740(2.38 Å)His 740(5.34 Å)
Val 711(5.23 Å)
Tyr 662(4.37 Å)Glu 205(1.95 Å)
Glu 206(1.99 Å)
Asp 663(4.63 Å)EACAF
10102.042 Arg125(1.90Å, 2.09 Å,
2.38 Å, 2.49 Å)
Glu205(2.58 Å)
Glu206(3.00 Å)
Ser209(1.83 Å)
Ser630(2.69 Å)
Tyr631(2.97 Å)
Tyr662(1.93Å, 2.34 Å)Phe357(4.12 Å) Arg 125(5.06 Å)
Glu 205(1.94 Å)
Glu 206(2.60 Å)
Tyr 662(4.41 Å)
Asp 663(5.12 Å)
Tyr 666(4.18 Å)DPP-IV包含一个洞穴状的活性中心,抑制剂通常与空腔中疏水活性口袋S1和带电的S2 活性口袋结合来竞争性地占据该活性中心。S1口袋由催化三联Ser630-Asp708-His740以及Tyr 547、Tyr 631、Trp 659、Val 656、Tyr 662、Tyr 666、Asn 710和Val 711组成[24],S2口袋包括Arg 125、Glu 205、Glu 206、Val 207、Ser 209、Arg 358和Phe 357[31-32]。由表5可知,GPQY能与S1中的Tyr 547、Ser 630、Tyr 631、Tyr 662、His 740和Val 711形成了氢键和疏水相互作用,与S2中Glu 205、Glu 206和Arg 125形成了静电相互作用和疏水相互作用。EACAF与S1中Ser 630、Tyr 631、Tyr 662和Tyr 666形成氢键和静电相互作用,与S2中Arg 125、Glu 205、Glu 206、Ser 209和Phe 357形成氢键、疏水作用和静电相互作用。有研究发现肽段与S1口袋形成疏水作用可以使肽段与酶结合更稳定,从而提高肽段的抑制率,对S2口袋中的疏水作用可以提高亲和力[18,32]。GPQY与S1口袋中活性残基形成个3个疏水作用,这三个疏水作用对GPQY抑制DPP-IV活性起到关键作用;EACAF未在S1口袋中形成疏水作用。虽然GPQY与EACAF表现为不同的抑制模式,但两者有一些相同的结合位点(Arg 125、Glu 205、Glu 206、Ser 630、Tyr 631、Tyr 662和Asp 663)与这些位点的结合可能有助于在与底物共存的体系中阻碍底物和酶活性部位的接触[16]。
2.5 网络药理学分析
2.5.1 GPQY作用靶点预测
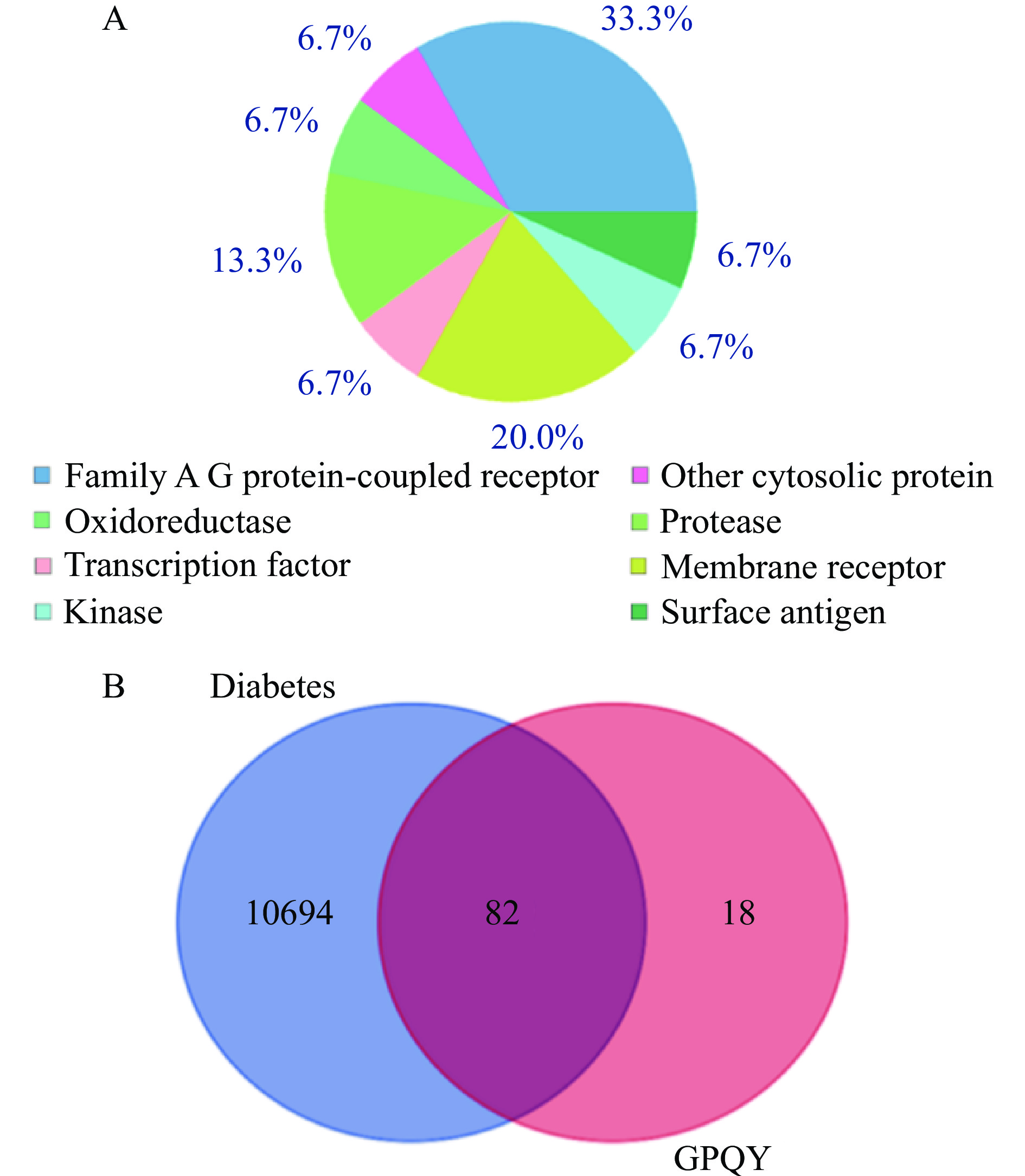
利用Swiss Target Prediction网站,预测到GPQY在体内有100个潜在作用靶点,其类型分布如图5A所示。由Genecards数据库收集到10776个糖尿病相关基因靶点,将GPQY与糖尿病靶点导入Venn diagrams软件绘制韦恩图(图5B),得到GPQY与糖尿病共有的82个潜在作用靶点,GPQY可能通过这82个潜在靶点作用与糖尿病的发生及发展过程。
2.5.2 PPI网络构建
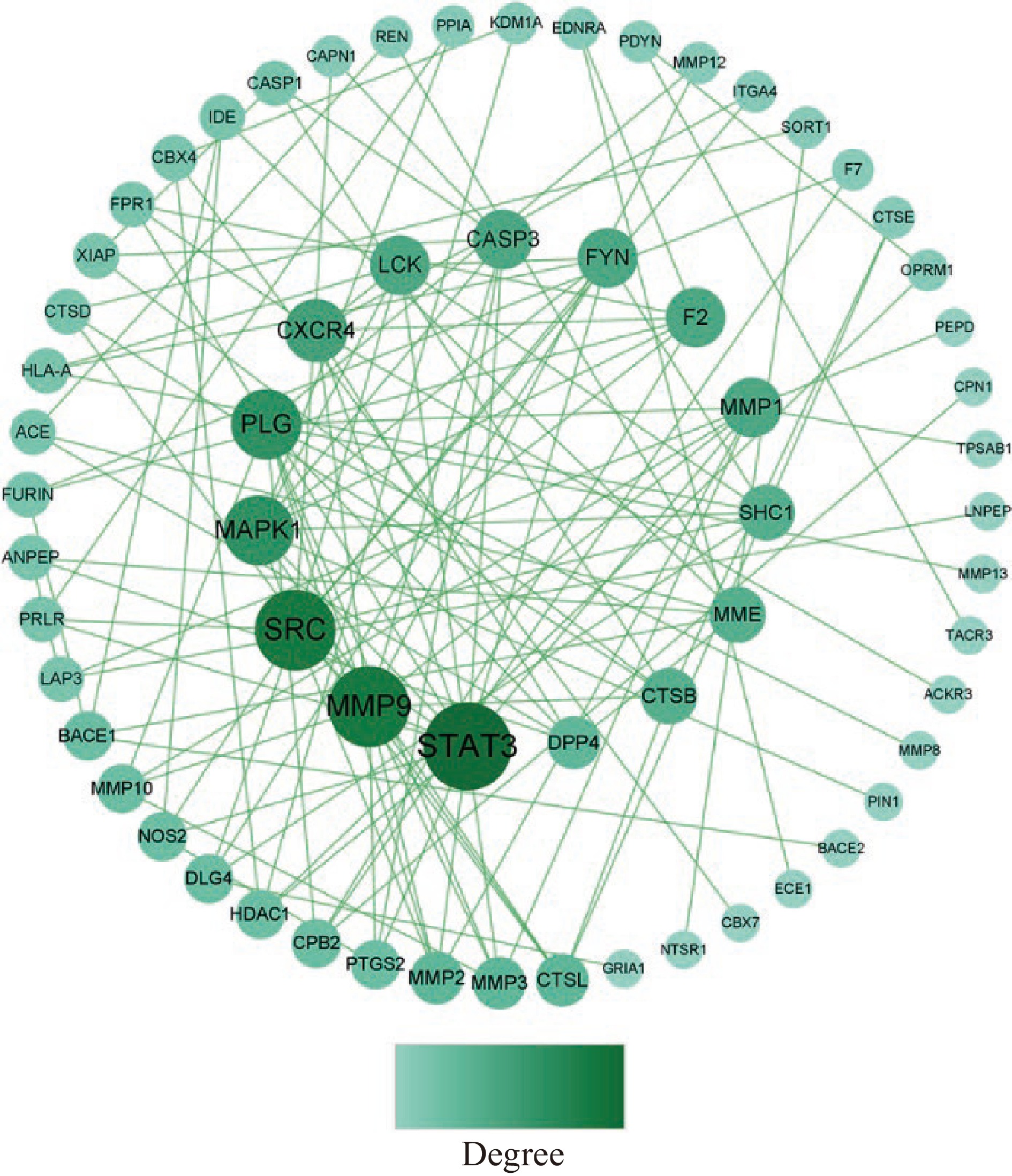
将82个靶点上传至STRING平台,生成PPI网络,将其导入Cytoscape3.9.0软件进一步修饰,结果如图6所示。PPI网络有63个节点、122个边,节点表示蛋白,边表示蛋白与蛋白间相互作用,节点大小表示度值(Degree),度值越高,说明靶点在网络中的位置越重要,一般度值大于其平均值,可认为该靶点为核心靶点[33],该网络平均度值为3.873,根据度值大小排序,筛选到25个核心靶点(表6),推测这些靶点为GPQY作用于糖尿病的关键靶点。从PPI网络图中可看到STAT3、MMP9、SRC、MAPK1、PLG节点较大,推测这些靶点在GPQY防治糖尿病过程中起到关键作用。
表 6 核心靶点拓扑参数Table 6. Core targets and topological parameters序号 靶点 Degree 序号 靶点 Degree 1 STAT3 15 14 MME 6 2 MMP9 13 15 MMP3 5 3 SRC 13 16 MMP2 5 4 PLG 10 17 CTSL 5 5 MAPK1 10 18 DPP4 5 6 CXCR4 8 19 MMP10 4 7 MMP1 7 20 NOS2 4 8 FYN 7 21 DLG4 4 9 LCK 7 22 CPB2 4 10 F2 7 23 HDAC1 4 11 CASP3 7 24 PTGS2 4 12 SHC1 6 25 BACE1 4 13 CTSB 6 STAT3是转录因子家族成员之一,信号转导和转录激活因子(STATs)是脊椎动物发育和成熟组织功能的成熟调节剂,激活STAT3会导致促炎因子表达增加[34]。研究表明,STAT3的磷酸化可调节促炎因子的表达水平,抑制STAT3蛋白磷酸化可减弱CD36的表达,进而抑制高脂饮食的糖尿病小鼠动脉粥样硬化病变的发展[35]。抑制STAT3可改善糖尿病大鼠肝脏炎症及糖代谢功能障碍[36]。MAPK属促分裂原活化蛋白激酶,是细胞传递应激信号的关键激酶,具有较强的分化作用,在胰岛素抵抗中,常常伴随慢性炎症反应,MAPK类蛋白对多种炎性细胞因子非常敏感,通过降低其表达水平可减轻炎性反应,因此在2型糖尿病炎症反应中也起到了重要作用[37]。李芳等[38]发现,MAPK与糖尿病大鼠的心肌纤维化有关,抑制MAPK1/3的表达可以改善糖尿病大鼠心肌纤维化。MMP9主要参与了血管的再生及炎性反应等过程,其可破坏细胞组织、产生炎性反应而发挥促炎作用。刘坤等[39]发现MMP9的含量直接影响糖尿病肾病的发生,高糖使MMP9蛋白的表达下调,从而影响其所占比例失衡,也加剧了糖尿病肾病的发生发展。
2.5.3 GO富集分析和KEGG通路富集分析
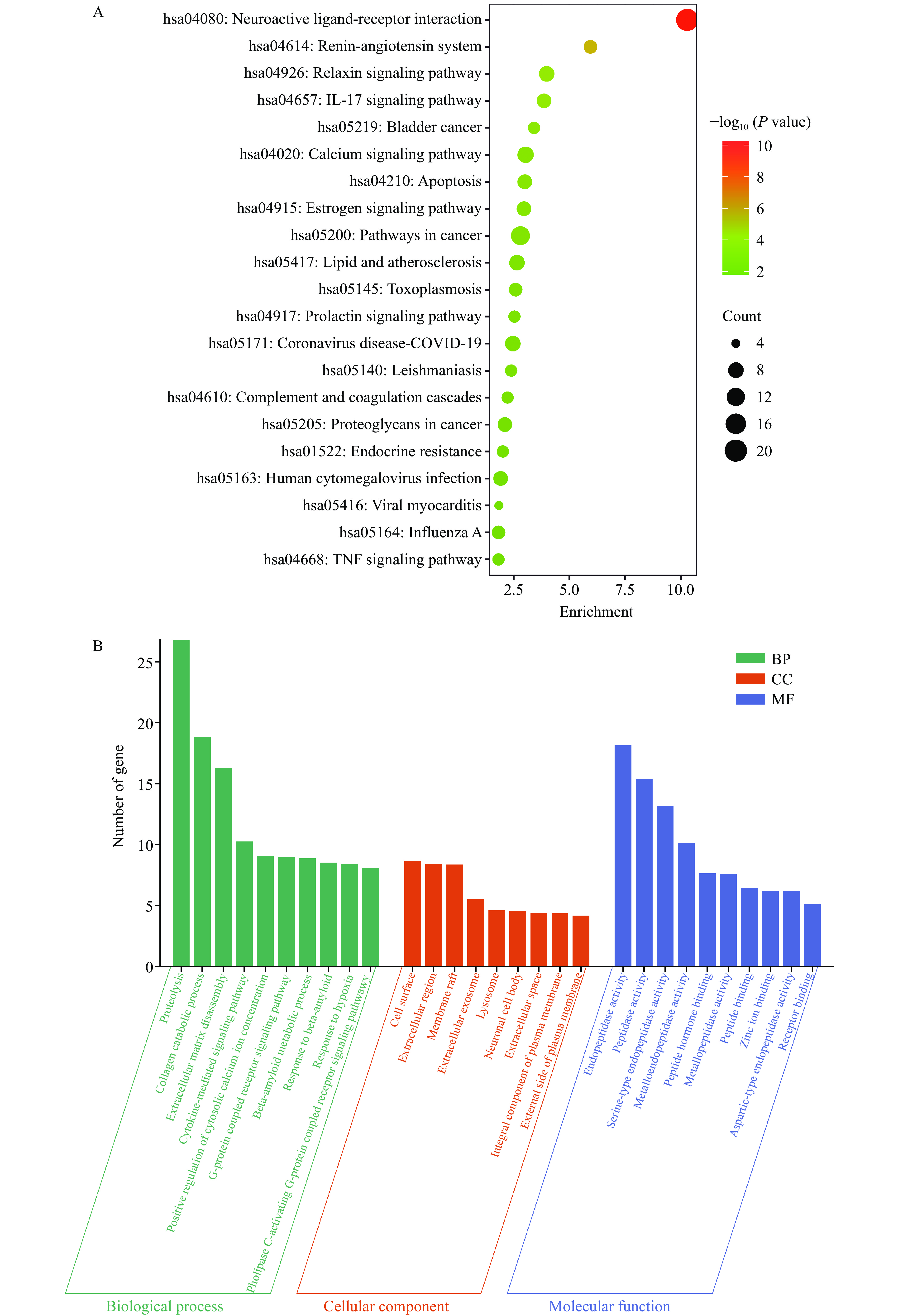
为了进一步探究GPQY防治糖尿病的潜在作用机制,利用DAVID数据库对交集靶点进行了GO分析和KEGG富集分析。GO分析包括三个方面:生物过程(Biological process, BP)、细胞组分(Cellular component, CC)和分子功能(Molecular function, MF)。GO富集分析得到170个BP,52个CC和66个MF,根据P<0.05筛选出前10个条目进行可视化,如图7B所示。BP结果显示,这些靶点主要参与到蛋白水解、胶原蛋白分解代谢和细胞溶质钙离子浓度的正向调节等生物过程。KEGG富集到57条信号通路,根据P<0.05对前20条通路可视化,这些靶点涉及神经活性配体-受体相互作用、肾素-血管紧张素系统、IL-17信号通路、松弛素信号通路、细胞凋亡、癌症的途径、钙离子信号通路、肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)信号通路和脂质和动脉粥样硬化等信号通路,具体如图7A。
糖尿病是持续炎症和动脉粥样硬化相关的慢性疾病。IL-17是一种促炎因子,与胰岛细胞的破坏密切相关,其通过激活NF-κB信号通路引起TNF-α等促炎因子释放,增加抑制胰岛素信号传导,从而促进胰岛素抵抗[40]。Rajendran等[41]证明IL-17可在在T1DM和T2DM胰岛β和α细胞中表达,并且在T2MD患者中表达水平更高。TNF信号通路在细胞增殖、分化、凋亡、免疫调节和炎症诱导等各种生理病理过程中发挥着重要作用,较高水平的TNF-α通过丝氨酸磷酸化加速胰岛素对脂肪细胞和外周组织的抵抗,从而破坏有助于发展糖尿病的胰岛素信号[18,42]。细胞凋亡在胰腺的正常生理和糖尿病的发病机制中起着至关重要的作用,GLP-1已被证明具有抗凋亡特性,并且在受到各种凋亡刺激物的攻击时能够促进胰腺β细胞的存活[43]。由驼乳LF衍生的DPP-IV抑制肽GPQY可延长DPP-IV对GLP-1的降解,从而抑制β细胞凋亡,同样DPP-IV抑制剂也被证明具有抗凋亡活性,可减轻糖尿病相关的细胞和组织损伤[44]。糖尿病往往伴随着一系列并发症,KEGG通路富集表明,除IL-17信号通路、细胞凋亡、肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)信号通路外,这些靶点在神经活性配体-受体相互作用、肾素-血管紧张素系统两个通路中显著富集,推测GPQY可通过作用于核心靶点对糖尿病并发症如神经病变,高血压等发挥协同作用。
3. 结论
本研究以驼乳LF为研究对象,结合模拟酶切、活性预测、分子对接以及人工合成验证快速筛选验证得到2条DPP-IV抑制肽GPQY和EACAF,并对其抑制模式和作用机理进行了分析。随后选择抑制作用较强的GPQY进行网络药理学分析,探讨了其对糖尿病的潜在作用机制。分析发现GPQY通过作用于STAT3、MMP9、SRC、MAPK1等核心靶点,参与IL-17信号通路、肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)信号通路、细胞凋亡代谢途径抑制炎症因子的分泌,参与抗炎反应,抑制β细胞凋亡,改善胰岛素抵抗对糖尿病发挥作用。此外,还发现GPQY通过调节神经活性配体-受体相互作用、肾素-血管紧张素系统、松弛素信号通路、癌症的途径和脂质和动脉粥样硬化等信号通路对糖尿病并发症,如心血管疾病、神经病变、糖尿病肾病、视网膜病变和癌症发挥协同作用。这些结果将为驼乳蛋白肽作为功能性食品成分预防和治疗糖尿病提供一些见解,但本研究仍存在一些不足,网络药理学是基于大数据背景进行的预测,具体机制仍需进一步通过实验验证。
-
表 1 模拟酶切结果
Table 1 Simulation of digestion results
蛋白酶种类 模拟酶解产
生肽段数目去除重复肽
段后数目特有肽
段数Peptide ranker
得分>0.5胰蛋白酶Trypsin
(EC3.4.21.4)75 73 72 23(32%) 胃蛋白酶pepsinpH1.3
(EC3.4.23.1)82 77 26 32(42%) 胰凝乳蛋白酶
Chymotrypsin
(EC3.4.21.1)125 110 49 33(30%) 木瓜蛋白酶papain
(EC3.4.22.2)186 144 114 35(24%) 碱性蛋白酶Subtilisin
(3.4.2.34)167 148 93 45(30%) 蛋白酶K proteinase K
(EC3.4.21.67)154 133 85 38(29%) 表 2 筛选肽段Peptide ranker评分
Table 2 Peptide ranker score for screening peptides
序号 肽段 Peptide ranker评分 序号 肽段 Peptide ranker评分 1 GF1 0.994712 16 SGF 0.947492 2 RF1 0.986556 17 GDF 0.941533 3 AF1 0.973259 18 IPM1 0.845096 4 IW 0.944175 19 DAF 0.804969 5 CP 0.943255 20 CPN 0.780467 6 DW 0.933025 21 APG1 0.745179 7 GP1 0.905487 22 SPL 0.665423 8 CL 0.879917 23 PAL 0.631952 9 VW 0.802223 24 GAL 0.594888 10 AP1 0.626856 25 DPY 0.586633 11 SP1 0.514894 26 IWKL 0.733588 12 CRF 0.98469 27 GPQY 0.643377 13 RPF 0.977766 28 PPEPL 0.684494 14 FGR 0.967011 29 DPYKL 0.579245 15 GAF 0.954769 30 EACAF 0.634993 注:1为已报道的肽。 表 3 分子对接打分表
Table 3 Molecular docking scoring
序号 肽段 -CDOCKER_ENERGY -CDOCKER_INTERACTION_
ENERGY1 EACAF 102.042 68.9447 2 IWKL 88.9743 79.7752 3 GPQY 84.6352 71.8239 4 DAF 81.4763 59.859 5 FGR 81.046 75.6303 6 GDF 80.4749 64.0784 7 DPYKL 75.5242 76.8073 8 GAF 74.7882 64.8822 9 GAL 73.5947 61.7327 10 SGF 73.5308 63.686 11 CRF 72.4341 68.7239 12 DPY 71.4961 63.9571 13 DW 68.2476 53.2253 14 IW 66.5734 63.7061 15 CPN 63.3028 65.4616 16 RPF 61.2769 71.9084 17 SPL 60.3406 67.1524 18 VW 60.2456 55.2833 19 IPI 60.1427 62.6373 20 PAL 57.1327 65.2958 21 PPEPL 54.4414 72.4935 22 CP 48.4354 53.0389 表 4 已报道的DPP-IV抑制肽的IC50值
Table 4 IC50 values of the reported DPP-IV inhibitory peptides
肽段 来源 DPP-IV IC50 参考文献 VPF 驼乳β-酪蛋白 55.1±5.8 μmol/L [3] YP 酪蛋白 658.1±8.0 μmol/L [20] LP 酪蛋白 712.5±11.0 μmol/L [20] LPLPL 酪蛋白 325.0±15.2 μmol/L [20] MPPLP 乳制品 490 μmol/L [23] ADF 鸡蛋肌球蛋白 16.83 mmol/L [24] MIR 鸡蛋肌球蛋白 4.86 mmol/L [24] MPVQA 驼乳蛋白 93.3±8.0 μmol/L [25] IPI κ-酪蛋白 3.5 μmol/L [26] IPV 鱼蛋白 5.61±0.20 μmol/L [27] LQP β-酪蛋白 118.1 μmol/L [28] GPFPILV 山羊乳酪蛋白 163.7±1.33 mmol/L [29] 表 5 肽段与DPP-IV对接最佳构象相互作用力
Table 5 Optimal conformational interaction force of peptide docking with DPP-IV
Peptides
(肽键)-CDOCKER_ENERGY
(亲和力)Residues with Hydrogen bonds
(氢键)Residues with Hydrophobic
(疏水相互作用)Residues with Electrostatic
(静电相互作用)IPI 60.1427 Asn 710(2.85 Å)
Arg 125(2.67Å,2.59 Å)
Tyr 662 (2.04 Å)Phe 357(5.21 Å)
Tyr 547(5.06Å, 5.21Å, 5.01 Å)
Tyr 666(5.10Å, 5.15Å)Arg 125(2.07 Å)
Glu 205(1.76 Å)
Glu 206(2.59 Å)
Asp 663(4.68 Å)GPQY 84.6352 Arg 125(1.93 Å)
Glu 205(1.90Å,2.75 Å)
Tyr 547(2.65Å)
Ser 630(2.97 Å)
Tyr 631(1.89 Å)
Tyr 662(1.81 Å, 2.33 Å)
His740(2.38 Å)His 740(5.34 Å)
Val 711(5.23 Å)
Tyr 662(4.37 Å)Glu 205(1.95 Å)
Glu 206(1.99 Å)
Asp 663(4.63 Å)EACAF
10102.042 Arg125(1.90Å, 2.09 Å,
2.38 Å, 2.49 Å)
Glu205(2.58 Å)
Glu206(3.00 Å)
Ser209(1.83 Å)
Ser630(2.69 Å)
Tyr631(2.97 Å)
Tyr662(1.93Å, 2.34 Å)Phe357(4.12 Å) Arg 125(5.06 Å)
Glu 205(1.94 Å)
Glu 206(2.60 Å)
Tyr 662(4.41 Å)
Asp 663(5.12 Å)
Tyr 666(4.18 Å)表 6 核心靶点拓扑参数
Table 6 Core targets and topological parameters
序号 靶点 Degree 序号 靶点 Degree 1 STAT3 15 14 MME 6 2 MMP9 13 15 MMP3 5 3 SRC 13 16 MMP2 5 4 PLG 10 17 CTSL 5 5 MAPK1 10 18 DPP4 5 6 CXCR4 8 19 MMP10 4 7 MMP1 7 20 NOS2 4 8 FYN 7 21 DLG4 4 9 LCK 7 22 CPB2 4 10 F2 7 23 HDAC1 4 11 CASP3 7 24 PTGS2 4 12 SHC1 6 25 BACE1 4 13 CTSB 6 -
[1] NONGONIERMA A B, FITZGERALD R J. Prospects for the management of type 2 diabetes using food protein-derived peptides with dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory activity[J]. Current Opinion in Food Science,2016,8:19−24. doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2016.01.007
[2] LI N, WANG L J, JIANG B, et al. Recent progress of the development of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry,2018,151:145−157. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.03.041
[3] NONGONIERMA A B, CADAMURO C, GOUIC A LE, et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory properties of a camel whey protein enriched hydrolysate preparation[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,279:70−79. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.11.142
[4] AULIFA D L, ADNYANA I K, SUKRASNO S, et al. Inhibitory activity of xanthoangelol isolated from Ashitaba (Angelica keiskei Koidzumi) towards alpha-glucosidase and dipeptidyl peptidase-IV: In silico and in vitro studies[J]. Heliyon,2022,8(5):e09501. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09501
[5] ARNIPALLI M S, NIMMU N V, BODDAPATI S N M, et al. New enantioselective liquid chromatography method development and validation of dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors using a macrocyclic glycopeptide (vancomycin) chiral stationary phase under polar ionic mode condition[J]. Chirality,2022,34(7):989−998. doi: 10.1002/chir.23448
[6] HOWSE P M, CHIBRIKOVA L N, TWELLS L K, et al. Safety and efficacy of incretin-based therapies in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and CKD: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Am J Kidney Dis,2016,68(5):733−742. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2016.06.014
[7] KHALESI M, SALAMI M, MOSLEHISHAD M, et al. Biomolecular content of camel milk: A traditional superfood towards future healthcare industry[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2017,62:49−58.
[8] IZADI A, KHEDMAT L, MOJTAHEDI S Y. Nutritional and therapeutic perspectives of camel milk and its protein hydrolysates: A review on versatile biofunctional properties[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2019:60.
[9] NONGONIERMA A B, PAOLELLA S, MUDGIL P, et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory properties of camel milk protein hydrolysates generated with trypsin[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2017,34:49−58. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2017.04.016
[10] MORENO-NAVARRETE J M, ORTEGA F J, RICART W, et al. Lactoferrin increases (172Thr) AMPK phosphorylation and insulin-induced (p473Ser) AKT while impairing adipocyte differentiation[J]. Journay Clin Endocrinol Metab,2009,33(9):991−1000.
[11] MORENO-NAVARRETE J M, ORTEGA F J, BASSOLS J, et al. Decreased circulating lactoferrin in insulin resistance and altered glucose tolerance as a possible marker of neutrophil dysfunction in type 2 diabetes[J]. Journay Clin Endocrinol Metab,2009,94(10):4036−4044. doi: 10.1210/jc.2009-0215
[12] KHAN F B, ANWAR I, REDWAN E M, et al. Camel and bovine milk lactoferrins activate insulin receptor and its related AKT and ERK1/2 pathways[J]. Journal of Dairy Science,2022,105(3):1848−1861. doi: 10.3168/jds.2021-20934
[13] GAMAL BADR N K R, LEILA H S, BADR M, et al. Why whey? Camel whey protein as a new dietary approach to the management of free radicals and for the treatment of different health disorders[J]. Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences, 2017, 20(4): 338−349.
[14] WANG Y, HU B, FENG S, et al. Target recognition and network pharmacology for revealing anti-diabetes mechanisms of natural product[J]. Journal of Computational Science,2020:45.
[15] 侯成杰, 聂彩清, 王彦茜, 等. α-乳白蛋白源ACE抑制肽快速筛选及验证[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(24):100−107. [HOU C J, NIE C Q, WANG Y Q, et al. Rapid screening and verification of α-lactalbumin-derived ACE inhibitory peptides[J]. Food Science,2021,42(24):100−107. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20201012-094 [16] 张颖. 牛、羊乳酪蛋白源DPP-Ⅳ抑制肽的制备、鉴定及抑制机理研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2016 ZHANG Y. Enzymatic preparation, identification and inbition mechanism of DPP-IV inhibitory peptides derived from bovine and caprine milk casein[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2016.
[17] ZHANG L, HAN L, MA J, et al. Exploring the synergistic and complementary effects of berberine and paeoniflorin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus by network pharmacology[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology,2022,919:174769. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.174769
[18] ZHAO L, ZHANG M, PAN F, et al. In silico analysis of novel dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory peptides released from Macadamia integrifolia antimicrobial protein 2 (MiAMP2) and the possible pathways involved in diabetes protection[J]. Current Research in Food Science,2021,4:603−611. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2021.08.008
[19] NONGONIERMA A B, FITZGERALD R J. Features of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory peptides from dietary proteins[J]. Journay Food Biochem,2019,43(1):e12451. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.12451
[20] NONGONIERMA A B, FITZGERALD R J. Susceptibility of milk protein-derived peptides to dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) hydrolysis[J]. Food Chemistry,2014,145:845−852. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.08.097
[21] NONGONIERMA A B, FITZGERALD R J. An in silico model to predict the potential of dietary proteins as sources of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory peptides[J]. Food Chemistry,2014,165:489−498. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.05.090
[22] WANG K, YANG X, LOU W, et al. Discovery of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitory peptides from Largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) by a comprehensive approach[J]. Bioorganic Chemistry,2020,105:104432. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104432
[23] LACROIX I M E, LI-CHAN E C Y. Dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory activity of dairy protein hydrolysates[J]. International Dairy Journal,2012,25(2):97−102. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2012.01.003
[24] ZHAO W, ZHANG D, YU Z, et al. Novel membrane peptidase inhibitory peptides with activity against angiotensin converting enzyme and dipeptidyl peptidase IV identified from hen eggs[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2020:64.
[25] NONGONIERMA A B, PAOLELLA S, MUDGIL P, et al. Identification of novel dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory peptides in camel milk protein hydrolysates[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,244:340−348. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.10.033
[26] NONGONIERMA A B, MOONEY C, SHIELDS D C, et al. In silico approaches to predict the potential of milk protein-derived peptides as dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitors[J]. Peptides,2014,57:43−51. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2014.04.018
[27] HARNEDY-ROTHWELL P A, MCLAUGHLIN C M, O'KEEFFE M B, et al. Identification and characterisation of peptides from a boarfish (Capros aper) protein hydrolysate displaying in vitro dipeptidyl peptidase-IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory and insulinotropic activity[J]. Food Research International,2020,131:108989. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.108989
[28] NONGONIERMA A B, FITZGERALD R J. Structure activity relationship modelling of milk protein-derived peptides with dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory activity[J]. Peptides,2016,79:1−7. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2016.03.005
[29] ZHANG Y, CHEN R, ZUO F, et al. Comparison of dipeptidyl peptidase IV-inhibitory activity of peptides from bovine and caprine milk casein by in silico and in vitro analyses[J]. International Dairy Journal,2016,53:37−44. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2015.10.001
[30] LACROIX I M, LI-CHAN E C. Isolation and characterization of peptides with dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory activity from pepsin-treated bovine whey proteins[J]. Peptides,2014,54:39−48. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2014.01.002
[31] PAN F, ZHOU N, LI J, et al. Identification of C-phycocyanin-derived peptides as angiotensin converting enzyme and dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors via molecular docking and molecular dynamic simulation[J]. ES Food & Agroforestry, 2020, 2: 58−69.
[32] ARAKI M, KANEGAWA N, IWATA H, et al. Hydrophobic interactions at subsite S1' of human dipeptidyl peptidase IV contribute significantly to the inhibitory effect of tripeptides[J]. Heliyon,2020,6(6):e04227. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04227
[33] 钱慧琴, 彭媛, 黄秀秀, 等. 基于网络药理学探讨预知子抗抑郁的作用机制[J].食品工业科技, 2021, 42 (14): 8−15 QIAN H Q, PENG Y, HUANG X X, et al. Mechanism of anti-depression mechanism of Akebiae fructus based on network pharmacology[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(14): 8−15.
[34] AGGARWAL B B, KUNNUMAKKARA A B, HARIKUMAR K B, et al. Signal transducer and activator of transcription-3, inflammation, and cancer: How intimate is the relationship?[J]. New York Academy of Sciences,2009,1171:59−76. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04911.x
[35] JIANG X X, BIAN W, ZHU Y R, et al. Targeting the KCa3.1 channel suppresses diabetes-associated atherosclerosis via the STAT3/CD36 axis[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract,2022,185:109776. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2022.109776
[36] LONG M H, ZHANG C, XU D Q, et al. PM2.5 aggravates diabetes via the systemically activated IL-6-mediated STAT3/SOCS3 pathway in rats' liver[J]. Environ Pollut,2020,256:113342. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113342
[37] 黄锦珠, 殷贝, 毕艺鸣, 等. 柴胡-白芍药对治疗2型糖尿病的网络药理学作用机制研究[J]. 中国药业,2022,31(4):43−48. [HUANG J Z, YIN B, BI Y M, et al. Mechanism of Bupleuri radix-Paeoniae alba radix drug pairs in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus based on network pharmacology[J]. China Pharmaceuticals,2022,31(4):43−48. [38] 李芳, 曾欧, 罗健, 等. 硫化氢对糖尿病大鼠心肌纤维化及MAPK1/3和MMP-8表达的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报,2015,35(4):549−552. [LI F, ZENG O, LUO J, et al. Effects of hydrogen sulfide on myocardial fibrosis and MAPK1/3 and MMP-8 expression in diabetic rats[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University,2015,35(4):549−552. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4254.2015.04.017 [39] 刘坤, 李娜, 程华, 等. 基于网络药理学的二陈丸治疗2型糖尿病的作用机制研究[J]. 中央民族大学学报(自然科学版),2022,31(1):78−85. [LIU K, LI N, CHEN H, et al. The effect of Er Chen Wan in the treatment of type 2 diabetes based on network pharmacology mechanism study[J]. Journal of MUC (Natural Sciences Edition),2022,31(1):78−85. [40] 唐卫荷, 刘湘, 张玥, 等. 基于网络药理学和分子对接探讨顾步汤治疗糖尿病足作用机制的研究[J]. 中国中西医结合外科杂志,2022,28(1):106−113. [TANG W H, LIU X, ZHANG Y, et al. Study on mechanism of Gubu decoction in treatment of diabetic foot based on network pharmacology and molecular docking[J]. Chinese Journal of Surgery of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine,2022,28(1):106−113. [41] RAJENDRAN S, QUESADA-MASACHS E, ZILBERMAN S, et al. IL-17 is expressed on beta and alpha cells of donors with type 1 and type 2 diabetes[J]. J Autoimmun,2021,123:102708. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2021.102708
[42] AKASH M S H, REHMAN K, LIAQAT A. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha: Role in development of insulin resistance and pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Journay Cell Biochem,2018,119(1):105−110. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26174
[43] LI L, EL-KHOLY W, RHODES C J, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 protects beta cells from cytokine-induced apoptosis and necrosis: Role of protein kinase B[J]. Diabetologia,2005,48(7):1339−1349. doi: 10.1007/s00125-005-1787-2
[44] LIU W, SONG D O, LAU H K, et al. Combined oral administration of GABA and DPP-4 inhibitor prevents beta cell damage and promotes beta cell regeneration in mice[J]. Front Pharmacol,2017,8:362. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00362
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)






 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



