Optimization and Characterization of Extraction Technology of Soluble Dietary Fiber from Yam Peel Residue
-
摘要: 为充分开发山药皮的利用价值,以山药皮残渣为原料,通过正交试验,探究碱法提取山药皮残渣中可溶性膳食纤维(Soluble Dietary Fiber,SDF)的最佳提取工艺条件。利用X射线衍射(X-ray diffraction,XRD)图谱、傅里叶红外光谱(Fourier infrared spectroscopy,FT-IR)、扫描电镜(Scanning Electron Microscopy,SEM)对提取物进行表征,并对其膨胀率(Swelling Capacity,SC)、持水力(Water Holding Capacity,WHC)、持油力(Oil Holding Capacity,OHC)等理化性质进行测定。结果表明,碱法提取山药皮残渣SDF的最优工艺为提取时间90 min,NaOH浓度12 g/L,液固比40:1(mL:g),提取温度为80 ℃;在最优工艺下,山药皮残渣SDF得率为11.52%±0.23%;山药皮残渣SDF属于纤维素I型,其红外吸收峰呈现出典型的多糖吸收峰;SEM结果显示,山药皮残渣SDF是由多个细小颗粒团聚在一起而形成的疏松结构;与山药皮SDF相比,山药皮残渣SDF有着更好的膨胀率、持水力、持油力,分别为7.63±0.32 mL/g、9.81±0.21 g/g、4.45±0.24 g/g。综上,山药皮残渣SDF有着良好的理化性质,这使其有成为功能性食品中有效成分的潜在价值。Abstract: In order to fully exploit the utilization value of Chinese yam peel, the optimal extraction conditions of soluble dietary fiber (SDF) from Chinese yam peel residue were investigated by orthogonal experiment. The extracts were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern, Fourier infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). And the physical and chemical properties of its swelling capacity (SC), water holding capacity (WHC) and oil holding capacity (OHC) were determined. The results showed that the optimal extraction process was 90 min, NaOH concentration was 12 g/L, liquid-solid ratio was 40:1(mL:g), and extraction temperature was 80 ℃. Under the optimal process, the SDF yield of yam peel residue was 11.52%±0.23%. SDF of yam peel residue belongs to cellulose type I, and its infrared absorption peak showed typical polysaccharide absorption peak. SEM results showed that the SDF of yam peel residue was a loose structure formed by many fine particles. Compared with SDF of yam peel, SDF of yam peel residue had better expansion rate, water holding capacity and oil holding capacity (7.63±0.32 mL/g, 9.81±0.21 g/g, 4.45±0.24 g/g, respectively). In conclusion, SDF of Chinese yam peel residue had good physical and chemical properties, which made it potential value as an effective ingredient in functional food.
-
膳食纤维(Dietary Fiber,DF)包括食品中天然存在的碳水化合物,通过物理、酶及化学方式从原材料中获得的碳水化合物,以及经证实对健康有益的合成碳水化合物[1]。水果、蔬菜、谷物和藻类是主要的天然DF来源,向食品添加DF可降低食品中的卡路里、胆固醇和脂肪含量,也可以作为功能性成分,改善水合作用、持油能力、粘度、质地、感官质量和保质期[2]。根据DF是否具有水溶性,可将其分为可溶性膳食纤维(Soluble Dietary Fiber,SDF),SDF主要包括果胶和树胶,以及水不溶性膳食纤维(Insoluble Dietary Fiber,IDF),如木质素、纤维素和一些半纤维素[3]。在食品工业中,SDF较IDF有着更为广泛的应用,这是因为SDF既可以在食品凝胶形成和乳化的过程中起重要作用,又能在不影响味道的情况下融入食品和饮料中[4],同时可以增加饮料的粘度并保留食品中的水分,此外SDF也具有一定的吸附能力,可降低人体内血糖和血浆胆固醇水平[5]。
山药中含有多种营养物质[6],除了具有生物活性的多糖、多酚和黄酮等物质外,其余绝大部分是膳食纤维[7]。山药皮经乙醇提取黄酮、多酚,水提多糖后,其残渣中仍含有丰富的SDF,但是关于如何有效地提取山药皮残渣中的SDF鲜有报道。目前主要提取SDF的方法有:传统的化学提取方法,如碱水解、酸水解和酶解法[8];新兴的仪器辅助提取,如微波、超声和超高压辅助提取[9];生物发酵提取。碱法提取有着工艺简单、成本低等优点,多应用于工业化大规模生产[10]。经过逐级提取后,山药皮残渣SDF可能存在于细胞壁中,在碱性条件,植物细胞壁基质中的氢和共价键被破坏,可以释放其中的多糖,从而提高提取产率[11],因此,本研究采用碱法提取山药皮残渣中SDF。
为充分开发山药皮的价值,本试验首次以经过醇提黄酮、多酚,水提多糖后的铁棍山药皮残渣为原料,采用单因素实验,探究碱法提取山药皮残渣中膳食纤维的最优工艺,分别以提取时间、液固比及NaOH浓度与提取温度为考察因素,以SDF得率为目标值,再利用正交法优化试验,以期为该资源开发利用提供依据,实现山药皮的综合利用。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
铁棍山药皮 市售新鲜山药,削皮烘干备用;中性蛋白酶(20万 U/g)、中温α-淀粉酶(10000 U/g) 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;氢氧化钠、盐酸、无水乙醇 分析纯,天津市富宇精细化工有限公司。
LG10-2.4A型离心机 北京医用离心机厂;BSA223S型分析天平 德国赛多利斯公司;SB-4200DT型数控超声清洗机 宁波新芝生物科技有限公司;SHZ-D型循环式多用真空泵 河南金友成仪器设备有限公司;DHG-9123A型电热鼓风干燥箱 上海精宏实验设备有限公司;YRE-52AA型旋转蒸发仪器 巩义市予华仪器有限责任公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 可溶性膳食纤维提取工艺
参考文献[12]方法,经过醇提黄酮(提取时间30 min,乙醇浓度60%,液固比60:1)、水提多糖(提取时间2 h,液固比20:1,提取温度50 ℃)后的铁棍山药皮残渣烘干、粉碎、过筛(80目),将10 g山药皮粉末加入一定量的去离子水,充分搅拌使得溶液混合均匀。向上述混合液中加入α-淀粉酶(1%),调节溶液pH为5,水浴(50 ℃,30 min)后,煮沸灭活。待溶液冷却至室温后加入中性蛋白酶(4%),调节溶液pH为7,水浴(50 ℃,30 min),煮沸灭活。向经过酶解的溶液中加入一定量的NaOH,水浴提取膳食纤维,提取完成后在4000 r/min条件下离心15 min,沉淀用蒸馏水漂洗2次,冷冻干燥得到IDF,同时收集上清液,加入4倍体积的95%乙醇,室温静置2 h,收集残渣并用无水乙醇清洗,然后在通风柜中干燥,得到SDF。得率按如下公式进行计算。
(1) 1.2.2 单因素实验
1.2.2.1 提取时间对SDF得率的影响
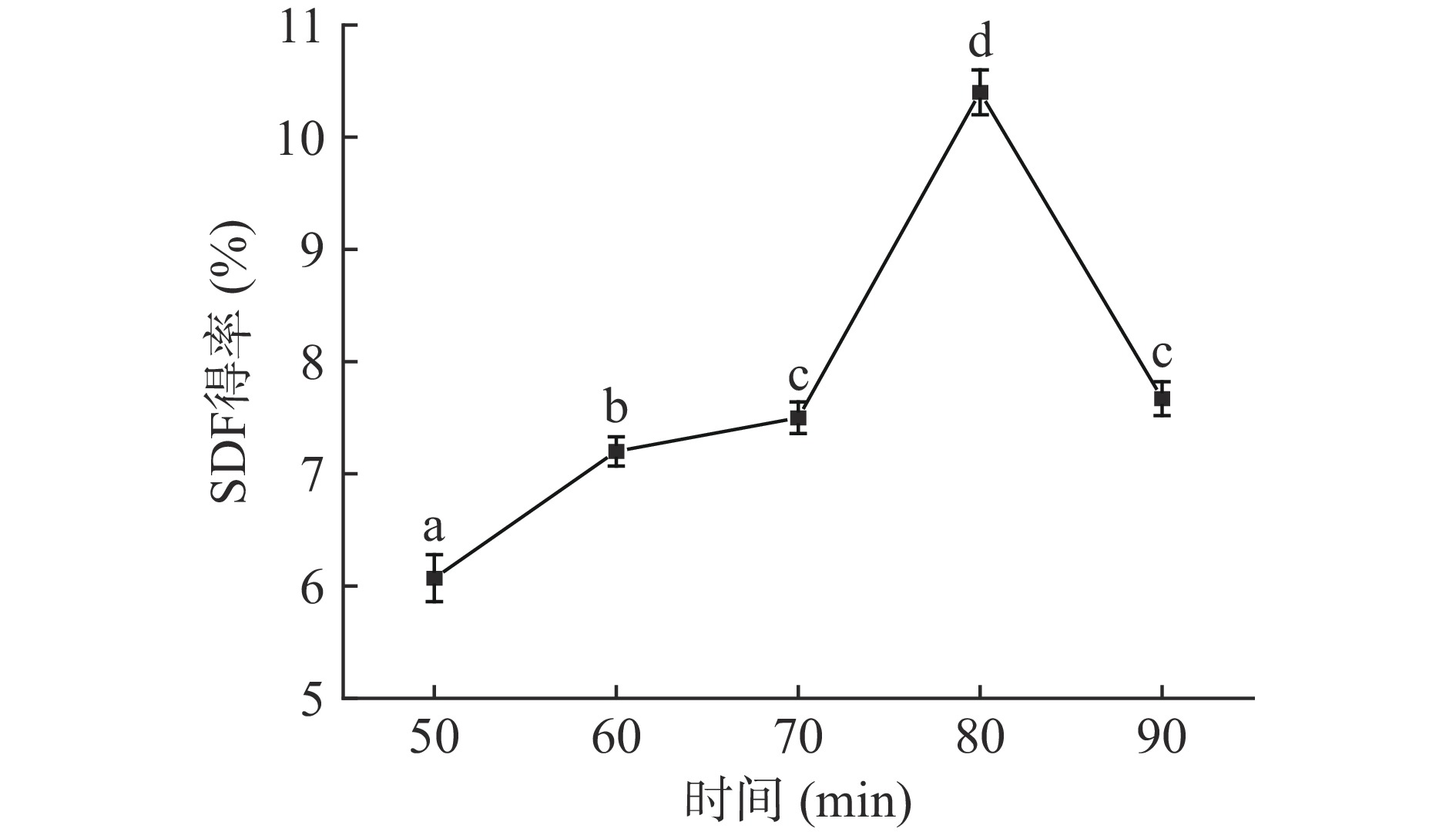
在NaOH浓度为12 g/L、液固比40:1 mL/g、提取温度80 ℃时,考察提取时间(50~90 min )对山药皮残渣SDF得率的影响。
1.2.2.2 NaOH浓度对SDF得率的影响
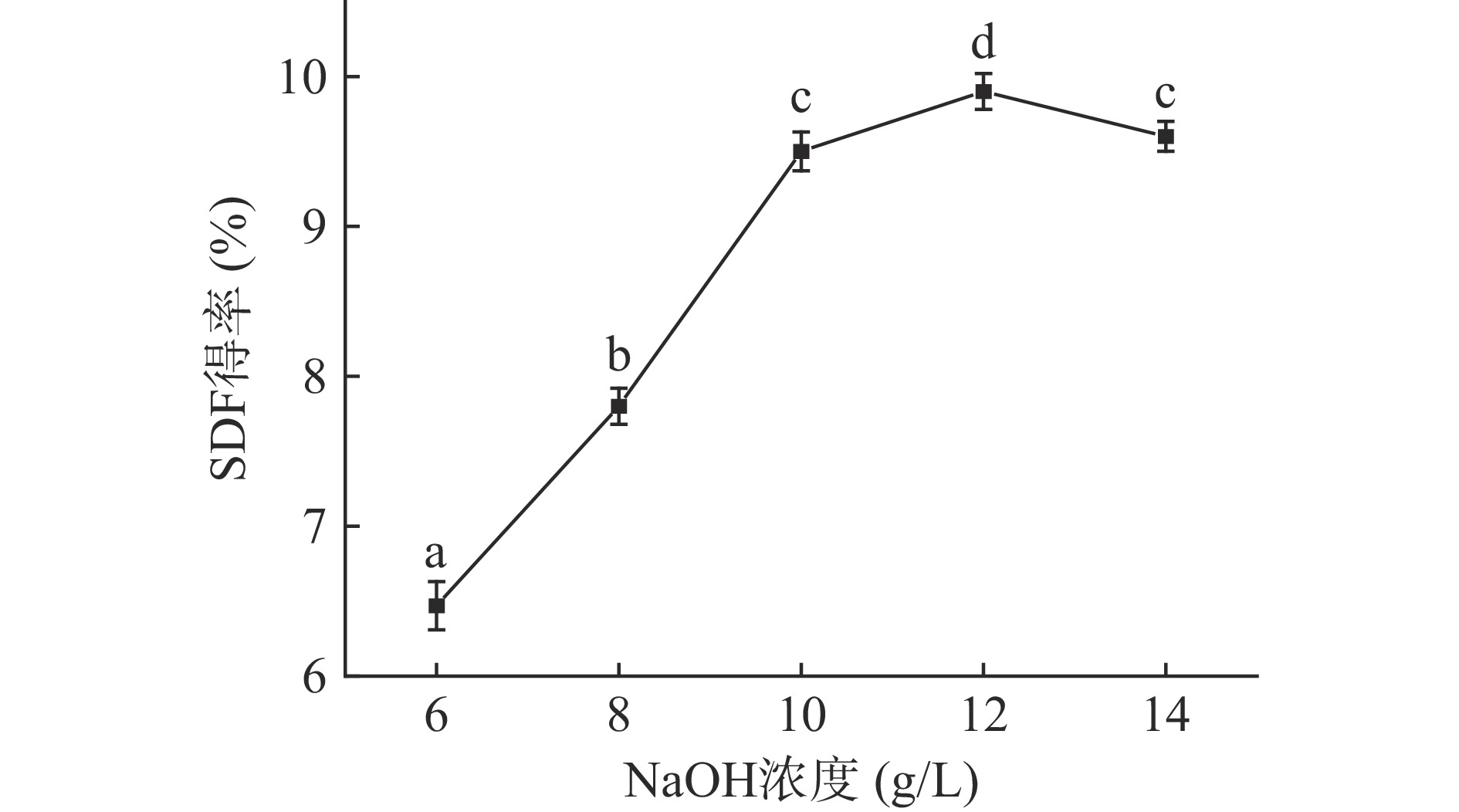
在液固比为40:1 mL/g、提取温度80 ℃、提取时间80 min时,考察NaOH浓度(6~14 g/L)对山药皮残渣SDF得率的影响。
1.2.2.3 液固比对SDF得率的影响
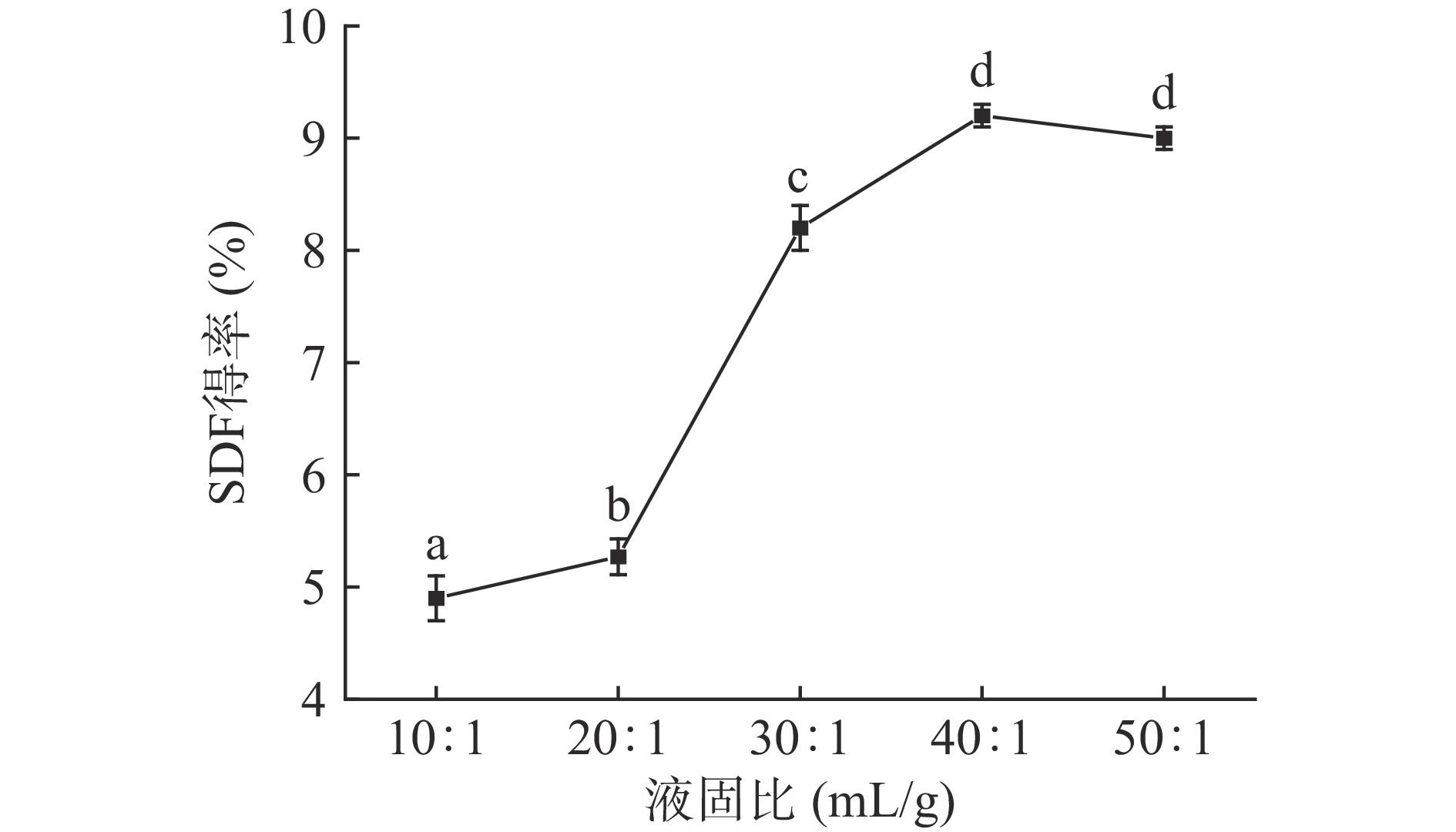
在NaOH浓度12 g/L、提取时间80 min、提取温度80 ℃时,考察液固比(10:1~50:1 mL/g)对山药皮残渣SDF得率的影响。
1.2.2.4 提取温度对SDF得率的影响
在NaOH浓度12 g/L、提取时间80 min、液固比40:1 mL/g时,考察提取温度(50~90 ℃)对山药皮残渣SDF得率的影响。
1.2.3 正交试验设计
分别以提取时间(A)、液固比(B)及NaOH浓度(C)与温度(D)考察因素,以SDF得率为目标值,考察各因素对SDF得率的影响,正交试验因素水平及编码见表1。
表 1 正交试验因素水平及编码Table 1. Levels and codes of experimental factors编码水平 因素 A提取时间
(min)B液固比
(mL/g)CNaOH浓度
(g/L)D温度
(℃)1 70 30 10 70 2 80 40 12 80 3 90 50 14 90 1.2.4 SDF表征以及理化性质测定
根据实验得出的最优工艺提取山药皮残渣中的SDF,通过X射线衍射(X-ray diffraction,XRD)图谱、傅里叶红外光谱(Fourier infrared spectroscopy,FT-IR)、扫描电镜(Scanning Electron Microscopy,SEM)检测,并对其膨胀率(Swelling Capacity,SC)、持水力(Water Holding Capacity,WHC)、持油力(Oil Holding Capacity,OHC)等理化性质进行检测。
1.2.4.1 XRD测定
参考文献[13]方法,在工作电压、电流和衍射角(2θ)的扫描范围分别为30 kV、20 mA和5°~35°的条件下,得到SDF样品的XRD谱图。
1.2.4.2 红外光谱测定
参考文献[14]方法,通过FTIR光谱仪分析SDF样品的化学结构,1 mg样品与100 mg溴化钾(烘箱干燥4~6 h)混合、研磨、压片,分辨率设置为0.4 cm−1,光谱记录范围为400~4000 cm−1。
1.2.4.3 扫描电镜(SEM)分析
采用SEM对SDF样品进行了形貌和微观结构研究,用胶带粘取干燥的SDF均匀涂开,并用吹去表面多余的样品,后在真空环境进行喷金,图像采集的加速电压为3.0 kV,选择合适的放大倍数进行拍摄[15]。
1.2.4.4 膨胀率(SC)测定
根据实验得出的最优工艺提取山药皮和山药皮残渣中的SDF,进行对比测定理化性质。膨胀率测定:参考文献[16]方法并加以修改,称取1.0 g的SDF样品(M1)置于20 mL量筒中测得体积(V1),加入10 mL去离子水浸没样品,24 h后测得膳食纤维膨胀后的体积(V2)。根据公式(2)计算得出SC:
(2) 1.2.4.5 持水力(WHC)测定
将1.0 g样品(W1)分别加入25 mL蒸馏水中,在37 ℃下平衡2 h,4800 r/min离心10 min后,立即提取残渣,测量重量(W2)。WHC由公式(3)确定:
(3) 1.2.4.6 持油力(OHC)测定
室温下,取冻干SDF样品(O1)1 g,加入25 mL大豆油中2 h。在4800 r/min离心10 min后提取沉积物,然后立即测量重量(O2),OHC根据公式(4)测定:
(4) 1.3 数据处理
试验数据均重复3次,采用Excel整理数据,用IBM SPSS Statistics 22.0软件程序Duncan检验法进行显著性分析(P<0.05),并以
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素实验结果
2.1.1 提取时间对SDF得率的影响
由图1可得,50~80 min时间段内,SDF得率与提取时间呈正相关,80 min时达SDF得率到峰值,SDF得率为10.40%±0.20%,此时SDF得率与其他实验组差异显著(P<0.05)。这可能是因为当碱水解时间过短时,果胶水解不充分,SDF的得率较低,但是SDF在碱液中时间过长会导致果胶被裂解,从而降低SDF得率[17]。所以,最适提取时间为80 min,选择70、80、90 min为正交试验水平。
2.1.2 NaOH浓度对SDF得率的影响
由图2可知,山药皮残渣中SDF提取的最佳NaOH浓度为12 g/L,此时SDF得率(9.90%±0.12%)显著高于其他各实验组(P<0.05)。碱性条件可以破坏细胞壁基质中的氢键和共价键,其中的多糖释放,可显著提高提取率,在碱法提取膳食纤维工艺中,NaOH浓度是影响得率的最重要因素之一,在一定浓度范围内NaOH浓度的增加使得膳食纤维得率增加。而结果显示NaOH浓度为10和14 g/L时,SDF得率并无显著性差异(P>0.05),这是因为当碱液浓度超过一定水平值时,膳食纤维又会进一步分解生成小分子葡萄糖,导致IDF和SDF的得率降低[18]。因此碱液浓度在12 g/L时是提取SDF的最佳条件,综合考虑,选择10、12、14 g/L为正交试验水平。
2.1.3 液固比对SDF得率的影响
由图3可知,山药皮残渣中SDF得率在液固比为10:1~40:1 mL/g区间内,显著增加(P<0.05),其峰值得率为9.23%±0.12%。这可能是因为在低比例的液固比下,溶液的粘度较高,离心分离比较困难,随着体系的液固比增加,萃取率提高,但当反应体系中存在大量的碱液时,膳食纤维会发生水解,导致膳食纤维损失,从而使提取率降低[19]。综合考虑,选择30:1、40:1、50:1 mL/g为正交试验水平。
2.1.4 温度对SDF得率的影响
SDF提取效率可能受提取温度的影响[20],由图4可知,在50~80 ℃范围内,SDF得率随这温度的上升而增加,在80 ℃时达到峰值,SDF得率为11.12%±0.15%,显著高于其他各实验组(P<0.05)。这可能是因为加热促进SDF在碱溶液中的溶解速率,使得膳食纤维得率增加,但是SDF并不具有良好的耐热性能,在高温下SDF会发生部分降解[21]。在最优提取温度80 ℃的基础上,选择70、80、90 ℃三个温度水平进行正交试验。
2.2 正交试验设计及结果
在单因素实验结果基础上,以SDF得率为评价指标,以提取时间(A)、液固比(B)及NaOH浓度(C)与温度(D)考察因素,每个因素设定3个水平,采用四因素三水平试验法进行提取工艺优化。
在单因素实验中,温度是影响SDF得率的一大因素,而正交试验结果表明,温度对SDF得率影响并不显著,这可能是因为各因素间存在交互作用,且单因素实验的路径不同也会对结果产生一定影响,因此正交试验的结果更为准确。
由表2和表3可知,提取时间、NaOH浓度、液固比对山药皮残渣SDF得率影响显著,因素次序为C>B>A,即NaOH浓度>液固比>提取时间,优化的最佳组合条件为C2B2A3D2,即液固比40:1(mL/g),NaOH浓度12 g/L,提取时间90 min,提取温度为80 ℃。
表 2 正交试验结果Table 2. Results of orthogonal test实验号 A(min) B(mL/g) C(g/L) D(℃) SDF(%) 1 70 30 10 70 4.24±0.12 2 70 40 12 80 10.45±0.06 3 70 50 14 90 9.27±0.08 4 80 30 12 90 7.62±0.09 5 80 40 14 70 8.63±0.09 6 80 50 10 80 6.32±0.10 7 90 30 14 80 8.15±0.08 8 90 40 10 90 7.82±0.06 9 90 50 12 70 11.35±0.12 K1 7.933 6.600 6.607 8.003 K2 7.533 9.000 9.800 8.300 K3 9.067 8.933 8.667 8.200 R 1.534 2.400 3.773 0.276 表 3 山药皮残渣SDF得率方差分析Table 3. Variance analysis of SDF yield of yam peel residue方差来源 偏差平方和 自由度 F值 显著性 A 3.796 2 34.857 0.028 B 11.209 2 102.939 0.01 C 21.982 2 201.878 0.005 D 0.109 2 0.029 0.972 2.3 验证试验
在实验得出的最优工艺下(提取时间90 min,NaOH浓度12 g/L,液固比40:1(mL/g),提取温度为80 ℃),山药皮残渣SDF的平均得率可达到11.52%±0.23%,其外观呈白棕色、粉末状且无特殊异味。
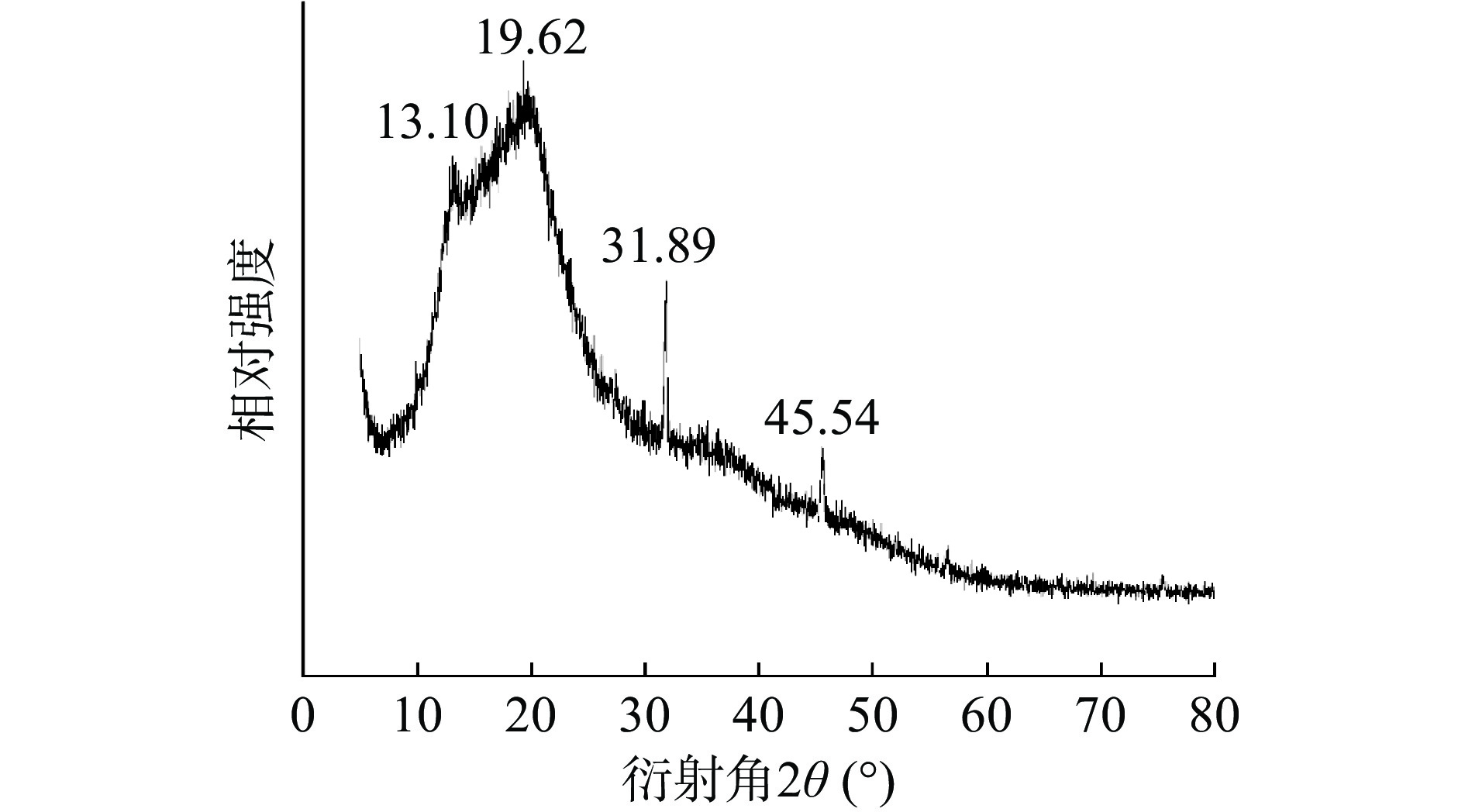
2.4 XRD测定结果
山药皮残渣SDF在2θ为19.62°附近有一个尖锐的晶体衍射峰,在2θ为13.10°和31.89°附近也有较强的晶体衍射峰(图5),这些都是纤维素I的特征衍射峰,因此可以确定山药皮残渣SDF属于纤维素I型[22]。Wang等[12]通过研究过氧化氢改性对山药皮膳食纤维的影响,发现山药皮SDF属于纤维素I型,说明山药皮残渣SDF与山药皮SDF属于同一类型。
2.5 红外光谱测定结果
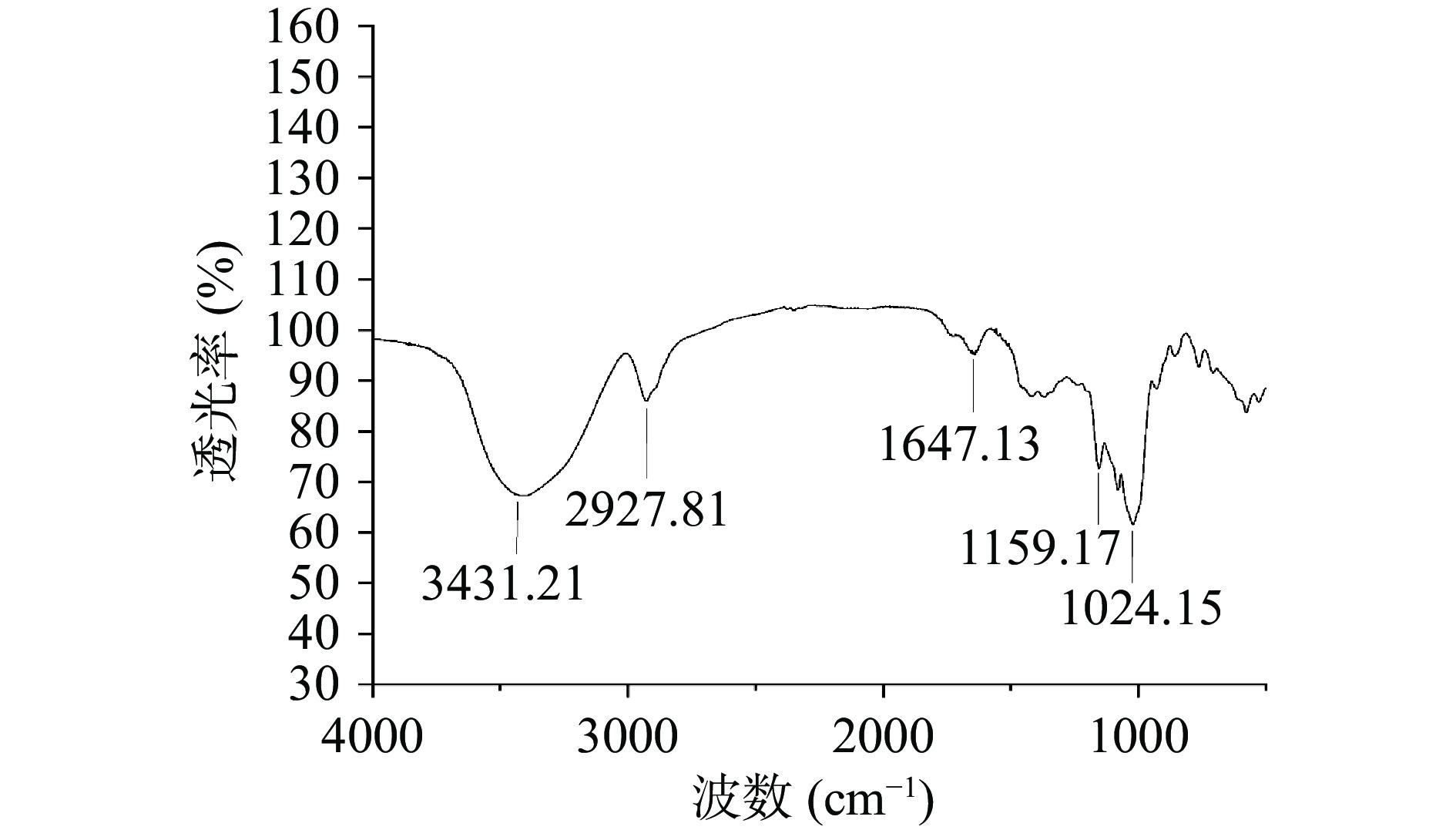
由图6所示,膳食纤维呈现出典型的多糖吸收峰,在3300~3500 cm−1范围内呈现出宽而强的条带,它是由醇、酚等氢键中O-H的拉伸振动形成的,表明了纤维素和半纤维素中的氢与羟基结合[23]。这条宽频带也表明果胶和半纤维素的存在,包括阿拉伯糖、半乳糖和木糖[24]。2920 cm−1处的吸收峰是由多糖亚甲基中的C-H振动带拉伸引起的[25];CH的变角度振动产生的1200~1400 cm−1处的吸收峰是SDF中糖的特征吸收峰[26];在1024.15 cm−1处的显著吸收带主要是由于功能性酸的C-O基团和芳香C-O-C中的醚基团的拉伸所形成[24]。
2.6 扫描电镜结果分析
图7为山药皮残渣SDF扫描电镜图,从图7中可以看出SDF是由多个细小颗粒团聚在一起而形成的疏松结构,内部空隙较大,这种结构使得SDF有着很大的比表面积。研究表明膳食纤维的空间结构与其持水性和膨胀性等理化指标有相关关系,空间结构疏松的膳食纤维样品往往有着更好的理化性质[27],因此,山药皮残渣SDF具有成为优秀吸附剂的潜质。
2.7 理化特性分析
WHC表示当施加外部压缩或离心力时,湿物质的持水能力,它与亲水性位点的化学性质和数量,以及SDF不同的表面积、密度和结构有关[28]。SDF的OHC在多种食品应用中发挥着至关重要的作用,如在烹饪时防止脂肪流失,或将人体多余的脂肪去除,它取决于水胶体表面性质、总电荷密度和疏水性[29]。由表4可知虽然山药皮残渣SDF得率小于山药皮SDF得率,但是山药皮残渣SDF的SC、WHC、OHC均高于山药皮SDF的SC、WHC、OHC。这可能是因为山药皮残渣经过醇提黄酮、多酚,水提多糖后,其纤维结构遭到破坏,增加了纤维素中羟基的暴露,导致更大的空隙,有助于增强其SC、WHC、OHC能力。
表 4 山药皮SDF与山药皮残渣SDF特性分析Table 4. SDF and SDF characteristics of yam peel residue样品 SC(mL/g) WHC(g/g) OHC(g/g) 得率(%) 山药皮SDF 4.19±0.23b 5.38±0.18b 2.41±0.15b 20.56±0.31a 山药皮残渣SDF 7.63±0.32a 9.81±0.21a 4.45±0.24a 11.52±0.23b 注:同列不同字母表示差异性显著,P<0.05。 3. 结论
通过单因素实验和正交试验得到碱法提取山药皮残渣SDF的最优工艺为提取时间90 min,NaOH浓度12 g/L,液固比40:1(mL/g),提取温度为80 ℃;在最优工艺下,山药皮残渣SDF得率为11.52%±0.23%,高于各个实验组;通过XRD、红外光谱、SEM表征,以及与山药皮SDF理化性质的对比测定,得出山药皮残渣SDF疏松的结构使其有着良好的SC、WHC、OHC,这在功能性食品的开发中具有重要的意义,研究结果为开发山药皮残渣的利用价值提供新的思路,这有助于增加山药产业的附加值。
-
表 1 正交试验因素水平及编码
Table 1 Levels and codes of experimental factors
编码水平 因素 A提取时间
(min)B液固比
(mL/g)CNaOH浓度
(g/L)D温度
(℃)1 70 30 10 70 2 80 40 12 80 3 90 50 14 90 表 2 正交试验结果
Table 2 Results of orthogonal test
实验号 A(min) B(mL/g) C(g/L) D(℃) SDF(%) 1 70 30 10 70 4.24±0.12 2 70 40 12 80 10.45±0.06 3 70 50 14 90 9.27±0.08 4 80 30 12 90 7.62±0.09 5 80 40 14 70 8.63±0.09 6 80 50 10 80 6.32±0.10 7 90 30 14 80 8.15±0.08 8 90 40 10 90 7.82±0.06 9 90 50 12 70 11.35±0.12 K1 7.933 6.600 6.607 8.003 K2 7.533 9.000 9.800 8.300 K3 9.067 8.933 8.667 8.200 R 1.534 2.400 3.773 0.276 表 3 山药皮残渣SDF得率方差分析
Table 3 Variance analysis of SDF yield of yam peel residue
方差来源 偏差平方和 自由度 F值 显著性 A 3.796 2 34.857 0.028 B 11.209 2 102.939 0.01 C 21.982 2 201.878 0.005 D 0.109 2 0.029 0.972 表 4 山药皮SDF与山药皮残渣SDF特性分析
Table 4 SDF and SDF characteristics of yam peel residue
样品 SC(mL/g) WHC(g/g) OHC(g/g) 得率(%) 山药皮SDF 4.19±0.23b 5.38±0.18b 2.41±0.15b 20.56±0.31a 山药皮残渣SDF 7.63±0.32a 9.81±0.21a 4.45±0.24a 11.52±0.23b 注:同列不同字母表示差异性显著,P<0.05。 -
[1] DE MENEZES E W, GIUNTINI E B, DAN M C T, et al. Codex dietary fibre definition–Justification for inclusion of carbohydrates from 3 to 9 degrees of polymerisation[J]. Food Chemistry,2013,140(3):581−585. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.02.075
[2] ELLEUCH M, BEDIGIAN D, ROISEUX O, et al. Dietary fibre and fibre-rich by-products of food processing: Characterisation, technological functionality and commercial applications: A review[J]. Food Chemistry,2011,124(2):411−421. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.06.077
[3] MUDGIL D, BARAK S. Composition, properties and health benefits of indigestible carbohydrate polymers as dietary fiber: A review[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2013,61:1−6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.06.044
[4] DAOU C, ZHANG H. Functional and physiological properties of total, soluble, and insoluble dietary fibres derived from defatted rice bran[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2014,51(12):3878−3885. doi: 10.1007/s13197-013-0925-y
[5] LIU Y L, FAN C H, TIAN M, et al. Effect of drying methods on physicochemical properties and in vitro hypoglycemic effects of orange peel dietary fiber[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation,2017,41(6):e13292. doi: 10.1111/jfpp.13292
[6] 张德纯. 焦作铁棍山药[J]. 中国蔬菜,2019(4):102. [ZHANG D C. Jiaozuo iron stick yam[J]. China Vegetables,2019(4):102. doi: 10.19928/j.cnki.1000-6346.2019.04.024 [7] MA F Y, ZHANG Y, YAO Y N, et al. Chemical components and emulsification properties of mucilage from Dioscorea opposite Thunb[J]. Food Chemistry,2017,228:315−322. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.01.151
[8] TEJADA-ORTIGOZA V, GARCIA-AMEZQUITA L E, TORRES J A, et al. Chemical processes for the extraction and modification of dietary fiber[M]. Science and Technology of Fibers in Food Systems. Springer, Cham, 2020: 343-361.
[9] WANG W J, MA X B, XU Y T, et al. Ultrasound-assisted heating extraction of pectin from grapefruit peel: Optimization and comparison with the conventional method[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,178:106−114. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.01.080
[10] SUN J T, ZHANG Z C, XIAO F G, et al. Ultrasound-assisted alkali extraction of insoluble dietary fiber from soybean residues[C]// IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2018, 392 ( 5 ) : 052005.
[11] MENG X M, LIU F, XIAO Y, et al. Alterations in physicochemical and functional properties of buckwheat straw insoluble dietary fiber by alkaline hydrogen peroxide treatment[J]. Food Chemistry: X,2019,3:100029. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2019.100029
[12] WANG H O, LIU S H, ZHOU X J, et al. Treatment with hydrogen peroxide improves the physicochemical properties of dietary fibres from Chinese yam peel[J]. International Journal of Food Science and Technology,2020,55(3):1289−1297. doi: 10.1111/ijfs.14405
[13] HIRAO N, KAWAGUCHI S I, HIROSE K, et al. New developments in high-pressure X-ray diffraction beamline for diamond anvil cell at SPring-8[J]. Matter and Radiation at Extremes,2020,5(1):018403. doi: 10.1063/1.5126038
[14] WANG K L, LI M, WEN X, et al. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of okra (Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench) polysaccharides based on response surface methodology and antioxidant activity[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,114:1056−1063. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.03.145
[15] GAN J P, HUANG Z Y, YU Q, et al. Microwave assisted extraction with three modifications on structural and functional properties of soluble dietary fibers from grapefruit peel[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2020,101:105549. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.105549
[16] WANG L, XU H B, YUAN F, et al. Preparation and physicochemical properties of soluble dietary fiber from orange peel assisted by steam explosion and dilute acid soaking[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,185:90−98. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.03.112
[17] 吴婧, 刘祚祚, 吴杰, 等. 滇橄榄果渣膳食纤维的提取及其体外吸附性能研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(2):174−181. [WU J, LIU Z Z, WU J, et al. Extraction and in vitro adsorption properties of dietary fiber from Phyllanthus emblica Linn. pomace[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(2):174−181. [18] 高晓丽, 王瑞, 闫艳华, 等. 碱法提取黍米粉膳食纤维的研究[J]. 安徽农学通报,2017,23(21):105−107. [GAO X L, WANG R, YAN Y H, et al. Study on extraction of dietary fiber from millet flour by alkaline method[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin,2017,23(21):105−107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7731.2017.21.043 [19] 邹兰, 任国文, 李梁. 碱法制备苹果梨渣膳食纤维工艺优化及物化特性研究[J]. 粮食与油脂,2019,32(4):72−75. [ZOU L, REN G W, LI L. Study on optimizing technology and physicochemical properties of dietary fiber from apple-pear pomace prepared by alkali method[J]. Cereals and Oils,2019,32(4):72−75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2019.04.021 [20] GARCIA-AMEZQUITA L E, TEJADA-ORTIGOZA V, SERNA-SALDIVAR S O, et al. Dietary fiber concentrates from fruit and vegetable by-products: Processing, modification, and application as functional ingredients[J]. Food and Bioprocess Technology,2018,11(8):1439−1463. doi: 10.1007/s11947-018-2117-2
[21] 郭艳峰, 李晓璐. 菠萝叶可溶性膳食纤维碱法提取工艺的优化[J]. 保鲜与加工,2019,19(5):104−108. [GUO Y F, LI X L. Optimazation of alkali extraction technique of soluble dietary fiber from pineapple leaf[J]. Storage and Process,2019,19(5):104−108. [22] FRENCH A D, SANTIAGO CINTRÓN M. Cellulose polymorphy, crystallite size, and the segal crystallinity index[J]. Cellulose,2013,20(1):583−588. doi: 10.1007/s10570-012-9833-y
[23] JIANG Y P, ZI W, PEI Z F, et al. Characterization of polysaccharides and their antioxidant properties from Plumula nelumbinis[J]. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal,2018,26(5):656−664. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2018.02.026
[24] MA Q Y, MA Z Y, WANG W X, et al. The effects of enzymatic modification on the functional ingredient-dietary fiber extracted from potato residue[J]. LWT,2022,153:112511. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112511
[25] YANG B, WU Q J, SONG X, et al. Physicochemical properties and bioactive function of Japanese grape (Hovenia dulcis) pomace insoluble dietary fibre modified by ball milling and complex enzyme treatment[J]. International Journal of Food Science and Technology,2019,54(7):2363−2373. doi: 10.1111/ijfs.14134
[26] WANG K L, LI M, WANG Y X, et al. Effects of extraction methods on the structural characteristics and functional properties of dietary fiber extracted from kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa)[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,110:106162. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.106162
[27] 桑嘉玘, 辜青青, 徐玉娟, 等. 提取方法对柚皮海绵层不溶性膳食纤维理化性质、功能及结构的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(3):149−154. [SANG J Q, GU Q Q, XU Y J, et al. Effects of extraction methods on the physicochemical properties, function and structure of insoluble-soluble dietary fiber in sponge layer of pomelo peel[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022,48(3):149−154. [28] XIE F, WANG Y Q, WU J H, et al. Functional properties and morphological characters of soluble dietary fibers in different edible parts of Angelica keiskei[J]. Journal of Food Science,2016,81(9):2189−2198. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.13399
[29] JIA M, CHEN J, LIU X, et al. Structural characteristics and functional properties of soluble dietary fiber from defatted rice bran obtained through Trichoderma viride fermentation[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2019,94:468−474. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.03.047






 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:



