Effect of Zein on Buckwheat Dough Properties
-
摘要: 为探究玉米醇溶蛋白(Zein)对荞麦无麸质面团流变学特性的影响,将气流膨化苦荞粉与甜荞粉以1:1混合制得基料粉(以下称混粉)。用90%乙醇溶液对Zein进行增塑处理,然后按照0%、5%、10%、15%、20%的添加量(以混粉计)与混粉及水揉混制得荞麦无麸质面团(以下称面团),并对面团静态流变学特性(质构特性、拉伸特性和应力松弛特性)、动态流变学特性、光学性质(色度和反光率)以及微观结构等进行测定。结果表明,随着Zein添加量从0%增加到20%,面团的硬度从482.38 g降低到346.60 g,弹性从0.21升高到0.29,拉伸距离从15.44 mm升高到38.16 mm,抗拉伸力从13.10 g升高到72.04 g。面团的残余应力、黏弹系数和松弛时间相对于对照组显著升高(P<0.05),但随着Zein添加量的增加均逐渐减小,面团G'和tanδ值、面团表面亮度及反光率均得到明显改善,微观结构相比对照组能够明显地观察到蛋白纤维丝。以上结果充分表明,Zein可有效地改善荞麦无麸质面团结合力和延伸性差的缺陷。本研究为无麸质食品结构及加工特性改善提供了一个新的途径。Abstract: To investigate the effect of zein addition on rheological properties of buckwheat-based gluten-free dough, atmosphere puffed tartary buckwheat flour was mixed with common buckwheat flour at a ratio of 1:1 to make a mxied base flour (MBF). Zein was plasticized with 90% ethanol solution, and then 0%, 5%, 10%, 15%, and 20% (MBF based) of the plasticized zein was mixed with MBF and water, respectively, to make a buckwheat-based gluten-free dough (BBGD) with gradient content of zein. The static rheological properties of dough (texture properties, tensile properties and stress relaxation properties), dynamic rheological properties, optical properties (chromaticity and reflectivity) and microstructure were measured. Results showed that, with the increasing of zein content from 0% to 20%, the hardness of BBGD decreased from 482.38 g to 346.60 g, while elasticity, tensile distance, and tensile strength increased from 0.21 to 0.29, 15.44 to 38.16 mm, and 13.10 to 72.04 g, respectively. The residual stress, viscoelastic coefficient and relaxation time increased significantly compared with the control (P<0.05), but decreased gradually with the increasing of zein addition. The G' and tanδ values, surface brightness, and reflectance rate of the dough were significantly improved, and the protein fiber was obviously observed in the microstructure compared with the control. The above results showed that zein could effectively improve the defects of poor adhesion and extensibility of buckwheat gluten-free dough. This study would provide a new way for improving the structure and processing properties of gluten-free foods.
-
Keywords:
- buckwheat dough /
- zein /
- gluten-free /
- rheological properties /
- airflow puffing
-
荞麦,蓼科(Polygonaceae)荞麦属(Fagopyrum),分为甜荞(F. esculentum)和苦荞(F. tataricum)[1]。荞麦有一定降血糖和排毒减肥功效[2-4],荞麦蛋白消化率低,但被机体利用率高于其他谷物[5]。荞麦中还含有大量的抗氧化成分,例如黄酮、芦丁和槲皮素等[6-7]。因此荞麦被作为药食同源食品,具有降血糖、降血脂、降低胆固醇等作用。本研究团队在前期中日合作项目研究中发现,苦荞籽粒可利用气流膨化直接有效去壳,同时实现胚乳糊化,有助于无麸质面团内部结构的形成,并促进酚类抗氧化因子的释放,芦丁和槲皮素的含量显著提高[8-9]。通过预试验发现当甜荞粉与气流膨化苦荞粉以1:1质量比混合时,制得的荞麦面团具有良好的加工特性。
麸质(Gluten)即小麦面筋蛋白,是复杂的蛋白质混合物,能够为面团提供黏弹性网络结构[10]。将荞麦作为基料粉,可以丰富无麸质产品的营养成分[11-12]。
玉米醇溶蛋白(Zein)主要存在玉米胚乳中,是玉米淀粉的工业副产物,是一种绿色环保的高分子生物材料,无毒无害,可食用,具有成膜性、成纤维性,由于其不溶于水的性质,在食品中的应用并不广泛[13]。Zein在作为无麸质产品改良剂的同时也可作为蛋白添加剂,弥补无麸质产品蛋白缺失的缺点。目前有学者研究了各种酶处理或高于玻璃态转变温度的Zein来改善无麸质面团的结构[14-15],也有学者将zein与米粉提前混合后加入乳酸制备面团,但这最终对无麸质米粉面团的改良效果并不理想[16],Akin等[17]研究发现用90%乙醇溶液对Zein进行预先改性处理之后可形成类似面筋蛋白的黏弹体,有助于无麸质面团结构的形成,乙醇溶液处理Zein之后会使混合Zein的高粱面团变得更软。因此本研究对Zein进行预先改性处理,通过添加不同比例Zein与荞麦加工制得无麸质面团,通过对荞麦无麸质面团质构特性、拉伸特性、应力松弛特性、动态流变学特性、微观结构、色度及反光率等性质进行测定,并对其进行分析,确定Zein改善荞麦无麸质面团结构的最优添加量,对拓宽Zein在食品中的应用有重要意义。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
甜荞粉 购自红盛小杂粮公司(陕西省榆林靖边县),原料品种为西农9976;苦荞籽粒 品种为西农9940,种植并收获于2021年,由红盛小杂粮公司(陕西榆林靖边县)提供;玉米醇溶蛋白(zein) 购于高邮日星药辅;无水乙醇 购于成都市科隆化学品有限公司;本研究中所用化学试剂 均为分析纯。
MY-B001-PC气流膨化机 贝聿铭俱乐部(日本);MY-B001-PC高速万能粉碎机 永康市久品工贸有限公司;TA.XT PLUS/50质构仪 STABLEMICRO公司(英国);DHR-1旋转流变仪 TA公司(美国);FlexSEM1000小型台式冷台扫描电镜 Hitachi公司(日本);CS-820分光测色仪 杭州彩谱科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 混粉的制备
气流膨化苦荞粉的制备:以西农9940籽粒为原料,去除杂物,放入气流膨化机进行膨化,手动去壳,其余原料均转移至高速万能粉碎机中进行磨粉,期间每研磨30 s停2 min,防止仪器温度过高导致籽粒糊化发黏。磨粉2 min后过筛60目,装入塑封袋保存备用。
混粉的制备:将气流膨化苦荞粉与甜荞粉按照1:1的比例进行复配得到甜荞粉与气流膨化苦荞粉的混合粉(以下称混粉)作为试验基料粉。
1.2.2 荞麦面团及小麦面团制备
将Zein与90%乙醇溶液按质量比1:1混合均匀,使Zein与乙醇溶液充分混匀呈现出黏稠状态,然后用水冲洗同时揉搓2 min,Zein出现完整的面团质感,然后与荞麦混粉、水充分揉搓10 min混合均匀(加水量与混粉质量比为1:1),使Zein均匀的分布在荞麦面团内部(Zein添加量为混粉质量的5%、10%、15%及20%),以不添加Zein为对照,制得荞面无麸质面团(除非特别说明,本文中以下称荞麦面团)。小麦面粉与水按质量比2.5:1混合均匀后充分揉搓15 min制得小麦面团。
1.2.3 荞麦面团及小麦面团质构特性的测定
参考董春霞[18]的方法略作修改,将上述荞麦面团用圆柱形模具制成直径25 mm,高34 mm的圆柱形,静置10 min(期间用保鲜膜包裹),于TA.XT PLUS/50质构仪上进行TPA模式测试。测试参数:P/36R探头,测试速度为1.0 mm/s,应变50%,间隔时间5 s,触发力5.0 g,平行试验5~8次。
1.2.4 荞麦面团及小麦面团拉伸特性的测定
参考Liu等[19]的方法,将上述荞麦面团压制成大小均一长80 mm,宽5 mm,高2 mm的面团条于TA.XT PLUS/50质构仪进行拉伸试验。测试参数如下:探头A/KIE,测前速度2.0 mm/s,测试速度3.3 mm/s,测后速度为10.0 mm/s,拉伸距离为80 mm,触发力为5.0 g,平行试验5~10次。
1.2.5 荞麦面团及小麦面团应力松弛试验
参考周星杰[20]的方法,将上述荞麦面团制备为直径25 mm,高为34 mm的面团,静置10 min(期间用保鲜膜包裹),用TA-XT Plus物性测定仪进行应力松弛实验。测试参数为:探头P/50,测试模式为压缩,测试速度1.0 mm/s,应变10%,触发力5.0 g,保持时间180 s,平行试验5~8次。主要依据为广义的Maxwell模型。通过三要素Maxwell 模型对荞麦面团应力松弛的松弛阶段进行非线性回归分析:
式中:
1.2.6 荞麦面团及小麦面团流变学特性
参考姬成宇[21]的方法略作修改,荞麦面团用保鲜膜密封,室温下放置30 min释放揉混形成的应力,于DHR-1旋转流变仪测定。选取直径40 mm平板,取适量荞麦面团置于两块平板间,平板间隙1500 μm,在平板周围涂矿物油防止水分挥发,样品在两板之间静置120 s以松弛残余应力。首先确定线性黏弹区,参数设置为:温度为25 ℃,角频率为10 rad/s。然后进行频率扫描,设置参数为:设置0.5%应变,频率0.1~40 Hz。测定储能模量(G')和损耗模量(G"),损耗正切tanδ=G"/G'代表物质黏性和弹性的比例。平行试验5~8次。
1.2.7 荞麦面团及小麦面团微观结构
将制得荞麦面静置30 min后将面团压成高1 mm,半径为4 mm的小圆片后于恒温烘箱25 ℃干燥24 h后,置于小型台式冷台扫描电镜(无需喷金),加速电压5 kV,在500倍下观察微观结构[22]。
1.2.8 荞麦面团及小麦面团色度及反光率
使用色度仪测定面片色度及反光率,将荞麦面团使用压延机压成2 mm面片,覆盖保鲜膜并将保鲜膜压平不留气泡。测试参数为:D65光源,10°视野,光圈开口直径18 mm,色度结果以CIE-L*a
*b*颜色空间表示,并记录反射率光谱图。平行试验5~8次。 1.3 数据处理
所有试验均重复5次以上,使用Minitab 18(Trial version)软件,采用最小显著性差异检验(Fisher)(P<0.05)进行均值分离和单因素方差分析(ANOVA);使用 Origin Pro 2021(Trial version)软件进行作图。
2. 结果分析
2.1 荞麦面团及小麦面团质构特性
由表1可知,随着Zein添加量的增加,试验组的硬度均显著低于(P<0.05)对照组,当Zein添加量为20%时,荞麦面团硬度从482.38 g降到346.60 g,硬度显著低于(P<0.05)小麦面团,面团的弹性随着Zein添加量升高显著提高(P<0.05),从0.21升到0.29,与小麦面团弹性存在显著差异(P<0.05)。黏聚性、咀嚼性和回复性无明显变化规律。对照组硬度大,弹性小,不利于面团的形成,这是因为未添加Zein的荞麦面团不存在形成结构的面筋蛋白[23],内部的黏性较大,使分子链之间相互运动时的摩擦增大,所以硬度较大,弹性较低[24]。添加Zein后之所以硬度降低,弹性升高是因为在面团混合过程中,因为荞麦淀粉颗粒可以与Zein结合形成更连续的蛋白相[25],面团内部的凝胶结构与蛋白纤维相结合形成新的结构主体,显著改善(P<0.05)荞麦面团硬度和弹性。面团黏聚性、咀嚼性和回复性没有显著的规律变化,有学者认为黏聚性的变化归因于其他组分与淀粉颗粒竞争游离水[26],而Zein的疏水性导致面团黏聚性没有显著的规律变化,由于硬度增大,弹性减小,所以咀嚼性无显著规律变化,在面团揉混阶段不断输入能量,β-折叠增加,面团结构得到改善,若温度减小,会导造成β-折叠降低[27],面团整体加工环境处于室温无温度变化,所以面团回复性无显著规律变化。
表 1 Zein对荞麦面团质构特性影响Table 1. Effects of zein on texture properties of buckwheat doughZein添加量(%) 硬度(g) 弹性 黏聚性 咀嚼性 回复性 0(对照) 482.38±16.76a 0.21±0.00d 0.29±0.01b 29.94±2.45b 0.08±0.00a 5 427.54±4.67b 0.23±0.00c 0.25±0.01c 24.58±0.42c 0.07±0.00b 10 406.64±5.39c 0.23±0.01c 0.24±0.03c 22.44±0.92d 0.06±0.01c 15 375.00±3.50d 0.27±0.00b 0.27±0.00b 27.34±1.20d 0.07±0.00b 20 346.60±9.57e 0.29±0.01a 0.27±0.01b 27.14±0.83c 0.07±0.00b 小麦面团 426.61±15.20b 0.27±0.02b 0.37±0.02a 41.65±1.36a 0.09±0.00a 注:数据表示为平均值±标准差;同一列中不同的字母表示有显著性差异(P<0.05);表2~表3同。 2.2 荞麦面团及小麦面团拉伸特性
面团的最大抗拉伸力和最大拉伸距离可体现面团的筋力,表征了面团的延展性与可塑性,与后续烘焙品质成正相关。Smith等[28]研究发现,在使用乙醇溶液对Zein进行处理后,会形成柔软且具有延展性的材料。
如表2所示,试验组的最大抗拉伸力和最大拉伸距离均显著高于(P<0.05)对照组,当Zein的添加量为20%时,最大抗拉伸力从13.10 g升到72.04 g,显著小于(P<0.05)小麦面团的160.37 g,最大拉伸距离从15.44 mm升到38.16 mm,显著高于(P<0.05)小麦面团的18.07 mm,这可能是因为对照组面团内部没有任何能够提供延展拉伸性的结构。随着Zein添加量的增加,面团的最大抗拉伸力和拉伸距离呈现规律增长,这可能是因为对Zein进行塑化并且揉混之后,Zein的舒展、翻折将结构内部的疏水性基团暴露在外,蛋白质间因为强烈的疏水性基团联结成网,增强了荞麦面团的延展性[17]。当Zein的添加量为20%时荞麦面团最大抗拉伸力显著(P<0.05)低于小麦面团,这是因为小麦蛋白网络类似于一种蛋白基质,淀粉颗粒牢固的嵌入或者被包裹[29],使得小麦面团抵抗外力的能力更强。小麦面团最大拉伸距离显著低于20% Zein面团,原因在于淀粉颗粒会附着在形成的玉米醇溶蛋白纤维丝表面[30],Zein面团的延展性强于小麦面团。Zein赋予面团延展性这一结果与Helene等 [31]研究Zein对燕麦麸水胶体所得结果一致。
表 2 Zein对荞麦面团拉伸特性影响Table 2. Effects of zein on tensile properties of buckwheat doughZein添加量(%) 最大抗拉伸力(g) 最大拉伸距离(mm) 0(对照) 13.10±0.02f 15.44±0.55e 5 24.36±2.38e 18.37±0.60d 10 45.76±3.93d 21.65±2.05c 15 60.80±3.96c 25.59±3.61b 20 72.04±4.10b 38.16±3.58a 小麦面团 160.37±4.72a 18.07±1.24d 2.3 荞麦面团及小麦面团应力松弛
不同比例Zein添加量对荞麦面团应力松弛影响如图1所示。应力松弛是对面团整体的黏弹性的全面分析[32]。面团被压缩到10%形变时的应力松弛阶段,此时内部的应力最大。可以看到对照组和试验组的应力曲线随着时间增加均呈现出下降并且趋于平缓的趋势,随着Zein添加量的增加,面团达到的最大应力以及松弛阶段的应力逐渐降低,当Zein添加量为20%时面团的最大应力以及松弛阶段应力仅小于小麦面团。
添加Zein的荞麦面团应力松弛曲线按三要素Maxwell模型用非线性回归法解析的结果如表3所示,E2残余应力,E2数值代表内部分子链之间相对运动引起高弹形变的强度, E2越大,达到应力平衡时所需的力越大,说明变化幅度在压缩后期会越来越大[33]。试验组的残余应力远大于对照组,这是因为对Zein进行塑化处理后形成Zein网络结构,加入后使得荞麦面团增加了抗形变能力导致达到平衡时需要的应力越大。外源蛋白结构物质的加入会有效改善无麸质面团的结构特性[34]。试验组E2随着Zein添加量的增加而降低,因为Zein的蛋白纤维丝穿插在面团内部,淀粉颗粒附着在纤维丝上,面团的延展性增加,面团内部分子链之间相对运动增强,抵抗形变的能力降低,E2降低。当Zein添加量为20%时,Zein面团的E2与小麦面团无显著差异,证明在无麸质面团中添加一定量Zein可达到与小麦相似的机械性质。
表 3 Zein对荞麦面团应力松弛影响Table 3. Effects of zein on stress relaxation of buckwheat doughZein添加量(%) E2(N·m−2·10−4) η(N·m−2·s·10-6) τ(s) 0(对照) 1.03±0.05d 54.90±3.65e 31.89±2.24a 5 86.46±4.93a 3072.41±36.18a 29.15±0.43a 10 72.12±7.98b 2946.92±20.61b 25.92±2.01b 15 63.63±3.07bc 1686.54±64.90c 25.42±2.07b 20 61.72±4.80c 1666.07±73.11c 23.71±0.28c 小麦面团 60.95±5.95c 1258.24±81.12d 20.89±2.05d η为阻尼黏滞系数,由内部分子链相互运动产生的摩擦力引起[35],为荞麦面团初始黏度[36]。τ为松弛时间,由黏性行为和弹性行为共同确定,τ减小,说明面团应力下降的速度快,面团黏性小,弹性大[37]。在对照组的荞麦面团中,由于面团内部结构简单,仅有糊化或破损淀粉与水结合形成的凝胶状结构,凝胶网络结合淀粉颗粒形成大量聚合物[38],面团内部的黏性较大,使分子链之间相互运动时的摩擦增大,所以η相较于试验组较小,τ较大。随着Zein添加量的增加,面团内部蛋白纤维丝与凝胶状结构相互结合减弱原有的凝胶结构,破坏凝胶网络结构,蛋白成为结构主体,淀粉附着在蛋白纤维丝表面,使得面团抵抗外界形变能力减弱,面团展现出较强的流动性[39],导致η与τ均减小。试验组的η与τ均高于小麦面团,尽管添加一定量Zein的无麸质面团在部分机械性质上能达到小麦面团的水平,但还是存在一定的差距。
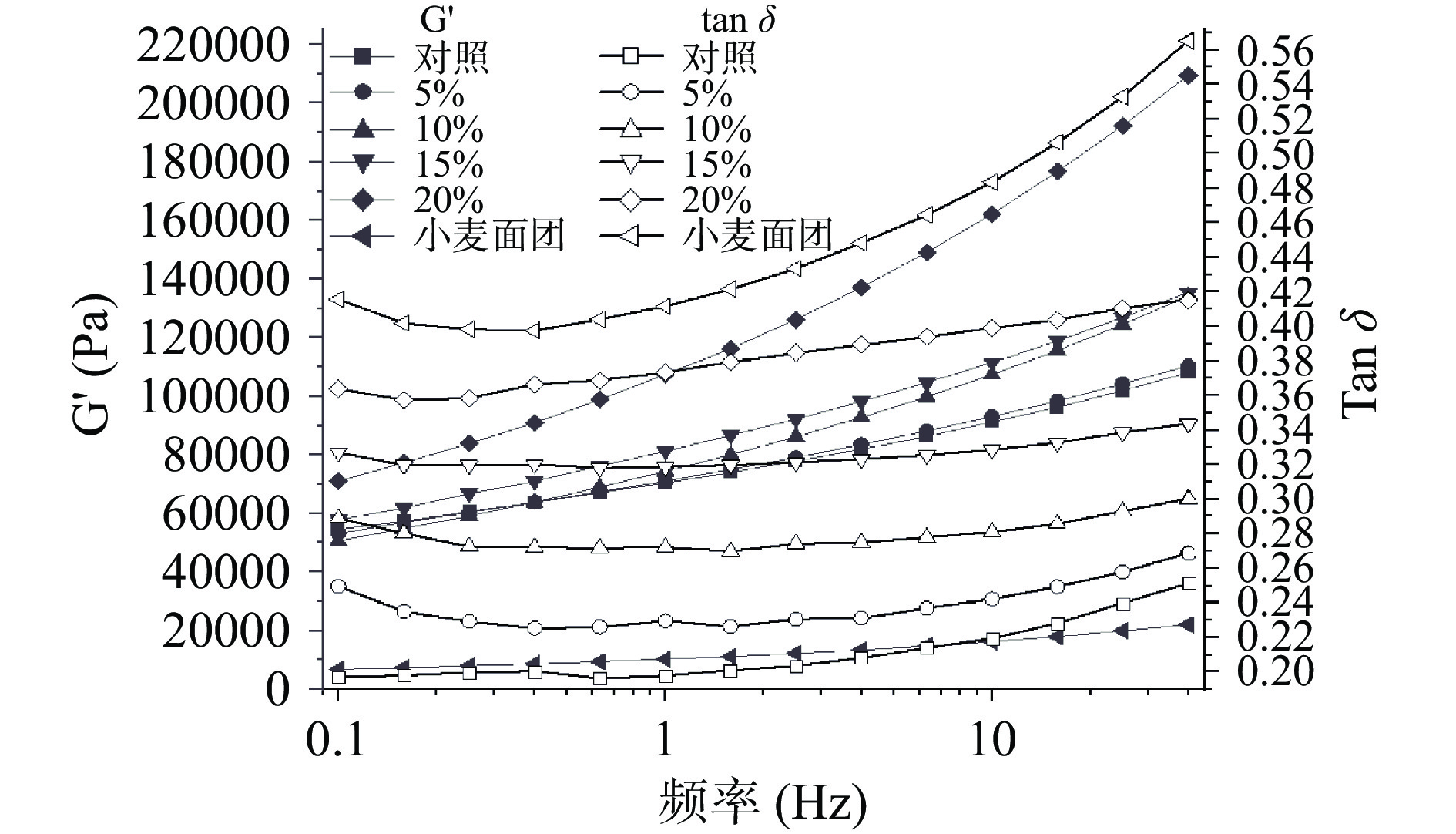
2.4 荞麦面团及小麦面团动态流变学特性
储能模量(G')与损耗模量(G'')分别反映了面团的弹性和黏性[40]。损耗角正切值(tanδ)为损耗模量与储能模量的比值,用来描述面团中的黏弹性。当tanδ的值越大时,黏性以及流动性强,分子间相互作用程度低;反之说明体系弹性强,分子间相互作用程度高[41]。
将Zein按照不同比例梯度添加到荞麦面团当中,经旋转流变仪频率扫描后得到的结果如图2所示。如图所示,G'均随着频率的增加而增加,说明面团样品具有频率依赖性[42]。在相同频率下,Zein的添加量越高,G'增加,这表明面团内部Zein与淀粉分子产生了强烈的交联作用,表现出典型的弱凝胶动态流变特性[43]。tanδ在相同频率下随着Zein的增加也在增加,Mattice等[44]研究发现,玉米醇溶蛋白使用乙醇处理时形成的蛋白质网络结构具有黏弹性,tanδ增加说明无麸质面团在添加Zein之后面团的弹性行为强于黏性行为,分子间互作用增强,这与应力松弛得到的结果相一致。而小麦面团的G'最低,tanδ最高的原因可能会是因为面筋蛋白的分子量范围为大约30000到超过1000万,远大于Zein的多肽单体大小,此外,面筋蛋白比Zein含有更多的半胱氨酸(2%),半胱氨酸对面筋的结构和功能也至关重要[45],推测较高的蛋白质分子量和半胱氨酸(与Zein相比)可能与面筋蛋白网络表现出的强弹性有关。
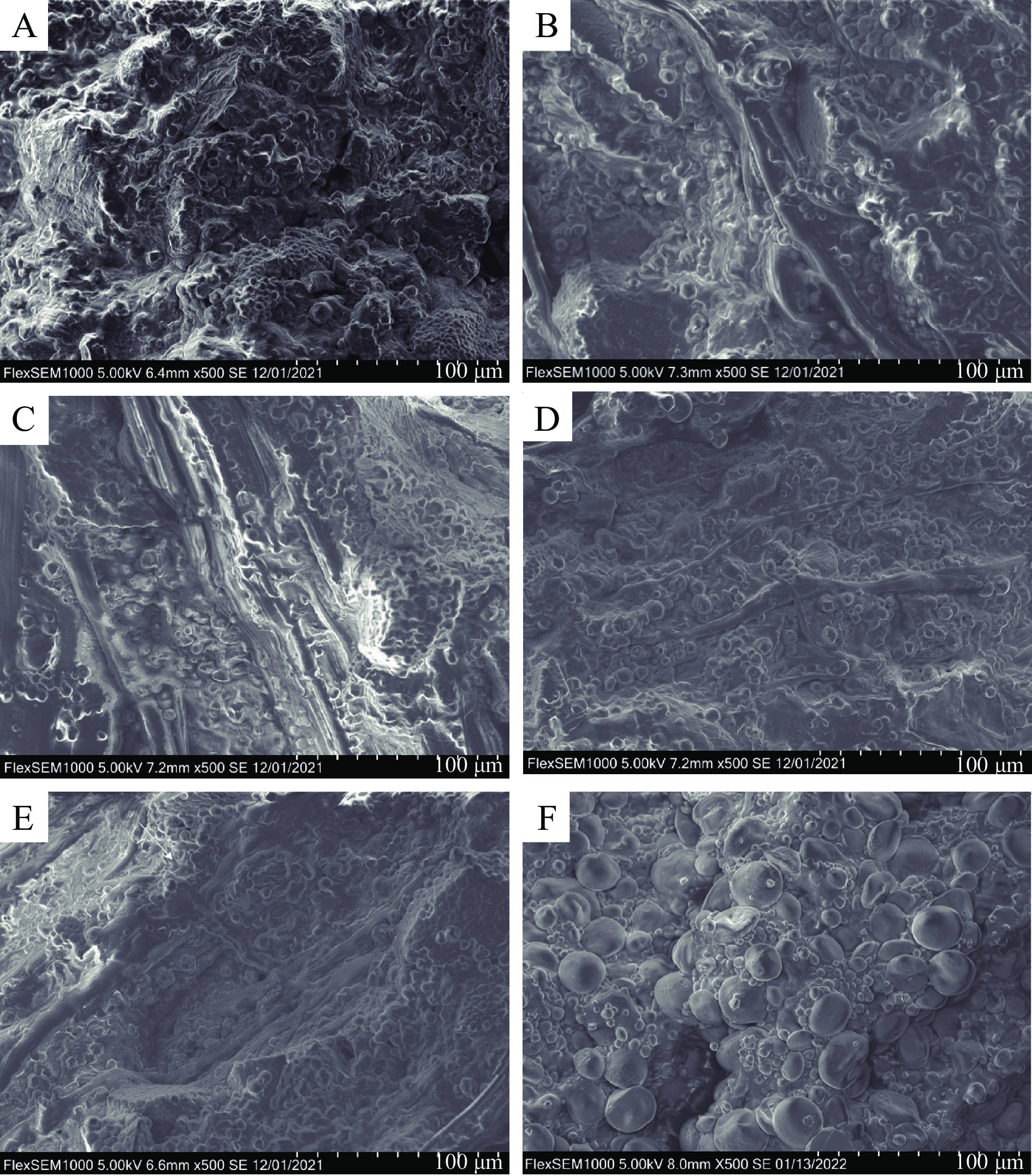
2.5 荞麦面团及小麦面团微观结构
荞麦面团添加不同比例Zein的微观结构如图3所示。对照组面团内部仅有零散的凝胶状物质连接淀粉颗粒以及部分淀粉颗粒聚集,未观察到明显的结构。随着Zein添加量的增加,荞麦面团内部形成的纤维状结构数量增加,从而形成稳定结构。当Zein添加量为20%时,Zein纤维丝的密度高于试验组并且于淀粉的结合更加紧密,但与小麦面团不同的是添加Zein的荞麦面团中淀粉颗粒吸附在纤维丝状蛋白上,而小麦蛋白则是形成蛋白网络来包裹淀粉颗粒,这是因为Zein与麦谷蛋白的分子结构不同造成[46]。Taylor等[47]研究发现当Zein形成具有黏弹性团块时,团块很容易被拉伸并且会出现纤维丝。
2.6 荞麦面团及小麦面团色度和反射率
L*代表明度,可作为面团表面结构性质表征的一个指标[48]。面团表面越平滑光洁,反射光的能力越强,则L*值越大。a*值及b*分别代表面团的红绿以及黄蓝程度,a*值为+代表红,相反代表绿;b*值为+代表黄,相反代表蓝。
由表4可知,随着Zein添加量的提高,a*值及b*值增加,面团表现出越来越深的棕黄色,小麦面团的a*值及b*值均小于试验组,这是由于Zein本身带有棕黄色所致。颜色加深一般会导致L*值降低,但随着Zein添加量的提高,颜色变深,但L*值反而显著增加(P<0.05),当Zein添加量为20%时,L*值可达到58.97,虽然仍旧达不到小麦的L*值,但也可说明添加zein有助于荞麦面团形成更光滑的表面结构。图4所示为不同波长下面团的反射率光谱,随着Zein添加量的增加,全波长范围内光谱反射率均增加,这也更加明确地说明添加Zein可使荞麦面团形成更光滑的表面结构。由于添加Zein后荞麦面团在压延后表面会裸露出部分Zein纤维丝,导致表面不平整,以及颜色变深(棕黄色),所以光谱反射率低于小麦面团。
表 4 Zein对荞麦面团色度及反射率影响Table 4. Influence of zein on buckwheat dough chroma and reflectanceZein添加量(%) L* a* b* 0(对照) 51.47±0.30f -0.23±0.04e 24.11±0.34e 5 53.01±0.06e 6.61±0.03c 26.42±0.14d 10 53.48±0.12d 6.95±0.04b 27.85±0.70c 15 55.00±0.09c 7.37±0.09a 29.35±0.06b 20 58.97±0.37b 7.25±0.28a 31.84±0.38a 小麦面团 78.39±0.10a 6.57±0.09d 15.01±0.35f 3. 结论
研究结果表明,随着Zein添加量的增加,无麸质面团的结构逐渐改善,并且趋近于小麦面团,当Zein的添加量为20%时,无麸质面团结构改善最为明显,荞麦面团的硬度降低135.78 g,弹性上升0.08,最大抗拉伸力上升58.94 g,最大拉伸距离升高22.72 mm,残余应力与松弛时间均接近小麦面团,这说明20% Zein添加量可以赋予荞麦无麸质面团类似小麦面团的机械性质。频率扫描结果表明荞麦面团添加Zein之后更趋向于流体的性质,通过微观结构的观察,Zein形成的蛋白质纤维丝能够粘附淀粉颗粒,穿插在内部形成结构支撑。Zein的添加使荞麦面团表面反光率明显提高,说明Zein可以明显增加面团内部分子间相互作用,并且改善面团表面光洁度。以上数据表明,添加Zein会有效改善荞麦无麸质面团的成团性以及面团的压延性,有利于后续加工;制得面条在蒸煮过后也会有较好的拉伸特性且断条率低。Zein可作为良好的无麸质改良剂应用于荞麦面团。
综上所述,Zein可通过形成网络结构有效地改善荞麦无麸质面团结构及加工特性。该研究为解决无麸质面团加工特性差的问题提供了思路和方法,为进一步拓展Zein在食品中的应用提供了新途径。
-
表 1 Zein对荞麦面团质构特性影响
Table 1 Effects of zein on texture properties of buckwheat dough
Zein添加量(%) 硬度(g) 弹性 黏聚性 咀嚼性 回复性 0(对照) 482.38±16.76a 0.21±0.00d 0.29±0.01b 29.94±2.45b 0.08±0.00a 5 427.54±4.67b 0.23±0.00c 0.25±0.01c 24.58±0.42c 0.07±0.00b 10 406.64±5.39c 0.23±0.01c 0.24±0.03c 22.44±0.92d 0.06±0.01c 15 375.00±3.50d 0.27±0.00b 0.27±0.00b 27.34±1.20d 0.07±0.00b 20 346.60±9.57e 0.29±0.01a 0.27±0.01b 27.14±0.83c 0.07±0.00b 小麦面团 426.61±15.20b 0.27±0.02b 0.37±0.02a 41.65±1.36a 0.09±0.00a 注:数据表示为平均值±标准差;同一列中不同的字母表示有显著性差异(P<0.05);表2~表3同。 表 2 Zein对荞麦面团拉伸特性影响
Table 2 Effects of zein on tensile properties of buckwheat dough
Zein添加量(%) 最大抗拉伸力(g) 最大拉伸距离(mm) 0(对照) 13.10±0.02f 15.44±0.55e 5 24.36±2.38e 18.37±0.60d 10 45.76±3.93d 21.65±2.05c 15 60.80±3.96c 25.59±3.61b 20 72.04±4.10b 38.16±3.58a 小麦面团 160.37±4.72a 18.07±1.24d 表 3 Zein对荞麦面团应力松弛影响
Table 3 Effects of zein on stress relaxation of buckwheat dough
Zein添加量(%) E2(N·m−2·10−4) η(N·m−2·s·10-6) τ(s) 0(对照) 1.03±0.05d 54.90±3.65e 31.89±2.24a 5 86.46±4.93a 3072.41±36.18a 29.15±0.43a 10 72.12±7.98b 2946.92±20.61b 25.92±2.01b 15 63.63±3.07bc 1686.54±64.90c 25.42±2.07b 20 61.72±4.80c 1666.07±73.11c 23.71±0.28c 小麦面团 60.95±5.95c 1258.24±81.12d 20.89±2.05d 表 4 Zein对荞麦面团色度及反射率影响
Table 4 Influence of zein on buckwheat dough chroma and reflectance
Zein添加量(%) L* a* b* 0(对照) 51.47±0.30f -0.23±0.04e 24.11±0.34e 5 53.01±0.06e 6.61±0.03c 26.42±0.14d 10 53.48±0.12d 6.95±0.04b 27.85±0.70c 15 55.00±0.09c 7.37±0.09a 29.35±0.06b 20 58.97±0.37b 7.25±0.28a 31.84±0.38a 小麦面团 78.39±0.10a 6.57±0.09d 15.01±0.35f -
[1] 方齐国, 沈汪洋, 赵梅荣, 等. 荞麦蛋白质的综合研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发,2022,43(8):185−192. [FANG Q G, SHEN W Y, ZHAO M R, et al. Comprehensive research progress of buckwheat protein[J]. Food Research and Development,2022,43(8):185−192. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2022.08.025 [2] ZHU F. Buckwheat starch: Structures, properties, and applications[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2016,49:121−135.
[3] 刘航, 徐元元, 马雨洁, 等. 不同品种苦荞麦淀粉的主要理化性质[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2012,38(5):47−51. [LIU H, XU Y Y, MA Y J, et al. Main physicochemical properties of different varieties of tartary buckwheat starch[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2012,38(5):47−51. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.2012.05.036 [4] GUO X, YAO H. Fractionation and characterization of tartary buckwheat flour proteins[J]. Food Chemistry,2006,98(1):90−94. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.05.055
[5] CAI Y, CORKE H, LI W. Buckwheat[J]. Encyclopedia of Grain Science,2004:120−128.
[6] LI S Q, ZHANG Q H. Advances in the development of functional foods from buckwheat.[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Technology,2001,41(6):451−464. doi: 10.1080/20014091091887
[7] BERNADETTA, KRKOKOVÁ. Prophylactic components of buckwheat[J]. Food Research International,2005,38(5):561−568. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2004.11.009
[8] 王佳敏. 气流膨化苦荞籽粒的理化性质及品质研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2021 WANG J M. Study on physicochemical properties and quality of puffed tartary buckwheat seeds [D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2021.
[9] 韩聪. 全苦荞挂面的研制及其品质改良[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2021 HAN C. Development and quality improvement of tartary buckwheat noodles[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2021.
[10] RIBEIRO M, PICASCIA S, RHAZI L, et al. Effect of in situ gluten-chitosan interlocked self-assembled supramolecular architecture on rheological properties and functionality of reduced celiac-toxicity wheat flour[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2019,90(5):266−275.
[11] RALLABHANDI P. Gluten and celiac disease-An immunological perspective[J]. Journal of AOAC International,2012,95(2):349−355. doi: 10.5740/jaoacint.SGE_Rallabhandi
[12] 马洁, 马蕾, 于笛笛, 等. 荞麦无麸质面包研究进展[J]. 中国粮油学报,2019,34(7):139−146. [MA J, MA L, YU D D, et al. Research progress of buckwheat gluten-free bread[J]. Chinese Journal of Grain and Oil,2019,34(7):139−146. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2019.07.024 [13] PATEL A R. Functional and engineered colloids from edible materials for emerging applications in designing the food of the future[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2020,30(18):1806809.1−1806809.34.
[14] PALABIYIK I, YILDIZ O, TOKER O S, et al. Investigating the addition of enzymes in gluten-free flours–The effect on pasting andtextural properties[J]. LWT-Food Science & Technology, 2016, 69: 633–641.
[15] KING B L, TAYLOR J R. Formation of a viscoelastic dough from isolated total zein (α-, β- and γ-zein) using a glacial acetic acid treatment[J]. Journal of Cereal Science, 2016, 71: 250–257.
[16] 刘昊. 乳酸调控玉米醇溶蛋白模拟面团加工特性的研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2021 LIU H. Study on the processing characteristics of zein simulated dough regulated by lactic acid [D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2021.
[17] AKIN P, BEAN S R, SMITH B M, TILLEY M. Factors influencing zein-whole sorghum flour dough formation and bread quality[J]. Journal of Food Science,2019,84(12):3522−3534. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.14832
[18] 董春霞. 添加气流膨化苦荞粉对小麦面团流变学特性及馒头品质的影响[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2021 DONG C X. Effects of puffed tartary buckwheat flour on rheological properties of wheat dough and quality of steamed bread [D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2021.
[19] LIU W, BRENNAN M A, SERVENTI L, et al. Effect of cellulase, xylanase and α-amylase combinations on the rheological properties of Chinese steamed bread dough enriched in wheat bran[J]. Food Chemistry,2017,234:93−102. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.04.160
[20] 周星杰. 添加挤压糊化苦荞粉对小麦面团性质的影响[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2017 ZHOU X J. Effect of extrusion gelatinized tartary buckwheat flour on the properties of wheat dough [D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2017.
[21] 姬成宇. 麦麸粉对冷冻面团中主要成分特性及馒头品质影响的研究[D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2018 JI C Y. Study on the effect of wheat bran powder on the main components of frozen dough and the quality of steamed bread [D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2018.
[22] LIN S, LIU X, CAO Y, et al. Effects of xanthan and konjac gums on pasting, rheology, microstructure, crystallinity and in vitro digestibility of mung bean resistant starch[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,339(1):128001.1−128001.7.
[23] 王杰琼. 燕麦和荞麦全粉对面团特性及馒头品质影响的研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2016 WANG J Q. Effects of oat and buckwheat flour on dough properties and steamed bread quality [D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2016.
[24] FEDERICI E, SELLING G W, CAMPANELLA O H, et al. Thermal treatment of dry zein to improve rheological properties in gluten-free dough[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,115(3−5):106629.1−106629.8.
[25] EFA B, OGJA B, GWS C, et al. Effect of zein extrusion and starch type on the rheological behavior of gluten-free dough[J]. Journal of Cereal Science,2019:91−108.
[26] YAMUL D K, NAVARRO A S. Effect of hydrocolloids on structural and functional properties of wheat/potato (50/50) flour dough[J]. Food Structure,2020,24(1):100138.1−100138.8.
[27] CARLA D, MEJIA, DAVID C, et al. Increasing and stabilizing β-sheet structure of maize zein causes improvement in its rheological properties[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2012,60(9):2316−2321. doi: 10.1021/jf203073a
[28] SMITH B M, BEAN S R, SELLING G, et al. Effect of salt and ethanol addition on zein-starch dough and bread quality[J]. Journal of Food Science,2017,82(3):613−621. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.13637
[29] 王丹, 郑惠华, 纪阳, 等. 木耳粉对面团流变学特性及面条品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(21):43−50. [WANG D, ZHENG H H, JI Y, et al. Effects of Auricularia auricular powder on rheological properties of dough and noodle quality[J]. Food Science,2019,40(21):43−50. [30] HANG Z, DENG Y, ZHANG W, et al. Towards coeliac-safe bread[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal,2020,18(4):1056−1065. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13273
[31] ANDERSSON H, ÖHGREN C, JOHANSSON D, et al. Extensional flow, viscoelasticity and baking performance of gluten-free zein-starch doughs supplemented with hydrocolloids[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2011,25(6):1587−1595.
[32] CHOI S M, MA C Y. Structural characterization of globulin from common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) using circular dichroism and raman spectroscopy[J]. Food Chemistry,2007,102(1):150−160. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.05.011
[33] 何曼君, 陈维孝, 董西侠. 高分子物理. 修订版[M]. 上海: 复旦大学出版社, 2000: 309-403 HE M J, CHEN W X, DONG X X. Polymer Physics. Revision [M]. Shanghai: Fudan University Press, 2000: 309-403.
[34] NOBILE M, CHILLO S, MENTANA A, et al. Use of the generalized Maxwell model for describing the stress relaxation behavior of solid-like foods[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2007,78(3):978−983. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2005.12.011
[35] BAAR U, KARAOLU M M. The Effects of cephalaria syriaca flour on physical, rheological and textural properties of sunn pest (Eurygaster integriceps) damaged wheat dough and bread[J]. Journal of Cereal Science,2021,99(3):1−8.
[36] 彭飞. 谷氨酰胺转氨酶(T-Gase)对燕麦面团流变学特性的影响[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2016 PENG F. Effect of transglutaminase on rheological properties of oat dough [D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2016.
[37] MA J, KAORI F, MA L, et al. The effects of extruded black rice flour on rheological and structural properties of wheat-based dough and bread quality[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2018,54(5):1729−1740.
[38] 许永亮, 熊善柏, 赵思明. 蒸煮工艺和化学成分对米饭应力松弛特性的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2007,23(10):235−260. [XU Y L, XIONG S B, ZHAO S M. Effects of cooking process and chemical composition on stress relaxation characteristics of rice[J]. Agricultural Engineering Journal,2007,23(10):235−260. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.2007.10.042 [39] RAO V K, MULVANEY S J, DEXTER J E. Rheological characterisation of long-and short-mixing flours based on stress-relaxation[J]. Journal of Cereal Science,2000,31(2):159−171. doi: 10.1006/jcrs.1999.0295
[40] 孙娟娟, 魏肖鹏, 邱燕燕, 等. 干法糊化对燕麦粉面团应力松弛特性的影响[J]. 中国粮油学报,2016,31(4):23−27. [SUN J J, WEI X P, QIU Y Y, et al. Effect of dry gelatinization on stress relaxation characteristics of oat flour dough[J]. China Journal of Grain and Oil,2016,31(4):23−27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2016.04.005 [41] 李经伟, 李玲伊, 刘建福. 豌豆全粉对小麦面团特性和面包品质的影响[J]. 中国粮油学报,2020,35(8):35−41. [LI J W, LI L Y, LIU J F. Effects of pea powder on wheat dough characteristics and bread quality[J]. Journal of China Grain and Oil,2020,35(8):35−41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2020.08.007 [42] WANG L, YE F, LI S, et al. Wheat flour enriched with oat β-glucan: A study of hydration, rheological and fermentation properties of dough[J]. Journal of Cereal Science,2017,75:143−150. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2017.03.004
[43] MARCOA C, ROSELL C M. Effect of different protein isolates and transglutaminase on rice flour properties[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2008,84(1):132−139. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2007.05.003
[44] MATTICE K D, MARANGONI A G. Functionalizing zein through antisolvent precipitation from ethanol or aetic acid[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,313:126127.1−126127.8.
[45] WIESER H. Chemistry of gluten proteins[J]. Food Microbiology,2007,24(2):115−119. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2006.07.004
[46] 孙华幸. 荞麦甜醅对小麦面团流变学特性和馒头品质的影响[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2019 SUN H X. Effect of buckwheat sweet fermented grains on rheological properties of wheat dough and quality of steamed bread [D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2019.
[47] TAYLOR J, ANYANGO J O, MUHIWA P J, et al. Comparison of formation of visco-elastic masses and their properties between zeins and kafirins[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,245(15):178−188.
[48] MATTICE K D, MARANGONI A G. Comparing methods to produce fibrous material from zein[J]. Food Research International,2019,128:108804.1−108804.8.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 陈金女,申丽媛. 基于区别化熟化处理方式的荞麦粉蛋白影响性研究. 贵阳学院学报(自然科学版). 2024(02): 75-80 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 黄姗姗,夏文栋,王津冬,汪师帅,郑芃园. 不同结构的魔芋葡甘聚糖在磨牙棒中的应用. 粮食与油脂. 2024(09): 87-91 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)











 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



