| [1] |
高金龙. 山羊皮中胶原蛋白的提取及理化特性研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2010.
GAO J L. Study on extraction and physicochemical properties of collagen from goat skin[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2010.
|
| [2] |
HAJFATHALIAN M, GHELICHI S, GARCÍA-MORENO P J, et al. Peptides: Production, bioactivity, functionality, and applications[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2018,58(18):3097−3129. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2017.1352564
|
| [3] |
ZHAO X, ZHANG X, LIU D, Collagen peptides and the related synthetic peptides: A review on improving skin health[J]. Journal of Functional Foods, 2021, 86: 104680.
|
| [4] |
WANG B, WANG Y M, CHI C F, et al. Isolation and characterization of collagen and antioxidant collagen peptides from scales of croceine croaker ( Pseudosciaena crocea)[J]. Marine Drugs,2013,11(11):4641−4661. doi: 10.3390/md11114641
|
| [5] |
GAO L, WANG Z, ZHENG L I, et al. The characterization of acid and pepsin soluble collagen from ovine bones (Ujumuqin sheep)[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture,2018,17(3):704−711. doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(17)61751-9
|
| [6] |
LEÓN LÓPEZ A, FUENTES JIMÉNEZ L, HERNÁNDEZ FUENTES A D, et al. Hydrolysed collagen from sheepskins as a source of functional peptides with antioxidant activity[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2019,20(16):3931. doi: 10.3390/ijms20163931
|
| [7] |
SIBILLA S, GODFREY M, BREWER S, et al. An overview of the beneficial effects of hydrolysed collagen as a nutraceutical on skin properties: Scientific background and clinical studies[J]. The Open Nutraceuticals Journal,2015,8(1):29−42. doi: 10.2174/1876396001508010029
|
| [8] |
周婷, 卢方云, 黄瑾, 等. 响应面法优化超声辅助酶法制备无骨鸡爪胶原蛋白肽[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(19):182−189. [ZHOU T, LU F Y, HUANG J, et al. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted enzymatic preparation of boneless chicken claw collagen peptide by response surface methodology[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(19):182−189.
|
| [9] |
瞿怡, 苏寒雨, 刘文涛, 等. 超声波辅助法提取牛皮胶原蛋白[J]. 皮革科学与工程,2018,28(2):5−9. [QU Y, SU H Y, LIU W T, et al. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of collagen from bovine skin[J]. Leather Science and Engineering,2018,28(2):5−9. doi: 10.19677/j.issn.1004-7964.2018.02.001
|
| [10] |
栾俊家, 李学鹏, 励建荣, 等. 响应面法优化秋刀鱼酶解制备抗氧化活性肽的工艺[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(5):172−181. [LUAN J J, LI X P, LI J R, et al. Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis process of antioxidant active peptides from Saury chinensis by response surface methodology[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(5):172−181.
|
| [11] |
ZOU Y E, XU P, LI P, et al. Effect of ultrasound pre-treatment on the characterization and properties of collagen extracted from soft-shelled turtle ( Pelodiscus sinensis)[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2017,82:72−81. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2017.04.024
|
| [12] |
国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 5009.3-2016 食品安全国家标准食品中水分的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016.
National Health and Family Planning Commission. GB 5009.3-2016 National standard for determination of moisture in food of national standard for food safety[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016
|
| [13] |
国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 5009.4-2016 食品安全国家标准食品中灰分的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016.
National Health and Family Planning Commission. GB 5009.4-2016 National standard for determination of ash content in national food safety standards[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
|
| [14] |
国家食品药品监督管理总局, 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 5009.6-2016 食品安全国家标准食品中脂肪的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016.
State Food and Drug Administration, National Health and Family Planning Commission. GB 5009.6-2016 Determination of fat in national food safety standards[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
|
| [15] |
国家食品药品监督管理总局, 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 5009.5-2016 食品安全国家标准食品中蛋白质的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016.
State Food and Drug Administration, National Health and Family Planning Commission. GB 5009.5-2016 Determination of protein in food of national standard for food safety[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
|
| [16] |
王杉杉, 罗学刚, 苏峰丙, 等. 牦牛皮胶原蛋白的提取及性能分析[J]. 精细化工,2018,35(5):830−837. [WANG S S, LUO X G, SU F B, et al. Extraction and characterization of yak skin collagen[J]. Fine Chemicals,2018,35(5):830−837. doi: 10.13550/j.jxhg.20170573
|
| [17] |
ANAND S, KAMATH S, CHUANG L, et al. Biochemical and thermo-mechanical analysis of collagen from the skin of Asian Sea bass ( Lates calcarifer) and Australasian Snapper ( Pagrus auratus), an alternative for mammalian collagen[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2013,236(5):873−882. doi: 10.1007/s00217-013-1950-9
|
| [18] |
LUAN X X, FENG M Q, SUN J. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum on antioxidant activity in fermented sausage[J]. Food Research International,2021,144:110351. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110351
|
| [19] |
程妍. 骨胶原蛋白酶解工艺及骨营养粉对大鼠补钙功效的研究[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2009.
CHENG Y. Study on osteosinolytic process and the effect of bone nutrition powder on calcium supplementation in rats[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2009.
|
| [20] |
鲁伟, 任国谱, 宋俊梅. 蛋白水解液中多肽含量的测定方法[J]. 食品科学,2005(7):169−171. [LU W, REN G P, SONG J M. Determination of polypeptides in protein hydrolysate[J]. Food Science,2005(7):169−171. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2005.07.039
|
| [21] |
曹振海, 乐彩虹, 陶宁萍, 等. 体外模拟消化对暗纹东方鲀鱼皮胶原蛋白肽结构特征及抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(23):61−69. [CAO Z H, LE C H, TAO N P, et al. Effects of simulated digestion in vitro on collagen peptide structure and antioxidant activity of Takifugu rubripes[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(23):61−69. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.028686
|
| [22] |
DING D, DU B, ZHANG C, et al. Isolation and identification of an antioxidant collagen peptide from skipjack tuna ( Katsuwonus pelamis) bone[J]. RSC Advances,2019,9(46):27032−27041. doi: 10.1039/C9RA04665H
|
| [23] |
OHATA M, UCHIDA S, ZHOU L, et al. Antioxidant activity of fermented meat sauce and isolation of an associated antioxidant peptide[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,194:1034−1039. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.08.089
|
| [24] |
窦丹彤. 梅花鹿皮胶原蛋白肽制备及其活性研究[D]. 沈阳: 辽宁大学, 2021
DOU D T. Preparation of chicken skin collagen peptide and development of peptide rich drink[D]. Shenyang: Liaoning University, 2013.
|
| [25] |
曾庆冉. 鸡皮胶原蛋白肽的制备及其富肽饮品的开发[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2013.
ZENG Q R. Preparation of chicken skin collagen peptide and development of peptide rich drink[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2013.
|
| [26] |
MOHAMMADI R, MOHAMMADIFAR M A, MORTAZAVIAN A M, et al. Extraction optimization of pepsin-soluble collagen from eggshell membrane by response surface methodology (RSM)[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,190:186−193. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.05.073
|
| [27] |
徐红萍, 谢辉, 梁建灏, 等. 超声波辅助酶解制备东海海参胶原蛋白低聚肽及其活性的研究[J]. 浙江海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2018,37(5):388−393. [XU H P, XIE H, LIANG J H, et al. Preparation of collagen oligopeptide from sea cucumber by ultrasound-assisted enzymatic hydrolysis and its activity[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science),2018,37(5):388−393. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-830X.2018.05.002
|
| [28] |
TAN Y, CHANG S K C. Isolation and characterization of collagen extracted from channel catfish ( Ictalurus punctatus) skin[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,242:147−155. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.09.013
|
| [29] |
YANG J, HUANG J, ZHU Z, et al. Investigation of optimal conditions for production of antioxidant peptides from duck blood plasma: Response surface methodology[J]. Poultry Science,2020,99(12):7159−7168. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2020.08.060
|
| [30] |
WANG D, ZHANG M, ZOU Y, et al. Optimization of flavourzyme hydrolysis condition for the preparation of antioxidant peptides from duck meat using response surface methodology[J]. The Journal of Poultry Science, 2018: 0160155.
|
| [31] |
苏继磊, 李姣, 陈敏, 等. 响应面法优化太平洋褶柔鱼肌肉蛋白水解物的抗氧化活性[J]. 食品科技,2021,46(6):121−128. [SU J L, LI J, CHEN M, et al. Optimization of antioxidant activity of muscle protein hydrolysates from Pleurophilus Pacific by response surface methodology[J]. Food Science and Technology,2021,46(6):121−128.
|
| [32] |
云一卿, 胡虞帆, 杨留明, 等. 体外模拟胃肠消化对缢蛏抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(5):1423−1429. [YUN Y Q, HU Y F, YANG L M, et al. Effects of simulated gastrointestinal digestion on antioxidant activity of Sinonovacula constricta[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2022,13(5):1423−1429.
|
| [33] |
GUO J J, YUAN J T, LIU G S. Ultrasound-assisted extraction and antioxidant activity of bovine bone collagen peptide [J]. Food and Fermentation Industry: 1−11 [2022-07-05]. DOI: 10.13995/j.nki.11-1802/TS.031714.
|
| [34] |
YU H C, TAN F J. Effect of ultrasonic pretreatment on the antioxidant properties of porcine liver protein hydrolysates[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2017,52(6):1392−1399.
|
| [35] |
HU Z, YANG P, ZHOU C, et al. Marine collagen peptides from the skin of Nile Tilapia ( Oreochromis niloticus): Characterization and wound healing evaluation[J]. Marine Drugs,2017,15(4):102. doi: 10.3390/md15040102
|
| [36] |
MARX J L. Oxygen free radicals linked to many diseases: The oxygen free radicals, although made as by-products of normal oxygen-using reactions, nevertheless have a wide potential for causing cell injury[J]. Science,1987,235(4788):529−531. doi: 10.1126/science.3810154
|
| [37] |
杨玉亮, 衣大龙, 刘春雨, 等. 体外模拟消化对牦牛骨胶原蛋白肽抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(13):769−784. [YANG Y L, YI D L, LIU C Y, et al. Effects of simulated digestion on antioxidant activity of yak ossein peptidein vitro[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(13):769−784.
|






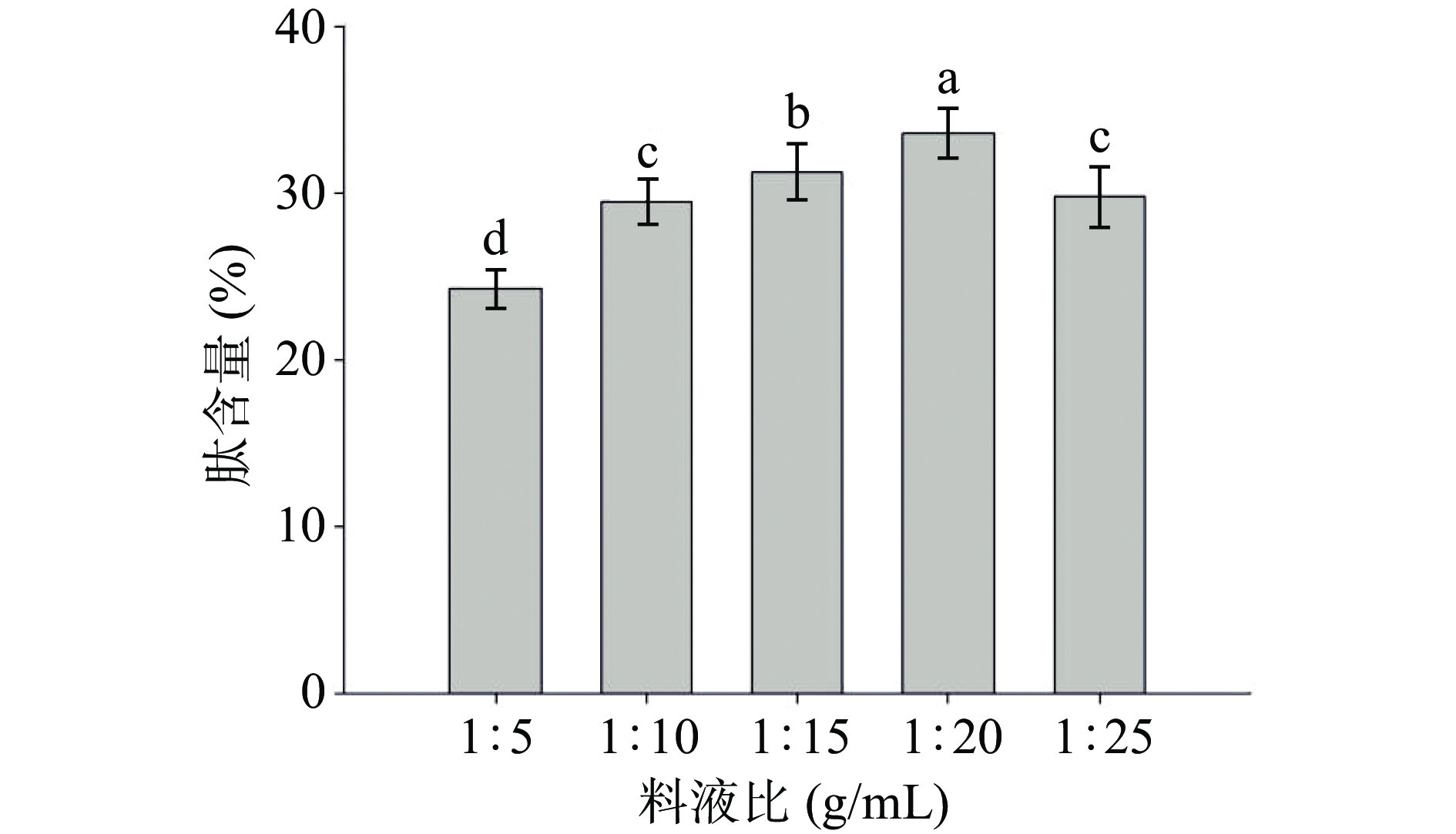




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: