| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
Lee H, Yoon H, Ji Y, et al. Functional properties of Lactobacillus strains isolated from kimchi[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2011,145(1):155−161. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2010.12.003
|
| [5] |
Jung J Y, Lee S H, Lee H J, et al. Effects of Leuconostoc mesenteroides starter cultures on microbial communities and metabolites during kimchi fermentation[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2012,153(3):378−387. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2011.11.030
|
| [6] |
戴志伟, 张玥, 严宏孟, 等. 四种乳酸菌发酵西梅浆的特性研究. 食品与发酵工业: 2021(1): 1−12.
|
| [7] |
Filannino P, Tlais A Z A A, Morozova K, et al. Lactic acid fermentation enriches the profile of biogenic fatty acid derivatives of Avocado fruit (Persea americana Mill.)[J]. Food Chemistry,2020:126384.
|
| [8] |
Gerardi C, Tristezza M, Giordano L, et al. Exploitation of Primus mahaleb fruit by fermentation with selected strains of Lactobacillus plantarum and Saccharomyces cerevisiae[J]. Food microbiology,2019(84):103262.1−103262.11.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
Verón H E , Risio H , Isla M I , et al. Isolation and selection of potential probiotic lactic acid bacteria from Opuntia ficus-indica fruits that grow in Northwest Argentina[J]. Lebensmittel-Wissenschaft,2017(84):79−83.
|
| [12] |
刘瀛. 新鲜蕨菜与腌制蕨菜的营养成分分析[J]. 辽宁林业科技,2020(3):34−35.
|
| [13] |
李敏. 不同发酵条件和发酵方式对泡菜感官品质的影响[J]. 北方园艺,2012(6):150−153.
|
| [14] |
中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB5009.239-2016 食品酸度的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017.
|
| [15] |
中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB5009.7-2016 食品中还原糖的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017.
|
| [16] |
Zhang L H, Li S F, Wang A J, et al. Mild heat treatment inhibits the browning of fresh-cut Agaricus bisporus during cold storage[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2017:82.
|
| [17] |
Surhone L M, Tennoe M T, Henssonow S F. GraphPad Prism[M]. Betascript Publishing, 2010(2): 12−15.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
罗红霞, 张杏媛, 王建, 等. 复合蔬菜发酵的工艺研究[J]. 中国果菜,2018,38(12):11−14.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
张娜威, 陈凤仪, 李二虎. 蓝莓酒渣对泡菜亚硝酸盐和生物胺的抑制作用[J]. 食品科学,2020(17):10−17.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
Peterman M A, Cline D J, Hanson T R, et al. Coloration characteristics of mechanically processed channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) fillets held in refrigerated storage for seven days[J]. Journal of Applied Aquaculture,2013.
|
| [26] |
卢嘉懿, 李汴生, 阮征. 乳酸菌发酵对梨汁的护色作用[J]. 现代食品科技,2019,35(3):148−153.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
Sila D N, Doungla E, Smout C, et al. Pectin fraction interconversions: Insight into understanding texture evolution of thermally processed carrots[J]. J Agric Food Chem,2006,54(22):8471−8479. doi: 10.1021/jf0613379
|
| [29] |
孙少斌. 超高压食品处理的温热效应及食品质构分析[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2012.
|
| [30] |
S Patricia. Sensory evaluation of food principles and practices[J]. Journal of Wine Research,2013,24(1):80−81. doi: 10.1080/09571264.2013.764662
|






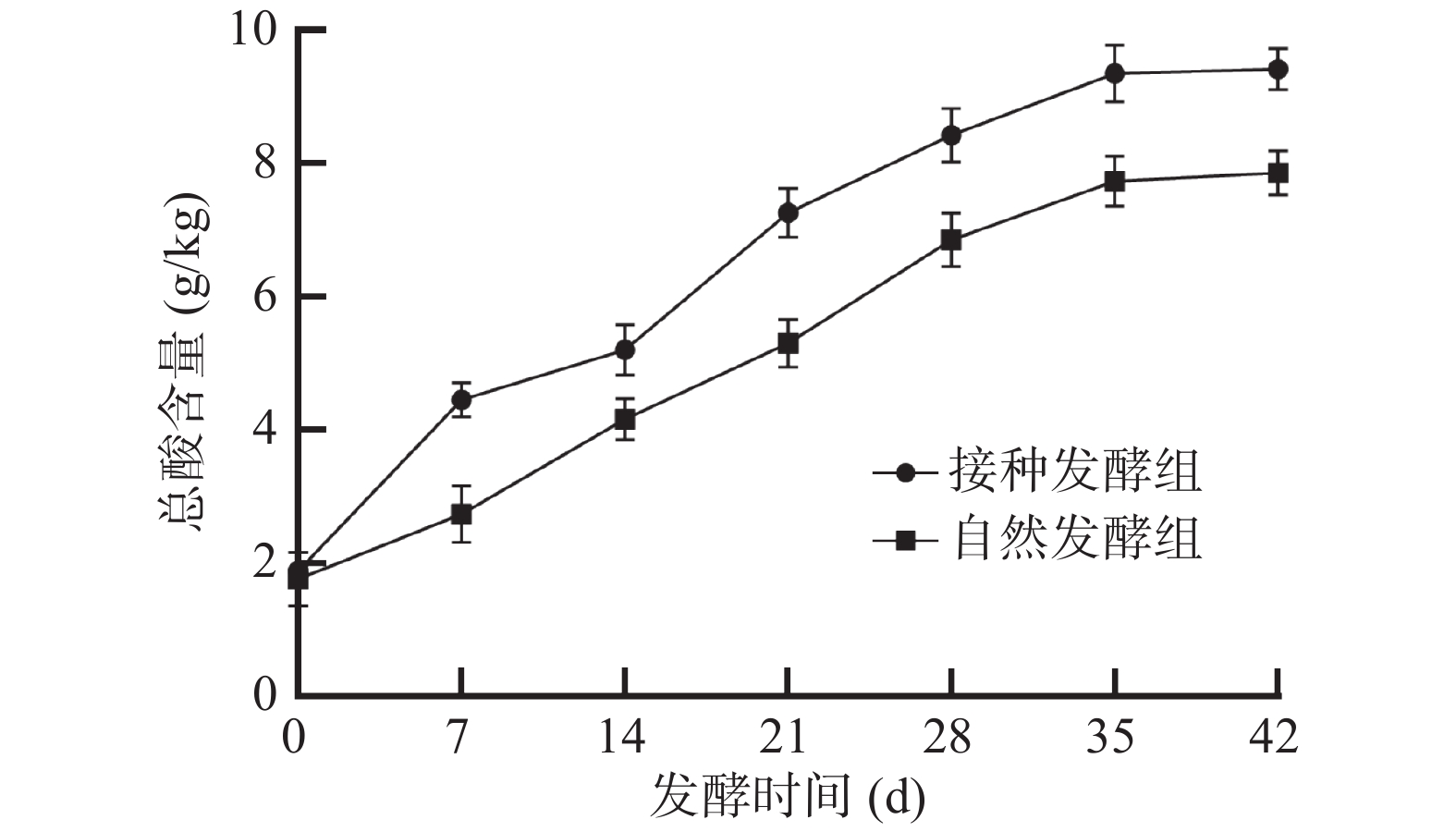




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: