Comprehensive Evaluation of Quality Characteristics and Processing Suitability of Different Varieties of Large-fruited Sea Buckthorn Juice from Xinjiang Using Multivariate Analysis Method
-
摘要: 本研究以‘深秋红’‘状元黄’‘巨人’‘无刺丰’和‘向阳’5种新疆大果沙棘汁和1种新疆混果沙棘汁为研究对象,采用采用气相色谱-离子迁移谱(gas chromatography-ion mobility spectroscopy,GC-IMS)技术和理化分析结合相关性和主成分等多元分析法对不同大果沙棘制汁的品质特性及适宜性进行综合评价。结果表明,‘状元黄’沙棘汁的b*、c、总酚(0.9 mg/mL)、维生素E(63.14 μg/g)和维生素C(69.61 mg/100 g)及DPPH(97.13%)、ABTS+自由基清除能力(61.99%)、FRAP抗氧化能力(0.85 μmol Trolox/mL)最高;‘向阳’沙棘汁的出汁率(56.43%)和总黄酮含量(8.55 mg/mL)最高。经相关性分析得到维生素C与总酚、总黄酮和FRAP呈极显著正相关(P<0.01)。共鉴定出58种挥发性成分,其中‘深秋红’沙棘汁的挥发性成分的总峰强度最高,混果沙棘汁次之。结合主成分分析明确色泽(L*、b*、c、h)、总酚、总黄酮、维生素C、褐变度、ABTS+和FRAP等是影响沙棘果汁品质的关键指标,‘状元黄’综合评价得分最高为2.12分,可作为最适宜制汁的加工品种。该研究为大果沙棘制汁加工专用品种的筛选提供了重要参考依据。Abstract: This study assessed the quality characteristics juice and processing suitability of six varieties of large-fruited sea buckthorn juice from Xinjiang using gas chromatography-ion mobility spectroscopy (GC-IMS) and multivariate physicochemical analysis combined with correlation and principal component analysis. The varieties included five large-fruited sea buckthorn types, namely SQH, ZYH, GR, WCF, and XY, along with one mixed-fruited variety (HG). The results indicated that ZYH exhibited the highest b* and c, as well as contents for total phenols (0.9 mg/mL), vitamin E (63.14 μg/g), vitamin C (69.61 mg/100 g), DPPH (97.13%), ABTS+ free radical scavenging capabilities (61.99%) , and FRAP antioxidant capacity (0.85 μmol Trolox/mL). XY sea buckthorn juice showed the highest juice yield (56.43%) and total flavonoid content (8.55 mg/mL). Correlation analysis revealed a significant positive correlation (P<0.01) between vitamin C and total phenols, total flavonoids, and FRAP. A total of 58 volatile components, with basilene determined as the predominant volatile component in SQH sea buckthorn juice. Furthermore, SQH exhibited the highest total peak intensity among the varieties tested, while HG sea buckthorn juice ranked second in peak intensity. Principal component analysis, combined with assessments of coloration (L*, b*, c, h ), total phenols, total flavonoids, vitamin C, browning degree, ABTS+, and FRAP were determined to be key indexes affecting the quality of sea buckthorn juice. ZYH received the highest comprehensive evaluation score of 2.12 grade, suggesting its suitability for juice production. Overall, this study serves as an important reference for the selection of sea buckthorn varieties optimized for the production of large-fruited sea buckthorn juice.
-
沙棘(Hippophae rhamnoides L.)为灌禾目胡颓子科沙棘属,别名醋柳、酸刺,主要分布于我国西北、华北和西南地区,是一种兼备生态效益、经济效益和社会效益的优质植物资源[1]。沙棘中富含各种营养物质和生物活性成分,包括类胡萝卜素、维生素、不饱和脂肪酸、多酚类化合物、类总黄酮、有机酸和挥发性成分等[2−3],具有抗氧化和免疫调节、抗炎、降糖、抗癌、保肝和抗血栓等作用,因其具有高营养价值和药用潜力而受到关注[4−7]。截至2022年,全国沙棘种植面积增至1058.35万亩,约占世界沙棘种植总面积的90%以上,主要分布于新疆、西藏和内蒙古等地[8]。研究发现,大果沙棘具有果大、产量高、品质优等特点,已在新疆、黑龙江等地区广泛栽培[9]。新疆大果沙棘种植面积达70万亩,挂果面积46万亩,形成了以阿勒泰、阿克苏、克州、塔城等地为主的优势产区,其中阿勒泰地区是大果沙棘的原产地,也是中国国家地理标志产品[10−11]。大果沙棘主栽品种有‘深秋红’‘状元黄’‘无刺丰’‘向阳’和‘巨人’等,加工产品主要为沙棘汁、沙棘果粉、沙棘油和沙棘茶等[12],其中沙棘汁因具有调节机体内部平衡、提高免疫力、生津止咳、健脾开胃和维持神经肌肉的兴奋等功效[13−15],备受消费者青睐。沙棘汁的品质受多因素的影响,除环境和加工工段影响以外,沙棘品种差异也是影响沙棘汁品质的重要因素之一[16−17]。
目前新疆大果沙棘加工企业普遍存在适宜制汁的加工专用原料品种不清,企业大多以收购的混果作为加工原料,混果原料的异质性导致产品质量不稳定,直接影响了果汁的品质和市场竞争力。现对沙棘汁品质和适宜制汁品种筛选的相关研究较少。杨培青等[18]对‘中国沙棘’‘深秋红’和‘圣女一号’3种沙棘汁的理化品质进行比较,结果表明‘中国沙棘’汁具有较高的超氧化物歧化酶活力、总酚及抗氧化能力。Andrea等[19]根据总类胡萝卜素、多酚和抗氧化活性的含量,评估11个不同品种沙棘汁的营养品质,研究得到‘拉娜’沙棘汁的多酚化合物含量和抗氧化活性最高,较适合于果汁加工。但这些研究仅对不同产地沙棘汁的部分理化指标进行检测,研究不够全面深入,尤其是采用多元分析法综合评价新疆不同品种大果沙棘汁的多维品质和加工适宜性尚未见报道。
因此,本研究以5种新疆大果沙棘(‘深秋红’‘状元黄’‘巨人’‘无刺丰’和‘向阳’)主栽品种和1种新疆混果为原料,运用多元分析方法,从理化指标、营养指标、抗氧化活性及挥发性成分分析四个维度对其适宜制汁沙棘品种开展科学系统的综合评价,筛选出适合制汁的大果沙棘品种,为新疆大果沙棘汁的加工生产提供科学依据和理论参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
大果沙棘鲜果 6个样品组,单果重均符合特等标准要求(单果重≥0.3 g),将采摘的沙棘果实液氮速冻后保存在−20 ℃冰箱待加工,具体样品信息如表1所示;草酸、碳酸氢钠、抗坏血酸钠、2,6-二氯酚靛酚钠盐、三氯化铝、石油醚、硫酸钾、硫酸酮、醋酸钾、无水乙醇、甲醇 分析纯,天津市致远化学试剂有限公司;福林酚试剂、芦丁、DPPH(1,1-二苯基苦基苯肼)、ABTS(2,2'-联氮双(3-乙基苯并噻唑啉-6-磺酸)二铵盐)、维生素C标准品、维生素E试剂盒 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;类胡萝卜素含量试剂盒、总抗氧化能力(FRAP法)试剂盒、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性测试试剂盒 苏州梦犀生物医药科技有限公司;2-戊酮、2-己酮、2-庚酮、2-辛酮、2-壬酮、2-丁酮 Sigma 公司。
表 1 不同大果沙棘样品信息Table 1. Sample information of sea buckthorn of different large fruitsUV-2600型紫外可见分光光度计 岛津企业管理(中国)有限公司;KQ32200DE型超声波清洗机 昆山市超声仪器有限公司;TP-A2000型电子天平 华志(福建)电子科技有限公司;榨汁机 九阳股份有限公司;DZKW-S-4型电热恒温水浴锅 北京市永光明医疗仪器有限公司;YS6060 台式分光测色仪 深圳市三恩时科技有限公司;Centrifge5810R型高速冷冻离心机 德国Eppendorf公司;SYNERGY型多功能微孔板检测仪 科瑞恩特(北京)科技有限公司;Flavour Spec气相离子迁移谱联用仪 德国G.A.S公司;糖酸仪 ATAGO (爱拓)中国分公司;testo205pH计 德图仪器国际贸易(上海)有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 大果沙棘汁的制备
挑选色泽均匀、成熟、饱满、无病害的新鲜大果沙棘,去除果梗后,用清水冲洗大果沙棘表面的泥土,沥干水分。将沥水后的沙棘果放入组织破碎机中破碎并除去籽皮,并立即用100目滤布进行过滤、罐装,4 ℃保存待测。
1.2.2 理化特性测定
pH:根据GB 5009.237-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品pH值的测定》测定。离心沉淀率:参考王妍惠等[20]的方法并改进,取10 mL沙棘汁(m1)于离心管中,离心(4000 r/min,15 min)后除去上清液,准确称得离心后的沉淀物质量(m0),沉淀率(Y)计算公式为Y(%)=m0/m1×100。浊度:使用浊度计测定果汁样品的浊度。固酸比:采用糖酸仪进行测定,可溶性固形物含量与可滴定酸含量的比值即为固酸比。出汁率:鲜果重和果汁重的比值可得[21]。褐变度:参考张娟等[13]的方法并改进,取12.5 g沙棘汁,加入4.5 mL无水乙醇,混匀后静置5 min后离心(4500 r/min,10 min),取上清液并过滤,于420 nm波长下测定吸光度,测得的吸光度值为褐变度。色泽分析测定:利用色差仪进行定量测定,白校正标准化后测定亮度(L*)、a*(+a为红色,−a为绿色)、b*(+b为黄色,−b为蓝色)、饱和度(c)及色度角(h°)。
1.2.3 营养指标测定
总酚:采用福林酚比色法[7]测定样品总酚含量;总黄酮:参照DB 43T476-2009《植物源性食品中总黄酮的测定》略作修改后测定,样液以8000 r/min离心10 min取上清液得待测液。准确配制芦丁标准液0.2 mg/mL,准确吸取0.5、1.0、2.0、3.0、4.0、5.0 mL,分别置于25 mL容量瓶中,于标准管和试样管分别加入2.0 mL三氯化铝溶液,混匀,各加入2.0 mL醋酸钾溶液,混匀,加30%的乙醇至刻度,静置15 min,于波长510 nm处测定吸光度,绘制标准曲线,同时做空白;维生素E:采用维生素E试剂盒进行测定并计算;维生素C:根据GB 5009.86-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品中抗坏血酸的测定》中第三法2,6-二氯靛酚滴定法进行测定;类胡萝卜素:使用植物类胡萝卜素含量检测的试剂盒进行检测,按照黄色或非绿色组织(不含叶绿素)类胡萝卜素含量的测定步骤与计算方法。
1.2.4 生物活性测定
DPPH和ABTS+自由基清除率:根据GB/T 39100-2020《多肽抗氧化性测定 DPPH和ABTS法》测定;FRAP自由基清除率:采用总抗氧化能力(FRAP法)试剂盒进行测定并计算;超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性:采用超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性测试试剂盒进行测定并计算。
1.2.5 挥发性物质测定条件
参考Wu等[22]的测定方法略作修改。称取3 mL沙棘汁放置于顶空进样瓶中进行在40 ℃、500 r/min下孵育30 min;进样针吸取顶空瓶中样品1 mL,不分流模式进样;载气为氮气(≥99.999%),载气流速为150 mL/min。
色谱柱型号:MXT-5(15 m,0.53 mm ID),温度保持在60 ℃;载气的流速梯度剖面设置为:0~2 min,2 mL/min;2~10 min,2~10 mL/min;10~20 min,10~100 mL/min;20~30 min,100~150 mL/min;30~35 min,150 mL/min。
戊酮、2-己酮、2-庚酮、2-辛酮、2-壬酮作为标准品(按照1:1:1:1:1:1,v:v)取样品液,并稀释5000倍),吸取1 mL标准品后建立标准曲线,确定样品中挥发性物质的保留时间和漂移时间。
1.3 数据处理
所有实验重复三次,结果表示为平均值±标准差。采用SPSS 20.0进行差异性显著分析(P<0.05)和主成分分析;Origin 21.0软件进行图的绘制。采用GC-IMS设备中的LAV(Laboratory Analytical Viewer)分析软件进行特征挥发性物质的定性和构建指纹图谱。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 理化特性分析
不同沙棘汁的pH、固酸比、出汁率、浊度、离心沉淀率和褐变度见表2。沙棘汁的pH范围在2.72~3.00,这与Beveridge等[23]研究一致。固酸比反映沙棘汁的风味,过低的固酸比会导致沙棘汁口感酸涩,影响消费者直接饮用的可接受度[24]。不同品种沙棘汁的固酸比有显著性差异(P<0.05),其中‘巨人’沙棘汁的固酸比最高为27.45,口感更好;‘状元黄’的固酸比最低为15.39,说明其风味偏酸,但其符合消费者对沙棘汁的可接受度[23]。出汁率是决定水果适宜制汁的重要指标之一,高出汁率可有效降低果汁生产成本。由表2可知,不同品种沙棘汁的出汁率范围在49.07%~56.43%之间,其中‘向阳’和‘状元黄’沙棘汁的出汁率较高,分别为56.43%和54.64%。不同品种沙棘出汁率的差异可能与成熟度、年份以及加工方法有关[25]。
表 2 不同沙棘汁基础理化指标分析Table 2. Analysis of basic physical and chemical indexes of different sea buckthorn juice品种 pH 固酸比 出汁率(%) 浊度(NTU) 离心沉淀率(%) 褐变度 ‘深秋红’ 2.89±0.03c 20.90±0.28c 49.07±0.05c 46730.00±26.87a 4.25±0.22c 0.44±0.00a ‘状元黄’ 2.72±0.01d 15.39±0.61d 54.64±0.01ab 28676.67±15.43d 3.64±0.22d 0.38±0.00b ‘巨人’ 3.00±0.02a 27.45±2.58a 49.92±0.01bc 40670.00±22.99c 4.72±0.18bc 0.16±0.00f ‘无刺丰’ 2.93±0.01bc 26.06±1.37ab 50.01±0.01bc 46906.67±69.58a 5.44±0.27a 0.17±0.00e ‘向阳’ 2.93±0.01bc 21.34±1.50c 56.43±0.01a 28326.67±15.80d 5.26±0.22a 0.25±0.00c 混果 2.97±0.03ab 23.60±0.83c 54.22±0.01ab 44223.33±45.15b 5.01±0.18ab 0.20±0.00d 浊度和离心沉淀率均是评价果汁稳定性和感官评分的重要指标[26]。由表可知,沙棘汁浊度范围在28326.67~46906.67NTU之间,‘状元黄’和‘向阳’的浊度较低且差异不显著(P>0.05),分别为28676.67 和28326.67 NTU,较低的浊度可能与高含量的酚类物质有关,当与蛋白类物质络合形成大分子聚合物后逐渐沉淀从而使浊度降低[27]。离心沉淀率反映了沙棘汁的物理稳定性,离心沉淀率越低则稳定效果越好[28]。‘状元黄’的离心沉淀率最低,为3.64%,说明其具有更好的稳定性。褐变度常用作评价果汁品质的基本指标[29],表2中不同品种沙棘汁的褐变度范围在0.16~0.44之间,其中‘深秋红’和‘状元黄’沙棘汁的褐变度较高,分别为0.44和0.38,这可能是由于两者的pH较低,在低酸性状态下维生素C裂解产物糠醛与5-羟甲基糠醛的生成速率较快,加速了美拉德反应,从而导致褐变度偏高[30]。
颜色是果汁的重要感官指标之一,会对消费者的接受程度产生影响。如表3所示,不同品种沙棘汁的颜色差异显著。5个单一品种中,‘向阳’沙棘汁的L*最大,为9.84;其次为‘状元黄’沙棘汁,L*为8.31,颜色的差异与成熟度、遗传基因不同等因素有关[31]。混果沙棘汁的L*最低为1.13,表明其颜色较深,这可能与混果原料的混合体系及原料经加工制汁发生的氧化变色反应有关[32]。a*越大,说明果汁颜色越红[33],其中‘深秋红’沙棘汁的颜色最红,为18.88。b*和c越大表示果汁颜色越鲜艳,‘状元黄’沙棘汁的颜色最佳,分别为14.2和21.28。
表 3 不同沙棘汁颜色分析Table 3. Color analysis of different sea buckthorn juice品种 L* a* b* c h(°) ‘深秋红’ 3.97±0.02e 18.88±0.25a 5.90±0.25e 19.78±0.30c 0.30±0.01e ‘状元黄’ 8.31±0.07b 15.85±0.13d 14.20±0.13a 21.28±0.47a 0.73±0.01b ‘巨人’ 4.40±0.05d 18.54±0.01b 7.51±0.01d 20.00±0.08bc 0.38±0.00d ‘无刺丰’ 4.77±0.02c 16.54±0.02c 8.09±0.02c 18.41±0.05d 0.46±0.00c ‘向阳’ 9.84±0.10a 14.93±0.18e 13.82±0.18b 20.34±0.12b 0.75±0.03a 混果 1.13±0.07f 5.61±0.020f 1.70±0.02f 5.86±0.05d 0.29±0.00e 综上所述,‘状元黄’和‘向阳’沙棘汁具有较高的出汁率、较低的离心沉淀率和浊度,且颜色较佳,基于以上能较好反映出沙棘汁加工特性的主要理化指标测定结果,初步确定了‘状元黄’和‘向阳’可作为适宜制汁品种。但以上理化指标无法完全反映沙棘汁产品品质及其加工适宜性,因此,仍需对其营养品质和挥发性成分等品质指标进一步分析。
2.2 营养指标分析
总酚和总黄酮是沙棘汁中重要的功能活性成分,在抗氧化活性中起重要作用。由表4可知,‘状元黄’沙棘汁的总酚含量最高为0.9 mg/mL,‘巨人’沙棘汁的含量最低为0.27 mg/mL。‘向阳’沙棘汁的总黄酮含量较高,‘状元黄’沙棘汁次之,分别为8.56 mg/mL和6.2 mg/mL,这与李珍等[10]的研究结果有所差异,这可能与原料品种的成熟度和采摘时间等有关。研究发现,维生素E可改善血液循环,降低和预防近视眼的发生[34−35]。沙棘汁中维生素E含量在12.63~75.90 μg/g之间[36],表4中‘状元黄’沙棘汁维生素E的含量最高,为63.14 μg/g;‘向阳’沙棘汁的最低,为13.81 μg/g。维生素C可作为抗氧化剂并保护细胞膜的完整性[37−38],且沙棘浆果不含降解抗坏血酸的抗坏血酸氧化酶,因此,加工后的沙棘汁仍富含维生素C[39−40]。如表4所示,在6种沙棘汁中‘状元黄’沙棘汁的维生素C含量最高为69.61 mg/100 g,说明其抗氧化活性较好。
表 4 不同沙棘汁营养指标分析Table 4. Nutritional index analysis of different sea buckthorn juice品种 总酚(mg/mL) 总黄酮(mg/mL) 维生素E(μg/g) 维生素C(mg/100 g) 类胡萝卜素(mg/g) ‘深秋红’ 0.43±0.03c 2.55±0.27c 54.95±0.82b 45.51±1.05c 0.35±0.00c ‘状元黄’ 0.90±0.01a 6.20±0.02b 63.14±1.82a 69.61±0.80a 0.54±0.01b ‘巨人’ 0.27±0.01e 2.14±0.21c 21.71±1.82c 20.71±0.60d 0.28±0.00d ‘无刺丰’ 0.35±0.02d 4.22±1.28bc 23.05±0.49c 24.94±0.00d 0.15±0.00f ‘向阳’ 0.57±0.01b 8.56±1.35a 13.81±0.36d 54.84±1.04b 0.27±0.00e 混果 0.42±0.01c 4.50±0.46bc 53.43±0.62b 55.38±0.39b 1.02±0.00a 沙棘中存在的大量类胡萝卜素物质,具有清除自由基、增强免疫力和预防癌症等功效[41−43]。由表4可知,不同品种沙棘汁的类胡萝卜素含量在0.15~1.02 mg/g,其中,5个单一品种沙棘汁中‘状元黄’沙棘汁的类胡萝卜素含量最高(0.54 mg/g),无刺丰沙棘汁含量最低(0.15 mg/g),各单一品种沙棘汁差异显著(P<0.05),不同单一品种沙棘汁中的类胡萝卜素差异显著与基因型和发育阶段等内在因素有关[44−45]。不同沙棘汁中,混果沙棘汁的类胡萝卜素最高,为1.02 mg/g,这可能与混果汁形成的混合体系有关。
通过对不同大果沙棘汁的营养成分分析发现,‘状元黄’沙棘汁的主要营养成分(总酚、维生素E和维生素C)含量显著高于其他品种沙棘汁(P<0.05),‘向阳’沙棘汁次之,这表明了具有较高营养活性成分的‘状元黄’和“向阳”这两个品种更适宜制汁,可进一步用于开发营养功效型饮品或配料等功能食品;‘深秋红’‘巨人’和‘无刺丰’沙棘汁可作为一般调味饮品或各用途配料产品原料。
2.3 生物活性测定分析
DPPH和ABTS+自由基清除率实验已被广泛用于评估生物活性化合物的抗氧化能力[46]。FRAP法反映样品的总抗氧化能力,越强说明对自由基的清除能力越高[47]。由表5可知,‘状元黄’沙棘汁的DPPH自由基清除率、ABTS+自由基清除率和FRAP值最高,分别为97.13%、61.99%和0.85 μmol Trolox/mL,这说明‘状元黄’沙棘汁具有较强的抗氧化能力。超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性与机体清除自由基水平呈正相关,随着SOD活性水平升高,延缓机体衰老的作用越强[5,48]。混果、‘状元黄’和‘无刺丰’沙棘汁的SOD活性最强,分别为91.27、85.24和86.88 U/mL,且三者之间差异不显著(P>0.05)。混果沙棘汁具有较高的SOD活性,这可能与混果原料的异质性及混果汁混合体系有关。通过以上结果可知,‘状元黄’沙棘汁的总体抗氧化能力显著高于其它品种沙棘汁(P<0.05),可作为高抗氧化剂产品或加工成具有高抗氧化能力的功能性食品。
表 5 不同沙棘汁的生物活性分析Table 5. Analysis of biological activities of different sea buckthorn juice品种 DPPH自由
基清除率
(%)ABTS+自由
基清除率
(%)FRAP
(μmol Trolox/mL)SOD 活性
(U/mL)‘深秋红’ 95.07±2.30a 25.38±1.95c 0.37±0.12bc 58.24±1.42b ‘状元黄’ 97.13±0.25a 61.99±1.90a 0.85±0.12a 85.24±0.09a ‘巨人’ 96.91±0.08a 26.98±2.01c 0.19±0.01c 22.74±2.78c ‘无刺丰’ 96.36±0.33a 24.38±1.37c 0.19±0.02c 86.88±0.30a ‘向阳’ 96.38±0.32a 35.06±1.03b 0.43±0.11b 29.49±0.96c 混果 96.57±0.24a 15.20±1.20d 0.31±0.02bc 91.17±2.38a 2.4 理化特性、营养指标和抗氧化性的相关性分析
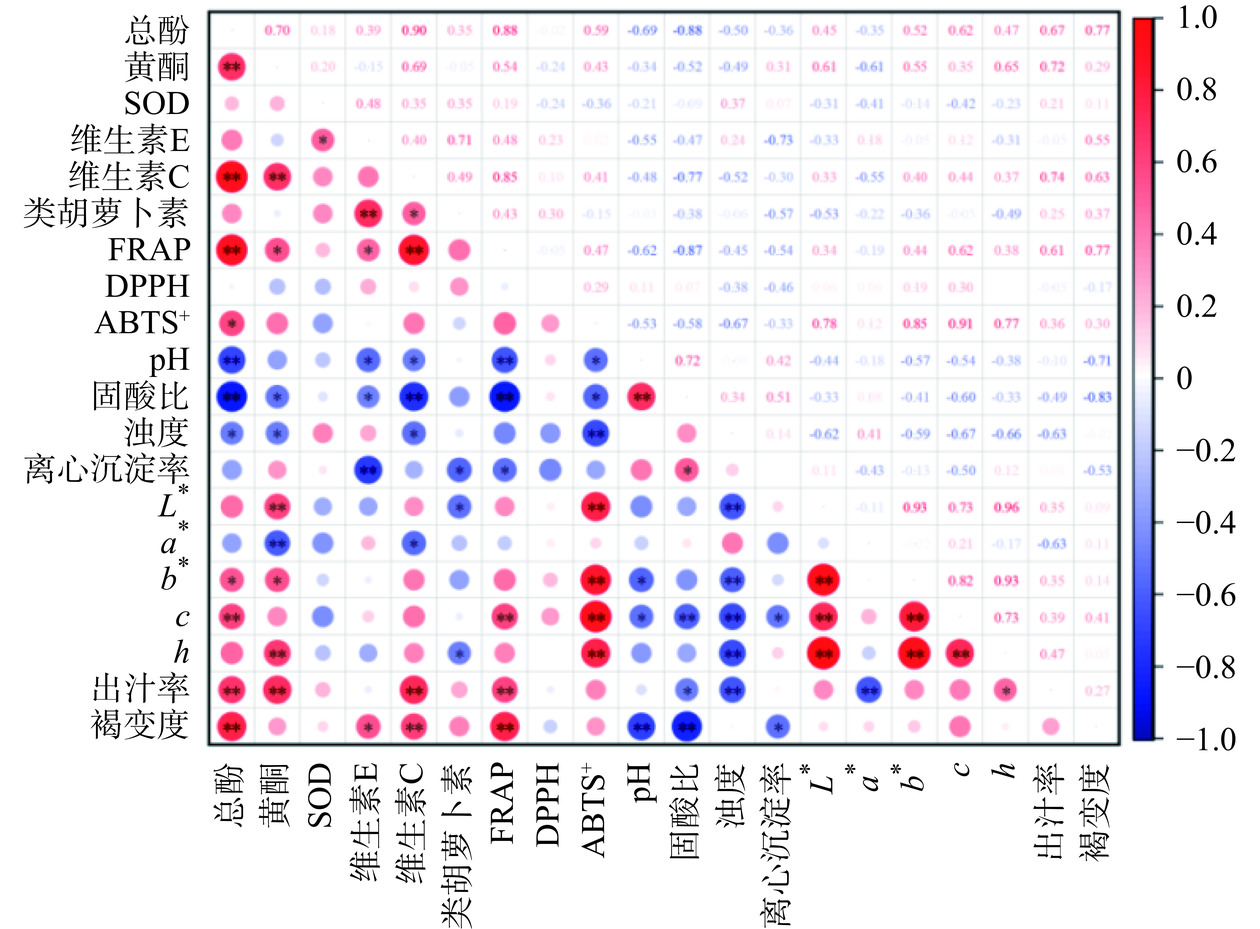
不同品种沙棘汁理化特性、营养指标和抗氧化性之间的相关性如图1所示,颜色表示指标之间呈正相关(红色)或负相关(蓝色),颜色强度越高表示相关系数越高。总体上相关系数为0.8~1.0,表示相关性极强;0.6~0.8,相关性强;0.4~0.6,相关性中等;0.2~0.4,相关性较弱;0.0~0.2,表示相关性非常弱或无相关性[49]。由图可知,总酚含量与ABTS+和FRAP测定的抗氧化能力呈正相关,具差异显著性(P<0.05),相关系数分别为0.59和0.88。总黄酮含量与FRAP呈显著正相关(P<0.05),相关系数为0.54,这与前人研究沙棘抗氧化潜力的结果基本一致[50−51]。维生素C与总酚、总黄酮和FRAP之间的相关性极显著(P<0.01),分别为0.90、0.69和0.85;与类胡萝卜素之间呈显著正相关(P<0.05),为0.49。由此可见,沙棘汁的抗氧化能力不仅与酚类物质有关,还与总黄酮和维生素C等有关,说明抗氧化活性并不是某一特定化合物呈现出来的作用,而是生物活性化合物共同呈现出来的结果,在阻止自由基对生物大分子的破坏中具有协同作用[52−53]。b*、c、h与L*呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),总酚、维生素C和出汁率之间呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),pH和离心沉淀率与固酸比呈极显著或显著正相关(P<0.01,P<0.05)、SOD活性与维生素E之间呈显著正相关(P<0.05)、类胡萝卜素与维生素E呈极显著相关(P<0.01)。结果表明,各指标之间均存在不同程度的正相关或负相关,为进一步系统分析不同大果沙棘品种的制汁适宜性,需在此基础上对各指标进行归一化处理和综合评价。
2.5 挥发性成分分析
从6种沙棘汁中共鉴定出58种挥发性物质,各物质的定性分析见表6。包括18种酯类、9种醇类、13种醛类、6种酮类和12种其他类化合物,其中共有9对物质是其单体二聚体或三聚体。研究表明,单体、二聚体和三聚体是同一种化合物,而二聚体和三聚体比单体具有更强的质子亲和力,是在通过漂移区时被分析离子和中性分子加合成的化合物,它们的形成与浓度和性质有关[54−55]。不同沙棘汁中检测到的大多数挥发性化合物都具有水果香味,这与前人研究一致[22]。沙棘汁的特征风味还呈现出苦味和酸味[56],从表6中的风味描述可见,正戊醛、戊酸和丁酸等是果汁愉悦感的负面因素,呈现出苦味、酸酪味和难闻味。其中丁酸(0.07%~1.51%)和戊酸(0.17%~1.06%)的形成可能是由于冷冻贮藏过程中果内细胞被破坏进而导致酯酶催化酯的水解产生[57]。‘深秋红’沙棘汁中4-甲基-1-戊醇、正己醛(二聚体)、正戊醛、乙酸异戊酯、乙酸甲酯、巴豆酸异丁酯和乙醇的相对含量较高(4.45%~9.43%),主要呈现出水果味、杏仁味和苦香味;混果沙棘汁的4-甲基-1-戊醇、正己醛(二聚体)、异戊酸甲酯(二聚体)、乙酸异戊酯(二聚体)、巴豆酸异丁酯和乙醇相对含量较高(5.24%~9.04%),主要呈现出水果味和苦香味;‘状元黄’沙棘汁中正己醛(二聚体)、乙醇和巴豆酸异丁酯的相对含量较高(分别为8.68%、8.09%和5.85%),主要呈现出水果香;‘巨人’沙棘汁中4-甲基-1-戊醇、异戊酸甲酯(二聚体)、正己醛(二聚体)和乙醇相对含量较高(7.42%~9.95%),主要呈现出清新杏仁味和药草味;‘无刺丰’和‘向阳’沙棘汁中正己醛(二聚体)和乙醇相对含量较高,主要表现出苹果味和甜味。综上所述,正己醛(二聚体)和乙醇是不同沙棘汁中共有的相对含量较高的挥发性化合物,相对含量分别在5.96%~8.68%和6.90%~8.09%之间,为沙棘汁提供苹果香、果味和甜味,因此初步推断正己醛(二聚体)和乙醇是沙棘汁主体香气的重要物质。
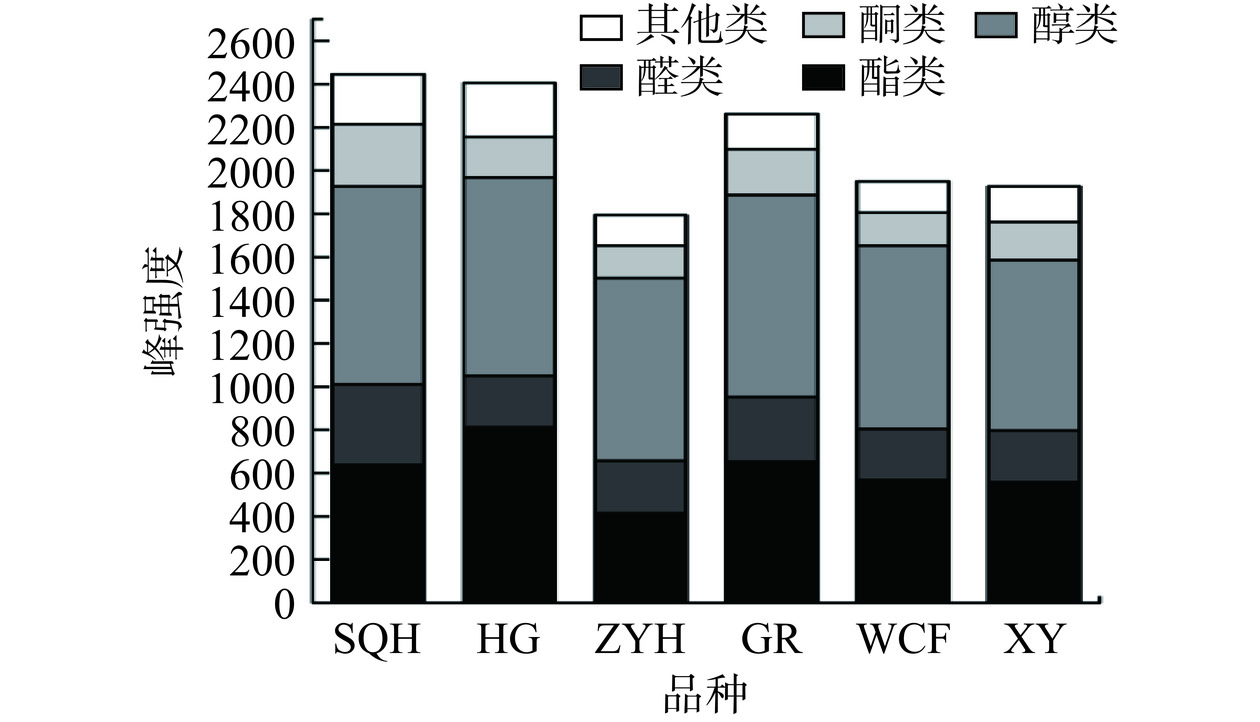
表 6 不同沙棘汁挥发性物质定性定量分析Table 6. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of volatile substances in different sea buckthorn juice序号 风味化合物 RI Rt(s) Dt(ms) 相对含量(%) 风味描述 SQH HG ZYH GR WCF XY 1 乙酸庚酯-M 1111.10 697.98 1.46 1.54±0.03e 2.47±0.02d 0.46±0.04f 3.26±0.03b 3.87±0.03a 3.04±0.05c 花香、清新 2 乙酸庚酯-D 1111.10 697.98 2.03 1.91±0.02d 1.84±0.02e 1.95±0.01d 2.07±0.01c 2.66±0.01b 2.88±0.06a 3 2-乙基-1-己醇 1014.70 494.52 1.80 1.69±0.04a 1.58±0.00b 1.72±0.01a 1.31±0.02c 0.62±0.02d 0.41±0.02e 玫瑰香 4 丁酸丁酯 992.70 458.05 1.34 1.55±0.02f 2.20±0.02e 3.70±0.03a 2.70±0.05d 3.27±0.01b 3.15±0.03c 花香 5 苯甲醛 951.00 397.29 1.15 1.07±0.01a 0.21±0.01c 0.24±0.01b 0.14±0.01d 0.13±0.00e 0.14±0.00d 水果香 6 2-蒎烯-M 925.30 364.55 1.21 1.28±0.03a 0.35±0.02d 0.47±0.01c 0.54±0.01b 0.36±0.01d 0.30±0.01e 雪松香 7 2-蒎烯-D 923.00 361.74 1.66 1.92±0.05a 0.66±0.01d 0.58±0.02e 0.55±0.01e 1.01±0.01c 1.27±0.02b 8 2-蒎烯-T 951.00 397.25 1.22 0.57±0.00a 0.27±0.00b 0.17±0.00d 0.19±0.00c 0.17±0.00d 0.16±0.00e 9 庚醛 894.70 329.76 1.33 0.67±0.01c 2.11±0.02a 0.25±0.03f 1.17±0.01b 0.51±0.01e 0.55±0.01d 柑橘味 10 丁酸丙酯 897.20 332.50 1.69 2.01±0.02a 0.79±0.00e 1.57±0.02b 1.17±0.01d 0.65±0.01f 1.34±0.02c 菠萝味、杏味 11 2-庚酮 872.90 307.51 1.26 2.05±0.00e 1.72±0.02f 3.07±0.04a 2.43±0.01d 2.87±0.02c 2.93±0.02b 酸酪味 12 4-甲基-1-戊醇 854.30 289.99 1.66 9.43±0.03e 9.04±0.02f 12.38±0.02a 9.95±0.01d 11.23±0.02b 10.97±0.03c 清新杏仁味 13 顺-3-己烯醇 837.10 274.94 1.24 1.7±0.01c 1.33±0.02e 2.20±0.08a 1.48±0.02d 1.84±0.03b 1.54±0.01d 叶草香 14 丙酸正丙酯 804.50 249.03 1.21 2.19±0.01e 1.56±0.01f 2.94±0.01a 2.28±0.02d 2.59±0.03c 2.64±0.02b 水果香 15 正己醛-M 785.00 235.11 1.26 1.46±0.02e 0.94±0.02f 2.34±0.05a 1.61±0.02d 2.09±0.01c 2.17±0.03b 苹果香 16 正己醛-D 795.20 242.28 1.56 7.18±0.04d 7.69±0.04b 8.68±0.07a 7.44±0.09c 6.93±0.02e 5.96±0.03f 17 异戊酸甲酯-M 771.10 225.84 1.20 1.86±0.01e 1.24±0.01f 2.89±0.03c 2.11±0.00d 3.23±0.01b 3.39±0.02a 药草味、水果香 18 异戊酸甲酯-D 768.50 224.15 1.54 2.96±0.04f 6.72±0.05d 4.58±0.03e 7.73±0.05c 10.11±0.02b 10.69±0.02a 19 正戊醛-M 689.60 180.72 1.19 4.45±0.03a 0.16±0.01e 1.26±0.01d 1.59±0.03b 1.57±0.02b 1.32±0.03c 苦味 20 正戊醛-D 689.90 180.90 1.42 1.73±0.03c 0.53±0.03d 2.64±0.01a 2±0.01b 2.66±0.01a 2.66±0.01a 21 1,1-二乙氧基乙烷 720.10 195.90 1.13 0.69±0.01b 0.82±0.00a 0.4±0.00d 0.61±0.02c 0.22±0.00e 0.13±0.01f 奶油味、水果香 22 异丁醇 644.90 161.60 1.17 0.86±0.00d 0.72±0.01e 1.63±0.03b 1.3±0.02c 1.79±0.02a 1.64±0.01b 茶叶香 23 乙酸乙酯 607.70 148.11 1.34 0.23±0.00c 1.00±0.01a 0.18±0.01d 0.36±0.01b 0.19±0.01d 0.15±0.01e 果酒味 24 丁醛 591.70 142.91 1.29 1.52±0.00b 1.05±0.00e 0.96±0.01f 1.78±0.01a 1.29±0.00c 1.16±0.02d 香蕉味 25 2,3-丁二酮 578.00 138.71 1.17 0.63±0.02a 0.39±0.00c 0.17±0.01e 0.42±0.01b 0.13±0.01f 0.26±0.00d 黄油味 26 乙酸乙酯 619.20 152.06 1.10 0.63±0.03f 0.74±0.00e 0.97±0.01d 1.57±0.01a 1.29±0.01b 1.15±0.00c 刺激性气味、酸味 27 1-戊烯-3-酮 675.00 174.12 1.08 0.69±0.01a 0.16±0.01e 0.29±0.00b 0.12±0.01f 0.24±0.01d 0.27±0.00c 芥末味 28 烯丙基腈 660.90 168.07 1.13 0.61±0.00b 0.83±0.01a 0.11±0.00d 0.3±0.00c 0.1±0.00d 0.05±0.00e 葱味 29 3-丁烯腈 632.50 156.87 1.13 0.3±0.00b 1.04±0.00a 0.05±0.01d 0.28±0.00c 0.06±0.00d 0.06±0.00d 葱味 30 3-甲基-3-丁烯-1-醇-M 732.40 202.58 1.25 1.92±0.00d 1.25±0.03e 3.37±0.07a 2.32±0.03c 3.15±0.00b 3.38±0.04a 焦糖味 31 3-甲基-3-丁烯-1-醇-D 730.00 201.28 1.50 2.36±0.02d 2.3±0.04d 3.43±0.06b 2.84±0.03c 3.45±0.01b 3.57±0.01a 32 乙硫醚 705.90 188.60 1.04 2.01±0.01a 1.44±0.00b 1.26±0.01c 1.42±0.01b 1.14±0.01e 1.16±0.00d 33 2-丁酮 581.20 139.66 1.25 1.8±0.01a 0.37±0.00d 0.12±0.01e 0.63±0.00b 0.13±0.01e 0.53±0.00c 水果香 34 2-甲基丙烯醛 581.00 139.61 1.22 0.16±0.00d 0.39±0.00a 0.18±0.01c 0.28±0.00b 0.15±0.00e 0.19±0.01c 香料味 35 戊酸 912.00 348.92 1.23 1.06±0.03a 0.32±0.11bc 0.23±0.01cd 0.34±0.01b 0.20±0.01d 0.17±0.02d 酸酪味 36 异丁酸乙酯-M 752.00 213.95 1.20 0.35±0.00d 1.42±0.01a 0.28±0.00e 1.16±0.01b 0.81±0.00c 1.43±0.01a 奶油味、水果香 37 异丁酸乙酯-D 754.20 215.25 1.56 0.11±0.00e 2.68±0.00a 0.07±0.00f 0.54±0.01b 0.17±0.00d 0.46±0.01c 38 苯乙醛 1043.60 547.51 1.25 0.09±0.00e 0.84±0.00b 1.58±0.00a 0.09±0.00e 0.16±0.00d 0.30±0.01c 风信子香、樱桃味 39 庚醛 875.20 309.82 1.70 1.87±0.01d 1.27±0.01e 2.96±0.06a 2.11±0.01c 2.12±0.00c 2.78±0.02b 40 乙酸异戊酯-M 877.50 312.08 1.31 1.78±0.09a 1.34±0.01d 1.58±0.05c 1.73±0.01c 1.65±0.00ab 1.56±0.02c 梨味 41 乙酸异戊酯-D 875.20 309.82 1.75 5.62±0.03a 5.54±0.03b 0.81±0.01e 2.77±0.00c 1.08±0.01d 0.80±0.02e 42 二乙基二硫醚 922.20 360.83 1.29 0.27±0.00f. 1.72±0.01e 2.16±0.02c 1.91±0.02d 2.52±0.01b 2.81±0.01a 卷心菜味 43 丙酸乙酯-M 708.00 189.67 1.15 0.37±0.01f 0.72±0.01e 2.86±0.00b 1.51±0.01d 2.78±0.00c 3.34±0.00a 苹果味 44 丙酸乙酯-D 704.00 187.66 1.46 0.06±0.00e 3.31±0.01a 0.07±0.00d 0.23±0.01c 0.95±0.00b 0.05±0.00e 45 1-戊烯-3-醇 687.30 179.67 1.36 0.75±0.00c 1.36±0.02a 0.14±0.00f 1.01±0.00b 0.27±0.00d 0.23±0.01e 黄油味 46 3-戊酮 690.20 181.02 1.11 0.1±0.00f 0.34±0.01b 0.11±0.00e 0.36±0.00a 0.13±0.00d 0.17±0.00c 丙酮味 47 2-甲基丁醛 645.60 161.89 1.41 0.52±0.01f 1.13±0.00b 0.63±0.01d 1.22±0.00a 0.96±0.01c 0.58±0.01e 可可味 48 丁酸甲酯 712.70 192.05 1.43 0.11±0.00f 1.2±0.00e 1.8±0.02c 1.53±0.00d 2.03±0.00b 2.3±0.03a 苹果味、干酪香气 49 乙酸甲酯 547.50 130.14 1.19 7.01±0.16a 4.91±0.00b 0.27±0.01e 2.63±0.01c 0.54±0.00d 0.35±0.01e 苦香味 50 2,3-戊二酮 690.00 180.95 1.22 0.2±0.00c 0.48±0.01a 0.17±0.00e 0.32±0.00b 0.15±0.00e 0.13±0.00f 奶油味、焦糖香 51 双戊烯 1044.30 548.90 1.21 0.04±0.00d 1.23±0.01a 1.16±0.03b 0.05±0.00cd 0.06±0.00cd 0.08±0.00c 柠檬香 52 罗勒烯 1043.00 546.24 1.71 0.06±0.00d 0.15±0.01b 0.75±0.00a 0.05±0.00e 0.07±0.00c 0.06±0.00d 水果香 53 丙烯醛 481.10 114.74 1.06 0.15±0.00e 0.16±0.00d 0.53±0.01a 0.28±0.01c 0.28±0.01c 0.40±0.00b 54 丙硫醇 621.50 152.90 1.17 0.27±0.00f 0.56±0.00c 0.37±0.01e 0.92±0.00a 0.73±0.01b 0.44±0.01d 卷心菜味 55 巴豆酸异丁酯 1000.50 470.62 1.81 6.32±0.01a 5.24±0.02c 5.85±0.04b 4.55±0.02d 2.59±0.04e 1.80±0.02f 水果香 56 丁酸 835.70 273.75 1.17 0.07±0.00f 0.3±0.00d 0.14±0.00e 0.44±0.01c 0.93±0.00b 1.51±0.02a 刺激性味、难闻味 57 正丁醛 607.00 147.87 1.10 1.75±0.01a 0.71±0.01c 0.15±0.00f 0.85±0.01b 0.23±0.00e 0.35±0.01d 香蕉味 58 乙醇 428.60 105.18 1.13 7.46±0.17b 7.18±0.05c 8.09±0.05a 7.42±0.07b 6.90±0.04d 6.69±0.03e 甜味、果味 注:RI表示保留指数;Rt表示保留时间;Dt表示迁移时间;M代表单体,D代表二聚体,T代表三聚体;;风味描述来自https://www.femaflavor.org/flavor-library 和 https://www.chemicalbook.com/。 为了更加系统全面地分析不同大果沙棘汁挥发性成分类别的风味信息。如图2所示,‘深秋红’和混果沙棘汁的相对峰强度高于其他品种,‘状元黄’沙棘汁的挥发性峰强度最低。醇类是沙棘汁中相对峰强度最高的挥发性成分,具有新鲜的水果香味。酯类为第二大挥发性成分主要对沙棘汁的果味和甜味等气味有贡献,这与黄蕊等[58]的研究基本一致。由表6和图2可知,酮类的相对峰强度占比在8%~12%之间,包括2-庚酮、2,3-丁二酮、1-戊烯-3-酮、2-丁酮、3-戊酮和2,3-戊二酮,呈现酸酪味、芥末味、水果香和焦糖香等气味,主要由不饱和脂肪酸氧化和美拉德反应等产生[59]。
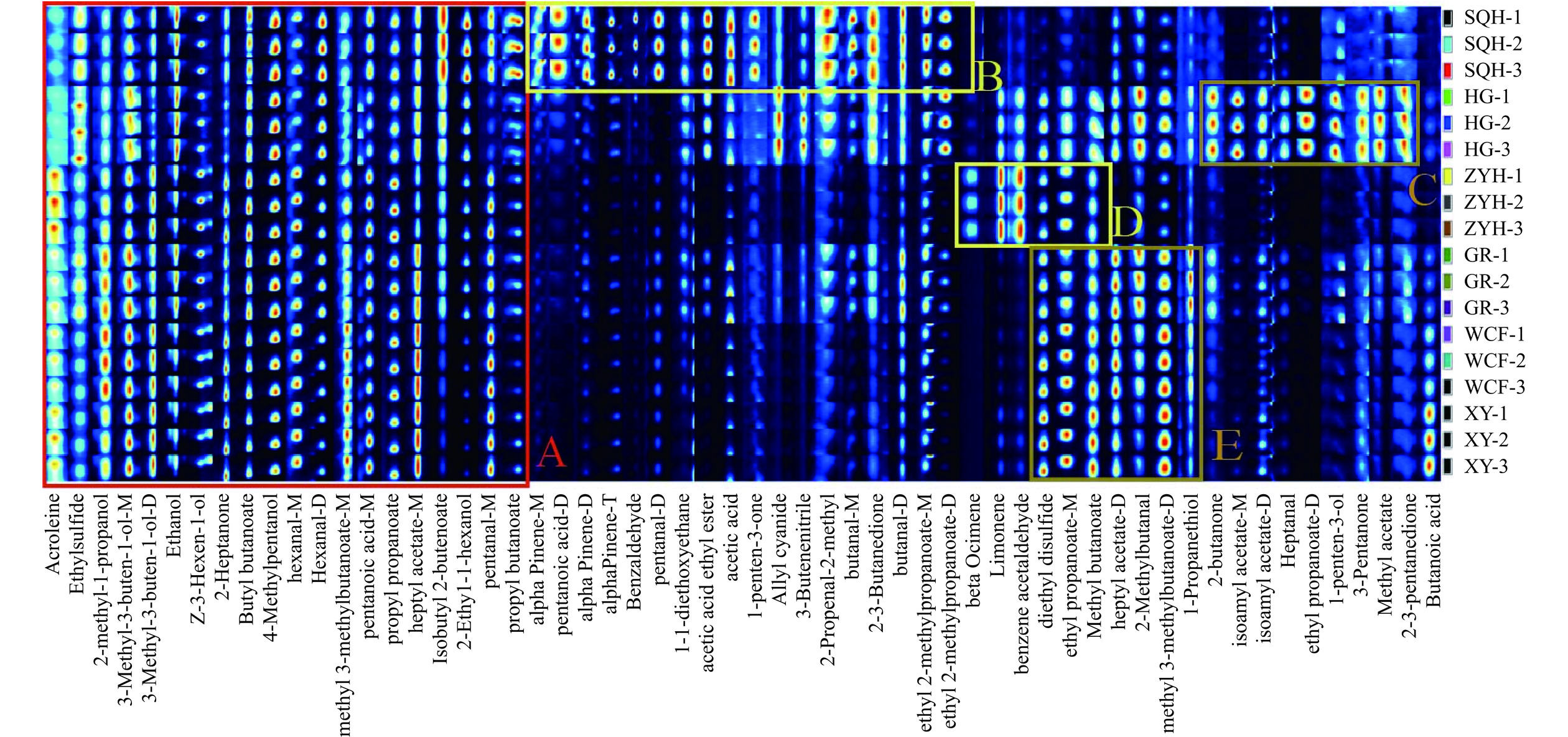
指纹图谱(图3)中,每行显示样品的所有信号峰,每列为不同样品中的相同挥发性化合物,右侧显示了6种沙棘汁的编号,每个样品有3个平行批次,3次平行的结果无明显差异,说明利用GC-IMS测定挥发性成分具有可行性。此外,颜色代表挥发性化合物的含量,颜色越亮表示含量越高,纯黑色表示该物质的浓度接近于零。如图3所示,各组样品中挥发性有机物的含量差异较大,混果沙棘汁的挥发性化合物种类最多,其次是‘深秋红’沙棘汁。根据指纹图谱所显示的颜色深浅,可以判断出‘深秋红’沙棘汁的挥发性化合物的含量最多,与图2的分析结果趋于一致。A框为所有样品主要的共有挥发性化合物的特征峰区域,有19种挥发性化合物,主要由有机酸和醇类酯化生成的酯类化合物,通常带有清新的果香味以及令人愉快的味道[60]。A框中包含两对单体和二聚体分别是3-甲基-3-丁烯-1-醇和正己醛,呈现出焦糖味和苹果香,而酯类和醛类的产生可能与脂肪酸的代谢有关,其中正己醛是亚油酸氧化的主要分解产物。B框为‘深秋红’沙棘汁特征性较强的挥发性化合物,主要是正戊醛(单体)、2-蒎烯(单体)、3-丁烯腈、2-3-丁二酮和1-戊烯-3-醇等,主要提供苦涩味、雪松香、水果香等风味。
C区显示的是混果沙棘汁的特征性挥发性化合物,所含的含量相较于其他沙棘汁更高,分别为2-丁酮、乙酸异戊酯(单体和二聚体)、庚醛、丙酸乙酯(单体)、1-戊烯-3-酮、3-戊酮、乙酸甲酯和2-3-戊二酮,主要提供沙棘汁水果香、梨味、苹果味和奶油味等风味。D区是‘状元黄’主要的特征性挥发性风味,分别是罗勒烯、双戊烯和苯乙醛。由图3和表6可得,‘状元黄’沙棘汁中的罗勒烯化合物的相对含量为0.75%,显著高于其他沙棘汁(P<0.05),作为单萜类化合物是在甲羟戊酸途径中合成的,具体呈现出清甜的水果香。E区域是‘巨人’‘无刺丰’和‘向阳’所得沙棘汁的特征挥发性化合物,分别是二乙基二硫醚、丙酸乙酯(二聚体)、异戊酸甲酯(二聚体)、丁酸甲酯、乙酸庚酯(二聚体)、丙硫醇和2-甲基丁醛,呈现出卷心菜味、苹果味、药草味和水果香等,3种沙棘汁的挥发性成分较相似,可能是由于原料品种近缘所致。
综上所述,不同沙棘汁中的挥发性成分存在一定差异,这与生长条件、成熟度和遗传背景等因素有关,而沙棘风味化合物的形成则与氧化反应、脂肪酸代谢、代谢途径等有关[61]。由不同沙棘汁的挥发性成分分析可知,‘状元黄’沙棘汁的酯类风味虽少于其他沙棘汁,但作为主要呈香物质—正己醛(二聚体)和乙醇的相对含量最高(分别为8.68%和8.09%),这说明‘状元黄’沙棘汁香气的浓郁程度较好,具有适宜制汁的优势。
2.6 主成分分析
基于不同沙棘汁理化特性、营养指标和抗氧化性之间的相关性,结合沙棘汁挥发性成分,选取所有指标数据进行主成分分析,综合评价各指标对沙棘汁品质的影响。以主成分分析得到特征值的累计方差贡献率大于80%为依据[62],由表7可知,前3个主成分的累计方差贡献率达到81.420%,能表征原始数据的绝大部分有效信息,符合主成分分析方法的要求。
表 7 特征值及方差贡献率Table 7. Characteristic values and variance contribution ratePC 初始特征值 特征值 方差贡献率(%) 累积方差贡献率(%) 1 8.873 42.254 42.254 2 5.507 26.225 68.478 3 2.718 12.942 81.420 4 1.787 8.507 89.928 5 1.345 6.406 96.334 由表7和表8可知,第一主成分(PC1)的方差贡献率为42.254%,主要反映L*、褐变度、b*、c、h、总酚、总黄酮、维生素C、ABTS+和FRAP表现出较高相关性且正相关,说明这些指标在大果沙棘制汁适宜性综合评价中占主要位置。第二主成分(PC2)的方差贡献率为26.225%,以pH、浊度、离心沉淀率、出汁率、DPPH、总挥发性成分等影响为主;第三主成分(PC3)的方差贡献率为12.942%,主要综合了维生素E、类胡萝卜素和SOD活性为主。将各指标进行标准化,并通过计算得出3个主成分的函数表达式:F1、F2、F3,如下所示。标准化处理后的数据进行PCA(图3)。
表 8 各指标主成分载荷矩阵Table 8. Principal component load matrix of each index指标 PC 1 2 3 pH −0.246 0.935 0.023 固酸比 −0.006 0.471 −0.042 浊度 −0.165 0.807 0.325 离心沉淀率 −0.107 0.914 −0.033 出汁率 −0.106 0.913 0.041 褐变度 0.762 0.193 0.217 L* 0.882 −0.061 −0.435 a* 0.503 0.388 −0.473 b* 0.887 −0.022 −0.445 c 0.632 0.353 −0.550 h 0.827 0.224 −0.358 总酚 0.969 0.021 0.129 总黄酮 0.824 0.002 −0.102 维生素E 0.662 0.009 0.663 维生素C 0.858 0.092 0.358 类胡萝卜素 0.543 −0.200 0.679 DPPH −0.240 0.910 0.022 ABTS+ 0.955 −0.041 −0.103 FRAP 0.958 −0.120 0.153 SOD活性 0.515 0.143 0.644 总挥发性成分 0.207 0.900 0.117 F1=−0.083X1−0.002X2−......+0.069X21 (1) F2=0.398X1−0.201X2+......+0.384X21 (2) F3=0.014X1−0.025X2−......+0.071X21 (3) 式中,X1~X21分别表示pH、固酸比、浊度、离心沉淀率、出汁率、褐变度、L*、a*、b*、c、h、总酚、总黄酮、维生素E、维生素C、类胡萝卜素含量、DPPH自由基清除率、ABTS+自由基清除率、FRAP、SOD活性和总挥发性成分。分别以3个主成分的方差贡献率为权重进行加权求和,构建主成分综合评价函数如下:
Z=0.42254×F1+0.26225×F2+0.12942×F30.89928 (4) 综合得分越高说明品质越好。6种沙棘汁的综合得分见表9,F1中‘状元黄’的得分较高,说明其总酚、总黄酮和维生素C等最高,制汁适宜性最好,‘向阳’次之;不同沙棘汁的综合排名依次是‘状元黄’>‘向阳’>‘深秋红’>混果>‘无刺丰’>‘巨人’。
表 9 不同品种沙棘汁综合得分及排名Table 9. Comprehensive scores and rankings of different sea buckthorn juice品种 F1 F2 F3 综合得分 综合排名 ‘深秋红’ −0.09 −0.61 0.71 −0.13 3 ‘状元黄’ 4.42 −0.71 0.33 2.12 1 ‘巨人’ −2.36 0.14 −1.66 −1.44 6 ‘无刺丰’ −1.45 0.92 −0.65 −0.56 5 ‘向阳’ 2.21 0.32 −2.45 0.86 2 混果 −1.92 −0.05 3.72 −0.42 4 3. 结论
本研究运用多元分析法综合评价了5个大果沙棘汁和1个混果汁的品质特性及加工适宜性。不同大果沙棘汁的总体差异较大,其中,‘状元黄’沙棘汁的色泽最佳,具有较低的浊度和离心沉淀率,较高的出汁率和抗坏血酸含量和较好的抗氧化能力。经进一步相关性分析发现,大果沙棘汁中的维生素C与总酚、总黄酮和FRAP之间的相关性极显著(P<0.01),且理化特性和营养指标之间存在一定的关联性。通过GC-IMS技术共检测出58种挥发性物质,主要以醇类、醛类、酮类和酯类为主,且大多数化合物表现出水果香味,‘深秋红’和混果沙棘汁的挥发性物质的峰强度高于其他品种,主要呈现出新鲜的水果香和奶油香。‘状元黄’沙棘汁中的罗勒烯化合物相对含量为0.75%,显著高于其他大果沙棘汁(P<0.05),呈现清甜的水果香。采用主成分分析综合评价得出‘状元黄’沙棘汁综合品质较好,说明该品种更适宜制汁,‘向阳’沙棘汁次之。‘状元黄’沙棘汁中含有较高的总酚、总黄酮、维生素C和抗氧化活性,可直接作为饮品或基料应用于功能性食品的开发;‘深秋红’沙棘汁的颜色最红、挥发性成分的含量最多,可作为食品加工辅料。不同品种沙棘汁作为终端或中间产品丰富沙棘产品种类。该研究为企业对大果沙棘制汁加工专用原料的选择和沙棘汁的深度开发提供了理论与应用依据。后期可在此基础上,深入挖掘大果沙棘品种资源中潜在的特征功效组分,建立营养品质及加工适宜性数据库,为企业标准化加工生产提供理论指导。此外,研究仅对比分析了不同品种沙棘汁挥发性成分,其风味变化形成途径和贮藏期营养品质变化仍有待探究。
-
表 1 不同大果沙棘样品信息
Table 1 Sample information of sea buckthorn of different large fruits
表 2 不同沙棘汁基础理化指标分析
Table 2 Analysis of basic physical and chemical indexes of different sea buckthorn juice
品种 pH 固酸比 出汁率(%) 浊度(NTU) 离心沉淀率(%) 褐变度 ‘深秋红’ 2.89±0.03c 20.90±0.28c 49.07±0.05c 46730.00±26.87a 4.25±0.22c 0.44±0.00a ‘状元黄’ 2.72±0.01d 15.39±0.61d 54.64±0.01ab 28676.67±15.43d 3.64±0.22d 0.38±0.00b ‘巨人’ 3.00±0.02a 27.45±2.58a 49.92±0.01bc 40670.00±22.99c 4.72±0.18bc 0.16±0.00f ‘无刺丰’ 2.93±0.01bc 26.06±1.37ab 50.01±0.01bc 46906.67±69.58a 5.44±0.27a 0.17±0.00e ‘向阳’ 2.93±0.01bc 21.34±1.50c 56.43±0.01a 28326.67±15.80d 5.26±0.22a 0.25±0.00c 混果 2.97±0.03ab 23.60±0.83c 54.22±0.01ab 44223.33±45.15b 5.01±0.18ab 0.20±0.00d 表 3 不同沙棘汁颜色分析
Table 3 Color analysis of different sea buckthorn juice
品种 L* a* b* c h(°) ‘深秋红’ 3.97±0.02e 18.88±0.25a 5.90±0.25e 19.78±0.30c 0.30±0.01e ‘状元黄’ 8.31±0.07b 15.85±0.13d 14.20±0.13a 21.28±0.47a 0.73±0.01b ‘巨人’ 4.40±0.05d 18.54±0.01b 7.51±0.01d 20.00±0.08bc 0.38±0.00d ‘无刺丰’ 4.77±0.02c 16.54±0.02c 8.09±0.02c 18.41±0.05d 0.46±0.00c ‘向阳’ 9.84±0.10a 14.93±0.18e 13.82±0.18b 20.34±0.12b 0.75±0.03a 混果 1.13±0.07f 5.61±0.020f 1.70±0.02f 5.86±0.05d 0.29±0.00e 表 4 不同沙棘汁营养指标分析
Table 4 Nutritional index analysis of different sea buckthorn juice
品种 总酚(mg/mL) 总黄酮(mg/mL) 维生素E(μg/g) 维生素C(mg/100 g) 类胡萝卜素(mg/g) ‘深秋红’ 0.43±0.03c 2.55±0.27c 54.95±0.82b 45.51±1.05c 0.35±0.00c ‘状元黄’ 0.90±0.01a 6.20±0.02b 63.14±1.82a 69.61±0.80a 0.54±0.01b ‘巨人’ 0.27±0.01e 2.14±0.21c 21.71±1.82c 20.71±0.60d 0.28±0.00d ‘无刺丰’ 0.35±0.02d 4.22±1.28bc 23.05±0.49c 24.94±0.00d 0.15±0.00f ‘向阳’ 0.57±0.01b 8.56±1.35a 13.81±0.36d 54.84±1.04b 0.27±0.00e 混果 0.42±0.01c 4.50±0.46bc 53.43±0.62b 55.38±0.39b 1.02±0.00a 表 5 不同沙棘汁的生物活性分析
Table 5 Analysis of biological activities of different sea buckthorn juice
品种 DPPH自由
基清除率
(%)ABTS+自由
基清除率
(%)FRAP
(μmol Trolox/mL)SOD 活性
(U/mL)‘深秋红’ 95.07±2.30a 25.38±1.95c 0.37±0.12bc 58.24±1.42b ‘状元黄’ 97.13±0.25a 61.99±1.90a 0.85±0.12a 85.24±0.09a ‘巨人’ 96.91±0.08a 26.98±2.01c 0.19±0.01c 22.74±2.78c ‘无刺丰’ 96.36±0.33a 24.38±1.37c 0.19±0.02c 86.88±0.30a ‘向阳’ 96.38±0.32a 35.06±1.03b 0.43±0.11b 29.49±0.96c 混果 96.57±0.24a 15.20±1.20d 0.31±0.02bc 91.17±2.38a 表 6 不同沙棘汁挥发性物质定性定量分析
Table 6 Qualitative and quantitative analysis of volatile substances in different sea buckthorn juice
序号 风味化合物 RI Rt(s) Dt(ms) 相对含量(%) 风味描述 SQH HG ZYH GR WCF XY 1 乙酸庚酯-M 1111.10 697.98 1.46 1.54±0.03e 2.47±0.02d 0.46±0.04f 3.26±0.03b 3.87±0.03a 3.04±0.05c 花香、清新 2 乙酸庚酯-D 1111.10 697.98 2.03 1.91±0.02d 1.84±0.02e 1.95±0.01d 2.07±0.01c 2.66±0.01b 2.88±0.06a 3 2-乙基-1-己醇 1014.70 494.52 1.80 1.69±0.04a 1.58±0.00b 1.72±0.01a 1.31±0.02c 0.62±0.02d 0.41±0.02e 玫瑰香 4 丁酸丁酯 992.70 458.05 1.34 1.55±0.02f 2.20±0.02e 3.70±0.03a 2.70±0.05d 3.27±0.01b 3.15±0.03c 花香 5 苯甲醛 951.00 397.29 1.15 1.07±0.01a 0.21±0.01c 0.24±0.01b 0.14±0.01d 0.13±0.00e 0.14±0.00d 水果香 6 2-蒎烯-M 925.30 364.55 1.21 1.28±0.03a 0.35±0.02d 0.47±0.01c 0.54±0.01b 0.36±0.01d 0.30±0.01e 雪松香 7 2-蒎烯-D 923.00 361.74 1.66 1.92±0.05a 0.66±0.01d 0.58±0.02e 0.55±0.01e 1.01±0.01c 1.27±0.02b 8 2-蒎烯-T 951.00 397.25 1.22 0.57±0.00a 0.27±0.00b 0.17±0.00d 0.19±0.00c 0.17±0.00d 0.16±0.00e 9 庚醛 894.70 329.76 1.33 0.67±0.01c 2.11±0.02a 0.25±0.03f 1.17±0.01b 0.51±0.01e 0.55±0.01d 柑橘味 10 丁酸丙酯 897.20 332.50 1.69 2.01±0.02a 0.79±0.00e 1.57±0.02b 1.17±0.01d 0.65±0.01f 1.34±0.02c 菠萝味、杏味 11 2-庚酮 872.90 307.51 1.26 2.05±0.00e 1.72±0.02f 3.07±0.04a 2.43±0.01d 2.87±0.02c 2.93±0.02b 酸酪味 12 4-甲基-1-戊醇 854.30 289.99 1.66 9.43±0.03e 9.04±0.02f 12.38±0.02a 9.95±0.01d 11.23±0.02b 10.97±0.03c 清新杏仁味 13 顺-3-己烯醇 837.10 274.94 1.24 1.7±0.01c 1.33±0.02e 2.20±0.08a 1.48±0.02d 1.84±0.03b 1.54±0.01d 叶草香 14 丙酸正丙酯 804.50 249.03 1.21 2.19±0.01e 1.56±0.01f 2.94±0.01a 2.28±0.02d 2.59±0.03c 2.64±0.02b 水果香 15 正己醛-M 785.00 235.11 1.26 1.46±0.02e 0.94±0.02f 2.34±0.05a 1.61±0.02d 2.09±0.01c 2.17±0.03b 苹果香 16 正己醛-D 795.20 242.28 1.56 7.18±0.04d 7.69±0.04b 8.68±0.07a 7.44±0.09c 6.93±0.02e 5.96±0.03f 17 异戊酸甲酯-M 771.10 225.84 1.20 1.86±0.01e 1.24±0.01f 2.89±0.03c 2.11±0.00d 3.23±0.01b 3.39±0.02a 药草味、水果香 18 异戊酸甲酯-D 768.50 224.15 1.54 2.96±0.04f 6.72±0.05d 4.58±0.03e 7.73±0.05c 10.11±0.02b 10.69±0.02a 19 正戊醛-M 689.60 180.72 1.19 4.45±0.03a 0.16±0.01e 1.26±0.01d 1.59±0.03b 1.57±0.02b 1.32±0.03c 苦味 20 正戊醛-D 689.90 180.90 1.42 1.73±0.03c 0.53±0.03d 2.64±0.01a 2±0.01b 2.66±0.01a 2.66±0.01a 21 1,1-二乙氧基乙烷 720.10 195.90 1.13 0.69±0.01b 0.82±0.00a 0.4±0.00d 0.61±0.02c 0.22±0.00e 0.13±0.01f 奶油味、水果香 22 异丁醇 644.90 161.60 1.17 0.86±0.00d 0.72±0.01e 1.63±0.03b 1.3±0.02c 1.79±0.02a 1.64±0.01b 茶叶香 23 乙酸乙酯 607.70 148.11 1.34 0.23±0.00c 1.00±0.01a 0.18±0.01d 0.36±0.01b 0.19±0.01d 0.15±0.01e 果酒味 24 丁醛 591.70 142.91 1.29 1.52±0.00b 1.05±0.00e 0.96±0.01f 1.78±0.01a 1.29±0.00c 1.16±0.02d 香蕉味 25 2,3-丁二酮 578.00 138.71 1.17 0.63±0.02a 0.39±0.00c 0.17±0.01e 0.42±0.01b 0.13±0.01f 0.26±0.00d 黄油味 26 乙酸乙酯 619.20 152.06 1.10 0.63±0.03f 0.74±0.00e 0.97±0.01d 1.57±0.01a 1.29±0.01b 1.15±0.00c 刺激性气味、酸味 27 1-戊烯-3-酮 675.00 174.12 1.08 0.69±0.01a 0.16±0.01e 0.29±0.00b 0.12±0.01f 0.24±0.01d 0.27±0.00c 芥末味 28 烯丙基腈 660.90 168.07 1.13 0.61±0.00b 0.83±0.01a 0.11±0.00d 0.3±0.00c 0.1±0.00d 0.05±0.00e 葱味 29 3-丁烯腈 632.50 156.87 1.13 0.3±0.00b 1.04±0.00a 0.05±0.01d 0.28±0.00c 0.06±0.00d 0.06±0.00d 葱味 30 3-甲基-3-丁烯-1-醇-M 732.40 202.58 1.25 1.92±0.00d 1.25±0.03e 3.37±0.07a 2.32±0.03c 3.15±0.00b 3.38±0.04a 焦糖味 31 3-甲基-3-丁烯-1-醇-D 730.00 201.28 1.50 2.36±0.02d 2.3±0.04d 3.43±0.06b 2.84±0.03c 3.45±0.01b 3.57±0.01a 32 乙硫醚 705.90 188.60 1.04 2.01±0.01a 1.44±0.00b 1.26±0.01c 1.42±0.01b 1.14±0.01e 1.16±0.00d 33 2-丁酮 581.20 139.66 1.25 1.8±0.01a 0.37±0.00d 0.12±0.01e 0.63±0.00b 0.13±0.01e 0.53±0.00c 水果香 34 2-甲基丙烯醛 581.00 139.61 1.22 0.16±0.00d 0.39±0.00a 0.18±0.01c 0.28±0.00b 0.15±0.00e 0.19±0.01c 香料味 35 戊酸 912.00 348.92 1.23 1.06±0.03a 0.32±0.11bc 0.23±0.01cd 0.34±0.01b 0.20±0.01d 0.17±0.02d 酸酪味 36 异丁酸乙酯-M 752.00 213.95 1.20 0.35±0.00d 1.42±0.01a 0.28±0.00e 1.16±0.01b 0.81±0.00c 1.43±0.01a 奶油味、水果香 37 异丁酸乙酯-D 754.20 215.25 1.56 0.11±0.00e 2.68±0.00a 0.07±0.00f 0.54±0.01b 0.17±0.00d 0.46±0.01c 38 苯乙醛 1043.60 547.51 1.25 0.09±0.00e 0.84±0.00b 1.58±0.00a 0.09±0.00e 0.16±0.00d 0.30±0.01c 风信子香、樱桃味 39 庚醛 875.20 309.82 1.70 1.87±0.01d 1.27±0.01e 2.96±0.06a 2.11±0.01c 2.12±0.00c 2.78±0.02b 40 乙酸异戊酯-M 877.50 312.08 1.31 1.78±0.09a 1.34±0.01d 1.58±0.05c 1.73±0.01c 1.65±0.00ab 1.56±0.02c 梨味 41 乙酸异戊酯-D 875.20 309.82 1.75 5.62±0.03a 5.54±0.03b 0.81±0.01e 2.77±0.00c 1.08±0.01d 0.80±0.02e 42 二乙基二硫醚 922.20 360.83 1.29 0.27±0.00f. 1.72±0.01e 2.16±0.02c 1.91±0.02d 2.52±0.01b 2.81±0.01a 卷心菜味 43 丙酸乙酯-M 708.00 189.67 1.15 0.37±0.01f 0.72±0.01e 2.86±0.00b 1.51±0.01d 2.78±0.00c 3.34±0.00a 苹果味 44 丙酸乙酯-D 704.00 187.66 1.46 0.06±0.00e 3.31±0.01a 0.07±0.00d 0.23±0.01c 0.95±0.00b 0.05±0.00e 45 1-戊烯-3-醇 687.30 179.67 1.36 0.75±0.00c 1.36±0.02a 0.14±0.00f 1.01±0.00b 0.27±0.00d 0.23±0.01e 黄油味 46 3-戊酮 690.20 181.02 1.11 0.1±0.00f 0.34±0.01b 0.11±0.00e 0.36±0.00a 0.13±0.00d 0.17±0.00c 丙酮味 47 2-甲基丁醛 645.60 161.89 1.41 0.52±0.01f 1.13±0.00b 0.63±0.01d 1.22±0.00a 0.96±0.01c 0.58±0.01e 可可味 48 丁酸甲酯 712.70 192.05 1.43 0.11±0.00f 1.2±0.00e 1.8±0.02c 1.53±0.00d 2.03±0.00b 2.3±0.03a 苹果味、干酪香气 49 乙酸甲酯 547.50 130.14 1.19 7.01±0.16a 4.91±0.00b 0.27±0.01e 2.63±0.01c 0.54±0.00d 0.35±0.01e 苦香味 50 2,3-戊二酮 690.00 180.95 1.22 0.2±0.00c 0.48±0.01a 0.17±0.00e 0.32±0.00b 0.15±0.00e 0.13±0.00f 奶油味、焦糖香 51 双戊烯 1044.30 548.90 1.21 0.04±0.00d 1.23±0.01a 1.16±0.03b 0.05±0.00cd 0.06±0.00cd 0.08±0.00c 柠檬香 52 罗勒烯 1043.00 546.24 1.71 0.06±0.00d 0.15±0.01b 0.75±0.00a 0.05±0.00e 0.07±0.00c 0.06±0.00d 水果香 53 丙烯醛 481.10 114.74 1.06 0.15±0.00e 0.16±0.00d 0.53±0.01a 0.28±0.01c 0.28±0.01c 0.40±0.00b 54 丙硫醇 621.50 152.90 1.17 0.27±0.00f 0.56±0.00c 0.37±0.01e 0.92±0.00a 0.73±0.01b 0.44±0.01d 卷心菜味 55 巴豆酸异丁酯 1000.50 470.62 1.81 6.32±0.01a 5.24±0.02c 5.85±0.04b 4.55±0.02d 2.59±0.04e 1.80±0.02f 水果香 56 丁酸 835.70 273.75 1.17 0.07±0.00f 0.3±0.00d 0.14±0.00e 0.44±0.01c 0.93±0.00b 1.51±0.02a 刺激性味、难闻味 57 正丁醛 607.00 147.87 1.10 1.75±0.01a 0.71±0.01c 0.15±0.00f 0.85±0.01b 0.23±0.00e 0.35±0.01d 香蕉味 58 乙醇 428.60 105.18 1.13 7.46±0.17b 7.18±0.05c 8.09±0.05a 7.42±0.07b 6.90±0.04d 6.69±0.03e 甜味、果味 注:RI表示保留指数;Rt表示保留时间;Dt表示迁移时间;M代表单体,D代表二聚体,T代表三聚体;;风味描述来自https://www.femaflavor.org/flavor-library 和 https://www.chemicalbook.com/。 表 7 特征值及方差贡献率
Table 7 Characteristic values and variance contribution rate
PC 初始特征值 特征值 方差贡献率(%) 累积方差贡献率(%) 1 8.873 42.254 42.254 2 5.507 26.225 68.478 3 2.718 12.942 81.420 4 1.787 8.507 89.928 5 1.345 6.406 96.334 表 8 各指标主成分载荷矩阵
Table 8 Principal component load matrix of each index
指标 PC 1 2 3 pH −0.246 0.935 0.023 固酸比 −0.006 0.471 −0.042 浊度 −0.165 0.807 0.325 离心沉淀率 −0.107 0.914 −0.033 出汁率 −0.106 0.913 0.041 褐变度 0.762 0.193 0.217 L* 0.882 −0.061 −0.435 a* 0.503 0.388 −0.473 b* 0.887 −0.022 −0.445 c 0.632 0.353 −0.550 h 0.827 0.224 −0.358 总酚 0.969 0.021 0.129 总黄酮 0.824 0.002 −0.102 维生素E 0.662 0.009 0.663 维生素C 0.858 0.092 0.358 类胡萝卜素 0.543 −0.200 0.679 DPPH −0.240 0.910 0.022 ABTS+ 0.955 −0.041 −0.103 FRAP 0.958 −0.120 0.153 SOD活性 0.515 0.143 0.644 总挥发性成分 0.207 0.900 0.117 表 9 不同品种沙棘汁综合得分及排名
Table 9 Comprehensive scores and rankings of different sea buckthorn juice
品种 F1 F2 F3 综合得分 综合排名 ‘深秋红’ −0.09 −0.61 0.71 −0.13 3 ‘状元黄’ 4.42 −0.71 0.33 2.12 1 ‘巨人’ −2.36 0.14 −1.66 −1.44 6 ‘无刺丰’ −1.45 0.92 −0.65 −0.56 5 ‘向阳’ 2.21 0.32 −2.45 0.86 2 混果 −1.92 −0.05 3.72 −0.42 4 -
[1] 崔立柱, 付依依, 刘士伟, 等. 沙棘营养价值及产业发展概况[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2021, 42(11):218-224. [CUI L Z, FU Y Y, LIU S W, et al. Nutritional value and industry development of sea buckthorn[J]. 2021, 42(11):218-224.] CUI L Z, FU Y Y, LIU S W, et al. Nutritional value and industry development of sea buckthorn[J]. 2021, 42(11): 218-224.
[2] JI M, GONG X, LI X, et al. Advanced research on the antioxidant activity and mechanism of polyphenols from Hippophae species—A review[J]. Molecules,2020,25(4):917. doi: 10.3390/molecules25040917
[3] CIESAROVÁ Z, MURKOVIC M, CEJPEK K, et al. Why is sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) so exceptional? A review[J]. Food Research International,2020,133:109170. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109170
[4] OLAS B, SKALSKI B, ULANOWSKA K. The anticancer activity of sea buckthorn [Elaeagnus rhamnoides L. A. Nelson][J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology,2018,9(232):365−371.
[5] LIU X L, LÜ M S, MAI R X G L, et al. Development of fermented sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) juice and investigation of its antioxidant and antimicrobial activity[J]. Frontiers in Nutrition,2023,10:1120748. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1120748
[6] CHEN Y, CAI Y, WANG K, et al Bioactive compounds in sea buckthorn and their efficacy in preventing and treating metabolic syndrome[J]. Foods, 2023, 12(10):1985.
[7] 葛亮, 李琦, 李森, 等. 沙棘果总多酚提取工艺的优化及其稳定性研究[J]. 化学与生物工程,2023,40(3):30−35. [GE L, LI Q, LI S, et al. Optimization in extraction process of total polyphenols from Hippophae rhamnoides L. fruits and lts stability[J]. Chemical and Biological Engineering,2023,40(3):30−35.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5425.2023.03.006 GE L, LI Q, LI S, et al. Optimization in extraction process of total polyphenols from Hippophae rhamnoides L. fruits and lts stability[J]. Chemical and Biological Engineering, 2023, 40(3): 30−35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5425.2023.03.006
[8] 陶翠, 王捷, 姚玉军, 等. 沙棘中白雀木醇表征方法及其分布规律[J]. 北京林业大学学报,2020,42(1):121−126. [TAO C, WANG J, YAO Y J, et al. Characterization and distribution rule of quebrachitol in Hippophae rhamnoides[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University,2020,42(1):121−126.] doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20190200 TAO C, WANG J, YAO Y J, et al. Characterization and distribution rule of quebrachitol in Hippophae rhamnoides[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2020, 42(1): 121−126. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20190200
[9] 曾奥, 许炳烨, 王雪, 等. 新疆大果沙棘原浆、籽油和果油气味特征及产品间相关性[J]. 北京林业大学学报,2024,46(2):132−142. [ZENG A, XU B Y, WANG X, et al. Odor characteristics and inter-product correlation of Xinjiang large berry sea buckthorn pulp, seed oil and fruit oil[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University,2024,46(2):132−142.] doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20230241 ZENG A, XU B Y, WANG X, et al. Odor characteristics and inter-product correlation of Xinjiang large berry sea buckthorn pulp, seed oil and fruit oil[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2024, 46(2): 132−142. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20230241
[10] 李珍, 李杰, 张湖林, 等. 阿勒泰地区大果沙棘质量分析研究[J]. 饮料工业,2023,26(2):48−51. [LI Z, LI J, ZHANG H L, et al. Research on quality analysis of large fruit sea buckthorn in Altay region[J]. Beverage Industry,2023,26(2):48−51.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7871.2023.02.009 LI Z, LI J, ZHANG H L, et al. Research on quality analysis of large fruit sea buckthorn in Altay region[J]. Beverage Industry, 2023, 26(2): 48−51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7871.2023.02.009
[11] 胡建忠, 温秀凤, 王东健. 新疆开展沙棘资源建设与开发利用工作的调研与建议[J]. 中国水土保持,2021(9):16−18. [HU J Z, WEN X F, WANG D J. Investigation and suggestions on the construction, development and utilization of sea buckthorn resources in Xinjiang[J]. China Soil and Water Conservation,2021(9):16−18.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0941.2021.09.009 HU J Z, WEN X F, WANG D J. Investigation and suggestions on the construction, development and utilization of sea buckthorn resources in Xinjiang[J]. China Soil and Water Conservation, 2021(9): 16−18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0941.2021.09.009
[12] 姚娜娜, 车凤斌, 李永海, 等. 沙棘的营养价值及综合开发利用概述[J]. 保鲜与加工,2020,20(2):226−232. [YAO N N, CHE F B, LI Y H, et al. Nutritional value and comprehensive development and utilization of Hipopophae rhamnoides[J]. Freshness and Processing,2020,20(2):226−232.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6221.2020.02.038 YAO N N, CHE F B, LI Y H, et al. Nutritional value and comprehensive development and utilization of Hipopophae rhamnoides[J]. Freshness and Processing, 2020, 20(2): 226−232. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6221.2020.02.038
[13] 张娟, 张存存, 谭志超, 等. 不同浓缩方法对沙棘汁中活性成分含量的影响[J]. 食品科技,2021,46(5):70−75. [ZHANG J, ZHANG C C, TAN Z C, et al. Effects of different concentration methods on the content of active components in sea buckthorn juice[J]. Food Science and Technology,2021,46(5):70−75.] ZHANG J, ZHANG C C, TAN Z C, et al. Effects of different concentration methods on the content of active components in sea buckthorn juice[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2021, 46(5): 70−75.
[14] 陆梦柯, 王梓琴, 张春, 等. 基于网络药理学与分子对接探讨沙棘抗肥胖作用机制[J]. 食品工业科技,2024,45(6):1−11. [LU M K, WANG Z Q, ZHANG C, et al. Exploring the mechanism of Hippophae fructus anti-obesity through network pharmacology and molecular docking[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2024,45(6):1−11.] LU M K, WANG Z Q, ZHANG C, et al. Exploring the mechanism of Hippophae fructus anti-obesity through network pharmacology and molecular docking[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2024, 45(6): 1−11.
[15] 管松滨, 邓斌, 王超, 等. 沙棘固体饮料的研制及其抗氧化活性评价[J]. 中医药导报,2023,29(7):63−69,73. [GUAN S B, DENG B, WANG C, et al. Preparation and sntioxidant activity evaluation of sea buckthorn solid beverage[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2023,29(7):63−69,73.] GUAN S B, DENG B, WANG C, et al. Preparation and sntioxidant activity evaluation of sea buckthorn solid beverage[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 29(7): 63−69,73.
[16] MEZEY J, HEGEDŰS O, MEZEYOVÁ I, et al. Thermal treatment influence on selected nutritional values of common sea buckthorn (Hyppophae rhamnoides) juice[J]. Agronomy,2022,12(8):1834. doi: 10.3390/agronomy12081834
[17] 郭凯华, 高晓丽, 魏莎, 等. 果胶酶处理对沙棘汁生产中主要理化指标的影响[J]. 广东化工,2022,49(16):58−60. [GUO K H, GAO X L, WEI S, et al. Effect of pectinase treatment on main physicochemical index in seabuckthorn juice production[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry,2022,49(16):58−60.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2022.16.019 GUO K H, GAO X L, WEI S, et al. Effect of pectinase treatment on main physicochemical index in seabuckthorn juice production[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2022, 49(16): 58−60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2022.16.019
[18] 杨培青, 王永涛, 吴晓蒙, 等. 超高压和高温短时杀菌对沙棘汁品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(13):23−32. [YANG P Q, WANG Y T, WU X M, et al. Effect of high pressure processing and high-temperature short-time sterilization on the quality of sea buckthorn juice[J]. Food Science,2022,43(13):23−32.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20210306-078 YANG P Q, WANG Y T, WU X M, et al. Effect of high pressure processing and high-temperature short-time sterilization on the quality of sea buckthorn juice[J]. Food Science, 2022, 43(13): 23−32. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20210306-078
[19] ANDREA M, ĽUBOMÍR M, PETER C, et al. Evaluation of carotenoids, polyphenols content and antioxidant activity in the sea buckthorn fruit[J]. Potravinarstvo,2016,10(1):59−64. doi: 10.5219/551
[20] 王妍惠, 张福娟, 于泳渤, 等. NFC苹果梨桑葚复合汁配方优化及其贮藏品质变化[J]. 包装工程,2021,42(19):77−84. [WANG Y H, ZHANG F J, YU Y B, et al. Formula optimization of NFC apple pear and mulberry compound juice and change of storage quality[J]. Packaging Engineering,2021,42(19):77−84.] WANG Y H, ZHANG F J, YU Y B, et al. Formula optimization of NFC apple pear and mulberry compound juice and change of storage quality[J]. Packaging Engineering, 2021, 42(19): 77−84.
[21] 丁燕, 汤晓宏, 林雪青, 等. 苹果中果胶及果胶酶活性和发酵方式对苹果酒中甲醇含量的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2024,50(19):142−147. [DING Y, TANG X H, LIN X Q, et al. Effects of pectin and pectinase activities in apples and fermentation mode on methanol content in apple cider[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2024,50(19):142−147.] DING Y, TANG X H, LIN X Q, et al. Effects of pectin and pectinase activities in apples and fermentation mode on methanol content in apple cider[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2024, 50(19): 142−147.
[22] WU D, XIA Q, CHENG H, et al. Changes of volatile flavor compounds in sea buckthorn juice during fermentation based on gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry[J]. Foods,2022,11(21):3471. doi: 10.3390/foods11213471
[23] BEVERIDGE T, HARRISON J E, DROVER J. Processing effects on the composition of sea buckthorn juice from Hippophae rhamnoides L. cv. Indian Summer[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2002,50(1):113−116. doi: 10.1021/jf010369n
[24] 付依依, 王永霞, 宋惠月, 等. 沙棘原浆苹果酸-乳酸发酵过程中理化指标及抗氧化能力的变化[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(5):89−97. [FU Y Y, WANG Y X, SONG H Y, et al. Changes in physical and chemical indicators and antioxidant capacity of sea buckthorn puree during malolactic fermentation[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2022,48(5):89−97.] FU Y Y, WANG Y X, SONG H Y, et al. Changes in physical and chemical indicators and antioxidant capacity of sea buckthorn puree during malolactic fermentation[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry, 2022, 48(5): 89−97.
[25] 乌仁斯庆, 姚玉军, 张宇, 等. 不同产地和品种沙棘果品质研究[J]. 食品安全导刊,2022(23):80−85,125. [WU R S Q, YAO Y J, ZHANG Y, et al. Comparative study on fruit quality of seabuckthorn from different producing habitats and varieties[J]. Food Safety Journal,2022(23):80−85,125.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0270.2022.23.spaqdk202223038 WU R S Q, YAO Y J, ZHANG Y, et al. Comparative study on fruit quality of seabuckthorn from different producing habitats and varieties[J]. Food Safety Journal, 2022(23): 80−85,125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0270.2022.23.spaqdk202223038
[26] YOU T, SUN L J, NISAR T, et al. Multivariate statistical analysis of the quality of apple juice to integrate and simplify juice industrial production technologies[J]. CyTA Journal of Food,2018,16(1):190−198. doi: 10.1080/19476337.2017.1372522
[27] 李娟娟. 小麦蛋白对樱桃酒澄清效果及其稳定性研究[D]. 太原:山西大学, 2018. [LI J J. Research on the clarification effect of wheat protein on cherry wine and its stability[D]. Taiyuan:Shanxi University, 2018.] LI J J. Research on the clarification effect of wheat protein on cherry wine and its stability[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi University, 2018.
[28] 王璇, 张志伟, 陈志玺, 等. 沙棘果食品开发利用研究进展与发展对策[J]. 保鲜与加工,2024,24(1):75−82. [WANG X, ZHANG Z W, CHEN Z X, et al. Research progress and development countermeasures on the development and utilization of sea buckthorn fruit food[J]. Freshness and Processing,2024,24(1):75−82.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6221.2024.01.012 WANG X, ZHANG Z W, CHEN Z X, et al. Research progress and development countermeasures on the development and utilization of sea buckthorn fruit food[J]. Freshness and Processing, 2024, 24(1): 75−82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6221.2024.01.012
[29] 曾悦, 邓慧萍, 蹇华丽. 不同酵母多糖及酵母种类对荔枝酒品质的影响[J]. 中国酿造,2019,38(11):67−70. [ZENG Y, DENG H P, JIAN H L. Effect of different yeast polysaccharide and yeast species on quality of litchi wine[J]. China Brewing,2019,38(11):67−70.] doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2019.11.014 ZENG Y, DENG H P, JIAN H L. Effect of different yeast polysaccharide and yeast species on quality of litchi wine[J]. China Brewing, 2019, 38(11): 67−70. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2019.11.014
[30] 袁超. 非浓缩还原苹果汁的原料分级和保质贮运技术研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐:新疆农业大学, 2020. [YUAN C. Research on raw material grading and preservation and transportation technology of non-concentrated reduced apple juice [D]. Urumqi:Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2020.] YUAN C. Research on raw material grading and preservation and transportation technology of non-concentrated reduced apple juice [D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2020.
[31] 连雅丽. 不同品种新疆大果沙棘冻干粉特性分析及泡腾片产品开发[D]. 乌鲁木齐:新疆农业大学, 2022. [LIAN Y L. Characterization of freeze-dried powder of different varieties of Xinjiang sea buckthorn with large fruits and product development of effervescent tablets [D]. Urumqi:Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2022.] LIAN Y L. Characterization of freeze-dried powder of different varieties of Xinjiang sea buckthorn with large fruits and product development of effervescent tablets [D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2022.
[32] SITII A D M Z, OMMI K M Y, AHMAD F O. Correlating the natural color of tropical fruit juice with its pH[J]. Color Research & Application,2020,46(2):467−476.
[33] 赵竞伊, 张鹏, 曹森, 等. 不同品种番茄采后品质和挥发性物质差异分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2024,45(15):274−282. [ZHAO J Y, ZHANG P, CAO S, et al. Analysis of postharvest quality and volatile substances of different tomato varieties[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2024,45(15):274−282.] ZHAO J Y, ZHANG P, CAO S, et al. Analysis of postharvest quality and volatile substances of different tomato varieties[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2024, 45(15): 274−282.
[34] MARTINEZ V C, PENAS E, HERNANDEZ L B. Pseudocereal grains:Nutritional value, health benefits and current applications for the development of gluten free foods[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2020,137(C):111178.
[35] 董诗婷, 陈云, 高群玉. 沙棘果生物活性成分及其功能的研究进展[J]. 中国酿造,2020,39(2):26−32. [DONG S T, CHEN Y, GAO Q Y. Research progress on bioactive compounds and function of sea buckthorn berry[J]. China Brewing,2020,39(2):26−32.] doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2020.02.005 DONG S T, CHEN Y, GAO Q Y. Research progress on bioactive compounds and function of sea buckthorn berry[J]. China Brewing, 2020, 39(2): 26−32. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2020.02.005
[36] GOMAS P, MISINA I, KRASNOVA I, et al. Tocopherol and tocotrienol contents in the sea buckthorn berry beverages in Baltic countries:Impact of the cultivar[J]. Fruits,2016,71(6):399−405. doi: 10.1051/fruits/2016030
[37] URBANIAK S, KAZMIERCZAK J, KARWOWSKI B T. Rokitnik zwyczajny (Hippophaë rhamnoides L.) jako skarbnica witaminy C[J]. Postepy Biochem,2019,65(3):212−216. doi: 10.18388/pb.2019_271
[38] KUHKHEIL A, BADI N H, MEHRAFARIN A, et al. Chemical constituents of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) fruit in populations of central Alborz Mountains in Iran[J]. Research Journal of Pharmacognosy,2017,4(3):1−12.
[39] KJERSTI A B, BERIT K M, GRETHE I A B, et al. Bioactive compounds and color of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) purees as affected by heat treatment and high pressure homogenization[J]. International Journal of Food Properties,2020,23(1):651−664. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2020.1752715
[40] KREJCAROV J, STRAKOVA E, SUCHY P, et al. Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) as a potential source of nutraceutics and its therapeutic possibilities a review[J]. Acta Veterinaria Brno,2015,84(3):257−268. doi: 10.2754/avb201584030257
[41] TKACZ K, GIL I Á, MEDINA S, et al. Phytoprostanes, phytofurans, tocopherols, tocotrienols, carotenoids and free amino acids and biological potential of sea buckthorn juices[J]. J Sci Food Agric,2022,102(1):185−197. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.11345
[42] SHI L K, ZHENG L, ZHAO C, et al. Chemical composition and antioxidant capacity of extracts from the whole berry, pulp and seed of Hippophae¨ rhamnoides ssp. yunnanensis[J]. Nat Prod Res,2019,33(24):3596−3600. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2018.1488703
[43] 王启林, 袁木荣. 沙棘类胡萝卜素研究进展[J]. 中国野生植物资源,2016,35(1):37−39,45. [WANG Q L, YUAN M R. The study progress of carotenoids in sea buckthorn[J]. China Wild Plant Resources,2016,35(1):37−39,45.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9690.2016.01.011 WANG Q L, YUAN M R. The study progress of carotenoids in sea buckthorn[J]. China Wild Plant Resources, 2016, 35(1): 37−39,45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9690.2016.01.011
[44] SU T T, ZHAO J M, ZHU Y T, et al. Comparison of nutrient composition, phytochemicals and antioxidant activities of two large fruit cultivars of sea buckthorn in Xinjiang of China[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2024,324(15):112602.
[45] YANG H, YANG S H, CHEN X Q, et al. Dynamic changes in flavonoid, phenolic, and polysaccharide contents in leaves and fruits of sea buckthorn during the growing season in southeastern Tibet plateau[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2023,307(3):111497.
[46] ZHANG J Q, LI C, HUANG Q, et al. Comparative study on the physicochemical properties and bioactivities of polysaccharide fractions extracted from Fructus Mori at different temperatures[J]. Food Function,2019,10(1):410−421. doi: 10.1039/C8FO02190B
[47] 郭敬宇, 苏伟航, 王忠, 等. 熵权法结合响应面法优化新疆沙枣花黄酮类成分的提取工艺及其体内外抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2024,35(2):67−78. [[GUO J Y, SU W H, WANG Z, et al. Optimization of extraction process of flavonoids from Xinjiang Elaeagnus angustifolia L. flowers using entropy weight method combined with response surface method and its antioxidant activity in vivo and in vitro[J]. China Food Additives,2024,35(2):67−78.] [GUO J Y, SU W H, WANG Z, et al. Optimization of extraction process of flavonoids from Xinjiang Elaeagnus angustifolia L. flowers using entropy weight method combined with response surface method and its antioxidant activity in vivo and in vitro[J]. China Food Additives, 2024, 35(2): 67−78.
[48] 沈晓溪, 张一鸣, 赵梓伊, 等. 沙棘粕槲皮素体外抗氧化及对衰老模型小鼠保护作用的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(20):348−354. [SHEN X X, ZHANG Y M, ZHAO Z Y, et al. Study on antioxidant activity of quercetin from sea buckthorn meal in vitro and its protective effect on aging mice[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(20):348−354.] SHEN X X, ZHANG Y M, ZHAO Z Y, et al. Study on antioxidant activity of quercetin from sea buckthorn meal in vitro and its protective effect on aging mice[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(20): 348−354.
[49] LI Y, LI P, YANG K, et al. Impact of drying methods on phenolic components and antioxidant activity of sea Buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) berries from different varieties in China[J]. Molecules,2021,26(23):7189. doi: 10.3390/molecules26237189
[50] SOBHY A E S, MOHAMED G S, ASHWANI M, et al. Nutritional Evaluation of sea buckthorn "Hippophae rhamnoides" berries and the pharmaceutical potential of the fermented juice[J]. Fermentation,2022,8(8):391. doi: 10.3390/fermentation8080391
[51] CRISTE A, URCAN A C, BUNEA A, et al. Phytochemical composition and biological activity of berries and leaves from four romanian sea buckthorn (Hippophae Rhamnoides L.) varieties[J]. Molecules,2020,25(5):1170. doi: 10.3390/molecules25051170
[52] CERRETI M, LIBURDI K, BENUCCI I, et al, et al. The effect of pectinase and protease treatment on turbidity and on haze active molecules in pomegranate juice[J]. LWT,2016,73:326−333. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2016.06.030
[53] RAIS J, JAFRI A, SIDDIQUI S, et al. Phytochemicals in the treatment of ovarian cancer[J]. Frontiers in Bioscience-Elite,2017,9(1):67−75. doi: 10.2741/e786
[54] DI W, JIAN Z, ZONGSHUAI Z, et al. Effect of ageing time on the flavour compounds in Nanjing water-boiled salted duck detected by HS-GC-IMS[J]. LWT,2022,155:112870. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112870
[55] 李善明, 樊正强, 黄成福, 等. 中草药释香型刨花板特征挥发性有机化合物的指纹图谱分析[J]. 木材科学与技术,2022,36(4):38−44. [LI S M, FAN Z Q, HUANG C F, et al. Fingerprint analysis of characteristic volatile organic compounds in fragrance scented particleboards with added Chinese herbal medicine[J]. Wood Science and Technology,2022,36(4):38−44.] doi: 10.12326/j.2096-9694.2021163 LI S M, FAN Z Q, HUANG C F, et al. Fingerprint analysis of characteristic volatile organic compounds in fragrance scented particleboards with added Chinese herbal medicine[J]. Wood Science and Technology, 2022, 36(4): 38−44. doi: 10.12326/j.2096-9694.2021163
[56] TANG X, KÄLVIÄINEN N, TUORILA H. Sensory and hedonic characteristics of juice of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) origins and hybrids[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2001,34(2):102−110. doi: 10.1006/fstl.2000.0751
[57] LEUNG G S, MARRIOTT R. Year to year variation in sea buckthorn juice volatiles using headspace solid phase microextraction[J]. Flavour and Fragrance Journal,2016,31(2):124−136. doi: 10.1002/ffj.3290
[58] 黄蕊, 盛文军, 李霁昕, 等. 超高压及热处理对中国沙棘原浆挥发性成分影响的比较[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(18):204−208. [HUANG R, SHENG W J, LI J X, et al. A comparison of the effects of ultra-high pressure and heat treatments on the volatile components of Chinese seabuckthorn pulp (Hippophae rhamnoides L. subsp. sinensis Rousi)[J]. Food Science,2018,39(18):204−208.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201818032 HUANG R, SHENG W J, LI J X, et al. A comparison of the effects of ultra-high pressure and heat treatments on the volatile components of Chinese seabuckthorn pulp (Hippophae rhamnoides L. subsp. sinensis Rousi)[J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(18): 204−208. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201818032
[59] CHEN J, LIU Y, YANG M, et al. Analysis of the differences in volatile organic compounds in different rice varieties based on GC-IMS technology combined with multivariate statistical modelling[J]. Molecules,2023,28(22):7566. doi: 10.3390/molecules28227566
[60] GUO X Y, WILFRIED S W, HE Z T, et al. Characterization of the aroma profiles of oolong tea made from three tea cultivars by both GC–MS and GC-IMS[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,376:131933. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131933
[61] TIITINEN K, HAKALA M, KALLIO H. Headspace volatiles from frozen berries of sea buckthorn (Hippophaë rhamnoides L.) varieties[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2006,223(4):455−460. doi: 10.1007/s00217-005-0224-6
[62] 曹勇, 许秀颖, 蔡丹, 等. 玉米籽粒后熟品质性状主成分分析与综合评价[J]. 食品科学,2024,45(11):1−7. [[CAO Y, XU X Y, CAI D, et al. Principal component analysis and comprehensive evaluation of corn postharvest ripening quality traits[J]. Food Science,2024,45(11):1−7.] [CAO Y, XU X Y, CAI D, et al. Principal component analysis and comprehensive evaluation of corn postharvest ripening quality traits[J]. Food Science, 2024, 45(11): 1−7.
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 谭永曌,张迪,吉宏武,刘书成. 凡纳滨对虾热处理过程中虾青素酯与肌原纤维蛋白的结合作用. 广东海洋大学学报. 2024(06): 73-79 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 付娌丽,饶璐,王智俊,刘东亮,陈黄琴,李月生. 荧光光谱法与分子模拟研究氨苄西林钠与牛血清蛋白相互作用及构象变化. 湖北科技学院学报(医学版). 2023(01): 21-25 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 任祥瑞,赵晓燕,刘红开,张晓伟,王萌,朱运平. 不同热改性乳清蛋白-虾青素复合物对色素稳定性的影响. 食品科技. 2023(08): 243-250 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 谢世英,赵英源,于靖薇,刘淑贤,张强,陈迪,王雪琴. H/J-聚集体虾青素/牛血清白蛋白纳米复合物的制备与表征. 河南工业大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(06): 26-35 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 曾婧,白雪媛,王悦,赵大庆,王思明. 铁皮石斛蛋白提取工艺优化、活性成分筛选及结构研究. 食品工业科技. 2022(19): 228-237 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(7)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
