Isolation and Identification of Functional Bacillus Strain from Cupei of Sichuan Bran Vinegar and Evaluation of Its Fermentation Characteristics
-
摘要: 芽孢杆菌作为四川麸醋发酵过程中重要的功能微生物,对稳定麸醋品质具有积极意义。本研究从四川麸醋醅中筛选、分离部分功能芽孢杆菌,通过生理生化试验、16S rRNA测序对菌株进行鉴定,对筛选鉴定的菌株进行耐酸、耐乙醇、耐温的发酵性能研究。结果表明共筛选出5株发酵优良的芽孢杆菌,分别为库氏类芽孢杆菌BA-6(Paenibacillus cookii)、贝莱斯芽孢杆菌BA-9(Bacillus velezensis)、热带芽孢杆菌BB-5(Bacillus tropicus)、枯草芽孢杆菌BB-13(Bacillus subtilis)、Calidifontibacillus erzurumensis BC-11,且该5株芽孢杆菌在30~40 ℃,pH5~7条件下能较好生长(OD600=0.23~0.52),具有一定的环境耐受性。部分芽孢杆菌水解蛋白(B. velezensis BA-9蛋白水解圈:3.7±0.3)和淀粉(P. cookie BA-6淀粉水解圈:3.8±0.5)的能力较强。为了进一步探究其在麸醋酿造中的应用,将芽孢杆菌与巴氏醋杆菌进行模拟混合固态发酵,研究表明,接种P. cookie BA-6、B. velezensis BA-9、C. erzurumensis BC-11可提高总酸、乳酸、乙酸、挥发性风味物质(苯甲醇、异戊醇、苯乙醇、愈创木酚等)含量,从而有效提升醋醅发酵品质。综上所述,本研究筛选的5株芽孢杆菌有利于醋醅发酵过程风味物质形成,研究结果为麸醋强化发酵提升其品质奠定理论基础。Abstract: Bacillus bacteria are critical functional strains during fermentation of Sichuan bran vinegar that contribute to maintain the quality of vinegar. In this study, some functional Bacillus bacteria were isolated from the Cupei (grains undergoing acetic acid fermentation) of Sichuan bran vinegar, and the strains were identified by biochemical tests and 16S rRNA sequencing. The fermentation properties of these strains were studied, and the 5 Bacillus strains with great fermentation performance were discovered. They were identified as Paenibacillus cookii BA-6, Bacillus velezensis BA-9, Bacillus tropicus BB-5, Bacillus subtilis BB-13, and Calidifontibacillus erzurumensis BC-11. The five strains grew well at 30~40 ℃ and pH5~7 (OD600=0.23~0.52), with a certain degree of tolerance for environmental factor. Some of the Bacillus strains had a strong ability to hydrolyze protein (proteolytic ring of B. velezensis BA-9: 3.7±0.3) and starch (starch hydrolysis ring of P. cookie BA-6: 3.8±0.5). The simulated solid-state fermentation of inoculation with Bacillus and Acetobacter was carried out to investigate their potential use in industrial bran vinegar fermentation. Results showed that inoculation of P. cookie BA-6, B. velezensis BA-9, and C. erzurumensis BC-11 could increase total acid, lactic acid, acetic acid, and volatile flavor compounds content (e.g., phenyl ethanol, benzyl alcohol, isopentanol, and guaicol), further raise the overall fermentation quality of the Cupei. Overall, the 5 strains of Bacillus identified in the study were beneficial for the formation of flavor compounds during the Cupei fermentation of bran vinegar. The study provides a theoretical foundation for enhancing the quality of Sichuan bran vinegar.
-
Keywords:
- Sichuan bran vinegar /
- Cupei /
- Bacillus /
- solid-state fermentation /
- flavor compounds
-
四川麸醋是中国四大名醋之一,以生麸皮为主要原料,中草药曲混合大米醪为发酵剂,采用独特三边同池发酵工艺(糖化、酒化、醋化在一个发酵池内同时进行)而成[1]。麸醋酿造是一个由多菌种共同参与、进行复杂生化反应的过程,发酵过程微生物主要来源于中药曲、种醅、原料等,多种微生物共同形成的麸醋酿造体系是影响食醋品质的重要因素[1−2]。近年来,研究人员主要集中于对山西陈醋、镇江香醋和四川麸醋等中国传统食醋发酵过程中微生物多样性及代谢产物的研究[3−4],在发酵醋醅中鉴定出乳杆菌(lactobacillus)、醋酸杆菌(Acetobacter)、假单胞菌(Pseudomonas)、魏斯氏菌(Weissella)、芽孢杆菌(Bacillus)等多个优势细菌属,值得注意的是芽孢杆菌属存在于整个发酵过程[5]。在山西老陈醋相关研究中发现,在酒精发酵阶段,乳杆菌属、魏斯氏菌属和芽孢杆菌属在细菌菌群中占据主导地位。基于相关性分析发现,芽孢杆菌属与多种挥发性风味物质和有机酸呈强正相关[6],说明芽孢杆菌属在发酵过程中起重要作用,其代谢产物有利于食醋风味物质的积累。
大多数芽孢杆菌能够分泌各种水解酶,如淀粉酶和蛋白酶,将原料中的淀粉和蛋白质降解为葡萄糖和氨基酸,从而促进风味化合物的形成,也可以通过自身三羧酸循环途径代谢各种酸类物质,改善食醋中的刺激性酸味,使口感变得柔和[6−7]。Zhang等[8]选择不同大曲对麸皮发酵性能进行分析,结果表明醋醅中以芽孢杆菌、乳酸菌和海洋芽孢杆菌为主,其中使用强化大曲(接种解淀粉芽孢杆菌的大曲)进行发酵,可有效提升麸醋中乙偶姻和四甲基吡嗪含量。本课题组研究发现芽孢杆菌和海洋杆菌对醋醅中有机酸、氨基酸、还原糖以及风味化合物如苯甲醛、苯乙醛、苯乙酸乙酯等有显著影响,这些潜在功能性芽孢杆菌可以产生多种有机酸且可能分泌水解酶来促进原料分解[9]。此外,相关研究表明,将芽孢杆菌接种于酒曲的发酵中可有效提高其发酵性能[10−11]。如He等[11]将贝莱斯芽孢杆菌与枯草芽孢杆菌接入大曲发酵后,大曲淀粉酶活性提高了6.4%,乙醇和苯乙醇的浓度分别提高了24.2%和50%。
目前,关于功能性芽孢杆菌的筛选和应用已有大量报道,而四川麸醋研究中关于芽孢杆菌发酵性能研究较少,因此本文从四川麸醋醋醅中分离的32株芽孢菌中筛选出5株不同种类的优良芽孢杆菌菌株,研究5株芽孢杆菌发酵性能,通过模拟固态发酵初步探究不同芽孢杆菌与巴氏醋杆菌多菌混合发酵对醋醅样品总酸、还原糖、有机酸、挥发性风味物质的影响,为进一步提高四川麸醋的风味和品质提供理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
醋醅 采集于四川宜宾思坡醋厂,采用五点取样法采集发酵过程中的醋醅,分别混合均匀后各收集3个重复样品,置于−20 ℃冷冻保存;培养基:YPD培养基、MRS培养基、牛肉蛋白胨培养基 北京奥博星生物技术有限责任公司;淀粉水解培养基、酪素水解培养基、糖发酵培养基 青岛高科技工业园海博生物技术有限公司;固态发酵培养基:每100 g固态发酵培养基包括50 g牛肉膏肉汤液体培养基、50 g麸皮 四川省宜宾市思坡醋业有限责任公司;所用试剂除特殊注明外,均为生物试剂;甲醇、乙腈 色谱纯,成都市诺尔施科技有限责任公司;有机酸标准品 上海麦克林生化科技股份有限公司;甲醛溶液 北京中科质检生物技术有限公司;冰乙酸、氯化钠 成都市科隆化学品有限公司;所用试剂除特殊注明外,均为分析纯。
Agilent 1220 Infinity LC高效液相色谱仪、GC-7890A-MSD5975C气相色谱-质谱联用仪 美国安捷伦公司;90-2数显高温磁力搅拌器 常州越新仪器制造有限公司;DVB/CAR/PDMS萃取头(50/30 μm) 美国Supelco公司;BWS-10恒温水槽与水浴锅 上海一恒科学仪器有限公司;Spectra Max M2多功能酶标仪 美谷分子仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 芽孢杆菌的分离纯化
样品前处理:称取醋醅样品1 g至10 mL无菌水中,使用涡旋混匀仪,2800 r/min室温涡旋5 min,置于60 ℃恒温水浴锅中水浴30 min。
分离纯化:取100 μL混合液,依次进行梯度稀释,稀释至10−5倍,取0.1 mL稀释液分别涂布于YPD、MRS、牛肉膏蛋白胨三种固体培养基,置于30 ℃恒温培养24 h,挑取单菌落于固体培养基中进行纯化,并于−20 ℃甘油中保藏。
1.2.2 优良芽孢杆菌的筛选
1.2.2.1 菌株形态学初筛
将菌株划线涂布于平板上,于30 ℃恒温培养24 h,观察菌落特征。如透明度、形状、边缘、颜色、隆起形状等。细胞形态观察,革兰氏染色在40倍镜观察其细胞形状初步筛选差异菌株。
1.2.2.2 菌株的生理生化鉴定
参考《常见细菌系统鉴定手册》[12]及《伯杰细菌鉴定手册》[13]中的方法,具体方法如下。
糖发酵试验:将菌株活化后接于不同糖类的发酵培养基,培养48 h,观察颜色变化,黄色为阳性,全部变黄(+++)、1/2变黄(++)、1/3变黄(+),蓝色为阴性(−);V-P 试验:将培养24 h的菌株,取5 mL培养液和0.25 mL 40%NaOH、0.25 mL 5% α-萘酚溶液混匀,10 min 后观察培养液是否呈红色,红色为阳性(+),否则为阴性(−);甲基红试验:将菌株活化后接于液体培养基,培养24 h。滴加0.1%甲基红试剂,观察试剂是否呈现红色,红色为阳性(+),否则为阴性(−);氧化酶试验:取白色洁净滤纸沾取单菌落,加入一滴盐酸二甲基对苯二胺溶液,阳性者呈粉红色,并逐渐加深;再加α-萘酚溶液一滴。阳性者于半分钟内呈蓝色,阴性于两分钟内不变色;明胶试验:活化好的菌株接种于明胶试验培养基中,其中未接菌的试管为对照,培养24 h,然后在冰箱冷藏,观察半固体的明胶培养基是否成为液体。
1.2.2.3 分子生物学鉴定
分离菌株DNA提取按天根DP302-02细菌基因组DNA提取试剂盒操作,将PCR扩增细菌16S rRNA片段,PCR产物送至北京擎科生物科技股份有限公司进行测序,测序引物选用细菌16S rRNA的通用引物27F和1492R。测序结果在NCBI数据库中进行同源序列检索,检索到与目标菌株具有较大同源性的菌种做比较并分析结果。
1.2.3 芽孢杆菌发酵性能分析
1.2.3.1 温度对菌株生物量的影响
挑选单菌落加入含1 mL牛肉蛋白胨培养基的离心管中设置温度梯度:26、28、30、32、36、40 ℃培养15 h,在600 nm波长测量OD值。
1.2.3.2 pH对菌株生物量的影响
用10 mL溶菌管加入5 mL牛肉蛋白胨培养基,乙酸调培养基的pH:7、6、5、4、3,接入2%种子培养基,恒温32 ℃静置培养48 h,在600 nm波长检测其OD值。
1.2.3.3 乙醇对菌株生物量的影响
用10 mL溶菌管加入5 mL牛肉蛋白胨培养基,无水乙醇添加量总体积的0%、1%、2%、3%、4%、5%、6%,配制种子液接种量2%,恒温32 ℃静置培养48 h,在600 nm波长测量OD值。
1.2.4 芽孢杆菌模拟固态发酵分析
将芽孢杆菌与巴氏醋杆菌按1:1比例接种到总接种量为2%的固态发酵培养基内进行模拟固态发酵,每8 h振荡一次,分别取2、4、6、8 d的发酵麸皮样品2 g置于烧杯中,加入15 mL蒸馏水,浸泡30 min后过滤,收集滤液用于理化指标测定。
1.2.4.1 理化指标测定
参照Tie等[9]方法测定发酵过程中麸皮浸出液中还原糖含量;参照孙列雄等[6]的方法测定发酵过程中麸皮总酸、氨基酸态氮含量。
1.2.4.2 有机酸测定
参照Tie等[9]方法对发酵过程中有机酸含量测定。分别称取乳酸和乙酸标准品,配制不同质量浓度的标准溶液,通过单独进样检测得到各有机酸的保留时间,后将标准品稀释成一定的浓度梯度混合进样,以峰面积为y值,有机酸浓度为x值计算得到有机酸线性回归方程及相关系数,如表1所示。
表 1 有机酸标准曲线线性参数Table 1. Linear parameters of organic acid standard curves有机酸 保留时间(min) 回归方程 相关系数(R2) 乳酸 11.99 y=8.3978x+0.6234 0.9996 乙酸 12.85 y=10.0693x+2.5424 0.9995 1.2.4.3 挥发性风味物质的测定
参照Tie等[9]所描述的方法,取1 g发酵麸皮样品于顶空瓶中,加入0.05 mL 2-辛醇(内标),60 ℃平衡10 min后插入萃取针萃取40 min,萃取完成后于250 ℃解吸5 min。并通过确定各物质保留时间并与NIST17文库进行比较定性,定量计算各挥发性风味物质的浓度。
GC条件:色谱柱采用DB-WAX毛细管柱(30 m×250 μm,φ=0.25 μm);氦气流量为1 mL/min,不分流模式;初始温度为40 ℃,保持2 min,然后以5 ℃/min升高到230 ℃,保持8 min。
MS条件:离子源温度: 230 ℃;四极杆温度:150 ℃。
1.3 数据处理
采用IBM SPSS Statistics 27.0.1中T检验对实验数据进行显著性分析(显著性水平P<0.05)使用Origin 2021、GraphPad Prism 9.5.1等软件对数据进行处理、作图。所有试验重复三次,以确保准确性。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 芽孢杆菌分离纯化与初筛结果
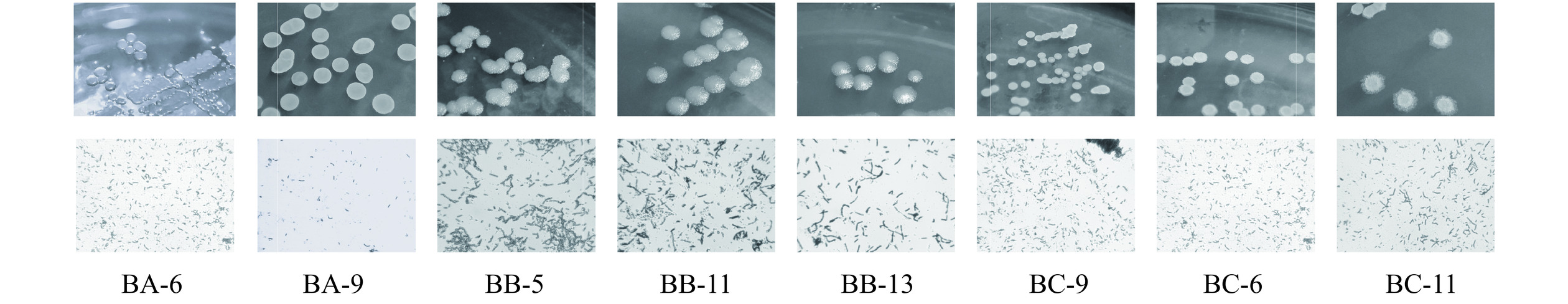
从醋醅中,通过MRS、NB、YPD三种培养基对醋醅内菌株进行初筛,通过菌落形态、革兰氏染色,初步筛选获得疑似芽孢杆菌33株菌株,分别编号为BA1-BA9(分离自MRS培养基)、BB1-BB13(分离自NB培养基)、为BC1-BC11(分离自YPD培养基)。对疑似目标菌株进行生理生化鉴定,结果见表2。根据生理生化试验结果,32株疑似芽孢杆菌初步分为8个类别,同一类菌株生理生化性质相似,可能为同一菌种,因此分别对该8类代表菌株(BA-6、BA-9、BB-5、BB-11、BB-13、BC-6、BC-11)进行形态学鉴定结果见图1,表3。
表 2 各菌株生理生化试验结果Table 2. Results of physiological and biochemical experimental of each strain编号 乳糖 麦芽糖 蔗糖 棉子糖 葡萄糖 壳聚糖 羧甲基纤维素钠 淀粉 V-P 试验 甲基红试验 氧化酶试验 明胶试验 BA-1 − + ++ − + ++ − − − + + + BA-2 − + + − + + − − + − + + BA-3 − + ++ − + ++ − − − + + + BA-4 + + + + + ++ − − − + + − BA-5 − + ++ − + ++ − − − + + + BA-6 + +++ +++ + +++ + − +++ − + + − BA-7 − + + − + + − − + − + + BA-8 − + + − + − − − + − + + BA-9 − ++ + − ++ + − + + − + + BA-10 + + + − + + − − + − + − BA-11 + + + − + + − − + − + − BB-1 − + + − + ++ − − − + + + BB-2 + + + + + ++ − − − + + − BB-3 − + + − + ++ − − − + + + BB-4 − + + − + ++ − − − + + + BB-5 − ++ ++ − +++ ++ − − − + + + BB-6 − + + − + ++ − − − + + + BB-7 − + + − + + − − − + + + BB-8 − + + − + + − − − + + + BB-9 − + + − + + − − − + + + BB-10 − + + − + + − − − + + + BB-11 − ++ ++ − ++ ++ − − − + + + BB-12 − + + − + + − − − + + + BB-13 − ++ + − +++ + − − − + + + BC-1 − + + − ++ +++ − − − + + + BC-2 − + + − + +++ − − − + + + BC-3 − + + − + + − − + − + + BC-4 − + + − ++ + − − + − + + BC-5 − + + − ++ + − − + − + + BC-6 − ++ + − +++ +++ − ++ + − + + BC-7 − + + − + ++ − − + − + + BC-8 − + + − + + − − + − + + BC-9 − ++ + − ++ + − + + − + + BC-10 − + + − + + − − + − + + BC-11 − +++ +++ − ++ + − ++ + − + + 注:“−”表示阴性;“+”表示阳性;糖发酵试验中“−”表示不分解糖产酸;“+”1/3颜色变黄;“++”1/2颜色变黄;“+++”全部颜色变黄。 表 3 样品中分离芽孢杆菌的形态特征及分类Table 3. Morphological characteristics and classification of isolated Bacillus in samples类别 菌落特征 菌体特征 革兰氏染色 分离得到的菌株 代表性菌株 1 圆形、直径偏小、透白色、半透明边缘整齐、无菌摸 杆状,成链 − 5 BA-6 2 椭圆形、直径中等、乳白色、不透明边缘整齐、有菌膜 杆状,成链 − 3 BA-9 3 圆形、直径偏大、白色、不透明边缘粗糙、无菌膜 杆状,成链 − 8 BB-5 4 圆形、直径偏大、白色、不透明边缘粗糙、无菌膜 杆状,成链 − 5 BB-11 5 圆形、直径偏大、白色、不透明边缘粗糙、无菌膜 杆状,成链 − 4 BB-13 6 圆形、直径中等、白色、不透明边缘粗糙、有菌膜 杆状,成链 − 2 BC-6 7 圆形、直径中等、白色、不透明边缘粗糙、有菌膜 杆状,成链 − 3 BC-9 8 椭圆形、直径中等、乳白色、不透明边缘整齐、有菌膜 杆状,成链 − 3 BC-11 注:“−”表示阴性。 2.2 菌株分子生物学鉴定
将8株菌株的16S rRNA基因序列上传至NCBI数据库进行BLAST同源性比对,选取相似性高于99%的菌株序列。结果如表4所示,菌株BA-6与库氏类芽孢杆菌(NR025372.1)亲缘关系最近,序列相似度为99.6%,鉴定为库氏类芽孢杆菌;菌株BA-9与贝莱斯芽孢杆菌(NR075005.2)亲缘关系最近,序列相似度为99.4%,鉴定为贝莱斯芽孢杆菌;菌株BB-5与热带芽孢杆菌(NR157736.1)亲缘关系最近,序列相似度为99.6%,鉴定为热带芽孢杆菌菌株;BB-11与热带芽孢杆菌(NR157736.1)亲缘关系最近,序列相似度为99.6%,鉴定为热带芽孢杆菌菌株;菌株BB-13与枯草芽孢杆菌(NR112116.2)亲缘关系最近,序列相似度为99.8%,鉴定为枯草芽孢杆菌;菌株BC-9与贝莱斯芽孢杆菌(NR075005.2)亲缘关系最近,序列相似度为99.4%,鉴定为贝莱斯芽孢杆菌;菌株BC-6、BC-11与Calidifontibacillus erzurumensis(NR180225.1)的亲缘关系最近,序列相似度分别为100%,鉴定为Calidifontibacillus erzurumensis。芽孢杆菌是醋醅酿造过程中的优势菌群,通过传统培养法可知,芽孢杆菌种类繁多,不同种类的芽孢杆菌可能对环境耐受性及产酶特性有所差异[14]。结合生理生化结果及16S rRNA序列鉴定,共获得5株不同种类优良芽孢杆菌分别是库氏类芽孢杆菌BA-6、贝莱斯芽孢杆菌BA-9、热带芽孢杆菌BB-5、枯草芽孢杆菌BB-13、C. erzurumensis BC-11。
表 4 菌株序列比对结果Table 4. Results of strain sequence alignment菌株编号 菌种名称 序列号 相似度 BA-6 Paenibacillus cookii NR025372.1 99.6% BA-9 Bacillus velezensis NR075005.2 99.4% BB-5 Bacillus tropicus NR157736.1 99.6% BB-11 Bacillus tropicus NR157736.1 99.6% BB-13 Bacillus subtilis NR112116.2 99.8% BC-6 Calidifontibacillus erzurumensis NR180225.1 100% BC-9 Bacillus velezensis NR075005.2 99.4% BC-11 Calidifontibacillus erzurumensis NR180225.1 100% 2.3 菌株发酵性能的测定
2.3.1 生长曲线的测定
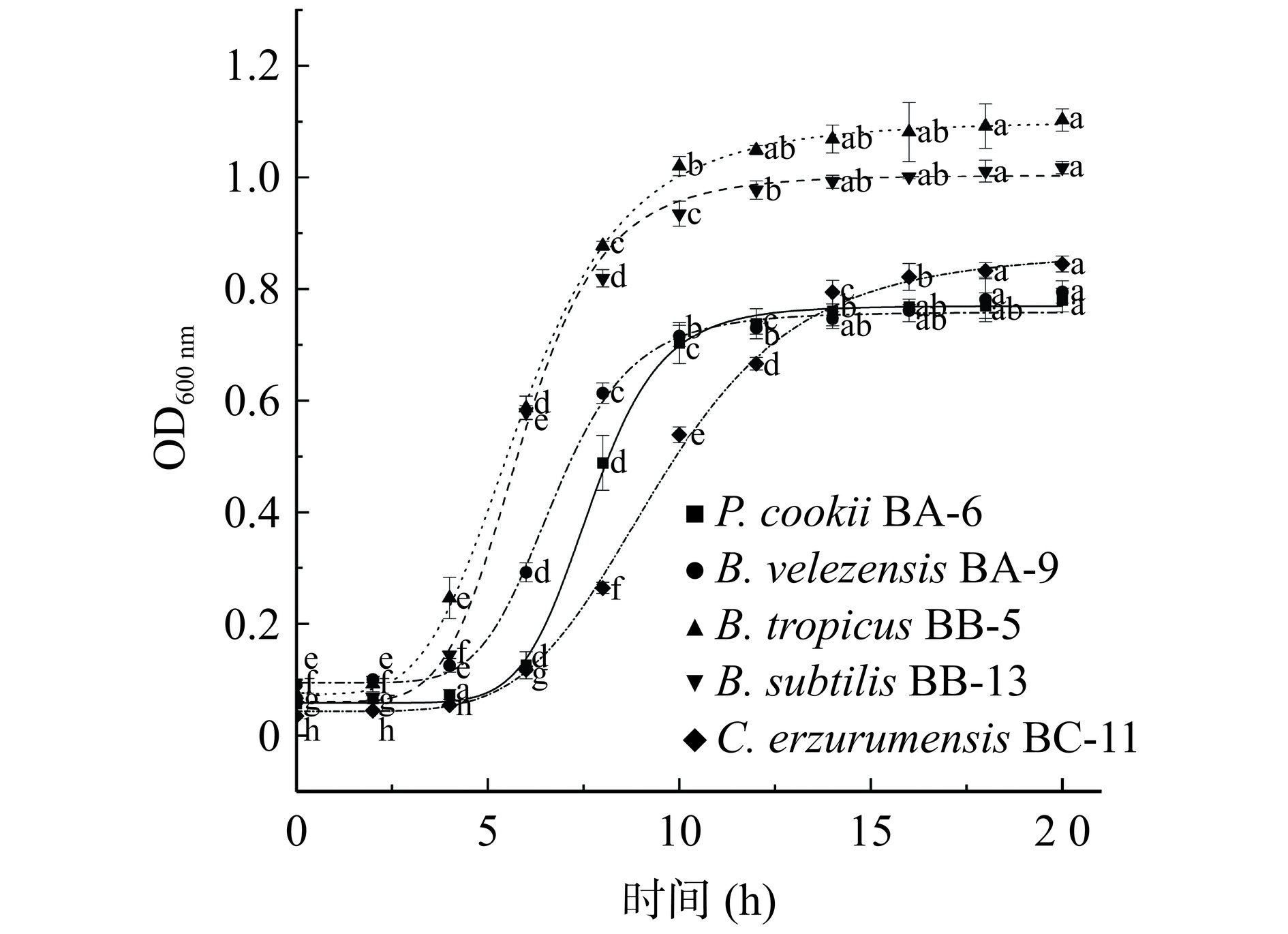
芽孢杆菌的生长曲线如图2所示。同菌株组内样品差异显著,其中库氏类芽孢杆菌BA-6、贝莱斯芽孢杆菌BA-9在0~5 h生物量无显著差异,处于生长迟缓期;5~10 h的生物量成对数上升,为对数生长期;10 h后OD值无显著差异性,表明进入生长稳定期。而热带芽孢杆菌BB-5、枯草芽孢杆菌BB-13生长速度较快,3 h后进入对数生长期,此时OD600达到1左右,8 h后进入生长停滞期。C. erzurumensis BC-11生长较为缓慢,0~5 h为生长迟缓期,5~15 h为对数生长期,15 h后进入稳定期。以上结果表明,库氏类芽杆菌BA-6、贝莱斯芽孢杆菌BA-9最快达到生长稳定期,在实际发酵过程可能与其它微生物相比有竞争优势。处于生长对数末期菌种代谢活跃,各种生化反应和代谢过程都在快速进行,所以选取生长对数末期的菌液进行耐受性试验,判断其在酿造环境中的受胁迫性[14]。
2.3.2 重要酿造环境因素对菌株生长条件的影响
在食品发酵过程中,环境因素对微生物动态变化和挥发性代谢物起着重要的作用。如温度、酸度和乙醇含量都处于连续波动状态,可能影响发酵过程中微生物结构、多样性和挥发性代谢产物[15−16]。测定5株差异菌株对酿造环境的耐受性,以探究其用于醋醅发酵潜力。
2.3.2.1 温度对芽孢杆菌生物量影响
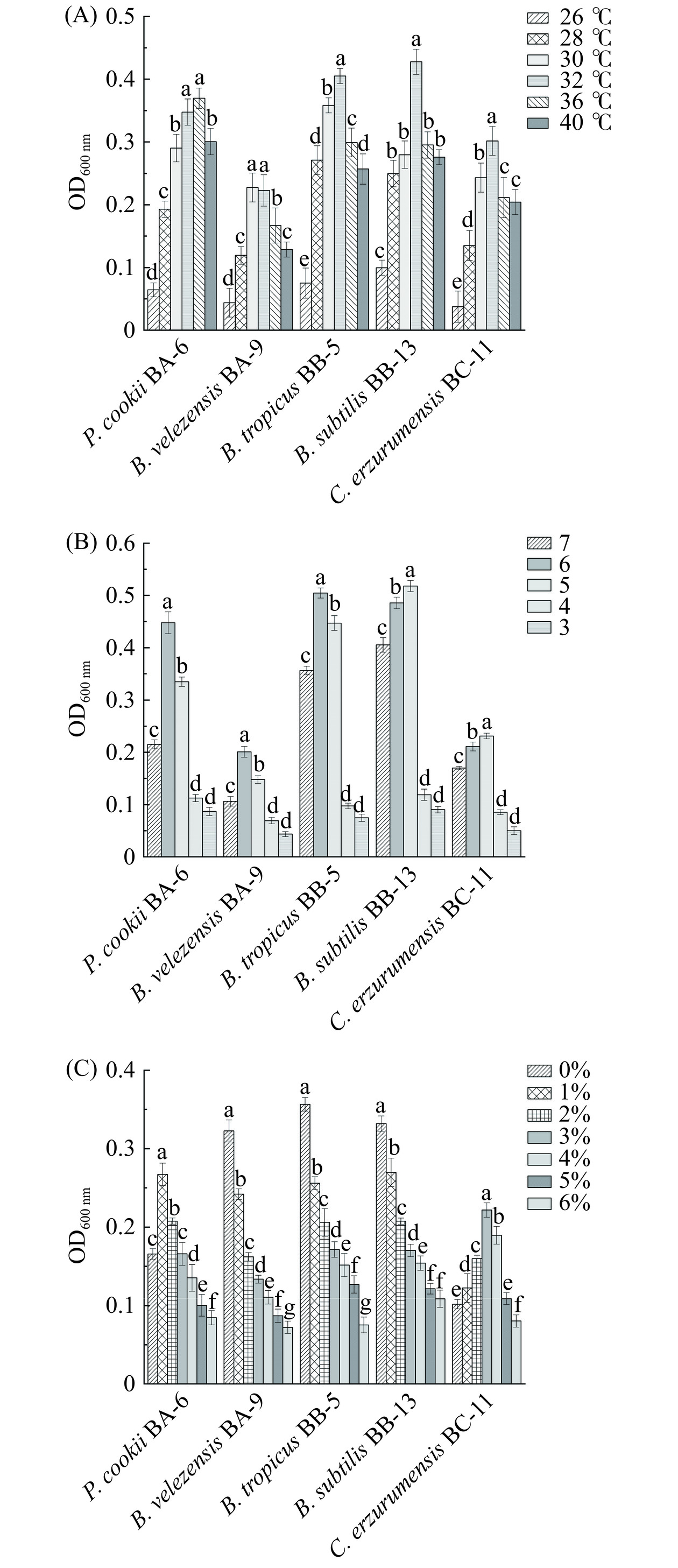
温度是影响微生物生长代谢重要因素,在发酵过程中,醋醅温度及变化模式影响底物分解和微生物代谢活性[16]。在麸醋发酵过程中,由于翻醅作用氧气供给较为充足,有利于醋醅中好氧微生物生长代谢,如醋酸杆菌等好氧菌在代谢旺盛期会产生生物热,使得醋醅的温度升高,杨宗朋[17]研究发酵过程中温度最高可达46 ℃,通过翻醅降温度控制在30~40 ℃之间。图3(A)表明,库氏类芽孢杆菌BA-6、贝莱斯芽孢杆菌BA-9分别在36 ℃、30 ℃时生长情况最好,为最适生长温度;热带芽孢杆菌BB-5、枯草芽孢杆菌BB-13和C. erzurumensis BC-11在32 ℃生物量最大,为最适生长温度。值得注意的是40 ℃下各菌株生长相对良好,而26 ℃下均受到明显抑制(P<0.05)。综上所述,各类芽孢杆菌在30~40 ℃能较好生长代谢,具有良好的耐热性,能够适应醋醅发酵。
2.3.2.2 pH对芽孢杆菌生物量影响
酸度是麸醋酿造过程中的重要指标,也是传统酿造食品发酵过程中重要环境驱动因子,同时还影响菌株生长代谢[18−19]。在醋酸发酵前期酸度增加pH逐渐下降,到发酵末期pH处于动态平衡(pH4.0~4.4)[17]。总酸含量不断增加,从而抑制微生物的生长代谢[20]。Ji等[19]研究了三种芝麻香型白酒发酵中影响微生物群动态的关键因素,结果表明,酸度是显著驱动细菌和真菌结构和多样性的重要环境因子。图3(B)结果表明,pH降低,各菌株生物量呈先上升后下降趋势;在pH6、pH5条件下,各芽孢杆菌生长明显较快,生物量较高,表明此条件有利于芽孢杆菌生长,促进代谢产物生成;当pH降低至3时,各菌株均受到不同程度的抑制,这种现象可能是由于环境过酸,影响芽孢杆菌相关酶活性,从而影响菌株的生长发酵[20−21]。
2.3.2.3 乙醇添加量对芽孢杆菌生物量影响
如图3(C)所示,乙醇添加量在1%时,库氏类芽孢杆菌BA-6增速较为明显,但随着乙醇添加量增加,生长速度逐渐下降;随着乙醇添加量的增加,C. erzurumensis BC-11生物量呈先增长后下降的趋势,在乙醇含量3%时生长速度最快,说明适量的乙醇可促进该类芽孢杆菌生长,可能有利于其在实际酒化阶段生长代谢;其余菌株随乙醇添加量增加均受到不同程度的抑制,当乙醇含量达到6%时,各菌株生长受到显著抑制(P<0.05)。以上结果表明各菌株对温度、酸度都表现出较强的耐受能力,可能在实际发酵过程中存在潜在应用价值。
2.3.3 菌株产酶试验结果
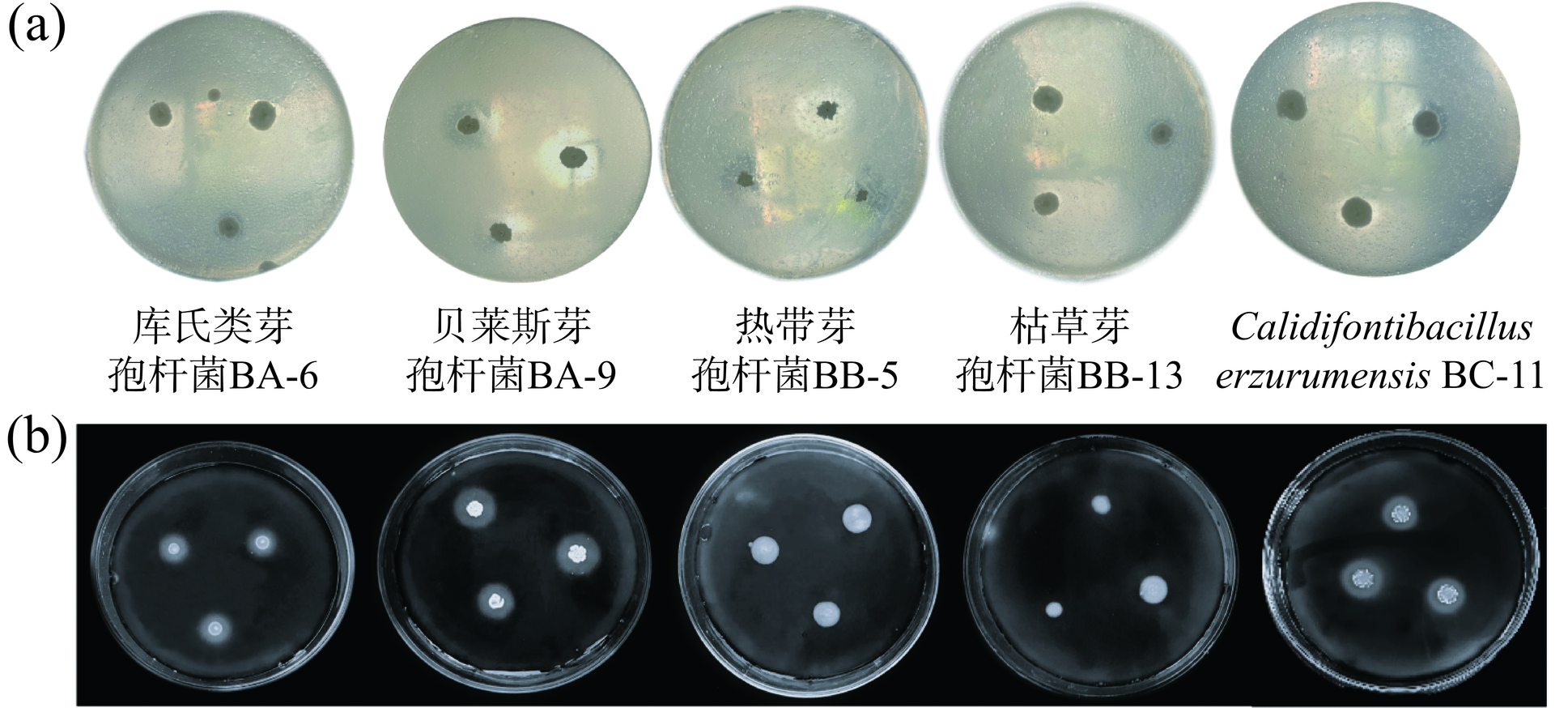
芽孢杆菌属可以产生多种胞外水解酶,主要有淀粉酶、蛋白酶等[22−24]。麸醋酿造以麸皮为主要原料,含有大量淀粉、粗多糖和蛋白质等大分子物质,经发酵降解产生小分子物质才能为微生物生长代谢提供碳源、氮源[25]。如图4、表5所示,根据透明圈与菌落直径比值,判定菌株产蛋白酶、淀粉水解酶能力,不同种类芽孢杆菌产酶性能有所差异[24]。库氏类芽孢杆菌BA-6、贝莱斯芽孢杆菌BA-9、热带芽孢杆菌BB-5、枯草芽孢杆菌BB-13、C. erzurumensis BC-11酪素水解圈与菌落直径之比分别为0、3.7±0.3、1.5±0.5、1.8±0.05、2.47±0.15,淀粉水解圈与菌落直径之比分别为3.8±0.5、1.5±0.3、0、0、2.4±0.3,结果表明贝莱斯芽孢杆菌BA-9产蛋白酶能力最强,库氏类芽孢杆菌BA-6无产蛋白酶能力;库氏类芽孢杆菌BA-6产淀粉酶能力最强,热带芽孢杆菌BB-5、枯草芽孢杆菌BB-13无产淀粉酶能力。
表 5 酪素、淀粉水解试验结果Table 5. Results of casein and starch hydrolysis tests试验名称 编号 菌落直径(d,cm) 透明圈直径(D,cm) 比值 酪素水解试验 BA-6 0.35±0.05 − − BA-9 0.6±0.17 2.2±0.37 3.7±0.3 BB-5 0.6±0.05 1.5±0.57 1.5±0.5 BB-13 0.9±0.1 2±0.1 1.8±0.05 BC-11 0.7±0.05 1.9±0.2 2.47±0.15 淀粉水解试验 BA-6 0.5±0.1 1.9±0.1 3.8±0.5 BA-9 1.2±0.4 1.8±0.2 1.5±0.3 BB-5 0.4±0.02 − − BB-13 0.5±0.02 − − BC-11 0.5±0.1 1.2±0.1 2.4±0.3 注:“−”表示不产水解圈。 2.3.4 模拟固态发酵试验
近年来食醋酿造过程越来越多的功能微生物被分离和鉴定出来,具有特定功能的微生物用于接种醋醅强化食醋发酵,以改变原醋醅微生物菌群结构,改善食醋风味品质[26]。以麸皮为原料模拟固态发酵对不同芽孢杆菌发酵过程中产生还原糖、氨基酸态氮、有机酸及挥发性风味物质能力进行研究,评价其潜在应用价值。
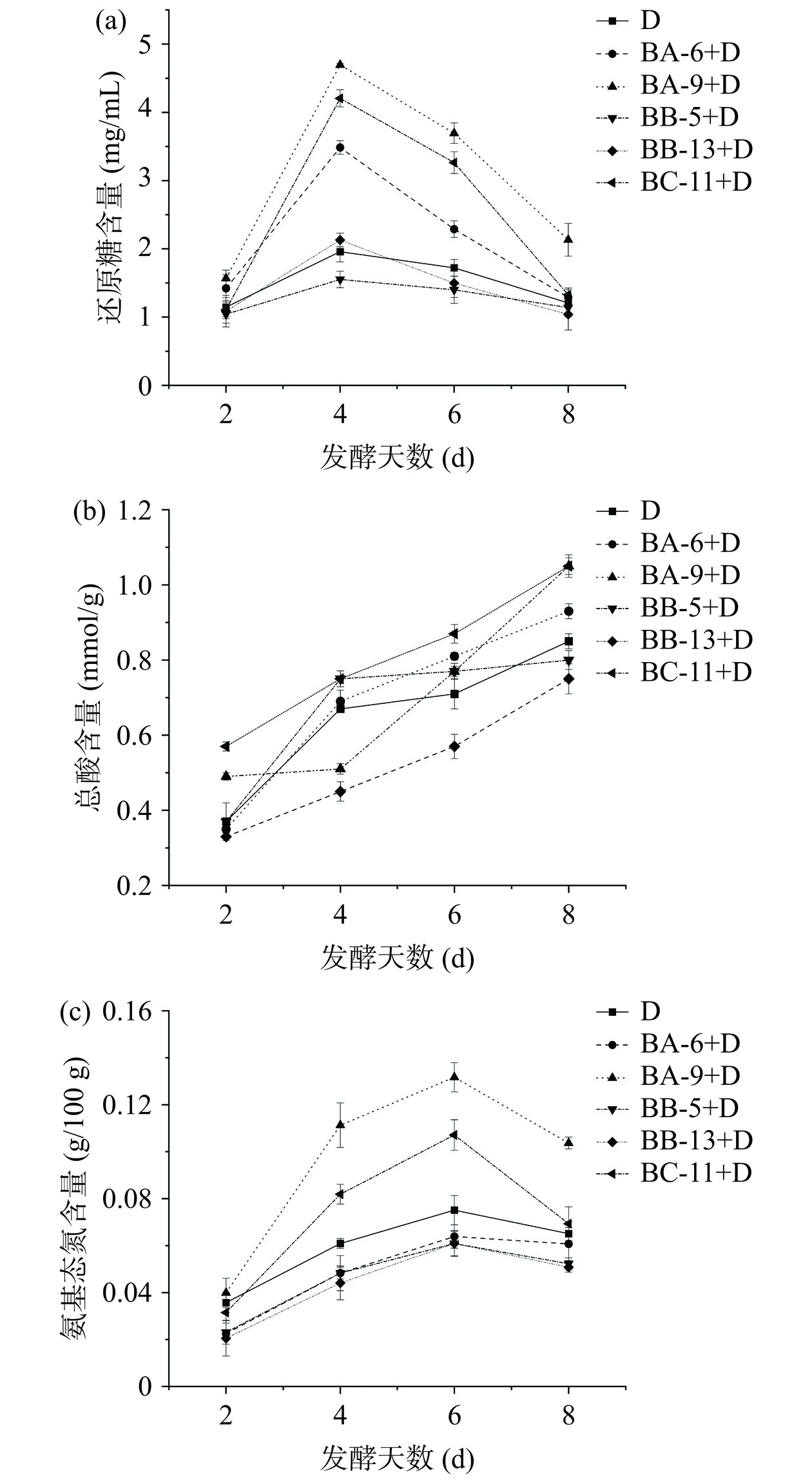
2.3.4.1 还原糖含量变化
还原糖主要由能分泌水解酶的微生物降解多聚糖产生,为其他微生物提供能量物质[24]。如图5(a)所示,随着发酵天数增加,还原糖含量整体呈先上升后下降趋势,在第4 d时均达到最高。BA-6+D、BA-9+D、BC-11+D三类发酵组合还原糖总体含量高于对照组,在第4 d含量分别为3.48、4.69、4.20 mg/mL,可能是由于库氏类芽孢杆菌BA-6、贝莱斯芽孢杆菌BA-9、C. erzurumensis BC-11产淀粉酶能力较强导致。此外,C. erzurumensis BC-11具有分解纤维素能力,可能充分释放麸皮中其他糖类物质,也可使还原糖含量上升;而BB-5+D、BB-13+D两组还原糖含量无明显变化,可能因为热带芽孢杆菌BB-5、枯草芽孢杆菌BB-13在该条件下产淀粉酶能力较弱。
2.3.4.2 总酸含量变化
总酸含量是判定食醋品质的重要指标,菌株产酸量是食醋发酵的重要指标[20]。如图5(b)所示,随着发酵天数增加,总酸呈持续上升趋势,与对照组相比在发酵第8 d时,BA-6+D、BA-9+D、BC-11+D发酵组合总酸含量均有所提升,含量分别为1.05、0.93、1.05 mmol/g,表明库氏类芽孢杆菌BA-6、贝莱斯芽孢杆菌BA-9、C. erzurumensis BC-11能与巴氏醋杆菌相互作用,提高利用糖类产酸能力,促进总酸含量提升。BB-5+D、BB-13+D两组总酸低于对照组,说明热带芽孢杆菌BB-5、枯草芽孢杆菌BB-13与巴氏醋杆菌可能存在竞争关系,导致巴氏醋杆菌生物量较低,降低了发酵产酸能力。
2.3.4.3 氨基酸态氮含量变化
氨基酸态氮是重要的滋味与营养物质,由蛋白质在高温高湿发酵过程由微生物和蛋白酶作用下分解产生[22]。由图5(c)可知,不同芽孢杆菌发酵过程中氨基酸态氮含量均呈先上升后下降趋势,在发酵第6 d时达到最高,之后逐渐下降。与发酵第6 d对照组中氨基酸态氮含量(0.07 g/100 g)相比,发酵组合BA-9+D、BC-11+D氨基酸态氮含量远高于对照组,分别为0.13、0.11 g/100 g。根据产酶试验得出贝莱斯芽孢杆菌BA-9、C. erzurumensis BC-11产蛋白酶能力较高,可能使接种贝莱斯芽孢杆菌、C. erzurumensis发酵后,氨基酸态氮含量有所提升;而BA-6+D、BB-5+D、BB-13+D三组氨基酸态氮含量均低于对照组,可能是由于菌株BA-6不产蛋白酶导致;热带芽孢杆菌BB-5、枯草芽孢杆菌BB-13虽生长速率较快但产蛋白酶能力较弱,也导致发酵后氨基酸态氮含量相对较低。发酵六天后,各发酵组合氨基酸态氮含量均下降,可能是由于氨基酸态氮作为氮源被各芽孢杆菌和巴氏醋杆菌利用。
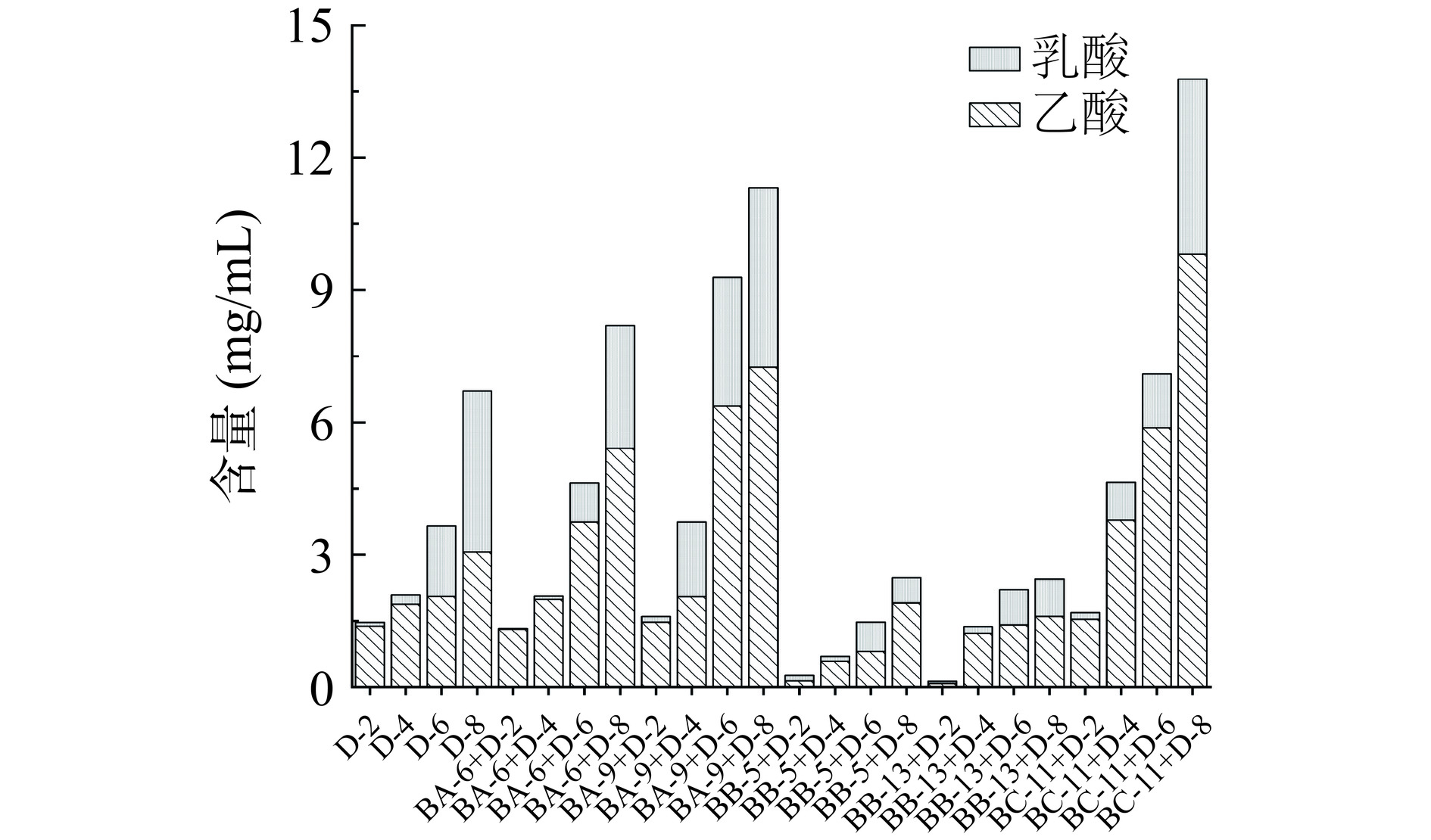
2.3.4.4 乙酸、乳酸含量变化
有机酸是食醋酸味物质的主要来源,其中乙酸作为主要挥发性酸,是食醋的主要酸味物质之一,具有刺激性特点;而乳酸是含量最多的非挥发性酸,为食醋提供了柔和的口感[1]。因此,乳酸和乙酸含量被认为是固态发酵品质的重要指标[26]。图6显示了6组发酵样品中乳酸和乙酸含量的变化,总含量随发酵天数呈上升趋势。发酵初期,乳酸和乙酸含量均较低,发酵结束时BA-6+D、BA-9+D、BC-11+D发酵组合相比对照组有机酸含量均有所提升,其中乙酸含量分别为2.81、7.26、5.02 mg/mL,较对照组(2.01 mg/mL)提高了40%、260%、149%;乳酸含量分别为3.07、4.07、4.09 mg/mL,较对照组(2.75 mg/mL)提升了11%、48%、48%。可能是由于库氏类芽孢杆菌BA-6、贝莱斯芽孢杆菌BA-9、C. erzurumensis BC-11具有较强的淀粉降解能力,促进原料底物分解,加速巴氏醋杆菌生长及有机酸代谢,因而使得乳酸和乙酸含量提升。该结果与李晓梅[25]的研究结果相似,其研究表明将芽孢杆菌JL1应用于山西陈醋发酵,相比对照组有机酸含量提高了72.50%,其中乙酸、乳酸含量显著提升。BB-5+D、BB-13+D发酵组合有机酸含量始终低于对照组,可能是由热带芽孢杆菌BB-5、枯草芽孢杆菌BB-13分解底物能力较差,且抑制巴氏醋杆菌生长导致其代谢产酸能力下降。该研究结果表明,库氏类芽孢杆菌BA-6、贝莱斯芽孢杆菌BA-9、C. erzurumensis BC-11有利于巴氏醋杆菌生长代谢,使得有机酸含量有所提升,在实际醋酸发酵阶段具有潜在应用价值。
2.3.4.5 挥发性风味物质含量测定
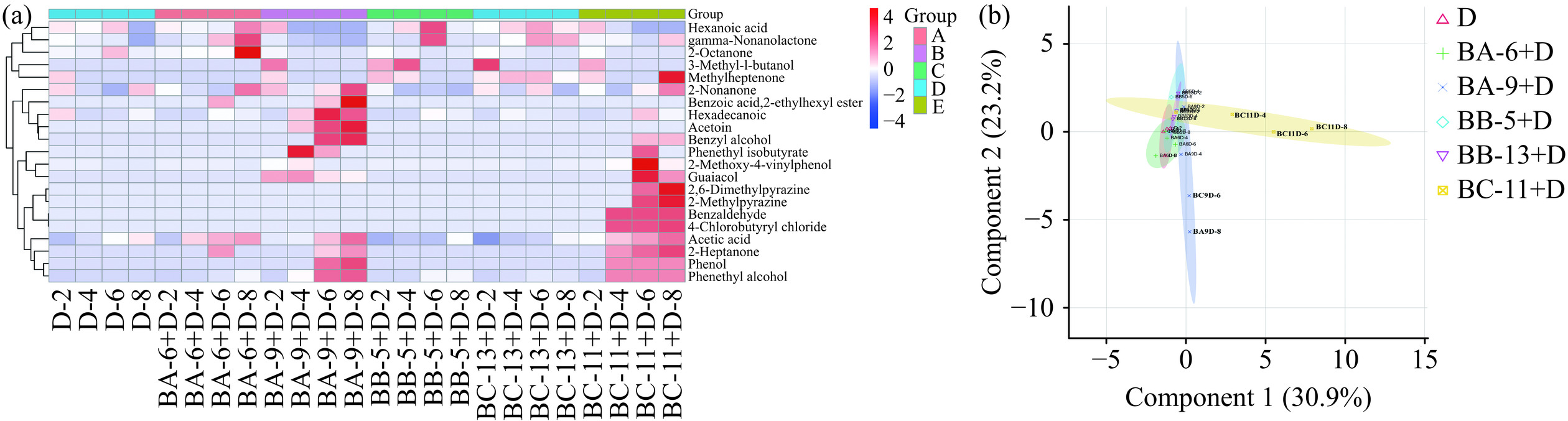
GC-MS分析结果表明,6组样品中共检测出21种挥发性风味物质,如图7(a)所示,酸类2种、醇类3种、醛类3种、酯类3种、酮类5种、酚类3种和吡嗪类2种。对6组发酵醋醅挥发性风味物质进行主成分分析,可以从总体上反映样本组间差异和组内差异。结果如图7(b)所示,样本BA-9+D、BC-11+D与其他发酵组分离显著,两个主成分约占总方差54.1%,其中PC1为30.9%,PC2为23.2%。与对照组(9种挥发性风味物质)相比,BA-6+D、BA-9+D、BB-5+D、BB-13+D、BC-11+D挥发性香气成分种类分别为10、17、10、10、19种,均有所增加,可能与芽孢杆菌生长代谢有关。
酸类物质是影响食醋风味的重要物质,是微生物在醋酸发酵过程中代谢产生的,包含挥发酸和不挥发酸,而乙酸作为发酵的主体挥发性酸类物质,与对照组相比BA-6+D、BA-9+D、BC-11+D发酵组合乙酸含量均有所提升,可能是芽孢杆菌促进巴氏醋杆菌代谢活动产生;而己酸无明显变化。
酯类物质主要是由有机酸和醇类物质在糖、酯酶作用下形成,具有果香或花香气味,是食醋中重要的香气成分[26],主要包括异丁酸苯乙酯、苯甲酸2-乙基己酯、棕榈酸甲酯。其中异丁酸苯乙酯仅在BA-9+D、BC-11+D组中检出,含量分别为0.67、0.44 mg/mL,苯甲酸2-乙基己酯仅在BA-6+D、BA-9+D检出,含量分别为0.69、2.33 mg/mL,可能是由于芽孢杆菌代谢酯酶发生酯化反应生成。
醇类物质通常具有植物香、芳香味等风味特征,主要包括苯乙醇、苯甲醇、异戊醇,苯乙醇。其中苯乙醇是杂醇油的重要组分之一[27],含量随发酵时间增加逐渐积累,各发酵组合苯乙醇含量均有所提升,在发酵结束时对照组苯乙醇含量为6.77 mg/mL,BA-6+D、BA-9+D、BB-5+D、BB-13+D、BC-11+D含量分别为7.14、58.45、12.91、7.64、18.03 mg/mL,可能是由于巴氏醋杆菌、芽孢杆菌协同发酵有利于苯乙醇含量提升,该结果与Xu等[28]研究结果一致,其将地衣芽孢杆菌和贝莱斯芽孢杆菌接种到大曲中,苯乙醇含量提高19.5%。此外苯甲醇、异戊醇仅在BA-9+D、BC-11+D组中检出,可能是由于贝莱斯芽孢杆菌BA-9、C. erzurumensis BC-11与氨基酸代谢有关。
醛类和酮类物质是食醋中重要的香气物质,具有奶油、水果香气[29]。乙偶姻仅在BA-9+D组检出,随发酵时间延长而增加,从0.42 mg/mL增加至1.70 mg/mL,可能是由于贝莱斯芽孢杆菌代谢合成乙偶姻;苯甲醛仅在BC-11+D组检出,随发酵天数逐渐增加至17.11 mg/mL,可能是由于C. erzurumensis BC-11分解苯丙氨酸、蛋氨酸氧化脱羧形成[30]。
吡嗪类物质主要包括2-甲基吡嗪和2,6-二甲基吡嗪,具有典型的巧克力、焙烤、坚果香气且阈值较低,仅在BC-11+D组检出,发酵结束时分别增至0.10、0.30 mg/mL,可能是由于C. erzurumensis BC-11代谢促进吡嗪类物质生成;酚类物质主要有愈创木酚、苯酚、4-乙烯基-2-甲氧基苯酚。其中愈创木酚仅在BA-9+D、BC-11+D组检出,可能是由于原料降解和微生物代谢活动产生[9]。
综上所述,巴氏醋杆菌、芽孢杆菌协同发酵有利于发酵过程挥发性香气成分产生和积累。其中接种库氏类芽孢杆菌BA-6、贝莱斯芽孢杆菌BA-9、C. erzurumensis BC-11可能与苯甲醛、异丁酸苯乙酯、愈创木酚、异戊醇、苯甲醇、苯乙醛等香气物质生成有关,这些物质是麸醋风味重要组成成分,其含量变化会对四川麸醋品质产生重要影响,在实际发酵过程这些芽孢杆菌可能具有潜在应用价值。
3. 结论
从四川麸醋醋醅中分离出的32株芽孢杆菌中,筛选5株不同种类优良芽孢杆菌,分别为库氏类芽孢杆菌BA-6(Paenibacillus cookii)、贝莱斯芽孢杆菌BA-9(Bacillus velezensis)、热带芽孢杆菌BB-5(Bacillus tropicus)、枯草芽孢杆菌BB-13(Bacillus subtilis)、C. erzurumensis BC-11。对其进行耐受性试验,结果表明该5株芽孢杆菌均具有优良耐酸和耐热性,且部分芽孢杆菌可以分泌大量淀粉酶和蛋白酶,以提高醋醅中水解酶的生成,促进微生物代谢和群落结构的稳定。此外通过模拟发酵试验得出,将库氏类芽孢杆菌BA-6、贝莱斯芽孢杆菌BA-9、C. erzurumensis BC-11与巴氏醋杆菌混合发酵可有效提升总酸、还原糖、氨基态氮、有机酸(乳酸、乙酸)、挥发性风味物质种类及含量(如异丁酸苯乙酯、苯甲醇、异戊醇、苯乙醇、愈创木酚等)。综上所述,芽孢杆菌在实际发酵过程中有利于提升醋醅品质,具有潜在应用价值。
-
表 1 有机酸标准曲线线性参数
Table 1 Linear parameters of organic acid standard curves
有机酸 保留时间(min) 回归方程 相关系数(R2) 乳酸 11.99 y=8.3978x+0.6234 0.9996 乙酸 12.85 y=10.0693x+2.5424 0.9995 表 2 各菌株生理生化试验结果
Table 2 Results of physiological and biochemical experimental of each strain
编号 乳糖 麦芽糖 蔗糖 棉子糖 葡萄糖 壳聚糖 羧甲基纤维素钠 淀粉 V-P 试验 甲基红试验 氧化酶试验 明胶试验 BA-1 − + ++ − + ++ − − − + + + BA-2 − + + − + + − − + − + + BA-3 − + ++ − + ++ − − − + + + BA-4 + + + + + ++ − − − + + − BA-5 − + ++ − + ++ − − − + + + BA-6 + +++ +++ + +++ + − +++ − + + − BA-7 − + + − + + − − + − + + BA-8 − + + − + − − − + − + + BA-9 − ++ + − ++ + − + + − + + BA-10 + + + − + + − − + − + − BA-11 + + + − + + − − + − + − BB-1 − + + − + ++ − − − + + + BB-2 + + + + + ++ − − − + + − BB-3 − + + − + ++ − − − + + + BB-4 − + + − + ++ − − − + + + BB-5 − ++ ++ − +++ ++ − − − + + + BB-6 − + + − + ++ − − − + + + BB-7 − + + − + + − − − + + + BB-8 − + + − + + − − − + + + BB-9 − + + − + + − − − + + + BB-10 − + + − + + − − − + + + BB-11 − ++ ++ − ++ ++ − − − + + + BB-12 − + + − + + − − − + + + BB-13 − ++ + − +++ + − − − + + + BC-1 − + + − ++ +++ − − − + + + BC-2 − + + − + +++ − − − + + + BC-3 − + + − + + − − + − + + BC-4 − + + − ++ + − − + − + + BC-5 − + + − ++ + − − + − + + BC-6 − ++ + − +++ +++ − ++ + − + + BC-7 − + + − + ++ − − + − + + BC-8 − + + − + + − − + − + + BC-9 − ++ + − ++ + − + + − + + BC-10 − + + − + + − − + − + + BC-11 − +++ +++ − ++ + − ++ + − + + 注:“−”表示阴性;“+”表示阳性;糖发酵试验中“−”表示不分解糖产酸;“+”1/3颜色变黄;“++”1/2颜色变黄;“+++”全部颜色变黄。 表 3 样品中分离芽孢杆菌的形态特征及分类
Table 3 Morphological characteristics and classification of isolated Bacillus in samples
类别 菌落特征 菌体特征 革兰氏染色 分离得到的菌株 代表性菌株 1 圆形、直径偏小、透白色、半透明边缘整齐、无菌摸 杆状,成链 − 5 BA-6 2 椭圆形、直径中等、乳白色、不透明边缘整齐、有菌膜 杆状,成链 − 3 BA-9 3 圆形、直径偏大、白色、不透明边缘粗糙、无菌膜 杆状,成链 − 8 BB-5 4 圆形、直径偏大、白色、不透明边缘粗糙、无菌膜 杆状,成链 − 5 BB-11 5 圆形、直径偏大、白色、不透明边缘粗糙、无菌膜 杆状,成链 − 4 BB-13 6 圆形、直径中等、白色、不透明边缘粗糙、有菌膜 杆状,成链 − 2 BC-6 7 圆形、直径中等、白色、不透明边缘粗糙、有菌膜 杆状,成链 − 3 BC-9 8 椭圆形、直径中等、乳白色、不透明边缘整齐、有菌膜 杆状,成链 − 3 BC-11 注:“−”表示阴性。 表 4 菌株序列比对结果
Table 4 Results of strain sequence alignment
菌株编号 菌种名称 序列号 相似度 BA-6 Paenibacillus cookii NR025372.1 99.6% BA-9 Bacillus velezensis NR075005.2 99.4% BB-5 Bacillus tropicus NR157736.1 99.6% BB-11 Bacillus tropicus NR157736.1 99.6% BB-13 Bacillus subtilis NR112116.2 99.8% BC-6 Calidifontibacillus erzurumensis NR180225.1 100% BC-9 Bacillus velezensis NR075005.2 99.4% BC-11 Calidifontibacillus erzurumensis NR180225.1 100% 表 5 酪素、淀粉水解试验结果
Table 5 Results of casein and starch hydrolysis tests
试验名称 编号 菌落直径(d,cm) 透明圈直径(D,cm) 比值 酪素水解试验 BA-6 0.35±0.05 − − BA-9 0.6±0.17 2.2±0.37 3.7±0.3 BB-5 0.6±0.05 1.5±0.57 1.5±0.5 BB-13 0.9±0.1 2±0.1 1.8±0.05 BC-11 0.7±0.05 1.9±0.2 2.47±0.15 淀粉水解试验 BA-6 0.5±0.1 1.9±0.1 3.8±0.5 BA-9 1.2±0.4 1.8±0.2 1.5±0.3 BB-5 0.4±0.02 − − BB-13 0.5±0.02 − − BC-11 0.5±0.1 1.2±0.1 2.4±0.3 注:“−”表示不产水解圈。 -
[1] 张雅琳, 李婧, 刘廷锐, 等. 四川麸醋发酵过程中有机酸及细菌解析[J]. 中国调味品,2022,47(11):61−63,67. [ZHANG Y L, LI J, LIU T R, et al. Analysis of organic acids and bacteria in Sichuan bran vinegar during fermentation[J]. China Condiment,2022,47(11):61−63,67.] ZHANG Y L, LI J, LIU T R, et al. Analysis of organic acids and bacteria in Sichuan bran vinegar during fermentation[J]. China Condiment, 2022, 47(11): 61−63,67.
[2] 张雅琳, 刘廷锐, 朱文优, 等. 基于Illumina MiSeq高通量测序技术解析四川麸醋发酵过程中微生物菌群结构[J]. 中国食品学报,2022,22(6):299−306. [ZHANG Y L, LIU T R, ZHU W Y, et al. Analysis of microbial community structure in Sichuan bran vinegar fermentation based on Illumina MiSeq high-throughput sequencing technology[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2022,22(6):299−306.] ZHANG Y L, LIU T R, ZHU W Y, et al. Analysis of microbial community structure in Sichuan bran vinegar fermentation based on Illumina MiSeq high-throughput sequencing technology[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2022, 22(6): 299−306.
[3] ZHU M, CHEN Z, LUO H B, et al. Study of the phase characteristics of Sichuan bran vinegar fermentation based on flavor compounds and core bacteria[J]. Journal of the American Society of Brewing Chemists,2021,79(2):201−211. doi: 10.1080/03610470.2020.1794738
[4] 刘稼鑫, 叶晓婷, 余永建, 等. 传统食醋发酵区系中微生物群落及相互作用关系研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2023,44(17):225−234. [LIU J X, YE X T, YU Y J, et al. Microbial communities and their interaction in traditional vinegar fermentation process:A review[J]. Food Science,2023,44(17):225−234.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20220926-281 LIU J X, YE X T, YU Y J, et al. Microbial communities and their interaction in traditional vinegar fermentation process: A review[J]. Food Science, 2023, 44(17): 225−234. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20220926-281
[5] JIANG Y J, LÜ X C, ZHANG C, et al. Microbial dynamics and flavor formation during the traditional brewing of Monascus vinegar[J]. Food Research International,2019,125:108531. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.108531
[6] 孙列雄. 山西老陈醋核心菌群解析及与风味物质的相关性[D]. 晋中:山西农业大学, 2020. [SUN L X. Analysis of the core flora of Shanxi old vinegar and its correlation with flavor substances[D]. Jinzhong:Shanxi Agricultural University, 2020.] SUN L X. Analysis of the core flora of Shanxi old vinegar and its correlation with flavor substances[D]. Jinzhong: Shanxi Agricultural University, 2020.
[7] ZHANG J B, HOU Y C, LIU Q S, et al. Fortified Jiuqu of the Chinese Baijiu:A review on its functional microorganisms, strengthening effects, current challenges, and perspectives[J]. Food Bioscience,2023,55:103045. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2023.103045
[8] ZHANG L Q, HUANG J, ZHOU R Q, et al. Evaluating the feasibility of fermentation starter inoculated with Bacillus amyloliquefaciens for improving acetoin and tetramethylpyrazine in Baoning bran vinegar[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2017,255:42−50. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2017.05.021
[9] TIE Y, ZHU W Y, ZHANG C, et al. Effect of temperature on chemical compounds of Cupei (precursor of bran vinegar) during in-situ aging and revelation of functional microorganisms in the process[J]. LWT, 2023, 182.
[10] FU G M, CAI W Q, DONG B, et al. Effects of Daqu inoculated with Aspergillus niger and Saccharomyces cerevisiae on microbial community, aroma compounds and physicochemical parameters of fermented grains during the brewing process of Chinese special-flavor Baijiu[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2022,103(1):273−282.
[11] HE G Q, HUANG J, WU C D, et al. Bioturbation effect of fortified Daqu on microbial community and flavor metabolite in Chinese strong-flavor liquor brewing microecosystem[J]. Food Research International,2020,129:108851. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.108851
[12] 东秀珠, 蔡妙英. 常见细菌系统鉴定手册[M]. 北京:科学出版社, 2001:353−398. [DONG X Z, CAI M Y. Handbook for identification of common bacterial systems[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 2001:353−398.] DONG X Z, CAI M Y. Handbook for identification of common bacterial systems[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2001: 353−398.
[13] BU K N. Berger bacterial identification manual[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 1984:729−830.
[14] 鄢妮. 优良组合菌株对山西老陈醋酿造的代谢调控[D]. 晋中:山西农业大学, 2021. [YAN N. Metabolic regulation of Shanxi mature vinegar brewing by fine combination strains[D]. Jinzhong:Shanxi Agricultural University, 2021].] YAN N. Metabolic regulation of Shanxi mature vinegar brewing by fine combination strains[D]. Jinzhong: Shanxi Agricultural University, 2021].
[15] ZHANG M H, WU N, FAN Y Q, et al. Proteomic profiling and stress response in Pediococcus acidilactici under acetic acid[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2022, 70(39).
[16] MA S Y, LUO H B, ZHAO D, et al. Environmental factors and interactions among microorganisms drive microbial community succession during fermentation of Nongxiangxing Daqu[J]. Bioresource Technology,2021,345:126549.
[17] 杨宗朋. 固态醋酸发酵影响因素及发酵设备[J]. 食品安全导刊,2023(13):152−155. [YANG Z P. Factors affecting solid-state acetic acid fermentation and fermentation equipment[J]. Food Safety Guide,2023(13):152−155.] YANG Z P. Factors affecting solid-state acetic acid fermentation and fermentation equipment[J]. Food Safety Guide, 2023(13): 152−155.
[18] WU Y F, XIA M L, ZHAO N, et al. Metabolic profile of main organic acids and its regulatory mechanism in solid-state fermentation of Chinese cereal vinegar[J]. Food Research International,2021,145:110400−110400. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110400
[19] JI X A, YU X W, ZHANG L Y, et al. Acidity drives volatile metabolites in the spontaneous fermentation of sesame flavor-type Baijiu[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2023,389:110101−110101. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2023.110101
[20] 于华, 黄丹, 陈卓, 等. 四川麸醋醋醅中产酸芽孢杆菌的分离及发酵特性研究[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2017(1):83−90. [YU H, HUANG D, CHEN Z, et al. Study on isolation of acid-producing Bacillus from Sichuan bran vinegar and its fermentation characteristics[J]. China Food Additives,2017(1):83−90.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2513.2017.01.006 YU H, HUANG D, CHEN Z, et al. Study on isolation of acid-producing Bacillus from Sichuan bran vinegar and its fermentation characteristics[J]. China Food Additives, 2017(1): 83−90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2513.2017.01.006
[21] 康雪梅, 罗雯, 郭建, 等. 固态食醋自然发酵醋醅中生淀粉酶产生菌的筛选及初步应用[J]. 中国调味品,2023,48(10):78−84. [KANG X M, LUO W, GUO J, et al. Screening and preliminary application of raw amylase-producing bacteria in fermented grains by natural fermentation of solid-state vinegar[J]. China Condiment,2023,48(10):78−84.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2023.10.013 KANG X M, LUO W, GUO J, et al. Screening and preliminary application of raw amylase-producing bacteria in fermented grains by natural fermentation of solid-state vinegar[J]. China Condiment, 2023, 48(10): 78−84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2023.10.013
[22] 冯国杨. 菌株TYF-FGY-BD17的筛选及其四甲基吡嗪生物合成机制研究[D]. 太原:太原理工大学, 2022. [FENG G Y. Screening of strain TYF-FGY-BD17 and study on biosynthesis mechanism of tetramethylpyrazine[D]. Taiyuan:Taiyuan University of Technology, 2022.] FENG G Y. Screening of strain TYF-FGY-BD17 and study on biosynthesis mechanism of tetramethylpyrazine[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2022.
[23] 冯洁雅. 四川晒醋固态发酵过程中细菌群落结构和风味物质的关联研究[D]. 宜宾:四川轻化工大学, 2021. [FENG J Y. Relationship between bacterial community and flavor substance during solid-state fermentation of Sichuan sun vinegar[D]. Yibin:Sichuan University of Science & Engineering, 2021.] FENG J Y. Relationship between bacterial community and flavor substance during solid-state fermentation of Sichuan sun vinegar[D]. Yibin: Sichuan University of Science & Engineering, 2021.
[24] 郭艳霞. 高产蛋白酶和乙偶姻的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌YB19的筛选鉴定及应用研究[D]. 晋中:山西农业大学, 2021. [GUO Y X. Screening, identification and application of Bacillus velezensis YB19 based on producing acetoin[D]. Jinzhong:Shanxi Agricultural University, 2021.] GUO Y X. Screening, identification and application of Bacillus velezensis YB19 based on producing acetoin[D]. Jinzhong: Shanxi Agricultural University, 2021.
[25] 李晓梅. 山西老陈醋源优良芽孢杆菌的筛选、互作及原位强化研究[D]. 晋中:山西农业大学, 2020. [LI X M. Screening of excellent Bacillus from Shanxi aged vinegar and study of interaction and enhancement with other excellent strains in alcohol fermentation[D]. Jinzhong:Shanxi Agricultural University, 2020.] LI X M. Screening of excellent Bacillus from Shanxi aged vinegar and study of interaction and enhancement with other excellent strains in alcohol fermentation[D]. Jinzhong: Shanxi Agricultural University, 2020.
[26] ZHANG G R, LI L, LIU J, et al. Comparing the metabolite components of Sichuan sun vinegar and other kinds of vinegar based on non-targeted metabolomic[J]. LWT, 2022, 164.
[27] 湛佳佳, 张香, 胡亚平, 等. 基于气相色谱检测法研究椪柑酒中甲醇、杂醇油的生成规律[J]. 食品研究与开发,2022,43(22):182−186,193. [ZHAN J J, ZHANG X, HU Y P, et al. Formation of ethanol and fusel oil in citrus wine based on gas chromatography[J]. Food Research and Development,2022,43(22):182−186,193.] ZHAN J J, ZHANG X, HU Y P, et al. Formation of ethanol and fusel oil in citrus wine based on gas chromatography[J]. Food Research and Development, 2022, 43(22): 182−186,193.
[28] XU B Y, XU S S, CAI J, et al. Analysis of the microbial community and the metabolic profile in medium-temperature Daqu after inoculation with Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus velezensis[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2022,160:113214. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113214
[29] 魏世东, 王素英, 娄婷婷, 等. 食醋中挥发性风味物质及其检测方法研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发,2022,43(24):215−224. [WEI S D, WANG S Y, LOU T T, et al. Research progress on volatile flavor compounds in vinegar and their detection methods[J]. Food Research and Development,2022,43(24):215−224.] WEI S D, WANG S Y, LOU T T, et al. Research progress on volatile flavor compounds in vinegar and their detection methods[J]. Food Research and Development, 2022, 43(24): 215−224.
[30] 郑宇, 程程, 刘静, 等. 中国传统固态发酵食醋主要特征风味物质组成分析[J]. 中国食品学报,2020,20(8):237−247. [ZHEN Y, CHENG C, LIU J, et al. Analysis of the main characteristics and flavor substance composition of traditional Chinese solid state fermented vinegar[J]. China Food News,2020,20(8):237−247.] ZHEN Y, CHENG C, LIU J, et al. Analysis of the main characteristics and flavor substance composition of traditional Chinese solid state fermented vinegar[J]. China Food News, 2020, 20(8): 237−247.
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 杨敏,张密,叶贤胜,曾长立,马爱民,牛蒙亮,许丹云. 大球盖菇多肽的制备、抗氧化及抗肿瘤活性的研究. 山西农业大学学报(自然科学版). 2025(01): 123-132 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 魏磊,景炳年,李宁洁,金饶,谢晓阳,刘雨晴,马艳妮,梁雅辉,王韬,王伟. 赤松茸乙醇提取物不同萃取相生物活性对比. 食品研究与开发. 2025(04): 39-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王小平,刘忠莹,钟洋,张定秋,陆阳,朱敏敏,郑红毅,何叶馨,王鑫,黄韬睿,江祖彬. 基于离子色谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱法分析木耳、香菇、松茸和茶树菇中砷形态分布. 食品工业科技. 2024(07): 254-260 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 韦菡燕,蒋军文. 等离子体对松茸多糖抗疲劳作用的影响. 保鲜与加工. 2024(10): 128-133 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 黄磊,何春梅,司灿,石鸿宇,段俊. 大球盖菇栽培研究进展. 中国食用菌. 2023(03): 8-14 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 魏磊,王伟,谢晓阳,周雍,刘雨晴,马艳妮,宁二娟,王韬,李宁洁,景炳年. 响应面优化博爱赤松茸多糖提取工艺及其抑菌和抗氧化活性研究. 食品工业科技. 2023(15): 213-220 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 曹燕妮,华蓉,邓雅元,王娟,游金坤. 食用菌中维生素测定方法研究. 中国食用菌. 2022(09): 44-47 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



