Speculate on the Formation Mechanism of Nonanal and Decanal from LPC (18:1) and LPE (18:1) in the Steaming of Chinese Water Chestnut Based on the in Vitro Model Study
-
摘要: 模拟荸荠的pH、油酸酰溶血磷脂酰胆碱18:1(LPC(18:1))和油酸酰溶血磷脂乙醇胺18:1(LPE(18:1))含量及荸荠蒸制条件,构建LPC(18:1)、LPE(18:1)和油酸的离体模型,以离体模型生成的壬醛、癸醛和油酸的含量以及过氧化值(POV)作为指标,探讨荸荠蒸制中LPC(18:1)和LPE(18:1)生成壬醛和癸醛的机制。结果表明,LPC(18:1)和LPE(18:1)氧化形成壬醛和癸醛的可能机制如下:LPC(18:1)和LPE(18:1)的不饱和酰基链上紧靠双键的C8位和C11位分别失去H,形成R·;R·可直接与O2和H反应形成8-氢过氧化物(8-ROOH),或经电子重排后再与O2和H反应形成9-氢过氧化物(9-ROOH)和10-氢过氧化物(10-ROOH);其中8-ROOH均裂形成癸醛,9-ROOH和10-ROOH的均裂形成壬醛。研究结果可为果蔬风味物质形成机制研究和风味品质调控提供科学参考。
-
关键词:
- 荸荠 /
- 油酸酰溶血磷脂酰胆碱18:1(LPC(18:1)) /
- 油酸酰溶血磷脂酰乙醇胺18:1(LPE(18:1)) /
- 壬醛 /
- 癸醛 /
- 形成机制
Abstract: The in vitro models of oleoyl lysophosphatidylcholine 18:1 (LPC(18:1)), oleoyl lysophosphatidyl ethanolamine 18:1 (LPE(18:1)) and oleic acid were constructed by simulating the pH, LPC(18:1) and LPE(18:1) contents and steaming conditions of Chinese water chestnut (CWC). The content of nonanal, decanal and oleic acid, and peroxide value (POV) produced by the in vitro models were used as indicators to investigate the formation mechanism of nonanal and decanal from LPC(18:1) and LPE(18:1) during the steaming of CWC. The results showed that the possible mechanism of the oxidation of LPC(18:1) and LPE(18:1) to form nonanal and decanal was as follows. First of all, the C8 and C11 positions close to the double bond on the unsaturated acyl chain of LPC(18:1) and LPE(18:1) lost H respectively, and then formed R·. In the second step, the R· directly reacted with O2 and H to form 8-hydroperoxide (8-ROOH), or reacted with O2 and H to form 9-hydroperoxide (9-ROOH) and 10-hydroperoxide (10-ROOH) after electron rearrangement. Finally, 8-ROOH split homogeneously to form decanal, 9-ROOH and 10-ROOH split homogeneously to form nonanal. The results can provide scientific reference for the formation mechanism of flavor substances and the regulation of flavor quality of fruits and vegetables. -
荸荠(Eleocharis dulcis (Burm. f.) Trin.)可鲜食也可熟食,其蒸煮后产生一种特有的香味,主要成分是壬醛和癸醛[1]。脂质氧化是生成醛类风味物质的主要反应[2-4]。鲜荸荠中含0.1%脂肪[5]。前期研究发现,油酸酰溶血磷脂酰胆碱18:1(LPC(18:1))和油酸酰溶血磷脂酰乙醇胺18:1(LPE(18:1))分别占鲜荸荠中溶血磷脂类物质的8%和4%,而蒸制30 min后LPC(18:1)和LPE(18:1)分别降为0.1953%和0.0001%,显然LPC(18:1)和LPE(18:1)发生了反应。溶血磷脂具有磷脂一般的化学性质,可发生脂质水解和脂质氧化反应[6-7]。目前,脂质氧化主要发生在腌制和热加工的水产品和肉类[8-10],而未见果蔬类食品加工过程发生脂质氧化的文献报道。
脂质氧化机理遵循自由基链式反应,包括引发、传递和终止三个阶段。在蒸制过程中,脂质氧化的引发因子主要是高温。引发阶段是脂质分子中不饱和酰基链上紧靠双键的亚甲基上的H被自由基提取形成烷基自由基(R·),R·再与O2反应生成过氧基(ROO·),ROO·可从其他脂质分子的不饱和酰基链上的双键α-位夺取氢原子形成氢过氧化物(ROOH)和新的R·[11-13]。在热氧化过程中,高温下生成的ROOH非常不稳定,-O-O-键容易断裂生成烷氧自由基(RO·)[14]。RO·中的-C-C-键和-C-O-键容易发生β-均裂生成具有低阈值的挥发性风味化合物[11]。ROOH的分解能够促进自由基链式反应的传播[15-16]。最后自由基发生双分子反应生成非自由基产物或者通过过氧化剂的干预来终止自由基链式反应。脂质氧化反应形成醛类风味物质机制研究主要有两种方法:一种是在原位模型中分析反应底物、中间产物、最终产物的相关性,并通过离体模型进行验证,推测挥发性风味物质可能形成的路径[17-18];另一种是采用同位素示踪技术定向示踪解析同位素标记物的离子片段演变的分子路径,研究反应底物向最终产物转变的分子路径[19-20]。与同位素示踪技术相比,离体模型在研究风味物质形成机制中具有成本低和操作简便的优点。
目前,溶血磷脂氧化反应主要基于脂氧合酶的催化下发生[21-23],而在蒸制中的氧化反应未见文献报道。荸荠蒸制中风味物质形成机制研究鲜见报道。本研究模拟荸荠的pH、LPC(18:1)和LPE(18:1)含量及蒸制条件,构建了LPC(18:1)、LPE(18:1)和油酸离体模型,以过氧化值(POV)和油酸含量作为蒸制过程中溶血磷脂发生氧化、水解反应的重要指标[24],探讨荸荠蒸制中壬醛和癸醛的形成机制,以期为果蔬风味物质形成机制研究和风味品质调控提供科学参考。
1. 材料和方法
1.1 材料与仪器
荸荠 新鲜,大小均匀,购于广西贺州市市场;LPC(18:1)、油酸 色谱纯,Sigma Aldrich(上海)贸易有限公司;LPE(18:1) 色谱纯,上海阿拉丁生化技术有限公司;碘酸钾 分析纯,天津市光复精细化工研究所;浓盐酸、三氯甲烷 分析纯,四川西陇科学有限公司;碘化钾 分析纯,天津市致远化学试剂有限公司;冰醋酸 色谱纯,天津市科密欧化学试剂有限公司;甲醇 色谱纯,上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;磷酸二氢钠、磷酸氢二钠 分析纯,天津市致远化学试剂有限公司;2,4,6-三甲基吡啶(98.0%) 上海甄准生物科技有限公司。
UV-9000紫外分光光度计 上海元析仪器有限公司;LC-2030-C3D液相色谱 岛津企业管理(中国)有限公司;蒸发光检测器(ELSD) 上海通微分析技术有限公司;TRACE1300-ISQQD气相色谱-质谱联用仪、ZORBAXRX-SIL色谱柱(5 μm×4.6 mm×250 mm) 美国Agilent公司;TG-5MS型色谱柱 30 m×0.25 mm×0.25 μm,广州德祥科技有限公司;50/30 mm DVB/CAR/PDMS Gray固相微萃取针 Supelco股份有限公司;MR Hei-Tec(CN)磁力搅拌器 海道尔夫仪器设备(上海)有限公司;PTX-FA110S电子天平 美国康州HZ电子科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 离体模型构建
采用pH计检测新鲜荸荠的pH为5.36。采用HPLC/ELSD检测新鲜荸荠中LPC(18:1)和LPE(18:1)的浓度分别为0.05和0.18 mg/mL,检测的色谱条件:正相色谱柱,柱温25 ℃;流动相为甲醇:水:冰醋酸(100:10:0.1,V/V/V),然后用三乙胺调节pH为6.00,流速1.0 mL·min−1;ELSD漂移管温度35 ℃;空气流速3.00 L·min−1;进样量15 μL。以上述检测结果和荸荠蒸制条件作为构建离体模型的模拟条件。
LPC(18:1)离体模型的构建:称取一定量的LPC(18:1),用pH5.36的磷酸缓冲液溶解为0.05 mg/mL溶液,量取2 mL LPC溶液(1.9×10−7 mol)置于20 mL的顶空瓶中,加入1 μL的0.2 μL/mL 2,4,6-三甲基吡啶作内标,使用蒸锅和电磁炉进行蒸制,功率为1000 W,蒸制时间为5~40 min,蒸锅内的水沸腾后加入顶空瓶并计时,蒸制完即得实验样品。
LPE(18:1)离体模型的构建:称取一定量的LPE(18:1),用pH5.36的磷酸缓冲液溶解为0.18 mg/mL溶液,量取2 mL LPE溶液(7.5×10−7 mol)置于20 mL的顶空瓶中,其它条件与LPC(18:1)离体模型相同。
油酸离体模型的构建:称取一定量的油酸,用pH5.36的磷酸缓冲液溶解为0.18 mg/mL,量取2 mL油酸溶液(1.27×10−6 mol)置于20 mL的顶空瓶中,其它条件与LPC(18:1)离体模型相同。
1.2.2 离体模型中醛类物质的检测
参考李官丽等[1]的方法,采用SPME-GC-MS检测离体模型生成的醛类物质。
SPME条件:取1.2.1的样品2 mL,置于恒温加热磁力搅拌器水浴加热,用老化好的固相微萃取针在80 ℃下萃取40 min后进入GC解析1 min,每个样品做3次平行实验。
GC条件:TG-5MS型色谱柱,进样口温度250 ℃;载气为高纯度氦气,载气流速1.00 mL/min,分流方式采用不分流;程序升温为初始温度45 ℃,保持2 min,以4 ℃/min上升到250 ℃,保持3 min。
MS条件:电离方式为电子轰击(elector ionization,EI)模式,电离能量70 eV,离子源温度230 ℃,接口温度280 ℃,扫描方式为全扫描监测模式,质量扫描范围30~500 m/z。
定性分析:采用Xcalibar软件分析所检测到的挥发物,并与Library-Mainlib的标准谱库相匹配,匹配度大于800作为鉴定依据。
定量分析:参考程华峰等[25]方法,以2,4,6-三甲基吡啶为内标物,按式(1)计算各挥发物的含量。
化合物浓度(ng⋅mL−1)=(V1V2)×0.1842×1000 (1) 式中:V1:挥发物的峰面积;V2:内标物的峰面积;0.184:内标物含量,μg;离体模型的样品量为2 mL。
1.2.3 离体模型中POV的检测
参考张唯等[26]方法,采用紫外分光光度计检测离体模型的POV。
标准曲线:分别取氯仿:冰醋酸(2:3,V/V)7 mL、饱和碘化钾溶液0.2 mL、蒸馏水5 mL加入干燥好的25 mL具塞的比色管中,再分别加入浓度为100 μg·mL−1的碘标准溶液:0、0.04、0.2、0.36、0.44、0.52 mL,此量相当于每管含有I2:0、4、20、36、44、52 μg,然后加水至刻度,加塞摇匀,静置5~10 min,待分层后取上层清液2 mL,在4.5 cm的玻璃比色皿中,以含I2量为0 μg的样品作参比,于353 nm波长处测其吸光度。以吸光度A为纵坐标,对应的I2含量(μg)为横坐标,绘制标准曲线。
样品测定:取1.2.1的样品2 mL至25 mL干燥的具塞的比色管,加入5 mL氯仿-冰醋酸溶液、0.2 mL饱和碘化钾溶液,轻摇30 s混匀,置暗处3 min,然后加水至刻度,加塞,混匀,静置5 min,取上层清液2 mL,在4.5 cm的玻璃比色皿中以未加样品作空白,于353 nm波长处测定吸光度,每个样品做3次平行实验。以标准曲线计算出各个样品中I2的含量X1,而后按式(2)计算样品的过氧化值。
过氧化值POV(µg/µL)=X12×1000 (2) 式中:X1:样品中I2含量,μg;样品量为2 mL。
1.2.4 离体模型中油酸的检测
参考董建军等[27]方法,采用SPME-GC-MS检测离体模型生成的油酸。
样品甲酯化和SPME条件:取1.2.1制备样品2.5 mL,加入0.8 g NaCl、30 μL浓盐酸、0.6 mL甲醇,盖上瓶盖,轻轻摇晃后置于恒温加热磁力搅拌器水浴加热,用老化好的固相微萃取针在80 ℃下萃取60 min后进入GC解析5 min,每个样品做3次平行实验。GC-MS检测方法参照1.2.2,其中GC条件的程序升温改为:初始温度50 ℃,保持1 min,以5 ℃/min上升到250 ℃,保持9 min。定性方法参照1.2.2,定量方法采用面积归一化法计算。
1.3 数据处理
采用SPSS26.0软件中的单因素方差分析法(One-Way ANOVA)对试验数据进行处理与分析,采用Origin 2021、ChemDraw 20.0软件绘图,每个样品平行试验3次。
2. 结果和分析
2.1 离体模型中的醛类物质
由表1可知,LPC(18:1)和LPE(18:1)离体模型生成的醛类物质总含量均随着蒸制时间的增加而增加,LPC(18:1)离体模型在25 min时达到最大值,LPE(18:1)离体模型在35 min时达到最大值,壬醛和癸醛的含量远远高于其他醛类物质,相同蒸制时间生成壬醛的量大于癸醛,这与荸荠蒸煮加工产生的醛类风味物质及其变化规律、最佳蒸制时间[28]一致,说明本研究构建的两个离体模型是科学合理的,LPC(18:1)和LPE(18:1)均是醛类物质的反应底物。
表 1 离体模型主要醛类物质含量(ng/mL)Table 1. Contents of main aldehydes in vitro model (ng/mL)模拟体系 蒸制
时间(min)壬醛 癸醛 反式-2-癸烯醛 十一
烯醛2-十一烯醛 十二烯醛 十八烯醛 合计 LPC(18:1)离体模型 0 21.90 2.89 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 24.79 5 27.36 23.47 0.00 2.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 52.83 10 27.03 12.22 0.00 0.47 0.00 0.00 0.00 39.71 15 58.87 25.70 0.05 1.21 0.00 0.00 0.00 85.82 20 74.49 41.73 0.29 4.10 0.00 0.00 0.00 120.61 25 85.60 81.60 0.00 6.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 173.20 30 36.93 26.05 0.21 1.23 0.00 0.00 0.00 64.42 35 31.53 27.65 0.32 1.32 0.00 0.00 0.00 60.83 40 27.71 14.73 0.15 0.79 0.03 0.00 0.00 43.38 LPE(18:1)离体模型 0 40.10 6.22 3.90 0.70 0.00 0.28 0.00 55.46 5 49.38 21.10 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 70.48 10 55.84 12.27 0.72 1.23 0.00 0.00 0.00 70.06 15 65.35 27.27 0.56 1.90 1.12 0.00 0.00 96.11 20 69.55 61.23 1.56 2.98 0.31 1.80 0.34 137.46 25 101.13 66.65 0.96 4.27 0.18 1.12 1.80 175.94 30 128.38 64.52 2.16 4.14 0.35 1.53 1.88 205.11 35 117.95 99.10 2.18 5.93 0.49 1.52 0.00 229.49 40 101.62 77.31 1.79 3.99 0.42 0.00 1.48 188.39 油酸
离体体型0 21.32 8.87 4.26 0.81 6.18 0.00 0.00 41.44 5 27.82 15.03 6.58 1.16 8.78 0.00 0.00 59.37 10 41.21 28.65 10.91 1.31 13.45 0.42 0.00 95.96 15 38.59 25.72 16.09 3.40 17.13 0.00 0.00 100.93 20 40.11 26.52 14.59 2.48 20.08 1.98 1.52 107.27 25 26.28 17.20 7.70 6.95 11.42 0.00 0.00 69.55 30 41.28 20.61 19.18 1.86 24.52 1.03 0.82 109.30 35 42.54 30.90 20.81 3.78 31.30 0.00 0.00 129.32 40 60.07 24.42 10.72 3.06 6.20 0.00 0.00 104.46 由表1还可以看出,油酸离体模型在相同的蒸制条件下也可生成壬醛和癸醛等醛类物质,这与LEA[29]、ESTÉVEZ等[30]研究结果一致。壬醛和癸醛均为三个离体模型生成的主要醛类物质,因此本研究以壬醛和癸醛为代表探讨LPC(18:1)和LPE(18:1)生成醛类物质的机理。
同一蒸制条件下,LPE(18:1)离体模型生成的醛类物质总量均大于LPC(18:1)离体模型,这是因为LPE(18:1)的浓度大于LPC(18:1)。蒸制5~25 min LPC(18:1)离体模型生成癸醛的含量大于LPE(18:1)离体模型,而蒸制30~40 min LPE(18:1)离体模型生成癸醛的量大于LPC(18:1)离体模型,这可能是两个离体模型在不同时间生成癸醛的主要机制不同。未开始蒸制时,已有壬醛和癸醛生成,而且LPE(18:1)生成壬醛和癸醛的量大于LPC(18:1),说明LPC(18:1)和LPE(18:1)离体模型在80 ℃固相微萃取时均已发生反应,由于LPE(18:1)的浓度大于LPC(18:1),故LPE(18:1)离体模型的反应速率大于LPC(18:1)离体模型。LPC(18:1)离体模型蒸制25 min壬醛和癸醛达到最大值,LPE(18:1)离体模型蒸制30 min壬醛达到最大值、35 min癸醛达到最大值,说明25~35 min生成壬醛和癸醛的反应速率最大。随后壬醛和癸醛的含量缓慢下降,这可能是顶空瓶内的压强随着蒸制时间的增加而增加,导致顶空瓶内的挥发性物质少量损失。
2.2 离体模型的过氧化值
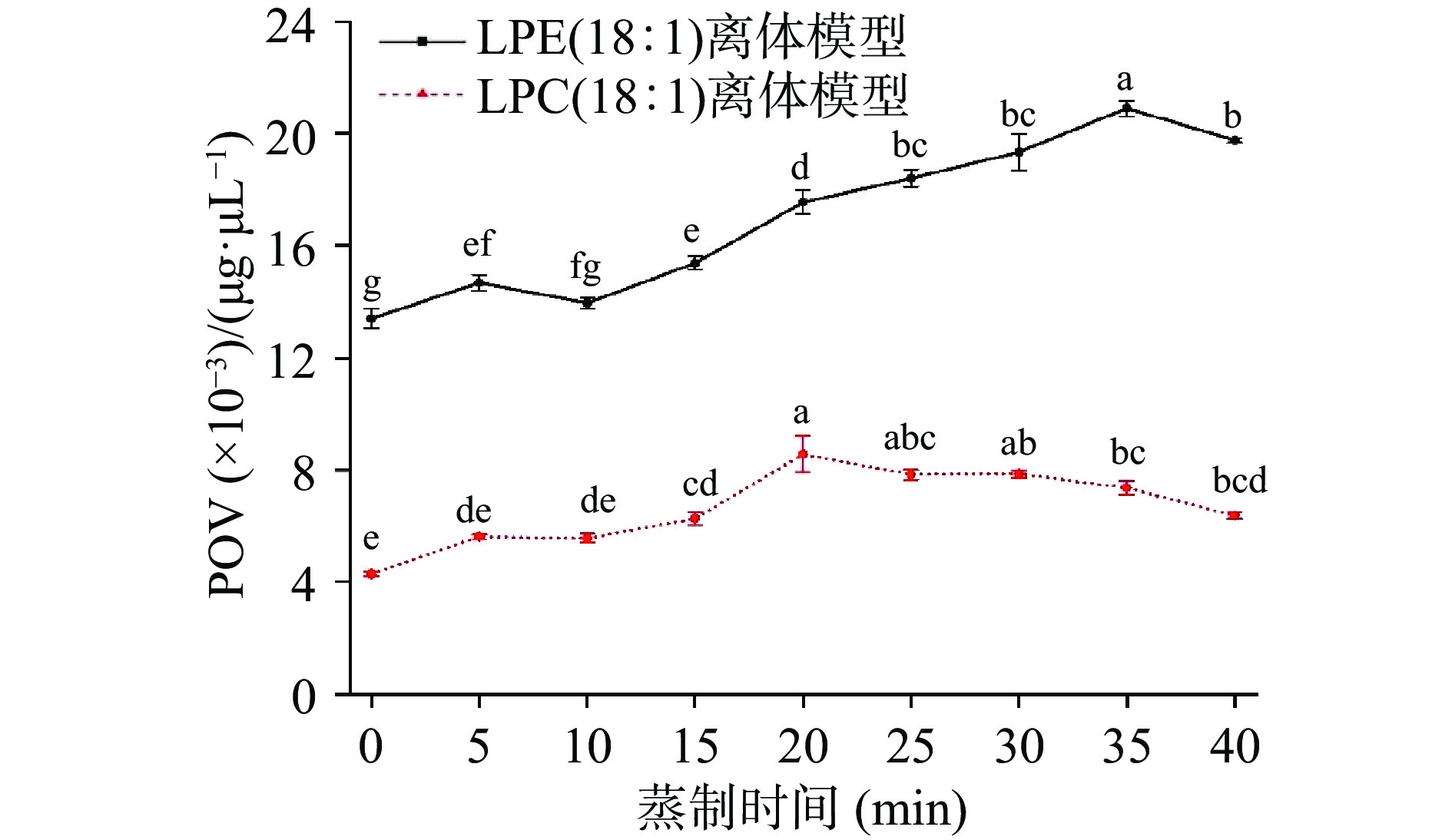
脂质发生氧化反应生成醛类物质,过氧化值(POV)可衡量脂质发生氧化反应的程度。如图1所示,两个离体模型在蒸制过程中POV总体呈上升趋势,在20~35 min时达到最大值,说明LPC(18:1)和LPE(18:1)离体模型均发生了氧化反应。LPE(18:1)离体模型的POV大于LPC(18:1)离体模型,这是由于LPE(18:1)的浓度大于LPC(18:1),使LPE(18:1)离体模型氧化反应速率大于LPC(18:1)离体模型,故LPE(18:1)离体模型生成的醛类物质总量大于LPC(18:1)离体模型。未开始蒸制时,两个离体模型的POV都大于0,说明LPE(18:1)和LPC(18:1)离体模型在常温时均已发生了氧化反应生成醛类物质。蒸制20~35 min时,两个离体模型的POV分别达到最大值,说明此时LPC(18:1)离体模型和LPE(18:1)离体模型的氧化反应速率达到最大,生成醛类物质的量最大。随后两个离体模型的POV缓慢下降,说明LPC(18:1)和LPE(18:1)离体模型生成醛类物质的量减少。上述分析结果与2.1一致。
![]() 图 1 蒸制时间对LPE(18:1)和LPC(18:1)离体模型POV的影响注:图中不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);图2同。Figure 1. Effect of steaming time on POV of LPE (18:1) and LPC (18:1) in vitro models
图 1 蒸制时间对LPE(18:1)和LPC(18:1)离体模型POV的影响注:图中不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);图2同。Figure 1. Effect of steaming time on POV of LPE (18:1) and LPC (18:1) in vitro models2.3 离体模型中的油酸
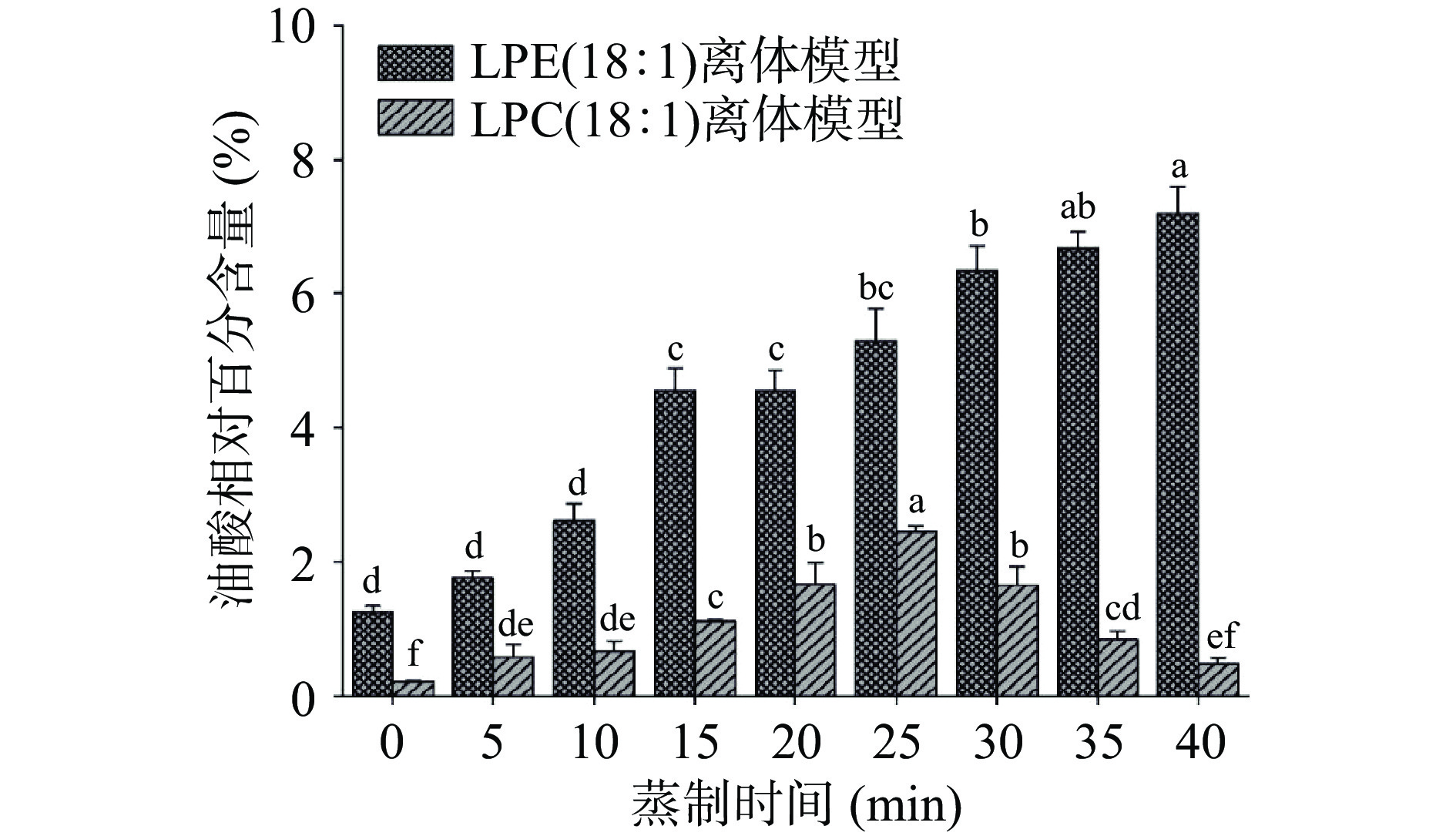
溶血磷脂是磷脂的单酰基形式,在水和热存在的情况下,均可发生水解反应,水解产物为脂肪酸,脂肪酸类型取决于溶血磷脂侧链所连接的脂肪酸。本研究中所用的LPC(18:1)和LPE(18:1)的不饱和酰基链均是油酸,故其水解产物为油酸,而油酸可发生脂质氧化反应生成壬醛和癸醛等醛类风味物质[27]。由图2可知,未开始蒸制时两个离体模型均检测到油酸,而且LPE(18:1)离体模型中的油酸含量大于LPC(18:1)离体模型,说明两个离体模型在80 ℃固相微萃取时即发生了水解反应,由于LPE(18:1)的浓度大于LPC(18:1),LPE(18:1)的水解反应速率大于LPC(18:1),故LPE(18:1)离体模型生成的油酸含量大于LPC(18:1)离体模型。LPE(18:1)离体模型中,油酸含量从未开始蒸制时的1.26%上升到40 min时的7.20%,说明LPE(18:1)水解生成油酸的速率大于油酸氧化生成醛类物质的速率。LPC(18:1)离体模型中,油酸含量从未开始蒸制时的0.22%上升到25 min时的2.45%,随后开始下降,直至40 min时的0.48%,说明0~25 min LPC(18:1)水解生成油酸的速率大于油酸氧化生成醛类物质的速率,25~40 min油酸氧化生成醛类物质的速率大于LPC(18:1)水解生成油酸的速率。
2.4 脂质氧化和水解与生成壬醛和癸醛的相关性分析
由表2可知,壬醛和癸醛与POV呈正相关(LPC(18:1)离体模型)或显著正相关(LPE(18:1)离体模型)(P<0.05),说明氧化反应对壬醛和癸醛生成有影响或显著影响;壬醛和癸醛与油酸呈显著正相关(P<0.05),说明油酸对壬醛和癸醛生成有显著影响;油酸与POV呈显著正相关(P<0.05),说明油酸发生了氧化反应,对POV有显著贡献。
表 2 脂质氧化和水解与生成壬醛和癸醛的相关性分析结果Table 2. Correlation analysis results of lipid oxidation and hydrolysis with nonal and decanal formation离体模型 POV 油酸 壬醛 LPC(18:1) 0.58 0.76* LPE(18:1) 0.88* 0.91* 癸醛 LPC(18:1) 0.56 0.68* LPE(18:1) 0.75* 0.76* 油酸 LPC(18:1) 0.85* 1* LPE(18:1) 0.91* 1* 注:*:在0.05水平(双侧上)显著相关。 从上述分析可知,壬醛和癸醛可能由LPC(18:1)、LPE(18:1)发生氧化反应生成,也可能由LPC(18:1)、LPE(18:1)发生水解反应生成的油酸再发生氧化反应生成。
2.5 壬醛和癸醛主要形成途径分析
比较相同物质的量的LPC(18:1)、LPE(18:1)和油酸离体模型系产生壬醛和癸醛的量,可以推测LPC(18:1)和LPE(18:1)离体模型产生壬醛和癸醛的主要途径。离体模型中,LPC(18:1)和LPE(18:1)的物质的量分别为:1.9×10−7和7.5×10−7 mol。假设LPC(18:1)和LPE(18:1)全部水解生成油酸,则两个离体模型中油酸的物质的量应分别为:1.9×10−7和7.5×10−7 mol。根据表1油酸(1.27×10−6 mol)离体模型生成壬醛和癸醛的情况,1.9×10−7和7.5×10−7 mol油酸在蒸制过程生成壬醛和癸醛的情况见表3。
表 3 与LPC(18:1)和LPE(18:1)相同物质的量的油酸蒸制过程生成壬醛和癸醛的含量(ng/mL)Table 3. Content of nonaldehyde and decanal generated during oleic acid evaporation with the same amount of substances as LPC (18:1) and LPE (18:1) (ng/mL)油酸的物质的量(mol) 蒸制时间(min) 壬醛 癸醛 1.9×10−7 0 3.19 1.33 5 4.16 2.25 10 6.17 4.29 15 5.77 3.85 20 6.00 3.97 25 3.93 2.57 30 6.18 3.08 35 6.36 4.62 40 8.99 3.65 7.5×10−7 0 12.59 5.24 5 16.43 8.88 10 24.34 16.92 15 22.79 15.19 20 23.69 15.66 25 15.52 10.16 30 24.38 12.17 35 25.12 18.25 40 35.47 14.42 比较表1和表3可知,LPC(18:1)和LPE(18:1)氧化生成壬醛和癸醛的含量,远远高于相同物质的量的油酸氧化生成壬醛和癸醛的含量,其差值结果如表4所示。实际上,蒸制过程中LPC(18:1)和LPE(18:1)并没有完全水解生成油酸,LPC(18:1)和LPE(18:1)水解生成的油酸也没有全部氧化生成壬醛和癸醛,故由LPC(18:1)和LPE(18:1)水解生成的油酸再氧化生成的壬醛和癸醛的含量很少。由此可推测,LPC(18:1)和LPE(18:1)模拟体系中生成壬醛和癸醛的主要途径是LPC(18:1)和LPE(18:1)的氧化反应。
表 4 相同物质的量的LPC(18:1)、LPE(18:1)和油酸模拟体系生成壬醛和癸醛的差值(ng/mL)Table 4. Difference between nonanal and decanal generated by LPC(18:1), LPE (18:1) and oleic acid simulation system with the same amount of substance (ng/mL)离体模型(mol) 蒸制时间(min) 壬醛 癸醛 LPC(18:1)
1.9×10−70 18.71 1.56 5 23.20 21.22 10 20.86 7.93 15 53.09 21.85 20 68.49 37.76 25 81.67 79.03 30 30.76 22.96 35 25.16 23.03 40 18.72 11.07 LPE(18:1)
7.5×10−70 27.52 0.98 5 32.95 12.22 10 31.50 -4.65 15 42.56 12.08 20 45.86 45.56 25 85.61 56.49 30 104.00 52.35 35 92.83 80.86 40 66.15 62.89 2.6 壬醛和癸醛的可能形成机制分析
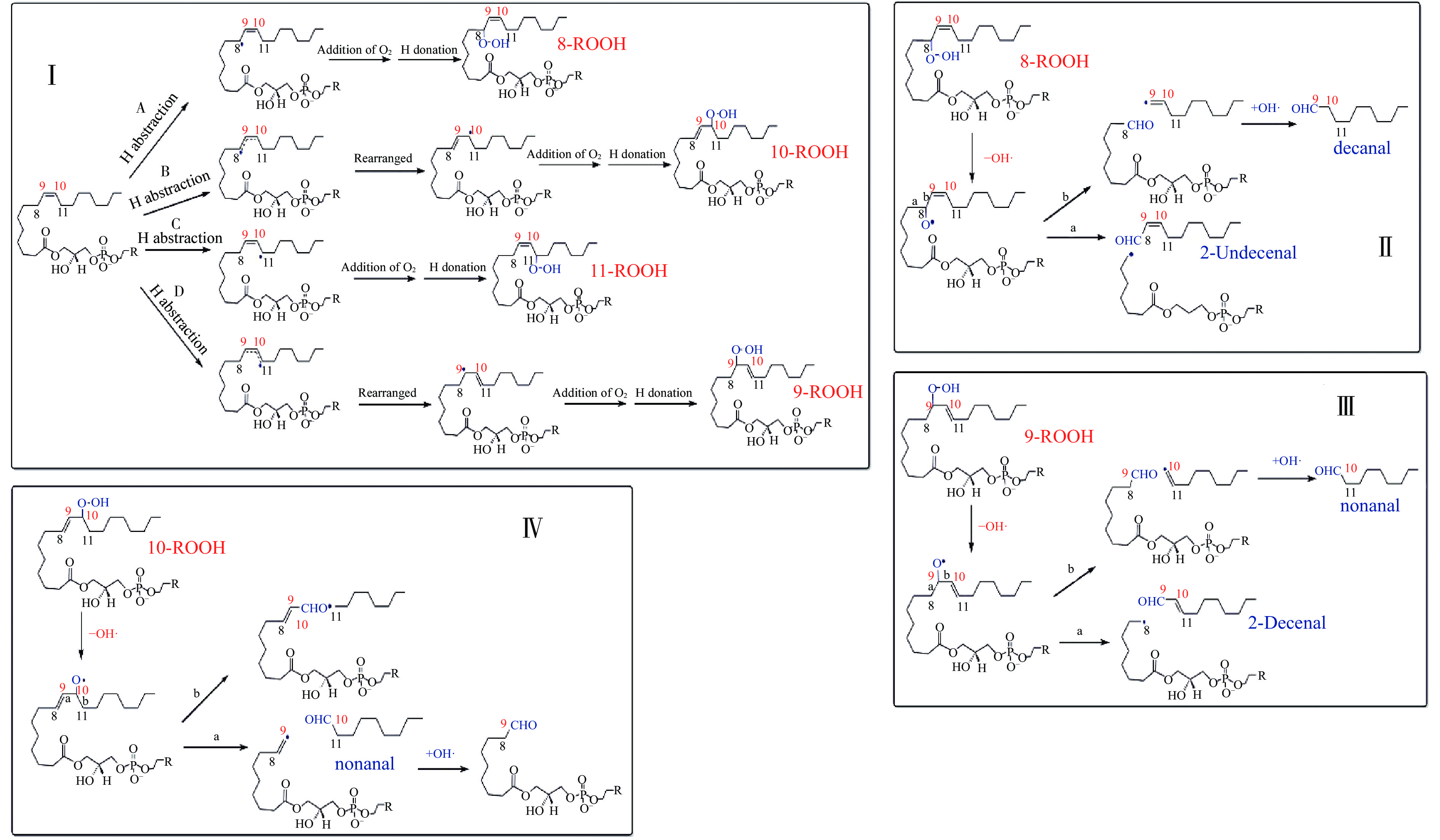
基于磷脂自由基链式反应原理[31-32],可推测出溶血磷脂(C18:1)生成壬醛和癸醛的可能氧化机制(图3)。酯中的多不饱和脂肪酸(PUFA)可以与游离的多不饱和脂肪酸(PUFA)以几乎相同的方式被氧化[31,33-34],故溶血磷脂(C18:1)的主要氧化修饰目标为侧链的油酸链。氧化初始步骤是,溶血磷脂中的不饱和酰基链上紧靠双键的C8和C11在高温下表现出低键能,极易失去H,形成烷基自由基(R·)。R·会与O2快速反应形成过氧自由基(ROO·),后者从模拟体系中的另一个溶血磷脂分子的不饱和酰基链上夺取H形成溶血磷脂氢过氧化物(ROOH)。ROOH的形成和裂解可分为如下两种情况:
第1种情况是R·未经电子重排,直接与O2和其它溶血磷脂分子的H反应形成8-ROOH和11-ROOH,如图3ⅠAB所示。C途径中11-ROOH生成的醛类物质是辛醛,而两个模拟体系和荸荠蒸制过程均未检出辛醛,故可排除此途径。第二种情况是R·经电子重排,再与O2和其它溶血磷脂分子的H反应形成9-ROOH和10-ROOH,如图3ⅠBD所示。8-ROOH、9-ROOH和10-ROOH等在高温下均不稳定,其-O-O-易断裂生成RO·[14],RO·中的-C-C-键可发生β-裂解生成挥发性化合物[11]。如图3所示,8-RO·的C8-C9键断裂生成癸醛,C7-C8键断裂生成2-十一烯醛(图3,Ⅱ);9-RO·的C8-C9键断裂生成2-癸烯醛,C9-C10键断裂生成壬醛(图3,Ⅲ);10-RO·的C9-C10键断裂生成壬醛(图3,Ⅳ)。
从上述分析可知,在蒸制过程(0~40 min)中LPC和LPE模拟体系中壬醛>癸醛(表1)的原因是,壬醛的形成途径有2条:9-ROOH、10-ROOH的形成及它们的C9-C10键断裂(图3,ⅠBD),而癸醛的形成途径只有1条:8-ROOH的形成及其C8-C9键断裂(图3,ⅠA)。蒸制25~35 min生成壬醛和癸醛的量达到最大值,说明增加蒸制时间可以促进8-ROOH、9-ROOH、10-ROOH的形成和β-裂解。
3. 结论
LPC(18:1)、LPE(18:1)和油酸三个离体模型实验结果表明,溶血磷脂氧化反应可以在蒸制条件下发生。LPC(18:1)和LPE(18:1)在蒸制中发生氧化反应生成壬醛和癸醛,其形成机制为:首先是不饱和酰基链中紧靠双键的C8和C11失去H形成R·;其次是R·直接与O2和其它分子的H反应形成8-ROOH,或者发生电子重排形成新的双键生成新的R·后再与O2和其它分子的H反应形成9-ROOH、10-ROOH;最后氢过氧化物在高温下裂解生成醛类物质,其中8-ROOH裂解生成癸醛,9-ROOH和10-ROOH裂解均生成壬醛。增加蒸制时间可以促进8-ROOH、9-ROOH、10-ROOH的形成和裂解,故生成壬醛和癸醛的量随着蒸制时间的增加而增加。壬醛的生成途径有2条,而癸醛的生成途径只有1条,故壬醛的含量大于癸醛。以上结论是由模拟荸荠的pH、LPC(18:1)和LPE(18:1)含量及荸荠蒸制加工条件构建的离体模型得到的,可用于解释荸荠蒸制过程LPC(18:1)和LPE(18:1)形成壬醛和癸醛的机制,调控荸荠蒸制过程的风味品质,为果蔬风味物质形成机制研究和风味品质调控提供科学参考。
-
图 1 蒸制时间对LPE(18:1)和LPC(18:1)离体模型POV的影响
注:图中不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);图2同。
Figure 1. Effect of steaming time on POV of LPE (18:1) and LPC (18:1) in vitro models
表 1 离体模型主要醛类物质含量(ng/mL)
Table 1 Contents of main aldehydes in vitro model (ng/mL)
模拟体系 蒸制
时间(min)壬醛 癸醛 反式-2-癸烯醛 十一
烯醛2-十一烯醛 十二烯醛 十八烯醛 合计 LPC(18:1)离体模型 0 21.90 2.89 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 24.79 5 27.36 23.47 0.00 2.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 52.83 10 27.03 12.22 0.00 0.47 0.00 0.00 0.00 39.71 15 58.87 25.70 0.05 1.21 0.00 0.00 0.00 85.82 20 74.49 41.73 0.29 4.10 0.00 0.00 0.00 120.61 25 85.60 81.60 0.00 6.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 173.20 30 36.93 26.05 0.21 1.23 0.00 0.00 0.00 64.42 35 31.53 27.65 0.32 1.32 0.00 0.00 0.00 60.83 40 27.71 14.73 0.15 0.79 0.03 0.00 0.00 43.38 LPE(18:1)离体模型 0 40.10 6.22 3.90 0.70 0.00 0.28 0.00 55.46 5 49.38 21.10 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 70.48 10 55.84 12.27 0.72 1.23 0.00 0.00 0.00 70.06 15 65.35 27.27 0.56 1.90 1.12 0.00 0.00 96.11 20 69.55 61.23 1.56 2.98 0.31 1.80 0.34 137.46 25 101.13 66.65 0.96 4.27 0.18 1.12 1.80 175.94 30 128.38 64.52 2.16 4.14 0.35 1.53 1.88 205.11 35 117.95 99.10 2.18 5.93 0.49 1.52 0.00 229.49 40 101.62 77.31 1.79 3.99 0.42 0.00 1.48 188.39 油酸
离体体型0 21.32 8.87 4.26 0.81 6.18 0.00 0.00 41.44 5 27.82 15.03 6.58 1.16 8.78 0.00 0.00 59.37 10 41.21 28.65 10.91 1.31 13.45 0.42 0.00 95.96 15 38.59 25.72 16.09 3.40 17.13 0.00 0.00 100.93 20 40.11 26.52 14.59 2.48 20.08 1.98 1.52 107.27 25 26.28 17.20 7.70 6.95 11.42 0.00 0.00 69.55 30 41.28 20.61 19.18 1.86 24.52 1.03 0.82 109.30 35 42.54 30.90 20.81 3.78 31.30 0.00 0.00 129.32 40 60.07 24.42 10.72 3.06 6.20 0.00 0.00 104.46 表 2 脂质氧化和水解与生成壬醛和癸醛的相关性分析结果
Table 2 Correlation analysis results of lipid oxidation and hydrolysis with nonal and decanal formation
离体模型 POV 油酸 壬醛 LPC(18:1) 0.58 0.76* LPE(18:1) 0.88* 0.91* 癸醛 LPC(18:1) 0.56 0.68* LPE(18:1) 0.75* 0.76* 油酸 LPC(18:1) 0.85* 1* LPE(18:1) 0.91* 1* 注:*:在0.05水平(双侧上)显著相关。 表 3 与LPC(18:1)和LPE(18:1)相同物质的量的油酸蒸制过程生成壬醛和癸醛的含量(ng/mL)
Table 3 Content of nonaldehyde and decanal generated during oleic acid evaporation with the same amount of substances as LPC (18:1) and LPE (18:1) (ng/mL)
油酸的物质的量(mol) 蒸制时间(min) 壬醛 癸醛 1.9×10−7 0 3.19 1.33 5 4.16 2.25 10 6.17 4.29 15 5.77 3.85 20 6.00 3.97 25 3.93 2.57 30 6.18 3.08 35 6.36 4.62 40 8.99 3.65 7.5×10−7 0 12.59 5.24 5 16.43 8.88 10 24.34 16.92 15 22.79 15.19 20 23.69 15.66 25 15.52 10.16 30 24.38 12.17 35 25.12 18.25 40 35.47 14.42 表 4 相同物质的量的LPC(18:1)、LPE(18:1)和油酸模拟体系生成壬醛和癸醛的差值(ng/mL)
Table 4 Difference between nonanal and decanal generated by LPC(18:1), LPE (18:1) and oleic acid simulation system with the same amount of substance (ng/mL)
离体模型(mol) 蒸制时间(min) 壬醛 癸醛 LPC(18:1)
1.9×10−70 18.71 1.56 5 23.20 21.22 10 20.86 7.93 15 53.09 21.85 20 68.49 37.76 25 81.67 79.03 30 30.76 22.96 35 25.16 23.03 40 18.72 11.07 LPE(18:1)
7.5×10−70 27.52 0.98 5 32.95 12.22 10 31.50 -4.65 15 42.56 12.08 20 45.86 45.56 25 85.61 56.49 30 104.00 52.35 35 92.83 80.86 40 66.15 62.89 -
[1] 李官丽, 伍淑婕, 罗秀娟, 等. 基于SPME-GC-MS萃取荸荠挥发性风味物质研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2022,43(14):70−78. [LI G L, WU S J, LUO X J, et al. Extraction of volatile flavor substances from Chinese water chestnut based on SPME-GC-MS[J]. Food Reserch and Development,2022,43(14):70−78. LI G L, WU S J, LUO X J, et al. Extraction of volatile flavor substances from Chinese water chestnut based on SPME-GC-MS[J]. Food Reserch and Development. 2022, 43(14): 70-78.
[2] ANTEQUERA T, LÓPEZ-BOTE C J, CÓRDOBA J J, et al. Lipid oxidative changes in the processing of Iberian pig hams[J]. Food Chemistry,1992,45(2):105−110. doi: 10.1016/0308-8146(92)90018-W
[3] BRUNA J M , ORDONEZ J A , FERNANDEZ M, et al. Microbial and physico-chemical changes during the ripening of dry fermented sausages superficially inoculated with or having added an intracellular cell-free extract of Penicillium aurantiogriseum[J]. Meat Science,2001,59(1):87−96. doi: 10.1016/S0309-1740(01)00057-2
[4] ANDRES A I, CAVA R, VENTANAS J, et al. Lipid oxidative changes throughout the ripening of dry-cured Iberian hams with different salt contents and processing conditions[J]. Food Chemistry,2004,84(3):375−381. doi: 10.1016/S0308-8146(03)00243-7
[5] USDA. National Nutrient Database for Standard [EB/OL]. https://ndb.nal.usda.gov/ndb/foods/show/302149 (most recent access April 12, 2021)
[6] PIKUL J, LESZCZYNSKI D E, KUMMEROW F A. Relative role of phospholipids, triacylglycerols, and cholesterol esters on malonaldehyde formation in fat extracted from chicken meat[J]. Journal of Food Science,1984,49(3):704−708. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.1984.tb13192.x
[7] SASAKI K, MITSUMOTO M, KAWABATA K. Relationship between lipid peroxidation and fat content in Japanese Black beef longissimus muscle during storage[J]. Meat Science,2001,59(4):407−410. doi: 10.1016/S0309-1740(01)00093-6
[8] HUAN Y J, ZHOU G H, ZHAO G M, et al. Changes in flavor compounds of dry-cured Chinese Jinhua ham during processing[J]. Meat Science,2005,71(2):291−299. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2005.03.025
[9] PENG C Y, LAN C H, LIN P C, et al. Effects of cooking method, cooking oil, and food type on aldehyde emissions in cooking oil fumes[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2017,324:160−167. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.10.045
[10] ZHANG J H, CAO J, PEI Z S, et al. Volatile flavour components and the mechanisms underlying their production in golden pompano (Trachinotus blochii) fillets subjected to different drying methods: A comparative study using an electronic nose, an electronic tongue and SDE-GC-MS[J]. Food Research International,2019,123:217−225. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.04.069
[11] PORTER N A. Mechanisms for the autoxidation of polyunsaturated lipids[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research,1986,19(9):262−268. doi: 10.1021/ar00129a001
[12] PAQUETTE G, KUPRANYCZ D B, VAN DE VOORT F R. The mechanisms of lipid autoxidation I. Primary oxidation products[J]. Canadian Institute of Food Science and Technology Journal,1985,18(2):112−118. doi: 10.1016/S0315-5463(85)71767-1
[13] AHMED M, PICKOVA J, AHMAD T, et al. Oxidation of lipids in foods[J]. Sarhad Journal of Agriculture,2016,32(3):230−238. doi: 10.17582/journal.sja/2016.32.3.230.238
[14] SILVAGNI A, FRANCO L, BAGNO A, et al. Thermo-induced lipid oxidation of a culinary oil: The effect of materials used in common food processing on the evolution of oxidised species[J]. Food Chemistry,2012,133(3):754−759. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.01.088
[15] FRANKEL E N. Recent advances in lipid oxidation[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,1991,54(4):495−511. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.2740540402
[16] SCHAICH K M. Lipid oxidation: Theoretical aspects[J]. Bailey's Industrial Oil and Fat Products,2005,6(6):269−355.
[17] IGENE J O, PEARSON A M, DUGAN L R, et al. Role of triglycerides and phospholipids on development of rancidity in model meat systems during frozen storage[J]. Food Chemistry,1980,5(4):263−276. doi: 10.1016/0308-8146(80)90048-5
[18] ZAMORA R, HIDALGO F J. Contribution of lipid oxidation products to acrylamide formation in model systems[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2008,56(15):6075−6080. doi: 10.1021/jf073047d
[19] 刘欢. 北京烤鸭关键挥发性风味物质鉴别及其形成机制研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2020 LIU H. Identification of key volatile flavor substances of Peking duck and their formation mechanism[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2022.
[20] 黄淑霞. 反-2-壬烯醛对啤酒新鲜度的影响与调控机制研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2017 HUANG S X. Effect of trans-2-nonenal on beer freshness and its regulation mechanism [D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2017.
[21] HUANG L S, KANG J S, KIN M R, et al. Oxygenation of arachidonoyl lysophospholipids by lipoxygenases from soybean, porcine leukocyte, or rabbit reticulocyte[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2008,56(4):1224−1232. doi: 10.1021/jf073016i
[22] HUANG L S, KIM M R, SOK D E. Regulation of lipoxygenase activity by polyunsaturated lysophosphatidylcholines or their oxygenation derivatives[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2008,56(17):7808−7814. doi: 10.1021/jf801082x
[23] HUANG L S, KIM M R, SOK D E. Linoleoyl lysophosphatidylcholine is an efficient substrate for soybean lipoxygenase-1[J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics,2006,455(2):119−126. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2006.09.015
[24] CAO J, JIANG X, CHEN Q Y, et al. Oxidative stabilities of olive and camellia oils: Possible mechanism of aldehydes formation in oleic acid triglyceride at high temperature[J]. LWT,2020,118(C):108858.
[25] 程华峰, 林琳, 葛孟甜, 等. 3种生态环境中华绒螯蟹肉挥发性风味特征的比较[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(23):247−256. [CHENG H F, LIN L, GE M T, et al. Comparison of volatile flavor characteristics of Chinese mitten crab meat in three ecological environments[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2019,45(23):247−256. CHENG H F, LIN L, GE M T, et al. Comparison of volatile flavor characteristics of Chinese mitten crab meat in three ecological environments[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2019, 45(23): 247-256.
[26] 张唯, 高斌富, 常新, 等. 紫外法与碘量法测定食用植物油中过氧化值的比较[J]. 中国油脂,1993(5):37−39. [ZHANG W, GAO B F, CHANG X, et al. Comparison of ultraviolet and iodometric methods for the determination of peroxide in edible vegetable oils[J]. China Oils Fats,1993(5):37−39. ZHANG W, GAO B F, CHANG X, et al. Comparison of ultraviolet and iodometric methods for the determination of peroxide in edible vegetable oils[J]. China Oils Fats. 1993(5): 37-39.
[27] 青岛啤酒股份有限公司. 瓶内甲酯化-顶空固相微萃取-气相色谱质谱联用测定啤酒中游离脂肪酸的检测方法: 中国, 102539609B[P]. 2014-07-16 Tsingtao Brewery Company Limited. Determination of free fatty acids in beer by in-bottle methylation with headspace solid-phase microextraction coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry: China, 102539609B[P]. 2014-07-16.
[28] 李官丽, 聂辉, 苏可珍, 等. 基于感官评价和电子鼻分析不同蒸煮时间荸荠挥发性风味物质[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(15):1−7,14. [LI G L, NIE H, SU K Z, et al. Analysis of volatile flavor compounds in Water chestnut with different steaming and cooking time based on sensory evaluation and electronic nose[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(15):1−7,14. LI G L, NIE H, SU K Z, et al. Analysis of volatile flavor compounds in Water chestnut with different steaming and cooking time based on sensory evaluation and electronic nose. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(15): 1-7.
[29] LEA C H. Recent developments in the study of oxidative deterioration of lipids[J]. Chem. Ind. (London),1953,49:1303−1309.
[30] ESTÉVEZ M, MORCUENDE D, VENTANAS S, et al. Analysis of volatiles in meat from Iberian pigs and lean pigs after refrigeration and cooking by using SPME-GC-MS[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2003,51(11):3429−3435. doi: 10.1021/jf026218h
[31] REIS A, SPICKETT C M. Chemistry of phospholipid oxidation[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Biomembranes,2012,1818(10):2374−2387. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2012.02.002
[32] PORTER N A, CALDWELL S E, MILLS K A. Mechanisms of free radical oxidation of unsaturated lipids[J]. Lipids,1995,30(4):277−290. doi: 10.1007/BF02536034
[33] BALAKRISHNA M, MA J, LIU T, et al. Hydrolysis of oxidized phosphatidylcholines by crude enzymes from chicken, pork and beef muscles[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,313:125956. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125956
[34] LU F S H, NIELSEN N S, BARON C P, et al. Marine phospholipids: The current understanding of their oxidation mechanisms and potential uses for food fortification[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2017,57(10):2057−2070. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2014.925422
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 唐雪梅,吴伟,朱武林. 离子色谱法在药品检验中的应用. 品牌与标准化. 2024(04): 28-30 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 罗景阳,李娇,关健,李巧莲,王岩松,袁帅. QuEChERS-高效液相色谱三重四级杆线性离子阱串联质谱法测定蔬菜中34种杀虫剂残留. 食品工业科技. 2024(17): 302-315 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 姚奕然,蒋凡,刘欢欢,周谧. 基于UPLC-MRM-IDA-EPI法高通量筛查保健食品中60种非法添加的化学药物. 中南药学. 2024(09): 2438-2446 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



