Preparation Technology and Antioxidant Activities of Different Molecular Weight Macadamia Nut Polypeptides
-
摘要: 采用不同蛋白酶水解澳洲坚果粕制备多肽,以ABTS+自由基清除率为评价指标,筛选制备抗氧化多肽适宜的蛋白酶。利用DA201-C大孔树脂纯化、超滤膜逐级分离,获得不同分子量澳洲坚果多肽(MNAP-1、MNAP-2、MNAP-3、MNAP-4)组分,并以谷胱甘肽为对照,研究了其对DPPH、羟基、ABTS+自由基的清除能力及还原能力。结果表明:制备澳洲坚果抗氧化多肽的适宜蛋白酶为复配蛋白酶,相同浓度下其对ABTS+自由基清除能力优于中性蛋白酶、酸性蛋白酶、碱性蛋白酶、木瓜蛋白酶与菠萝蛋白酶。不同分子量澳洲坚果多肽呈现不同的抗氧化效果,其对DPPH、ABTS+自由基具有较强的清除作用,具有一定的羟基自由基清除能力和还原能力。其中,MNAP-4(分子量小于1000 Da)的抗氧化活性最好,其对DPPH、ABTS+、羟基自由基清除能力及还原能力的半抑制浓度(half maximal inhibitory concentration,IC50)分别为0.36、6.75、0.08、3.19 mg/mL,低于其他分子量多肽。相关性分析得出不同分子量澳洲坚果多肽与其清除DPPH自由基(r=0.947,P<0.01)、羟基自由基(r=0.964,P<0.01)、ABTS+自由基(r=0.948,P<0.01)及还原能力(r=0.856,P<0.01)之间存在极显著相关。澳洲坚果复配蛋白酶酶解产物含有抗氧化活性较好的肽类,研究结果可为其抗氧化肽的制备与应用提供一定的理论依据。Abstract: Macadamia nut polypeptides were prepared by enzymatic hydrolysis of macadamia nut meal, and suitable proteases for the preparation of macadamia antioxidant polypeptides were screened with ABTS+ radical scavenging effects as evaluation indicators. Four constituents (MNAP-1, MNAP-2, MNAP-3, MNAP-4) were obtained by DA201-C macroporous resin and dialysis technology. The scavenging capacity against 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl radical (DPPH·), hydroxyl radical and 2,2’-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonate radicals) radical (ABTS+·), and reducing power were investigated by comparing with glutathione as controls. The results showed that the suitable protease was complex protease for the preparation of macadamia antioxidant polypeptides, which was better than neutral protease, acid protease, alkaline protease, papain and bromelain at the same concentration. Antioxidant activities of different molecular weight macadamia nut polypeptides were different, which all had strong scavenging capacity against DPPH and ABTS+ radicals, and also had certain scavenging capacity against hydroxyl radical and reducing power. MNAP-4 (molecular weight less than 1000 Da) had the strongest scavenging capacity against DPPH, ABTS+ and hydroxyl radicals and the highest reducing power with half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 0.36, 6.75, 0.08 and 3.19 mg/mL, respectively, which was lower than other molecular weight polypeptides. Correlation analysis showed different molecular weight macadamia nut polypeptides had good correlations with their DPPH, hydroxyl and ABTS+ radicals scavenging capacity and reducing power with r values of 0.947, 0.964, 0.948 and 0.856 (P<0.01), respectively. The complex protease hydrolysates from macadamia nut meal contained good antioxidant activity polypeptides, which could provide a theoretical basis for the preparation and application of antioxidant peptides.
-
Keywords:
- macadamia nut /
- peptides /
- different molecular weight /
- preparation /
- antioxidant activity
-
澳洲坚果(Macadamia SPP.)为山龙眼科澳洲坚果属的常绿乔木果树,原产于澳大利亚昆士兰东南部和新南威尔士东北部沿岸的亚热带雨林地区,别称夏威夷果、澳洲核桃等[1]。澳洲坚果果仁蛋白质丰富,含量在8%~20%之间[2],澳洲坚果果仁中氨基酸的总含量平均为81.82 mg/g,种类齐全,共富含17种氨基酸,其中包括7种人体必需氨基酸[3-4]。近年来,澳洲坚果产业发展迅猛,2020年末我国澳洲坚果种植面积为26.61万hm2,云南省澳洲坚果种植面积为23.53万hm2,含水量10%的壳果产量为7.50万吨[5],澳洲坚果油将成为主要的产品形式[6],榨油后的副产物澳洲坚果粕营养价值较高,其含有蛋白质32.25%、氨基酸25.05%、脂肪21.11%、膳食纤维20.98%、碳水化合物17.92%、总糖14.50%、还原糖2.80%、粗多糖0.90%[7]。
蛋白质经蛋白酶水解可获得许多具有生物功能的生物活性肽,具有降血压、抗氧化和抑菌等生理活性[4,8-9]。不同蛋白酶作用肽键位点的不同,通过酶解得到的肽段长度、氨基酸序列不同,致使多肽的分子量、疏水性不同[10-11],且分子量、疏水性也会影响多肽的生物活性[12-13],因此,选择适宜的酶是制备高活性抗氧化肽的前提条件。蛋白质酶解液中含有多糖、游离氨基酸、无机盐、不同分子质量的肽、蛋白质等,均会影响多肽的生物活性,因此需要对酶解液进行分离纯化,文献研究表明,超滤、纳滤、大孔树脂吸附等方法可以有效的对多肽进行分离纯化[14-16]。目前,利用生物酶法制备澳洲坚果多肽,研究其抑菌活性、抗氧化活性的研究已有少量报道[17],但有关不同分子量澳洲坚果多肽组分的分离纯化工艺及其抗氧化活性还未见报道。为此,本研究采用了不同蛋白酶水解澳洲坚果粕制备多肽,以ABTS+自由基的清除能力为指标筛选适宜的蛋白酶,利用大孔树脂吸附、超滤分级技术进行分离纯化,通过测定不同分子量澳洲坚果多肽对DPPH、羟基、ABTS+自由基清除能力及还原能力评价其抗氧化能力,旨在筛选得到抗氧化活性较高的多肽组分,为澳洲坚果多肽的深度研究及产品的开发利用提供数据支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
液压压榨澳洲坚果粕 西双版纳云垦澳洲坚果科技开发有限公司;酸性蛋白酶(20万U/g)、中性蛋白酶(30万U/g)、碱性蛋白酶(20万U/g)、木瓜蛋白酶(20万U/g)、菠萝蛋白酶(20万U/g)、复配蛋白酶(20万U/g) 南宁东恒华道生物科技有限责任公司;DA201-C大孔树脂 郑州和成新材料科技有限公司;还原型谷胱甘肽 上海金穗生物科技有限公司;1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(DPPH)、2,2’-联氮双(3-乙基苯并噻唑啉-6-磺酸)二胺盐(ABTS) 美国Sigma公司;氢氧化钠、三氯乙酸、酒石酸钾钠、苯酚、硫酸等试剂 国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
RV10型旋转蒸发仪 艾卡仪器设备有限公司;ME204E型电子分析天平 梅特勒-托利多仪器有限公司;DLSB-5L型低温冷却液循环泵 巩义市予华仪器有限责任公司;HHS型电热恒温水浴锅 上海博迅实业有限公司;UV754N型紫外可见分光光度计 上海精风仪器有限公司;TGL-16C型离心机 上海安亭科学仪器厂;FiveEasy型pH计、HS7型磁力搅拌器、FiveEasy型电导仪 梅特勒托利多仪器有限公司;114B型粉碎机 浙江瑞安市永历制药机械有限公司;DBS-160型部分收集器 上海嘉鹏科技有限公司;JLCLM9003型超滤杯 杭州九龄科技有限公司;玻璃层析柱(φ 3.0 cm×30 cm) 江苏三爱思科学仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 酶解工艺及蛋白酶的筛选
参照蛋白酶使用说明书及郭刚军等[7]的实验结果制定酶解工艺条件如表1所示。澳洲坚果粕的酶解工艺参照郭刚军等[7]的实验方法,将液压压榨的澳洲坚果果粕进行粉碎过60目筛(孔径0.25 mm),取筛下物加水调浆,沸水浴10 min后冷却至酶适合温度,加入蛋白酶并将pH调至酶解条件,然后进行恒温酶解,酶解完成后沸水浴15 min灭酶,冷却至室温后4000 r/min离心20 min,取上清液调pH至4.6(澳洲坚果蛋白等电点)静置30 min,4000 r/min离心10 min,取上清液调pH至7.0为多肽液备用。将多肽液统一浓度为2.0 mg/mL后进行ABTS+自由基清除率测定,筛选出适宜的蛋白酶。
表 1 不同蛋白酶酶解澳洲坚果粕的工艺条件Table 1. Enzymatic hydrolysis process conditions of macadamia nut meal by different proteases蛋白酶种类 酶解温度(℃) 酶解时间(h) 底物浓度(g/L) 酶解pH 加酶量(%)
(以果粕质量计)中性蛋白酶 55 4.0 100 6.0 0.3 酸性蛋白酶 40 4.0 100 3.0 0.5 碱性蛋白酶 45 3.5 110 10.0 0.5 复配蛋白酶 55 3.0 100 7.5 0.5 木瓜蛋白酶 55 3.0 100 7.0 0.5 菠萝蛋白酶 55 3.0 100 7.0 0.5 1.2.2 多肽浓度的测定
参照郭刚军等[18]的方法,采用双缩脲法进行测定,以酪蛋白为标准品制作标准曲线,得出吸光值为纵坐标(Y),酪蛋白质量浓度为横坐标(X)的回归方程为Y=0.0461X+0.0053(R2=0.9995)。将样液与等体积的10%三氯乙酸(TCA)混合,静置30 min,在4000 r/min下离心20 min,以除去不溶性的蛋白质和长肽链,取1 mL上清液于试管中,加入4 mL双缩脲试剂,混匀后在室温下静置30 min,于540 nm波长处测定吸光值,代入回归方程计算得到上清液中的多肽浓度。
1.2.3 大孔树脂动态吸附纯化
用大孔树脂对“1.2.1”水解澳洲坚果粕制备的多肽液进行脱糖、脱盐纯化。大孔树脂采用湿法装柱,参照张巧智等[19]的方法稍作修改,上样及水洗脱工艺条件为:上样流速1 mL/min、上样浓度15 mg/mL,上样体积200 mL;水洗脱流速2 mL/min,水洗脱体积400 mL。流出液每10 mL收集为1管,测定总糖、无机盐含量(总糖含量测定采用苯酚-硫酸法[20],无机盐含量采用电导仪直接测定),直至总糖含量及无机盐含量趋于稳定。用400 mL体积分数为75%的乙醇溶液进行解吸,流速为2 mL/min,解吸液每10 mL收集1管,测定解吸液的多肽浓度判定解吸是否完成,收集的解吸液减压浓缩后备用。
1.2.4 超滤分级
将“1.2.3”中经大孔树脂纯化的多肽液用10000、5000、1000 Da分子量的超滤膜分级,超滤压力为0.25 MPa,温度为25 ℃,得到MNAP-1(Mw>10000 Da)、MNAP-2(5000 Da<Mw<10000 Da)、MNAP-3(1000 Da<Mw<5000 Da)、MNAP-4(Mw<1000 Da)4种组分,减压浓缩后备用。
1.2.5 澳洲坚果多肽的抗氧化活性测定
1.2.5.1 DPPH自由基清除率测定
参照Sethi等[21]的方法稍作修改。用无水乙醇配制DPPH溶液0.2 mmol/L,避光保存。精确量取样液2 mL于试管中,加入2 mL的DPPH溶液并摇匀,在室温避光反应30 min,在517 nm波长下测其吸光度为A1,用2 mL无水乙醇代替DPPH溶液,测其吸光度为A2,用2 mL蒸馏水代替样液,测其吸光度为A0。按照公式(1)计算DPPH自由基清除率。
清除率(%)=(1−A1−A2A0)×100 (1) 式中:A0表示空白组的吸光值;A1表示多肽液的吸光值;A2表示对照组的吸光值。
1.2.5.2 羟基自由基清除率的测定
参照Li等[22]的方法稍作修改。取1 mL样液于试管中,加入1 mL 9 mmol/L水杨酸-乙醇溶液,1 mL 9 mmol/L FeSO4溶液,再加入1 mL 8.8 mmol/L H2O2,启动Fenton反应,37 ℃水浴30 min,在510 nm波长下测其吸光度为A1;用1 mL蒸馏水代替H2O2,反应后测其吸光度为A2;用1 mL蒸馏水替代样液,反应后测其吸光度为A0。按照公式(1)计算羟基自由基清除率。
1.2.5.3 ABTS+自由基清除率的测定
参照Lu等[23]的方法稍作修改。将配制好的140 mmol/L过硫酸钾440 μL加入到25 mL 7 mmol/L的ABTS溶液中,得到ABTS+自由基工作液,避光反应12~16 h。使用时,用95%的乙醇稀释,使其吸光度在0.7±0.02。取2.85 mL ABTS稀释液加入0.15 mL样液,在734 nm波长下测其吸光度为A1,2.85 mL ABTS稀释液加入0.15 mL乙醇溶液,测其吸光度为A0。按照公式(2)计算ABTS+自由基清除率。
清除率(%)=A0−A1A0×100 (2) 式中:A0表示空白组的吸光值;A1表示多肽液的吸光值。
1.2.5.4 还原能力的测定
参照卢柏山等[24]的方法。量取1 mL样液(空白用1 mL蒸馏水代替,其他试剂依次同下)于烧杯中,依次加入2.5 mL pH6.6的磷酸盐缓冲溶液和2.5 mL 1%的铁氰化钾溶液,混匀后于50 ℃水浴反应20 min,加入2.5 mL 10%的三氯乙酸溶液,混匀后4000 r/min离心10 min,取2.5 mL上清液于试管中,依次加入0.5 mL 0.1%的FeCl3溶液和2.5 mL蒸馏水,摇匀静置15 min后在700 nm波长下测其吸光度。吸光度与样品的还原能力有关,A值越大则样品的还原能力越强。
1.2.5.5 抗氧化能力评价指标的计算
以样品的质量浓度为横坐标,抗氧化能力为纵坐标,计算得出线性回归方程及相关系数r(r值越接近1,相关性越好),利用回归方程计算50%的清除率对应的样品浓度为半抑制浓度(half maximal inhibitory concentration,IC50)(IC50越小,抗氧化能力越强),回归方程中的斜率越大则抗氧化能力随质量浓度增加越快[25]。
1.3 数据处理
所有实验重复三次,结果用平均值±标准差(mean±SD)表示。采用Microsoft Excel 2019进行数据录入、处理与计算线性回归方程;采用SPSS 27.0统计软件进行数据分析,组间差异用多重比较分析(LSD)、单因素方差分析(One-way ANOVA)进行处理,P<0.05表示差异显著;用皮尔森法(Pearson’s)进行相关性分析,P<0.01为极显著性相关。使用Origin 2021对进行作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 蛋白酶种类的筛选
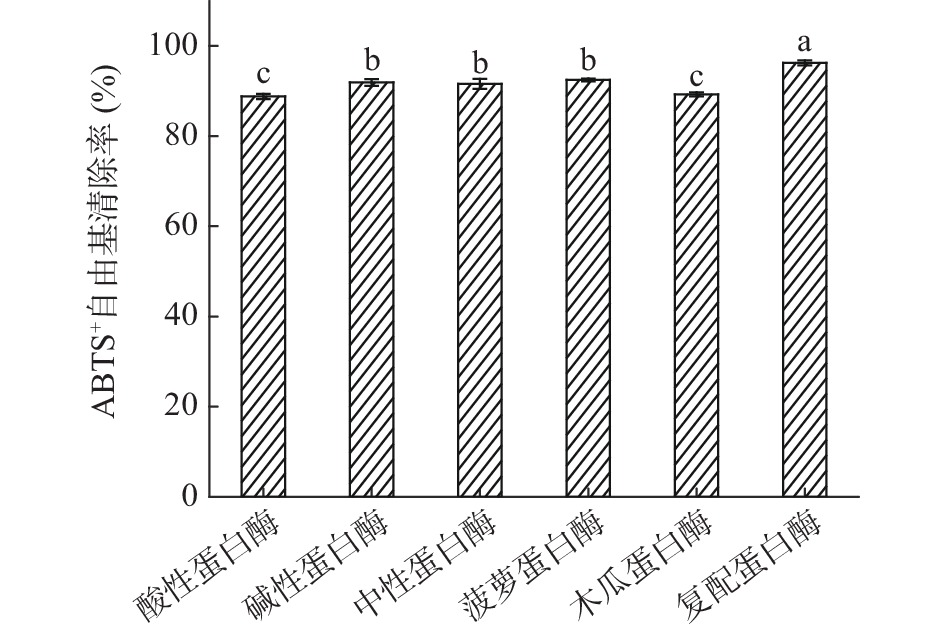
多肽C端具有大分子疏水性氨基酸会使其具有较高的抗氧化活性,不同蛋白酶对肽键的作用位点不同,产生的多肽C端、N端及相对分子质量不尽相同,所以对蛋白酶进行筛选是极为重要的[26]。如图1所示,复配蛋白酶制备的粗多肽对ABTS+自由基的清除率为96.23%±0.57%,显著高于其它蛋白酶(P<0.05);其次是碱性蛋白酶、中性蛋白酶和菠萝蛋白酶,清除率分别为91.87%±0.76%、91.57%±1.07%、92.46%±0.31%,它们之间差异不显著(P>0.05);酸性蛋白酶和木瓜蛋白酶的清除率最低,分别为88.79%±0.56%、89.24%±0.45%,两者之间无显著性差异(P>0.05)。因此选择复配蛋白酶水解制备澳洲坚果粗多肽。
2.2 DA201-C大孔树脂对澳洲坚果多肽的纯化效果
2.2.1 大孔树脂吸附过程中多糖和无机盐的变化
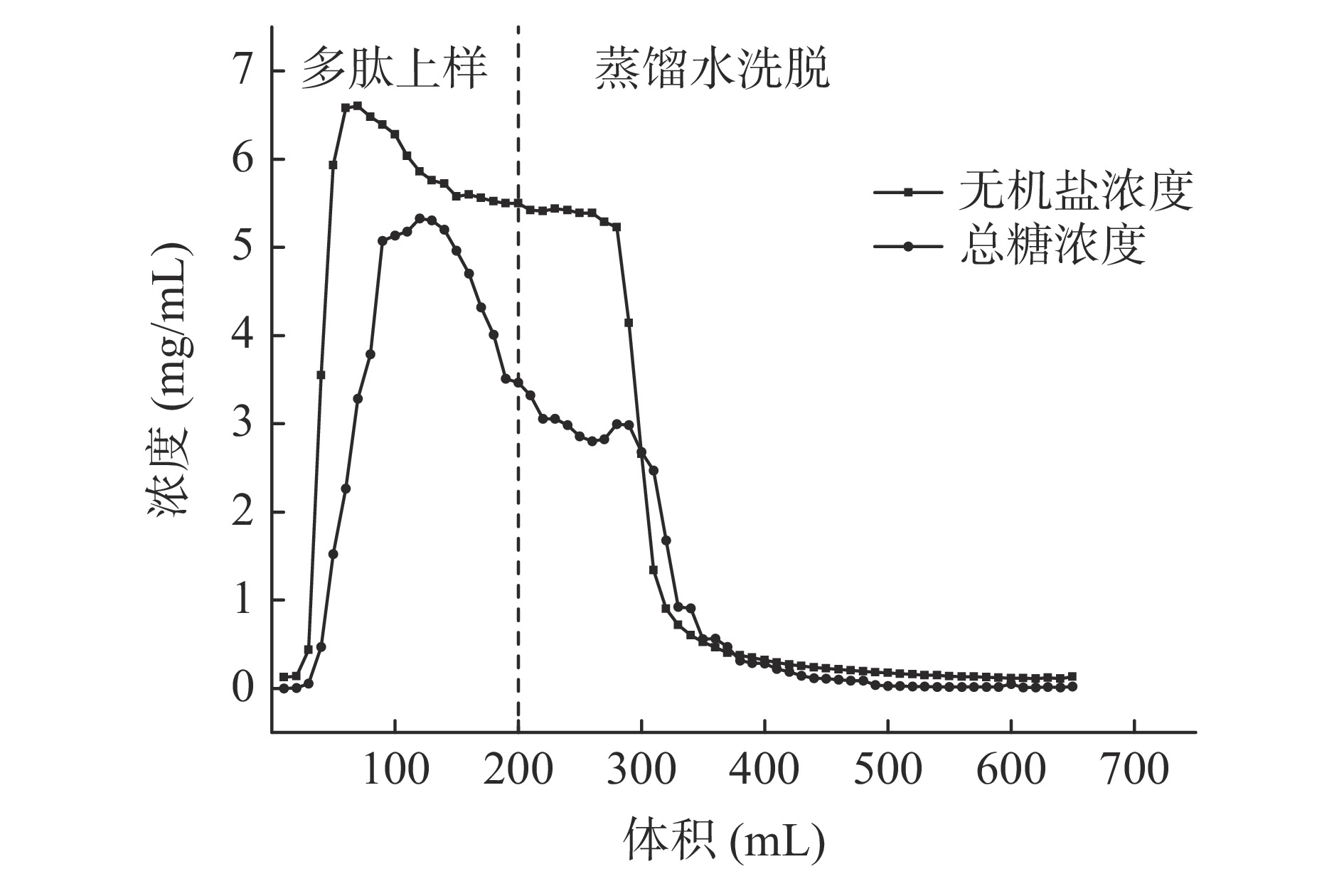
不同型号的树脂适用于分离不同极性的物质,实验中采用对多肽吸附能力较好的DA201-C大孔吸附树脂[19]。如图2所示,在多肽上样及蒸馏水洗脱过程中,流出液的总糖及无机盐含量均为先上升后下降的一个趋势,当蒸馏水洗脱体积达到300 mL时,流出液中总糖及无机盐含量分别为0.03、0.16 mg/mL,且趋于稳定。
2.2.2 大孔树脂解吸过程中多肽含量的变化
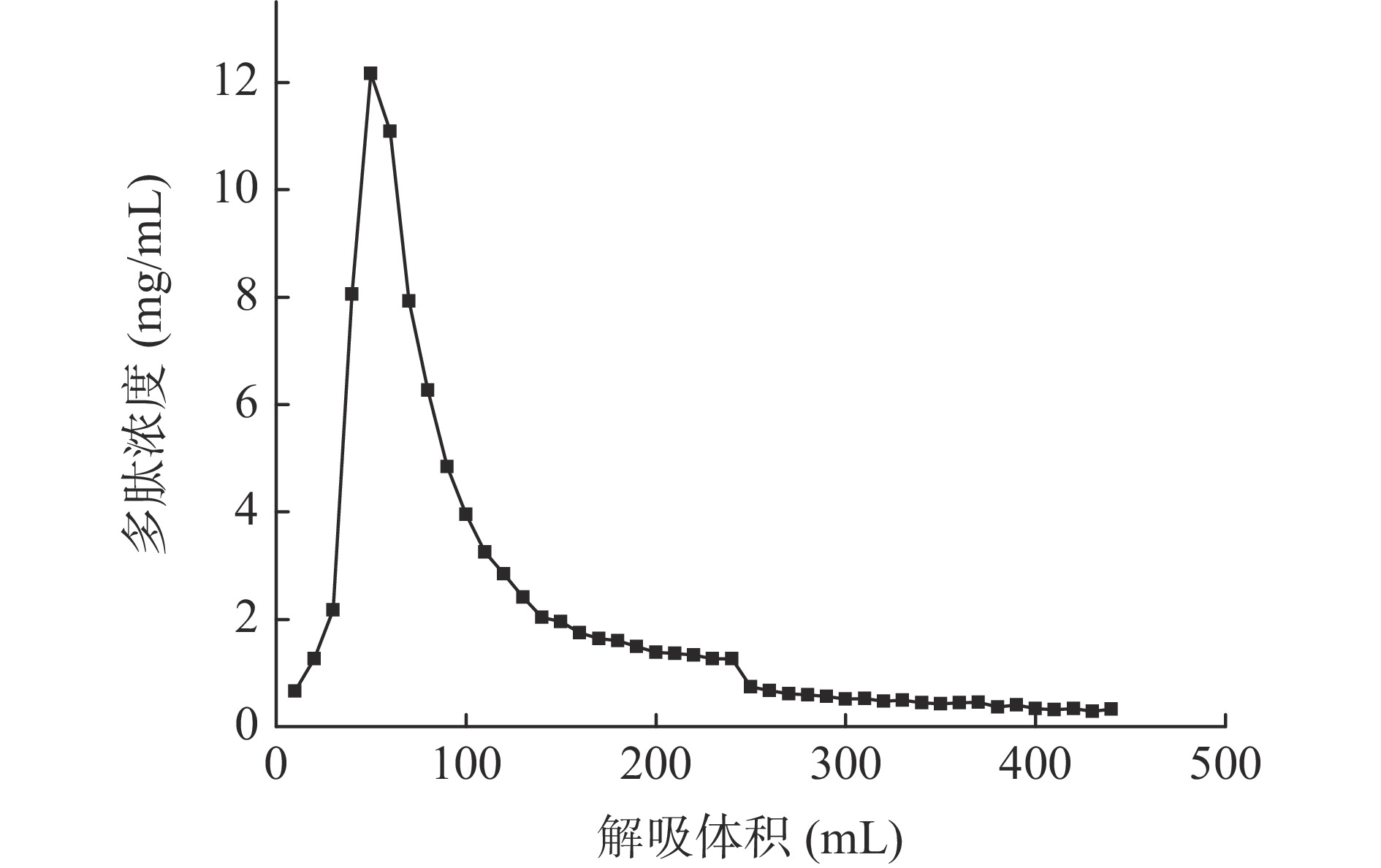
多肽液经吸附平衡、蒸馏水洗涤层析柱除去无机盐和糖类物质后,用乙醇溶液进行解吸,流出液每10 mL收集为1管测定其多肽含量,多肽含量变化曲线如图3所示。从图3可以看出,解吸体积为250 mL时,解吸液中多肽浓度小于1.0 mg/mL,且趋于稳定。陈丽丽等[27]在利用大孔树脂对草鱼蛋白水解液纯化处理中认为解吸曲线拖尾的原因是部分多肽组分不能很好的溶解在乙醇溶液中,因此在本实验中将洗脱体积选择为400 mL,这样既能避免多肽的损失保证多肽的回收,也能减少解吸液的体积。DA201-C大孔树脂对澳洲坚果多肽具有较好的吸附效果,本研究的纯化工艺可用于澳洲坚果多肽的纯化,可以有效去除酶解液中的多糖和无机盐。
2.3 不同分子量澳洲坚果多肽的抗氧化活性
以谷胱甘肽标准品作为对照,利用多重抗氧化评估体系(DPPH、羟基、ABTS+自由基清除率、还原能力)研究不同分子量澳洲坚果多肽的抗氧化活性。
2.3.1 不同分子量澳洲坚果多肽对DPPH自由基的清除作用
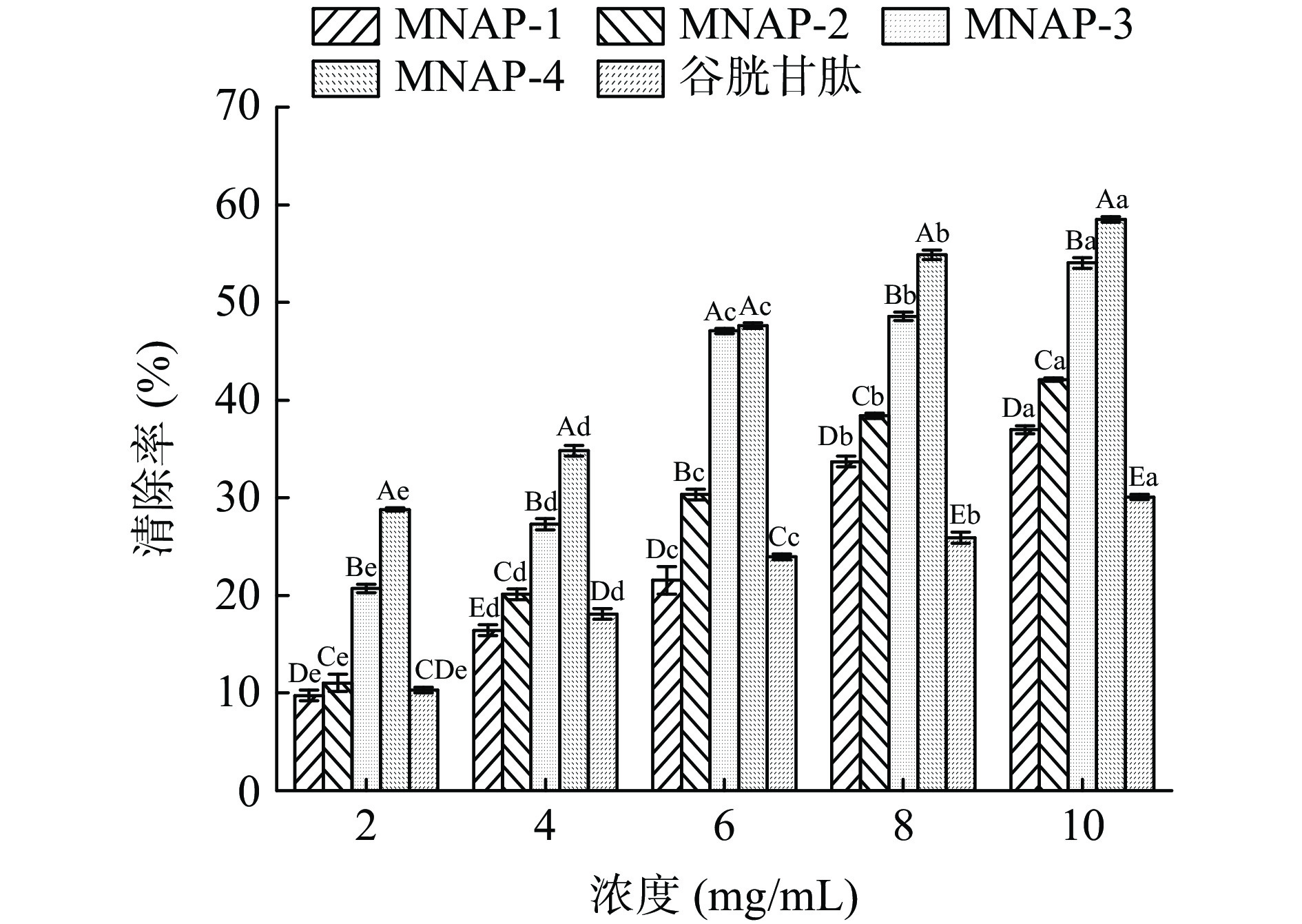
DPPH自由基的清除能力广泛应用于研究物质的体外抗氧化活性[28]。由图4及表2可见,4种不同分子量的多肽及谷胱甘肽对DPPH自由基均有较强的清除作用,且清除率随着样品浓度的增加而增强,有较好的量-效关系。在相同浓度下,MNAP-4的清除能力优于MNAP-1、MNAP-2、MNAP-3,4种不同分子量的多肽对DPPH的清除率具有显著性差异(P<0.05),且均低于谷胱甘肽。在浓度0.2 mg/mL时,MNAP-4的清除率最优为35.29%±0.13%,其后依次为MNAP-3(34.77%±0.17%)、MNAP-2(32.35%±0.14%)、MNAP-1(30.72%±0.51%)。随着浓度的增加,MNAP-4清除率的增加速率高于其它组分及谷胱甘肽。当浓度达到1.0 mg/mL时,MNAP-4的清除率最优为82.55%±0.22%。从评价样品对自由基清除能力的IC50值来看,不同分子量多肽及谷胱甘肽对DPPH自由基清除能力大小顺序为:谷胱甘肽(IC50 0.01 mg/mL)>MNAP-4(IC50 0.36 mg/mL)>MNAP-3(IC50 0.37 mg/mL)>MNAP-2(IC50 0.45 mg/mL)>MNAP-1(IC50 0.55 mg/mL),不同分子量多肽对DPPH自由基的清除能力不同,分子量越小清除能力越强。分子量较小的多肽因其具有较小的空间位阻,能更好的与自由基发生反应,表现出较好的DPPH自由基清除率,这与不同分子量的核桃、红花籽多肽的抗氧化活性研究结果相同,均表现为分子量较小的多肽对DPPH自由基清除效果较好[29-30]。
表 2 不同分子量多肽对DPPH自由基清除率的回归方程分析Table 2. Regression equation on scavenging rates of DPPH radical of different molecular weight polypeptides样品 回归方程 IC50(mg/mL) r MNAP-1 y=20.62 ln(x)+62.28 0.55 0.9829 MNAP-2 y=24.62 ln(x)+69.92 0.45 0.9769 MNAP-3 y=26.38 ln(x)+76.25 0.37 0.9958 MNAP-4 y=29.02 ln(x)+79.90 0.36 0.9866 谷胱甘肽 y=12.07 ln(x)+102.31 0.01 0.9597 2.3.2 不同分子量澳洲坚果多肽对羟基自由基的清除作用
羟基自由基是广泛存在于生物体内的一种自由基,是氧自由基中最活泼的自由基,羟基自由基会引起生物体损伤,羟基自由基清除率是反映物质抗氧化作用的重要指标[31]。从图5及表3可以看出,4种不同分子量的多肽及谷胱甘肽对羟基自由基有较强的清除能力,且清除率与其浓度呈正相关。MNAP-4对羟基自由基的清除率最大,在浓度2.0 mg/mL时,MNAP-4的清除率最优为28.78%±0.16%,MNAP-1、谷胱甘肽的清除率最低分别为9.75%±0.56%、10.31%±0.28%,且两者之间无显著性差异(P>0.05)。随着浓度的增加,清除率的增加速率大小顺序为MNAP-3、MNAP-2、MNAP-4、MNAP-1、谷胱甘肽。当浓度达到10.0 mg/mL,4种多肽的清除率均高于谷胱甘肽且具有显著性差异(P<0.05),MNAP-4的清除率最优为58.50%±0.28%。从评价样品对自由基清除能力的IC50值来看,不同分子量多肽及谷胱甘肽对羟基自由基清除能力大小顺序为:MNAP-4(IC50 6.75 mg/mL)>MNAP-3(IC50 8.37 mg/mL)>MNAP-2(IC50 15.35 mg/mL)>MNAP-1(IC50 23.94 mg/mL)>谷胱甘肽(IC50 54.78 mg/mL),不同分子量多肽对羟基自由基的清除能力不同,分子量越小清除能力越强,这与桃仁多肽的研究结果相同[32],这是由于分子量较小的多肽可阻断自由基链式反应,促使自由基转化成更加稳定的物质,表现出更好的羟基自由基清除能力。
表 3 不同分子量多肽对羟基自由基清除率的回归方程分析Table 3. Regression equation on scavenging rates of hydroxyl radical of different molecular weight polypeptides样品 回归方程 IC50(mg/mL) r MNAP-1 y=17.27 ln(x)−4.84 23.94 0.9557 MNAP-2 y=19.99 ln(x)−4.60 15.35 0.9883 MNAP-3 y=22.07 ln(x)+3.10 8.37 0.9605 MNAP-4 y=19.58 ln(x)+12.61 6.75 0.9735 谷胱甘肽 y=12.04 ln(x)+1.80 54.78 0.9964 2.3.3 不同分子量澳洲坚果多肽对ABTS+自由基的清除作用
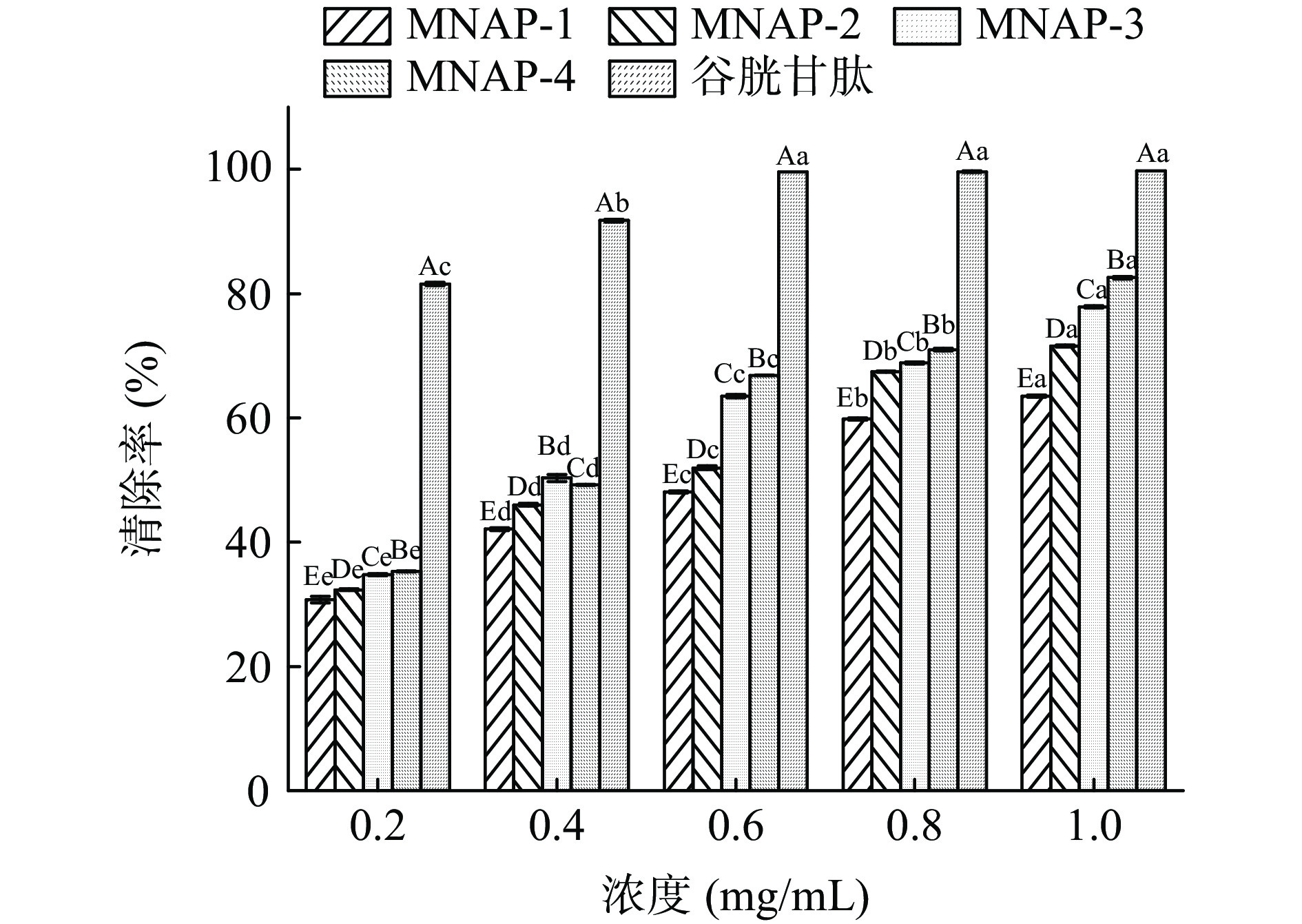
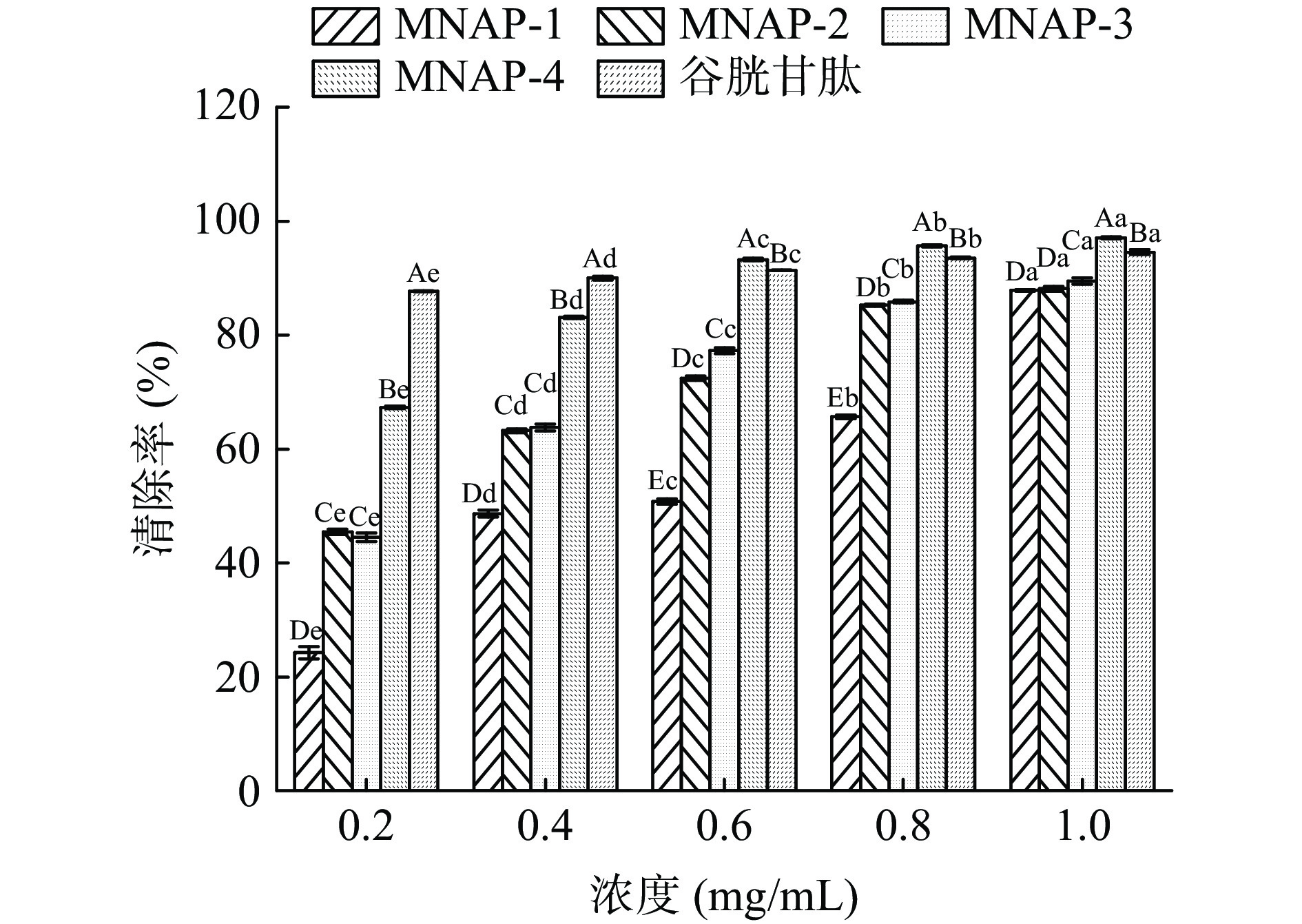
ABTS+自由基清除率广泛运用于体外抗氧化活性的评价[33-34]。由图6及表4可见,4种不同分子量的多肽及谷胱甘肽对ABTS+自由基的清除能力均随样品质量浓度的增加而增大。MNAP-4、谷胱甘肽的清除率高于MNAP-1、MNAP-2、MNAP-3,浓度为0.2、0.4 mg/mL时,4种不同分子量多肽的清除率低于谷胱甘肽,MNAP-2与MNAP-3的清除率无显著差异(P>0.05)。随着浓度的增加,清除率的增加速率大小顺序为MNAP-3、MNAP-2、MNAP-1、MNAP-4、谷胱甘肽。当浓度达到0.6 mg/mL时,MNAP-4的清除率为93.25%±0.25%,高于谷胱甘肽的清除率91.37%±0.08%。当浓度达到1.0 mg/mL时,MNAP-4的清除率为97.05%±0.18%优于其它评价样品,MNAP-2与MNAP-3的清除率分别为88.14%±0.42%、89.47%±0.58%,两者之间无显著性差异(P>0.05)。从评价样品对自由基清除能力的IC50值来看,不同分子量多肽及谷胱甘肽对ABTS+自由基清除能力大小顺序为:谷胱甘肽(IC50 0.00003 mg/mL)>MNAP-4(IC50 0.08 mg/mL)>MNAP-2、MNAP-3(IC50 0.24 mg/mL)> MNAP-1(IC50 0.45 mg/mL),MNAP-4对ABTS+自由基的清除能力最强,这可能是由于ABTS+自由基是一种亲水性自由基,分子量小的多肽的亲水性较好,更易与ABTS+自由基发生反应,从而表现出更好的ABTS+自由基清除能力,这与油茶饼粕多肽的研究结果相同[35]。MNAP-2、MNAP-3的清除能力相近,这可能是由于MNAP-2、MNAP-3两者的亲水性相似,导致两者对ABTS+自由基的清除能力相近[36]。
表 4 不同分子量多肽对ABTS+自由基清除率的回归方程分析Table 4. Regression equation on scavenging rates of ABTS+ radical of different molecular weight polypeptides样品 回归方程 IC50(mg/mL) r MNAP-1 y=34.99 ln(x)+78.24 0.45 0.9489 MNAP-2 y=27.26 ln(x)+88.66 0.24 0.9944 MNAP-3 y=28.83 ln(x)+90.96 0.24 0.9979 MNAP-4 y=19.24 ln(x)+99.81 0.08 0.9824 谷胱甘肽 y=4.27 ln(x)+94.21 0.00003 0.9861 2.3.4 不同分子量澳洲坚果多肽还原能力分析
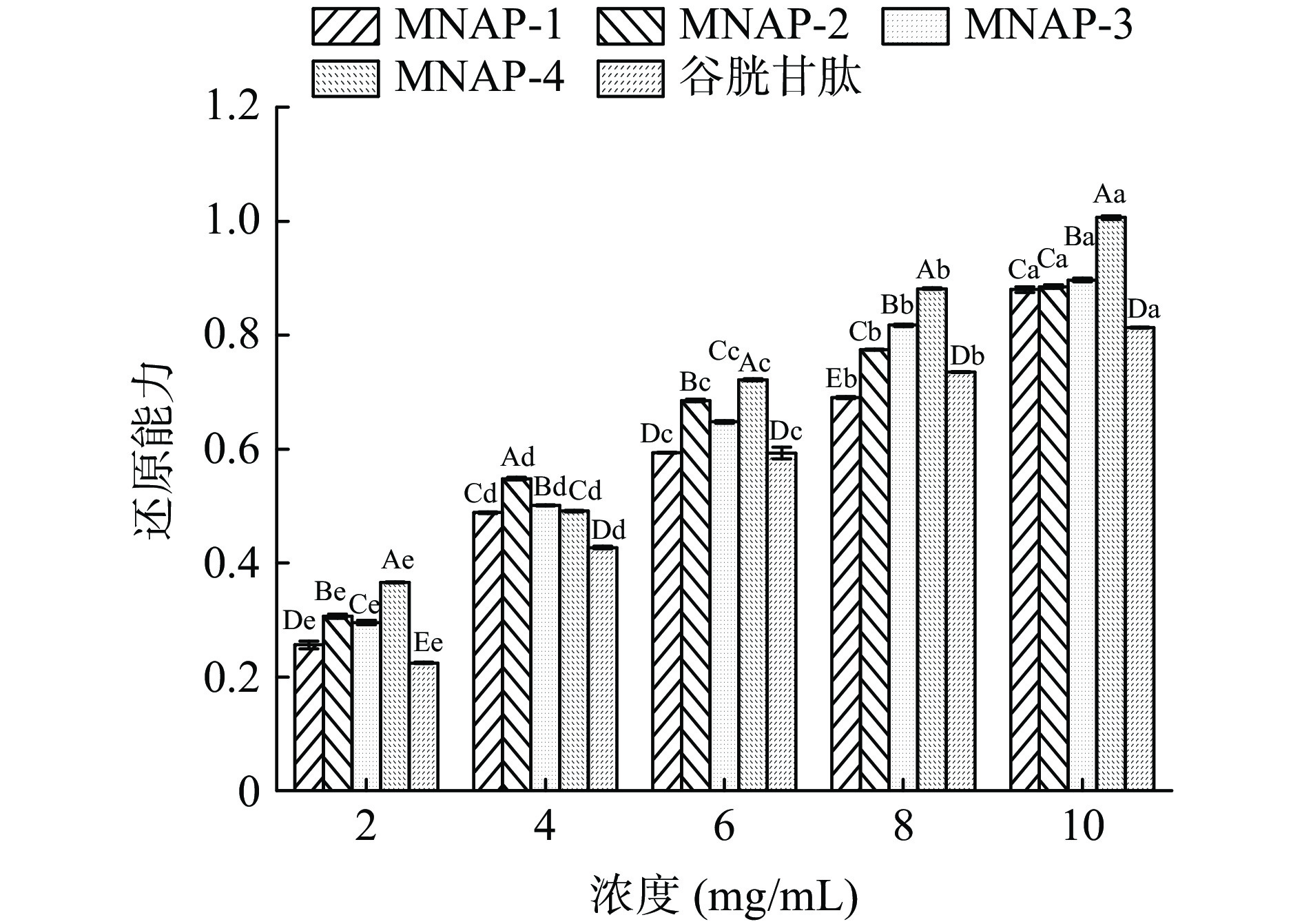
还原能力是指其将Fe3+还原为Fe2+的能力,也是评估抗氧化活性的重要指标之一,吸光值越大还原力越强[37]。从图7及表5可以看出,不同分子量的多肽及谷胱甘肽均具有还原能力,还原能力与浓度呈正相关。MNAP-4的还原能力优于MNAP-1、MNAP-2、MNAP-3及谷胱甘肽。在浓度2.0 mg/mL时,MNAP-4的还原能力为0.366±0.001,优于其它评价样品,谷胱甘肽还原能力最弱为0.224±0.002。随着浓度的增加,还原能力的增加速率大小顺序为MNAP-4、MNAP-3、谷胱甘肽、MNAP-1、MNAP-2。当浓度达到10.0 mg/mL时,4种不同分子量多肽的还原能力均优于谷胱甘肽,MNAP-4的还原能力最优为1.006±0.003,MNAP-1、MNAP-2的还原能力分别为0.880±0.005、0.885±0.003,两者之间无显著性差异(P>0.05)。从评价样品对自由基清除能力的IC50值来看,不同分子量多肽及谷胱甘肽还原能力大小顺序为:MNAP-4(IC50 3.19 mg/mL)>MNAP-2(IC50 3.45 mg/mL)>MNAP-3(IC50 3.61 mg/mL)>MNAP-1(IC50 4.08 mg/mL)>谷胱甘肽(IC50 4.35 mg/mL),MNAP-4表现出最强的还原能力,这是由于肽段越短使具有较多电子的基团暴露越充分,因此还原能力最强,这与松仁、核桃、桃仁等多种植物蛋白的研究结果相同[16,29,32]。而分子质量相对较高的MNAP-2可能是因为具有较多电子致密的基团暴露在外,转移电子的能力也较强而表现出高于MNAP-3的还原能力[32]。
表 5 不同分子量多肽还原能力的回归方程分析Table 5. Regression equation on reducing power of different molecular weight polypeptides样品 回归方程 IC50(mg/mL) r MNAP-1 y=0.3725 ln(x)−0.0236 4.08 0.9877 MNAP-2 y=0.3624 ln(x)+0.0510 3.45 0.9985 MNAP-3 y=0.3870 ln(x)+0.0029 3.61 0.9825 MNAP-4 y=0.4162 ln(x)+0.0171 3.19 0.9641 谷胱甘肽 y=0.3812 ln(x)−0.0606 4.35 0.9869 2.4 不同分子量澳洲坚果多肽与抗氧化活性相关性分析
用皮尔森法(Pearson’s)对不同分子量澳洲坚果多肽与抗氧化活性指标的IC50值进行相关性分析。结果如表6所示,不同分子量澳洲坚果多肽与清除DPPH自由基(r=0.947,P<0.01)、羟基自由基(r=0.964,P<0.01)、ABTS+自由基(r=0.948,P<0.01)及还原能力(r=0.856,P<0.01)之间存在极显著相关。多肽分子量的大小对其抗氧化活性影响巨大,结合2.3中的分析可知分子量小于1000 Da的澳洲坚果多肽抗氧化活性最好,这可能是分子量小的多肽空间位阻较小,活性基团(巯基、酚羟基)暴露,更好的与自由基发生反应,表现出更好的抗氧化活性。Feng等[38]认为多肽的抗氧化活性与分子量大小、氨基酸组成种类及排列顺序有关,Lin等[39]研究水解蛋清蛋白发现分子质量小于1000 Da的组分抗氧化活性明显高于其他分子质量组,Zou等[40]发现的不同来源的42种抗氧化肽在1000 Da以下的3~6肽具有更好的自由基清除活性。
表 6 不同分子量的澳洲坚果多肽与抗氧化活性相关性Table 6. Correlations between macadamia nut polypeptides with different molecular weights and antioxidant activities成分 DPPH
自由基羟基
自由基ABTS+
自由基还原能力 不同分子量澳洲坚果多肽 r=0.947** r=0.964** r=0.948** r=0.856** 注:**表示相关性极显著(P<0.01)。 3. 结论
本文研究了不同蛋白酶酶解澳洲坚果粕的ABTS+自由基清除能力,采用DA201-C大孔吸附树脂、超滤分级等技术对澳洲坚果多肽进行分离纯化得到不同分子量多肽,考察其清除DPPH、羟基、ABTS+自由基能力及还原能力,分析得出不同分子量多肽与抗氧化活性之间存在显著相关性。筛选得到了抗氧化活性高的多肽组分MNAP-4(Mw<1000 Da),后续可对其进一步纯化,研究其多肽结构及体内抗氧化活性,为新型抗氧化肽功能性产品的开发与工业化应用提供理论依据,促进澳洲坚果产业的发展。
-
表 1 不同蛋白酶酶解澳洲坚果粕的工艺条件
Table 1 Enzymatic hydrolysis process conditions of macadamia nut meal by different proteases
蛋白酶种类 酶解温度(℃) 酶解时间(h) 底物浓度(g/L) 酶解pH 加酶量(%)
(以果粕质量计)中性蛋白酶 55 4.0 100 6.0 0.3 酸性蛋白酶 40 4.0 100 3.0 0.5 碱性蛋白酶 45 3.5 110 10.0 0.5 复配蛋白酶 55 3.0 100 7.5 0.5 木瓜蛋白酶 55 3.0 100 7.0 0.5 菠萝蛋白酶 55 3.0 100 7.0 0.5 表 2 不同分子量多肽对DPPH自由基清除率的回归方程分析
Table 2 Regression equation on scavenging rates of DPPH radical of different molecular weight polypeptides
样品 回归方程 IC50(mg/mL) r MNAP-1 y=20.62 ln(x)+62.28 0.55 0.9829 MNAP-2 y=24.62 ln(x)+69.92 0.45 0.9769 MNAP-3 y=26.38 ln(x)+76.25 0.37 0.9958 MNAP-4 y=29.02 ln(x)+79.90 0.36 0.9866 谷胱甘肽 y=12.07 ln(x)+102.31 0.01 0.9597 表 3 不同分子量多肽对羟基自由基清除率的回归方程分析
Table 3 Regression equation on scavenging rates of hydroxyl radical of different molecular weight polypeptides
样品 回归方程 IC50(mg/mL) r MNAP-1 y=17.27 ln(x)−4.84 23.94 0.9557 MNAP-2 y=19.99 ln(x)−4.60 15.35 0.9883 MNAP-3 y=22.07 ln(x)+3.10 8.37 0.9605 MNAP-4 y=19.58 ln(x)+12.61 6.75 0.9735 谷胱甘肽 y=12.04 ln(x)+1.80 54.78 0.9964 表 4 不同分子量多肽对ABTS+自由基清除率的回归方程分析
Table 4 Regression equation on scavenging rates of ABTS+ radical of different molecular weight polypeptides
样品 回归方程 IC50(mg/mL) r MNAP-1 y=34.99 ln(x)+78.24 0.45 0.9489 MNAP-2 y=27.26 ln(x)+88.66 0.24 0.9944 MNAP-3 y=28.83 ln(x)+90.96 0.24 0.9979 MNAP-4 y=19.24 ln(x)+99.81 0.08 0.9824 谷胱甘肽 y=4.27 ln(x)+94.21 0.00003 0.9861 表 5 不同分子量多肽还原能力的回归方程分析
Table 5 Regression equation on reducing power of different molecular weight polypeptides
样品 回归方程 IC50(mg/mL) r MNAP-1 y=0.3725 ln(x)−0.0236 4.08 0.9877 MNAP-2 y=0.3624 ln(x)+0.0510 3.45 0.9985 MNAP-3 y=0.3870 ln(x)+0.0029 3.61 0.9825 MNAP-4 y=0.4162 ln(x)+0.0171 3.19 0.9641 谷胱甘肽 y=0.3812 ln(x)−0.0606 4.35 0.9869 表 6 不同分子量的澳洲坚果多肽与抗氧化活性相关性
Table 6 Correlations between macadamia nut polypeptides with different molecular weights and antioxidant activities
成分 DPPH
自由基羟基
自由基ABTS+
自由基还原能力 不同分子量澳洲坚果多肽 r=0.947** r=0.964** r=0.948** r=0.856** 注:**表示相关性极显著(P<0.01)。 -
[1] BIRCH J, YAP K, SILCOCK P. Compositional analysis and roasting behaviour of gevuina and macadamia nuts[J]. International Journal of Food Science and Technology,2010,45:81−86.
[2] MARO L A C, PIO R, PENONI E DOS S, et al. Chemical characterization and fatty acids profile in macadamia walnut cultivars[J]. Ciência Rural,2012,42(12):2166−2171.
[3] 杜丽清, 曾辉, 邹明宏, 等. 澳洲坚果果仁氨基酸含量的差异性分析[J]. 经济林研究,2008,26(4):49−52. [DU L Q, ZENG H, ZOU M H, et al. Differences analysis of amino acid contents in macadamia kernel[J]. Non-Wood Forest Research,2008,26(4):49−52. doi: 10.14067/j.cnki.1003-8981.2008.04.011 DU L Q, ZENG H, ZOU M H, et al. Differences analysis of amino acid contents in macadamia kernel[J]. Non-Wood Forest Research, 2008, 26(4): 49-52. doi: 10.14067/j.cnki.1003-8981.2008.04.011
[4] 张齐, 阎怡竹, 刘清清, 等. 文冠果降血压肽的制备及其活性研究[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版),2018,48(4):551−556. [ZHANG Q, YAN Y Z, LIU Q Q, et al. Preparation and bioactivity of antihypertensive peptides from Xanthoceras sorbifolia B J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition),2018,48(4):551−556.
[5] 贺熙勇, 聂艳丽, 吴霞, 等. 云南澳洲坚果产业高质量发展的建议[J]. 中国南方果树,2022,51(4):205−210. [HE X Y, NIE Y L, WU X, et al. Suggestions of macadamia industry for high-quality development in Yunnan Province[J]. South China Fruits,2022,51(4):205−210. doi: 10.13938/j.issn.1007-1431.20210529 HE X Y, NIE Y L, WU X, et al. Suggestions of macadamia industry for high-quality development in Yunnan Province[J]. South China Fruits, 2022, 51(4): 205-210. doi: 10.13938/j.issn.1007-1431.20210529
[6] 贺熙勇, 陶亮, 柳觐, 等. 我国澳洲坚果产业概况及发展趋势[J]. 热带农业科技,2015,38(3):12−16,19. [HE X Y, TAO L, LIU J, et al. Overview of macadamia industry and its development trend in China[J]. Tropical Agricultural Science & Technology,2015,38(3):12−16,19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-450X.2015.03.004 HE X Y, TAO L, LIU J, et al. Overview of macadamia industry and its development trend in china[J]. Tropical Agricultural Science & Technology, 2015, 38(3): 12-16, 19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-450X.2015.03.004
[7] 郭刚军, 建邹云, 胡小静, 等. 液压压榨澳洲坚果粕酶解制备多肽工艺优化[J]. 食品科学,2016,37(17):17−18. [GUO G J, ZOU J Y, HU X J, et al. Optimizing the preparation of crude peptides from hydraulic macadamia nut meal by enzymatic hydrolysis[J]. Food Science,2016,37(17):17−18. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201617029 GUO G J, ZOU J Y, HU X J, et al. Optimizing the preparation of crude peptides from hydraulic macadamia nut meal by enzymatic hydrolysis[J]. Food Science, 2016, 37(17): 17-18. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201617029
[8] ZHANG S H, LUO L, SUN X Y, et al. Bioactive peptides: A promising alternative to chemical preservatives for food preservation[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2021,69:12369−12384. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c04020
[9] 范方宇, 阚欢, 郭安, 等. 澳洲坚果蛋白质提取及多肽的制备[J]. 农业机械,2011(35):131−135. [FAN F Y, KAN H, GUO A, et al. Protein extraction and polypeptide preparation from macadamia nut[J]. Farm Machinery,2011(35):131−135. doi: 10.16167/j.cnki.1000-9868.2011.35.044 FAN F Y, KAN H, GUO A, et al. Protein extraction and polypeptide preparation from macadamia nut[J]. Farm Machinery, 2011, (35): 131-135. doi: 10.16167/j.cnki.1000-9868.2011.35.044
[10] 刘恩岐, 贺菊萍, 陈振家, 等. 黑豆蛋白质酶水解物体外抗氧化活性的研究[J]. 中国粮油学报,2009,24(11):38−41. [LIU E Q, HE J P, CHEN Z J, et al. Study on antioxidant activity of black bean protein hydrolyzed by enzyme[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2009,24(11):38−41. LIU E Q, HE J P, CHEN Z J, et al. Study on antioxidant activity of black bean protein hydrolyzed by enzyme[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2009, 24(11): 38-41.
[11] 马尚玄, 郭刚军, 黄克昌, 等. 不同分子量澳洲坚果多肽氨基酸组成与抑菌活性[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(7):83−88. [MA S X, GUO G J, HAUNG K C, et al. Amino acid compositions and antibacterial activities of different molecular weight macadamia nut polypeptides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(7):83−88. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020060376 MA S X, GUO G J, HAUNG K C, et al. Amino acid compositions and antibacterial activities of different molecular weight macadamia nut polypeptides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(7): 83-88. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020060376
[12] FENG Y X, RUAN G R, JIN F, et al. Purification, identification, and synthesis of five novel antioxidant peptides from Chinese chestnut (Castanea mollissima Blume) protein hydrolysates[J]. LWT,2018,92:40−46. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2018.01.006
[13] AGRAWAL H, JOSHI R, GUPTA M. Isolation, purification and characterization of antioxidative peptide of pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum) protein hydrolysate[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,204:365−372. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.02.127
[14] 崔婷婷, 贾爱荣, 张绵松, 等. 大孔吸附树脂分离纯化海蜇ACE抑制肽的工艺研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(10):216−222. [CUI T T, JIA A R, ZHANG J S, et al. Separation and purification of ACE inhibitory peptide from jellyfish by macroporous resin[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(10):216−222. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021080193 CUI T T, JIA A R, ZHANG J S, et al. Separation and purification of ACE inhibitory peptide from jellyfish by macroporous resin[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(10): 216-222. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021080193
[15] LI Z Y, HE Y, HE H Y, et al. Purification identification and function analysis of ACE inhibitory peptide from Ulva prolifera protein[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,401:134127.
[16] 卢红妍, 杨行, 方丽, 等. 松仁清蛋白抗氧化肽的分离纯化及结构鉴定[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(24):40−45. [LU H Y, YANG H, FNAG L, et al. Isolation, purification and structural identification of antioxidant peptides derived from enzymatic hydrolysis of pine nut kernel (Pinus koraiensis Sieb. et Zucc.) albumin[J]. Food Science,2019,40(24):40−45. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181114-164 LU H Y, YANG H, FNAG L, et al. Isolation, purification and structural identification of antioxidant peptides derived from enzymatic hydrolysis of pine nut kernel (Pinus koraiensis Sieb. et Zucc. ) albumin[J]. Food Science, 2019, 40(24): 40-45. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181114-164
[17] 杜丽清, 帅希祥, 涂行浩, 等. 澳洲坚果蛋白肽制备工艺及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 热带农业工程,2016,40(Z1):1−6. [DU L Q, SHUAI X X, TU X H, et al. Analysis on the preparation technology of protein peptide and antioxidant activity of macadamia nut[J]. Tropical Agricultural Engineering,2016,40(Z1):1−6. DU L Q, SHUAI X X, TU X H, et al. Analysis on the preparation technology of protein peptide and antioxidant activity of macadamia nut[J]. Tropical Agricultural Engineering, 2016, 40(Z1): 1-6.
[18] 郭刚军, 胡小静, 马尚玄, 等. 液压压榨澳洲坚果粕蛋白质提取工艺优化及其组成分析与功能性质[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(18):266−271. [GUO G J, HU X J, MA S X, et al. Extraction, composition analysis and functional properties of protein isolate from hydraulic expeller-pressed macadamia nut meal[J]. Food Science,2017,38(18):266−271. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201718041 GUO G J, HU X J, MA S X, et al. Extraction, composition analysis and functional properties of protein isolate from hydraulic expeller-pressed macadamia nut meal[J]. Food Science, 2017, 38(18): 266-271. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201718041
[19] 张巧智, 毕爽, 马文君, 等. 水酶法水解液中大豆多肽的吸附纯化及其氨基酸组成分析[J]. 大豆科技,2019(S1):416−424. [ZHANG Q Z, BI S, MA W J, et al. Purification and amino acid composition of peptides from soybean byproduct protein hydrolysate from aqueous enzymatic extraction of soybean oil[J]. Soybean Science & Technology,2019(S1):416−424. ZHANG Q Z, BI S, MA W J, et al. Purification and amino acid composition of peptides from soybean byproduct protein hydrolysate from aqueous enzymatic extraction of soybean oil[J]. Soybean Science & Technology, 2019, (S1): 416-424.
[20] 孔庆龙, 余汪平, 郭冬梅, 等. 苯酚-硫酸法测定三七枸杞酒中多糖含量[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2017,8(6):2267−2271. [KONG Q L, YU W P, GUO D M, et al. Determination of polysaccharide in the alcoholic drink of Sanqi Gouqi by phenol-sulfuric acid colorimetry method[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2017,8(6):2267−2271. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2017.06.052 KONG Q L, YU W P, GUO D M, et al. Determination of polysaccharide in the alcoholic drink of Sanqi Gouqi by phenol-sulfuric acid colorimetry method[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality, 2017, 8(6): 2267-2271. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2017.06.052
[21] SETHI S, JOSHI A, ARORA B, et al. Significance of FRAP, DPPH, and CUPRAC assays for antioxidant activity determination in apple fruit extracts[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2020,246(3):591−598. doi: 10.1007/s00217-020-03432-z
[22] LI Z R, WANG B, CHI C F, et al. Influence of average molecular weight on antioxidant and functional properties of collagen hydrolysates from Sphyrna lewini, Dasyatis akjei and Raja porosa[J]. Food Research International,2013,51(1):283−293. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2012.12.031
[23] LU X, ZHANG L X, SUN Q, et al. Extraction, identification and structure-activity relationship of antioxidant peptides from sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) protein hydrolysate[J]. Food Research International,2019,116:707−716. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.09.001
[24] 卢柏山, 董会, 史亚兴, 等. 不同品种鲜食玉米体外抗氧化能力综合评价[J]. 华北农学报,2021,36(S1):101−110. [LU B S, DONG H, SHI Y X, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of antioxidant capacity in vitro of different varieties of fresh corn[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica,2021,36(S1):101−110. doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.20191766 LU B S, DONG H, SHI Y X, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of antioxidant capacity in vitro of different varieties of fresh corn[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2021, 36(S1): 101-110. doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.20191766
[25] 郭刚军, 胡小静, 彭志东, 等. 不同压榨方式澳洲坚果油品质及抗氧化活性比较[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(13):125−132. [GUO G J, HU X J, PENG Z D, et al. Comparison of quality and antioxidant activity of press-processed macadamia (Macadamia ternifolia F. Muell.) oils[J]. Food Science,2018,39(13):125−132. GUO G J, HU X J, PENG Z D, et al. Comparison of quality and antioxidant activity of press-processed macadamia (Macadamia ternifolia F. Muell. ) oils[J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(13): 125-132.
[26] 张靖, 苏琳, 陈晓雨, 等. 羊骨抗氧化肽酶解法制备和响应面工艺优化[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2021,40(3):18−27. [ZHANG J, SU L, CHEN X Y, et al. Optimization of enzymatic preparation of antioxidant peptides from sheep bone by response surface methodology[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology,2021,40(3):18−27. ZHANG J, SU L, CHEN X Y, et al. Optimization of enzymatic preparation of antioxidant peptides from sheep bone by response surface methodology[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology, 2021, 40(3): 18-27.
[27] 陈丽丽, 赵利, 袁美兰, 等. 大孔吸附树脂对草鱼蛋白水解液脱盐的作用[J]. 食品科学,2016,37(5):84−88. [CHEN L L, ZHAO L, YUAN M L, et al. Desalination of grass carp protein hydrolysate using macroporous adsorption resin[J]. Food Science,2016,37(5):84−88. CHEN L L, ZHAO L, YUAN M L, et al. Desalination of grass carp protein hydrolysate using macroporous adsorption resin[J]. Food Science, 2016, 37(5): 84-88.
[28] 李明杨, 刘帅光, 卢梦娇, 等. 不同抗氧化剂体外抗氧化活性及其对肉品氧化稳定性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(1):67−75. [LI M Y, LIU S G, LU M J, et al. Comparison of antioxidant activity in vitro of antioxidants used in heat-processed meat products and their effects on oxidation[J]. Food Science,2022,43(1):67−75. LI M Y, LIU S G, LU M J, et al. Comparison of antioxidant activity in vitro of antioxidants used in heat-processed meat products and their effects on oxidation[J]. Food Science, 2022, 43(1): 67-75.
[29] 谢翠品, 敬思群, 刘帅, 等. 核桃蛋白酶解物分离纯化及体外抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品科技,2013,38(3):67−70. [XIE C P, JING S Q, LIU S, et al. Purification and in vitro antioxidative activity of walnut protein hydrolysate[J]. Food Science and Technology,2013,38(3):67−70. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2013.03.038 XIE C P, JING S Q, LIU S, et al. Purification and in vitro antioxidative activity of walnut protein hydrolysate[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2013, 38(3): 67-70. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2013.03.038
[30] 刘晓艺, 周玉岩, 过利敏, 等. 不同分子量红花籽抗氧化肽稳定性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(13):94−102. [LIU X Y, ZHOU Y Y, GUO L M, et al. Study on the stability of antioxidant peptides from safflower seeds with different molecular weight[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(13):94−102. LIU X Y, ZHOU Y Y, GUO L M, et al. Study on the stability of antioxidant peptides from safflower seeds with different molecular weight[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(13): 94-102.
[31] 张雯雯, 张艳妮, 杨丽荣, 等. 4种天然物质抗氧化能力的研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2022,43(2):43−50. [ZHANG W W, ZHANG Y N, YANG L R, et al. Study of the antioxidant capacities of four natural substances[J]. Food Research and Development,2022,43(2):43−50. ZHANG W W, ZHANG Y N, YANG L R, et al. Study of the antioxidant capacities of four natural substances[J]. Food Research and Development, 2022, 43(2): 43-50.
[32] 季晓彤, 孙培冬. 桃仁多肽的分离及其抗氧化性能研究[J]. 中国油脂,2018,43(7):77−81. [JI X T, SUN P D. Isolation of peach kernel polypeptide and its antioxidant capacities[J]. China Oils and Fats,2018,43(7):77−81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7969.2018.07.018 JI X T, SUN P D. Isolation of peach kernel polypeptide and its antioxidant capacities[J]. China Oils and Fats, 2018, 43(7): 77-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7969.2018.07.018
[33] HE H J, HUANG N, CAO R J, et al. Structures, antioxidation mechanism, and antioxidation test of the common natural antioxidants in plants[J]. Biophysics,2015,3(1):25−47. doi: 10.12677/BIPHY.2015.31004
[34] KIM D O, LEE K W, LEE H J, et al. Vitamin C equivalent antioxidant capacity (VCEAC) of phenolic phytochemicals[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2002,50(13):3713−3717. doi: 10.1021/jf020071c
[35] 杨洁茹, 刘海波, 李晴, 等. 油茶饼粕中多肽的分离纯化及抗氧化研究[J]. 粮食与食品工业,2022,29(5):4−9. [YANG J R, LIU H B, LI Q, et al. Separation and purification of polypeptides and antioxidant studies in Camellia oleifera cake meal[J]. Cereal & Food Industry,2022,29(5):4−9. YANG J R, LIU H B, LI Q, et al. Separation and purification of polypeptides and antioxidant studies in camellia oleifera cake meal[J]. Cereal & Food Industry, 2022, 29(5): 4-9.
[36] 关海宁, 徐筱君, 孙薇婷, 等. 超高压协同酶法条件下不同分子量大豆分离蛋白水解肽乳化性及抗氧化性研究[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(12):3780−3786. [GUAN H N, XU X J, SUN W T, et al. Study on emulsification and antioxidant properties of soy protein isolate hydrolysatic peptides with different molecular weight by enzymatic hydrolysis under high hydrostatic pressure[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2022,13(12):3780−3786. Study on emulsification and antioxidant properties of soy protein isolate hydrolysatic peptides with different molecular weight by enzymatic hydrolysis under high hydrostatic pressure[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality, 2022, 13(12): 3780-3786.
[37] JUNTACHOTE T, BERGHOFER E. Antioxidative properties and stability of ethanolic extracts of Holy basil and Galangal[J]. Food Chemistry,2005,92(2):193−202. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.04.044
[38] FENG L, PENG F, WANG X J, et al. Identification and characterization of antioxidative peptides derived from simulated in vitro gastrointestinal digestion of walnut meal proteins[J]. Food Research International,2019,116:518−526. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.08.068
[39] LIN S Y, JIN Y, LIU M Y, et al. Research on the preparation of antioxidant peptides derived from egg white with assisting of high-intensity pulsed electric field[J]. Food Chemistry,2013,139(1/4):300−306.
[40] ZOU T B, HE T P, LI H B, et al. The structure-activity relationship of the antioxidant peptides from natural proteins[J]. Molecules,2016,21(1):72. doi: 10.3390/molecules21010072
-
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 周涛,聂艳丽,李翠萍,王大玮. 云南澳洲坚果果实内含物测定及多样性分析. 种子. 2025(01): 31-38 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 曾丽琴,陈雅茹,刘淑集,张玉苍,陈晓婷,苏永昌,罗联钰,刘智禹. 沙丁鱼鱼鳞胶原蛋白肽的制备及其抗氧化活性研究. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2024(03): 214-224 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 付镓榕,马尚玄,魏元苗,徐文婷,郭刚军,贺熙勇. 澳洲坚果抗氧化肽的分离纯化及肽段鉴定. 食品工业科技. 2024(06): 91-99 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 袁高阳,秦心睿,聂晓兵,金文芳,杨玉玉,刘诗菡,范宝磊,苗潇磊. 基于熵权TOPSIS模型对白芨多糖脱蛋白体系的评价研究. 食品工业科技. 2024(07): 76-85 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 徐文婷,付镓榕,马尚玄,魏元苗,杨悦雪,黄克昌,郭刚军,贺熙勇. 不同包装和贮藏温度的澳洲坚果果仁贮藏品质及货架期预测. 食品科学. 2024(16): 232-243 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 焦婷,朱北平,郭文亮,焦健,韩善明,房桂干,谢章红. 3种木质纤维原料热水抽出物抗氧化性的研究. 中国造纸学报. 2024(03): 63-70 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 赵艺科,吴桐,孙孟琪,万茜淋,张哲,杨洪梅. 高分辨液相色谱-串联质谱法分析冻干西洋参抗氧化多肽. 质谱学报. 2024(06): 851-860 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 常茹菲,葛运兵,杨晓丽,张红星,谢远红. 酶解法制备澳洲坚果蛋白肽工艺优化研究. 中国粮油学报. 2024(10): 102-108 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 赵一萌,索晓雄,刘彩霞,杜晨晖,闫艳,裴香萍. 不同分子质量酸枣仁多肽制备及功能特性研究. 食品与发酵工业. 2024(24): 91-96 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 洪燕婷,颜阿娜,汪少芸,蔡茜茜. 马鲛鱼骨抗氧化肽的酶解工艺及性质研究. 青海大学学报. 2024(06): 58-66+82 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



