Effects of Phenyllactic Acid on Listeria monocytogenes Biofilms
-
摘要: 为研究苯乳酸(Phenyllactic Acid,PLA)对单增李斯特菌(Listeria monocytogenes,Lm)生物被膜的影响,采用结晶紫法检测Lm生物被膜生物量、倒置显微镜和扫描电镜观察Lm生物被膜结构;分别采用苯酚硫酸法、福林酚法和二苯胺法测定生物被膜中胞外多糖、胞外蛋白和胞外DNA的含量;利用实时荧光定量PCR检测PLA对Lm生物被膜形成相关基因转录水平的影响。结果表明:PLA对8株Lm菌株的最小抑菌浓度值均为6 mg/mL。PLA通过抑制胞外多糖和胞外蛋白的合成抑制Lm生物被膜的形成。对于Lm成熟生物被膜,PLA通过减少胞外多糖和胞外蛋白的量破坏生物被膜结构、降低生物被膜生物量。PLA还能抑制Lm的运动性。在PLA作用下Lm群体感应系统agr的转录水平显著(P<0.05)降低。作为一种天然抗菌物质,PLA在控制Lm及其生物被膜对食品污染方面具有潜在的应用价值。Abstract: To investigate the effect of phenyllactic acid (PLA) on Listeria monocytogenes biofilms, crystal violet method was used to measure the biomass of L. monocytogenes biofilms, and inverted microscope and scanning electron microscope were used to observe the structure of L. monocytogenes biofilms, the content of extracellular polysaccharide, extracellular protein and extracellular DNA in biofilm was measured by phenol-sulfuric acid method, Folin-phenol method and diphenylamine method, respectively. The effect of PLA on the transcription of genes associated with biofilm formation of L. monocytogenes was detected by real-time quantitative PCR. The results showed that the minimum inhibitory concentration values of PLA against eight L. monocytogenes strains were 6 mg/mL. PLA inhibited L. monocytogenes biofilm formation by reducing the synthesis of extracellular polysaccharides and extracellular proteins. For mature biofilms of L. monocytogenes, PLA destroyed the biofilm structure and reduced the biofilm biomass by reducing the amount of extracellular polysaccharides and extracellular proteins. PLA also inhibited the swarming motility of L. monocytogenes. The transcription levels of quorum sensing system agr in L. monocytogenes were significantly (P<0.05) decreased in the presence of PLA. As a natural antimicrobial compound, PLA had the potential application to control food contamination by L. monocytogenes and its biofilms.
-
单增李斯特菌(Listeria monocytogenes,Lm)是一种重要的食源性致病菌,在自然界中广泛存在。该菌能够引起人畜共患病——李斯特菌病,典型的临床症状表现为脑膜炎、败血症、流产等[1]。李斯特菌病的发病率不高,但是致死率可高达33%,严重威胁人类身体健康[2]。大量研究表明,食用被Lm污染的食品是造成李斯特菌病散发和爆发流行的主要原因[3]。Lm可粘附在食品接触表面形成生物被膜,被膜态的Lm能够在食品加工环境中存活数月乃至数年之久[4]。被膜态Lm分泌的胞外聚合物主要由胞外多糖、胞外蛋白和胞外DNA组成,这些胞外物质可形成物理屏障,阻碍抗菌药物向被膜内扩散,提高Lm在不利环境中的存活能力[5-6]。Lm生物被膜是一种潜在的污染源,可能引起食品交叉污染和加工后污染,威胁食品安全[7]。因此,寻找能够有效抑制Lm及其生物被膜的抗菌物质对预防和控制Lm引起的食源性疾病显得尤为重要。
苯乳酸(Phenyllactic acid,PLA)广泛存在于许多植物和食品中,如雪莲、天麻、蜂蜜、乳酸菌发酵食品等[8-9]。PLA抗菌谱广,对革兰氏阳性菌、革兰氏阴性菌以及真菌均表现出良好的抗菌活性[10-12]。研究发现PLA作用后细菌细胞壁结构被破坏,胞内成分泄漏,表明细胞壁可能是PLA的作用靶点之一。PLA还能通过与细菌基因组DNA结合阻止DNA复制从而干扰细胞正常功能[13-15]。PLA具有水溶性好、理化性质稳定、安全性高等优点,在食品工业中具有广阔的应用前景[16-17]。
目前的研究主要集中在PLA对浮游态细菌的抑菌活性和抑菌机制方面[8,13-15],而关于PLA对细菌生物被膜抑制效果的研究相对较少。本文主要研究PLA对Lm生物被膜形成的抑制及成熟生物被膜的清除效果,通过检测生物被膜胞外聚合物的含量、Lm运动性以及生物被膜相关基因转录水平初步探究PLA对Lm生物被膜的作用机制,为PLA在控制Lm及其生物被膜方面的应用奠定理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
Lm 标准菌株EGD-e和10403S 由华中师范大学罗勤教授惠赠,Lm食品分离株L1、L44、L46、L60、L69和L82由本实验室保存,菌株信息见表1;脑心浸液培养基(Brain Heart Infusion,BHI) OXOID;PALCAM琼脂 青岛高科园海博生物技术有限公司;草酸铵 山东豪顺化工有限公司;结晶紫 天津市大茂化学试剂厂;无水乙醇 天津富宇精化工有限公司;戊二醛 上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;叔丁醇 天津市大茂化学试剂厂;苯酚 济南鑫沃化学有限公司;胰蛋白胨大豆肉汤培养基(Tryptic Soy Broth,TSB) 青岛高科园海博生物技术有限公司;福林酚 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;小牛胸腺DNA 上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;RealMaster Mix (SYBR Green)试剂盒 天根生化科技(北京)有限公司;细菌RNA提取试剂盒 上海碧云天生物技术有限公司;荧光定量PCR试剂盒 北京天根生化科技有限公司。
表 1 菌株信息Table 1. Strain information菌株 来源 血清型 EGD-e 动物 1/2a 10403S 人 1/2a L1 生猪肉 1/2c L44 生鸡肉 1/2c L46 速冻米面制品 4b L60 生猪肉 1/2c L69 速冻米面制品 4b L82 速冻米面制品 1/2a JSM-6390LV场发射扫描式电子显微镜(Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy,FE-SEM) 日本株式会社日立高新技术公司;DMi1倒置显微镜 Leica公司;LightCycle96 实时荧光定量PCR仪 ABI公司;Synergy H1酶标仪 美国安捷伦Bio Tek公司;SW-CJ-2FD超净工作台 苏州安泰空气技术有限公司;HZQ-X300C恒温振荡器 上海一恒科学仪器有限公司;LHS-800C生化恒温培养箱 上海力辰仪器科技有限公司;JIDI-20R冷冻离心机 广州吉迪仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 最小抑菌浓度(Minimal Inhibitory Concentration,MIC)的测定
采用琼脂稀释法检测PLA对Lm菌株的MIC值[18]。以无菌去离子水为溶剂配制为20 mg/mL的PLA母液。配制含有不同浓度PLA(终浓度分别为0、2、4、6和8 mg/mL)的BHI平板,取1 μL(稀释比例为1:5)稀释后的菌液接种至BHI平板,37 ℃培养2 d。
1.2.2 PLA对Lm生物被膜形成的影响
1.2.2.1 结晶紫法
采用结晶紫染色法测定PLA对8株菌生物被膜形成的影响[19]。挑取单个菌落接种于BHI液体培养基中过夜培养。将过夜培养物按1%的比例加入培养基中,然后加入PLA(终浓度分别为1/10MIC、1/8MIC和1/4MIC,不添加PLA作为对照),37 ℃分别孵育1、2、3 d。孵育结束后,用无菌PBS洗涤3次以去除浮游细菌。生物被膜经草酸铵结晶紫染色和95%的乙醇脱色后,用酶标仪检测OD595 nm,并置于倒置显微镜下拍照观察。
1.2.2.2 FE-SEM观察Lm生物被膜
本研究选择菌株10403S进行FE-SEM观察生物被膜结构及生物被膜胞外多聚物含量检测的研究。在微孔板中培养菌株10403S生物被膜2 d后,小心去除孔中的液体,使用无菌的PBS缓冲液冲洗3遍。在每个孔中加入4%戊二醛,充分混匀后4 ℃静置9 h,再用PBS缓冲液洗涤3次。乙醇依次以30%、50%、70%、85%、90%和100%的梯度脱水3次,每次脱水10 min。晾干后用100%叔丁醇置换100%乙醇3次,每次10 min。将菌体干燥后利用离子喷溅射镀膜仪在样品表面镀100-120 A的金膜,放置观察室中进行观察[20]。
1.2.2.3 PLA对Lm生物被膜胞外多聚物形成的影响
根据Dai等[21]的方法提取菌株10403S生物被膜胞外多聚物。分别采用苯酚硫酸法[22]、福林酚法[23]和二苯胺法[24]测定胞外多聚物中胞外多糖、胞外蛋白和胞外DNA的含量。葡萄糖、蛋白质和DNA的标曲方程及相关系数分别为y=11.65x+0.0698(R2=0.9984),y=29.229x+0.0441(R2=0.9966),y=0.004+0.0291(R2=0.9902)。
1.2.3 PLA对Lm成熟生物被膜的影响
1.2.3.1 结晶紫法
根据Zhou等[25]的方法制备成熟生物被膜。将8株Lm接种到BHI培养基中,在96孔板中培养2 d以形成成熟的生物被膜,用无菌PBS冲洗生物被膜,然后分别添加不同浓度的PLA(0、1/2MIC、MIC、2MIC),孵育1 h,用PBS洗涤后用草酸铵结晶紫染色和95%的乙醇脱色后,用酶标仪检测OD595nm,并置于倒置显微镜下拍照观察。
1.2.3.2 FE-SEM观察生物被膜
将菌株10403S生物被膜培养2 d后分别添加0、1/2MIC、MIC、2MIC的PLA,孵育1 h后用无菌PBS洗3遍,然后加入4%戊二醛固定,后续方法同1.2.2.2。
1.2.3.3 PLA对Lm成熟生物被膜胞外多聚物的影响
将菌株10403S生物被膜培养2 d后分别添加0、1/2MIC、MIC、2MIC的PLA,孵育1 h,后续按照1.2.2.3的方法测定胞外多聚物含量。
1.2.4 PLA对Lm运动性的影响
含有0.3%琼脂的TSB平板用于游泳运动性的检测,含有0.5%琼脂的TSB平板用于群集运动性的检测[26]。在TSB平板中加入不同浓度的PLA(1/10MIC、1/8MIC、1/4MIC)以调查PLA对Lm菌株10403S运动性的影响。取1 μL菌液点接至培养皿中心,25 ℃培养2 d。使用游标卡尺测量菌圈直径,并计算抑制率。
1.2.5 PLA对Lm生物被膜相关基因转录水平的影响
将菌株10403S菌液(OD600 nm约为0.2)分为两组,一组不加任何药物作为对照组,另一组加入3 mg/mL的PLA作为实验组,继续培养30 min。按照细菌RNA提取试剂盒的使用说明提取细菌总RNA,利用超微量分光光度计测定RNA的浓度和纯度。将总RNA反转录为cDNA,以cDNA作为模板,使用RealMaster Mix(SYBR Green)试剂盒进行实时荧光定量PCR检测。以16S rRNA为内参基因,采用2–ΔΔCT法进行基因转录水平的分析。目的基因在实验组中的转录水平与其在对照组中的转录水平的比值即为该基因的相对转录水平。所需引物参考文献[27]设计,如表2所示。
表 2 本研究中使用的引物Table 2. Primers used in this study基因 引物名称 序列(5'-3') 16S rRNA RT16S1
RT16S2GGGAGGCAGCAGTAGGGA
CCGTCAAGGGACAAGCAGluxS RTlmo1288-1
RTlmo1288-2AAGCACCTTTTGTGAGACTGG
CCGTTAGTGTTGTAGCGATGAagrBD RTlmo0048/49-1
RTlmo0048/49-1GCTGGAAAGATGATGAAGAA
ATTAATCCTCCACTGTCTAAagrC RTlmo0050-1
RTlmo0050-2GCTGGAAAGATGATGAAGAA
ATTAATCCTCCACTGTCTAAagrA RTlmo0051-1
RTlmo0051-2GCTGGAAAGATGATGAAGAA
ATTAATCCTCCACTGTCTAAmotA RTlmo0685-1
RTlmo0685-2TTACGGGATGTTTGGAA
TCGCTAAGTTTGTCTGGGTTmotB RTlmo0686-1
RTlmo0686-2TTACGGGATGTTTGGAA
TCGCTAAGTTTGTCTGGGTTflaA RTlmo0690-1
RTlmo0690-2GCTGGTATGAGTCGCCTTAG .
CATTTGCGGTGTTTGGT1.3 数据处理
所有样品均设置3个平行,处理后的数据以平均值±标准差表示。利用GraphPad Prism8软件对所得的实验数据进行双尾t检验分析(与对照组相比,*代表P<0.05,**代表P<0.01,***代表P<0.001)。PLA对Lm生物被膜的抑制率和清除率、胞外多聚物的抑制率和清除率及运动性的抑制率计算公式如下:
抑制率/清除率(%)=[(A0−A1)/A0]×100 式中A0:未经PLA处理组;A1:PLA处理组。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 PLA对Lm生物被膜形成的抑制
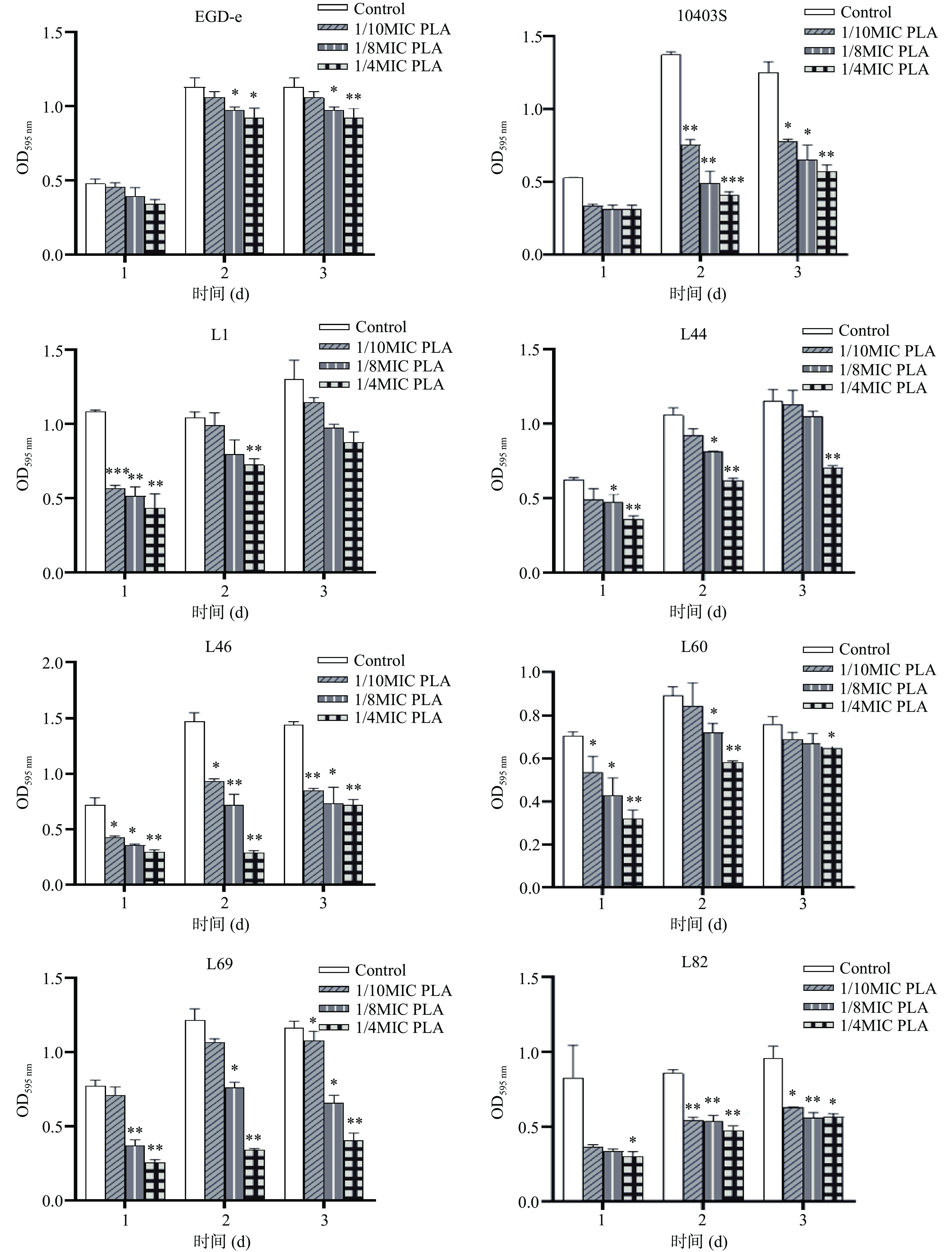
测得PLA对所有受试菌株的MIC值均为6 mg/mL。如图1所示:8株Lm菌株均能在实验条件下形成生物被膜,但不同菌株的被膜形成能力存在差异,这可能是由于菌株自身特性不同造成的。在亚抑制浓度(低于MIC的药物浓度)PLA的作用下,8株Lm形成生物被膜的能力受到不同程度的抑制。其中,菌株10403S为Lm标准菌株,具有较强的生物被膜形成能力,且PLA对其生物被膜的抑制效果较好,因此选择菌株10403S进行后续的FE-SEM观察生物被膜结构及胞外多聚物含量检测。当培养2 d时,1/10 MIC、1/8MIC和1/4MIC的PLA对菌株10403S生物被膜的抑制率分别为45.07%、64.12%和70.32%。结果表明,亚抑制浓度PLA呈浓度依赖性抑制Lm生物被膜的形成。
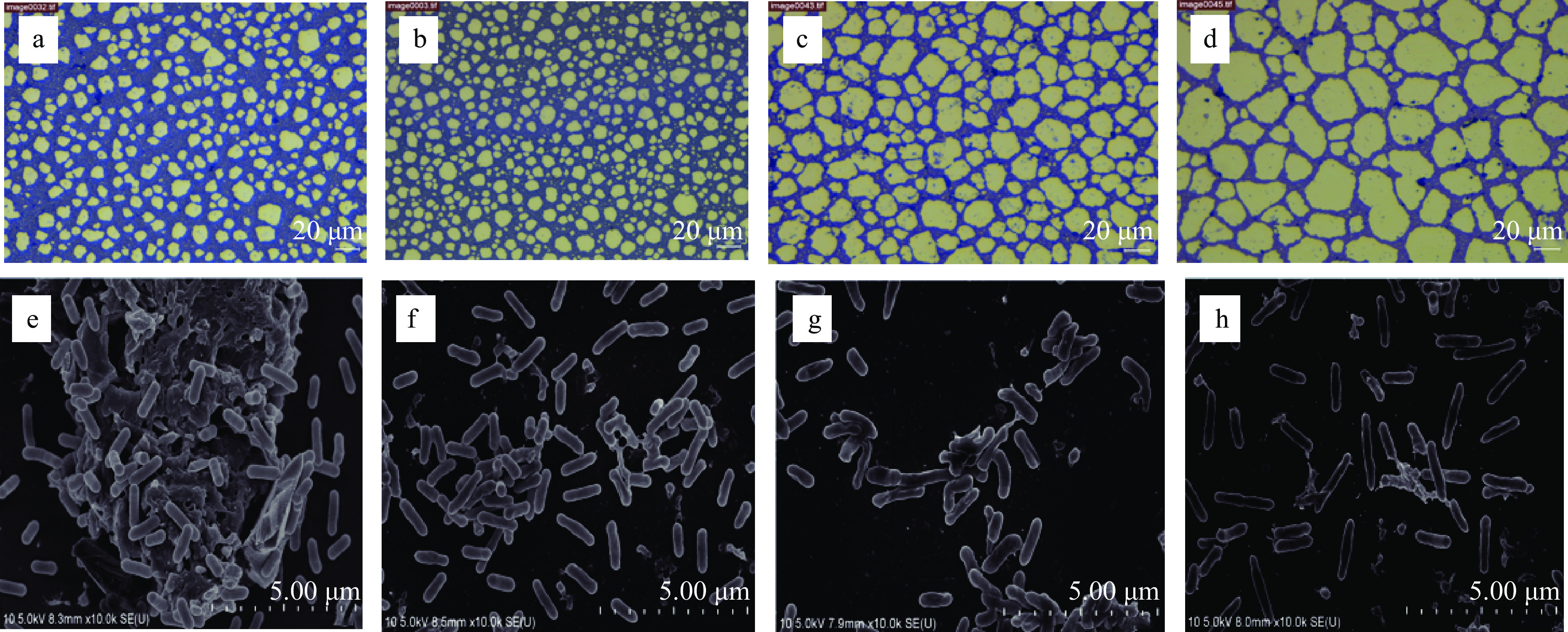
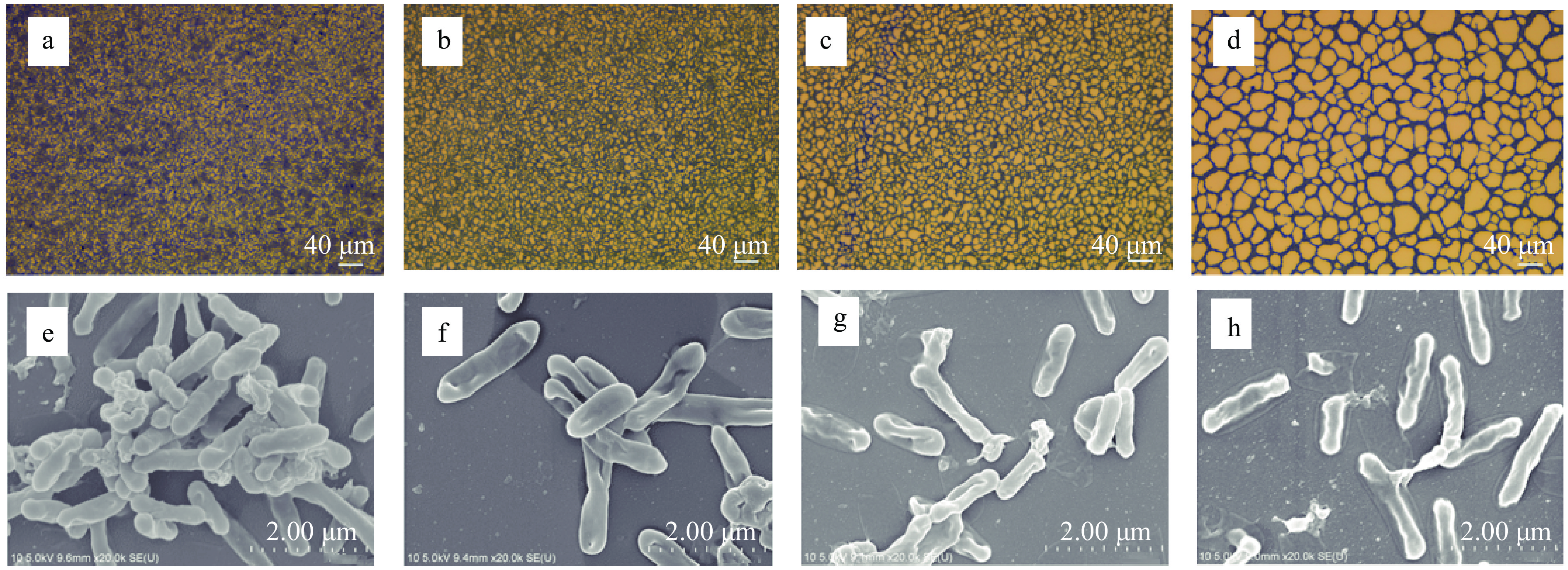
利用倒置显微镜观察不同浓度PLA对Lm菌株10403S生物被膜形态的影响。经过2 d的培养,对照组形成均匀且致密的生物被膜,见图2a。加入PLA后,菌株形成的生物被膜变得疏松,见图2b~图2d。由FE-SEM结果可知,未经PLA处理的菌株10403S菌株细胞形态完好,大量细胞聚集成团,丰富的胞外聚合物将细菌包裹起来,见图2e。经1/10MIC和1/8MIC的PLA处理后,粘附的细胞减少,胞外多聚物也减少,见图2f~图2g。经1/4MIC的PLA处理后,粘附的细胞进一步减少,同时能观察到破损的细胞,见图2h。这可能是由于生物被膜中的细胞失去胞外聚合物的保护后直接受到PLA的作用,导致细胞结构被破坏、细胞壁破裂。
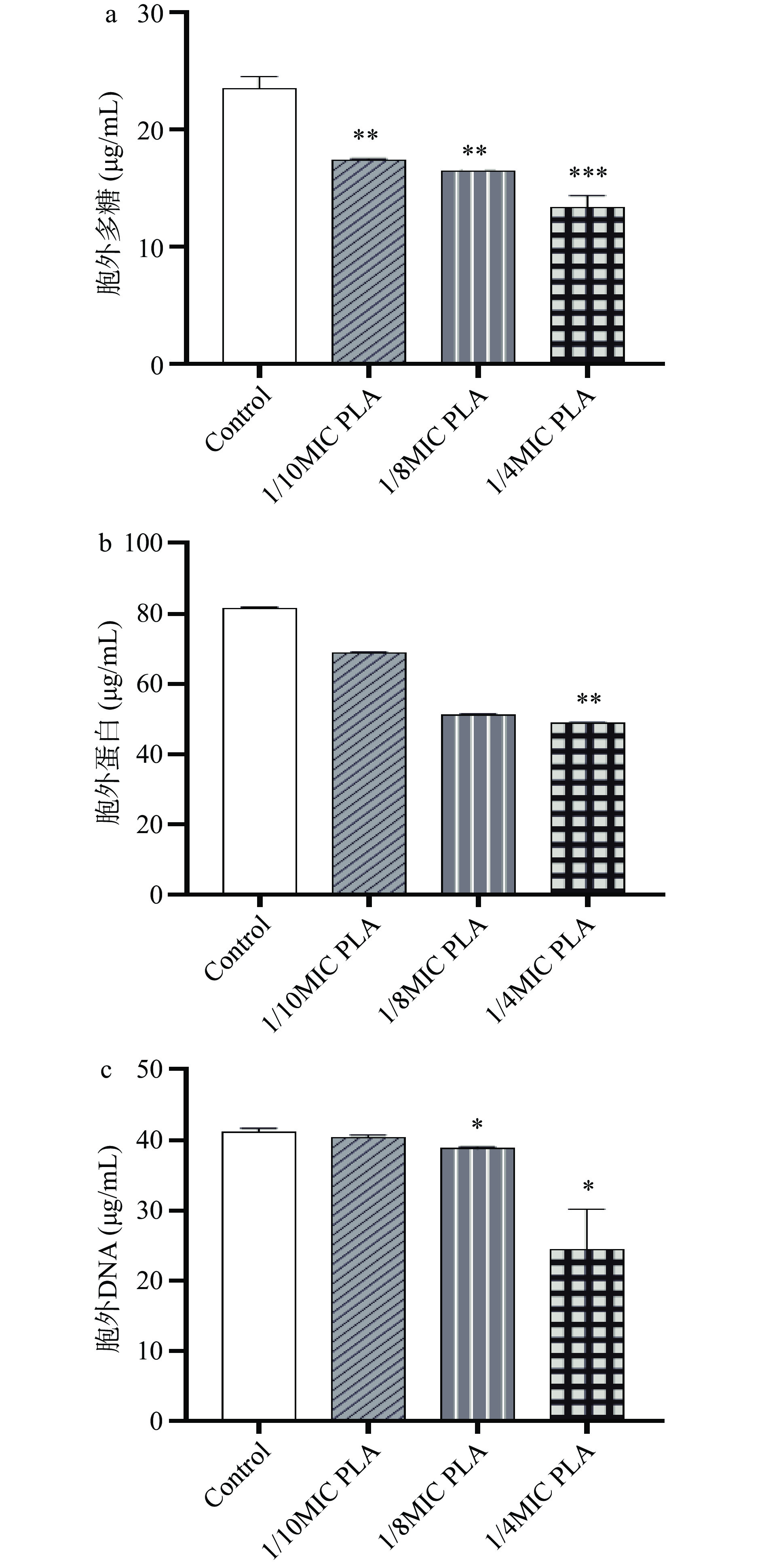
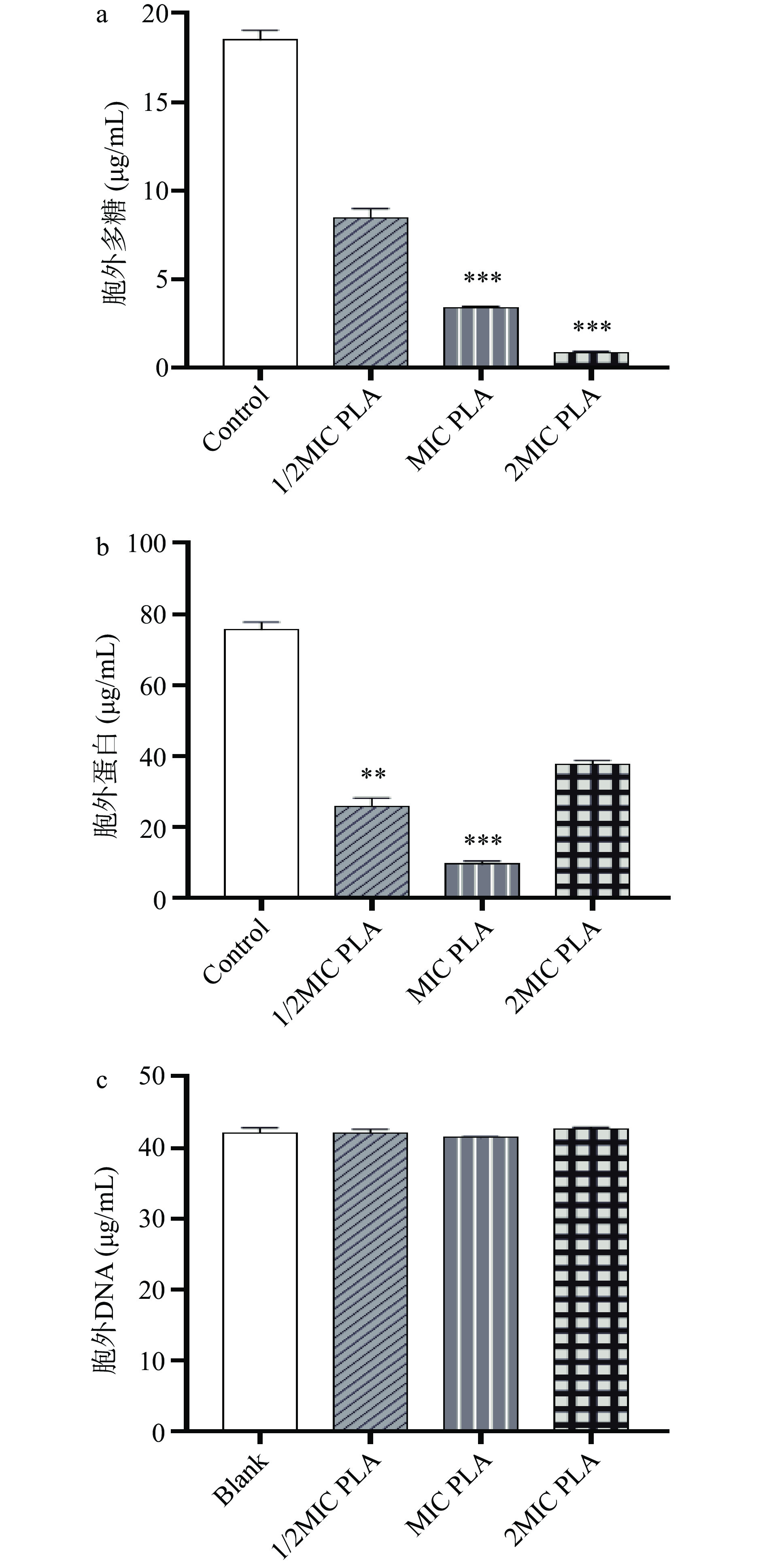
由图3可知,经1/10 MIC、1/8MIC和1/4MIC的PLA处理后,生物被膜中胞外多糖的含量显著降低(P<0.05)。胞外蛋白仅1/4MIC组与对照组有统计学差异,而胞外DNA的含量在1/8MIC和1/4MIC两个浓度下均与对照组有统计学差异(P<0.05)。
胞外聚合物主要由胞外多糖、胞外蛋白质和胞外DNA组成,是生物被膜的重要组成部分,在生物被膜中起稳定结构和保护的作用[28]。胞外聚合物的成分和比例在不同种细菌中存在很大差异。大多数细菌生物被膜的胞外聚合物中占比最高的是胞外多糖[29]。而在Lm生物被膜的胞外聚合物中胞外蛋白的含量最高,其次是胞外DNA和胞外多糖[6]。研究表明,胞外蛋白和胞外DNA在Lm的初始粘附和生物被膜形成的早期阶段发挥重要作用[30]。本研究中,亚抑菌浓度PLA能够抑制Lm生物被膜的形成,进一步研究发现Lm生物被膜中胞外多糖和胞外蛋白含量降低。以上证据表明,亚抑制浓度的 PLA可以通过减少胞外多糖和细胞外蛋白的分泌来抑制Lm生物被膜的形成。
2.2 PLA对Lm成熟生物被膜的清除
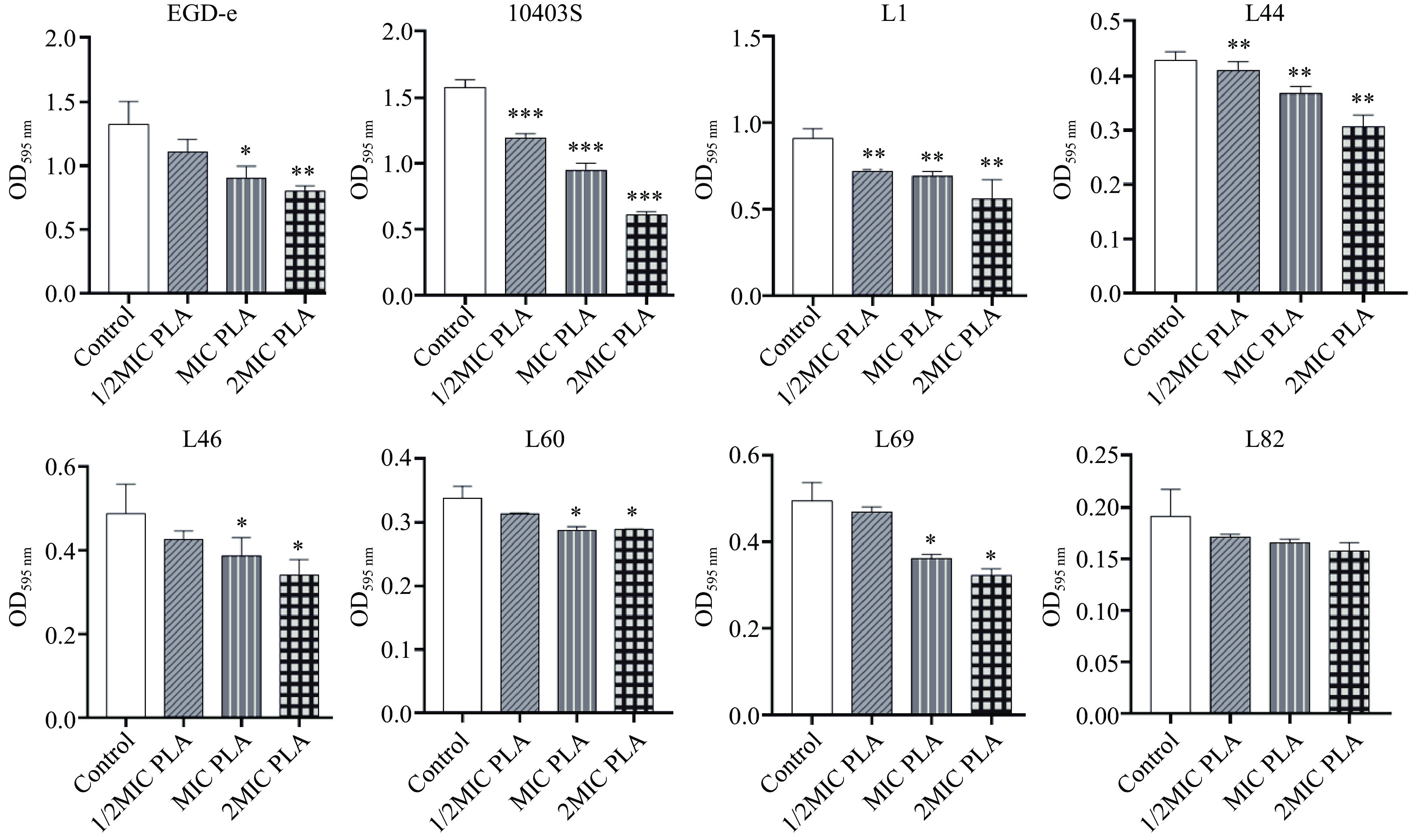
由图4可知,Lm成熟生物被膜经1/2MIC、MIC和2MIC的PLA处理后,生物被膜量均减少,其中菌株10403S和L1的生物被膜量显著减少(P<0.05)。1/2 MIC、MIC和2MIC的PLA对菌株10403S生物被膜的清除率分别为24.03%、39.56%和61.32%。相同的作用时间,PLA的浓度越高,菌株的生物被膜越少,即PLA对Lm菌株生物被膜的清除作用呈浓度依赖性。
倒置显微镜观察结果显示,与对照相比(图5a),PLA处理组的生物被膜更加疏松(图5b~图5d)。FE-SEM结果显示,PLA处理后,Lm粘附细胞变少,细胞出现皱缩和塌陷,当PLA浓度为2MIC时,这种变化更加明显,甚至能够观察到细胞内容物的外泄(图5f~图5g)。
如图6所示,经MIC和2MIC的PLA处理后,成熟生物被膜中胞外多糖的含量显著降低,分别降低了81.6%和95.3%(P<0.05)。与对照相比,PLA作用下成熟生物被膜中胞外蛋白的含量明显降低。PLA处理对成熟生物被膜中胞外DNA的含量没有产生明显影响(P>0.05)。
成熟生物被膜对抗菌物质的抵抗力很强,难以清除。本研究结果显示Lm成熟生物被膜经PLA处理后生物被膜生物量降低,表明PLA对Lm成熟生物被膜具有清除作用。PLA处理后,Lm生物被膜中胞外多糖的含量急剧下降。当PLA的浓度为1/2MIC时,胞外多糖含量减少超过一半;当PLA的浓度为2MIC时,几乎所有的胞外多糖被破坏。PLA处理后,Lm生物被膜中胞外蛋白的含量也明显降低。值得注意的是,2MIC的PLA作用后胞外蛋白的含量高于1/2MIC和MIC处理组。这可能是由于在2MIC PLA作用下Lm细胞被破坏,细胞内蛋白质泄漏所致。这些结果表明PLA可以通过作用于胞外多糖和胞外蛋白来破坏Lm的生物被膜结构。
2.3 PLA对Lm运动性的影响
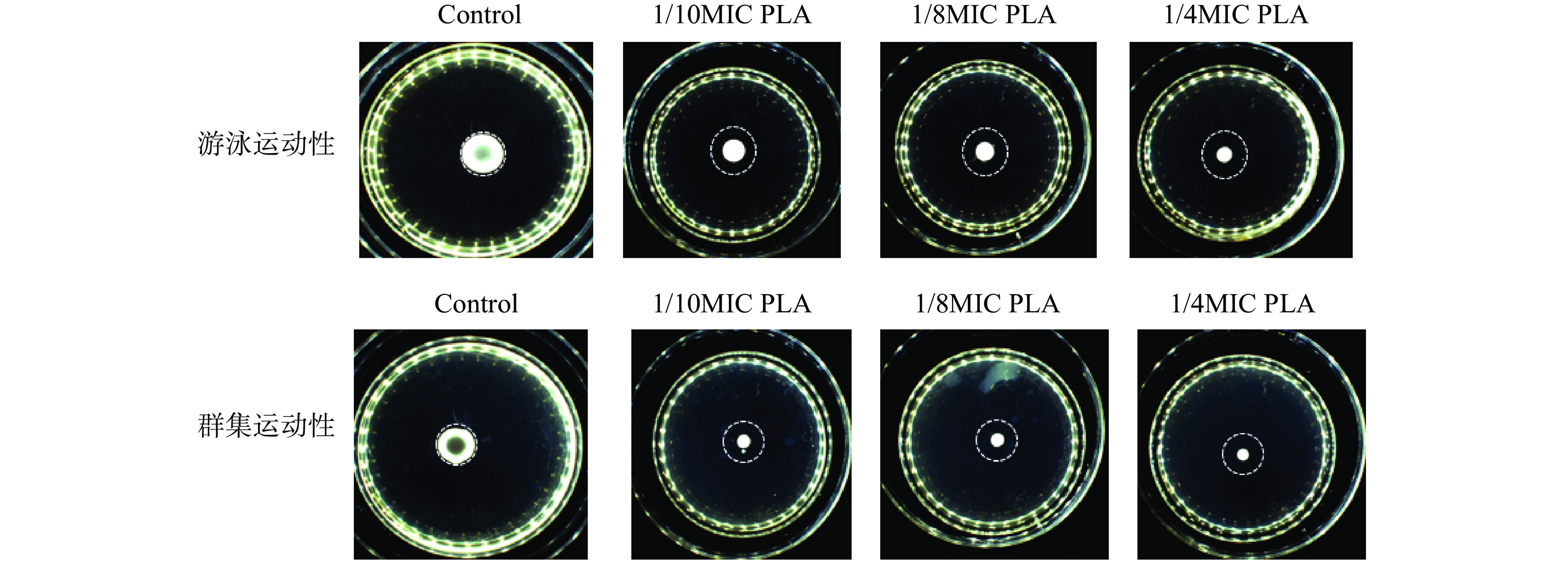
如图7所示,亚抑菌浓度PLA作用下Lm菌株10403S形成的运动圈直径减小。如表3所示,在1/10 MIC、1/8 MIC和1/4 MIC的PLA作用下菌株游泳运动性的抑制率分别为31.68%、36.29%和55.68%;群集运动性的抑制率分别为57.94%、62.40%、68.90%。由此可见PLA对Lm的运动性有较好的抑制效果。
表 3 PLA对Lm运动性的抑制Table 3. Inhibition of PLA on motility of L. monocytogenesPLA浓度 游泳运动性 群集运动性 直径(mm) 抑制率(%) 直径(mm) 抑制率(%) Control 11.71 10.77 1/10MIC PLA 8.00 31.68% 4.53 57.94% 1/8MIC PLA 7.46 36.29% 4.05 62.40% 1/4MIC PLA 5.19 55.68% 3.35 68.90% 大量文献表明,鞭毛介导的运动性在细菌生物被膜形成中发挥重要作用[31]。鞭毛介导的运动性可以使细菌向有营养物质存在的表面游动同时克服表面张力达到物体表面,从而促进生物被膜的形成。鞭毛介导的运动性可分为游泳运动性和群集运动性,前者是细菌的个体运动,而后者可以协调细菌在固体表面的运动,因此群集运动性与细菌生物被膜的形成关系更密切[32]。本研究表明PLA能够抑制Lm的群集运动性,这可能也进一步导致了Lm生物被膜形成能力的降低。
2.4 PLA作用下Lm生物被膜相关基因的转录水平
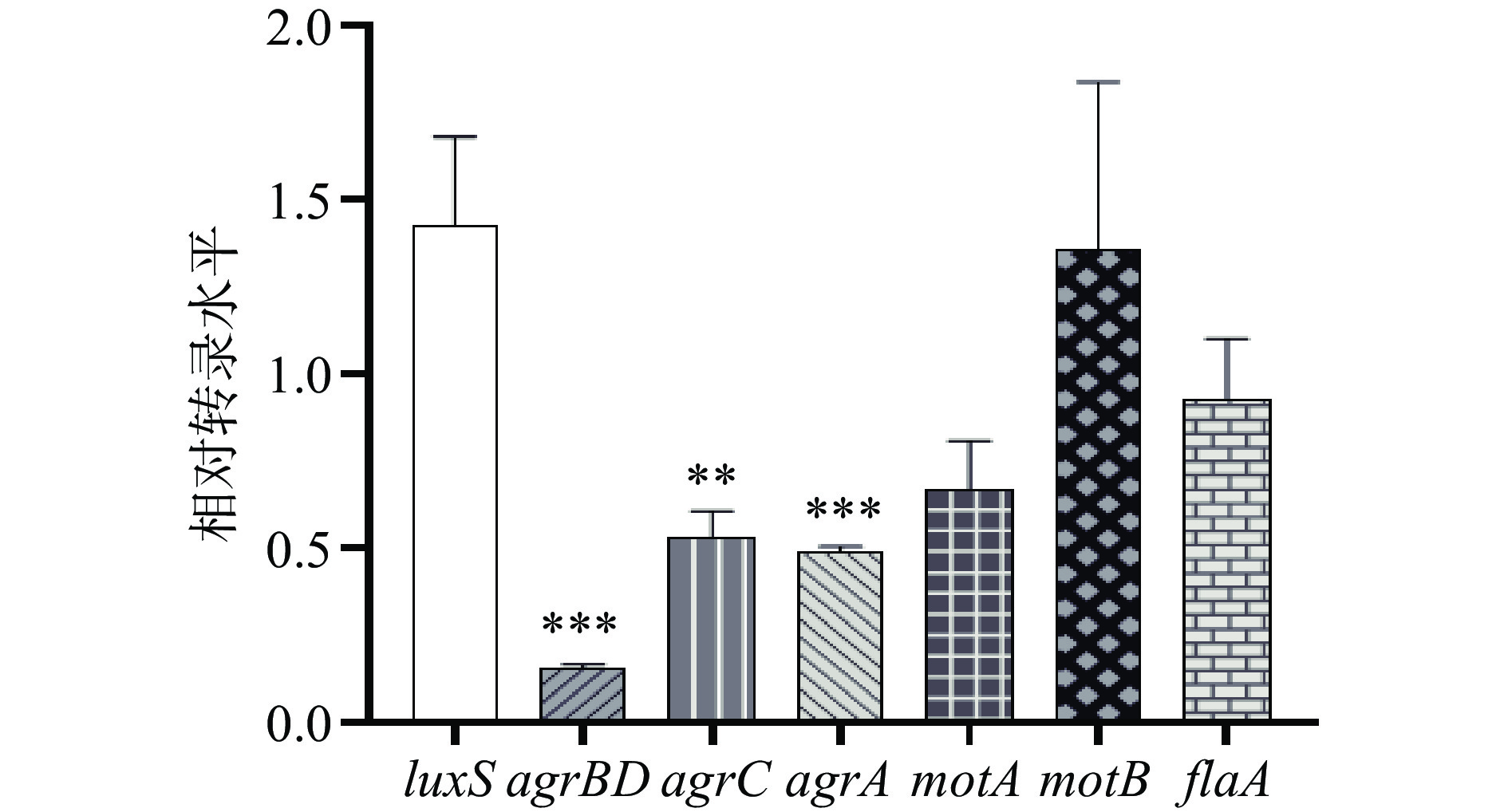
采用qRT-PCR研究PLA对鞭毛介导运动性的相关基因(motA、motB和flaA)和群体感应相关基因(luxS、agrBD、agrC和agrA)转录水平的影响(图8)。在PLA的作用下,agr操纵子所有基因的转录水平均显著下降(P<0.01);其余基因的转录水平没有明显变化:luxS和motB的转录水平分别为1.42和1.36倍(P>0.05);motA和flaA的转录水平分别为0.69倍和0.93倍(P>0.05)。
群体感应是细菌通过自身产生的信号分子进行信息交流和协调群体行为的过程。群体感应系统在调控细菌生物被膜形成过程中发挥至关重要的作用,利用群体感应抑制剂干扰群体感应系统成为控制细菌生物被膜危害的有效策略。目前研究者已在Lm中发现两个群体感应系统,即LuxS和Agr系统。前人研究证实luxS负调控Lm生物被膜的形成[33]。Agr系统是由agrBDCA四个基因组成的操纵子,agr基因的缺失导致Lm生物被膜形成能力降低,即Lm生物被膜的形成受Agr系统正调控[34]。PLA作用下luxS的转录水平没有明显变化,而agr系统所有基因的转录水平均显著降低,表明PLA可能是Agr群体感应系统的抑制剂。PLA作用下flaA、motA和motB的转录水平没有明显变化,推测PLA可能通过抑制其他运动相关基因来抑制Lm的运动性。
3. 结论
本论文主要研究PLA对Lm生物被膜的影响及其作用机制。结果表明,PLA不仅能有效抑制Lm生物被膜的形成,对成熟生物被膜也表现出良好的清除效果。在PLA的作用下,生物被膜胞外多糖和胞外蛋白的分泌量减少,同时Lm运动性及agr群体感应系统的转录水平也明显受到抑制。本研究为PLA在控制Lm及其生物被膜方面的应用奠定理论基础。作为一种天然抗菌物质,PLA在控制Lm及其生物被膜方面具有潜在应用价值。
-
表 1 菌株信息
Table 1 Strain information
菌株 来源 血清型 EGD-e 动物 1/2a 10403S 人 1/2a L1 生猪肉 1/2c L44 生鸡肉 1/2c L46 速冻米面制品 4b L60 生猪肉 1/2c L69 速冻米面制品 4b L82 速冻米面制品 1/2a 表 2 本研究中使用的引物
Table 2 Primers used in this study
基因 引物名称 序列(5'-3') 16S rRNA RT16S1
RT16S2GGGAGGCAGCAGTAGGGA
CCGTCAAGGGACAAGCAGluxS RTlmo1288-1
RTlmo1288-2AAGCACCTTTTGTGAGACTGG
CCGTTAGTGTTGTAGCGATGAagrBD RTlmo0048/49-1
RTlmo0048/49-1GCTGGAAAGATGATGAAGAA
ATTAATCCTCCACTGTCTAAagrC RTlmo0050-1
RTlmo0050-2GCTGGAAAGATGATGAAGAA
ATTAATCCTCCACTGTCTAAagrA RTlmo0051-1
RTlmo0051-2GCTGGAAAGATGATGAAGAA
ATTAATCCTCCACTGTCTAAmotA RTlmo0685-1
RTlmo0685-2TTACGGGATGTTTGGAA
TCGCTAAGTTTGTCTGGGTTmotB RTlmo0686-1
RTlmo0686-2TTACGGGATGTTTGGAA
TCGCTAAGTTTGTCTGGGTTflaA RTlmo0690-1
RTlmo0690-2GCTGGTATGAGTCGCCTTAG .
CATTTGCGGTGTTTGGT表 3 PLA对Lm运动性的抑制
Table 3 Inhibition of PLA on motility of L. monocytogenes
PLA浓度 游泳运动性 群集运动性 直径(mm) 抑制率(%) 直径(mm) 抑制率(%) Control 11.71 10.77 1/10MIC PLA 8.00 31.68% 4.53 57.94% 1/8MIC PLA 7.46 36.29% 4.05 62.40% 1/4MIC PLA 5.19 55.68% 3.35 68.90% -
[1] 张辉, 崔焕忠, 郑鑫. 单核细胞增生性李斯特菌生物被膜形成调控机制研究进展[J]. 中国兽医杂志,2013,49(8):53−55. [ZHANG H, CUI H Z, ZHENG X. Research progress on regulation mechanism of biofilm formation of Listeria monocytogenes[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine,2013,49(8):53−55. ZHANG H, CUI H Z, , ZHENG X. Research progress on regulation mechanism of biofilm formation of Listeria monocytogenes [J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2013, 49(8): 53-55.
[2] HEDBERG C. Food-related illness and death in the United States[J]. Emerging Infectious Diseases,1999,5(6):840−842. doi: 10.3201/eid0506.990624
[3] BERMUUDEZ-CAPDVILA M, CERVANTES-HUAMÁN B R H, RODRÍGUEZ-JEREZ J J, et al. Repeated sub-inhibitory doses of cassia essential oil do not increase the tolerance pattern in Listeria monocytogenes cells[J]. LWT Food Science and Technology,2022,165:113681. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113681
[4] 付娇娇, 王旭, 刘海泉, 等. 不同培养条件下sigB对单增李斯特菌生物被膜形成的影响[J]. 上海海洋大学学报,2016,25(4):634−640. [FU J J, WANG X, LIU H Q, et al. Effect of sigB on biofilm formation of Listeria monocytogenes under different culture conditions[J]. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University,2016,25(4):634−640. FU J J, WANG X, LIU H Q, et al. Effect of sigB on biofilm formation of Listeria monocytogenes under different culture conditions[J]. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 2016, 25(4): 634-640.
[5] 杨帅. 铜绿假单胞菌粘附表型及其差异的研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2018 YANG Shuai. A study of attaching-behaviorsand -phenotype variation inplanktonic cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2018.
[6] COLAGIORGI A, DI CICCIO P, ZANARDI E, et al. A look inside the Listeria monocytogenes biofilms extracellular matrix[J]. Hefei:Microorganisms,2016,4(3):22. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms4030022
[7] 王园, 孙琳珺, 程颖, 等. 食品加工环境胁迫因素对单核细胞增生李斯特菌生物膜形成的影响研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(21):246−255. [WANG Y, SUN L J, CHENG Y, et al. Progress in the study of the effect of food processing environmental stresses on Listeria monocytogenes biofilm formation[J]. Food Science,2021,42(21):246−255. WANG Y, SUN L J, CHENG Y, et al. Progress in the study of the effect of food processing environmental stresses on Listeria monocytogenes biofilm formation [J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(21): 246-255.
[8] NING Y W, YAN A H, YANG K, et al. Antibacterial activity of phenyllactic acid against Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli by dual mechanisms[J]. Food Chemistry,2017,228:533−540. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.01.112
[9] 黄国昌, 顾斌涛, 于一尊, 等. 植物乳杆菌BLPC002产苯乳酸发酵工艺优化[J]. 中国酿造,2021,40(12):75−80. [HUANG G C, GU B T, YU Y Z, et al. Optimization of fermentation process of phenyllactic acid production by Lactobacillus plantarum BLPC002[J]. China Brewing,2021,40(12):75−80. HUANG G C, GU B T, YU Y Z, et al. Optimization of fermentation process of phenyllactic acid production by Lactobacillus plantarum BLPC002 [J]. China Brewing, 2021, 40(12): 75-80.
[10] 邓廷山, 武国干, 孙宇, 等. 苯乳酸生物合成的研究进展[J]. 中国生物工程杂志,2020,40(9):62−68. [DENG T S, WU G G, SUN Y, et al. Research progress of phenyllactic acid biosynthesis[J]. Chinese Journal of Bioengineering,2020,40(9):62−68. DENG T S, WU G G, SUN Y, et al. Research progress of phenyllactic acid biosynthesis[J]. Chinese Journal of Bioengineering, 2020, 40(9): 62-68.
[11] 谢全喜, 侯楠楠, 王梅, 等. 高产苯乳酸菌株的筛选及其在豆粕发酵中的应用[J]. 中国酿造,2021,40(7):65−70. [XIE Q X, HOU N N, WANG M, et al. Screening of high-yield phenyllactic acid strain and its application in soybean meal fermentation[J]. China Brewing,2021,40(7):65−70. XIE Q X, HOU N N, WANG M, et al. Screening of high-yield phenyllactic acid strain and its application in soybean meal fermentation [J]. China Brewing, 2021, 40(7): 65-70.
[12] 黄云坡. 苯乳酸对食源性致病菌的抑菌机理研究[D]. 石家庄: 河北科技大学, 2015 HUANG Yunpo. Study on the antibacterial mechanism of phenyllactic acid with food-borne pathogens[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei University of Science and Technology, 2015
[13] WANG F T, WU H H, JIN P P, et al. Antimicrobial activity of phenyllactic acid against Enterococcus faecalis and its effect on cell membrane[J]. Shijiazhuang: Foodborne Pathogens Disease,2018,15(10):645−652. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2018.2470
[14] QIAN W D, LI X C, SHEN L F, et al. Retracted: Antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of ursolic acid against carbapenem-resistant Enterobacter cloacae[J]. Food Control,2020,129(5):528−534.
[15] LIU F, SUN Z L, WANG F T, et al. Inhibition of biofilm formation and exopolysaccharide synthesis of Enterococcus faecalis by phenyllactic acid[J]. Food Microbiology,2020,86:103344. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2019.103344
[16] 孟秀梅, 吴杰, 李明华. 苯乳酸对黄曲霉抑菌活性及其作用机制初步研究[J]. 食品科技,2022,47(5):317−322. [MENG X M, WU J, LI M H. Antifungal activity and mechanism of action of 2-chloro-N-phenylacetamide: A new molecule with activity against strains of Aspergillus flavus[J]. Food Science and Technology,2022,47(5):317−322. MENG X M, WU J, LI M H. Antifungal activity and mechanism of action of 2-chloro-N -phenylacetamide: a new molecule with activity against strains of Aspergillus flavus [J]. Food Science and Technology, 2022, 47(5): 317-322.
[17] 刘韵昕. 苯乳酸的抑菌活性及抑菌机理研究[D]. 太原: 山西师范大学, 2017 LIU Yunxin. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of phenyllactic acid[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi Normal University, 2017.
[18] FAN Q X, ZHANG Y Y, YANG H, et al. Effect of Coenzyme Q0 on biofilm formation and attachment-invasion efficiency of Listeria monocytogenes[J]. Food Control,2018,90:274−281. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2018.02.047
[19] 杨超, 于涛, 姜晓冰. 绿色魏斯氏菌发酵液对单核细胞增生李斯特菌的抑制及其在冷却猪肉保鲜中的应用[J]. 肉类研究,2021,35(4):51−56. [YANG C, YU T, JIANG X B. Inhibition of Weissella viridescens fermentation broth on Listeria monocytogenes and its application in chilled pork preservation[J]. Meat Research,2021,35(4):51−56. YANG C, YU T, JIANG X B. Inhibition of Weissella viridescens fermentation broth on Listeria monocytogenes and its application in chilled pork preservation[J]. Meat Research, 2021, 35(4): 51-56.
[20] YU T, JIANG X J, XU X B, et al. Andrographolide inhibits biofilm and virulence in Listeria monocytogenes as a quorum-sensing inhibitor[J]. Molecules,2022,27(10):3234. doi: 10.3390/molecules27103234
[21] DAI Y F, XIAO Y, ZHANG E H, et al. Effective methods for extracting extracellular polymeric substances from Shewanellaoneidensis MR-1[J]. Water Science & Technology,2016,74(12):2987−2996.
[22] 王雅莹. 基于群体感应研究香芹酚对鱼源荧光假单胞菌单/混生物被膜的抑制作用[D]. 杭州: 浙江工商大学, 2020 WANG Yaying. Inhibition of carvacrol against the mono/dual-biofilm of Pseudomonas fluorescens based on quorum sensing [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Gongshang University, 2020.
[23] 高英, 俞玉忠. 福林酚法测定脑蛋白水解物溶液中的多肽含量[J]. 海峡药学,2004(6):57−58. [GAO Y, YU Y Z. Determination of polypeptide content in cerebroprotein hydrolysate solution by Folin phenol method[J]. Strait Pharmaceutical Journal,2004(6):57−58. GAO Y, YU Y Z. Determination of polypeptide content in cerebroprotein hydrolysate solution by Folin phenol method[J]. Strait Pharmaceutical Journal, 2004(6): 57-58.
[24] BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid[J]. Biochemical Journal,1956,62(2):315−23. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315
[25] ZHOU J W, LUO H Z, JIANG H, et al. Hordenine: A novel quorum sensing inhibitor and antibiofilm agent against Pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2018,66(7):1620−1628. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b05035
[26] CAO J J, LIU H, WANG Y, et al. Antimicrobial and antivirulence efficacies of citral against foodborne pathogen Vibrio parahaemolyticus RIMD2210633[J]. Food Control,2021,120:107507. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107507
[27] JIANG X B, REN S Y, GENG Y M, et. Role of the VirSR-VirAB system in biofilm formation of Listeria monocytogenes EGD-e[J]. Food Research International,2021,145:110394. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110394
[28] ZHANG Z, YANG G Q, MAI Q J, et al. Physiological potential of extracellular polysaccharide in promoting Geobacter biofilm formation and extracellular electron transfer[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,741:140365. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140365
[29] FLEMMING H C, WINGENDER J. The biofilm matrix[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology,2010,8:623−633. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2415
[30] COMBROUS T, SADOVSKAVA I, FAILLE C, et al. Quantification of the extracellular matrix of the Listeria monocytogenes biofilms of different phylogenic lineages with optimization of culture conditions[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology,2013,114(4):1120−1131. doi: 10.1111/jam.12127
[31] 许绵, 周明旭, 朱国强. 细菌鞭毛运动、黏附和免疫逃逸机制的研究进展[J]. 中国兽医学报,2017,37(2):369−375,380. [XU M, ZHOU M X, ZHU G Q. Progress in the mechanism of bacterial flagellum motility, adhesion and immune escape[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine,2017,37(2):369−375,380. XU M, ZHOU M X, ZHU G Q. Progress in the mechanism of bacterial flagellum motility, adhesion and immune escape[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2017, 37(2): 369-375, 380.
[32] 丁莉莎, 王瑶. 鞭毛介导的运动性与细菌生物膜的相互关系[J]. 微生物学报,2009(4):417−422. [DING L S, WANG Y. The relationship between flagella mediated mobility and bacterial biofilm[J]. Journal of Microbiology,2009(4):417−422. DING L S, WANG Y. The relationship between flagella mediated mobility and bacterial biofilm[J]. Journal of Microbiology, 2009(4): 417-422.
[33] 林才云, 姚琳, 李风铃, 等. LuxS/AI-2群体感应系统及其对细菌致病性和耐药性的调控[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2019,10(18):5983−5991. [LIN C Y, YAO L, LI F L, et al. LuxS/AI-2 quorum sensing of bacteria and its regulation on pathogenicity and antimicrobial resistance[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection,2019,10(18):5983−5991. LIN C Y, YAO L, LI F L, et al. LuxS/AI-2 quorum sensing of bacteria and its regulation on pathogenicity and antimicrobial resistance[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection, 2019, 10(18): 5983-5991.
[34] YUAN Q, FENG W, WANG Y, et al. Luteolin attenuates the pathogenesis of Staphylococcus aureus by interfering with the agr system[J]. Microbial Pathogenesis,2022,165:105496. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105496
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 张艳芳,刘水琳,郭梦伽,吕孟敏,吕欣然,白凤翎,励建荣,崔方超,檀茜倩,董浩. 苯乳酸对食源创伤弧菌生物膜抑制作用研究. 食品工业科技. 2025(02): 152-158 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(3)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



