Rheological Properties of Tamarind Xyloglucan Treated by Ultrasound and Enzymolysis
-
摘要: 研究了超声处理1.5和2.5 h和半乳糖苷酶酶解16、32和48 h对罗望子木葡聚糖(Xyloglucan,XG)流变特性的影响。使用旋转流变仪对处理前后的木葡聚糖在静态剪切和动态剪切下的黏度和模量进行了分析,并利用凝胶色谱-多角度激光光散射和动态激光光散射仪对木葡聚糖分子量分布和平均粒径进行了分析,同时使用扫描电子显微镜对木葡聚糖的微观结构进行了观察。温度扫描结果表明,在5 ℃时,超声和酶解处理过的木葡聚糖的黏度显著降低(P<0.05),但不同处理时间的样品差异较小。在5~60 ℃范围内,木葡聚糖的弹性模量与黏性模量均接近于7 Pa。超声处理的样品黏度随温度增加而降低,且总体呈现出以黏性为主的流变特性。48 h酶解处理的木葡聚糖弹性特征高于16及32 h酶解木葡聚糖的弹性特性。分子量分析结果显示,超声处理1.5和2.5 h的木葡聚糖平均分子量从原885 kDa分别降低至780和520 kDa;而酶解的木葡聚糖由低分子量(101~478 kDa)和高分子量(4591~12173 kDa)两部分组成,其中低分子量组分比例占80%以上。动态光散射结果表明,经半乳糖苷酶酶解的木葡聚糖平均粒径增大,而超声对样品的粒径影响较小。本研究为物理及生物法改性木葡聚糖,以获得具有不同流变特性的多糖胶体提供了一定经验,有利于进一步拓展其在食品工业中的应用。Abstract: The effects of 1.5 and 2.5 h of ultrasonic treatment and 16, 32 and 48 h of enzymatic hydrolysis with galactosidase on the rheological properties of Xyloglucan (XG) from tamarind were studied. The viscosity and module of untreated and treated XG were studied under static and dynamic shear using a rotational rheometer. The molecular weight distribution and average particle size were analyzed using gel chromatography with multi-angle laser light scattering and dynamic laser light scattering instruments. In addition, the microstructure of XG samples were observed via scanning electron microscope. Results of the temperature sweep showed that the viscosity of XG treated by ultrasound and enzymatic hydrolysis significantly decreased at 5 ℃, but the difference of samples treated for different durations was small. In the range of 5 to 60 ℃, the elastic and viscous modulus of XG were close to 7 Pa. The viscosity of ultrasonic treated XG decreased with the increasing of temperature, and the rheological properties of ultrasonic samples was viscous-dominant. The elastic properties of XG treated with 48 h enzymatic hydrolysis were higher than those treated with 16 and 32 h enzymatic hydrolysis. The results of molecular weight analysis showed that the average molecular weight of ultrasonic-treated 1.5 and 2.5 h XG decreased from 885 kDa to 780 and 520 kDa respectively. The enzymatic hydrolysis of XG was composed of a low molecular weight (101~478 kDa) ratio and a high molecular weight (4591~12173 kDa) ratio, of which the low molecular weight component accounted for more than 80%. The results of dynamic light scattering showed that the average particle size of XG increased after galactosidase hydrolysis, while ultrasonic treatment had little effect on the particle size of XG. This study would provide experience on the physical and biological modification on xyloglucan to obtain carbohydrate colloids with various rheological properties, which is beneficial for its further application in food industry.
-
Keywords:
- tamarind /
- xyloglucan /
- rheology /
- food hydrocolloids /
- gel chromatography
-
罗望子(Tamarindus indica L.),又名酸角,是一种苏木科的大型乔木,主要以野生或半野生状态分布在我国的南方地区[1]。罗望子种子中的木葡聚糖(Xyloglucan,XG)含量高达60%[2],是木葡聚糖最丰富的来源之一[3]。木葡聚糖是高等植物初生细胞壁中的一种半纤维素多糖[4-5]。罗望子木葡聚糖的化学结构由β-1,4-D-葡聚糖连接的主链及在D-吡喃葡萄糖残基的O-6位置部分被α-D-木糖取代的支链组成,且支链中的部分木糖中的O-2位置被β-D-半乳糖进一步取代[6],其半乳糖分子含量约为13.2%[7]。木葡聚糖的分子组成及其微观结构赋予了其独特的化学和物理性能[8],如良好的热稳定性、耐酸碱、高黏度等特点,在食品工业中有广泛的应用[9]。罗望子种子中提取的木葡聚糖是FDA批准的生物聚合物,可用作食品添加剂[10],作为稳定剂[11]、增稠剂[12]、胶凝剂[13-14]、乳化剂[15]等改善食品产品的流变等性能。作为增稠剂,木葡聚糖的性能与果胶类似,因而木葡聚糖在制作蛋黄酱、糖果、果冻、增稠酱、冰激凌、果酱等食品过程中可以替代部分果胶[16]。在面团发酵时加入木葡聚糖,可以提高面团的稳定性,并改善面包的柔软性[17]。此外,木葡聚糖具有优异的成膜性,可以用来制备生物可降解薄膜,且制成的薄膜具有较高的强度、硬度和阻氧性能[18]。Indira等[19]用木葡聚糖作为填充剂制备了可完全生物降解的纳米复合膜,这种纳米膜具有优异的拉伸和抗菌性能,可应用于食品包装领域。
天然状态下,木葡聚糖在水中的溶解性较差,同时自身不能形成凝胶,限制了其应用范围。同时,木葡聚糖等生物多糖的许多功能特性受其分子质量和分子结构影响较大。比如,在医疗和化妆品领域中,低分子量的多糖由于较为容易在生物组织中扩散,而比高分子量的多糖具有更好的优势[20]。此外,对多糖分子支链和糖苷结构的修饰可以获得悬浮性、亲水性或稳定性更好的胶体产品[21]。因此,可以对木葡聚糖进行改性处理以制备出具有不同流变特性的木葡聚糖产品并开发应用到新的领域。多糖的流变性质可以通过对其分子结构的修饰进行调整[22],往往通过物理、生物、化学等方法进行修饰。超声波法是常用的物理改性手段,可以快速将多糖分散在稀溶液中。此外,超声波还被广泛用于改变多糖相对分子质量、颗粒大小、黏度和活化能等物理化学性质[23]。有报道称,超声波法可降低木葡聚糖的平均分子量[24]。另一方面,生物改性方法中,常使用半乳糖苷酶去除木葡聚糖支链上的半乳糖苷,以获得具有更高黏弹性的木葡聚糖溶液以形成水凝胶。Kochumalayil等[25]用β-半乳糖苷酶酶解木葡聚糖去除部分半乳糖侧链来制备薄膜,改性后的木葡聚糖样品在高湿度条件下的透氧率降低且弹性模量显著提高。Brun-Graeppi等[26]使用β-半乳糖苷酶酶解罗望子木葡聚糖发现,随着半乳糖去除率的增加,木葡聚糖溶胶-凝胶的转变温度降低。然而,目前尚未有报道系统讨论超声和酶解处理木葡聚糖后微观结构及流变特性的变化。
本研究讨论并比较了超声及酶解处理的木葡聚糖分子在不同温度、剪切速率和应变振幅/频率下的黏度和剪切模量等流变特性。结合凝胶色谱-多角度激光光散射(SEC-MALS)、动态激光光散射仪和扫描电子显微镜等手段,分析了木葡聚糖在超声及酶解处理后的分子量分布、粒径大小和微观形貌特征。此研究对罗望子木葡聚糖分子结构物理及生物修饰方法提供了一定经验,有利于进一步开发木葡聚糖作为增稠剂等食品添加剂的应用潜力。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
罗望子木葡聚糖(纯度95%)、β-半乳糖苷酶(4000 U/mL) 爱尔兰Megazyme公司;醋酸钠 天津市大茂化学试剂厂;冰醋酸 上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司。
MR Hei-Tec 磁力搅拌加热器 德国Heidolph公司;MCR702流变仪 奥地利Anton Paar公司;EM-30 PLUS台式扫描电镜 韩国Coxem公司;JY92-IIN超声波细胞破碎机 宁波新芝生物科技股份有限公司;DynaProNanoStar动态激光光散射仪、SEC-MALS多角度激光光散射凝胶色谱联用仪 美国Wyatt公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 超声处理木葡聚糖
参考Talantikite等[27]的方法,适当修改。使用超声波细胞破碎机,以直径6 mm的超声波变幅杆,功率为180 W条件下对浓度为1%(w/w)的木葡聚糖溶液进行超声处理,分别制备超声处理1.5和2.5 h的木葡聚糖溶液。
1.2.2 酶解木葡聚糖的制备
将木葡聚糖在室温(26 ℃)下使用磁力搅拌器以600 r/min的转速溶解于去离子水中,配制成1%(w/w)的溶液。根据Brun-Graeppi等[26]的方法,用半乳糖苷酶对木葡聚糖进行酶解。用醋酸钠缓冲液将样品的pH调至5.0。半乳糖苷酶的酶量为3.7 U/mL,在50 ℃下进行酶解反应,分别反应16、32、48 h,然后将样品在100 ℃下加热20 min使酶失活。
1.2.3 木葡聚糖流变特性测试
使用应变控制型旋转流变仪测定原木葡聚糖及经过处理的木葡聚糖的流变特性。使用25 mm不锈钢平行板对样品进行测试,测量间隙设为0.1 mm。装样时,将样品适量滴加到流变仪的下平板的中心区域上,并平衡5 min。将硅油添加于样品圆形几何形状的周围,以减少水分蒸发。每种样品进行3次平行实验以获取算数平均值和标准差。
1.2.3.1 旋转模式−恒定剪切速率下的温度扫描
参考苏攀峰等[28]的方法,适当修改。剪切速率固定为50 s−1,将温度由5 ℃升至60 ℃,升温速率2 ℃/min,记录剪切黏度和温度的关系。
1.2.3.2 旋转模式−恒定温度下的黏度曲线
参考陈发河等[29]的方法,适当修改。在0.1~100 s−1范围以对数增加的剪切速率进行测试,温度恒定为50 ℃,记录未处理木葡聚糖、超声处理的木葡聚糖和酶解木葡聚糖在不同剪切速率下的剪切黏度。
1.2.3.3 振荡模式-温度扫描
参考Busato等[30]的方法,稍作修改,温度扫描范围为5~60 ℃,温度梯度为1 ℃/min,振幅和频率分别固定在0.1%和1 Hz(线性黏弹区内),记录储存(弹性)模量(G')和损耗(黏性)模量(G'')随温度的变化,同时记录损耗因子(tanδ)。
1.2.3.4 振荡模式−振幅扫描
分别在5、37和50 ℃的温度下,以1 Hz的恒定频率,将剪切应变振幅以对数增加方式从0.1%增加到100%对样品进行振幅扫描,记录储能模量(G')和损耗模量(G'')。
1.2.3.5 振荡模式−频率扫描
分别在5、37和50 ℃温度下,以0.1%的固定振幅,使频率从0.1 Hz增加到10 Hz,记录不同频率下的储能模量(G')和损耗模量(G'')。
1.2.4 木葡聚糖分子量测定
使用SEC-MALS测定未处理和超声及酶解的木葡聚糖的相对分子质量。色谱柱为SB-805HQ(日本Shodex公司),检测器为示差折光检测器与激光检测器联用。流动相为0.02%(w/w)NaCl水溶液,流速为0.5 mL/min,进样量为200 μL。重均分子量(MW)通过使用Zimm模型[31]的线性拟合计算得到:
KCRθ=(1MW+2BC)[1+16π¯R2g3λ2sin2θ2] (1) 式中:K是一个实验常数,取决与光的波长和多糖的折射率增量;Rθ是用来确定大分子在θ角上散射的光与入射光的完整性之比的瑞利比率;B是第二维利系数,单位为mL·mol·g−2;Rg是旋转半径,单位为cm。
1.2.5 木葡聚糖粒径测定
使用动态激光光散射仪测量原木葡聚糖及经过超声和酶解处理的木葡聚糖水溶液的平均粒径,测试温度为25 ℃。每个样品进行3次重复实验。
1.2.6 木葡聚糖微观结构观察
为保持处理温度一致性,所有样品均在37 ℃的显微镜载玻片上固定,用液氮淬火,真空冷冻干燥48 h。然后采用离子溅射仪在10~20 mA的溅射电流下在样品表面喷金约60 s,最后使用扫描电子显微镜进行成像观察。仪器参数设置如下:加速电压为5 kV,工作距离为6 mm,放大倍数为500倍。每个样品选择至少3个不同的位置拍摄照片。
1.3 数据处理
使用Excel 2019和Wyatt公司ASTRA软件(版本6.1.1.17)处理数据,并使用Origin Pro 2021 软件进行绘图。所有试验均重复3次,数据用平均值±标准差表示。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 木葡聚糖流变特性分析
2.1.1 旋转模式−恒定剪切速率−温度扫描和旋转模式−恒定温度−剪切速率扫描
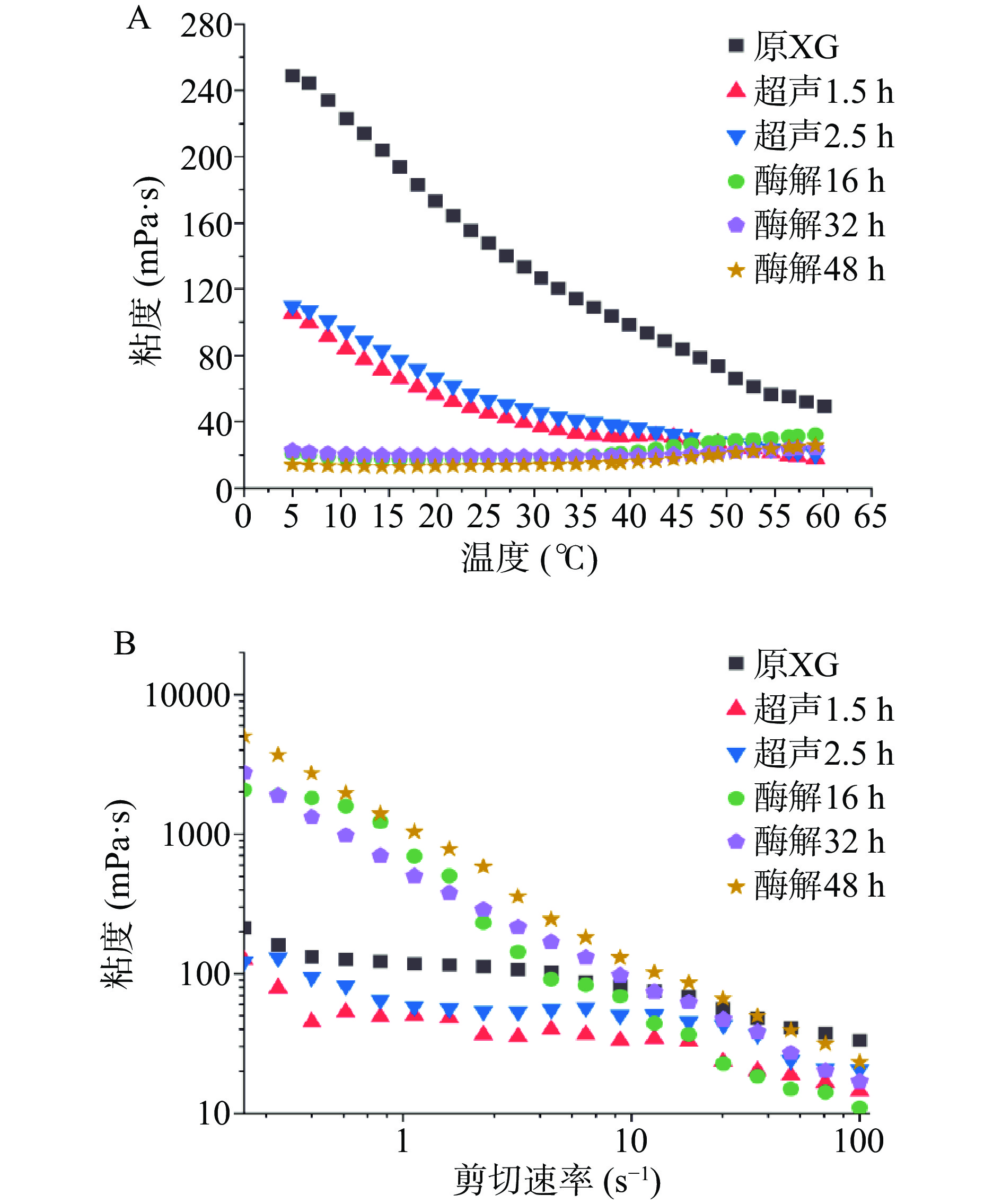
图1展示了未处理与超声及酶解处理的木葡聚糖在剪切速率为50 s−1下黏度和温度的关系(图1A)以及在温度为50 ℃时黏度和剪切速率的关系(图1B)。在剪切速率为50 s−1,温度5~45 ℃时,经超声和酶解处理的木葡聚糖的黏度低于未经处理的木葡聚糖,而在同样条件下,超声处理的木葡聚糖黏度大于酶解木葡聚糖黏度(图1A)。但相同处理方法,不同处理时间的样品黏度差异较小。低温情况下(5 ℃),原木葡聚糖的黏度为249 mPa·s;而超声1.5和2.5 h的木葡聚糖黏度分别为105和110 mPa·s;酶解16、32、48 h的木葡聚糖黏度分别为21、23、14 mPa·s。未处理的木葡聚糖的黏度随温度升高而大幅下降。而超声木葡聚糖的黏度也表现出强温度依赖性,黏度随温度下降明显,从5 ℃到60 ℃下降至约原来黏度的18%。另一方面,酶解木葡聚糖在5~40 ℃范围内温度敏感性较低,但在高温度(40~60 ℃)下出现黏度随温度升高而增高的现象。在55 ℃左右,黏度超过了超声处理木葡聚糖。当固定测试温度50 ℃,增加剪切速率时,酶解木葡聚糖样品在近零剪切速率(0.2 s−1)时表现出高于未处理木葡聚糖的表观黏度,且黏度随着酶解时间增长而增加。酶解16、32、48 h的木葡聚糖零剪切黏度分别为2079、2746、5018 mPa·s,而原木葡聚糖的零剪切黏度为212 mPa·s。Han等[32]发现使用β-半乳糖苷酶在与本实验相同的条件下对罗望子木葡聚糖进行酶解,酶解16、32和48 h后半乳糖的脱除率分别约为39%、42%和43%。另一方面,超声处理降低了木葡聚糖的零剪切黏度,但不同处理时长间的黏度差距较小。超声1.5和2.5 h的木葡聚糖黏度分别为126和122 mPa·s。随着剪切速率的增加,所有的样品都表现出典型高分子溶液的剪切稀化行为,但流动行为有所区别。未处理及超声的木葡聚糖样品黏度表现出“下降−平台期−下降”的三段式剪切稀化行为。但酶解木葡聚糖样品随着剪切速率上升表现出黏度持续下降的流动特性,且下降幅度远高于原木葡聚糖和超声样品。
在恒定剪切速率下,未处理的木葡聚糖的黏度随着温度的升高下降,这与Sims等[33]在研究不同来源的木葡聚糖的流变特性时得出的结论一致。升温会提升物质能量,分子运动速度加快,分子间接触时间更短,因此内部摩擦力更小,表观黏度下降。超声木葡聚糖符合这一规律,证明超声处理可能不能改变原木葡聚糖分子间相互作用类型。但超声的黏度总体出现下降,可能是由于超声处理降低了木葡聚糖分子的平均分子量,减少了总体内摩擦力。而酶解木葡聚糖分子可能与未处理及超声处理木葡聚糖具有不同的分子结构,导致了不同的流变行为。酶解的木葡聚糖的高温增稠性表明分子间运动加剧时,去除半乳糖支链的木葡聚糖分子碰撞时发生了更强的结合,这些分子发生聚集产生了更大的摩擦力,导致黏度上升。
在固定温度,增加剪切速率的条件下,酶解样品表现出的高零剪切黏度,说明酶解后的木葡聚糖在水溶液中可能有更大的平均粒径,而超声样品的低零剪切黏度表明平均粒径出现了下降。同时,酶解木葡聚糖的剪切稀化行为相比于原木葡聚糖和超声木葡聚糖更为明显,证明原木葡聚糖和超声处理木葡聚糖的分子量分布较为均匀,同时“三段式”剪切稀化行为表明相互缠绕的长链木葡聚糖分子可以在高剪切速率下解缠并取向。而酶解木葡聚糖样品中分子量分布不均匀,随剪切速率增加不存在黏度平台期,说明酶解木葡聚糖分子在高剪切速率下仍然无法完全解缠,分子间结合力较原木葡聚糖和超声木葡聚糖更高。因剪切过程中涉及到能量的储存与损耗,应进一步使用振荡模式分析木葡聚糖分子在超声和酶解处理后的储能和损耗模量变化情况。
2.1.2 振荡模式-温度、振幅、频率扫描
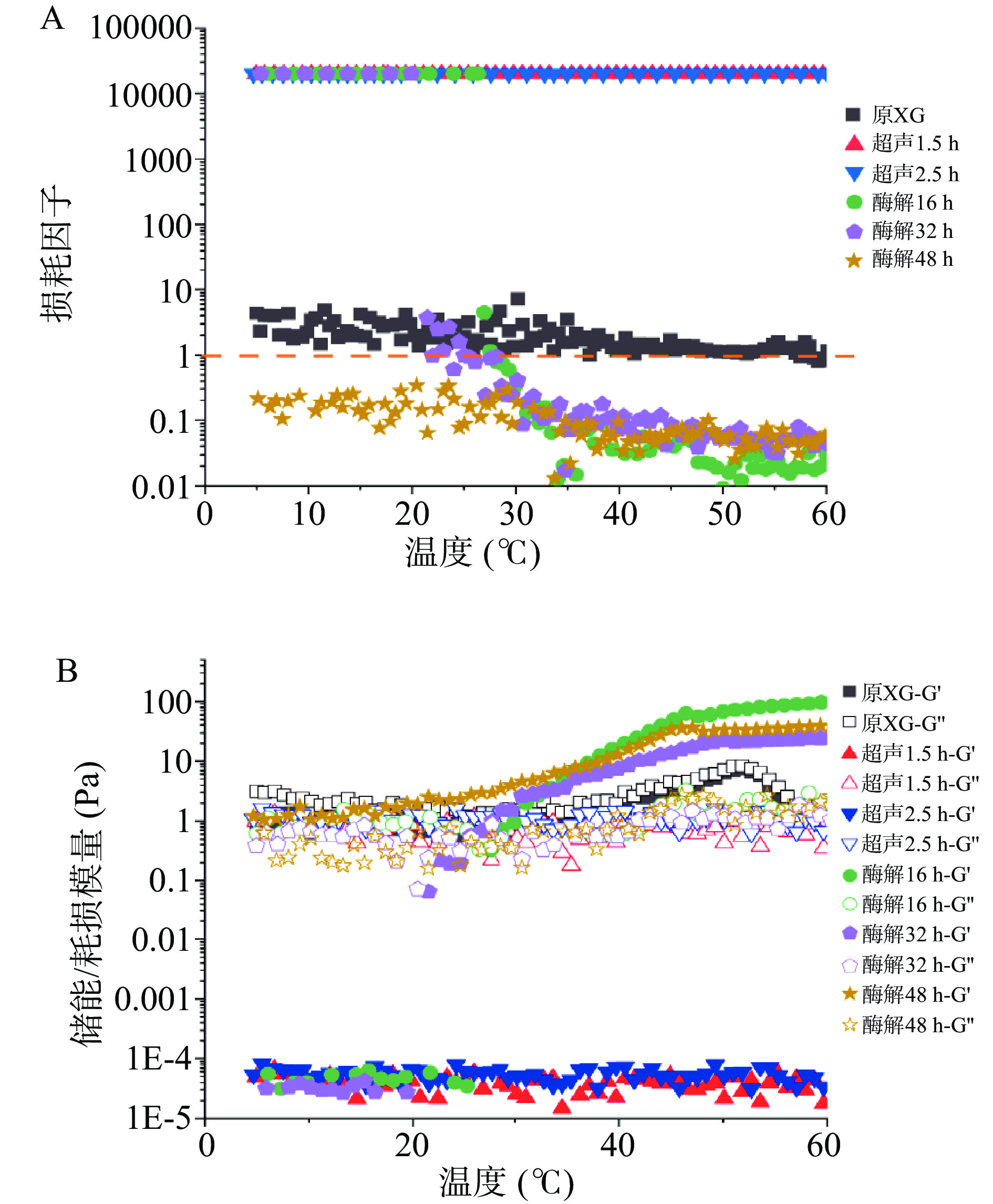
由图2A可知,原木葡聚糖和超声处理的木葡聚糖在振荡模式下的温度敏感性较低。原木葡聚糖的损耗因子(tanδ)维持在1左右,呈现出一种介乎液体和固体之间的弱凝胶状态。而超声处理的木葡聚糖在5~60 ℃范围内的tanδ远大于1,呈现出较强的液体流动特征。酶解16和32 h的木葡聚糖样品在5~27 ℃的条件下同样表现出黏性为主的流变特性,而在接近27 ℃时tanδ降低到1,达到凝胶点(图2B)。而在温度超过27 ℃之后,tanδ保持在1以下且弹性模量逐渐升高,凝胶强度随温度升高逐渐增强,在约45 ℃后趋于稳定。而酶解时间48 h的样品在5~60 ℃温度范围内,tanδ始终小于1,说明酶解48 h的木葡聚糖样品在更容易形成凝胶。Miyazakid等[34]的研究中将木葡聚糖用β-半乳糖苷酶酶解16 h后木葡聚糖形成凝胶的温度为27 ℃,与本文所得结果一致。而经半乳糖苷酶酶解的木葡聚糖随着酶解时间的增加,转变成凝胶的温度降低。这一结论与Brun-Graeppi等[26]对在同样条件下酶解罗望子木葡聚糖形成的水凝胶的溶胶−凝胶转变研究得出的结论一致。
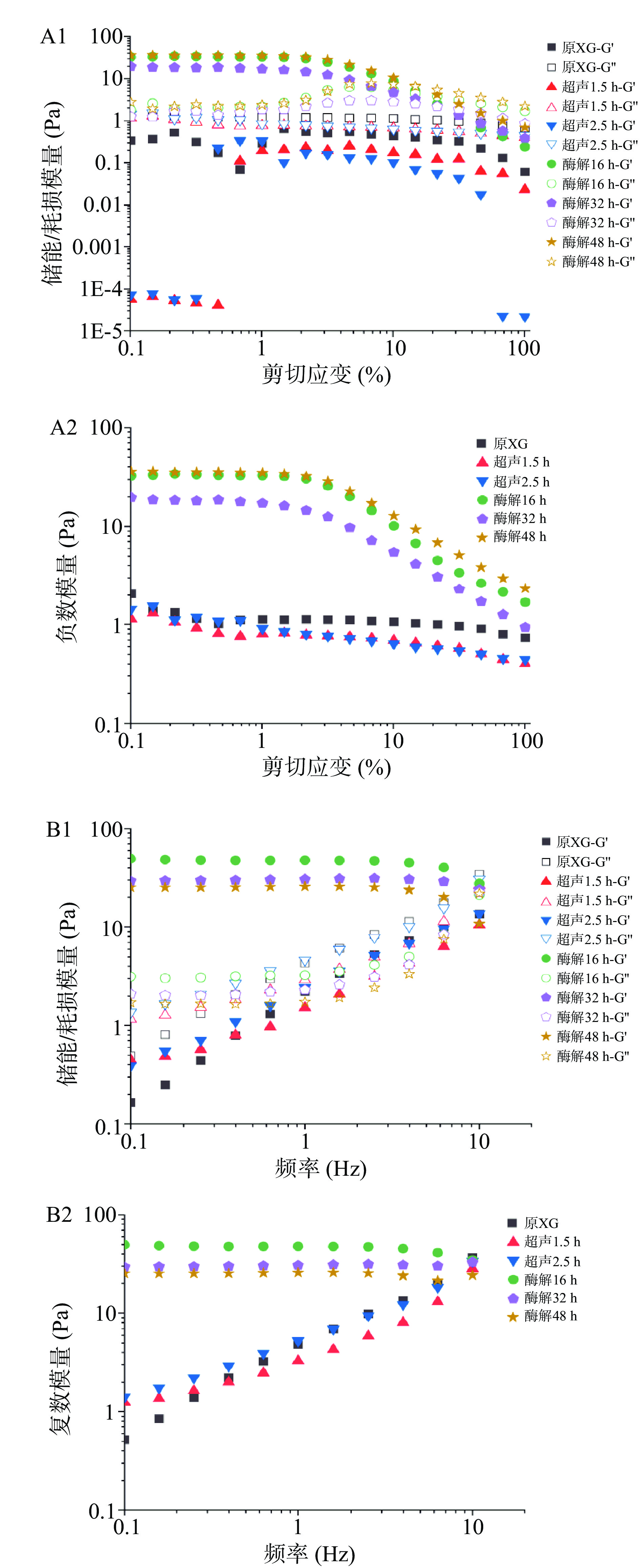
图3展示了原木葡聚糖和经超声及酶解处理木葡聚糖在50 ℃的恒定温度下,振荡模式下的振幅和频率扫描结果。可以看出酶解木葡聚糖是弹性为主体的黏弹性凝胶,振幅扫描中酶解木葡聚糖线性黏弹区的应变振幅上限约为0.3%,同时在10%的应变振幅下出现了G"过冲超过G'的Payne效应线现象[35]。原木葡聚糖和超声处理的木葡聚糖的损耗模量G"始终大于储能模量G',样品呈现液体特性。在应变到达1%时,样品进入非线性黏弹区且G'增大并接近G",弹性增强,证明在高剪切应变下原本呈溶液状态的木葡聚糖表现出一定弹性。酶解木葡聚糖的复数模量G*显著(P<0.05)高于未处理和超声的木葡聚糖样品(图3A2),说明酶解作用增强了木葡聚糖分子间的相互作用,进而增加了凝胶刚度,这与旋转模式实验结果一致。而在频率扫描中,酶解木葡聚糖在1 Hz以内的低频条件下表现出弱凝胶的线性黏弹性,但在频率高于1 Hz后损耗模量G"出现上升,说明凝胶在高频剪切下易发生崩解而流动特性增强。而原木葡聚糖和超声处理木葡聚糖在0.1~10 Hz的频率范围,模量对频率的依赖性较大。随着频率的增大,G'、G"和G*均增大,始终表现出明显的液体特征。
木葡聚糖骨架内的半乳糖残基是亲水性的,而骨架的其余部分本质上是疏水的。酶解的样品因去除了部分半乳糖,随着温度的升高分子碰撞加剧,更多的疏水结构域聚集在一起,致木葡聚糖之间的相互作用力增强使其形成凝胶[36]。振荡模式-温度扫描的结果与旋转模式结果一致,证明酶解木葡聚糖在加温过程中有更强的储能过程。此储能过程大致可分为三个阶段,第一阶段(5~27 ℃)的黏性为主的无序流动阶段,第二阶段(27~45 ℃)的凝胶网络逐渐形成的阶段,和第三阶段(45~60 ℃)凝胶状态趋于稳定的阶段。而通过对凝胶已经成型后的振幅扫描和频率扫描分析可知,1%浓度的脱半乳糖苷木葡聚糖水凝胶为一种弱凝胶,通过疏水键形成的分子网络易在高剪切应变和高振荡频率下发生崩解而表现出液体特性。而超声处理的木葡聚糖样品的在振荡模式下的流变行为与原木葡聚糖类似,证明超声处理并不能达到酶解处理增强木葡聚糖分子间的作用力的效果。
2.2 超声和酶解处理对木葡聚糖平均分子质量和粒径的影响
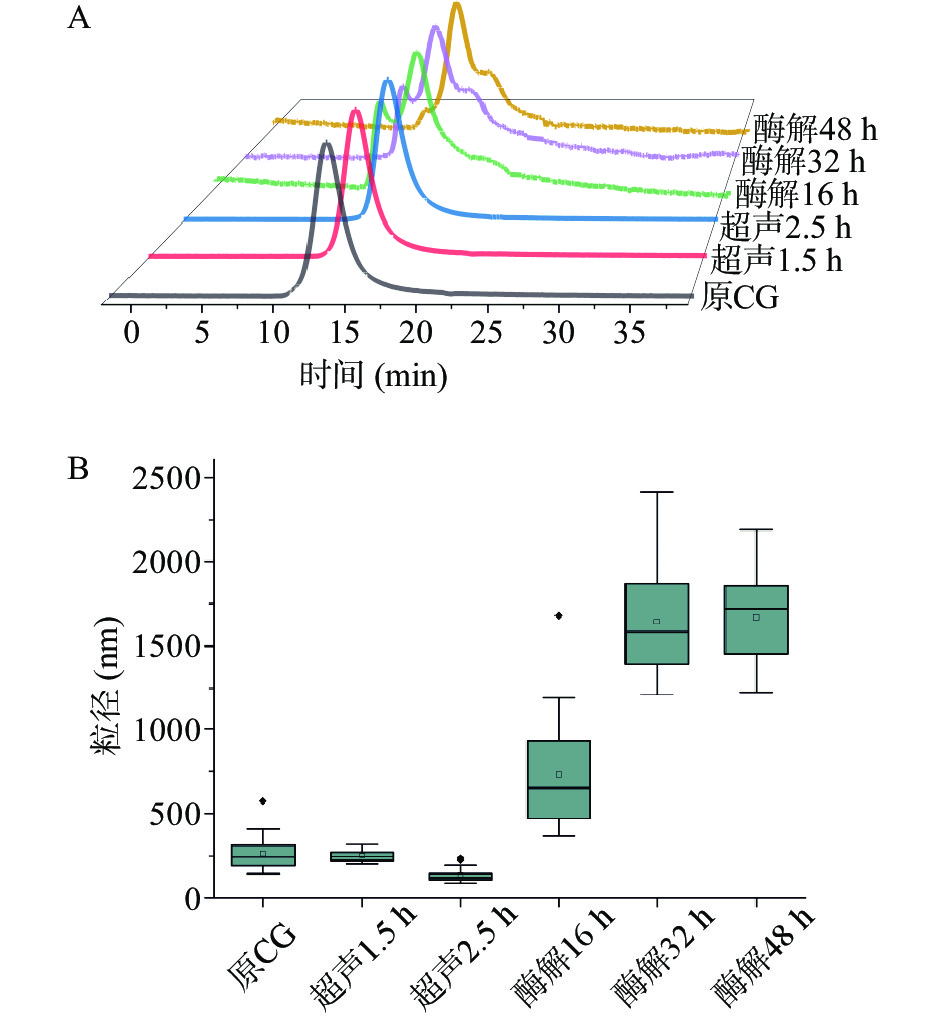
从表1可知原木葡聚糖的重均分子量为885 kDa,这与先前报道结果接近[27]。木葡聚糖的重均分子量随超声处理时长的增加而减少。超声1.5 h和超声2.5 h的木葡聚糖重均分子量分别为780 和520 kDa。且超声处理样品均匀性较好,SEC-MALS分析结果显示只存在出峰时间为12 min的一个信号峰(图4A)。而酶解木葡聚糖为一种高分子量(4591~12173 kDa)和低分子量(101~478 kDa)物质组成的混合物,出峰时间分别为9~11 min和14~18 min。低分子量占80%以上(酶解16、32和 48 h分别占比95%、93%、和85%)。且酶解样品在保留时间为16~23 min的范围内出现了馒头状峰,证明溶液中可能存在一定的高分子间的纠缠。从箱线图4B可以看出,动态光散射的结果表明,原木葡聚糖溶液的平均粒径为266 nm。超声降低了木葡聚糖的平均粒径,经1.5和2.5 h超声时长处理的木葡聚糖分子粒径分别降低到252和135 nm。而酶解反而增大了木葡聚糖的平均粒径,经16、32、48 h酶解的木葡聚糖分子粒径分别为734、1644和1669 nm。但由箱线图的数据分布可以看出,酶解木葡聚糖样品的粒径测量整体误差较大,进一步说明了酶解后增加的木葡聚糖分子间疏水作用力造成了分子的团聚,溶液中出现部分大颗粒物质,降低了光散射的测量准确性,这些结果与黏度及剪切模量测试的结果一致。
表 1 原木葡聚糖及酶解和超声处理后的木葡聚糖分子量Table 1. Molecular weight of XG with different treatment methods样品 主峰面积(%) MW(kDa) 原XG 100 885±2 超声1.5 h 100 780±3 超声2.5 h 100 520±2 酶解16 h 95 478±6 酶解32 h 93 108±2 酶解48 h 85 102±3 2.3 超声及酶解后的木葡聚糖的微观形貌特征
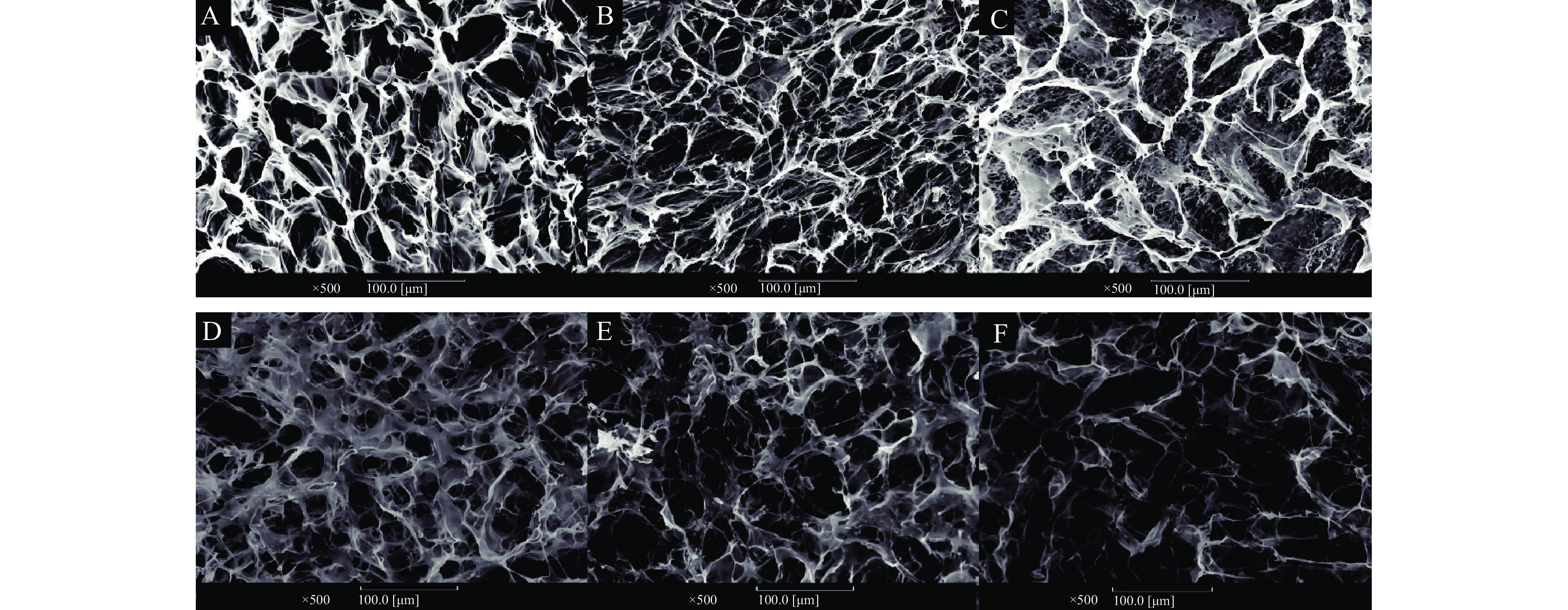
使用扫描电子显微镜观察了未处理、超声及酶解后的木葡聚糖的微观形貌特征。从图5可以看出,原木葡聚糖(图5A)和超声的样品(图5B~图5C)形貌区别不大,所有木葡聚糖样品都呈现出多孔状网络结构,而酶解时间越长的木葡聚糖样品,形成的孔洞越多(图5D~图5F)。Nisbet等[37]研究也发现将2%(w/w)木葡聚糖酶解,在37 ℃下凝胶化后冷冻干燥,样品在扫描电镜中显示凝胶结构出现崩塌。可能的原因是48 h的酶解样品由于分子成胶性强,分子网络持水性能更好,因此在冻干过程中由于水的升华更容易形成塌陷,从而形成了更为疏松的网络结构;而16 h的样品,分子间作用力相对较小,因此在冻干后大尺寸孔洞较少。总体而言,酶解的样品并未与原木葡聚糖及超声木葡聚糖在微观形态上有较大的区别。原因可能是木葡聚糖的总体黏弹性较弱,在冻干过程中导致木葡聚糖分子脱水收缩,造成原有结构的破坏。
3. 结论
本研究讨论了超声及酶解处理的罗望子木葡聚糖的流变性能及微观结构特征。结果表明通过半乳糖苷酶处理的木葡聚糖分子可以增强分子间相互作用力,导致其平均粒径增加,从而增强了其剪切黏度和模量,而超声处理降低了平均分子量和粒径,但整体流变行为与原木葡聚糖差异不大。此外,经酶解处理的木葡聚糖的剪切模量对温度表现出较强依赖性,酶解16和32 h的木葡聚糖在温度为27 ℃左右会形成凝胶,而酶解48 h的木葡聚糖在5~60 ℃范围内均呈现凝胶状态。但酶解木葡聚糖凝胶强度较弱,在高频振荡条件下易发生崩解而出现流动特性。本研究为改性木葡聚糖材料的研发提供了流变学依据,对木葡聚糖在食品包装、食品添加剂等领域的深化利用提供了一定意义。
-
表 1 原木葡聚糖及酶解和超声处理后的木葡聚糖分子量
Table 1 Molecular weight of XG with different treatment methods
样品 主峰面积(%) MW(kDa) 原XG 100 885±2 超声1.5 h 100 780±3 超声2.5 h 100 520±2 酶解16 h 95 478±6 酶解32 h 93 108±2 酶解48 h 85 102±3 -
[1] 任丽琨, 安琪, 边鑫, 等. 罗望子种仁球蛋白结构和功能特性的构效关系[J]. 中国食品学报,2021,21(9):272−280. [REN L G, AN Q, BIAN X, et al. Structure-activity relationship between the structure and functional properties of seed kernel globulin from Bergamind[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Science,2021,21(9):272−280. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2021.09.030 [2] ALESSIA A, SABATINO M A, TODARO S, et al. Xyloglucan-based hydrogel films for wound dressing: Structure-property relationships[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2018, 179: 262−272.
[3] ARKADIUSZ K, JUSTYNA C. Evaluation of structure and assembly of xyloglucan from tamarind seed (Tamarindus indica L.) with atomic force microscopy[J]. Food Biophysics,2015,10(4):396−402. doi: 10.1007/s11483-015-9395-2
[4] SIMI C K, ABRAHAM T E. Physico chemical properties of aminated tamarind xyloglucan[J]. Colloids & Surfaces B Biointerfaces,2010,81(2):513−520.
[5] HAYASHI T, KAIDA R. Functions of xyloglucan in plant cells[J]. Molecular Plant,2011,4(1):17−24. doi: 10.1093/mp/ssq063
[6] 韩明会, 刘彦涛, 朱妙馨, 等. 不同温度下分级水提罗望子多糖的结构与性质[J]. 林业科技开发,2018,3(5):71−77. [HAN M H, LIU Y T, ZHU M X, et al. Structure and properties of polysaccharides from tamarind by fractional water extraction at different temperatures[J]. Development of Forestry Science and Technology,2018,3(5):71−77. [7] POOMMARINVARAKUL S, TATTIYAKUL J, MUANGNAPOH C. Isolation and rheological properties of tamarind seed polysaccharide from tamarind kernel powder using protease enzyme and high-intensity ultrasound[J]. Journal of Food Science,2010,75(5):E253−60. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2010.01649.x
[8] CHEN D D, GUO P, CHEN S, et al. Properties of xyloglucan hydrogel as the biomedical sustained-release carriers[J]. Journal of Materials Science Materials in Medicine,2012,23(4):955−962. doi: 10.1007/s10856-012-4564-z
[9] DUTTA P, GIRI S, GIRI T K. Xyloglucan as green renewable biopolymer used in drug delivery and tissue engineering[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,160(197):55−68.
[10] DISPENZA C, TODARO S, SABATINO M A, et al. Multi-scale structural analysis of xyloglucan colloidal dispersions and hydro-alcoholic gels[J]. Cellulose,2020,27(1):3025−3035.
[11] KUMAR C S, BHATTACHARYA S. Tamarind seed: Properties, processing and utilization[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2008,48(1):1−20. doi: 10.1080/10408390600948600
[12] MISHRA A, MALHOTRA A V. Tamarind xyloglucan: A polysaccharide with versatile application potential[J]. ChemInform,2009,19:8528−8536.
[13] KULKARNI A D, JOSHI A A, PATIL C L, et al. Xyloglucan: A functional biomacromolecule for drug delivery applications[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2017,104:799−812. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.06.088
[14] YAMANAKA S, YUGUCHI Y, URAKAWA H, et al. Gelation of tamarind seed polysaccharide xyloglucan in the presence of ethanol[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2000,14(2):125−128. doi: 10.1016/S0268-005X(99)00057-0
[15] YUJI S, 鈴木 祐次, SOICHIRO K, et al. Heat-resistant acidic O/W-type emulsion food, JP特開2000-60481(P2000-60481A)A[P]. 2000. [16] 蒋建新, 唐蒙, 韩明会. 罗望子木葡聚糖结构凝胶性质及应用研究进展[J]. 林业工程学报,2020,5(6):9. [JIANG J X, TANG M, HAN M H. Research progress on the structure, gel properties and application of xyloglucan of bergamind[J]. Journal of Forestry Engineering,2020,5(6):9. [17] MAEDA T, YAMASHITA H, MORITA N. Application of xyloglucan to improve the gluten membrane on breadmaking[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2007,68(4):658−664. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2006.07.034
[18] SANTOS N L, BRAGA R C, BASTOS M, et al. Preparation and characterization of xyloglucan films extracted from Tamarindus indica seeds for packaging cut-up 'Sunrise Solo' papaya[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,132:1163−1175. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.04.044
[19] INDIRA D M, NALLAMUTHU N, RAJINI N, et al. Antimicrobial properties of poly (propylene) carbonate/Ag nanoparticle-modified tamarind seed p-olysaccharide with composite films[J]. Ionics,2019,25:3461−3471. doi: 10.1007/s11581-019-02895-9
[20] HUANG S, CHEN F, CHENG H, et al. Modification and application of polysaccharide from traditional Chinese medicine such as Dendrobium officinale[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,157:385−393. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.04.141
[21] ZHANG C, YANG F. Konjac glucomannan, a promising polysaccharide for OCDDS[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2014,104:175−181. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.12.081
[22] SHIRAKAWA M, YAMATOYA K, NISHINARI K. Tailoring of xyloglucan properties using an enzyme[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,1998,12(1):25−28. doi: 10.1016/S0268-005X(98)00052-6
[23] VILLARES A, BIZOT H, MOREAU C, et al. Effect of xyloglucan molar mass on its assembly onto the cellulose surface and its enzymatic susceptibility[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2016,157:1105−1112.
[24] VODENICAROVÁ M, DRÍMALOVÁ G, HROMÁDKOVÁ Z, et al. Xyloglucan degradation using different radiation sources: A comparative study[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2006,13(2):157−164. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2005.03.001
[25] KOCHUMALAYIL J J, BERGLUND L A. Water-soluble hemicelluloses for high humidity applications-enzymatic modification of xyloglucan for mechanical and oxygen barrier properties[J]. Green Chemistry,2014:16.
[26] BRUN-GRAEPPI A, RICHARD C, BESSODES M, et al. Study on the sol-gel transition of xyloglucan hydrogels[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2010,80(2):555−562. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.12.026
[27] TALANTIKITE M, STIMPSON T C, GOURLAY A, et al. Bioinspired thermoresponsive xyloglucan–cellulose nanocrystal hydrogels[J]. Biomacromolecules,2021,22(2):743−753. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.0c01521
[28] 苏攀峰, 唐庆九, 陈盛, 等. 葛仙米多糖理化性质和流变学特性的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(14):39−43. [SU P F, TANG Q J, CHEN S, et al. Study on physicochemical and rheological properties of polysaccharide from Radix Puerariae[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(14):39−43. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2018.14.008 [29] 陈发河, 周彦强, 吴光斌. 黄秋葵发酵酒渣果胶多糖的流变学性质[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(22):64−73. [CHEN F H, ZHOU Y Q, WU G B. Rheological properties of pectin polysaccharide from fermented wine residue of okra[J]. Food Science,2020,41(22):64−73. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190916-180 [30] BUSATO A P, REICHER F, OMINGUES R, et al. Rheological properties of thermally xyloglucan gel from the seeds of Hymenaea courbaril[J]. Materials Science & Engineering C,2009,29(2):410−414.
[31] ZIMM, BRUNO H. The scattering of light and the radial distribution function of high polymer solutions[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics,1948,16(12):1093−1099. doi: 10.1063/1.1746738
[32] HAN M, LIU Y, ZHANG F, et al. Effect of galactose side-chain on the self-assembly of xyloglucan macromolecule[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2020,246:116577. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116577
[33] SIMS I M, GANE A M, DUNSTAN D, et al. Rheological properties of xyloglucans from different plant species[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,1998,37(1):61−69. doi: 10.1016/S0144-8617(97)00105-7
[34] MIYAZAKID S, SUISHA F, KAWASAKI N, et al. Thermally reversible xyloglucan gels as vehicles for rectal drug delivery[J]. Journal of Controlled Release,1998,56(1−3):75−83. doi: 10.1016/S0168-3659(98)00079-0
[35] SONG Y, XU Z, WANG W, et al. Payne effect of carbon black filled natural rubber nanocomposites: Influences of extraction, cros-slinking, and swelling[J]. Journal of Rheology,2021,65(5):807−820. doi: 10.1122/8.0000270
[36] SHIRAKAWA M, UNO Y, YAMATOYA K, et al. Rheological and thermal studies on the sol-gel transition of aqueous solutions of enzymatically modified xyloglucan[J]. Gums and Stabilisers for the Food Industry 9, 1998: 94-103.
[37] NISBET D R, CROMPTON K E, HAMILTON S D, et al. Morphology and gelation of thermosensitive xyloglucan hydrogels[J]. Biophysical Chemistry,2006,121(1):14−20. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2005.12.005
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 李兴阳,王贝琦,郭超,操慧,于瑞莲,王琴. 蝉花孢子油的提取工艺优化及对炎症和肠上皮细胞氧化损伤的影响. 食品工业科技. 2025(05): 187-195 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 李梦杰,徐宝成,赵东坤,刘丽莉,陈树兴. 水酶法提油关键技术研究进展. 食品与发酵工业. 2024(19): 381-387 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 高惠静,袁圆,冯文玲,吴洁茹,许少全,赵军. 黑加仑平脂胶囊制备工艺及质量标准研究. 中国药业. 2023(19): 80-85 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)






 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
