Comprehensive Quality Evaluation and Processing Suitability Analysis of Xinjiang Dried Pepper
-
摘要: 为筛选加工专用的辣椒品种,以新疆主栽的12个干椒品种为材料,比较各品种间品质指标差异,并通过主成分分析和聚类分析对12份辣椒资源进行品质综合评价和加工适宜性分析。结果表明,不同品种辣椒间各项指标存在不同程度差异,裕红113号的单果重(6.166 g)最大,长线1号的果形指数(14.322)最大,可溶性还原糖含量(354.311 mg/g)最高,大叶朝天椒的可食率(96.973%)最高。通过比较色差、粗脂肪、辣椒素等16个指标的变异系数,发现辣椒素含量的变异系数最大,高达76.104%。12份辣椒的平均隶属度相差0.203,表明品种间差异明显;主成分分析提取出4个主成分,累计贡献率达88.369%,得到品质较优的品种有红素三号、长线1号、红安6号、聚源5号、红龙23号。经R型聚类筛选出辣椒品质的核心指标为单果重、辣椒红素、脂肪、维生素C含量、a*,经Q型聚类将12种辣椒聚为4类。经综合分析发现:线椒适宜做发酵辣椒酱、辣椒丝和油辣椒的原料;朝天椒适宜提取辣椒碱,也可作为制粉、辣椒油等调味料的原料;板椒适宜辣椒红色素的提取。红素三号是12份辣椒中品质最优、最适宜制干的辣椒品种。Abstract: In this study, to select special pepper varieties for processing, 12 dry pepper varieties mainly grown in Xinjiang were used as materials to compare the differences of quality indexes among different varieties. Next, the comprehensive quality evaluation and processing suitability analysis of the 12 pepper resources were performed through principal component analysis and cluster analysis. The results showed that differences were present in various indexes among the different pepper varieties. Yuhong 113 had the largest single fruit weight (6.166 g). Changxian 1 had the largest fruit shape index (14.322) and the highest soluble reducing sugar content (354.311 mg/g). And large leaf pod pepper had the highest edible rate (96.973%). By comparing the coefficient of variation of 16 indicators, including color difference, crude fat and capsaicin, it was observed that the coefficient of variation of capsaicin content was the greatest, as high as 76.104%. The difference in the average membership degree of the 12 pepper varieties was 0.203, thus indicating that there were significant differences among the varieties. Four principal components were extracted by principal component analysis, and the cumulative contribution rate reached 88.369%. The results showed that the varieties possessing superior quality were Hongsu 3, Changxian 1, Hong'an 6, Juyuan 5 and Honglong 23. The core indexes of pepper quality were selected as single fruit weight, capsanthin, fat, vitamin C content and a*, according to the R-type clustering. The 12 varieties of pepper were grouped into four categories by Q-cluster. Through comprehensive analysis, it was found that the line pepper was suitable for use as the raw material of fermented pepper sauce, pepper shreds and oil pepper. Pod pepper was suitable for extracting capsaicin, and could also be used as the raw material for making powder, pepper oil and other seasonings. And horn pepper was suitable for extracting capsanthin. Hongsu 3 was the best pepper variety with the best quality and was the most suitable one for drying among the 12 pepper varieties.
-
辣椒(Capsicum ssp.) 属于茄科,是茄果类的重要蔬菜之一[1],是人们生活中必不可少的辣味调味品[2],因其独特的口味深受消费者的喜爱。辣椒富含可溶性糖、蛋白质、维生素C、辣椒红素、辣椒素、有机酸、钙、磷等有效成分,具有较高的营养保健价值,其中辣椒中的维生素C含量堪称“蔬菜之冠”[3],能参与机体的代谢,提高身体免疫力,缓解牙龈出血等症状[4];辣椒红素是很好的自由基清除剂[5-6],该物质与辣椒素分别具有抗炎、抗糖尿病、抗肿瘤、抗辐射[7]和改善肠道菌群多样性[8]、降血脂[9]、抗癌[10]、抗菌消炎、调节免疫力[11-12]的功效。因此,辣椒不仅能用于食品及食品加工行业,其提取物辣椒碱在医药[13]、化工、军工等方面的用途也较广泛。
辣椒是全球重要的经济性蔬菜作物之一,据国家大宗蔬菜产业技术体系统计,2021年我国辣椒播种面积突破153.33万hm2(2300万亩),占全球辣椒播种面积的40%[14]。同时我国也是世界第一大辣椒生产国与消费国[15]。随着辣椒产业的迅速发展,新疆凭借独特的地理优势和日照时间长,昼夜温差大等条件成为新的一支辣椒生产基地,已形成天山以南的巴州、天山以北的昌吉州、伊犁州和塔城四大辣椒产区。辣椒生产分鲜椒和制干两大类,与我国辣椒主要产地相比,新疆的主栽品种为制干用辣椒,干辣椒年产量高达15万至20万t,占全国总产量的60%左右[16],其产品除满足我国辣椒加工业的需求外,还出口至韩国、日本、美国及欧洲国家,在国际市场享有较高的声誉。但新疆种植的部分品种种性混杂,退化严重,造成辣椒产量不稳定[17],加工主要以粗加工为主,高附加值综合深加工制品生产较少[18],已成为制约其生产的主要因素之一。此外,加工原料品种的选取会影响产品品质[19],辣椒加工企业收购原料时因缺乏科学的选料依据使得生产出的产品质量不稳定,严重阻碍了辣椒产业的标准化发展。
因此,该试验通过对12份新疆制干辣椒资源的多个品质指标的测定与分析,对其进行差异显著性分析和隶属函数分析,并将主成分和聚类分析法相结合对其进行综合评价,可以有效发掘新疆本地辣椒优势,对提高辣椒加工产品品质的均一性也具有非常重要的意义。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
辣椒 选用在新疆广泛种植、可用于开展制干类型辣椒的辣椒资源,共12份,其中编号XH开头的材料从和静县搜集,编号XA开头的材料从阿克苏搜集,编号 XY 开头的材料从焉耆搜集,编号 XB 开头的材料从博湖搜集,编号XK开头的材料从库尔勒获取。材料编号及来源见表1;蒽酮 上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;硫酸、盐酸 成都市科隆化学品有限公司;考马斯亮兰-G250、牛血清蛋白 天津市大茂化学试剂场;无水乙醇、磷酸、石油醚 天津市鑫铂特化工有限公司;钼酸铵、偏磷酸 天津市北辰方正试剂厂;抗坏血酸 天津永晟精细化工有限公司;以上试剂 均为分析纯。
表 1 供试材料名称Table 1. Name of test materials编号 品种名称 来源 XH-1 线椒10号 和静 XH-2 长线1号 和静 XH-3 红安6号 和静 XK-4 泰星四号 库尔勒 XA-5 红丹丹1号 阿克苏 XA-6 朝地椒 阿克苏 XB-7 大叶朝天椒 博湖 XB-8 红龙13 博湖 XB-9 红龙23 博湖 XY-10 裕红113 焉耆 XB-11 聚源5号 博湖 XB-12 红素三号 博湖 TU-1810PC紫外可见分光光度计 北京普析通用仪器有限责任公司;TDL-5-A低速台式离心机 上海安亭科学仪器厂;FW-100高速万能粉碎机 北京市永光明医疗仪器有限公司;MX-S涡旋振荡器 上海奥然科贸有限公司;HY-2A数显调速多用振荡器 常州亚特实验仪器有限公司;NH-310色差仪 北京光学仪器厂;SZF-06B脂肪测定仪 浙江托普仪器有限公司;Agilent LC1100高效液相色谱仪 上海林理仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 不同品种辣椒商品品质的测定
1.2.1.1 单果重及果形指数的测定
每个品种随机选择15个果实,使用电子天平对其进行称重,重复测定3次。并用游标卡尺对其横径与纵径进行测量,重复测定3次,计算其果型指数,果形指数=纵径/横径。
1.2.1.2 可食比率的测定
每个品种随机选取15个果实用电子天平测定其单果重,再去除辣椒蒂进行称重,记录数据平均值。可食率(%)=去蒂可食部分质量/全果质量×100。
1.2.1.3 色度的测定
本实验中不同品种辣椒果实的色度采用色度色差仪检测,经过零位校正和白板校正后对L*、a*、b*、H和C 5个参数值进行测定,平行测10次,依据a*、b*值计算综合色度指标色度角H=tan−1(b*/a*)和饱和度(
C=√a*+b* )[20]。1.2.2 不同品种辣椒营养指标测定
1.2.2.1 可溶性糖含量的测定
采用蒽酮-硫酸显色法[21]测定,以蔗糖为标样绘制标准曲线。制备样品时准确称取0.5 g辣椒粉至试管,加入沸水,在水浴中加盖煮沸10 min。测定时,准确吸取1 mL已稀释的提取液,加入4 mL蒽酮试剂,在620 nm处测定吸光度;在标准曲线上查出可溶性糖含量。
1.2.2.2 蛋白质含量的测定
采用马斯亮蓝G-250比色法[22]测定,以牛血清蛋白为标样绘制标准曲线,制备样品时准确称取1 g辣椒粉至离心管,加入蒸馏水,4000 r/min离心20 min,吸取上清液,测定时取1 mL已稀释过的待测样,加入马斯亮蓝G-250试剂5 mL,放置2 min后在595 nm处测定吸光度;通过标准曲线查得样品提取液中蛋白质的含量。
1.2.2.3 维生素C含量测定
采用钼酸铵比色法[3]测定,以抗坏血酸为标样绘制标准曲线,制备样品时准确称取1 g辣椒粉至离心管,加入适量草酸-EDTA溶液,7000 r/min离心15 min,取20 mL上清液,测定时取已稀释过的待测样5 mL,依次加入0.5 mL 3%偏磷酸-乙酸溶液、1 mL 5%硫酸溶液、2 mL l%钼酸铵溶液,放置20 min后在709 nm处测定吸光度,在标准曲线上查出样品中的维生素C含量。
1.2.2.4 粗脂肪含量的测定
采用脂肪测定仪进行,准确称量2 g研磨好的辣椒粉,置于滤纸筒中,确保滤纸筒要紧密,将石油醚加入萃取室内,使得液面高于滤纸筒1.5~2 cm,回流速度不低于12次/h,提取温度为65 ℃,提取时间为6 h。
1.2.2.5 辣椒红色素含量的测定
辣椒红色素含量测定参照国标GB/T 22299-2008《辣椒粉 天然着色物质总含量的测定》。
1.2.2.6 辣椒素含量的测定
采用高效液相色谱法(HPLC)对鲜果中辣味物质的含量进行测定[23-24],HPLC色谱条件流动相:甲醇(A)-0.1%磷酸水溶液(B),梯度洗脱(0~10 min,A:10%~20%,10~20 min,A:20%~40%,20~35 min,A:40%~70%,35~50 min,A:70%~70%,50~55 min,A:70%~10%,55~60 min,A:10%~10%),检测波长235 nm,色谱柱:Agilent ZORBAX SB-C18 (5 μm,4.6 mm×250 mm),流速1 mL/min,柱温30 ℃,进样量15 μL。
1.3 数据处理
应用SPSS 26软件计算各指标的最大值、最小值、平均值和标准差,并对数据进行Duncan's差异显著性分析,P<0.05时显著。对数据进行主成分分析和聚类分析,聚类分析采用系统聚类的组间连接法。
采用Excel软件计算变异系数,并进行隶属函数分析;隶属函数公式为:Tij=(Xij−Xjmin)/(Xjmax−Xjmin),式中:i表示某个辣椒品种;j表示某个品质指标;Tij表示i辣椒品种j品质指标的隶属函数值;Xij表示i辣椒品种j品质指标的实际测量值;Xjmax和Xjmin分别表示12份辣椒品种中j品质指标的最大值和最小值[25]。分别计算出12份辣椒品种的品质指标隶属函数值后再求均值,得平均隶属函数值。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同品种辣椒品质分析
2.1.1 不同品种辣椒商品品质比较
2.1.1.1 不同品种辣椒形态指标比较
由表2可知,辣椒单果重的范围在0.673~6.166 g之间,平均重量为2.781 g,高于3.000 g的有XB-8(红龙13)、XB-9(红龙23)、XY-10(裕红113)、XB-11(聚源5号)、XB-12(红素三号),均属于大果形的板椒,其中XY-10(裕红113)的单果质量最大,为6.166 g,其中XK-4(泰星4号)的单果质量最小,为0.673 g,XB-9(红龙23)和XB-12(红素三号)单果重相当,与其余品种差异显著(P<0.05);纵径最大的是XH-2(长线1号),为22.881 cm,与其余差异显著(P<0.05);横径最大的是XB-9(红龙23),为3.579 cm,与其余品种差异显著(P<0.05);果形指数是判定果实形状的最直观标准,果形指数最大的是XH-2(长线1号),为14.322,显著高于其他各个品种(P<0.05),果形指数最小的是XB-8(红龙13),为4.417;可食比率最大的是XB-7(大叶朝天椒),为96.973%,其次是XA-6(朝地椒)、XA-5(红丹丹1号)、XK-4(泰星四号),均属于朝天椒。该5个形态指标中,单果重、横径、纵径、果形指数4个指标的变异系数都大于10%,表明该12份辣椒品种的表型较丰富。
表 2 不同品种辣椒形态指标比较Table 2. Comparison of agronomic traits of different pepper varieties品种 单果重(g) 纵径(cm) 横径(cm) 果形指数 可食比率(%) XH-1 1.907±0.010g 12.252±0.120g 0.984±0.010i 12.452±0.000b 94.777±0.030cd XH-2 2.177±0.000e 21.881±0.100a 1.528±0.010g 14.322±0.010a 94.735±0.040cd XH-3 1.778±0.030h 12.274±0.010g 1.584±0.010g 7.746±0.030d 94.740±0.010cd XK-4 0.673±0.010j 6.946±0.000j 1.223±0.010h 5.680±0.030f 96.681±0.010b XA-5 2.081±0.040f 13.093±0.070e 2.106±0.010f 6.217±0.010e 96.774±0.010b XA-6 1.618±0.000i 8.120±0.010i 1.595±0.010g 5.092±0.030g 96.783±0.000b XB-7 1.621±0.000i 11.233±0.010h 1.287±0.000h 8.728±0.000c 96.973±0.010a XB-8 3.349±0.050d 12.181±0.050g 2.758±0.050e 4.417±0.100i 94.879±0.010c XB-9 3.666±0.010c 18.410±0.080b 3.579±0.130a 5.149±0.210g 94.848±0.040c XY-10 6.166±0.070a 16.061±0.050c 3.181±0.050b 5.050±0.100g 94.612±0.150d XB-11 4.678±0.080b 14.690±0.010d 2.996±0.020c 4.904±0.030h 94.598±0.330d XB-12 3.665±0.020c 12.714±0.300f 2.874±0.030d 4.424±0.130i 94.627±0.040d 最大值 6.166 21.881 3.579 14.322 96.973 最小值 0.673 6.946 0.984 4.417 94.598 平均值 2.781 13.321 2.141 7.015 95.419 标准差 1.558 4.096 0.889 3.272 1.028 变异系数(%) 56.021 30.749 41.519 46.648 1.077 注:同列不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);表2~表4同。 2.1.1.2 不同品种辣椒色度比较
色泽是评价鲜椒商品性的重要指标,辣椒干制加工后产品的颜色对商品性的评价更为重要[26]。目前在食品检测中常用的颜色表示系统为CIELAB表色系和Hunter Lab 表色系[27],L*值表示光泽的明亮度,L*值越大,亮度越高;a*值为色度中的红绿色差指标,正值越大,红色越深;b*值表示黄蓝度,正值越大,黄色越深[28];H值为色调参数中的色度角,变化幅度0~180之间,H<50时,H值越小,红色越深[29];C值为饱和度,又称纯度,表示含色的多少,低饱和度意味着色泽稀疏暗淡,高饱和度则表示饱满、强烈的颜色[30]。通过对12个品种辣椒的5个色度进行分析,结果见表3,L*值在50.259~44.787之间,最高的品种为XK-4(泰星4号),表明该品种果皮亮度较高,与其余品种差异显著(P<0.05),最低的品种为XB-11(聚源5号);a*值在23.793~30.746之间,最高的品种为XB-9(红龙23),最低的品种为XB-7(大叶朝天椒);b*值最高的品种为XH-3(红安6号),表明该品种表皮黄色较深;H值在31.486~49.965之间,红色最深的品种为XB-9(红龙23),最淡的品种为XH-3(红安6号);C值在33.805~38.401之间。五个色泽指标变异系数依次为H>a*>b*>C>L*,说明该12份辣椒品种之间的色泽差异主要表现在H值和a*上。产生这种差异的原因一是实验选择的辣椒品种以红椒为主,二是板椒和朝天椒品种居多,该两类辣椒表皮的明亮度较线椒高。
表 3 不同品种辣椒色度比较Table 3. Comparison of different varieties of pepper color degree品种 L* a* b* H C XH-1 46.523±0.280f 25.471±0.180d 22.292±0.030g 39.385±0.240g 33.849±0.150g XH-2 46.811±0.110e 25.473±0.040d 23.813±0.230e 42.068±0.340d 34.871±0.180f XH-3 46.511±0.060f 25.699±0.020d 28.534±0.130a 49.965±0.260a 38.401±0.090a XK-4 50.259±0.050a 24.234±0.080f 25.335±0.080c 47.045±0.280b 35.060±0.040f XA-5 49.619±0.100b 24.236±0.020f 26.779±0.040b 49.722±0.030a 36.118±0.050e XA-6 48.952±0.080c 24.625±0.020e 23.160±0.060f 42.323±0.130d 33.805±0.040g XB-7 48.573±0.340d 23.793±0.110g 24.262±0.150d 45.887±0.490c 33.982±0.040g XB-8 44.915±0.180hi 30.667±0.410a 21.562±0.370h 31.638±0.120h 37.488±0.550c XB-9 44.900±0.150hi 30.746±0.210a 21.512±0.220h 31.486±0.470h 37.525±0.150c XY-10 45.688±0.090g 28.446±0.010b 25.138±0.120c 39.768±0.190g 37.962±0.080b XB-11 44.787±0.050i 27.298±0.050c 25.168±0.040c 41.489±0.020e 37.130±0.060d XB-12 45.140±0.100h 28.313±0.060b 25.329±0.020c 40.257±0.060f 37.989±0.050b 最大值 50.259 30.746 28.534 49.965 38.401 最小值 44.787 23.793 21.512 31.486 33.805 平均值 46.890 26.584 24.407 41.753 36.182 标准差 1.976 2.466 2.097 6.000 1.776 变异系数(%) 4.215 9.275 8.592 14.371 4.908 2.1.2 不同品种辣椒营养品质比较
通过对12个品种辣椒的可溶性糖、粗脂肪、可溶性蛋白质、维生素C、辣椒素含量和ASTA色度进行测定,结果如表4所示,可溶性糖的含量范围在153.177~354.311 mg/g之间,平均含量为233.523 mg/g,含量最高的是XH-2(长线1号),显著高于其他各个品种(P<0.05),脂肪含量最高的是XB-12(红素3号),为15.307 g/100 g,最低的是XA-5(红丹丹1号),为9.652 g/100 g,各品种间的差异显著(P<0.05)。可溶性蛋白含量最高的是XB-12(红素三号),为14.740 mg/g,除XB-11(聚源5号)外,其余的品种与其差异显著(P<0.05);维生素C含量最高的是XA-5(红丹丹1号),为4.587 mg/g,含量最低的是XH-1(线椒10号),为1.558 mg/g,其中XH-3和XB-8的维生素C含量差异不显著(P>0.05)。ASTA色度最大的是XB-12(红素三号),为646.715,最小的是XH-1(线椒10号),为248.713,其中XA-5(红丹丹1号)和XA-6(朝地椒)的差异性不显著(P>0.05)。辣椒素含量的范围在6.906~237.610 mg/100 g之间,XB-7(大叶朝天椒)的辣椒素含量高达237.610 mg/100 g。该6个营养指标的变异系数在11.468%~76.104%之间,表明12个品种的营养成分含量互不相同,各有特点。线椒的可溶性糖、可溶性蛋白含量高于板椒和朝天椒,粗脂肪含量和板椒相当,辣椒素含量适中。因此从营养价值角度来说,本研究中线椒的营养价值高于板椒和朝天椒。
表 4 不同品种辣椒营养指标比较Table 4. Comparison of nutritional indexes of different pepper varieties品种 可溶性糖
(mg/g)脂肪
(g/100 g)可溶性蛋白质
(mg/g)维生素C
(mg/g)ASTA色度 辣椒素
(mg/100 g)XH-1 287.638±0.370c 14.329±0.030d 9.477±0.000g 1.558±0.000k 248.713±0.130k 129.930±0.020d XH-2 354.311±0.060a 13.276±0.030f 14.659±0.010b 3.437±0.000b 324.692±0.080i 108.890±0.040e XH-3 213.886±0.010g 12.779±0.020i 13.357±0.010c 3.397±0.000c 459.171±0.730d 65.970±0.000f XK-4 221.418±0.100f 11.862±0.010j 9.748±0.000f 2.734±0.050g 404.475±0.060g 156.390±0.150b XA-5 213.890±0.000g 9.652±0.020k 11.215±0.000d 4.587±0.010a 341.573±0.010h 38.560±0.050h XA-6 153.177±0.000k 14.794±0.010b 5.864±0.010k 1.782±0.020j 341.573±0.000h 146.730±0.100c XB-7 179.098±0.030i 14.757±0.010c 8.803±0.010h 3.108±0.010d 292.483±0.010j 237.610±0.010a XB-8 249.649±0.000e 13.262±0.010f 8.291±0.000i 3.376±0.000c 436.822±0.030f 6.910±0.170l XB-9 189.057±0.010h 14.056±0.010e 10.925±0.000e 2.977±0.000e 449.189±0.010e 37.220±0.240i XY-10 300.244±0.010b 13.162±0.010g 7.257±0.000j 2.497±0.000h 465.320±0.010c 31.410±0.160k XB-11 267.864±0.020d 12.945±0.010h 14.733±0.000a 2.838±0.000f 528.074±0.070b 57.970±0.480g XB-12 172.043±0.040j 15.307±0.010a 14.740±0.000a 2.059±0.000i 646.715±0.010a 33.610±0.120j 最大值 354.311 15.307 14.740 4.587 646.715 237.610 最小值 153.177 9.652 5.864 1.558 248.713 6.906 平均值 233.523 13.348 10.756 2.862 411.567 87.598 标准差 59.925 1.531 3.055 0.831 110.444 66.666 变异系数(%) 25.661 11.468 28.402 29.028 26.835 76.104 2.2 不同品种辣椒综合品质差异性分析
利用模糊数学中的隶属函数值分析法,对12份辣椒的单果重、脂肪、蛋白质、辣椒素含量等指标的隶属函数分别进行计算,并分别计算出12个辣椒品种的平均隶属函数,评价12份辣椒的综合品质之间的差异,结果如表5所示,12份辣椒的13个品质指标的平均隶属度在0.313~0.516之间,相差0.203,表明12份辣椒的综合品质之间存在较大差异。
表 5 12份辣椒的综合品质的平均隶属度值Table 5. Average membership values for the overall quality of the 12 chili peppers品种 总隶属度 平均隶属度 XH-1 4.633 0.356 XH-2 6.723 0.516 XH-3 6.251 0.481 XK-4 6.038 0.464 XA-5 6.302 0.485 XA-6 4.679 0.360 XB-7 6.451 0.496 XB-8 4.087 0.313 XB-9 4.360 0.335 XY-10 5.333 0.410 XB-11 5.927 0.456 XB-12 5.605 0.431 2.3 不同品质辣椒主成分分析
主成分分析可以解析复杂信息中的主要影响因素,简化评价过程[31]。本研究采用主成分分析法对12个辣椒品种的单果重、可食比率、可溶性糖含量、可溶性蛋白含量等指标结果进行分析,结果如表6、表7所示,以特征值大于1为标准,提取出4个主成分,累计贡献率达88.369%,所表达的综合信息可以用来反映全部性状的信息[32]。第一主成分的特征值为4.798,包含原来信息量的43.614%,L*、可食比率、a*值、单果重、辣椒红素、辣椒素的绝对值排在前几位,表明第一主成分由这些指标综合反映,其中产生负向影响的为L*、可食比率和辣椒素含量;第二主成分的特征值为2.375,包含原来信息量的21.589%,脂肪和维生素C含量的特征向量值相对较高,表明第二主成分主要综合了辣椒的维生素C和脂肪含量的信息;第三主成分的特征值为1.416,包含原来信息量的12.869%,主要反映辣椒的可溶性糖含量;第四主成分的特征值为1.133,包含原来信息量的10.296%,主要由可溶性蛋白含量决定。将4个主成分得分分别记为A1、A2、A3和A4,用4组主成分的特征值除以特征值总和作为权重数,得到主成分综合得分模型[33-34],计算公式如下:
表 6 主成分特征值及累计贡献率Table 6. Characteristic values of principal components and cumulative contribution rate of contribution主成分 特征值 贡献率(%) 累计贡献率(%) 1 4.798 43.614 43.614 2 2.375 21.589 65.204 3 1.416 12.869 78.073 4 1.133 10.296 88.369 表 7 主成分载荷结果Table 7. Principal component load指 标 主成分 1 2 3 4 L* −0.938 0.031 −0.198 −0.021 可食率 −0.881 −0.122 −0.317 −0.236 a* 0.863 −0.007 0.013 −0.370 单果重 0.802 0.120 0.163 −0.318 辣椒素含量 −0.773 −0.420 0.221 0.271 辣椒红素含量 0.758 −0.080 −0.529 0.023 粗脂肪含量 0.289 −0.870 0.235 0.133 维生素C含量 −0.165 0.824 −0.355 −0.055 b* −0.512 0.581 0.396 −0.229 可溶性糖含量 0.228 0.524 0.700 0.293 可溶性蛋白含量 0.396 0.338 −0.303 0.778 A1=−0.428X1−0.4022X2+0.394X3+0.3661X4−0.3529X5+0.346X6+0.1319X7−0.0753X8−0.2337X9+0.104X10+0.1808X11
A2=0.0201X1−0.0792X2−0.0045X3+0.0779X4−0.2725X5−0.0519X6−0.5645X7+0.5347X8+0.3770X9+0.34X10+0.2193X11
A3=−0.1664X1−0.2664X2+0.0109X3+0.1370X4+0.1857X5−0.4446X6+0.1975X7−0.2983X8+0.3328X9+0.5883X10−0.2546X11
A4=−0.019X1−0.2216X2−0.3474X3−0.2986X4+0.2544X5+0.0216X6+0.1249X7−0.0516X8−0.215X9+0.2751X10+0.7304X11
A综=0.43614A1+0.21589A2+0.12869A3+0.10296A4
前4个表达式中,X1~X11分别为单果重、可食比率、L*、a*、b*、ASTA色度、脂肪、维生素C含量、可溶性糖含量、可溶性蛋白含量、辣椒素含量检测值经标准化处理后的值。
12份辣椒的综合评分如表8所示,综合评分由高到低依次为XB-12(红素3号)、XH-2(长线1号)、XH-3(红安6号)、XB-11(聚源5号)、XB-9(红龙23)、XK-4(泰星4号)、XH-1(线椒10号)、XB-8(红龙13)、XB-7(大叶朝天椒)、XA-5(红丹丹1号)、XA-6(朝地椒)、XY-10(裕红113)。辣椒加工企业可以根据主成分数值大小判定品种的特征,结合主成分综合得分进行原料品种的选择。
表 8 不同品种辣椒主成分评分和综合评分Table 8. Principal component scores and comprehensive scores of different pepper varieties品 种 A1 A2 A3 A4 A综 排名 XH-1 −0.193 −0.803 1.380 0.630 −0.013 7 XH-2 −0.447 1.707 1.747 0.453 0.447 2 XH-3 0.183 0.400 0.420 0.587 0.283 3 XK-4 0.323 0.183 −0.790 0.130 0.093 6 XA-5 −1.137 1.973 −0.947 −1.183 −0.313 10 XA-6 0.200 −2.340 −1.090 0.280 −0.530 11 XB-7 −0.210 −0.707 −1.067 1.523 −0.223 9 XB-8 −0.020 0.143 −0.120 −1.280 −0.127 8 XB-9 0.480 −0.407 0.123 −0.393 0.097 5 XY-10 −1.090 −0.290 −0.190 −0.947 −0.660 12 XB-11 −0.403 0.697 0.740 0.487 0.120 4 XB-12 2.310 −0.563 −0.203 −0.283 0.830 1 2.4 不同品种辣椒品质聚类分析
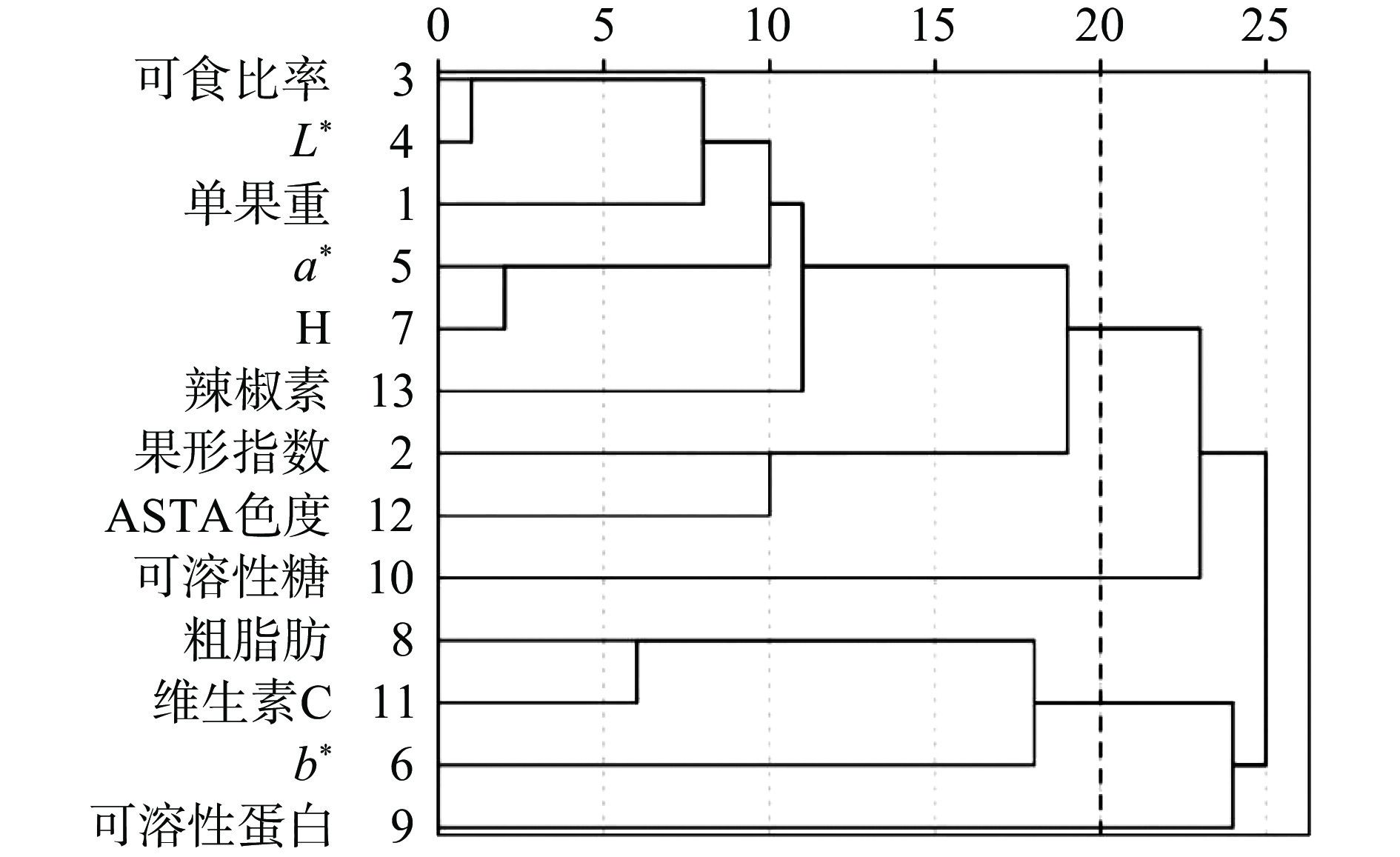
对12份辣椒品种的13个品质性状测试结果标准化后进行R型聚类,结果见图1,在组间距离为20时,13个品质性状被聚为4大类群,第一类为单果重、可食比率、L*值、a*、H值、果形指数、ASTA色度和辣椒素含量。第二类为可溶性糖含量。第三类为粗脂肪、维生素C含量和b*。第四类为可溶性蛋白含量。结合主成分载荷表中的数值较大的正载荷量,确定干椒品质的核心指标包括a*、单果重、维生素C、辣椒红素、可溶性蛋白、可溶性糖含量。
对12份辣椒品种进行Q型聚类,由图2可知,在组间距离为8时,12分辣椒品种被分为4类群,第一类包含五种板椒和一种线椒,分别为XB-8(红龙13)、XB-9(红龙23)、XY-10(裕红113)、XB-11(聚源5号)、XH-3(红安6号)和XA-5(红丹丹1号)。在对XH-3品种进行品质评价时,其可食比率、b*、可溶性糖、粗脂肪、和辣椒红素含量与板椒较为相似,因此该品种也被聚在第一类。该类群单果重、a*值和ASTA色度的均值分别为3.620 g、27.849和446.692,均高于平均值,表明该类群辣椒品种果型较大,红色较深,适宜制干,可用做提取辣椒红素的原料。第二类将XH-1(线椒10号)和XH-2(长线1号)两种线椒聚为一类,该类群果形指数和可溶性糖含量均值分别为13.387和320.975 mg/g,均为4个类群中最大,较其他三个类群差异明显,表明该类群辣椒品种的果形呈线状,味道较佳,适合干制加工。第三类将12份资源中的全部朝天椒聚为一类,分别为XA-6(朝地椒)、XB-7(大叶朝天椒)、XK-4(泰星4号),该类的可食比率和L*值均值分别为96.8130%和49.261,为四个类群中最高,且与其他三个类群差异显著(P<0.05)。表明该类群品种为亮度较高的小果型辣椒,但因朝天椒水分含量和籽含量较高,因此该品种属于鲜食加工皆可品种。第四类包含XB-12(红素3号),该品种虽也属于板椒,但因其粗脂肪、蛋白质、ASTA色度值均为四类群中最高,且与其他三类群差异显著(P<0.05),因此被单独分为一类。该品种在主成分综合评分中排名第一,不仅品质最优,制干加工适应性也最好。
3. 讨论与结论
辣椒的综合品质主要可分为商品品质、感官品质和营养品质。在商品品质中,单果重与辣椒产量有直接联系,果形指数也是重要的商品品质之一,本研究在比较不同品种辣椒商品品质时,发现线椒10号和长线1号品种的果形指数较大,聚源5号等板椒的单果重较大,且单果重和果形指数的变异系数排名靠前,表明线椒和板椒的产量高于朝天椒。企业在选择原料品种时,也较容易筛出产量较高的品种。在营养品质中,蛋白质是人体所必需的基础物质,可溶性糖含量是决定辣椒味道的关键指标,维生素C是一种人体所必需的营养元素,能降低缺铁性贫血的发病率[35]。脂肪不仅是食品中重要的营养指标,其含量的多少会还会直接影响辣椒风味与口感,粗脂肪含量高则适口性和香味更佳[36],辣椒素是辣椒中的主要生物活性成分。在对比不同辣椒的营养和感官品质时发现,线椒的可溶性糖含量较高,有利于改善辣椒产品的口感风味,也有利于微生物发酵[37]。因此线椒是发酵辣椒酱用优质干椒原料。朝天椒的辣椒素含量较高,含籽较多。因此,朝天椒可作为提取辣椒素的原料,也较适宜用来制粉、制辣椒油和火锅底料类调味料[38]。品种特性是造成辣椒产品品质差异的的首要因素,加工品种的选择会直接影响到产品品质的均一性和稳定性,因此拥有科学的选料依据对辣椒生产企业而言显得至关重要。近年来,多元统计分析法成为评价辣椒资源的有效途径。高佳等[39]对10个线椒品种的主要品质指标进行隶属函数分析和聚类分析筛选出品质最优的品种为红冠4号,为线椒加工品种辅助选择提供理论依据。聂楚楚等[40]利用聚类分析将57份辣椒材料划分为四大类群,通过主成分分析结果将6个农艺性状转化为3个主成分,为辣椒资源分类提供了一定的数据依据。
本研究采用多元分析方法对12个辣椒品种的16个品质指标进行测定与分析,结果表明11个指标的变异系数均大于10%,其中辣椒素含量的变异系数最大,为76.104%,说明12个样品间辣度指标差异较大,与高佳等[39]和刘宇鹏等[41]的研究结果一致,由此可知,这些品种的品质性状具有丰富的遗传多样性;隶属函数结果表明12份辣椒的综合品质之间存在较大差异。采用主成分分析法提取出四个主成分,累计贡献率达到88.369%,得到综合评分排名前五的辣椒XB-12(红素三号)、XH-2(长线1号)、XH-3(红安6号)、XB-11(聚源5号)和XB-9(红龙23)。经聚类分析,评定指标和辣椒品种均被聚为4类,R型聚类反映出影响干辣椒品质的重要指标包含单果重、辣椒红素、脂肪、维生素C含量和a*;Q型聚类中,第一类包括红龙13、红龙23、裕红113、聚源5号红安6号,第二类包括线椒10号和长线1号,第三类包括朝地椒、大叶朝天椒和泰星4号,第四类包括红素三号。经综合分析,发现线椒的可溶性糖和粗脂肪含量较高,适宜做发酵辣椒酱、辣椒丝和油辣椒的原料,朝天椒的辣椒素含量较高,适宜提取辣椒碱,也可作为制粉、辣椒油等调味料的原料。板椒的产量和ASTA色度较高,适宜辣椒红色素的提取。12份辣椒中品质最优、最适宜制干的辣椒为红素三号。本研究旨在辣椒加工时品种的选择提供可靠依据,也可在一定程度上促进新疆辣椒资源合理配置。后续研究可通过增加更多的测定指标来提高筛选的准确性。
-
表 1 供试材料名称
Table 1 Name of test materials
编号 品种名称 来源 XH-1 线椒10号 和静 XH-2 长线1号 和静 XH-3 红安6号 和静 XK-4 泰星四号 库尔勒 XA-5 红丹丹1号 阿克苏 XA-6 朝地椒 阿克苏 XB-7 大叶朝天椒 博湖 XB-8 红龙13 博湖 XB-9 红龙23 博湖 XY-10 裕红113 焉耆 XB-11 聚源5号 博湖 XB-12 红素三号 博湖 表 2 不同品种辣椒形态指标比较
Table 2 Comparison of agronomic traits of different pepper varieties
品种 单果重(g) 纵径(cm) 横径(cm) 果形指数 可食比率(%) XH-1 1.907±0.010g 12.252±0.120g 0.984±0.010i 12.452±0.000b 94.777±0.030cd XH-2 2.177±0.000e 21.881±0.100a 1.528±0.010g 14.322±0.010a 94.735±0.040cd XH-3 1.778±0.030h 12.274±0.010g 1.584±0.010g 7.746±0.030d 94.740±0.010cd XK-4 0.673±0.010j 6.946±0.000j 1.223±0.010h 5.680±0.030f 96.681±0.010b XA-5 2.081±0.040f 13.093±0.070e 2.106±0.010f 6.217±0.010e 96.774±0.010b XA-6 1.618±0.000i 8.120±0.010i 1.595±0.010g 5.092±0.030g 96.783±0.000b XB-7 1.621±0.000i 11.233±0.010h 1.287±0.000h 8.728±0.000c 96.973±0.010a XB-8 3.349±0.050d 12.181±0.050g 2.758±0.050e 4.417±0.100i 94.879±0.010c XB-9 3.666±0.010c 18.410±0.080b 3.579±0.130a 5.149±0.210g 94.848±0.040c XY-10 6.166±0.070a 16.061±0.050c 3.181±0.050b 5.050±0.100g 94.612±0.150d XB-11 4.678±0.080b 14.690±0.010d 2.996±0.020c 4.904±0.030h 94.598±0.330d XB-12 3.665±0.020c 12.714±0.300f 2.874±0.030d 4.424±0.130i 94.627±0.040d 最大值 6.166 21.881 3.579 14.322 96.973 最小值 0.673 6.946 0.984 4.417 94.598 平均值 2.781 13.321 2.141 7.015 95.419 标准差 1.558 4.096 0.889 3.272 1.028 变异系数(%) 56.021 30.749 41.519 46.648 1.077 注:同列不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);表2~表4同。 表 3 不同品种辣椒色度比较
Table 3 Comparison of different varieties of pepper color degree
品种 L* a* b* H C XH-1 46.523±0.280f 25.471±0.180d 22.292±0.030g 39.385±0.240g 33.849±0.150g XH-2 46.811±0.110e 25.473±0.040d 23.813±0.230e 42.068±0.340d 34.871±0.180f XH-3 46.511±0.060f 25.699±0.020d 28.534±0.130a 49.965±0.260a 38.401±0.090a XK-4 50.259±0.050a 24.234±0.080f 25.335±0.080c 47.045±0.280b 35.060±0.040f XA-5 49.619±0.100b 24.236±0.020f 26.779±0.040b 49.722±0.030a 36.118±0.050e XA-6 48.952±0.080c 24.625±0.020e 23.160±0.060f 42.323±0.130d 33.805±0.040g XB-7 48.573±0.340d 23.793±0.110g 24.262±0.150d 45.887±0.490c 33.982±0.040g XB-8 44.915±0.180hi 30.667±0.410a 21.562±0.370h 31.638±0.120h 37.488±0.550c XB-9 44.900±0.150hi 30.746±0.210a 21.512±0.220h 31.486±0.470h 37.525±0.150c XY-10 45.688±0.090g 28.446±0.010b 25.138±0.120c 39.768±0.190g 37.962±0.080b XB-11 44.787±0.050i 27.298±0.050c 25.168±0.040c 41.489±0.020e 37.130±0.060d XB-12 45.140±0.100h 28.313±0.060b 25.329±0.020c 40.257±0.060f 37.989±0.050b 最大值 50.259 30.746 28.534 49.965 38.401 最小值 44.787 23.793 21.512 31.486 33.805 平均值 46.890 26.584 24.407 41.753 36.182 标准差 1.976 2.466 2.097 6.000 1.776 变异系数(%) 4.215 9.275 8.592 14.371 4.908 表 4 不同品种辣椒营养指标比较
Table 4 Comparison of nutritional indexes of different pepper varieties
品种 可溶性糖
(mg/g)脂肪
(g/100 g)可溶性蛋白质
(mg/g)维生素C
(mg/g)ASTA色度 辣椒素
(mg/100 g)XH-1 287.638±0.370c 14.329±0.030d 9.477±0.000g 1.558±0.000k 248.713±0.130k 129.930±0.020d XH-2 354.311±0.060a 13.276±0.030f 14.659±0.010b 3.437±0.000b 324.692±0.080i 108.890±0.040e XH-3 213.886±0.010g 12.779±0.020i 13.357±0.010c 3.397±0.000c 459.171±0.730d 65.970±0.000f XK-4 221.418±0.100f 11.862±0.010j 9.748±0.000f 2.734±0.050g 404.475±0.060g 156.390±0.150b XA-5 213.890±0.000g 9.652±0.020k 11.215±0.000d 4.587±0.010a 341.573±0.010h 38.560±0.050h XA-6 153.177±0.000k 14.794±0.010b 5.864±0.010k 1.782±0.020j 341.573±0.000h 146.730±0.100c XB-7 179.098±0.030i 14.757±0.010c 8.803±0.010h 3.108±0.010d 292.483±0.010j 237.610±0.010a XB-8 249.649±0.000e 13.262±0.010f 8.291±0.000i 3.376±0.000c 436.822±0.030f 6.910±0.170l XB-9 189.057±0.010h 14.056±0.010e 10.925±0.000e 2.977±0.000e 449.189±0.010e 37.220±0.240i XY-10 300.244±0.010b 13.162±0.010g 7.257±0.000j 2.497±0.000h 465.320±0.010c 31.410±0.160k XB-11 267.864±0.020d 12.945±0.010h 14.733±0.000a 2.838±0.000f 528.074±0.070b 57.970±0.480g XB-12 172.043±0.040j 15.307±0.010a 14.740±0.000a 2.059±0.000i 646.715±0.010a 33.610±0.120j 最大值 354.311 15.307 14.740 4.587 646.715 237.610 最小值 153.177 9.652 5.864 1.558 248.713 6.906 平均值 233.523 13.348 10.756 2.862 411.567 87.598 标准差 59.925 1.531 3.055 0.831 110.444 66.666 变异系数(%) 25.661 11.468 28.402 29.028 26.835 76.104 表 5 12份辣椒的综合品质的平均隶属度值
Table 5 Average membership values for the overall quality of the 12 chili peppers
品种 总隶属度 平均隶属度 XH-1 4.633 0.356 XH-2 6.723 0.516 XH-3 6.251 0.481 XK-4 6.038 0.464 XA-5 6.302 0.485 XA-6 4.679 0.360 XB-7 6.451 0.496 XB-8 4.087 0.313 XB-9 4.360 0.335 XY-10 5.333 0.410 XB-11 5.927 0.456 XB-12 5.605 0.431 表 6 主成分特征值及累计贡献率
Table 6 Characteristic values of principal components and cumulative contribution rate of contribution
主成分 特征值 贡献率(%) 累计贡献率(%) 1 4.798 43.614 43.614 2 2.375 21.589 65.204 3 1.416 12.869 78.073 4 1.133 10.296 88.369 表 7 主成分载荷结果
Table 7 Principal component load
指 标 主成分 1 2 3 4 L* −0.938 0.031 −0.198 −0.021 可食率 −0.881 −0.122 −0.317 −0.236 a* 0.863 −0.007 0.013 −0.370 单果重 0.802 0.120 0.163 −0.318 辣椒素含量 −0.773 −0.420 0.221 0.271 辣椒红素含量 0.758 −0.080 −0.529 0.023 粗脂肪含量 0.289 −0.870 0.235 0.133 维生素C含量 −0.165 0.824 −0.355 −0.055 b* −0.512 0.581 0.396 −0.229 可溶性糖含量 0.228 0.524 0.700 0.293 可溶性蛋白含量 0.396 0.338 −0.303 0.778 表 8 不同品种辣椒主成分评分和综合评分
Table 8 Principal component scores and comprehensive scores of different pepper varieties
品 种 A1 A2 A3 A4 A综 排名 XH-1 −0.193 −0.803 1.380 0.630 −0.013 7 XH-2 −0.447 1.707 1.747 0.453 0.447 2 XH-3 0.183 0.400 0.420 0.587 0.283 3 XK-4 0.323 0.183 −0.790 0.130 0.093 6 XA-5 −1.137 1.973 −0.947 −1.183 −0.313 10 XA-6 0.200 −2.340 −1.090 0.280 −0.530 11 XB-7 −0.210 −0.707 −1.067 1.523 −0.223 9 XB-8 −0.020 0.143 −0.120 −1.280 −0.127 8 XB-9 0.480 −0.407 0.123 −0.393 0.097 5 XY-10 −1.090 −0.290 −0.190 −0.947 −0.660 12 XB-11 −0.403 0.697 0.740 0.487 0.120 4 XB-12 2.310 −0.563 −0.203 −0.283 0.830 1 -
[1] 毛立霞, 魏小春, 原玉香, 等. 辣椒红素的生物合成及代谢研究进展[J]. 分子植物育种,2018,16(1):115−122. [MAO Lixia, WEI Xiaochun, YUAN Yuxiang, et al. Progress in the biosynthesis and metabolism of capsanthin[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding,2018,16(1):115−122. [2] 邹学校, 马艳青, 戴雄泽, 等. 辣椒在中国的传播与产业发展[J]. 园艺学报,2020,47(9):1715−1726. [ZOU Xuexiao, MA Yanqing, DAI Xiongze, et al. Spread and industry development of pepper in China[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2020,47(9):1715−1726. [3] 占文婷, 胡思卓, 黄倞文, 等. 辣椒粉中还原型维生素C含量的测定[J]. 中国调味品,2017,42(3):104−109. [ZHAN Wenting, HU Sizhuo, HUANG Jingwen, et al. Determination of the reduced vitamin C content in paprika[J]. China Condiment,2017,42(3):104−109. [4] 曾翔云. 维生素C的生理功能与膳食保障[J]. 中国食物与营养,2005(4):52−54. [ZENG Xiangyun. The physiological function and dietary guarantee of vitamin C[J]. Chinese Food and Nutrition,2005(4):52−54. [5] MAHESH A, ROYAPURAM P P, HANNAH R V, et al. Dynamic action of carotenoids in cardioprotection and maintenance of cardiac health[J]. Molecules,2012,17(4):4755−4769. doi: 10.3390/molecules17044755
[6] JI-SUN K, WOO-MOON L, HAN C R, et al. Red paprika (Capsicum annuum L.) and its main carotenoids, capsanthin and β-carotene, prevent hydrogen peroxide-induced inhibition of gap-junction intercellular communication[J]. Chemico-Biological Interactions,2016,254:146−155. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2016.05.004
[7] WU J Y, CHIEN Y, TSAI I, et al. Capsanthin induces G1/S phase arrest, erlotinib-sensitivity and inhibits tumor progression by suppressing EZH2-mediated epigenetically silencing of p21 in triple-negative breast cancer cells[J]. Aging (Albany NY),2021:13.
[8] 沈伟. 辣椒素对高脂饮食诱导肥胖小鼠肠道菌群的影响研究[D]. 重庆: 第三军医大学, 2017 SHEN Wei. Effect of capsaicin on intestinal flora of high-fat diet induced obese mice[D]. Chongqing: The Third Military Medical University, 2017.
[9] 聂乾忠, 夏延斌, 曾晓楠, 等. 辣椒素类物质对高脂血症大鼠血脂的影响[J]. 食品与机械,2010,26(1):77−80. [NIE Qianzhong, XIA Yanbing, ZENG Xiaonan, et al. Effect of capsaicin substances on blood lipids in hyperlipidemic rats[J]. Food and Machinery,2010,26(1):77−80. [10] BRUNNO F R C, MARIANA B T, NATALIA E F P, et al. Capsaicin reduces genotoxicity, colonic cell proliferation and preneoplastic lesions induced by 1,2-dimethylhydrazine in rats[J]. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology,2017,338:93−102.
[11] CLARK R, LEE S H. Anticancer properties of capsaicin against human cancer[J]. Anticancer Research,2016,36(2):837−844.
[12] MONICA R L, ALESSANDRO P, MARCO B, et al. Evaluation of chemical profile and antioxidant activity of twenty cultivars from Capsicum annuum, Capsicum baccatum, Capsicum chacoense and Capsicum chinense: A comparison between fresh and processed peppers[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2015,64(2):623−631. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2015.06.042
[13] FABELA M M F, CUEVAS B J C, AYORA T T, et al. Trends in capsaicinoids extraction from habanero chili pepper (Capsicum chinense Jacq.): Recent advanced techniques[J]. Food Reviews International,2020,36(2):105−134. doi: 10.1080/87559129.2019.1630635
[14] 王立浩, 张宝玺, 张正海, 等. 多抗、优质甜椒优异种质资源的创新及新品种选育[J]. 中国科技成果,2021,22(24):28−29. [WANG Lihao, ZHANG Baoxi, ZHANG Zhenghai, et al. Innovation of excellent sweet pepper germplasm resources with high resistance and breeding of new varieties[J]. China Science and Technology Achievements,2021,22(24):28−29. [15] 王艳玲. 柘城: 红火小辣椒脱贫大产业[J]. 河南农业,2019(28):57−58. [WANG Yanling. Zhecheng: red-hot small pepper poverty alleviation big industry[J]. Henan Agriculture,2019(28):57−58. [16] 李宁, 杨涛, 帕提古丽, 等. 适于新疆制干类型辣椒种质资源遗传多样性的 SRAP 和 SCOT 分析[J]. 分子植物育种,2017,15(8):3331−3340. [LI Ning, YANG Tao, PATIGULI, et al. Suitable for SRAP and SCOT analysis of genetic diversity in Xinjiang[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding,2017,15(8):3331−3340. [17] 李艳, 王亮, 刘志刚. 新疆绿洲干旱区制干辣椒生产技术现状与产业发展对策[J]. 北方园艺,2014(13):189−192. [LI Yan, WANG Liang, LIU Zhigang. Current production technology and industrial development countermeasures of dried pepper in Xinjiang oasis arid area[J]. Northern Gardening,2014(13):189−192. [18] 蔡永艳, 郝会娟, 关振亚, 等. 辣风味研究及其常见辣椒品种品质分析[J]. 中国调味品,2021,46(9):193−196. [CAI Yongyan, HAO Huijuan, GUAN Zhengya, et al. Research on spicy flavor and its quality analysis of common pepper varieties[J]. Chinina Condiment,2021,46(9):193−196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2021.09.038 [19] 王立浩, 张宝玺, 张正海, 等. “十三五”我国辣椒育种研究进展、产业现状及展望[J]. 中国蔬菜,2021(2):21−29. [WANG Lihao, ZHANG Baoxi, ZHANG Zhenghai, et al. Status in breeding and production of Capsicum spp. in China during "the thirteenth five-year plan" period and future prospect[J]. China Vegetables,2021(2):21−29. [20] 汪琳, 应铁进. 番茄果实采后贮藏的颜色动力学研究[J]. 食品科技,2000(5):49−51. [WANG Ling, YING Tiejin. Color dynamics of tomato fruit storage[J]. Food Technology,2000(5):49−51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2000.05.024 [21] 龙小琴, 戴应和. 蒽酮-硫酸显色法测定白及块茎与非药用部位中白及多糖含量的比较研究[J]. 农业与技术,2021,41(13):30−32. [LONG Xiaoqin, DAI Yinghe. Comparative study on polysaccharide content in stems of Bletilla and non medicinal parts by anthrone-sulphuric acid colorimetry[J]. Agriculture and Technology,2021,41(13):30−32. [22] 徐亚, 范会芬, 赵玎玲, 等. 考马斯亮蓝法测定大豆水溶性蛋白提取方法的优化[J]. 大豆科学,2022,41(2):196−202. [XU Ya, FAN Huifeng, ZHAO Dingling, et al. Optimization of the extraction method for water-soluble protein determination by coomassie bright blue method[J]. Soybean Science,2022,41(2):196−202. [23] 冯华, 王祥培, 王世俊, 等. 辣椒药材的HPLC指纹图谱建立及聚类分析和主成分分析[J]. 中国药房,2019,30(8):1078−1082. [FENG Hua, WANG Xiangpei, WANG Shijun, et al. Establishment of HPLC fingerprint, cluster analysis and principal component analysis of Capsicum annuum[J]. China Pharmacy,2019,30(8):1078−1082. [24] 周勇. 中药材干辣椒中辣椒素和二氢辣椒素含量测定方法分析[J]. 临床医药文献电子杂志,2020,7(15):162. [ZHOU Yong. Assay method analysis of capsaicin and dihydrocapsaicin in dried pepper[J]. Electronic Journal of Clinical Medical Literature,2020,7(15):162. [25] 任朝辉, 廖卫琴, 周安韦, 等. 不同线椒品种品质评价[J]. 中国瓜菜,2019,32(7):26−30. [REN Chaohui, LIAO Weiqin, ZHOU Anwei, et al. Quality evaluation of different line pepper varieties[J]. Chinese Melons and Vegetables,2019,32(7):26−30. [26] SCALA K D, CRAPISTE G. Drying kinetics and quality changesduring drying of red pepper[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2008,41:789−795. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2007.06.007
[27] CHARLES P. Background colour & its impact on foodperception & behaviour[J]. Food Quality and Preference,2018,68:156−166. doi: 10.1016/j.foodqual.2018.02.012
[28] 苏美玲, 周之珞, 林林, 等. 不同套袋对三红蜜柚果皮色泽及果实品质的影响试验[J]. 农业研究与应用,2019,32(2):912. [SU Meiling, ZHOU Zhiluo, LIN Lin, et al. Effects of different bagging treatment on peel color and fruit quality of Sanhongmiyou[J]. Agricultural Research and Application,2019,32(2):912. [29] 王利群, 戴雄泽. 色差计在辣椒果实色泽变化检测中的应用[J]. 辣椒杂志,2009(3):23−26. [WANG Liqun, DAI Xiongze. Application of color meter in color change of pepper fruit[J]. The Pepper Magazine,2009(3):23−26. [30] 汪琳, 应铁进. 番茄果实采后贮藏过程中的颜色动力学模型及其应用[J]. 农业工程学报,2001,17(3):118−121. [WANG Ling, YING Tiejin. Kinetic model on surface color in tomato fruits during the post -harvest storage and its application[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering,2001,17(3):118−121. [31] GAO Boyan, LU Yingjian, SHENG Yi, et al. Differentiating organic and conventional sage by chromatographic and mass spectrometry flow injection fingerprints combined with principal component analysis[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2013,61(12):2957−2963. doi: 10.1021/jf304994z
[32] LI Liming, ZHAO Jing, WANG Chongrong, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of robotic global performance based on modified principal component analysis[J]. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems,2020,17(4):1−11.
[33] GENTILE C, GREGORIO D E, STEFANO D V, et al. Food quality and nutraceutical value of nine cultivars of mango (Mangifera indica L.) fruits grown in Mediterranean subtropical environment[J]. Food Chemistry, 2019, 277: 471−479.
[34] HAO J, GAO L H, TANG X W, et al. Comparison in quality characters of five different tomato cultivars[J]. Acta Horticulturae,2010,856:133−140.
[35] 张瑞祥, 米富丽, 马慧霞, 等. 市场上常见辣椒品种的维生素C和辣椒碱含量分析[J]. 现代食品,2021(19):215−217. [ZHANG Ruixiang, MI Fuli, MA Huixia, et al. Analysis of vitamin C and capsaicin content of common pepper varieties on the market[J]. Modern Food,2021(19):215−217. [36] 王瑞, 孙长霞, 张泽生. 几种坚果植物中脂肪酸含量的分析研究[J]. 天津农学院学报,2007,14(4):39−41. [WANG Rui, SUN Changxia, ZHANG Zesheng. Analysis of fatty acid content in several nut plants[J]. Journal of Tianjin Agricultural College,2007,14(4):39−41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5394.2007.04.010 [37] 程晓齐. 干辣椒制作发酵型辣椒酱的研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2021 CHENG Xiaoqi. Study on the preparation of fermented chili sauce with dried chili[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2021.
[38] 王兴波, 饶雷, 王永涛, 等. 9个品种干辣椒的品质分析及评价[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(18):300−310. [WANG Xingbo, RAO Lei, WANG Yongtao, et al. Quality analysis and evaluation of 9 varieties of dried pepper[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(18):300−310. [39] 高佳, 田玉肖, 罗芳耀, 等. 10个线椒品种干制品品质分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(14):284−288. [GAO Jia, TIAN Yuxiao, LUO Fangyao, et al. Quality analysis of 10 dried line pepper varieties[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(14):284−288. [40] 聂楚楚, 王秀峰, 毛芙蓉, 等. 辣椒品种的聚类及主成分分析[J]. 北方园艺,2017(17):86−91. [NIE Chuchu, WANG Xiufeng, MAO Furong, et al. Clustering and principal component analysis of the pepper varieties[J]. Northern Gardening,2017(17):86−91. doi: 10.11937/bfyy.20170385 [41] 刘宇鹏, 张皓, 陈芳, 等. 贵州地方辣椒品种品质差异分析[J]. 中国瓜菜,2022,35(1):42−46. [LIU Yupeng, ZHANG Hao, CHEN Fang, et al. Analysis on differences of quality of local pepper varieties in Guizhou[J]. China Cucurbits and Vegetables,2022,35(1):42−46. -
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 许津阁,郑卓琦,侯鹏颉,马高兴,熊彦娣,马壮,刘萌,赵靓,廖小军. 不同产地酱用卡宴辣椒原料品质评价. 食品工业科技. 2025(01): 317-332 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 杨晶,沙迪昕,张月,麦迪乃·尤努斯,沙黑兰·尼亚孜,杨海燕,黄文书. 不同贮藏条件下干辣椒颜色劣变的主要途径. 食品研究与开发. 2024(04): 58-67 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 黄冬福,杨娅,范高领,付文婷,涂祥敏,吴迪,詹永发,何建文. 基于主成分和聚类分析7个深绿线椒品种的商品品质和产量评价. 贵州农业科学. 2024(02): 15-21 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 周群星,胡昊,吕春茂,孟宪军,于艳奇. 不同品种榛子加工榛子露适宜性评价. 现代食品科技. 2024(02): 213-220 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 陈菊,李文馨,孙惠桉,王雪雅,蓬桂华,孙小静,何建文. 不同地区指形朝天椒品质差异分析及综合评价. 食品研究与开发. 2024(07): 116-124 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 裴艳婷,魏龙雪,李娜娜,白静,朱金英. 不同辣椒种质资源品质性状分析. 安徽农业科学. 2024(11): 27-31 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 屠大伟,翁盈秋,李青青,冯露萍,刘文俊. 火锅常用干辣椒品质及挥发性成分研究. 食品工业科技. 2023(16): 358-366 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



