Optimization of Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Tilapia Scale Calcium Binding Peptides by Response Surface Methodology and Its Structural Characterization
-
摘要: 为研究罗非鱼鳞钙结合肽酶解制备最佳工艺条件及其螯合特性,从而为促钙吸收活性物质的研究提供基础,本研究以脱钙罗非鱼鳞为原料,钙螯合活性为指标,选用木瓜蛋白酶对罗非鱼鳞酶解工艺进行优化,获得罗非鱼鳞钙结合肽,并通过氨基酸分析、紫外光谱和红外光谱表征肽钙螯合特性。结果表明,罗非鱼鳞钙结合肽的最优酶解条件为底物浓度8%、时间2 h、酶底比0.3%、pH7、温度60 ℃,在此条件下酶解物钙螯合活性为(38.31±0.4) µg/mL。表征结果表明,螯合钙离子后,肽钙螯合物中天冬氨酸、谷氨酸、甘氨酸、赖氨酸、丝氨酸、半胱氨酸及组氨酸的含量分别增加了0.88%、1.48%、0.34%、0.53%、0.04%、0.38%、0.46%。钙结合肽中的羧基氧和氨基氮等基团参与了与钙离子的结合,形成了罗非鱼鳞肽钙螯合物。罗非鱼鳞钙结合肽具有较高的钙螯合活性,这为补钙剂的生产应用奠定了基础。Abstract: In order to obtain the optimum enzyme hydrolysis conditions and chelating properties of tilapia scale calcium binding peptides, and provide basis for study of promoting calcium absorption of active material, in this study, the decalcified tilapia scales as raw material and calcium chelation activity as an index, papain was selected to optimize enzyme hydrolysis of the tilapia scales to obtain tilapia scale calcium binding peptides. The properties of the tilapia scale calcium binding peptides were characterized by amino acid analysis, ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy and fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The optimal enzymatic hydrolysis conditions were as follows: the concentration of substrate 8%, time 2 h, enzyme to substrate ratio 0.3%, pH7 and temperature 60 ℃. Under these conditions, the calcium chelation activity of the enzymatic hydrolysate was (38.31±0.4) µg/mL. The results of characterization showed that, after chelating calcium, the contents of aspartic acid, glutamic acid, glycine, lysine, serine, cysteine and histidine in peptide-calcium chelate increased by 0.88%, 1.48%, 0.34%, 0.53%, 0.04%, 0.38% and 0.46%, respectively. The carboxyl oxygen and amino nitrogen groups in the calcium binding peptides participated in binding with calcium ions to form the tilapia scale peptide-calcium chelate. Tilapia scale calcium binding peptides has high calcium chelation activity, which lays a foundation for the production and application of calcium supplements.
-
Keywords:
- tilapia scales /
- enzymolysis /
- calcium binding peptides /
- structural characterization
-
我国是全球最大罗非鱼养殖加工国[1],约占同年全球总产量的13%,此中大部分罗非鱼被用于鱼片加工。罗非鱼加工过程中产生的副产物占所用鱼体总质量的54%,其中鱼头、鱼鳞占43%。然而我国目前对加工副产物合理利用率较低,不但造成了生物资源浪费,也为环境增加负担。因此,开发利用罗非鱼副产物具有丰富的原料基础和广阔的应用前景。
钙是人体的常量元素,占人体体重的1.5%~2%[2],在人体代谢活动中起着重要的作用,如提高细胞内的代谢水平、促进骨骼生长、维持心脏功能的稳定等[3]。研究表明钙摄入不足,会导致一系列疾病的发生,如骨质疏松症、佝偻病[4]、结肠癌[5]、高血压[6]等。我国成年居民钙摄入不足的比例超过95%[7],且由于植物源食材在人类饮食结构中占据很大比例,其所含草酸、植酸等成分在人体小肠弱碱性环境下易与钙元素形成不溶性钙盐,阻碍机体钙吸收,并可能引发结石等病变[8]。目前针对缺钙的治疗以药物治疗为主,如雌激素、雷洛昔芬、氟化物等[9-11],但大多数药物具有较强的副作用,如长期进行雌激素替代治疗可能会导致乳腺癌[12-14]、血栓形成的风险性増加,氟化物可导致腹痛、恶心、呕吐等胃肠道症状[15]。因此,针对缺钙可能诱发的疾病和健康风险,迫切需要研究开发能安全有效提升钙生物利用率的天然生物活性物质。
研究发现,蛋白酶解物具有良好的结合钙和促钙吸收活性。目前有研究在南极鳞虾[16]、鳕鱼皮[17],酪蛋白[18]、猪骨跟牛骨[19-20]等酶解物中获得钙结合肽,并有效提高钙的生物利用率。但以罗非鱼鳞获得钙结合活性肽并对其钙螯合特性进行系统表征的研究鲜见报道。本文利用响应面法对罗非鱼鳞的胶原蛋白的酶解工艺进行优化,从而得到钙结合肽。采用氨基酸分析仪、紫外吸收光谱和红外吸收光谱对罗非鱼鳞钙结合肽的特性进行了分析。为后续罗非鱼鳞钙结合肽的工业化生产及应用提供一定的理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
罗非鱼鳞 广东茂名新洲海产有限公司;木瓜蛋白酶(酶活力为2×105 U/g) 广西南宁庞博生物工程有限公司;无水氯化钙、8-羟基喹啉和乙醇胺 天津宏达化学试剂厂;邻甲酚酞络合剂 山东西亚化学工业有限公司;其余试剂 均为分析纯。
PHS-3CW pH计 赛多利斯科学仪器(京)有限公司;DF-101S数显恒温水浴锅 巩义予华仪器有限公司;L530台式低速离心机 湖南湘仪实验室仪器开发有限公司;FD-1型冷冻干燥机 海门市其林贝尔仪器制造有限公司;S-433D氨基酸分析仪 日本日立公司;UV-240IPC型紫外分光光度计 日本岛津公司;Vertex70傅立叶变换红外光谱仪 布鲁克公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 罗非鱼鳞预处理
罗非鱼鳞脱脂脱钙处理[21],具体操作如下:罗非鱼鳞用自来水将杂质洗干净,放入0.1 mol/L NaOH溶液(w/v 1:10)搅拌24 h,清洗至中性;放入10% EDTA-2Na(pH 7.2,w/v 1:10)中,并置于4 ℃冷库中,期间进行搅拌处理5 d,随后将鱼鳞清洗至中性后,用质量分数4%的盐酸处理18 h后水洗至中性,即得到脱钙罗非鱼鳞。将水洗至中性的鱼鳞中水分滴干,随后置于55 ℃烘箱中烘干,取出置于密封袋中备用。
1.2.2 罗非鱼鳞酶解工艺
罗非鱼鳞按底物浓度加入蒸馏水→加入木瓜蛋白酶→调节pH和温度→恒温酶解→灭酶→冷却→离心→取上清
称取罗非鱼鳞于50 mL离心管,按一定量的底物浓度加入蒸馏水,按一定的加酶量加入木瓜蛋白酶,调节一定的pH,设定一定的温度后在水浴锅中振荡酶解一定的时间。所得酶解物经90 ℃加热10 min灭酶,冷却至室温,随后4000 r/min离心20 min,取上清液即得罗非鱼鳞酶解物。
1.2.3 罗非鱼鳞钙结合肽酶解工艺单因素实验
酶解的单因素实验采用改变其中一个因素,保持其他因素不变方式,探究底物浓度、酶底比、pH、温度和时间对罗非鱼鳞钙螯合活性的影响。单因素基础条件设为:底物浓度6%,酶底比0.3%,pH7,酶解温度55 ℃和酶解时间3 h。各个因素的水平梯度为,底物浓度:4%、6%、8%、10%;酶底比:0.1%、0.2%、0.3%、0.4%;pH:5.5、6、6.5、7、7.5;酶解温度:45、50、55、60、65 ℃;酶解时间:2、3、4、5 h。
1.2.4 响应面试验
以底物浓度及酶解时间和酶底比为自变量,设计三因素三水平响应面试验,试验设计如表1所示。
表 1 响应面试验因素水平设计Table 1. Factor and level of response surface experiment编码 因素 水平 -1 0 1 A 底物浓度(%) 4 6 8 B 酶解时间(h) 2 3 4 C 酶底比(%) 0.2 0.3 0.4 1.2.5 钙螯合活性测定
1.2.5.1 钙标准曲线的建立
分别取标准钙工作液(50 μg/mL)0、0.1、0.2、0.3、0.4、0.5、0.6 mL于2 mL离心管中,分别加一级水1.0、0.9、0.8、0.7、0.6、0.5、0.4 mL混匀,在96孔板上每孔30 µL,再加工作显色液150 µL,摇匀,于570 nm处内比色,作标准曲线。
1.2.5.2 酶解液钙螯合活性测定
取1 mL的酶解上清液,1 mL 5 mmol/L CaCl2及2 mL的磷酸盐缓冲液(pH7.8)于10 mL的离心管中,在37 ℃水浴反应1 h,在4000 r/min离心20 min。取上清液30 µL于96孔板,在加入150 µL的邻甲酚酞工作液反应后,在570 nm测波长。钙螯合活性计算公式如下:
标准曲线公式:
y=0.0064x+0.0642 (1) 钙螯合活性(µg/mL)则为:
M=y−0.06420.0064 (2) 1.2.6 罗非鱼鳞肽钙螯合物的制备
将冻干的最优条件下获得的酶解物,加入蒸馏水,配置成5 mg/mL的溶液,按肽钙比1:1加入无水氯化钙,在pH8,42 ℃下螯合47 min,加入反应体系5倍体积的无水乙醇后,4000 r/min离心20 min,弃上清,取沉淀,冷冻干燥,获得罗非鱼鳞肽钙螯合物。
1.2.7 氨基酸含量测定
样品氨基酸含量测定参照 GB5009.124-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品中氨基酸的测定》方法。
1.2.8 紫外吸收光谱测定
以蒸馏水为空白对照,将罗非鱼鳞钙结合肽和肽钙螯合物分别配制1.0 mg/mL的水溶液,在200~400 nm下进行紫外扫描。
1.2.9 红外吸收光谱测定
分别称取2 mg罗非鱼鳞钙结合肽、肽钙螯合物样品放入玛瑙研钵中,加入200 mg干燥光谱纯KBr,混合研磨均匀,装入模具加压得透明样品压片,采用傅里叶变换红外光谱仪在400~4000 cm−1区间扫描。
1.3 数据处理
所有的实验进行3次重复,结果表示为平均值±标准差(X±SD)。用最小二乘法比较三组实验均值在(P<0.05)水平上是否存在显著性差异。Origin8.6进行数据处理与作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 罗非鱼鳞钙结合肽酶解制备
2.1.1 单因素实验
2.1.1.1 底物浓度对钙螯合活性的影响
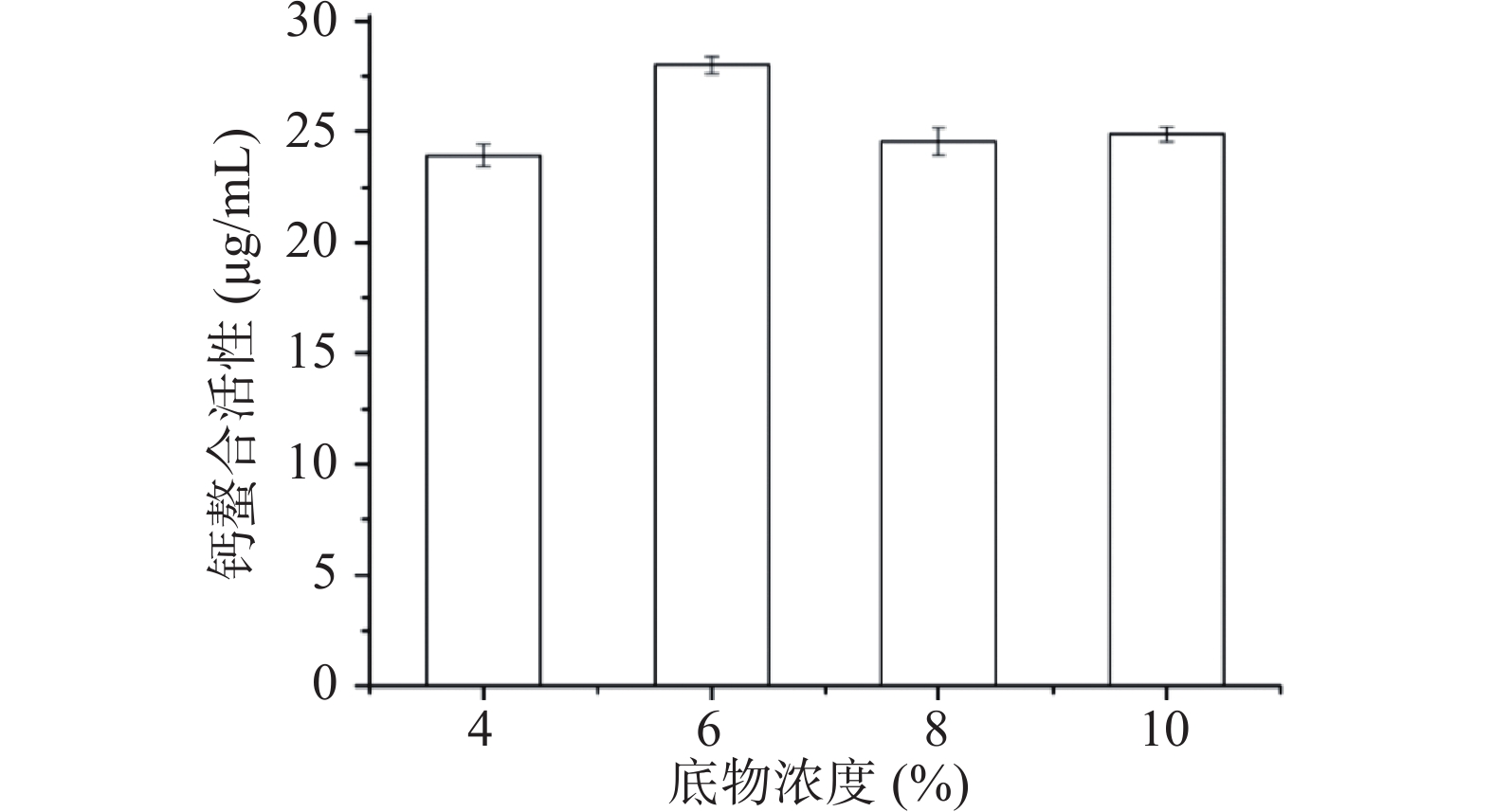
如图1所示,底物浓度在4%~6%,钙螯合活性逐渐上升,在6%~8%,钙螯合活性开始下降,在底物浓度为6%时,钙螯合活性最高,达到(28±0.5)µg/mL。这是因为随着底物浓度的增加,酶与底物的接触增加。当达到一定浓度时,会达到水解峰值[23]。当底物浓度继续增加时,会抑制分子的扩散和碰撞,从而降低了酶解的效率,钙螯合活性降低。因此,选取底物浓度为4%、6%和8%进一步响应面优化。
2.1.1.2 酶底比对钙螯合活性的影响
如图2所示,随着酶对底物的作用增加,罗非鱼鳞的钙螯合活性增加,当酶底比为0.3%时,钙螯合活性最大。酶底比在0.3%以下,鱼鳞蛋白的浓度一定时,酶解反应并未达到饱和状态,故钙螯合活性小。随着酶底比的增加,底物与酶饱和,酶水解效率不再与酶底比成正比,甚至呈下降趋势[24]。因此选取酶底比为0.2%、0.3%和0.4%进一步响应面优化。
2.1.1.3 pH对钙螯合活性的影响
如图3所示,当pH在5.5~7.5之间时,随着pH的增加,钙螯合活性先缓慢增加后下降,pH为7时,钙螯合活性最大值为(28.63±0.3)µg/mL。当pH在7~7.5之间时,螯合钙活性降低。pH可以通过影响酶的活性基团和空间结构影响酶解的效果[25]。当pH高于或低于最佳pH时,酶的活性中心构象发生变化,破坏其空间结构,从而抑制酶活性,钙螯合活性也因此下降[26]。
2.1.1.4 酶解温度对钙螯合活性的影响
如图4所示,随着酶解温度的升高,钙螯合的活性急剧上升,在60 ℃达到最大值后,活性缓慢下降。这是因为适当的温度可以增加分子的热运动,加速分子间的运动与碰撞,从而促进酶解效果。当酶解温度低于最佳温度时,酶分子的活性降低,从而减少了酶与底物的接触。当酶解温度高于其最佳温度时,酶的结构破坏,导致酶失活,最终导致酶解效果减弱[27-28]。因此酶解温度为60 ℃。
2.1.1.5 酶解时间对钙螯合活性的影响
如图5所示,随着酶解时间的延长,钙螯合活性呈现先升高后降低的趋势。在初始阶段水解,底物浓度高,酶解效果增加,但随着酶解时间增加,水解的底物浓度低于初始体系,因此,反应速率降低,钙螯合活性也减少[29]。因此选取酶解时间为2、3和4 h进行进一步响应面优化。
2.1.2 响应面优化结果及分析
以底物浓度以及酶解时间和酶底比为自变量,钙螯合活性为指标设计三因素三水平响应面试验,结果见表2。响应面分析图可以直观地表明2个因素间相互作用对响应值的影响程度,底物浓度(A)、酶解时间(B)、酶底比(C)3个因素之间耦合作用对螯合活性的影响,如图6所示。
表 2 响应面优化试验设计及结果Table 2. Response surface experiment design and results试验号 A
底物浓度B
时间C
酶底比钙螯合活性
(µg/mL)1 −1 −1 0 26.54 2 −1 0 1 29.77 3 0 −1 −1 30.71 4 1 −1 0 37.27 5 0 0 0 31.65 6 0 0 0 31.96 7 0 −1 1 32.58 8 0 0 0 32.58 9 0 0 0 33.83 10 −1 1 0 29.46 11 0 0 0 31.33 12 1 1 0 36.33 13 0 1 1 26.96 14 1 0 −1 35.4 15 −1 0 −1 24.77 16 0 1 −1 30.71 17 1 0 1 31.96 由回归方程模型的方差分析及显著性分析结果(表3)可知,模型P值为0.0055(P<0.01),失拟项0.1086(P>0.05)不显著,这表明模型显著,试验误差小,实验结果与模型拟合度好。此外,R2的计算值为0.91,表明实验结果与模型预测结果一致性良好,证明该模型结果可靠,可用此模型预测和优化实验结果。此外,方差分析还显示,A、AC、C2对钙螯合活性有显著影响(P<0.05)。
表 3 回归模型显著性检验及方差分析Table 3. Significant test and variance analysis for the regression model方差来源 自由度 平方和 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 163.36 9 18.15 8.22 0.0055 ** A 115.67 1 115.67 52.41 0.0002 ** B 1.66 1 1.66 0.75 0.4150 C 0.013 1 0.013 5.800E-003 0.9414 AB 3.72 1 3.72 1.69 0.2350 AC 17.81 1 17.81 8.07 0.0250 * BC 7.90 1 7.90 3.58 0.1005 A2 0.14 1 0.14 0.064 0.8082 B2 0.012 1 0.012 5.258E-003 0.9442 C2 16.47 1 16.47 7.46 0.0293 * 残差 15.45 7 2.21 失拟项 11.56 3 3.85 3.96 0.1086 不显著 纯误差 3.89 4 0.97 总和 178.81 16 注:*表示差异显著P<0.05;**表示差异极显著P<0.01。 以钙螯合活性(Y)为响应值的回归方程为:
Y=32.27+3.80A−0.45B−0.040C−0.97AB−2.11AC−1.40BC+0.18A2−0.052B2−1.98C2 (3) 响应面得到的最优的酶解条件为底物浓度8%,时间2 h,酶底比0.3%,pH7,温度60 ℃;钙螯合活性预测37.62 µg/mL。验证结果钙螯合活性为(38.31±0.4) µg/mL,与预测值相接近。
2.2 氨基酸分析
最优条件下酶解物(罗非鱼鳞钙结合肽)及其肽钙螯合物的氨基酸含量如表4所示。与酶解物相比,在肽钙螯合物中,甘氨酸、天冬氨酸、谷氨酸、半胱氨酸、赖氨酸、组氨酸和丝氨酸的相对含量均出现不同程度的增加,其中增幅较大的是天冬氨酸、谷氨酸、赖氨酸和组氨酸,分别增加0.88%、1.48%、0.53%、0.46%,这说明这些氨基酸存在与钙离子结合的作用位点。研究表明,甘氨酸的α-氨基氮原子可与钙结合[30],天冬氨酸和谷氨酸的游离羧基,可以与钙结合形成肽钙螯合物[31],赖氨酸的ε氨基氮与钙有较强的结合能力[32],而组氨酸的N末端含咪唑环、丝氨酸的羟基以及半胱氨酸的巯基与钙都有较强的结合能力[33-34]。
表 4 氨基酸分析Table 4. Amino acid analysis氨基酸 比例(%) 肽 肽钙螯合物 天冬氨酸(Asp) 5.996 6.875 苏氨酸(Thr) 3.406 3.295 丝氨酸(Ser) 4.098 4.138 谷氨酸(Glu) 11.166 12.645 甘氨酸(Gly) 24.882 25.224 丙氨酸(Ala) 10.020 9.084 半胱氨酸(Cys) 0.330 0.714 缬氨酸(Val) 2.625 2.066 蛋氨酸(Met) 1.749 1.230 异亮氨酸(Ile) 1.654 1.415 亮氨酸(Leu) 3.148 2.436 酪氨酸(Tyr) 1.060 0.936 苯丙氨酸(Phe) 2.471 2.080 赖氨酸(Lys) 1.502 2.036 组氨酸(His) 3.520 3.982 精氨酸(Arg) 8.548 8.406 脯氨酸(Pro) 13.825 12.718 总计 100 100 注:酸水解过程中色氨酸完全被破坏。 2.3 紫外吸收光谱分析
在紫外分光光度计中,金属离子与有机配体形成复合物会导致新的吸收峰的出现或原始吸收峰的转移或消失[35]。从图7可以看出,罗非鱼鳞钙结合肽在220 nm、280 nm附近处有高的吸收峰,这分别是肽键羰基和芳香族氨基酸残基的特征吸收峰[34]。结合钙后,肽钙螯合物的吸收强度都增加。这是因为肽中的显色基团(C=O和-COOH)和助色基团(-NH2和-NH)空间结构改变,引起紫外光谱强度变化[6]。现象说明罗非鱼钙结合肽与钙结合产生新的物质,并且可以推测-NH-和-NH2的氮原子和-C=O和-COOH的氧原子参与了螯合作用。
2.4 红外吸收光谱分析
钙离子螯合前后的红外吸收峰的特征变化是反映金属离子与有机配体基团相互作用的有效证据[36-37]。如图8所示,钙结合肽在3326.12 cm−1有一个强的吸收峰,螯合钙离子之后,波数则变为3332.84 cm−1,这是因为诱导效应或偶极场效应和肽中N-H的电子云密度增强所致[38],这也说明N-H与钙离子有一定的结合作用。钙结合肽在1657.10 cm−1处的吸收带主要是酰胺I(1700~1600 cm−1)的振动。酰胺I区的二级结构:β-转角,1660~1700 cm−1;α螺旋,1645~1659 cm−1;不规则结构,1640~1644 cm−1;和β折叠,1620~1640 cm−1[39]。结合钙后,波数(1657.10 cm−1)移至较低频率(1648.65 cm−1),表明C=O基团参与了与钙的共价键合反应,且肽钙螯合物形成α螺旋结构。钙结合肽中-COO的波数(1400.65 cm−1)向更高的频率(1412.09 cm−1)移动,这可能是由于羰基氧的自由电子对螯合钙离子,表明-COOH可能与钙结合[40]。在500~1000 cm−1范围内,与钙结合后,几个吸收峰发生了变化,这是由N-Ca键取代C-H键和N-H键振动引起的[41]。总的来说,罗非鱼鳞钙结合肽中的羧基氧和氨基氮等基团参与了与钙离子结合,形成了罗非鱼鳞肽钙螯合物。
3. 结论
本研究通过单因素和响应面优化试验,获得罗非鱼鳞钙结合肽的最优酶解工艺条件(底物浓度8%、时间2 h、酶底比0.3%、pH7、温度60 ℃),钙螯合活性为(38.31±0.4)µg/mL。最优酶解条件下制得的罗非鱼鳞钙结合肽及其肽钙螯合物的表征结果表明,肽钙螯合物中的天冬氨酸、谷氨酸、甘氨酸、赖氨酸、丝氨酸、半胱氨酸及组氨酸含量增加,说明这些氨基酸在与钙离子结合的过程起到关键作用;且钙结合肽中的羧基氧和氨基氮等基团参与了与钙离子结合,形成肽钙螯合物。本研究制备的罗非鱼鳞钙结合肽对于替代传统的补钙剂具有一定的市场优势和前景。
-
表 1 响应面试验因素水平设计
Table 1 Factor and level of response surface experiment
编码 因素 水平 -1 0 1 A 底物浓度(%) 4 6 8 B 酶解时间(h) 2 3 4 C 酶底比(%) 0.2 0.3 0.4 表 2 响应面优化试验设计及结果
Table 2 Response surface experiment design and results
试验号 A
底物浓度B
时间C
酶底比钙螯合活性
(µg/mL)1 −1 −1 0 26.54 2 −1 0 1 29.77 3 0 −1 −1 30.71 4 1 −1 0 37.27 5 0 0 0 31.65 6 0 0 0 31.96 7 0 −1 1 32.58 8 0 0 0 32.58 9 0 0 0 33.83 10 −1 1 0 29.46 11 0 0 0 31.33 12 1 1 0 36.33 13 0 1 1 26.96 14 1 0 −1 35.4 15 −1 0 −1 24.77 16 0 1 −1 30.71 17 1 0 1 31.96 表 3 回归模型显著性检验及方差分析
Table 3 Significant test and variance analysis for the regression model
方差来源 自由度 平方和 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 163.36 9 18.15 8.22 0.0055 ** A 115.67 1 115.67 52.41 0.0002 ** B 1.66 1 1.66 0.75 0.4150 C 0.013 1 0.013 5.800E-003 0.9414 AB 3.72 1 3.72 1.69 0.2350 AC 17.81 1 17.81 8.07 0.0250 * BC 7.90 1 7.90 3.58 0.1005 A2 0.14 1 0.14 0.064 0.8082 B2 0.012 1 0.012 5.258E-003 0.9442 C2 16.47 1 16.47 7.46 0.0293 * 残差 15.45 7 2.21 失拟项 11.56 3 3.85 3.96 0.1086 不显著 纯误差 3.89 4 0.97 总和 178.81 16 注:*表示差异显著P<0.05;**表示差异极显著P<0.01。 表 4 氨基酸分析
Table 4 Amino acid analysis
氨基酸 比例(%) 肽 肽钙螯合物 天冬氨酸(Asp) 5.996 6.875 苏氨酸(Thr) 3.406 3.295 丝氨酸(Ser) 4.098 4.138 谷氨酸(Glu) 11.166 12.645 甘氨酸(Gly) 24.882 25.224 丙氨酸(Ala) 10.020 9.084 半胱氨酸(Cys) 0.330 0.714 缬氨酸(Val) 2.625 2.066 蛋氨酸(Met) 1.749 1.230 异亮氨酸(Ile) 1.654 1.415 亮氨酸(Leu) 3.148 2.436 酪氨酸(Tyr) 1.060 0.936 苯丙氨酸(Phe) 2.471 2.080 赖氨酸(Lys) 1.502 2.036 组氨酸(His) 3.520 3.982 精氨酸(Arg) 8.548 8.406 脯氨酸(Pro) 13.825 12.718 总计 100 100 注:酸水解过程中色氨酸完全被破坏。 -
[1] 张红燕, 袁永明, 贺艳辉, 等. 世界罗非鱼生产和贸易现状分析[J]. 农业展望,2016,12(5):77−80. [ZHANG H Y, YUAN Y M, HE Y H, et al. Current situation on global tilapia production and trade[J]. Agricultural Outlook,2016,12(5):77−80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3908.2016.05.018 [2] SUN N, WU H T, DU M, et al. Food protein-derived calcium chelating peptides: A review[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2016,58:140−148.
[3] 高敏, 汪建明, 甄灵慧, 等. 牛骨多肽螯合物的制备及结构表征[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(8):256−261. [GAO M, WANG J M, ZHEN L H, et al. Preparation and structural characterization of bovine bone polypeptide-calcium chelate[J]. Food Science,2020,41(8):256−261. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181217-183 [4] WALTERS M E, ESFANDI R, TSOPMO A. Potential of food hydrolyzed proteins and peptides to chelate iron or calcium and enhance their absorption[J]. Foods (Basel, Switzerland),2018,7(10):172.
[5] ZHAO N N, HU J, HOU T, et al. Effects of desalted duck egg white peptides and their products on calcium absorption in rats[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2014,8:234−242. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2014.03.022
[6] WU W M, HE L C, LIANG Y H, et al. Preparation process optimization of pig bone collagen peptide-calcium chelate using response surface methodology and its structural characterization and stability analysis[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,284:80−89. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.01.103
[7] 范轶欧, 刘爱玲, 何宇纳, 等. 中国成年居民营养素摄入状况的评价[J]. 营养学报,2012,34(1):15−19. [FAN Y O, LIU A L, HE Y N, et al. Assessment of nutrient adequacy of adult residents in China[J]. Journal of Nutrition,2012,34(1):15−19. [8] HEANEY R P, WEAVER C M, FITZSIMMONS M L. Soybean phytate content: Effect on calcium absorption[J]. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition,1991,53(3):745−747. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/53.3.745
[9] 曾勇, 李庆, 何睿, 等. 单一钙制剂与钙制剂联合维生素D干预治疗老年男性骨质疏松症疗效的随机对照临床研究[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志,2014,13(8):625−629. [ZENG Y, LI Q, HE R, et al. The comparison research of calcium and calcium joint vitamin D intervention in the treatment of osteoporosis in older men[J]. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine,2014,13(8):625−629. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2014.08.007 [10] 杜春莹, 胡肇衡, 陈玲, 等. 阿仑膦酸钠对绝经后骨质疏松症患者骨代谢指标的影响[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2014,20(1):22−25. [DU C Y, HU Z H, CHEN L, et al. Effect of alendronate sodium on bone metabolism in postmenopausal osteoporosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Osteoporosis,2014,20(1):22−25. [11] 许闫严, 张克良, 魏忠民, 等. 雌激素对去势骨质疏松症大鼠骨密度和骨代谢影响的实验研究[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(6):776−780. [XU Y Y, ZHANG K L, WEI Z M, et al. Experimental study of the effect of estrogen on bone mineral density and bone metabolism in osteoporosis rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Osteoporosis,2018,24(6):776−780. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2018.06.014 [12] 李国新, 袁忠治, 温健, 等. 口服及静脉应用双磷酸盐治疗绝经后的骨质疏松临床研究[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2013,19(9):988−990. [LI G X, YUAN Z Z, WEN J, et al. Clinical study of oral administration or intravenous injection of bisphosphonate for the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Osteoporosis,2013,19(9):988−990. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2013.09.025 [13] MACLAUGHLIN E J, SLEEPER R B, MCNATTY D, et al. Management of age-related osteoporosis and prevention of associated fractures[J]. Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management,2006,2(3):281−295. doi: 10.2147/tcrm.2006.2.3.281
[14] OLGA R I K, ZDENKO K, PETR K, et al. Real-world management of women with postmenopausal osteoporosis treated with denosumab:A prospective observational study in the czech republic and slovakia[J]. Advances in Therapy,2018,35:1713−1728. doi: 10.1007/s12325-018-0779-9
[15] LI L N, ZENG Z, CAI G P. Comparison of neoeriocitrin and naringin on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation in MC3T3-E1[J]. Phytomedicine,2011,18(11):985−989. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2011.03.002
[16] LIU W Y, LU J, GAO F, et al. Preparation, characterization and identification of calcium-chelating Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) ossein oligopeptides[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2015,241(6):851−860. doi: 10.1007/s00217-015-2510-2
[17] CHEN Q R, GUO L D, DU F, et al. The chelating peptide (GPAGPHGPPG) derived from Alaska pollock skin enhances calcium, zinc and iron transport in Caco-2 cells[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2017,52(5):1283−1290.
[18] PEREGO S, DEL F E, DE LUCA P, et al. Calcium bioaccessibility and uptake by human intestinal like cells following in vitro digestion of casein phosphopeptide-calcium aggregates[J]. Food & Function,2015,6(6):1796−1807.
[19] 赵梓月, 王思远, 廖森泰, 等. 多肽螯合钙的研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发,2020,41(5):200−206. [ZHAO Z Y, WANG S Y, LIAO S T, et al. Progress in research on peptide chelated calcium[J]. Food Research and Development,2020,41(5):200−206. [20] AUudrey D, Janne P, Véronique F S, et al. Biological effect of hydrolyzed collagen on bone metabolism[J]. Taylor & Francis,2017,57(9):1922−1937.
[21] 廖婉雯, 苗建银, 陈雨馨, 等. 罗非鱼骨胶原钙螯合肽的酶解制备[J]. 现代食品科技,2019,35(1):129−136. [LIAO W W, MIAO J Y, CHEN Y X, et al. Preparation of tilapia bone collagen calcium chelating peptides by enzymatic hydrolysis[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2019,35(1):129−136. [22] LIAO W W, LIU S J, LIU X R, et al. The purification, identification and bioactivity study of a novel calcium-binding peptide from casein hydrolysate.[J]. Food & Function,2019,10(12):7724−7732.
[23] Meenal S P, Virendra K R, Aniruddha B P. Enzymatic hydrolysis of castor oil: Process intensification studies[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal,2006,31(1):31−41. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2006.05.017
[24] YAO Y M, WANG M Y, LIU Y, et al. Insights into the improvement of the enzymatic hydrolysis of bovine bone protein using lipase pretreatment[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,302:1251991−1251998.
[25] 曹吉利, 张倩, 谭源, 等. 响应面法优化酶解羊乳酪蛋白制备抗氧化肽[J]. 食品工业,2018,39(3):107−111. [CAO J L, ZHANG Q, TAN Y, et al. Optimization of preparation of antioxidant peptides from goat milk casein by enzymatic hydrolysis[J]. The Food Industry,2018,39(3):107−111. [26] 王琴, 向斌, 薛飞, 等. 酶法去除米糠淀粉及其酶解动力学研究[J]. 农产品加工·综合刊,2009(12):68−70. [WANG Q, XIANG B, XUE F, et al. Study on enzymatic removal of rice bran starch and its enzymatic hydrolysis kinetics[J]. Farm Products Processing,2009(12):68−70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9646-C.2009.12.038 [27] HONG H, FAN H B, CHALAMAIAH M, et al. Preparation of low-molecular-weight, collagen hydrolysates (peptides): Current progress, challenges, and future perspectives[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,301:125222. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125222
[28] Baha E A, Joaquín G, Assaad S, et al. Characteristics and functional properties of gelatin extracted from squid (Loligo vulgaris) skin[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2016,65(1):924−931.
[29] SONG S Q, LI S S, FAN L, et al. A novel method for beef bone protein extraction by lipase-pretreatment and its application in the Maillard reaction[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,208(1):81−88.
[30] MANYAK A R, MURPHY C B, MARTELL A E. Metal chelate compounds of glycylglycine and glycylglycylglycine[J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics,1955,59(2):373−382. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(55)90504-X
[31] CHAUD M V, IZUMI C, NAHAAL Z, et al. Iron derivatives from casein hydrolysates as a potential source in the treatment of iron deficiency[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2002,50(4):871. doi: 10.1021/jf0111312
[32] LIAO W W, CHEN H, JIN W, et al. Three newly isolated calcium-chelating peptides from tilapia bone collagen hydrolysate enhance calcium absorption activity in intestinal Caco-2 cells[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2020,68(7):2091−2098. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b07602
[33] 刘晓容, 郭俊斌, 廖婉雯, 等. 酶法制备乳源钙螯合肽及其特性表征[J]. 食品研究与开发,2020,41(8):60−67. [LIU X R, GUO J B, LIAO W W, et al. Preparation and characterization of milk-derived calcium chelating peptide by enzymatic method[J]. Food Research and Development,2020,41(8):60−67. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2020.08.010 [34] HUANG G R, REN Z Y, JIAN J X. Separation of iron-binding peptides from shrimp processing by-products hydrolysates[J]. Food and Bioprocess Technology,2011,4(8):1527−1532. doi: 10.1007/s11947-010-0416-3
[35] SUN N, JIN Z Q, LI D M, et al. An exploration of the calcium-binding mode of egg white peptide, Asp-His-Thr-Lys-Glu, and in vitro calcium absorption studies of peptide-calcium complex[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2017,65(44):9782. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b03705
[36] Peng Z, Hou H, Zhang K, et al. Effect of calcium-binding peptide from Pacific cod (Gadus macrocephalus) bone on calcium bioavailability in rats[J]. Food Chemistry,2017,221(15):373−378.
[37] Miller G D, Jarvis J K, McBean L D. The importance of meeting calcium needs with foods[J]. Journal of the American College of Nutrition,2001,20(2 Suppl):168S−185S.
[38] El H H, Fakharedine N, Ait B G, et al. Treatment of olive mill waste-water by aerobic biodegradation: An analytical study using gel permeation chromatography, ultraviolet-visible and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy[J]. Bioresource Technology,2007,98(18):3513−3520. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2006.11.033
[39] Farrell H J, Qi P X, Wickham E D, et al. Secondary structural studies of bovine caseins: Structure and temperature dependence of beta-casein phosphopeptide (1-25) as analyzed by circular dichroism, FTIR spectroscopy, and analytical ultracentrifugation[J]. Journal of Protein Chemistry,2002,21(5):307−321. doi: 10.1023/A:1019992900455
[40] WANG Y, CUI F Z, ZHAI Y, et al. Investigations of the initial stage of recombinant human-like collagen mineralization[J]. Materials Science & Engineering C,2005,26(4):635−638.
[41] CHEN D, LIU Z Y, HUANG W Q, et al. Purification and characterisation of a zinc-binding peptide from oyster protein hydrolysate[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2013,5(2):689−697. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2013.01.012
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 吴雨柔,王成维,李金虎,冉东,吴纯洁. 响应面法优化羚羊角多肽提取工艺研究. 中药与临床. 2024(02): 33-37 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张笑莹,钟婉滢,马凤,叶灏铎,苗建银,李静,巩发永. 苦荞蛋白降血脂肽的酶解制备、氨基酸组成及活性研究. 食品工业科技. 2024(21): 129-139 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 宋丽,朱临娴,宋璐杉,司凯,巩婷婷,刘会平,张晓维. 钙结合卵黄高磷蛋白磷酸肽的制备及其肽钙螯合物的结构表征. 食品科学. 2023(06): 125-133 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 叶灏铎,管晓盛,马凤,毛远辉,孙世利,曹庸,苗建银. 英红九号茶蛋白降尿酸肽的酶解制备及不同分子量组分的活性对比. 现代食品科技. 2023(03): 147-155 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 马凤,叶灏铎,夏珍,徐燕,孙世利,曹庸,苗建银. 英红九号茶蛋白ACE抑制肽的制备、氨基酸组成及不同超滤组分的活性评价. 现代食品科技. 2023(07): 237-245 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 钟婉滢,苗建银,叶灏铎,马凤,胡一晨. 藜麦蛋白肽的酶解制备及体外降血脂与降尿酸活性研究. 食品工业科技. 2023(23): 156-166 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 叶灏铎,苗建银,李龙星,黄嘉芹,刘本英,孙云南,邹琴,曹庸. 勐库大叶茶蛋白降血脂肽的酶解制备及活性分析. 食品工业科技. 2022(09): 212-221 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:










 下载:
下载:



