| [1] |
何佳仪. 葛连降糖丸治疗2型糖尿病(胃热炽盛证)的临床疗效观察[D]. 长沙: 湖南中医药大学, 2020.
HE Jiayi. Clinical observation of Gexing Jiangtang pill in treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (fever of stomach heat)[D]. Changsha: Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, 2020.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
Ch N H, Shaw J E, Karuranga S, et al. IDF diabetes arlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045[J]. Diabetes Reseach & Clinical Practice,2018,138:271.
|
| [4] |
Kriti Kushwaha, Sandeep Sharma, Jeena Gupta. Metabolic memory and diabetic nephropathy: Beneficial effects of natural epigenetic modifiers[J]. Biochimie,2020:140−151, 170.
|
| [5] |
刘明, 孙利华, 刘国恩. 中国城镇居民 5 种慢性疾病的经济负担和经济风险[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版),2014,46(5):782−789. [Liu Ming, Sun Lihua, Liu Gordon. Economic burden and economic risk of five major chronic diseases among Chinese urban residents[J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences),2014,46(5):782−789.
|
| [6] |
Asman A G, Hoogendoorn C J, McKee M D, et al. Assessing the association of depression and anxiety with symptom reporting among individuals with type 2 diabetes[J]. Journal of Behavioral Medicine,2020,43(1):57−68. doi: 10.1007/s10865-019-00056-x
|
| [7] |
叶文斌, 樊亮. 纹党多糖对四氧嘧啶诱导糖尿病大鼠血糖血脂的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2015,36(20):359−363. [YE Wenbin, FAN Liang. Effect of polysaccharides extract from Codonopisis pilosula on glycemia and lipidemia in alloxan-induced diabetic rats[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2015,36(20):359−363.
|
| [8] |
牛强. 软枣猕猴桃枝条多糖的分离纯化及降血糖活性研究[D]. 佳木斯: 佳木斯大学, 2020.
Niu Qiang. Study on the separation, purification and hypoglycemic activity of polysaccharides from the branches of Actinidia arguta[D]. Jiamusi: Jiamusi University, 2020.
|
| [9] |
刘胜范. 东北黑蜂保护区重要蜜源植物窄叶毛水苏[J]. 中国蜂业,2018,69(8):48. [Liu Shengfan. An important nectar plant, Perilla angustifolia, in the northeast black bee reserve[J]. Apiculture of China,2018,69(8):48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0412-4367.2018.08.026
|
| [10] |
金琼, 刘悦, 刘德江, 等. 毛水苏组织培养技术研究[J]. 种子,2020,39(6):155−157, 163. [Jin Qiong, Liu Yue, Liu Dejiang, et al. Study on tissue culture technology of Perilla frutescens[J]. Seed,2020,39(6):155−157, 163.
|
| [11] |
Arab Khaled, GhanbarzadehBabak, Ayaseh Ali, et al. Extraction, purification, physicochemical properties and antioxidant activity of a new polysaccharide from Ocimum album L. seed[J]. Int J BiolMacromol,2021,180:643−653. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.03.088
|
| [12] |
李栋, 薛瑞婷. 响应面耦合遗传算法优化超声辅助复合酶提取红枣多糖工艺[J]. 食品研究与开发,2021,42(6):96−103. [Li Dong, Xue Ruiting. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted complex enzyme extraction polysaccharides from jujube by response surface methodology coupled with genetic algorithm[J]. Food Research and Development,2021,42(6):96−103.
|
| [13] |
姚志仁, 李豫, 朱开梅, 等. 黄花倒水莲不同极性部位抗氧化和降血糖活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(7):55−59, 64. [Yao Zhiren, Li Yu, Zhu Kaimei, et al. Antioxidant and hypoglycemic activities of different polar parts of Polygala fallax[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(7):55−59, 64.
|
| [14] |
朱作艺, 张玉, 王君虹, 等. 蜂王浆蛋白肽的制备及其降血糖和抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(17):45−50, 57. [Zhu Zuoyi, Zhang Yu, Wang Junhong, et al. Preparation of royal jelly protein peptide and its hypoglycemic and antioxidant activities[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(17):45−50, 57.
|
| [15] |
魏奇. 姬松茸多酚降血糖活性及其作用机制的研究[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2020.
Wei Qi. Study on the hypoglycemic activity and its mechanism of polyphenol from Agaricus blazei Murrill fruiting bodies[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2020.
|
| [16] |
张敏杰, 方翼. rhGLP-1(7-36)对糖尿病肾病大鼠肾脏的保护机制研究[J]. 中国现代应用药学,2021,38(3):281−285. [Zhang Minjie, Fang Yi. Protective mechanism of rhGLP-1 (7-36) on kidney in diabetic nephropathy rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Modern Applied Pharmacy,2021,38(3):281−285.
|
| [17] |
李廷灿, 叶瑞航, 叶宏平. 短期胰岛素泵强化治疗对2型糖尿病患者血糖、血脂水平及胰岛β细胞功能的影响[J]. 慢性病学杂志,2021,22(5):729−731. [Li Yancan, Ye Ruihang, Ye Hongping. Short term intensive insulin pump therapy for blood glucose, blood lipids and islets in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus β the influence of cell function[J]. Chronic Pathematology Journal,2021,22(5):729−731.
|
| [18] |
赵耀, 杨建华, 谯明, 等. 尿囊素对糖尿病肾病大鼠肾脏保护作用及机制探讨[J]. 新疆医科大学学报,2020,43(8):1025−1030. [Zhao Yao, Yang Jianhua, Qiao Ming. Protective effects and mechanism of allantoinon on renal injury of diabetic nephropathy rats[J]. Journal of Xinjiang Medical University,2020,43(8):1025−1030. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5551.2020.08.008
|
| [19] |
Chen W, Xia Y P, Chen W J, et al. Improvement of myocardial glycolipid metabolic disorder in diabetic hamster with Astragalus polysaccharides treatment[J]. Molecular Biology Reports,2012,39(7):7609−7615. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-1595-y
|
| [20] |
孙波, 蔡鑫君, 吴婷婷, 等. 红花提取液对小鼠缺血再灌注脑损伤保护作用的实验研究[J]. 中国中医药科技,2018,25(2):205−207. [Sun Bo, Cai Xinjun, Wu Tingting. Protective effect of safflower extract on cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury in mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Traditional Medical Science and Technology,2018,25(2):205−207.
|
| [21] |
李霄, 孙延平, 王秋红, 等. 商陆及其性味拆分组分对阿霉素肾病大鼠肾脏的保护作用研究[J]. 中医药学报,2021,49(6):12−17. [Li Xiao, Sun Yanping, Wang Qiuhong, et al. Protective effect of radix phytolaccae and its components on kidney in rats with doxorubicin-induced nephropathy[J]. Acta Chinese Medicine and Pharmacology,2021,49(6):12−17.
|
| [22] |
马启珍, 王小萍, 张茜, 等. 苦参碱对异丙肾上腺素致心肌缺血大鼠机体抗氧化酶的影响[J]. 宁夏医学杂志,2014,36(12):1089−1090. [Ma Qizhen, Wang Xiaoping, Zhang Qian, et al. Effects of matrine on antioxidant parameters in rats with isoproterenol-induced myocardial ischemia injury[J]. Ningxia Medical Journal,2014,36(12):1089−1090.
|
| [23] |
严晗. 野黄芩苷通过Nrf2/HO-1信号通路在db/db小鼠中降血糖及肾脏保护活性的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2020.
Yan Han. Scutellarin exerts hypoglycemic and renal protective effects in db/db mice via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2020.
|
| [24] |
盛钊君, 谭永权, 葛思媛, 等. 新会柑胎仔和青皮、陈皮提取物的多酚含量及抗氧化活性比较研究[J]. 河南工业大学学报(自然科学版),2018,39(1):78−82. [Sheng Zhaojun, Tan Yongquan, Ge Siyuan. Quantitative determination of polyphenol contents comparison of antioxidant activities of extracts of xinhui tangerine buds, green tangerine peel and tangerine peel[J]. J Henan Univ Technol(Nat Sci Ed),2018,39(1):78−82.
|
| [25] |
Chen X, Qian L, Wang B, et al. Synergistic hypoglycemic effects of pumpkin polysaccharides and puerarin on type II diabetes mellitus mice[J]. Molecules,2019,24(5):955. doi: 10.3390/molecules24050955
|
| [26] |
洪燕青. 2型糖尿病患者不同体质量指数与尿白蛋白肌酐比的相关性[J]. 中南医学科学杂志,2021,49(4):473−476. [Hong Yanqing. Correlation between body mass index and urinary albumin creatinine ratio in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. J Univ South China(Med Ed),2021,49(4):473−476.
|
| [27] |
Hills C E, Squires P E. The role of TGF-β and epithelial to mesenchymal transition in diabetic nephropathy[J]. Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews,2011,22(3):131−139.
|
| [28] |
Qian Ying, Feldman Eva, Pennathur Subramanian, et al. From fibrosis to sclerosis: Mechanisms of glomerulosclerosis in diabetic nephropathy.[J]. Diabetes,2008,57(6):1439−1445. doi: 10.2337/db08-0061
|
| [29] |
Chen J, Hou X F, Wang G, et al. Terpene glycoside component from moutan cortex ameliorates diabetic neph ropathy by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress-related inflammatory responses[J]. J Ethnopharmacol,2016,193:433. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.09.043
|
| [30] |
姚淑琼, 李志华, 蒋梅香, 等. 石斛消渴饮对糖尿病肾病大鼠肾脏保护作用的研究[J]. 山东化工,2021,50(5):23−24, 28. [Yao Shuqiong, Li Zhihua, Jiang Meixiang. Efficacy of the shihuxiaokeyin on kidney in rats with type 2 diabetic nephropathy[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry,2021,50(5):23−24, 28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2021.05.010
|
| [31] |
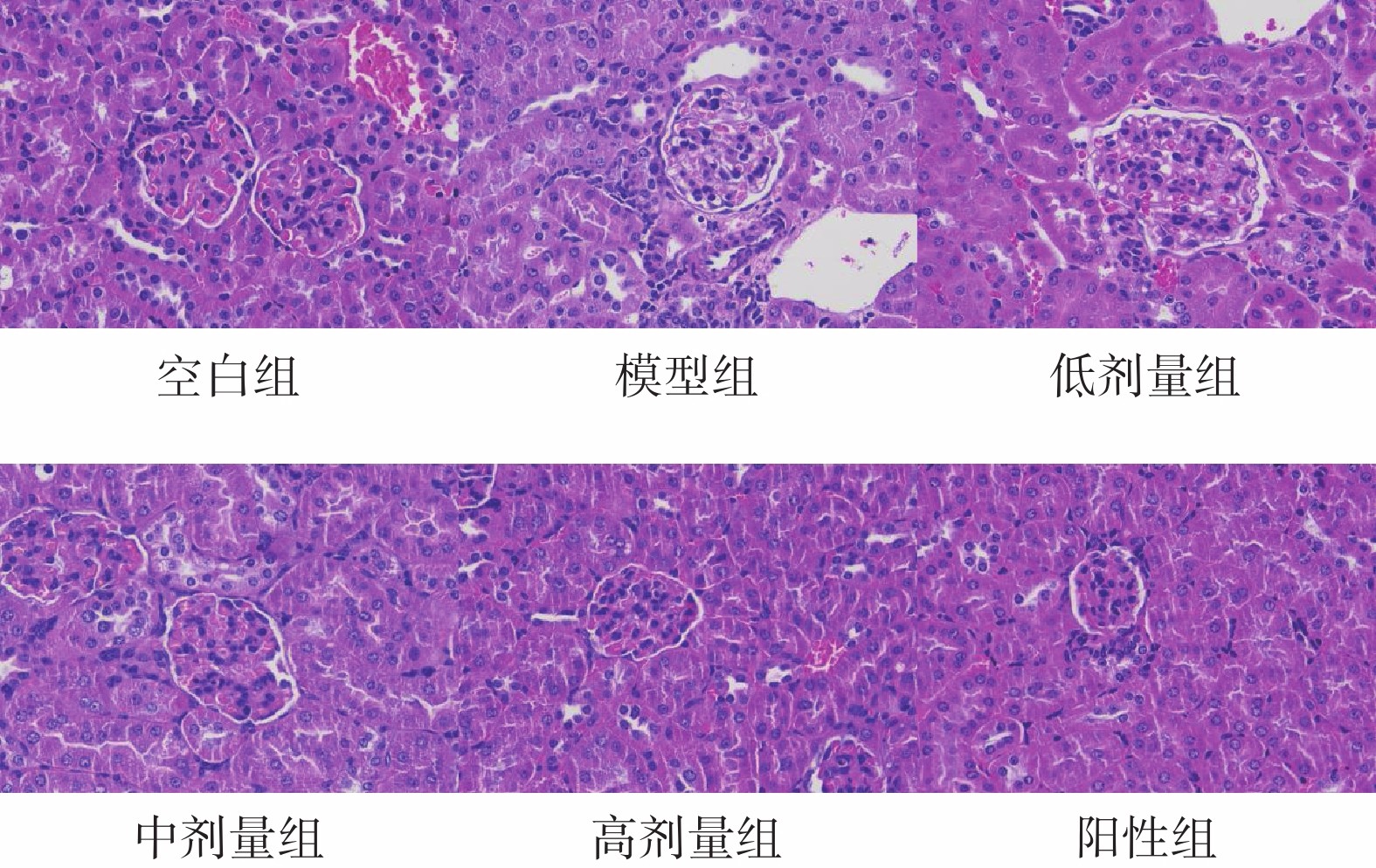
张萌, 杨立诚, 陈娟, 等. 牡丹皮多糖组分对糖尿病肾病大鼠肾脏损伤的保护作用研究[J/OL]. 中国中药杂志: 1−9[2021−06−23]. https://doi.org/10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20210224.402.
Zhang Meng, Yang Licheng, Chen Juan. Protective effects of moutan cortex polysaccharides components on renal injury in diabetic nephropathy rats[J/OL]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica: 1−9[2021−06−23]. https://doi.org/10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20210224.402.
|










 DownLoad:
DownLoad: