| [1] |
中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 食品安全国家标准 GB 10136-2015动物性水产制品[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2015.
National Health and Family Planning Commission of China. National food safety standard. GB 10136-2015 Animal aquatic products[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2015.
|
| [2] |
赵延宁, 王玉, 王睿迪, 等. 咸干鱼中危害因子分析及其控制的研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(14):320−324. [ZHAO Y N, WANG Y, WANG R D, et al. Research progress on hazards factor analysis and control of salted dry fish[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(14):320−324.
|
| [3] |
丁海燕, 孙晓杰, 宁劲松, 等. 储藏温度对3种海水鱼产生生物胺的规律影响研究[J]. 食品科技,2018,43(9):177−182. [DING H Y, SUN X J, NING J S, et al. Study on the regular of biogenic amines from three marine fish stored at different temperature[J]. Food Science and Technology,2018,43(9):177−182.
|
| [4] |
常娅妮, 马俪珍, 杨梅, 等. 不同冷冻方式对调味鱼贮藏品质的影响[J]. 食品科技,2020,45(2):137−143. [CHANG Y N, MA L Z, Yang M, et al. Effects of different freezing methods on the storage quality of seasoned channel catfish[J]. Food Science and Technology,2020,45(2):137−143.
|
| [5] |
LALY S J, ANUPAMA T K, KUMAR K A, et al. Quality and freshness of fish available in supermarkets of Cochin, India based on biogenic amine content[J]. Fishery Technology,2019,56(1):212−220.
|
| [6] |
COSTA C, GRAZHDAN D, FIUTOWSKI J, et al. Meat and fish freshness evaluation by functionalized cantilever-based biosensors[J]. Microsystem Technologies,2020,26(4):1−5.
|
| [7] |
HE S, CHEN Y N, YANG X Q, et al. Determination of biogenic amines in chub mackerel from different storage methods[J]. Journal of Food Science,2020,85(6):1699−1706. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.15146
|
| [8] |
朱作艺, 张玉, 王君虹, 等. 不同贮藏条件下大黄鱼生物胺变化[J]. 浙江农业学报,2018,30(9):1592−1598. [ZHU Z Y, ZHANG Y, WANG J H, et al. Changes of biogenic amines in large yellow croaker stored at different conditions[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis,2018,30(9):1592−1598. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2018.09.21
|
| [9] |
SUN Y Y, GAO P, XU Y S, et al. Effect of storage conditions on microbiological characteristics, biogenic amines, and physicochemical quality of low-salt fermented fish[J]. Journal of Food Protection,2020,83(6):1057−1065. doi: 10.4315/JFP-19-607
|
| [10] |
中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 食品安全国家标准 GB 5009.3-2016 食品中水分的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016.
National Health and Family Planning Commission of China. National food safety standard. GB 5009.3-2016 Determination of moisture in foods[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
|
| [11] |
中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 食品安全国家标准 GB 5009.237-2016 食品pH值的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016.
National Health and Family Planning Commission of China. National food safety standard. GB 5009.237-2016 Determination of pH value in foods[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
|
| [12] |
中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 食品安全国家标准 GB 5009.42-2016 食盐指标的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016.
National Health and Family Planning Commission of China. National food safety standard. GB 5009.42-2016 Determination of salt index[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
|
| [13] |
中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 食品安全国家标准GB 5009.227-2016 食品中过氧化值的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016.
National Health and Family Planning Commission of China. National food safety standard. GB 5009.227-2016 Determination of peroxide value in foods[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
|
| [14] |
中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 食品安全国家标准 GB 5009.228-2016食品中挥发性盐基氮的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016.
National Health and Family Planning Commission of China. National food safety standard. GB 5009.228-2016 Determination of total volatile basic nitrogen in foods[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
|
| [15] |
国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 食品安全国家标准 GB 4789.2-2016食品微生物学检验 菌落总数测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016.
National Health and Family Planning Commission of China. National food safety standard. GB 4789.2-2016 Microbiological examination: aerobic plate count[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
|
| [16] |
杨春婷, 赵晓娟, 白卫东. 肉类中的生物胺形成及其在肉类新鲜度评价中的应用研究进展[J]. 肉类研究,2017,31(1):55−59. [YANG C T, ZHAO X J, BAI W D, et al. Formation of biogenic amines during meat storage and their application in assessment of meat freshness[J]. Meat Research,2017,31(1):55−59. doi: 10.7506/rlyj1001-8123-201701010
|
| [17] |
张晓艳, 杨宪时, 郭全友, 等. 水分含量对淡腌大黄鱼贮藏性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2012,33(9):364−366, 375. [ZHANG X Y, YANG X S, GUO Q Y, et al. Effect of moisture content on storage properties in light salted Pseudosciaena crocea[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2012,33(9):364−366, 375.
|
| [18] |
吴燕燕, 钱茜茜, 李来好, 等. 基于Illumina MiSeq技术分析腌干鱼加工过程微生物群落多样性[J]. 食品科学,2016,38(12):8−15. [WU Y Y, QIAN X X, LI L H et al. Microbial community diversity in dried-salted fish during processing revealed by illumina MiSeq sequencing[J]. Food Science,2016,38(12):8−15.
|
| [19] |
WU Y Y, CHEN Y F, LI L H, et al. Study on biogenic amines in various dry salted fish consumed in China[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China,2016,15(4):681−689. doi: 10.1007/s11802-016-2958-0
|
| [20] |
KÖSE S, KORAL S, TUFAN B, et al. Biogenic amine contents of commercially processed traditional fish products originating from European countries and Turkey[J]. European Food Research & Technology,2012,235(4):669−683.
|
| [21] |
LIN C S, LIU, F L, LEE Y C, et al. Histamine contents of salted seafood products in Taiwan and isolation of hatotolerant histamine-forming bacteria[J]. Food Chemistry,2012,131(2):574−579. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.09.027
|
| [22] |
赵延宁, 王玉, 王睿迪, 等. 市售咸干鲅鱼的安全性分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(14):215−220. [ZHAO Y N, WANG Y, WANG R D, et al. Safety analysis of commercially available salted and dried Spanish markerel[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2019,45(14):215−220.
|
| [23] |
陈申如, 张其标, 胡阳, 等. 温度对液熏鳗鱼质量特性的影响[J]. 食品研究与开发,2018,39(7):95−99. [CHEN S R, ZHANG Q B, HU Y, et al. The effect of temperature on the quality characteristics of liquid-smoked eel[J]. Food Research and Development,2018,39(7):95−99.
|
| [24] |
LEHANE L, OLLEY J. Histamine fish poisoning revisited[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2000,58(1-2):1−37. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1605(00)00296-8
|
| [25] |
US FDA. Fish and fishery products hazards and controls guide. 3rd ed. Scombrotoxin (histamine) formation[S]. Washington: Food and Drug Administration, 2001.
|
| [26] |
European Commission (EC). Commission recommendation of 10 January 2003 concerning a coordinated programme for the official control of foodstuffs for 2003 (2003/10/EC)[S]. Brussels: Official Journal of the European Communities, 2003.
|
| [27] |
PRESTER L. Biogenic amines in fish, fish products and shellfish: A review[J]. Food Additives & Contaminants,2011,28(11):1547−1560.
|
| [28] |
TEN B B, DAMINK C, JOOSTEN H M, et al. Occurrence and formation of biologically active amines in foods[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,1990,11(1):73−84. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(90)90040-C
|
| [29] |
陈玉峰, 吴燕燕, 李来好, 等. 腌干鱼贮藏过程生物胺的变化及其货架期研究[J]. 核农学报,2016,30(8):1548−1557. [CHEN Y F, WU Y Y, LI L H, et al. Study on the change of biogenic amines and its shelf life of dried-salted fish at storage[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2016,30(8):1548−1557. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2016.08.1548
|
| [30] |
景智波, 田建军, 杨明阳, 等. 食品中与生物胺形成相关的微生物菌群及其控制技术研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(15):272−278. [JING Z B, TIAN J J, YANG M Y, et al. Progress in understanding and controlling the microbial community involved in biogenic amine production[J]. Food Science,2018,39(15):272−278.
|





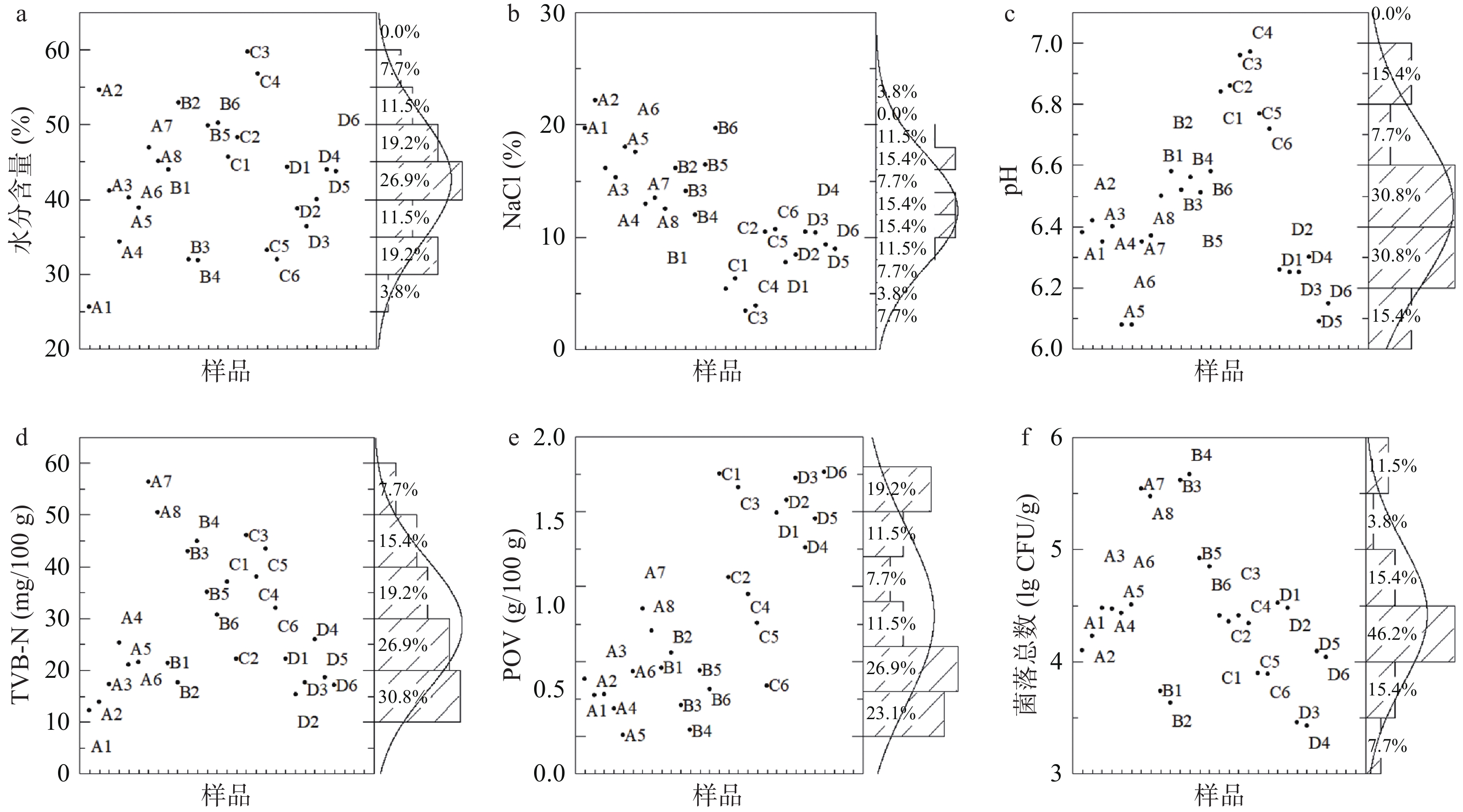




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: