| [1] |
|
| [2] |
周红姿, 周方园, 赵晓燕. 小麦赤霉病生防菌的筛选及其田间防效研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报,2020,22(1):67−77.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
刘盼, 蔡俊, 廖兆民, 等. 降解玉米赤霉烯酮菌株的鉴定及其发酵条件优化[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(21):119−123.
|
| [5] |
雷元培, 周建川, 王利通, 等. 2018年中国饲料原料及配合饲料中霉菌毒素污染调查报告[J]. 饲料工业,2020,41(10):60−64.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
周建川, 雷元培, 王利通, 等. 2017年中国饲料原料及配合饲料中霉菌毒素污染调查报告[J]. 饲料工业,2018,39(11):52−56.
|
| [8] |
李安平, 朱连勤, 陈甫, 等. 2017年山东地区鸡饲料及原料中AFB-1、DON和ZEN污染情况调查[J]. 中国家禽,2018,40(10):69−72.
|
| [9] |
宋丹, 李蕴玉, 杨彩然, 等. 河北省蛋鸡配合饲料及原料中霉菌毒素的污染情况[J]. 中国家禽,2019,41(10):78−80.
|
| [10] |
Volko A, Karlovsky P. Biological detoxification of fungal toxins and its use in plant breeding, feed and food production[J]. Natural Toxins,1998(7):1−23.
|
| [11] |
孙玲玉. 枯草芽孢杆菌泰山株的分离鉴定及其对黄曲霉毒素的降解作用研究[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2014.
|
| [12] |
Yunus A W, Razzazi-fazeli E, Bohm J. Aflatoxin B 1 in affecting broiler’s performance, immunity, and gastrointestinal tract: A review of history and contemporary issues[J]. Toxins,2011,3(6):566−590. doi: 10.3390/toxins3060566
|
| [13] |
张俊楠, 王金全, 杨凡, 等. 饲料霉菌毒素生物降解研究进展[J]. 饲料工业,2019,40(21):51−58.
|
| [14] |
Mannon J, Johnaon E. Fungi down on the farm[J]. New Scientist,1985,105:12−16.
|
| [15] |
Kriszt R, Krifaton C, Szoboszlay S, et al. A new zearalenone biodegradation strategy using non-pathogenic Rhodococcus pyridinivorans K408 strain[J]. Plos One,2012,7(9):e43608. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043608
|
| [16] |
龙淼, 何润霞, 刘义, 等. 玉米赤霉烯酮降解菌的分离与鉴定[J]. 畜牧与兽医,2015,47(8):34−38.
|
| [17] |
Cho K J, Kang J S, Cho W T, et al. In vitro degradation of zearalenone by Bacillus subtilis[J]. Biotechnology Letters,2010,32(12):1921−1924. doi: 10.1007/s10529-010-0373-y
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
Harkai P, Szabṓ I, Cserhati M, et al. Biodegradation of aflatoxin B1 and zearalenone by Streptomyces sp. collection[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation,2016,108:48−56.
|
| [20] |
Saumuel M S, Sivaramakrishna A, Mehta A. Degradation and detoxification of aflatoxin B1 by Pseudomonas putida[J]. International Biodeterioration& Biodegradation,2014,86:202−209.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
Bakutis B, Baliukoniene V, Paṥkevicius A. Use of biological method for detoxification of mycotoxins[J]. Botanica Lithuanica,2005,7:123−129.
|
| [23] |
王亚楠, 陈莹莹, 吴玉洪, 等. 甲基营养型芽孢杆菌对黄瓜促生作用及其机理研究[J]. 北方园艺,2020(12):1−7.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
胡晓丹, 王建伟, 李孝敬. 赤霉病菌拮抗菌Bacillus subtilis AF0907抗菌物质研究[J]. 中国生物防治学报,2015,31(3):378−385.
|
| [26] |
潘丽婷. 玉米赤霉烯酮降解菌的分离鉴定、降解特性及机理研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2018.
|
| [27] |
何润霞. 玉米赤霉烯酮降解菌的筛选鉴定及降解特性研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2016.
|
| [28] |
张倩. 玉米赤霉烯酮脱毒菌株的筛选及Fosmid文库构建[D]. 华南理工大学, 2016.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
骆翼. 玉米赤霉烯酮的微生物脱毒研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2014.
|
| [31] |
Yi P J, Pai C K, Liu J R. Isolation and characterization of a Bacillus licheniformis strain capable of degrading zearalenone[J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology,2011,27:1035−1043. doi: 10.1007/s11274-010-0548-7
|
| [32] |
谭辉. 牛瘤胃液中玉米赤霉烯酮降解菌的分离、鉴定及降解特性研究[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2014.
|
| [33] |
雷元培. ANSB01G菌对玉米赤霉烯酮的降解机制及其动物试验效果研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2014.
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
王国兵. 一株高效降解玉米赤霉烯酮细菌的研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2015.
|
| [36] |
Xu J H, Wang H, Zhu Z, et al. Isolation and characterization of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens ZDS-1: Exploring the degradation of zearalenone by Bacillus spp.[J]. Food Control,2016,68:244−250. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.03.030
|
| [37] |
唐彧, 张琼琼, 郭永鹏, 等. 一株同时降解玉米赤霉烯酮和黄曲霉毒素B1的谷氨酸棒状杆菌及其降解特性研究[J]. 饲料工业,2019,40(20):34−39.
|






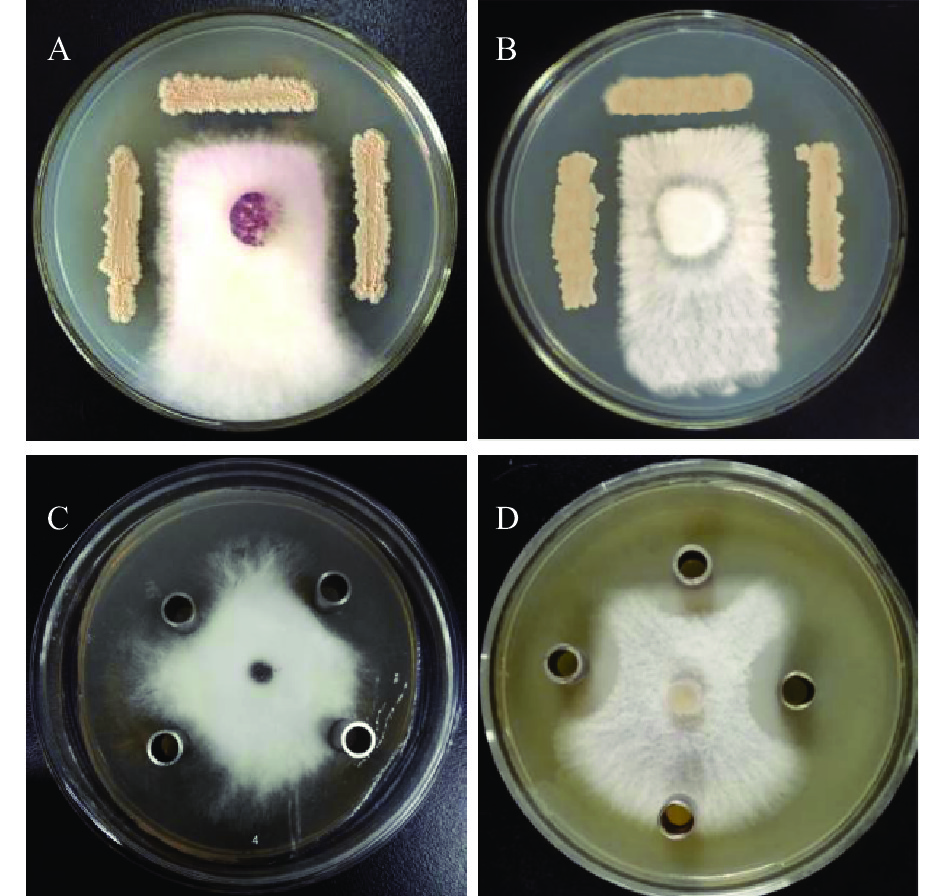




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: