| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
文雅欣. 远红外辐照-热风干燥八角的动力学及品质变化研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2019: 4−77.
|
| [4] |
李琳, 王桢. 果蔬干燥技术研究进展[J]. 中国果菜,2020,40(3):9−17.
|
| [5] |
Fangfang Xu, Xin Jin, Lu Zhang, et al. Investigation on water status and distribution in broccoli and the effects of drying on water status using NMR and MRI methods[J]. Food Research International,2017,96(JUN):191−197.
|
| [6] |
孙炳新, 赵宏侠, 冯叙桥, 等. 基于低场核磁和成像技术的鲜枣贮藏过程水分状态的变化研究[J]. 中国食品学报,2016,16(5):252−257.
|
| [7] |
Pamela F Faure, Sabine Care, Julie Magat, et al. Drying effect on cement paste porosity at early age observed by NMR methods[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2012,29(4):496−503.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
任永申, 郑尧, 雷蕾, 等. 低场核磁共振及成像技术分析天花粉干燥过程中水分变化规律[J]. 中南民族大学学报(自然科学版),2019,38(3):415−419.
|
| [11] |
朱文学. 中药材干燥原理与技术[M]. 化学工业出版社: 北京, 2007: 145−146.
|
| [12] |
彭程, 胡长利. 八角茴香的加工及开发利用[J]. 农业工程技术(农产品加工),2007(6):39−43.
|
| [13] |
陈路, 吴献娟, 潘富林, 等. 八角茴香产地加工方法的对比研究[J]. 现代中药研究与实践,2019,33(1):1−5.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
Chua K J, Mujumdar A S, Chou S K, et al. Convectivedryingofbananaguava and potato pieces: Effect of cyclical variations of air temperature on drying kinetics and color change[J]. Drying Technology,2000,18(4−5):907−936. doi: 10.1080/07373930008917744
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
Song X, Hu H, Zhang B. Drying characteristics of Chinese Yam ( Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) by far-infrared radiation and heat pump[J]. Journal of the Saudi Society of Agricultural ences,2018,17(3):290−296. doi: 10.1016/j.jssas.2016.05.008
|
| [18] |
许丛丛. 胡萝卜冷、热加工后力学性能变化及与水状态关系的研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2015.
|
| [19] |
Hii C L , Law C L , Law M C. Simulation of heat and mass transfer of cocoa beans under stepwise drying conditions in a heat pump dryer[J]. Applied Thermal Energy,2013,54(1):264−271. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2013.02.010
|
| [20] |
Cüneyt Tunckal, İbrahim Doymaz. Performance analysis and mathematical modelling of banana slices in a heat pump drying system[J]. Renewable Energy,2020,150:918−923. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2020.01.040
|
| [21] |
李湘利, 刘静, 朱乐乐, 等. 热风、微波及其联合干燥对蒜片品质的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(15):136−140.
|
| [22] |
麦馨允, 曾维标, 吴健. 白玉菇热风干燥工艺优化及其对品质的影响[J]. 中国食用菌,2019,38(7):71−78.
|
| [23] |
Xiao-Hui G, Chun-Yan X, Yu-Rong T, et al. Mathematical modeling and effect of various hot-air drying on mushroom( Lentinus edodes)[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture,2014,13(1):207−216. doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(13)60265-8
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
Eungyu Kang, Hae Ri Park, Jeongbin Yoon, et al. A simple method to determine the water content in organic solvents using the 1H NMR chemical shifts differences between water and solvent[J]. Microchemical Journal,2018,138:395−400. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2018.01.034
|
| [28] |
|






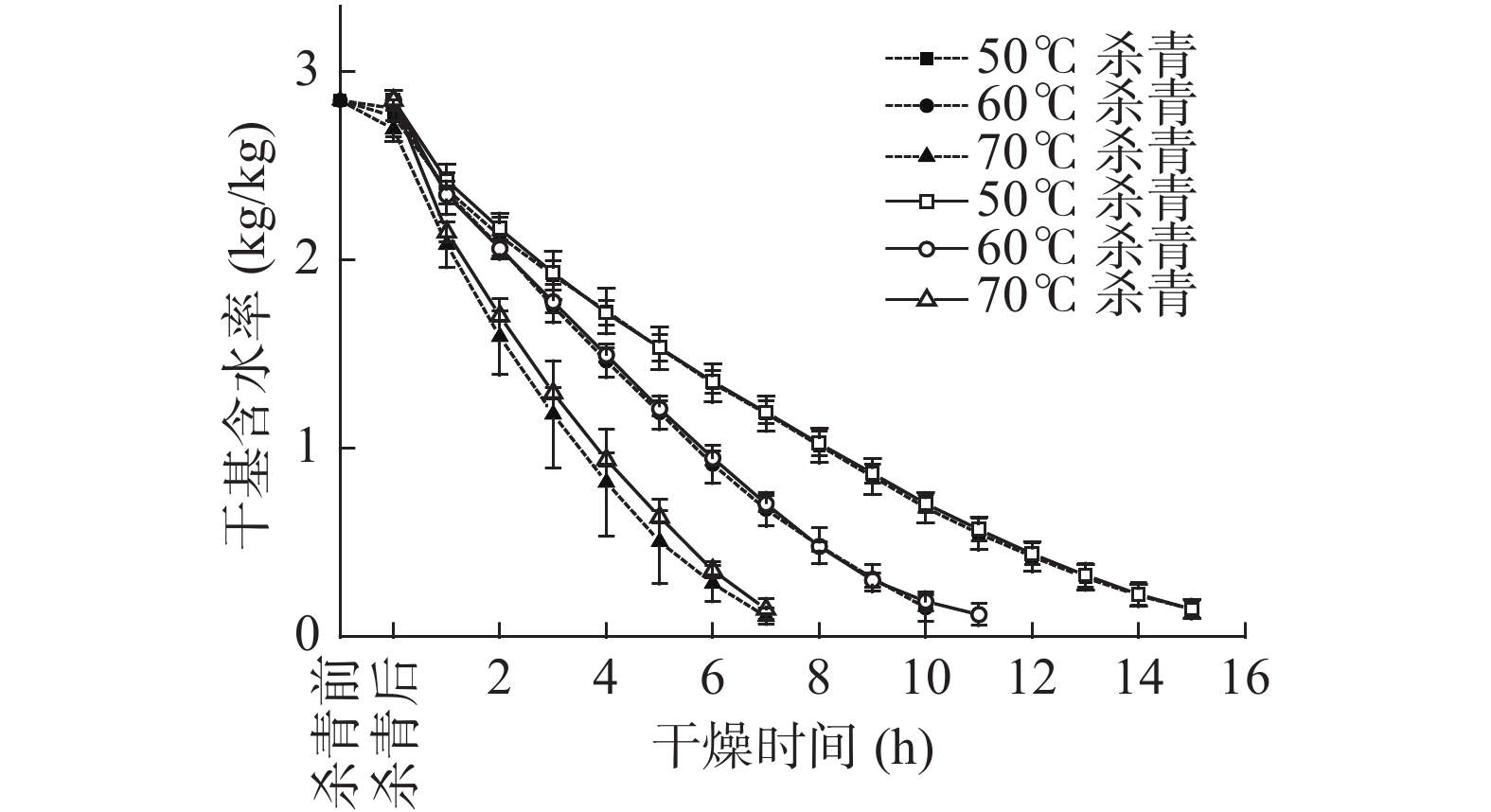




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: