| [1] |
张辉. 太平洋牡蛎(Crassostrea gigas Thunberg)中氨基酸和寡肽的提取及活性初步研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2005.
|
| [2] |
Gao Y, Wu J, Li Z, et al. Curcumin-mediated photodynamic inactivation (PDI) against DH5a contaminated in oysters and cellular toxicological evaluation of PDI-treated oysters[J]. Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy,2019,26(JUN.):244−251.
|
| [3] |
Liu F, Li Z, Cao B, et al. The effect of a novel photodynamic activation method mediated by curcumin on oyster shelf life and quality[J]. Food Research International,2016,87(sep.):204−210.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
刘芸, 于维森, 吕晓静, 等. 青岛市市售贝类中多环芳烃与多氯联苯的含量水平、组成特征及居民健康影响风险评估[J]. 现代预防医学,2018,45(23):4269−4272.
|
| [7] |
徐香. 海洋环境中有机污染物降解机理及构效关系的理论研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2012.
|
| [8] |
Yi W, Xiao H J, Jian Y H, et al. Trophic dilution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in a marine food web from Bohai Bay, north China[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2007,41(9):3109−3114.
|
| [9] |
Baumard P, Budzinski H, Garrigues P, et al. Concentrations of PAHs (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons) in various marine organisms in relation to those in sediments and to trophic level[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,1998,36(12):951−960. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(98)00088-5
|
| [10] |
Piccardo M T, Coradeghini R, Valerio F. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollution in native and caged mussels[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2001,42(10):951−956. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(01)00057-1
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
马虹. 油田采出水中多环芳烃的光催化氧化处理方法研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2012.
|
| [13] |
Wainwright M. Photodynamic antimicrobial chemotherapy (PACT)[J]. The Journal of antimicrobial chemotherapy,1998(1):13−28.
|
| [14] |
Miri K, Haw J, Hyun P. Topical PDT in the treatment of benign skin diseases: Principles and new applications[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2015,16(10):23259−23278. doi: 10.3390/ijms161023259
|
| [15] |
RobleroBartolón G V, RamónGallegos E. Use of nanoparticles (NP) in photodynamic therapy (PDT) against cancer[J]. Gaceta Médica De México,2015,151(1):85.
|
| [16] |
曹斌斌. 光动力非热力杀菌技术在生鲜牡蛎加工中的应用[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2015.
|
| [17] |
于金珅, 张芳. 姜黄素介导的光动力技术对鲜切马铃薯的杀菌效果[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,42(4):259−263, 270.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
陆长元, 韩镇辉, 蔡喜臣, 等. 核黄素(维生素B2)的光物理和光化学性质[J]. 中国科学: 化学,2000,30(5):428−435.
|
| [21] |
Jiang Y, Leung A W, Hua H, et al. Photodynamic action of LED-activated curcumin against Staphylococcus aureus involving intracellular ROS increase and membrane damage[J]. International Journal of Photoenergy,2014(6):11054−11066.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
Keshishyan E S, Zaporozhtseva Z V, Zenina O M, et al. Photodynamic inactivation of bacteria in vitro under the effect of blue light[J]. Bulletin of Experimental Biology & Medicine,2015,158(4):475−477.
|
| [24] |
Wu J, Hou W, Cao B, et al. Virucidal efficacy of treatment with photodynamically activated curcumin on murine norovirus bio-accumulated in oysters[J]. Photodiagnosis & Photodynamic Therapy,2015,12(3):385−392.
|
| [25] |
Zhang X, Wu J, Xu C, et al. Inactivation of microbes on fruit surfaces using photodynamic therapy and its influence on the postharvest shelf-life of fruits[J]. Food Science and Technology International,2020:108201322092133. doi: 10.1177/1082013220921330
|
| [26] |
Gong C, Li Y, Gao R, et al. Inactivation of specific spoilage organism ( Pseudomonas) of sturgeon by curcumin-mediated photodynamic inactivation[J]. Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy,2020:101827. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2020.101827
|
| [27] |
Wu J, Mou H, Xue C, et al. Photodynamic effect of curcumin on Vibrio parahaemolyticus[J]. Photodiagnosis & Photodynamics Therapy,2016(15):36−39.
|
| [28] |
Aponiene K, Paskeviciute E, Reklaitis I, et al. Reduction of microbial contamination of fruits and vegetables by hypericin-based photosensitization: Comparison with other emerging antimicrobial treatments[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2015,144(Jan.):29−35.
|
| [29] |
曹斌斌, 武娟, 许川山, 等. 姜黄素介导的光动力冷杀菌方法对牡蛎杀菌的效果研究[J]. 食品科学,2016,37(5):46−49.
|
| [30] |
武娟. 生鲜牡蛎中大肠杆菌和诺如病毒的检测及光动力非热力杀菌相关研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2015.
|
| [31] |
廖文崇, 朱长波, 张汉华. 体规格对香港巨牡蛎摄食和代谢的影响[J]. 中国渔业质量与标准,2011,1(3):41−46.
|
| [32] |
刘哲, 田华. 多环芳烃在风积沙土壤中的光降解研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境,2015,29(9):193−197.
|
| [33] |
李万龙. 水体中菲的光降解途径与影响因素研究[D]. 沈阳: 辽宁大学, 2016.
|
| [34] |
章豪, 杨挺, 江潇潇, 等. 污泥中多环芳烃的光催化降解[J]. 浙江农业科学,2015,56(12):2039−2041.
|
| [35] |
|





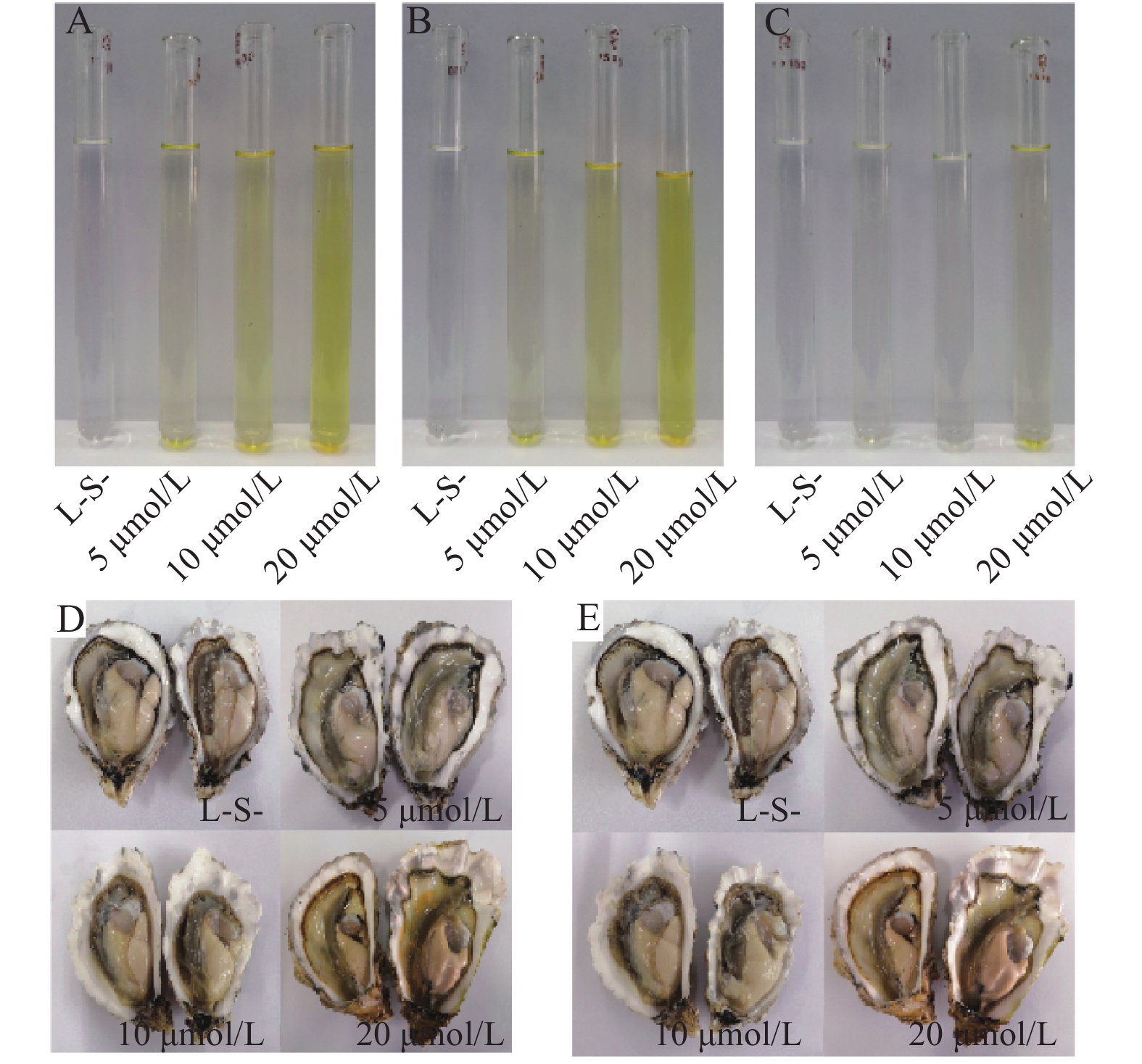




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: