| [1] |
贾哲, 韩婷, 刘欢, 等. 基于多元统计分析的食用槟榔及药用槟榔主要化学成分的含量对比研究[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2017,32(11):5158−5161.
|
| [2] |
孔丹丹, 李歆悦, 赵祥升, 等. 药食两用槟榔的国内外研究进展[J]. 中国中药杂志,2021,46(5):1053−1059.
|
| [3] |
张丹, 李丹, 许启泰, 等. 槟榔提取物不同部位的抗氧化性比较及成分研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2015,36(2):102−104.
|
| [4] |
Chavan Y V, Singhal R S. Separation of polyphenols and arecoline from areca nut (Areca catechu L.) by solvent extraction, its antioxidant activity, and identification of polyphenols. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2013, 93(10): 2580-2589.
|
| [5] |
Tang S N, Zhang J, Liu D. et al. et al. Three new areca alkaloids from the nuts of areca catechu[J]. Journal of Asian Natural Products Research,2017,19(12):1155−1159. doi: 10.1080/10286020.2017.1307187
|
| [6] |
姚力. 对槟榔原籽果壳、果核槟榔碱含量进行测定[J]. 中小企业管理与科技(中旬刊),2014(7):308−309.
|
| [7] |
Meng R C, Ying K L, Han W Y, et al. Hplc-based qualitative and quantitative analyses of alkaloids in chewable areca products from different geographic regions[J]. Journal of AOAC International,2020(5):1−21.
|
| [8] |
罗士数, 张海德, 朱莉, 等. 槟榔中槟榔碱的乙醇回流提取工艺研究[J]. 食品科学,2010,31(20):106−110.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
康丽如, 符素芳, 曾广琳, 等. 响应面法优化亚临界水提取槟榔籽中槟榔碱的工艺研究[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2016,7(9):3773−3780.
|
| [12] |
韩志萍, 黄茂芳, 朱德明, 等. 超临界CO2萃取槟榔碱工艺研究[J]. 食品科技,2009,34(10):187−190.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
杨雅蛟, 孔维军, 孙兰, 等. 槟榔化学成分和药理作用及临床应用研究进展[J]. 世界科学技术: 中医药现代化,2019(12):2583−2591.
|
| [15] |
潘虹. 槟榔碱提取及分析方法研究进展[J]. 亚太传统医药,2019,15(4):188−191.
|
| [16] |
梁振纲, 徐志伟, 孟茹, 等. 高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定食用槟榔中4种黄曲霉毒素的含量[J]. 理化检验(化学分册),2018,54(10):1153−1157.
|
| [17] |
Jain V, Garg A, Parascandola M, et al. Analysis of alkaloids in areca nut-containing products by liquid chromatography-tandem mass-spectrometry[J]. Journal of the Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2017,65(9):1977−1983. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b05140
|
| [18] |
Gheddar L, Ricaut F X, Ameline A, et al. Testing for betel nut alkaloids in hair of papuans abusers using UPLC-MS/MS and UPLC-Q-Tof-MS[J]. Journal of Analytical Toxicology,2019,44(1):41−48.
|
| [19] |
Pan H, Li Y, Huang L, et al. Development and validation of a rapid LC-MS/MS method for simultaneous quantification of arecoline and its two active metabolites in rat plasma and its application to a pharmacokinetic study[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis,2018,154:397−403. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2018.03.033
|
| [20] |
普义鑫. 槟榔多酚提取、纯化及组分分析[D]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学, 2012.
|
| [21] |
李冰, 周绪正, 杨亚军, 等. 高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定血浆中氢溴酸槟榔碱的含量[C]//甘青宁色谱协作中心、甘肃省化学会色谱委员会: 甘肃省化学会, 2012: 287-290.
|
| [22] |
Yu H, Tang L, Wu H, et al. Determination of contents of four alkaloids inPericarpium arecae by quantitative analysis of multi-components by single-marker[J]. Pakistan Journal of Pharmaceutical Ences,2016,29(4):1269.
|
| [23] |
Srimany A, George C, Naik H R, et al. Developmental patterning and segregation of alkaloids in areca nut (seed ofAreca catechu) revealed by magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry imaging[J]. Phytochemistry,2016,125:34−42.
|
| [24] |
国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典[M]. 1版. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2015: 365.
|
| [25] |
高晓婷. 槟榔生物碱的分离纯化及其热处理工艺参数的优化设计[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2016.
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
李春燕, 张学敏, 岳璐, 等. HPLC法测定槟榔中槟榔碱和槟榔次碱的含量[J]. 中医药学报,2018,46(3):21−23.
|
| [28] |
汤丽娟, 吴皓, 郁红礼. HPLC同时测定大腹皮中4种生物碱含量[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2014,29(11):3583−3586.
|
| [29] |
毛春芹, 陆兔林, 季德, 等. 高效液相色谱法测定不同产地大腹皮中槟榔碱的含量[J]. 中国药学杂志,2013,48(11):909−911.
|
| [30] |
张卫东, 戴国梁, 白永涛, 等. HPLC法同时测定四磨汤口服液中5种成分[J]. 中成药,2018,40(1):120−123.
|






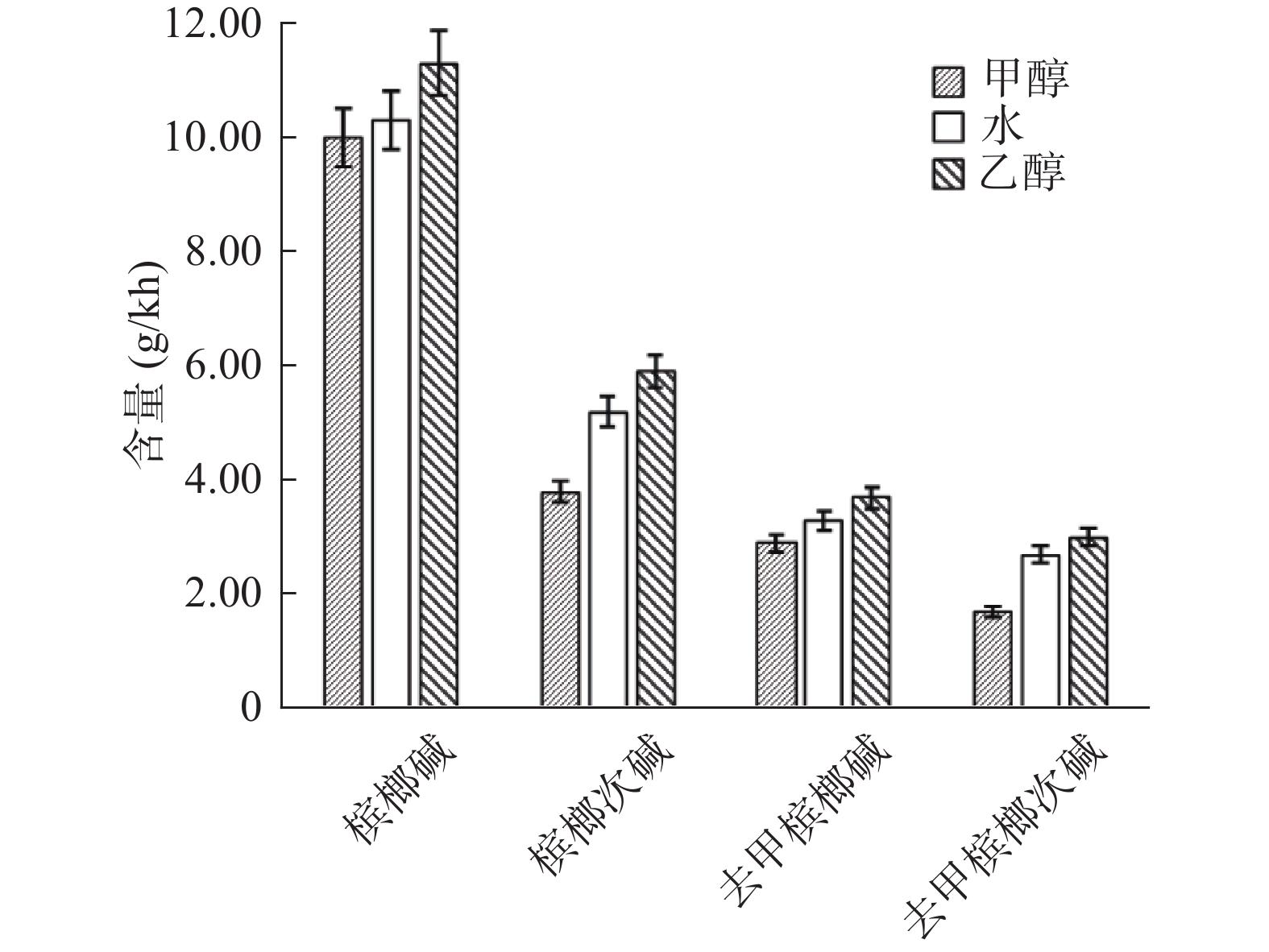

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: