| [1] |
王燕平. 中国药典[J]. China Standardization, 2020.
|
| [2] |
Xiao J, Wang J, Xing F, et al. Zeaxanthin dipalmitate therapeutically improves hepatic functions in an alcoholic fatty liver disease model through modulating MAPK pathway[J]. PLoS One,2014,9:e95214. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095214
|
| [3] |
Kim H P, Lee E J, Kim Y C, et al. Zeaxanthin dipalmitate from Lycium chinense fruit reduces experimentally induced hepatic fibrosis in rats[J]. Biol Pharm Bull,2002,25:390−392. doi: 10.1248/bpb.25.390
|
| [4] |
Johnson E J. Role of lutein and zeaxanthin in visual and cognitive function throughout the lifespan[J]. Nutr Rev,2014,72:605−612. doi: 10.1111/nure.12133
|
| [5] |
Milani A, Basirnejad M, Shahbazi S, et al. Carotenoids: biochemistry, pharmacology and treatment[J]. British Journal of Pharmacology,2017,174(11):1290−1324. doi: 10.1111/bph.13625
|
| [6] |
Liu Y, Zeng S, Sun W, et al. Comparative analysis of carotenoid accumulation in two goji ( Lycium barbarum L. and L. ruthenicum Murr.) fruits[J]. BMC Plant Biology,2014,14 (1):269. doi: 10.1186/s12870-014-0269-4
|
| [7] |
肖佳, 高昊, 周正群, 等. 枸杞属中枸杞红素类成分研究进展[J]. 科学通报,2017,62(16):1691−1698.
|
| [8] |
白光灿, 李娅琦, 张泽坤, 等. 枸杞HPLC指纹图谱的建立及3种成分测定[J]. 中成药,2019,41(7):1721−1724.
|
| [9] |
Weller P, Breithaupt D E. Identification and quantification of zeaxanthin esters in plants using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry,2003,51(24):7044−7049.
|
| [10] |
Leung I, Tso M, Li W, et al. Absorption and tissue distribution of zeaxanthin and lutein in rhesus monkeys after taking Fructus lycii (Gou Qi Zi) extract[J]. Invest Ophthalmology & Visual Science,2001,42(2):466−471.
|
| [11] |
Breithaupt D E, Weller P, Wolters M, et al. Comparison of plasma responses in human subjects after the ingestion of 3R, 3R′-zeaxanthin dipalmitate from wolfberry ( Lycium barbarum) and non-esterified 3R, 3R′-zeaxanthin using chiral high-performance liquid chromatography[J]. British journal of nutrition,2004,91(5):707−713. doi: 10.1079/BJN20041105
|
| [12] |
Scripsema N K, Hu D N, Rosen R B. Lutein, zeaxanthin, and meso-zeaxanthin in the clinical management of eye disease[J]. Journal of Ophthalmology,2015,2015:865179. doi: 10.1155/2015/865179
|
| [13] |
Firdous A P, Sindhu E R, Kuttan R. Hepato-protective potential of carotenoid meso-zeaxanthin against paracetamol, CCl4 and ethanol induced toxicity[J]. Indian J Exp Biol,2011,49:44−49.
|
| [14] |
李静静. 枸杞红素在慢性乙肝合并非酒精性脂肪肝小鼠模型中的保护作用研究[D]. 广州: 暨南大学, 2017.
|
| [15] |
廖国玲, 杨文, 张自萍. RP-HPLC法测定不同产地宁夏枸杞甜菜碱含量[J]. 宁夏医学杂志,2007,29(6):492−493.
|
| [16] |
崔治家, 刘峰林, 张启立, 等. 不同产地枸杞子中枸杞多糖含量的比较分析[J]. 华西药学杂志,2020,35(1):63−65.
|
| [17] |
Tai A, Gohda E. Determination of ascorbic acid and its related compounds in foods and beverages by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography[J]. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life,2007,853(1-2):214−220. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2007.03.024
|
| [18] |
杨延超, 董慧燕, 殷梦龙, 等. HPLC测定枸杞提取物中枸杞酸的含量[J]. 食品工业,2014(10):255−257.
|
| [19] |
张自萍, 李弘武, 廖国玲, 等. 枸杞子中2-O-β-D-葡萄糖基-L-抗坏血酸抑制黑素合成的研究[J]. 中国新药杂志,2007(9):689−692.
|
| [20] |
前田满, 中尾正宏, 深见治一. 2-O-(β-D-吡喃葡萄糖基)抗坏血酸, 其生产方法以及包含含有它的组合物的食品和化妆品: 中国, 02826317.0[P]. 2002-12-27.
|
| [21] |
Zhang Z, Liu X, Zhang X, et al. Comparative evaluation of the antioxidant effects of the natural vitamin C analog 2-O- β-D-glucopyranosyl-L-ascorbic acid isolated from goji berry fruit[J]. Archives of Pharmacal Research,2011,34(5):801−810. doi: 10.1007/s12272-011-0514-4
|
| [22] |
周芹, 吴玉梅. 亲水性液相色谱串联质谱法测定红甜菜中甜菜碱含量.[J]. 中国农学通报. 2019(7): 134-138.
|
| [23] |
庄红艳, 姜振邦, 潘广文, 等. 离子色谱法测定枸杞子和大枣中甜菜碱含量
J]. 中华中医药杂志,2017(9):1641−1646.
|
| [24] |
Toyoda-Ono, Yoshiko, et al. 2-O-(β-D-Glucopyranosyl) ascorbic acid, a Novel ascorbic acid analogue isolated from Lycium fruit[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2004,52(7):2092−2096. doi: 10.1021/jf035445w
|
| [25] |
Yoshiko Toyada, et al. A novel vitamin C analog, 2-O-(beta-d-glucopyranosyl) ascorbic acid: Examination of enzymatic synthesis and biological activity.[J]. Journal of Bioence & Bioengineering,2005,99(4):361−365.
|
| [26] |
李赫, 陈敏, 马文平. 不同成熟期枸杞中类胡萝卜素含量的变化规律[J]. 中国农业科学,2006,39(3):599−605.
|
| [27] |
郭荣. 枸杞果实发育过程AA-2βG、甜菜碱及黄酮含量变化研究[D]. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2008.
|
| [28] |
陈敏, 李赫, 文平, 等. 反相高效液相色谱法测定枸杞中类胡萝卜素及酯类化合物[J]. 分析化学,2006,34(1):27−30.
|
| [29] |
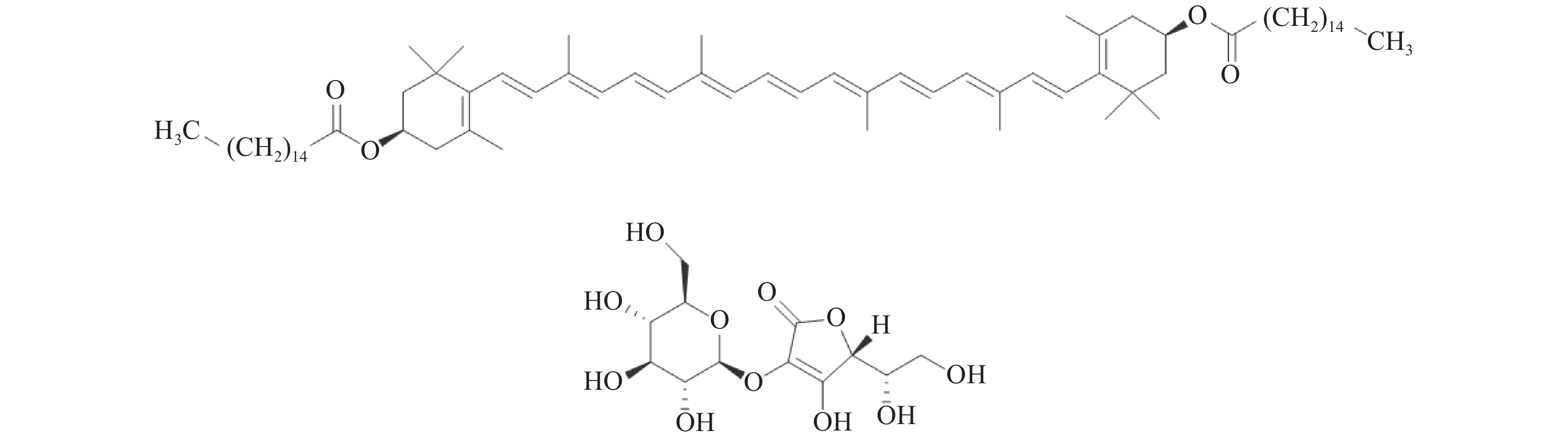
Karioti A, Bergonzi M C, Vincieri F F, et al. Validated method for the analysis of goji berry, a rich source of Zeaxanthin dipalmitate[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2014,62(52):12529−12535. doi: 10.1021/jf503769s
|










 DownLoad:
DownLoad: