| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
程萌, 佟钰, 左利君, 等. 钠盐摄入与脑卒中发生风险关系的Meta分析[J]. 现代预防医学,2018,45(22):4208−4212.
|
| [4] |
Inguglia E S, Zhang Z, Tiwari B K, et. al. Salt reduction strategies in processed meat products-A review[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2017,59:70−78.
|
| [5] |
Schmidt U S, Pietsch V L, Rentschler C, et al. Influence of the degree of esterification on the emulsifying performance of conjugates formed between whey protein isolate and citrus pectin[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2016,56(5):1−8.
|
| [6] |
Marchetti L, Andres S C, Califano A N. Physicochemical, microbiological and oxidative changes during refrigerated storage of n-3 PUFA enriched cooked meat sausages with partial NaCl substitution[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation,2017,41(3):1−11.
|
| [7] |
Zhang W M, Dong Q L, Song X Y, et al. Progress of sodium lactate as a preservative in meat and meat products[J]. Food Science,2016,37(1):235−240.
|
| [8] |
马晓丽, 黄雅萍, 张龙涛, 等. 肉制品加工中的低钠策略研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(14):256−262.
|
| [9] |
Tobin B D, O'sullivan M G, Hamill R M, et al. Effect of varying salt and fat levels on the sensory and physiochemical quality of frankfurters[J]. Meat Science,2012,92(4):659−666. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2012.06.017
|
| [10] |
郝红涛, 赵改名, 李苗云, 等. 低脂低钠肉类制品的研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2010,36(2):163−167.
|
| [11] |
Horita, C N, Messias V C, Morgano, M A, et al. Textural, microstructural and sensory properties of reduced sodium frankfurter sausages containing mechanically deboned poultry meat and blends of chloride salts[J]. Food Research International,2014:66.
|
| [12] |
Barat J M, Perez-esteve E, Aristoy M C, et al. Partial replacement of sodium in meat and fish products by using magnesium salts: A review[J]. Plant and Soil,2013,368(1/2):179−188.
|
| [13] |
Rudnitskaya A, Rocha S M, Legin A, et al. Evaluation of the feasibility of the electronic tongue as a rapid analytical tool for wine age prediction and quantification of the organic acids and phenolic compounds. The case-study of madeira wine[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta,2010,662 (1):82−89. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2009.12.042
|
| [14] |
Escuder G L, Peris M. Review: Highlights in recent applications of electronic tongues in food analysis[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta,2010,665(1):15−25. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2010.03.017
|
| [15] |
魏常敏, 许卫猛, 邢永锋, 等. 不同年份玉米杂交种主要农艺性状与产量的灰色关联度分析[J]. 浙江农业科学,2019,60(10):1756−1759.
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
肖轲, 苏东林, 李志坚, 等. 基于改进AHP和灰色关联度分析法用于稻米蛋白质营养学评价[J]. 食品与机械,2019,35(11):52−57.
|
| [18] |
龚雨虹, 罗光明, 张风波, 等. 基于灰色关联度法评价栀子药材质量[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2017,23(13):74−79.
|
| [19] |
张阳, 李可强, 张鹏, 等. 灰色关联度分析法评价北豆根药材质量研究[J]. 辽宁中医杂志,2016,43(2):367−369.
|
| [20] |
Xiong Y L, Noel D C, Moody W G. Textural and sensory properties of low-fat beef sausages with added water and polysaccharides as affected by pH and salt[J]. Journal of Food Science,1999,64(3):550−554. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.1999.tb15083.x
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
李双艳, 邓力, 汪孝, 等. 基于电子鼻、电子舌比较分析冷藏方式对小香鸡风味的影响[J]. 肉类研究,2017,31(4):50−55.
|
| [23] |
邓聚龙. 灰色系统基础方法[M]. 华中理工大学出版社, 1987: 10−13.
|
| [24] |
Zhou Q H, Lin L Q, Chen G, et al. Prediction and optimization of electrospun polyacrylonitrile fiber diameter based on grey system theory[J]. Materials (Basel, Switzerland),2019,12(14):2237−2252. doi: 10.3390/ma12142237
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
肖轲, 吴跃辉, 李志坚, 等. 基于灰色关联度的柑橘果汁食味品质综合评价[J]. 湖南农业科学,2019(10):80−82, 85.
|
| [27] |
Fellendorf S, Kerry J P, Hamill R M, et al. Impact on the physicochemical and sensory properties of salt replacers[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2018,92(6):584−592.
|
| [28] |
赵希荣, 汤芸. 低钠肉制品的开发研究进展[J]. 徐州工程学院学报(自然科学版),2016,31(3):29−36.
|
| [29] |
马晓丽, 黄雅萍, 张龙涛, 等. 肉制品加工中的低钠策略研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(14):256−262.
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|





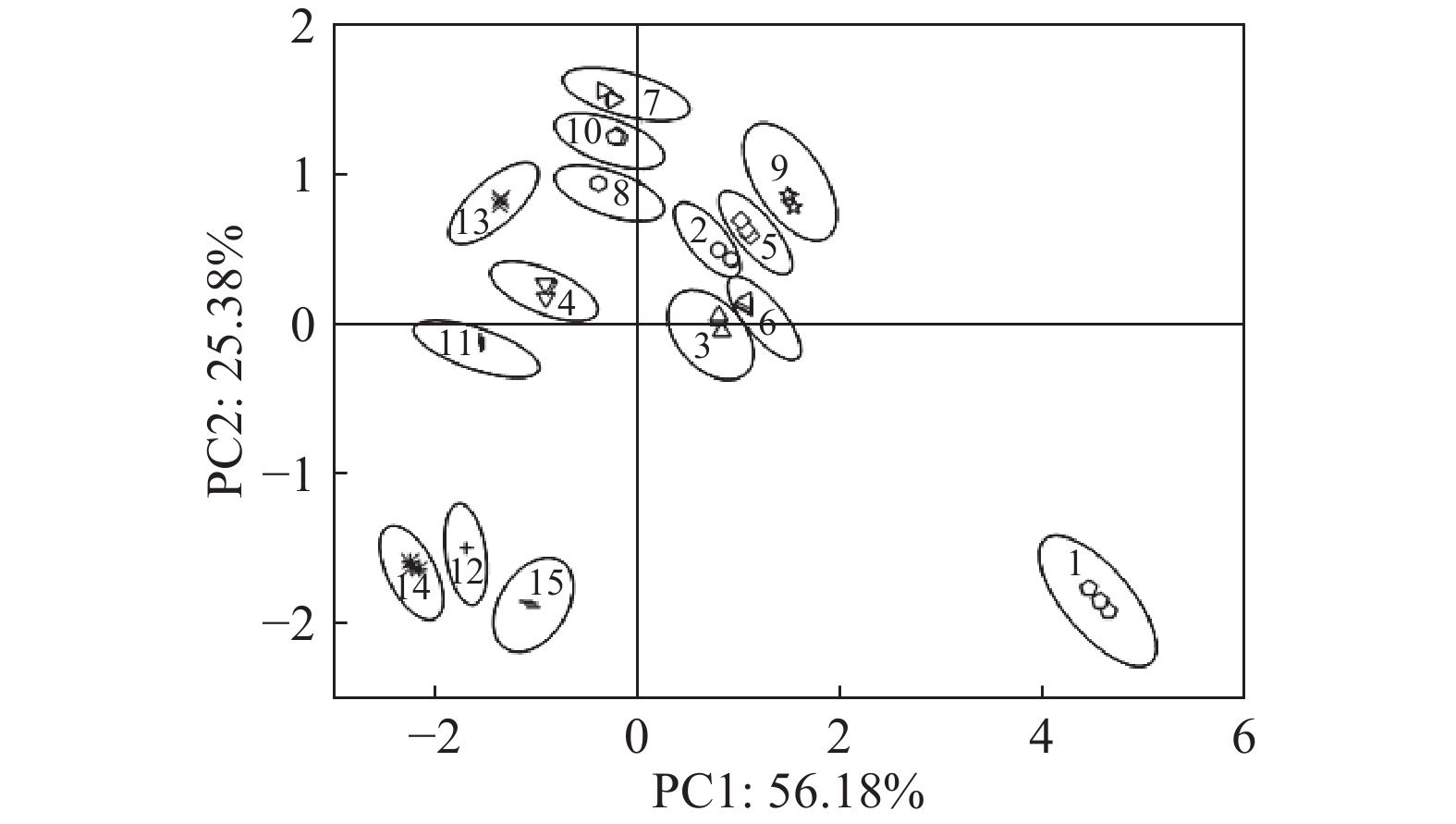




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: